User login
In 1938, the year that cystic fibrosis (CF) was first described clinically, four of five children born with the disease did not live past their first birthdays.
In 2019, the median age at death for patients enrolled in the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation (CFF) registry was 32 years, and the predicted life expectancy for patients with CF who were born from 2015 through 2019 was 46 years.
Those numbers reflect the remarkable progress made in the past 4 decades in the care of patients with CF, but also highlight the obstacles ahead, given that the predicted life expectancy for the overall U.S. population in 2019 (pre–COVID-19) was 78.9 years.
Julie Desch, MD, is a CF survivor who has beaten the odds and then some. At age 61, the retired surgical pathologist is a CF patient advocate, speaker, and a board member of the Cystic Fibrosis Research Institute, a not-for-profit organization that funds CF research and offers education, advocacy, and psychosocial support for persons with CF and their families and caregivers.
In an interview, Dr. Desch said that while there has been remarkable progress in her lifetime in the field of CF research and treatment, particularly in the development of drugs that modulate function of the underlying cause of approximately 90% of CF cases, there are still many CF patients who cannot benefit from these therapies.
“There are still 10% of people who don’t make a protein to be modified, so that’s a huge unmet need,” she said.
Genetic disorder
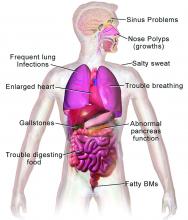
CF is a chronic autosomal recessive disorder with multiorgan and multisystem manifestations. It is caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, which codes for the protein CF transmembrane conductance regulator. CFTR controls transport of chloride ions across cell membranes, specifically the apical membrane of epithelial cells in tissues of the airways, intestinal tract, pancreas, kidneys, sweat glands, and the reproductive system, notably the vas deferens in males.
The F508 deletion (F508del) mutation is the most common, occurring in approximately 70% of persons with CF. It is a class 2-type protein processing mutation, leading to defects in cellular processing, protein stability, and chloride channel gating defects.
The CFTR protein also secretes bicarbonate to regulate the pH of airway surface liquid, and inhibits the epithelial sodium channel, which mediates passive sodium transport across apical membranes of sodium-absorbing epithelial cells in the kidneys, intestine, and airways.
CF typically presents with the buildup in the lungs of abnormally viscous and sticky mucus leading to frequent, severe infections, particularly with Pseudomonas aeruginosa, progressive lung damage and, prior to the development of effective disease management, to premature death. The phenotype often includes malnutrition due to malabsorption, and failure to thrive.
Diagnosis
In all 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia, newborns are screened for CF with an assay for immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT) an indirect marker for pancreatic injury that is elevated in serum in most newborns with CF, but also detected in premature infants or those delivered under stressful circumstances. In some states newborns are tested only for IRT, with a diagnosis confirmed with a sweat chloride test and/or a CFTR mutation panel.
Treatment
There is no cure for CF, but the discovery of the gene in 1989 by Canadian and U.S. investigators has led to life-prolonging therapeutic interventions, specifically the development of CFTR modulators.
CFTR modulators include potentiators such as ivacaftor (Kalydeco), and correctors such as lumacaftor and tezacaftor (available in the combination Orkambi), and most recently in the triple combination of elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor (Trikafta; ETI).
Neil Sweezey, MD, FRCPC, a CF expert at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) in Toronto, told this news organization that the ideal therapy for CF, genetic correction of the underlying mutations, is still not feasible, but that CFTR modulators are a close second.
“For 90% of patients, the three-drug combination Trikafta has been shown to be quite safe, quite tolerable, and quite remarkably beneficial,” he said.
In a study reported at CHEST 2021 by investigators from Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, 32 adults who were started on the triple combination had significantly improved in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), gain in body mass index, decreased sweat chloride and decreased colonization by Pseudomonas species. In addition, patients had significant improvements in blood inflammatory markers.
Christopher H. Goss, MD, FCCP, professor of pulmonary critical care and sleep medicine and professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington in Seattle, agreed that with the availability of the triple combination, “these are extraordinary times. An astounding fact is that most patients have complete resolution of cough, and the exacerbation rates have just plummeted,” he said in an interview.
Some of the reductions in exacerbations may be attributable to the COVID-19 pandemic, he noted, because patients in isolation have less exposure to circulating respiratory viruses.
“But it has been miraculous, and the clinical effect is certainly still more astounding than the effects of ivacaftor, which was the first truly breakthrough drug. Weight goes up, well-being increases, and the population lung function has shifted up to better grade lung function, in the entire population,” he said.
In addition, the need for lung and heart transplantation has sharply declined.
“I had a patient who had decided to forgo transplantation, despite absolutely horrible lung function, and he’s now bowling and leading a very productive life, when before he had been preparing for end of life,” Dr. Goss said.
Dr. Sweezey emphasized that as with all medications, patients being started on the triple combination require close monitoring for potential adverse events that might require dose modification or, for a small number of patients, withdrawal.
Burden of care
CFTR modulators have reduced but not eliminated the need for some patients to have mucolytic therapy, which may include dornase alfa, a recombinant human deoxyribonuclease (DNase) that reduces the viscosity of lung secretions, hypertonic saline inhaled twice daily (for patients 12 and older), mannitol, and physical manipulations to help patients clear mucus. This can include both manual percussion and the use of devices for high-frequency chest wall oscillation.
The complex nature of CF often requires a combination of other therapies to address comorbidities. These therapies may include infection prophylaxis and treatment with antibiotics and antifungals, nutrition support, and therapy for CF-related complications, including gastrointestinal issues, liver diseases, diabetes, and osteopenia that may be related to poor nutrient absorption, chronic inflammation, or other sequelae of CF.
In addition, patients often require frequent CF care center visits – ideally a minimum of every 3 months – which can result in significant loss of work or school time.
“Outcomes for patients in the long run have been absolutely proven to be best if they’re followed in big, established, multidisciplinary well-organized CF centers,” Dr. Sweezey said. “In the United States and Canada if you’re looked after on a regular basis, which means quarterly, every 3 months – whether you need it or not, you really do need it – and if the patients are seen and assessed and checked every 3 months all of their lives, they have small changes caught early, whether it’s an infection you can slap down with medication or a nutrition problem that may be affecting a child’s growth and development.”
“We’re really kind of at a pivotal moment in CF, where we realize things are changing,” said A. Whitney Brown, MD, senior director for clinical affairs at the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, and an adult CF and lung transplant physician in the Inova Advanced Lung Disease Program in Falls Church, Va.
“Patient needs and interest have evolved, because of the pandemic and because of the highly effective modulator therapy, but we want to take great effort to study it in a rigorous way, to make sure that as we are agile and adapt the care model, that we can maintain the same quality outcomes that we have traditionally done,” she said in an interview.
The Lancet Respiratory Medicine Commission on the future of CF care states that models of care “need to consider management approaches (including disease monitoring) to maintain health and delay lung transplantation, while minimizing the burden of care for patients and their families.”
‘A great problem to have’
One of the most significant changes in CF care has been the growing population of CF patients like Dr. Desch who are living well into adulthood, with some approaching Medicare eligibility.
With the advent of triple therapy and CFTR modulators being started earlier in life, lung function can be preserved, damage to other organs can be minimized, and life expectancy for patients with CF will continue to improve.
“We’re anticipating that there may be some needs in the aging CF population that are different than what we have historically had,” Dr. Brown said. “Will there be geriatric providers that need to become experts in CF care? That’s a great problem to have,” she said.
Dr. Goss agreed, noting that CF is steadily shifting from a near uniformly fatal disease to a chronic disorder that in many cases can be managed “with a complex regimen of novel drugs, much like HIV.”
He noted that there are multiple drug interactions with the triple combination, “so it’s really important that people don’t start a CF patient on a drug without consulting a pharmacist, because you can totally inactivate ETI, or augment it dramatically, and we’ve seen both happen.”
Cost and access
All experts interviewed for this article agreed that while the care of patients with CF has improved exponentially over the last few decades, there are still troubling inequities in care.
One of the largest impediments is the cost of care, with the triple combination costing more than $300,000 per year.
“Clearly patients aren’t paying that, but insurance companies are, and that’s causing all kinds of trickle-down effects that definitely affect patients. The patients like myself who are able to have insurance that covers it benefit, but there are so many people that don’t,” Dr. Desch said.
Dr. Sweezey noted that prior to the advent of ETI, patients with CF in Canada had better outcomes and longer life expectancy than did similar patients in the United States because of universal access to care and coordinated services under Canada’s health care system, compared with the highly fragmented and inefficient U.S. system. He added that the wider availability of ETI in the United States vs. Canada may begin to narrow that gap, however.
As noted before, there is a substantial proportion of patients – an estimated 10% – who have CFTR mutations that are not correctable by currently available CFTR modulators, and these patients are at significant risk for irreversible airway complications and lung damage.
In addition, although CF occurs most frequently among people of White ancestry, the disease does not respect distinctions of race or ethnicity.
“It’s not just [Whites] – a lot of people from different racial backgrounds, ethnic backgrounds, are not being diagnosed or are not being diagnosed soon enough to have effective care early enough,” Dr. Desch said.
That statement is supported by the Lancet Respiratory Medicine Commission on the future of cystic fibrosis care, whose members noted in 2019 that “epidemiological studies in the past 2 decades have shown that cystic fibrosis occurs and is more frequent than was previously thought in populations of non-European descent, and the disease is now recognized in many regions of the world.”
The commission members noted that the costs of adequate CF care may be beyond the reach of many patients in developing nations.
Still, if the substantial barriers of cost and access can be overcome, the future will continue to look brighter for patients with CF. As Dr. Sweezey put it: “There are studies that are pushing lower age limits for using these modulators, and as the evidence builds for the efficacy and safety at younger ages, I think all of us are hoping that we’ll end up being able to use either the current or future modulators to actually prevent trouble in CF, rather than trying to come along and fix it after it’s been there.”
Dr. Brown disclosed advisory board activity for Vertex that ended prior to her joining the CF Foundation. Dr. Desch, Dr. Goss, and Dr. Sweezey reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
In 1938, the year that cystic fibrosis (CF) was first described clinically, four of five children born with the disease did not live past their first birthdays.
In 2019, the median age at death for patients enrolled in the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation (CFF) registry was 32 years, and the predicted life expectancy for patients with CF who were born from 2015 through 2019 was 46 years.
Those numbers reflect the remarkable progress made in the past 4 decades in the care of patients with CF, but also highlight the obstacles ahead, given that the predicted life expectancy for the overall U.S. population in 2019 (pre–COVID-19) was 78.9 years.
Julie Desch, MD, is a CF survivor who has beaten the odds and then some. At age 61, the retired surgical pathologist is a CF patient advocate, speaker, and a board member of the Cystic Fibrosis Research Institute, a not-for-profit organization that funds CF research and offers education, advocacy, and psychosocial support for persons with CF and their families and caregivers.
In an interview, Dr. Desch said that while there has been remarkable progress in her lifetime in the field of CF research and treatment, particularly in the development of drugs that modulate function of the underlying cause of approximately 90% of CF cases, there are still many CF patients who cannot benefit from these therapies.
“There are still 10% of people who don’t make a protein to be modified, so that’s a huge unmet need,” she said.
Genetic disorder
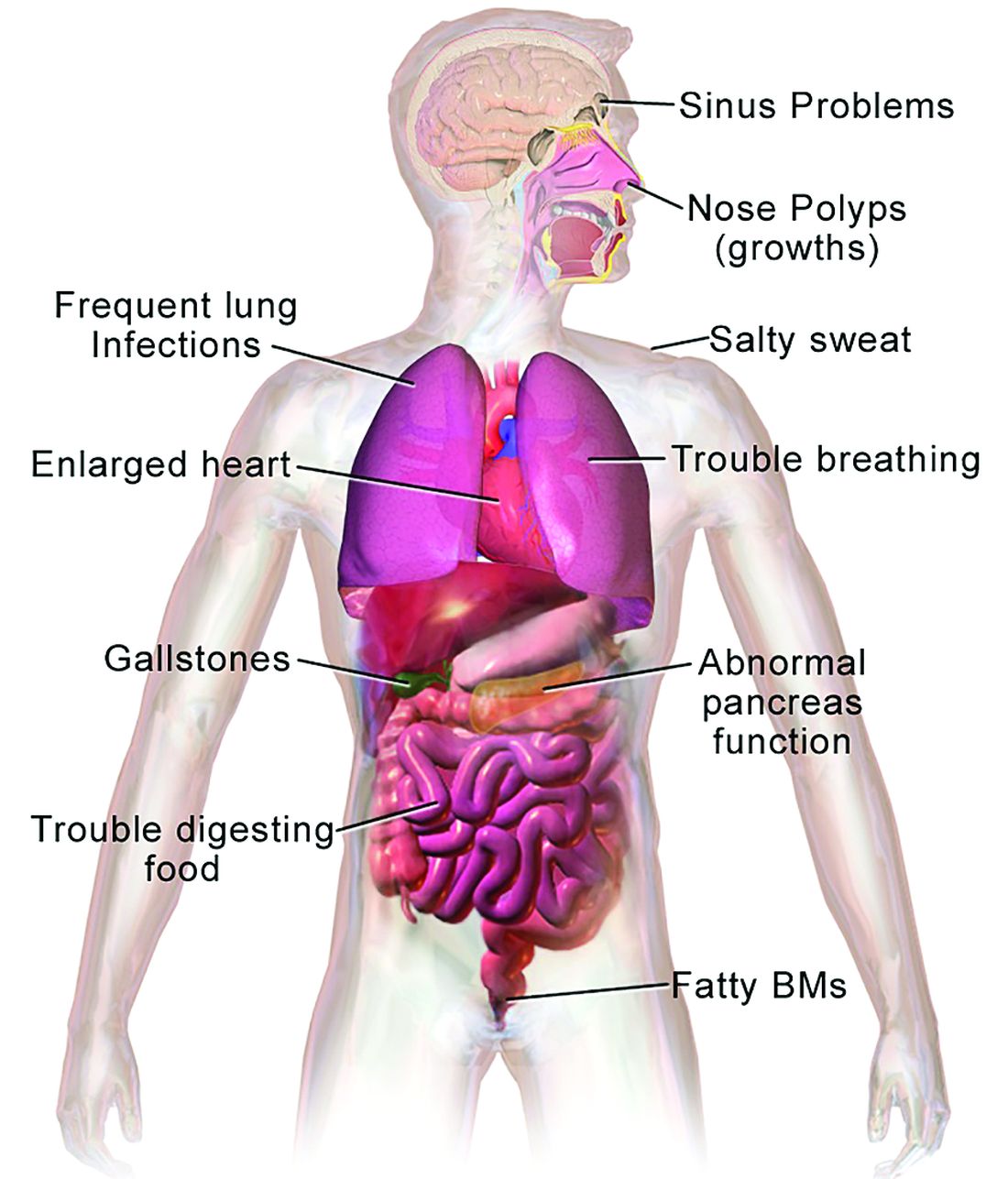
CF is a chronic autosomal recessive disorder with multiorgan and multisystem manifestations. It is caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, which codes for the protein CF transmembrane conductance regulator. CFTR controls transport of chloride ions across cell membranes, specifically the apical membrane of epithelial cells in tissues of the airways, intestinal tract, pancreas, kidneys, sweat glands, and the reproductive system, notably the vas deferens in males.
The F508 deletion (F508del) mutation is the most common, occurring in approximately 70% of persons with CF. It is a class 2-type protein processing mutation, leading to defects in cellular processing, protein stability, and chloride channel gating defects.
The CFTR protein also secretes bicarbonate to regulate the pH of airway surface liquid, and inhibits the epithelial sodium channel, which mediates passive sodium transport across apical membranes of sodium-absorbing epithelial cells in the kidneys, intestine, and airways.
CF typically presents with the buildup in the lungs of abnormally viscous and sticky mucus leading to frequent, severe infections, particularly with Pseudomonas aeruginosa, progressive lung damage and, prior to the development of effective disease management, to premature death. The phenotype often includes malnutrition due to malabsorption, and failure to thrive.
Diagnosis
In all 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia, newborns are screened for CF with an assay for immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT) an indirect marker for pancreatic injury that is elevated in serum in most newborns with CF, but also detected in premature infants or those delivered under stressful circumstances. In some states newborns are tested only for IRT, with a diagnosis confirmed with a sweat chloride test and/or a CFTR mutation panel.
Treatment
There is no cure for CF, but the discovery of the gene in 1989 by Canadian and U.S. investigators has led to life-prolonging therapeutic interventions, specifically the development of CFTR modulators.
CFTR modulators include potentiators such as ivacaftor (Kalydeco), and correctors such as lumacaftor and tezacaftor (available in the combination Orkambi), and most recently in the triple combination of elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor (Trikafta; ETI).
Neil Sweezey, MD, FRCPC, a CF expert at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) in Toronto, told this news organization that the ideal therapy for CF, genetic correction of the underlying mutations, is still not feasible, but that CFTR modulators are a close second.
“For 90% of patients, the three-drug combination Trikafta has been shown to be quite safe, quite tolerable, and quite remarkably beneficial,” he said.
In a study reported at CHEST 2021 by investigators from Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, 32 adults who were started on the triple combination had significantly improved in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), gain in body mass index, decreased sweat chloride and decreased colonization by Pseudomonas species. In addition, patients had significant improvements in blood inflammatory markers.
Christopher H. Goss, MD, FCCP, professor of pulmonary critical care and sleep medicine and professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington in Seattle, agreed that with the availability of the triple combination, “these are extraordinary times. An astounding fact is that most patients have complete resolution of cough, and the exacerbation rates have just plummeted,” he said in an interview.
Some of the reductions in exacerbations may be attributable to the COVID-19 pandemic, he noted, because patients in isolation have less exposure to circulating respiratory viruses.
“But it has been miraculous, and the clinical effect is certainly still more astounding than the effects of ivacaftor, which was the first truly breakthrough drug. Weight goes up, well-being increases, and the population lung function has shifted up to better grade lung function, in the entire population,” he said.
In addition, the need for lung and heart transplantation has sharply declined.
“I had a patient who had decided to forgo transplantation, despite absolutely horrible lung function, and he’s now bowling and leading a very productive life, when before he had been preparing for end of life,” Dr. Goss said.
Dr. Sweezey emphasized that as with all medications, patients being started on the triple combination require close monitoring for potential adverse events that might require dose modification or, for a small number of patients, withdrawal.
Burden of care
CFTR modulators have reduced but not eliminated the need for some patients to have mucolytic therapy, which may include dornase alfa, a recombinant human deoxyribonuclease (DNase) that reduces the viscosity of lung secretions, hypertonic saline inhaled twice daily (for patients 12 and older), mannitol, and physical manipulations to help patients clear mucus. This can include both manual percussion and the use of devices for high-frequency chest wall oscillation.
The complex nature of CF often requires a combination of other therapies to address comorbidities. These therapies may include infection prophylaxis and treatment with antibiotics and antifungals, nutrition support, and therapy for CF-related complications, including gastrointestinal issues, liver diseases, diabetes, and osteopenia that may be related to poor nutrient absorption, chronic inflammation, or other sequelae of CF.
In addition, patients often require frequent CF care center visits – ideally a minimum of every 3 months – which can result in significant loss of work or school time.
“Outcomes for patients in the long run have been absolutely proven to be best if they’re followed in big, established, multidisciplinary well-organized CF centers,” Dr. Sweezey said. “In the United States and Canada if you’re looked after on a regular basis, which means quarterly, every 3 months – whether you need it or not, you really do need it – and if the patients are seen and assessed and checked every 3 months all of their lives, they have small changes caught early, whether it’s an infection you can slap down with medication or a nutrition problem that may be affecting a child’s growth and development.”
“We’re really kind of at a pivotal moment in CF, where we realize things are changing,” said A. Whitney Brown, MD, senior director for clinical affairs at the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, and an adult CF and lung transplant physician in the Inova Advanced Lung Disease Program in Falls Church, Va.
“Patient needs and interest have evolved, because of the pandemic and because of the highly effective modulator therapy, but we want to take great effort to study it in a rigorous way, to make sure that as we are agile and adapt the care model, that we can maintain the same quality outcomes that we have traditionally done,” she said in an interview.
The Lancet Respiratory Medicine Commission on the future of CF care states that models of care “need to consider management approaches (including disease monitoring) to maintain health and delay lung transplantation, while minimizing the burden of care for patients and their families.”
‘A great problem to have’
One of the most significant changes in CF care has been the growing population of CF patients like Dr. Desch who are living well into adulthood, with some approaching Medicare eligibility.
With the advent of triple therapy and CFTR modulators being started earlier in life, lung function can be preserved, damage to other organs can be minimized, and life expectancy for patients with CF will continue to improve.
“We’re anticipating that there may be some needs in the aging CF population that are different than what we have historically had,” Dr. Brown said. “Will there be geriatric providers that need to become experts in CF care? That’s a great problem to have,” she said.
Dr. Goss agreed, noting that CF is steadily shifting from a near uniformly fatal disease to a chronic disorder that in many cases can be managed “with a complex regimen of novel drugs, much like HIV.”
He noted that there are multiple drug interactions with the triple combination, “so it’s really important that people don’t start a CF patient on a drug without consulting a pharmacist, because you can totally inactivate ETI, or augment it dramatically, and we’ve seen both happen.”
Cost and access
All experts interviewed for this article agreed that while the care of patients with CF has improved exponentially over the last few decades, there are still troubling inequities in care.
One of the largest impediments is the cost of care, with the triple combination costing more than $300,000 per year.
“Clearly patients aren’t paying that, but insurance companies are, and that’s causing all kinds of trickle-down effects that definitely affect patients. The patients like myself who are able to have insurance that covers it benefit, but there are so many people that don’t,” Dr. Desch said.
Dr. Sweezey noted that prior to the advent of ETI, patients with CF in Canada had better outcomes and longer life expectancy than did similar patients in the United States because of universal access to care and coordinated services under Canada’s health care system, compared with the highly fragmented and inefficient U.S. system. He added that the wider availability of ETI in the United States vs. Canada may begin to narrow that gap, however.
As noted before, there is a substantial proportion of patients – an estimated 10% – who have CFTR mutations that are not correctable by currently available CFTR modulators, and these patients are at significant risk for irreversible airway complications and lung damage.
In addition, although CF occurs most frequently among people of White ancestry, the disease does not respect distinctions of race or ethnicity.
“It’s not just [Whites] – a lot of people from different racial backgrounds, ethnic backgrounds, are not being diagnosed or are not being diagnosed soon enough to have effective care early enough,” Dr. Desch said.
That statement is supported by the Lancet Respiratory Medicine Commission on the future of cystic fibrosis care, whose members noted in 2019 that “epidemiological studies in the past 2 decades have shown that cystic fibrosis occurs and is more frequent than was previously thought in populations of non-European descent, and the disease is now recognized in many regions of the world.”
The commission members noted that the costs of adequate CF care may be beyond the reach of many patients in developing nations.
Still, if the substantial barriers of cost and access can be overcome, the future will continue to look brighter for patients with CF. As Dr. Sweezey put it: “There are studies that are pushing lower age limits for using these modulators, and as the evidence builds for the efficacy and safety at younger ages, I think all of us are hoping that we’ll end up being able to use either the current or future modulators to actually prevent trouble in CF, rather than trying to come along and fix it after it’s been there.”
Dr. Brown disclosed advisory board activity for Vertex that ended prior to her joining the CF Foundation. Dr. Desch, Dr. Goss, and Dr. Sweezey reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
In 1938, the year that cystic fibrosis (CF) was first described clinically, four of five children born with the disease did not live past their first birthdays.
In 2019, the median age at death for patients enrolled in the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation (CFF) registry was 32 years, and the predicted life expectancy for patients with CF who were born from 2015 through 2019 was 46 years.
Those numbers reflect the remarkable progress made in the past 4 decades in the care of patients with CF, but also highlight the obstacles ahead, given that the predicted life expectancy for the overall U.S. population in 2019 (pre–COVID-19) was 78.9 years.
Julie Desch, MD, is a CF survivor who has beaten the odds and then some. At age 61, the retired surgical pathologist is a CF patient advocate, speaker, and a board member of the Cystic Fibrosis Research Institute, a not-for-profit organization that funds CF research and offers education, advocacy, and psychosocial support for persons with CF and their families and caregivers.
In an interview, Dr. Desch said that while there has been remarkable progress in her lifetime in the field of CF research and treatment, particularly in the development of drugs that modulate function of the underlying cause of approximately 90% of CF cases, there are still many CF patients who cannot benefit from these therapies.
“There are still 10% of people who don’t make a protein to be modified, so that’s a huge unmet need,” she said.
Genetic disorder
CF is a chronic autosomal recessive disorder with multiorgan and multisystem manifestations. It is caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, which codes for the protein CF transmembrane conductance regulator. CFTR controls transport of chloride ions across cell membranes, specifically the apical membrane of epithelial cells in tissues of the airways, intestinal tract, pancreas, kidneys, sweat glands, and the reproductive system, notably the vas deferens in males.
The F508 deletion (F508del) mutation is the most common, occurring in approximately 70% of persons with CF. It is a class 2-type protein processing mutation, leading to defects in cellular processing, protein stability, and chloride channel gating defects.
The CFTR protein also secretes bicarbonate to regulate the pH of airway surface liquid, and inhibits the epithelial sodium channel, which mediates passive sodium transport across apical membranes of sodium-absorbing epithelial cells in the kidneys, intestine, and airways.
CF typically presents with the buildup in the lungs of abnormally viscous and sticky mucus leading to frequent, severe infections, particularly with Pseudomonas aeruginosa, progressive lung damage and, prior to the development of effective disease management, to premature death. The phenotype often includes malnutrition due to malabsorption, and failure to thrive.
Diagnosis
In all 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia, newborns are screened for CF with an assay for immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT) an indirect marker for pancreatic injury that is elevated in serum in most newborns with CF, but also detected in premature infants or those delivered under stressful circumstances. In some states newborns are tested only for IRT, with a diagnosis confirmed with a sweat chloride test and/or a CFTR mutation panel.
Treatment
There is no cure for CF, but the discovery of the gene in 1989 by Canadian and U.S. investigators has led to life-prolonging therapeutic interventions, specifically the development of CFTR modulators.
CFTR modulators include potentiators such as ivacaftor (Kalydeco), and correctors such as lumacaftor and tezacaftor (available in the combination Orkambi), and most recently in the triple combination of elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor (Trikafta; ETI).
Neil Sweezey, MD, FRCPC, a CF expert at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) in Toronto, told this news organization that the ideal therapy for CF, genetic correction of the underlying mutations, is still not feasible, but that CFTR modulators are a close second.
“For 90% of patients, the three-drug combination Trikafta has been shown to be quite safe, quite tolerable, and quite remarkably beneficial,” he said.
In a study reported at CHEST 2021 by investigators from Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, 32 adults who were started on the triple combination had significantly improved in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), gain in body mass index, decreased sweat chloride and decreased colonization by Pseudomonas species. In addition, patients had significant improvements in blood inflammatory markers.
Christopher H. Goss, MD, FCCP, professor of pulmonary critical care and sleep medicine and professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington in Seattle, agreed that with the availability of the triple combination, “these are extraordinary times. An astounding fact is that most patients have complete resolution of cough, and the exacerbation rates have just plummeted,” he said in an interview.
Some of the reductions in exacerbations may be attributable to the COVID-19 pandemic, he noted, because patients in isolation have less exposure to circulating respiratory viruses.
“But it has been miraculous, and the clinical effect is certainly still more astounding than the effects of ivacaftor, which was the first truly breakthrough drug. Weight goes up, well-being increases, and the population lung function has shifted up to better grade lung function, in the entire population,” he said.
In addition, the need for lung and heart transplantation has sharply declined.
“I had a patient who had decided to forgo transplantation, despite absolutely horrible lung function, and he’s now bowling and leading a very productive life, when before he had been preparing for end of life,” Dr. Goss said.
Dr. Sweezey emphasized that as with all medications, patients being started on the triple combination require close monitoring for potential adverse events that might require dose modification or, for a small number of patients, withdrawal.
Burden of care
CFTR modulators have reduced but not eliminated the need for some patients to have mucolytic therapy, which may include dornase alfa, a recombinant human deoxyribonuclease (DNase) that reduces the viscosity of lung secretions, hypertonic saline inhaled twice daily (for patients 12 and older), mannitol, and physical manipulations to help patients clear mucus. This can include both manual percussion and the use of devices for high-frequency chest wall oscillation.
The complex nature of CF often requires a combination of other therapies to address comorbidities. These therapies may include infection prophylaxis and treatment with antibiotics and antifungals, nutrition support, and therapy for CF-related complications, including gastrointestinal issues, liver diseases, diabetes, and osteopenia that may be related to poor nutrient absorption, chronic inflammation, or other sequelae of CF.
In addition, patients often require frequent CF care center visits – ideally a minimum of every 3 months – which can result in significant loss of work or school time.
“Outcomes for patients in the long run have been absolutely proven to be best if they’re followed in big, established, multidisciplinary well-organized CF centers,” Dr. Sweezey said. “In the United States and Canada if you’re looked after on a regular basis, which means quarterly, every 3 months – whether you need it or not, you really do need it – and if the patients are seen and assessed and checked every 3 months all of their lives, they have small changes caught early, whether it’s an infection you can slap down with medication or a nutrition problem that may be affecting a child’s growth and development.”
“We’re really kind of at a pivotal moment in CF, where we realize things are changing,” said A. Whitney Brown, MD, senior director for clinical affairs at the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, and an adult CF and lung transplant physician in the Inova Advanced Lung Disease Program in Falls Church, Va.
“Patient needs and interest have evolved, because of the pandemic and because of the highly effective modulator therapy, but we want to take great effort to study it in a rigorous way, to make sure that as we are agile and adapt the care model, that we can maintain the same quality outcomes that we have traditionally done,” she said in an interview.
The Lancet Respiratory Medicine Commission on the future of CF care states that models of care “need to consider management approaches (including disease monitoring) to maintain health and delay lung transplantation, while minimizing the burden of care for patients and their families.”
‘A great problem to have’
One of the most significant changes in CF care has been the growing population of CF patients like Dr. Desch who are living well into adulthood, with some approaching Medicare eligibility.
With the advent of triple therapy and CFTR modulators being started earlier in life, lung function can be preserved, damage to other organs can be minimized, and life expectancy for patients with CF will continue to improve.
“We’re anticipating that there may be some needs in the aging CF population that are different than what we have historically had,” Dr. Brown said. “Will there be geriatric providers that need to become experts in CF care? That’s a great problem to have,” she said.
Dr. Goss agreed, noting that CF is steadily shifting from a near uniformly fatal disease to a chronic disorder that in many cases can be managed “with a complex regimen of novel drugs, much like HIV.”
He noted that there are multiple drug interactions with the triple combination, “so it’s really important that people don’t start a CF patient on a drug without consulting a pharmacist, because you can totally inactivate ETI, or augment it dramatically, and we’ve seen both happen.”
Cost and access
All experts interviewed for this article agreed that while the care of patients with CF has improved exponentially over the last few decades, there are still troubling inequities in care.
One of the largest impediments is the cost of care, with the triple combination costing more than $300,000 per year.
“Clearly patients aren’t paying that, but insurance companies are, and that’s causing all kinds of trickle-down effects that definitely affect patients. The patients like myself who are able to have insurance that covers it benefit, but there are so many people that don’t,” Dr. Desch said.
Dr. Sweezey noted that prior to the advent of ETI, patients with CF in Canada had better outcomes and longer life expectancy than did similar patients in the United States because of universal access to care and coordinated services under Canada’s health care system, compared with the highly fragmented and inefficient U.S. system. He added that the wider availability of ETI in the United States vs. Canada may begin to narrow that gap, however.
As noted before, there is a substantial proportion of patients – an estimated 10% – who have CFTR mutations that are not correctable by currently available CFTR modulators, and these patients are at significant risk for irreversible airway complications and lung damage.
In addition, although CF occurs most frequently among people of White ancestry, the disease does not respect distinctions of race or ethnicity.
“It’s not just [Whites] – a lot of people from different racial backgrounds, ethnic backgrounds, are not being diagnosed or are not being diagnosed soon enough to have effective care early enough,” Dr. Desch said.
That statement is supported by the Lancet Respiratory Medicine Commission on the future of cystic fibrosis care, whose members noted in 2019 that “epidemiological studies in the past 2 decades have shown that cystic fibrosis occurs and is more frequent than was previously thought in populations of non-European descent, and the disease is now recognized in many regions of the world.”
The commission members noted that the costs of adequate CF care may be beyond the reach of many patients in developing nations.
Still, if the substantial barriers of cost and access can be overcome, the future will continue to look brighter for patients with CF. As Dr. Sweezey put it: “There are studies that are pushing lower age limits for using these modulators, and as the evidence builds for the efficacy and safety at younger ages, I think all of us are hoping that we’ll end up being able to use either the current or future modulators to actually prevent trouble in CF, rather than trying to come along and fix it after it’s been there.”
Dr. Brown disclosed advisory board activity for Vertex that ended prior to her joining the CF Foundation. Dr. Desch, Dr. Goss, and Dr. Sweezey reported no relevant conflicts of interest.