User login
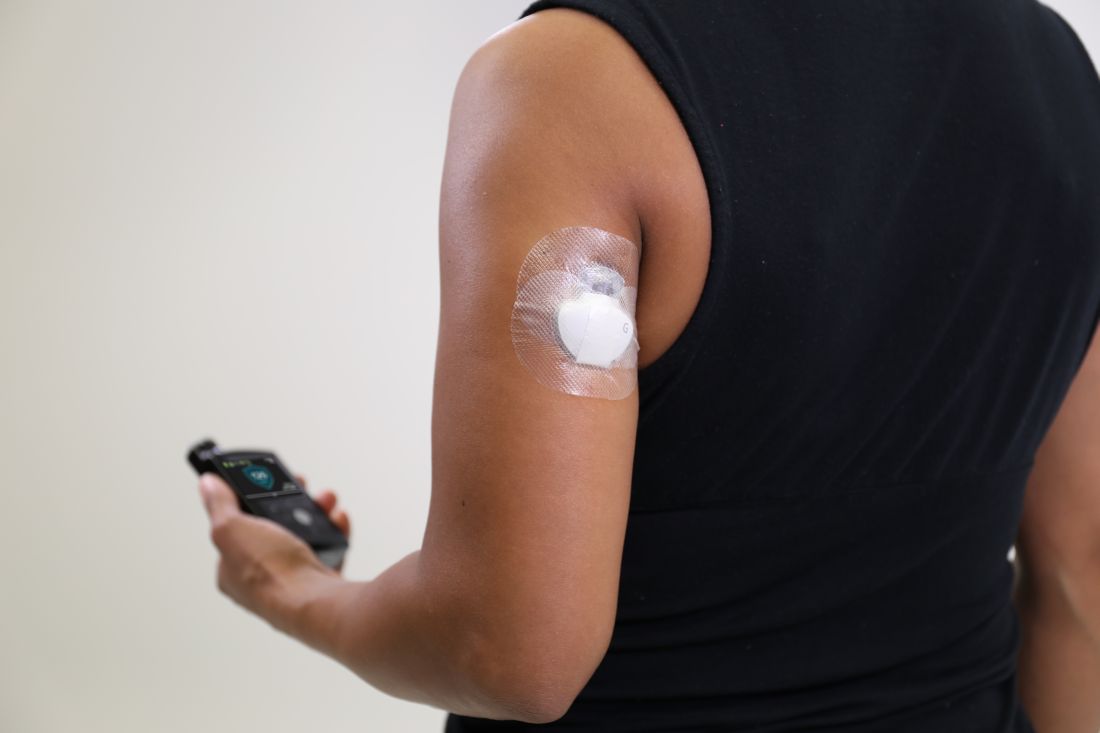
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a new indication for the Guardian Sensor 3 continuous glucose monitor (CGM), allowing patients to position it on their arms, according to an announcement by Medtronic, the sensor’s manufacturer.
Although previously only the abdomen had FDA approval as a CGM site, findings from at least one study have shown that most patients prefer to position their sensors elsewhere. This new indication gives these patients more flexibility in where they can place their CGMs. The site of CGM placement did not affect the failure rate or noncompliance.
The sensor works in tandem with an automated insulin delivery system known as the MiniMed 670G system, also manufactured by Medtronic. This system is approved for people with type 1 diabetes aged 14 years and older and adjusts basal insulin levels every 5 minutes – “based on real-time data delivered by the Guardian Sensor 3,” according to Medtronic.
Read more in Medtronic’s press release.
Correction, 3/21/18: A previous version of this article contained a photo of a device that was not the Guardian 3 Sensor.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a new indication for the Guardian Sensor 3 continuous glucose monitor (CGM), allowing patients to position it on their arms, according to an announcement by Medtronic, the sensor’s manufacturer.
Although previously only the abdomen had FDA approval as a CGM site, findings from at least one study have shown that most patients prefer to position their sensors elsewhere. This new indication gives these patients more flexibility in where they can place their CGMs. The site of CGM placement did not affect the failure rate or noncompliance.
The sensor works in tandem with an automated insulin delivery system known as the MiniMed 670G system, also manufactured by Medtronic. This system is approved for people with type 1 diabetes aged 14 years and older and adjusts basal insulin levels every 5 minutes – “based on real-time data delivered by the Guardian Sensor 3,” according to Medtronic.
Read more in Medtronic’s press release.
Correction, 3/21/18: A previous version of this article contained a photo of a device that was not the Guardian 3 Sensor.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a new indication for the Guardian Sensor 3 continuous glucose monitor (CGM), allowing patients to position it on their arms, according to an announcement by Medtronic, the sensor’s manufacturer.
Although previously only the abdomen had FDA approval as a CGM site, findings from at least one study have shown that most patients prefer to position their sensors elsewhere. This new indication gives these patients more flexibility in where they can place their CGMs. The site of CGM placement did not affect the failure rate or noncompliance.
The sensor works in tandem with an automated insulin delivery system known as the MiniMed 670G system, also manufactured by Medtronic. This system is approved for people with type 1 diabetes aged 14 years and older and adjusts basal insulin levels every 5 minutes – “based on real-time data delivered by the Guardian Sensor 3,” according to Medtronic.
Read more in Medtronic’s press release.
Correction, 3/21/18: A previous version of this article contained a photo of a device that was not the Guardian 3 Sensor.