User login
Marijuana, drug use a mystery in IBD
AUSTIN, TEX. – As more states legalize recreational and medical marijuana and cannabinoid products, and as evidence shows that up to 40% of patients with inflammatory bowel disease may be users, their gastroenterologists and other medical providers may be failing to even ask if they’re using, let alone talk to them about how it could impact their disease, according to a study of a hospital population in Washington, where recreational marijuana is legal.
The single-center, chart-review study at George Washington University found that providers noted they inquired about marijuana/CBD use in fewer than half of encounters with IBD patients – 47.8% to be precise – and that 4.9% of charts actually noted patients were users, according to a poster at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“This study acknowledges the growth of recreational and medical marijuana use as well as CBD products,” said poster presenter Scott Baumgartner, PA, a fourth-year medical student. “Understanding that because there’s increased legalization of both medical and recreational marijuana, our patients may be using them at increased rates. But are we asking them?”
According to the Drug Policy Alliance, recreational marijuana is legal in 11 states as well as Washington, which legalized recreational pot in 2014, and medical marijuana is legal in 33 states. The prevalence of cannabis use in patients with IBD has been reported at 15%-40% (Gastroenterol Hepatol [NY]. 2016;12:668-79).
The study consisted of a retrospective review of 381 charts of patients with IBD. Of the 19 charts that noted marijuana/CBD use, only 2 noted a prescription for medical purposes, although 4 noted IBD symptoms as the reason for use. Three charts noted recreational use and 12 gave no reason.
Mr. Baumgartner noted that it’s important gastroenterologists and other providers ask about marijuana/CBD use in their patients because of the inconclusive evidence about how it affects the disease (Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:2696-8). “If you’re using marijuana for an IBD such as Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis because you think it’s relieving your symptoms, does it actually work in your long-term course?” he asked. “Does it relieve some symptoms but make other disease manifestations worse. We need more research in that area.”
The takeaway of the study: “We need to do a better job of asking whether or not patients are using recreational drugs,” Mr. Baumgartner said. “And if they are using recreational drugs, what recreational drugs they are using, because it could have a big impact on the outcome of their disease.”
The next steps for this research, Mr. Baumgartner said, is to focus on the specific questions providers are asking about their patients’ marijuana and recreational drug use and how they’re documenting those responses. “Once we see that, we could consider looking at a cohort of patients who are using and see if they are reporting symptom relief, or if we are seeing disease remission, or not,” Mr. Baumgartner said.
Mr. Baumgartner has no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Baumgartner S et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020. 2020 Jan 23. Poster 011.
AUSTIN, TEX. – As more states legalize recreational and medical marijuana and cannabinoid products, and as evidence shows that up to 40% of patients with inflammatory bowel disease may be users, their gastroenterologists and other medical providers may be failing to even ask if they’re using, let alone talk to them about how it could impact their disease, according to a study of a hospital population in Washington, where recreational marijuana is legal.
The single-center, chart-review study at George Washington University found that providers noted they inquired about marijuana/CBD use in fewer than half of encounters with IBD patients – 47.8% to be precise – and that 4.9% of charts actually noted patients were users, according to a poster at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“This study acknowledges the growth of recreational and medical marijuana use as well as CBD products,” said poster presenter Scott Baumgartner, PA, a fourth-year medical student. “Understanding that because there’s increased legalization of both medical and recreational marijuana, our patients may be using them at increased rates. But are we asking them?”
According to the Drug Policy Alliance, recreational marijuana is legal in 11 states as well as Washington, which legalized recreational pot in 2014, and medical marijuana is legal in 33 states. The prevalence of cannabis use in patients with IBD has been reported at 15%-40% (Gastroenterol Hepatol [NY]. 2016;12:668-79).
The study consisted of a retrospective review of 381 charts of patients with IBD. Of the 19 charts that noted marijuana/CBD use, only 2 noted a prescription for medical purposes, although 4 noted IBD symptoms as the reason for use. Three charts noted recreational use and 12 gave no reason.
Mr. Baumgartner noted that it’s important gastroenterologists and other providers ask about marijuana/CBD use in their patients because of the inconclusive evidence about how it affects the disease (Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:2696-8). “If you’re using marijuana for an IBD such as Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis because you think it’s relieving your symptoms, does it actually work in your long-term course?” he asked. “Does it relieve some symptoms but make other disease manifestations worse. We need more research in that area.”
The takeaway of the study: “We need to do a better job of asking whether or not patients are using recreational drugs,” Mr. Baumgartner said. “And if they are using recreational drugs, what recreational drugs they are using, because it could have a big impact on the outcome of their disease.”
The next steps for this research, Mr. Baumgartner said, is to focus on the specific questions providers are asking about their patients’ marijuana and recreational drug use and how they’re documenting those responses. “Once we see that, we could consider looking at a cohort of patients who are using and see if they are reporting symptom relief, or if we are seeing disease remission, or not,” Mr. Baumgartner said.
Mr. Baumgartner has no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Baumgartner S et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020. 2020 Jan 23. Poster 011.
AUSTIN, TEX. – As more states legalize recreational and medical marijuana and cannabinoid products, and as evidence shows that up to 40% of patients with inflammatory bowel disease may be users, their gastroenterologists and other medical providers may be failing to even ask if they’re using, let alone talk to them about how it could impact their disease, according to a study of a hospital population in Washington, where recreational marijuana is legal.
The single-center, chart-review study at George Washington University found that providers noted they inquired about marijuana/CBD use in fewer than half of encounters with IBD patients – 47.8% to be precise – and that 4.9% of charts actually noted patients were users, according to a poster at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“This study acknowledges the growth of recreational and medical marijuana use as well as CBD products,” said poster presenter Scott Baumgartner, PA, a fourth-year medical student. “Understanding that because there’s increased legalization of both medical and recreational marijuana, our patients may be using them at increased rates. But are we asking them?”
According to the Drug Policy Alliance, recreational marijuana is legal in 11 states as well as Washington, which legalized recreational pot in 2014, and medical marijuana is legal in 33 states. The prevalence of cannabis use in patients with IBD has been reported at 15%-40% (Gastroenterol Hepatol [NY]. 2016;12:668-79).
The study consisted of a retrospective review of 381 charts of patients with IBD. Of the 19 charts that noted marijuana/CBD use, only 2 noted a prescription for medical purposes, although 4 noted IBD symptoms as the reason for use. Three charts noted recreational use and 12 gave no reason.
Mr. Baumgartner noted that it’s important gastroenterologists and other providers ask about marijuana/CBD use in their patients because of the inconclusive evidence about how it affects the disease (Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:2696-8). “If you’re using marijuana for an IBD such as Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis because you think it’s relieving your symptoms, does it actually work in your long-term course?” he asked. “Does it relieve some symptoms but make other disease manifestations worse. We need more research in that area.”
The takeaway of the study: “We need to do a better job of asking whether or not patients are using recreational drugs,” Mr. Baumgartner said. “And if they are using recreational drugs, what recreational drugs they are using, because it could have a big impact on the outcome of their disease.”
The next steps for this research, Mr. Baumgartner said, is to focus on the specific questions providers are asking about their patients’ marijuana and recreational drug use and how they’re documenting those responses. “Once we see that, we could consider looking at a cohort of patients who are using and see if they are reporting symptom relief, or if we are seeing disease remission, or not,” Mr. Baumgartner said.
Mr. Baumgartner has no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Baumgartner S et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020. 2020 Jan 23. Poster 011.
REPORTING FROM CROHN’S & COLITIS CONGRESS
IBD fertility has improved
AUSTIN, TEX. – Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who want to have children can benefit from better education about recent findings that disease control, laparoscopic surgery, and in vitro fertilization (IVF) have improved their chances of conceiving, according to a review of published reports presented here at the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, a partnership of the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
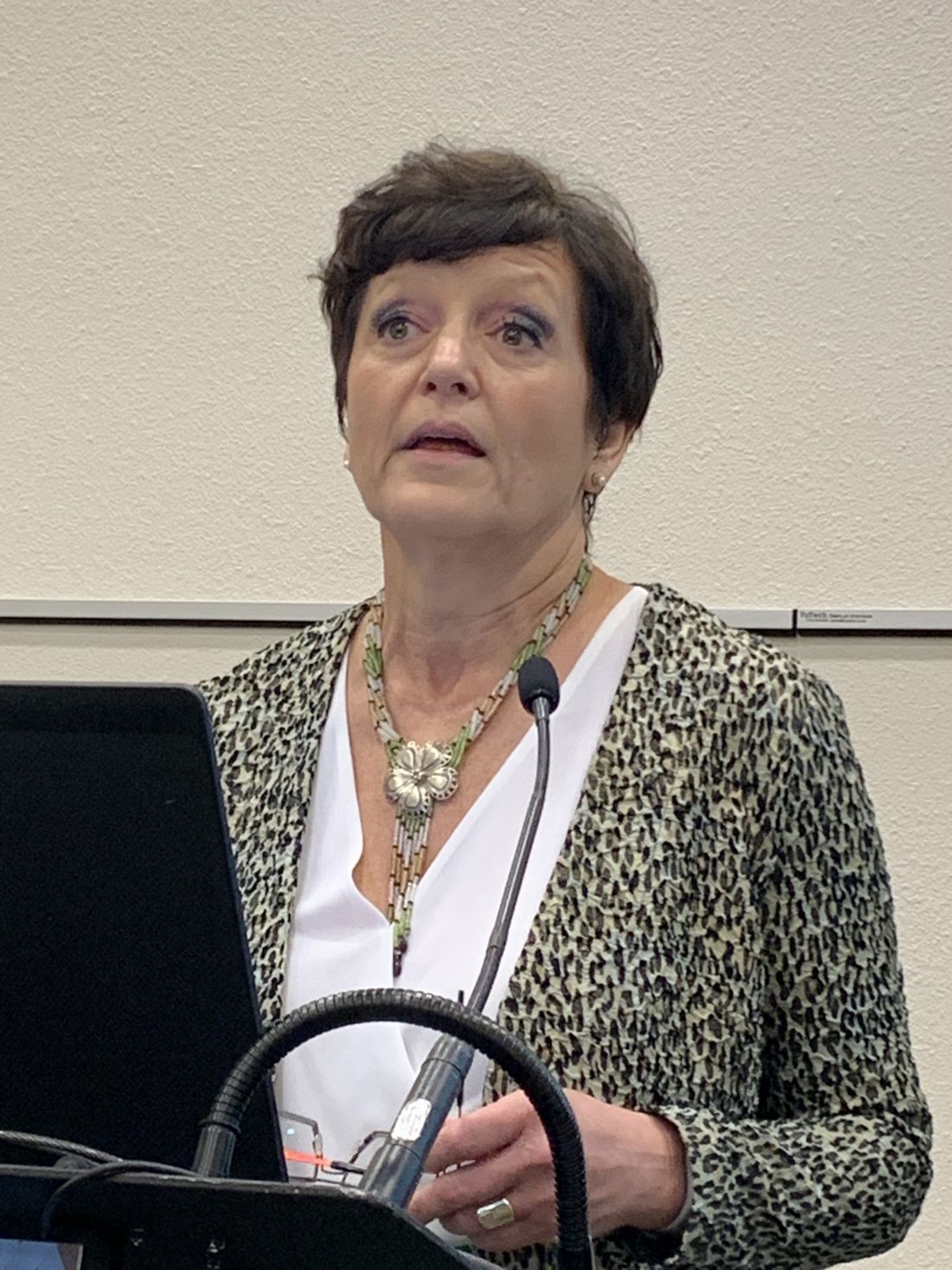
“Decreased fertility in IBD is due to voluntary childlessness, which we can change with education; surgery for IBD, which we can improve with laparoscopic surgery; and increased disease activity, which we can also make a difference in,” Sonia Friedman, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
Dr. Friedman and coauthors last year published an analysis of the Danish National Birth Cohort, which showed women with IBD had an 28% greater relative risk of taking a year or more to get pregnant than controls without IBD, and that the relative risk was even higher in women with Crohn’s disease — 54% (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.08.031). “We found that women with Crohn’s surgery had decreased fertility by 2.54 times greater relative risk,” she said.
“Fertility, pregnancy is the most important thing to patients,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “That’s what people ask me about the most. In the population of IBD patients, the onset is age 15-35, and these people are in the prime of their reproductive years.” Sexual function, known to be decreased in men and women with IBD, is also an overriding concern in these patients, she said. “There needs to be a lot more information out there about it.”
She said gastroenterologists should keep in mind that much of the evidence documenting reduced fertility after ileo-pouch anal anastomosis is dated and focused on open surgery, which caused profound scarring of the pelvis and fallopian tubes, thus hindering conception. Laparoscopic ileoanal J-pouch surgery (IPAA) has yielded much improved outcomes in women of child-bearing age, she said, citing a study late last year that reported women who had laparoscopic IPAA had a median time to pregnancy of 3.5 months versus 9 months for women who had open IPAA (Surgery. 2019;166:670-7).
“It’s really important to discuss the issues of fertility, especially for patients contemplating surgery,” Dr. Friedman said. “Emphasize that there are good outcomes with laparoscopic surgery, and they can have assisted reproductive technology [ART], or in vitro fertilization, if needed. Never withhold surgery based on fear of infertility.”
Her practice is to refer women with IBD in remission for IVF if they’ve tried to get pregnant every month for a year or more and to refer women with IBD surgery for IVF after trying to get pregnant for 6 months. Dr. Friedman coauthored two studies of the Danish National Birth Cohort of ART in women with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) along with controls (Gut. 2016;65:767-76; Gut. 2017;66:556-58). “We found that women with Crohn’s and UC had a decreased chance of having a clinical pregnancy, but they had no problem carrying the pregnancy to term,” she said.
Those findings raised questions about the etiology of decreased fertility in IBD patients, which could include factors such as IVF technique, reproductive hormone and microbiome changes, or IBD medications. “How can we carry that forward to all women with IBD?” she said. Women with IBD have less chance of conceiving with each IVF treatment cycle than do women without IBD, she said. “The most interesting thing is that the reduced chance of live birth after IVF treatment in Crohn’s and UC is related to the stages of implantation and not to the ability to maintain the fetus throughout pregnancy,” she said.
Dr. Friedman has no financial relationships to disclose.
The AGA IBD Parenthood Project can help guide your patients with IBD throughout their pregnancy, from trying to conceive through postpartum care. Learn more at IBDParenthoodProject.org.
SOURCE: Friedman S. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, Session Sp86.
AUSTIN, TEX. – Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who want to have children can benefit from better education about recent findings that disease control, laparoscopic surgery, and in vitro fertilization (IVF) have improved their chances of conceiving, according to a review of published reports presented here at the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, a partnership of the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“Decreased fertility in IBD is due to voluntary childlessness, which we can change with education; surgery for IBD, which we can improve with laparoscopic surgery; and increased disease activity, which we can also make a difference in,” Sonia Friedman, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
Dr. Friedman and coauthors last year published an analysis of the Danish National Birth Cohort, which showed women with IBD had an 28% greater relative risk of taking a year or more to get pregnant than controls without IBD, and that the relative risk was even higher in women with Crohn’s disease — 54% (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.08.031). “We found that women with Crohn’s surgery had decreased fertility by 2.54 times greater relative risk,” she said.
“Fertility, pregnancy is the most important thing to patients,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “That’s what people ask me about the most. In the population of IBD patients, the onset is age 15-35, and these people are in the prime of their reproductive years.” Sexual function, known to be decreased in men and women with IBD, is also an overriding concern in these patients, she said. “There needs to be a lot more information out there about it.”
She said gastroenterologists should keep in mind that much of the evidence documenting reduced fertility after ileo-pouch anal anastomosis is dated and focused on open surgery, which caused profound scarring of the pelvis and fallopian tubes, thus hindering conception. Laparoscopic ileoanal J-pouch surgery (IPAA) has yielded much improved outcomes in women of child-bearing age, she said, citing a study late last year that reported women who had laparoscopic IPAA had a median time to pregnancy of 3.5 months versus 9 months for women who had open IPAA (Surgery. 2019;166:670-7).
“It’s really important to discuss the issues of fertility, especially for patients contemplating surgery,” Dr. Friedman said. “Emphasize that there are good outcomes with laparoscopic surgery, and they can have assisted reproductive technology [ART], or in vitro fertilization, if needed. Never withhold surgery based on fear of infertility.”
Her practice is to refer women with IBD in remission for IVF if they’ve tried to get pregnant every month for a year or more and to refer women with IBD surgery for IVF after trying to get pregnant for 6 months. Dr. Friedman coauthored two studies of the Danish National Birth Cohort of ART in women with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) along with controls (Gut. 2016;65:767-76; Gut. 2017;66:556-58). “We found that women with Crohn’s and UC had a decreased chance of having a clinical pregnancy, but they had no problem carrying the pregnancy to term,” she said.
Those findings raised questions about the etiology of decreased fertility in IBD patients, which could include factors such as IVF technique, reproductive hormone and microbiome changes, or IBD medications. “How can we carry that forward to all women with IBD?” she said. Women with IBD have less chance of conceiving with each IVF treatment cycle than do women without IBD, she said. “The most interesting thing is that the reduced chance of live birth after IVF treatment in Crohn’s and UC is related to the stages of implantation and not to the ability to maintain the fetus throughout pregnancy,” she said.
Dr. Friedman has no financial relationships to disclose.
The AGA IBD Parenthood Project can help guide your patients with IBD throughout their pregnancy, from trying to conceive through postpartum care. Learn more at IBDParenthoodProject.org.
SOURCE: Friedman S. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, Session Sp86.
AUSTIN, TEX. – Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who want to have children can benefit from better education about recent findings that disease control, laparoscopic surgery, and in vitro fertilization (IVF) have improved their chances of conceiving, according to a review of published reports presented here at the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, a partnership of the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“Decreased fertility in IBD is due to voluntary childlessness, which we can change with education; surgery for IBD, which we can improve with laparoscopic surgery; and increased disease activity, which we can also make a difference in,” Sonia Friedman, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
Dr. Friedman and coauthors last year published an analysis of the Danish National Birth Cohort, which showed women with IBD had an 28% greater relative risk of taking a year or more to get pregnant than controls without IBD, and that the relative risk was even higher in women with Crohn’s disease — 54% (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.08.031). “We found that women with Crohn’s surgery had decreased fertility by 2.54 times greater relative risk,” she said.
“Fertility, pregnancy is the most important thing to patients,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “That’s what people ask me about the most. In the population of IBD patients, the onset is age 15-35, and these people are in the prime of their reproductive years.” Sexual function, known to be decreased in men and women with IBD, is also an overriding concern in these patients, she said. “There needs to be a lot more information out there about it.”
She said gastroenterologists should keep in mind that much of the evidence documenting reduced fertility after ileo-pouch anal anastomosis is dated and focused on open surgery, which caused profound scarring of the pelvis and fallopian tubes, thus hindering conception. Laparoscopic ileoanal J-pouch surgery (IPAA) has yielded much improved outcomes in women of child-bearing age, she said, citing a study late last year that reported women who had laparoscopic IPAA had a median time to pregnancy of 3.5 months versus 9 months for women who had open IPAA (Surgery. 2019;166:670-7).
“It’s really important to discuss the issues of fertility, especially for patients contemplating surgery,” Dr. Friedman said. “Emphasize that there are good outcomes with laparoscopic surgery, and they can have assisted reproductive technology [ART], or in vitro fertilization, if needed. Never withhold surgery based on fear of infertility.”
Her practice is to refer women with IBD in remission for IVF if they’ve tried to get pregnant every month for a year or more and to refer women with IBD surgery for IVF after trying to get pregnant for 6 months. Dr. Friedman coauthored two studies of the Danish National Birth Cohort of ART in women with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) along with controls (Gut. 2016;65:767-76; Gut. 2017;66:556-58). “We found that women with Crohn’s and UC had a decreased chance of having a clinical pregnancy, but they had no problem carrying the pregnancy to term,” she said.
Those findings raised questions about the etiology of decreased fertility in IBD patients, which could include factors such as IVF technique, reproductive hormone and microbiome changes, or IBD medications. “How can we carry that forward to all women with IBD?” she said. Women with IBD have less chance of conceiving with each IVF treatment cycle than do women without IBD, she said. “The most interesting thing is that the reduced chance of live birth after IVF treatment in Crohn’s and UC is related to the stages of implantation and not to the ability to maintain the fetus throughout pregnancy,” she said.
Dr. Friedman has no financial relationships to disclose.
The AGA IBD Parenthood Project can help guide your patients with IBD throughout their pregnancy, from trying to conceive through postpartum care. Learn more at IBDParenthoodProject.org.
SOURCE: Friedman S. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, Session Sp86.
REPORTING FROM CROHN’S & COLITIS CONGRESS
IBD quality initiative slashes ED utilization
AUSTIN, TEX. – A quality improvement initiative aimed at patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has reduced emergency department visits and hospitalizations by 20% or more and slashed opioid use by half, according to study results presented at the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, a partnership of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
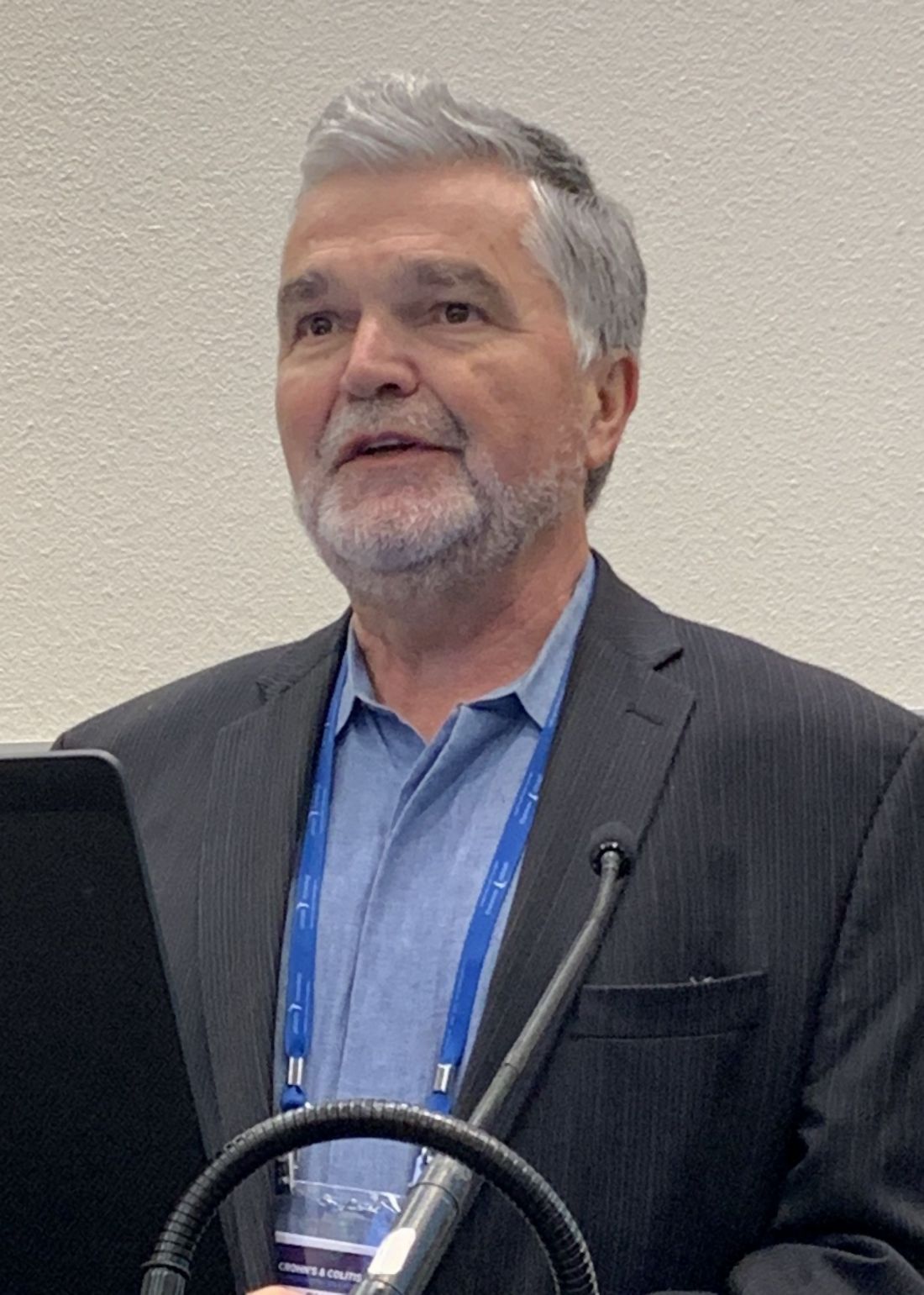
After 15 months, the quality improvement program saw emergency department visit rates decline from 18% to 14%, a 22% relative decrease, Gil Y. Melmed, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said. Additionally, the study documented a similar decrease in the rate of hospitalization, declining from 14% to 11%, while opioid utilization rates declined from 8% to 4%. “We also found decreases in special-cause variation in other measures of interest, including CT scan utilization as well as corticosteroid use, which was reduced 29% during the course of the program,” he said.
The quality initiative was conducted through the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation as an outgrowth of its IBD Qorus quality improvement program. The 15-month study involved 20,392 patient visits at 15 academic and 11 private/community practices from January 2018 to April 2019. “This specific project within Qorus is focused specifically around the concept of improving access during times of urgent care need,” Dr. Melmed told this news organization. The goal was to identify practice changes that can drive improvement.
The intervention consisted of 19 different strategies, called a “Change Package,” and participating sites could choose to test and implement one or more of them, Dr. Melmed said. Some examples included designating urgent care slots in the clinic schedule, installing a nurse hotline, a weekly “huddle” to review high-risk patients, and patient education on using urgent care.
One of the drivers of the program was to provide immediate care improvement to patients, Dr. Melmed said in the interview. “As opposed to investments into the cure of IBD that we need, but which can take years to develop, this research has immediate, practical applicability for patients today,” he said.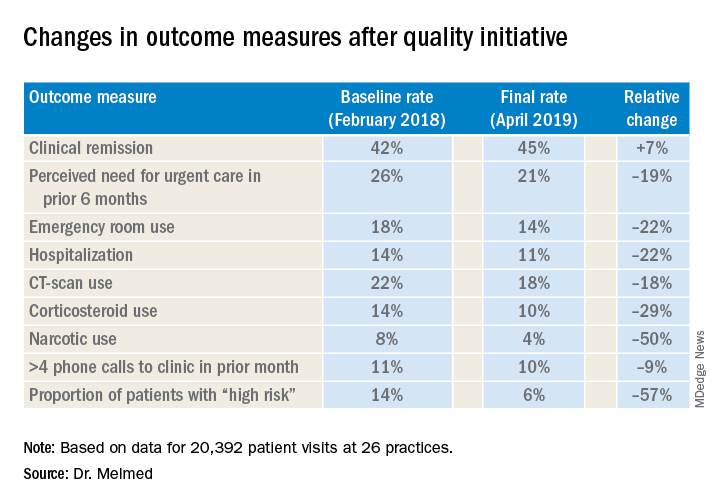
“The fact that we were able to demonstrate reduction in emergency room utilization and hospitalization, steroid use, and narcotic use has really energized the work that we were doing. We can now show that very-low-cost process changes at a site level lead to robust improvement in patient outcomes. These changes are potentially implementable in any practice setting,” Dr. Melmed said in the interview.
After Dr. Melmed’s presentation, Maria T. Abreu, MD, director of the Crohn’s and Colitis Center at the University of Miami, asked about the cost of the interventions. Dr. Melmed said the costs were nominal, such as paying for a new phone line for a patient hotline. “But overall the cost really involved in the program was the time that it took to review the high-risk list on a weekly basis with the team, and that is essentially a 15-minute huddle,” he said.
Later, Dr. Abreu said in an interview that the program was “a terrific example of how measuring outcomes and sharing ideas can make huge impacts in the lives of patients.” She added, “An enormous amount of money is spent on clinical trials of expensive biologics which have revolutionized treatment, yet the humanistic aspects of our care have just as great of an impact. In this study, each center focused on ways they could lower ER visits and hospitalizations. One size did not fit all, yet they could learn from each other. The very platform they used to conduct the study is a model for all of us.”
Corey A. Siegel, MD, of the Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., and Dr. Melmed's coprincipal investigator on Qorus, said the quality initiative now includes 49 GI practices across the country with plans to grow to 60 by the end of the year. "We have created this 'collaboratory' for providers from actross the country to work togetherr to learn how to best deliver high-qulaity care for patients with IBD," he said.
Another feature of the quality initiative allowed participating sites to see how they compared with others anonymously, Dr. Melmed said. “Using the data, we called out high-performing sites to teach the rest of us what they were doing that enabled them to improve, so that all of us could learn from their successes,” he said.
The researchers are aiming to evaluate costs and identify the most successful interventions, with the plan to present the latter at Digestive Disease Week® 2020 and use them to develop a toolkit practices can use. “Ultimately,” said Dr. Melmed, “this is scalable.”
Dr. Melmed disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Jannsen, GSK, Medtronic, Pfizer, Samsung Bioepis, Takeda, and Techlab; IBD Qorus receives support from Abbvie, AMAG, Helmsley Charitable Trust, Janssen, Nephoroceuticals, Pfizer, Takeda, and UCB.
SOURCE: Melmed GT et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020, Session 28.
AUSTIN, TEX. – A quality improvement initiative aimed at patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has reduced emergency department visits and hospitalizations by 20% or more and slashed opioid use by half, according to study results presented at the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, a partnership of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
After 15 months, the quality improvement program saw emergency department visit rates decline from 18% to 14%, a 22% relative decrease, Gil Y. Melmed, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said. Additionally, the study documented a similar decrease in the rate of hospitalization, declining from 14% to 11%, while opioid utilization rates declined from 8% to 4%. “We also found decreases in special-cause variation in other measures of interest, including CT scan utilization as well as corticosteroid use, which was reduced 29% during the course of the program,” he said.
The quality initiative was conducted through the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation as an outgrowth of its IBD Qorus quality improvement program. The 15-month study involved 20,392 patient visits at 15 academic and 11 private/community practices from January 2018 to April 2019. “This specific project within Qorus is focused specifically around the concept of improving access during times of urgent care need,” Dr. Melmed told this news organization. The goal was to identify practice changes that can drive improvement.
The intervention consisted of 19 different strategies, called a “Change Package,” and participating sites could choose to test and implement one or more of them, Dr. Melmed said. Some examples included designating urgent care slots in the clinic schedule, installing a nurse hotline, a weekly “huddle” to review high-risk patients, and patient education on using urgent care.
One of the drivers of the program was to provide immediate care improvement to patients, Dr. Melmed said in the interview. “As opposed to investments into the cure of IBD that we need, but which can take years to develop, this research has immediate, practical applicability for patients today,” he said.
“The fact that we were able to demonstrate reduction in emergency room utilization and hospitalization, steroid use, and narcotic use has really energized the work that we were doing. We can now show that very-low-cost process changes at a site level lead to robust improvement in patient outcomes. These changes are potentially implementable in any practice setting,” Dr. Melmed said in the interview.
After Dr. Melmed’s presentation, Maria T. Abreu, MD, director of the Crohn’s and Colitis Center at the University of Miami, asked about the cost of the interventions. Dr. Melmed said the costs were nominal, such as paying for a new phone line for a patient hotline. “But overall the cost really involved in the program was the time that it took to review the high-risk list on a weekly basis with the team, and that is essentially a 15-minute huddle,” he said.
Later, Dr. Abreu said in an interview that the program was “a terrific example of how measuring outcomes and sharing ideas can make huge impacts in the lives of patients.” She added, “An enormous amount of money is spent on clinical trials of expensive biologics which have revolutionized treatment, yet the humanistic aspects of our care have just as great of an impact. In this study, each center focused on ways they could lower ER visits and hospitalizations. One size did not fit all, yet they could learn from each other. The very platform they used to conduct the study is a model for all of us.”
Corey A. Siegel, MD, of the Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., and Dr. Melmed's coprincipal investigator on Qorus, said the quality initiative now includes 49 GI practices across the country with plans to grow to 60 by the end of the year. "We have created this 'collaboratory' for providers from actross the country to work togetherr to learn how to best deliver high-qulaity care for patients with IBD," he said.
Another feature of the quality initiative allowed participating sites to see how they compared with others anonymously, Dr. Melmed said. “Using the data, we called out high-performing sites to teach the rest of us what they were doing that enabled them to improve, so that all of us could learn from their successes,” he said.
The researchers are aiming to evaluate costs and identify the most successful interventions, with the plan to present the latter at Digestive Disease Week® 2020 and use them to develop a toolkit practices can use. “Ultimately,” said Dr. Melmed, “this is scalable.”
Dr. Melmed disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Jannsen, GSK, Medtronic, Pfizer, Samsung Bioepis, Takeda, and Techlab; IBD Qorus receives support from Abbvie, AMAG, Helmsley Charitable Trust, Janssen, Nephoroceuticals, Pfizer, Takeda, and UCB.
SOURCE: Melmed GT et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020, Session 28.
AUSTIN, TEX. – A quality improvement initiative aimed at patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has reduced emergency department visits and hospitalizations by 20% or more and slashed opioid use by half, according to study results presented at the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, a partnership of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
After 15 months, the quality improvement program saw emergency department visit rates decline from 18% to 14%, a 22% relative decrease, Gil Y. Melmed, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said. Additionally, the study documented a similar decrease in the rate of hospitalization, declining from 14% to 11%, while opioid utilization rates declined from 8% to 4%. “We also found decreases in special-cause variation in other measures of interest, including CT scan utilization as well as corticosteroid use, which was reduced 29% during the course of the program,” he said.
The quality initiative was conducted through the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation as an outgrowth of its IBD Qorus quality improvement program. The 15-month study involved 20,392 patient visits at 15 academic and 11 private/community practices from January 2018 to April 2019. “This specific project within Qorus is focused specifically around the concept of improving access during times of urgent care need,” Dr. Melmed told this news organization. The goal was to identify practice changes that can drive improvement.
The intervention consisted of 19 different strategies, called a “Change Package,” and participating sites could choose to test and implement one or more of them, Dr. Melmed said. Some examples included designating urgent care slots in the clinic schedule, installing a nurse hotline, a weekly “huddle” to review high-risk patients, and patient education on using urgent care.
One of the drivers of the program was to provide immediate care improvement to patients, Dr. Melmed said in the interview. “As opposed to investments into the cure of IBD that we need, but which can take years to develop, this research has immediate, practical applicability for patients today,” he said.
“The fact that we were able to demonstrate reduction in emergency room utilization and hospitalization, steroid use, and narcotic use has really energized the work that we were doing. We can now show that very-low-cost process changes at a site level lead to robust improvement in patient outcomes. These changes are potentially implementable in any practice setting,” Dr. Melmed said in the interview.
After Dr. Melmed’s presentation, Maria T. Abreu, MD, director of the Crohn’s and Colitis Center at the University of Miami, asked about the cost of the interventions. Dr. Melmed said the costs were nominal, such as paying for a new phone line for a patient hotline. “But overall the cost really involved in the program was the time that it took to review the high-risk list on a weekly basis with the team, and that is essentially a 15-minute huddle,” he said.
Later, Dr. Abreu said in an interview that the program was “a terrific example of how measuring outcomes and sharing ideas can make huge impacts in the lives of patients.” She added, “An enormous amount of money is spent on clinical trials of expensive biologics which have revolutionized treatment, yet the humanistic aspects of our care have just as great of an impact. In this study, each center focused on ways they could lower ER visits and hospitalizations. One size did not fit all, yet they could learn from each other. The very platform they used to conduct the study is a model for all of us.”
Corey A. Siegel, MD, of the Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., and Dr. Melmed's coprincipal investigator on Qorus, said the quality initiative now includes 49 GI practices across the country with plans to grow to 60 by the end of the year. "We have created this 'collaboratory' for providers from actross the country to work togetherr to learn how to best deliver high-qulaity care for patients with IBD," he said.
Another feature of the quality initiative allowed participating sites to see how they compared with others anonymously, Dr. Melmed said. “Using the data, we called out high-performing sites to teach the rest of us what they were doing that enabled them to improve, so that all of us could learn from their successes,” he said.
The researchers are aiming to evaluate costs and identify the most successful interventions, with the plan to present the latter at Digestive Disease Week® 2020 and use them to develop a toolkit practices can use. “Ultimately,” said Dr. Melmed, “this is scalable.”
Dr. Melmed disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Jannsen, GSK, Medtronic, Pfizer, Samsung Bioepis, Takeda, and Techlab; IBD Qorus receives support from Abbvie, AMAG, Helmsley Charitable Trust, Janssen, Nephoroceuticals, Pfizer, Takeda, and UCB.
SOURCE: Melmed GT et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020, Session 28.
REPORTING FROM CROHN’S & COLITIS CONGRESS
ERAS takes its place in IBD surgery
AUSTIN, TEX. – Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols have been around for decades, but typically excluded patients having surgery for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). However, recent studies have shown strategies to optimize these patients, including presurgery carbohydrate loading and early postsurgery feeding, can improve outcomes, according to a review of evidence presented at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“It’s really important that we implement strategies to help mitigate the impact that malnutrition is going to have on our perioperative patients, and one of the ways we do that is by using an ERAS or enhanced recovery after surgery protocol,” said Kelly Issokson, MS, RD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles. She noted that patients with IBD are five times more likely to be malnourished than non-IBD patients, and those with fistulizing Crohn’s disease and bowel resections are at greatest risk (Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14:1139-46).
“I constantly see patients who are kept NPO [nothing by mouth] 12 or 24 hours before surgery, maybe even longer sometimes, unfortunately,” she said. “We should really be minimizing that NPO to help mitigate the catabolic effect that surgery has on our patients and help them recover more quickly.”
To screen surgery patients for nutrition risk, Ms. Issokson said that gastroenterologists can ask two questions from the malnutrition screening tool: Did the patient have recent unintentional weight loss, and is the patient eating less because of poor appetite? A yes to either question merits referral to a registered dietician. Malnutrition, weight loss of 5%-10% of total body weight, and sarcopenia are predictors of surgical complications for IBD patients, the latter an independent predictor in patients aged 40 years and older.
The ERAS protocol involves optimizing preoperative and postoperative nutrition, she said. It has been linked with improved outcomes in elective colorectal surgery (World J Surg. 2014;38:1531-41), although the evidence in IBD isn’t as robust. She cited a retrospective study reported at the 2019 annual Digestive Disease Week of patients with Crohn’s disease that found no difference in readmissions, complications, or reoperations between ERAS and standard-care patients.
Preoperative nutrition optimization in ERAS involves anemia and fluid management, oral nutrition supplementation, and – based on European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) 2017 guidelines – delaying the operation where possible if the patient is malnourished. “Patients who receive preoperative nutrition support have been shown to have better outcomes postoperatively,” Ms. Issokson said, citing a meta-analysis of 1,111 Crohn’s disease patients that reported the complication rate was 20% in patients on nutrition support versus 60% for those on standard care; in those on enteral nutrition, the disparity was more pronounced: 21% versus 73% (Eur J Gastro Hep. 2018;30:997-1002).
Gastroenterologists should not be afraid of implementing total parenteral nutrition (TPN) perioperatively in these patients, Ms. Issokson said. “This can really help to improve outcomes and quality of life in our patients, and it’s something that we really should not shy away from,” she added in an interview. “If our patients are malnourished and meet the criteria for TPN, then we should really not be withholding it.” Patients with severe IBD who are not absorbing from their gut and can’t meet 60% of their needs by mouth are prime candidates for TPN, she said, referencing a 2019 study that reported that preoperative TPN in malnourished IBD patients resulted in a rate of overall noninfectious complications half that of no-TPN patients: 8.3% versus 16.8% (Gastroenterol Rep. 2019 Apr;7:107-14).
Carbohydrate loading before surgery is a big part of ERAS in these patients. “Surgery has a huge impact on the catabolic state of a patient,” Ms. Issokson said. “It’s similar to running a marathon; you wouldn’t go out and run a marathon without fueling up the night before with a whole bunch of carbohydrates. So we use this same strategy in our surgical patients.”
ERAS society guidelines call for 100 g of carbohydrates the night before and 50 g 2 hours before surgery in the form of a clear liquid beverage, along with permitting a light meal up to 6 hours before, with exceptions in gastroparesis, motility disorders, and emergency surgery.
Another key component of ERAS in IBD is early postoperative feeding. “Postoperatively we want to feed our patients as soon as possible,” Ms. Issokson said. ESPEN guidelines call for feeding patients with new nondiverted colorectal anastomosis within 4 hours. “Studies show that patients aren’t able to eat enough calories to help them recover postoperatively, so implementing an oral nutrition supplement might be helpful there,” she added.
Ms. Issokson is a Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation board member, and disclosed financial relationships with Orgain, RMEI, and Medscape.
SOURCE: Issokson K et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020, Session Sp83.
AUSTIN, TEX. – Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols have been around for decades, but typically excluded patients having surgery for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). However, recent studies have shown strategies to optimize these patients, including presurgery carbohydrate loading and early postsurgery feeding, can improve outcomes, according to a review of evidence presented at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“It’s really important that we implement strategies to help mitigate the impact that malnutrition is going to have on our perioperative patients, and one of the ways we do that is by using an ERAS or enhanced recovery after surgery protocol,” said Kelly Issokson, MS, RD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles. She noted that patients with IBD are five times more likely to be malnourished than non-IBD patients, and those with fistulizing Crohn’s disease and bowel resections are at greatest risk (Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14:1139-46).
“I constantly see patients who are kept NPO [nothing by mouth] 12 or 24 hours before surgery, maybe even longer sometimes, unfortunately,” she said. “We should really be minimizing that NPO to help mitigate the catabolic effect that surgery has on our patients and help them recover more quickly.”
To screen surgery patients for nutrition risk, Ms. Issokson said that gastroenterologists can ask two questions from the malnutrition screening tool: Did the patient have recent unintentional weight loss, and is the patient eating less because of poor appetite? A yes to either question merits referral to a registered dietician. Malnutrition, weight loss of 5%-10% of total body weight, and sarcopenia are predictors of surgical complications for IBD patients, the latter an independent predictor in patients aged 40 years and older.
The ERAS protocol involves optimizing preoperative and postoperative nutrition, she said. It has been linked with improved outcomes in elective colorectal surgery (World J Surg. 2014;38:1531-41), although the evidence in IBD isn’t as robust. She cited a retrospective study reported at the 2019 annual Digestive Disease Week of patients with Crohn’s disease that found no difference in readmissions, complications, or reoperations between ERAS and standard-care patients.
Preoperative nutrition optimization in ERAS involves anemia and fluid management, oral nutrition supplementation, and – based on European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) 2017 guidelines – delaying the operation where possible if the patient is malnourished. “Patients who receive preoperative nutrition support have been shown to have better outcomes postoperatively,” Ms. Issokson said, citing a meta-analysis of 1,111 Crohn’s disease patients that reported the complication rate was 20% in patients on nutrition support versus 60% for those on standard care; in those on enteral nutrition, the disparity was more pronounced: 21% versus 73% (Eur J Gastro Hep. 2018;30:997-1002).
Gastroenterologists should not be afraid of implementing total parenteral nutrition (TPN) perioperatively in these patients, Ms. Issokson said. “This can really help to improve outcomes and quality of life in our patients, and it’s something that we really should not shy away from,” she added in an interview. “If our patients are malnourished and meet the criteria for TPN, then we should really not be withholding it.” Patients with severe IBD who are not absorbing from their gut and can’t meet 60% of their needs by mouth are prime candidates for TPN, she said, referencing a 2019 study that reported that preoperative TPN in malnourished IBD patients resulted in a rate of overall noninfectious complications half that of no-TPN patients: 8.3% versus 16.8% (Gastroenterol Rep. 2019 Apr;7:107-14).
Carbohydrate loading before surgery is a big part of ERAS in these patients. “Surgery has a huge impact on the catabolic state of a patient,” Ms. Issokson said. “It’s similar to running a marathon; you wouldn’t go out and run a marathon without fueling up the night before with a whole bunch of carbohydrates. So we use this same strategy in our surgical patients.”
ERAS society guidelines call for 100 g of carbohydrates the night before and 50 g 2 hours before surgery in the form of a clear liquid beverage, along with permitting a light meal up to 6 hours before, with exceptions in gastroparesis, motility disorders, and emergency surgery.
Another key component of ERAS in IBD is early postoperative feeding. “Postoperatively we want to feed our patients as soon as possible,” Ms. Issokson said. ESPEN guidelines call for feeding patients with new nondiverted colorectal anastomosis within 4 hours. “Studies show that patients aren’t able to eat enough calories to help them recover postoperatively, so implementing an oral nutrition supplement might be helpful there,” she added.
Ms. Issokson is a Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation board member, and disclosed financial relationships with Orgain, RMEI, and Medscape.
SOURCE: Issokson K et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020, Session Sp83.
AUSTIN, TEX. – Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols have been around for decades, but typically excluded patients having surgery for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). However, recent studies have shown strategies to optimize these patients, including presurgery carbohydrate loading and early postsurgery feeding, can improve outcomes, according to a review of evidence presented at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“It’s really important that we implement strategies to help mitigate the impact that malnutrition is going to have on our perioperative patients, and one of the ways we do that is by using an ERAS or enhanced recovery after surgery protocol,” said Kelly Issokson, MS, RD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles. She noted that patients with IBD are five times more likely to be malnourished than non-IBD patients, and those with fistulizing Crohn’s disease and bowel resections are at greatest risk (Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14:1139-46).
“I constantly see patients who are kept NPO [nothing by mouth] 12 or 24 hours before surgery, maybe even longer sometimes, unfortunately,” she said. “We should really be minimizing that NPO to help mitigate the catabolic effect that surgery has on our patients and help them recover more quickly.”
To screen surgery patients for nutrition risk, Ms. Issokson said that gastroenterologists can ask two questions from the malnutrition screening tool: Did the patient have recent unintentional weight loss, and is the patient eating less because of poor appetite? A yes to either question merits referral to a registered dietician. Malnutrition, weight loss of 5%-10% of total body weight, and sarcopenia are predictors of surgical complications for IBD patients, the latter an independent predictor in patients aged 40 years and older.
The ERAS protocol involves optimizing preoperative and postoperative nutrition, she said. It has been linked with improved outcomes in elective colorectal surgery (World J Surg. 2014;38:1531-41), although the evidence in IBD isn’t as robust. She cited a retrospective study reported at the 2019 annual Digestive Disease Week of patients with Crohn’s disease that found no difference in readmissions, complications, or reoperations between ERAS and standard-care patients.
Preoperative nutrition optimization in ERAS involves anemia and fluid management, oral nutrition supplementation, and – based on European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) 2017 guidelines – delaying the operation where possible if the patient is malnourished. “Patients who receive preoperative nutrition support have been shown to have better outcomes postoperatively,” Ms. Issokson said, citing a meta-analysis of 1,111 Crohn’s disease patients that reported the complication rate was 20% in patients on nutrition support versus 60% for those on standard care; in those on enteral nutrition, the disparity was more pronounced: 21% versus 73% (Eur J Gastro Hep. 2018;30:997-1002).
Gastroenterologists should not be afraid of implementing total parenteral nutrition (TPN) perioperatively in these patients, Ms. Issokson said. “This can really help to improve outcomes and quality of life in our patients, and it’s something that we really should not shy away from,” she added in an interview. “If our patients are malnourished and meet the criteria for TPN, then we should really not be withholding it.” Patients with severe IBD who are not absorbing from their gut and can’t meet 60% of their needs by mouth are prime candidates for TPN, she said, referencing a 2019 study that reported that preoperative TPN in malnourished IBD patients resulted in a rate of overall noninfectious complications half that of no-TPN patients: 8.3% versus 16.8% (Gastroenterol Rep. 2019 Apr;7:107-14).
Carbohydrate loading before surgery is a big part of ERAS in these patients. “Surgery has a huge impact on the catabolic state of a patient,” Ms. Issokson said. “It’s similar to running a marathon; you wouldn’t go out and run a marathon without fueling up the night before with a whole bunch of carbohydrates. So we use this same strategy in our surgical patients.”
ERAS society guidelines call for 100 g of carbohydrates the night before and 50 g 2 hours before surgery in the form of a clear liquid beverage, along with permitting a light meal up to 6 hours before, with exceptions in gastroparesis, motility disorders, and emergency surgery.
Another key component of ERAS in IBD is early postoperative feeding. “Postoperatively we want to feed our patients as soon as possible,” Ms. Issokson said. ESPEN guidelines call for feeding patients with new nondiverted colorectal anastomosis within 4 hours. “Studies show that patients aren’t able to eat enough calories to help them recover postoperatively, so implementing an oral nutrition supplement might be helpful there,” she added.
Ms. Issokson is a Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation board member, and disclosed financial relationships with Orgain, RMEI, and Medscape.
SOURCE: Issokson K et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020, Session Sp83.
REPORTING FROM THE CROHN’S & COLITIS CONGRESS
IBD fertility has improved
AUSTIN, TEX. – Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who want to have children can benefit from better education about recent findings that disease control, laparoscopic surgery, and in vitro fertilization (IVF) have improved their chances of conceiving, according to a review of published reports presented here at the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, a partnership of the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“Decreased fertility in IBD is due to voluntary childlessness, which we can change with education; surgery for IBD, which we can improve with laparoscopic surgery; and increased disease activity, which we can also make a difference in,” Sonia Friedman, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
Dr. Friedman and coauthors last year published an analysis of the Danish National Birth Cohort, which showed women with IBD had an 28% greater relative risk of taking a year or more to get pregnant than controls without IBD, and that the relative risk was even higher in women with Crohn’s disease — 54% (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.08.031). “We found that women with Crohn’s surgery had decreased fertility by 2.54 times greater relative risk,” she said.
“Fertility, pregnancy is the most important thing to patients,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “That’s what people ask me about the most. In the population of IBD patients, the onset is age 15-35, and these people are in the prime of their reproductive years.” Sexual function, known to be decreased in men and women with IBD, is also an overriding concern in these patients, she said. “There needs to be a lot more information out there about it.”
She said gastroenterologists should keep in mind that much of the evidence documenting reduced fertility after ileo-pouch anal anastomosis is dated and focused on open surgery, which caused profound scarring of the pelvis and fallopian tubes, thus hindering conception. Laparoscopic ileoanal J-pouch surgery (IPAA) has yielded much improved outcomes in women of child-bearing age, she said, citing a study late last year that reported women who had laparoscopic IPAA had a median time to pregnancy of 3.5 months versus 9 months for women who had open IPAA (Surgery. 2019;166:670-7).
“It’s really important to discuss the issues of fertility, especially for patients contemplating surgery,” Dr. Friedman said. “Emphasize that there are good outcomes with laparoscopic surgery, and they can have assisted reproductive technology [ART], or in vitro fertilization, if needed. Never withhold surgery based on fear of infertility.”
Her practice is to refer women with IBD in remission for IVF if they’ve tried to get pregnant every month for a year or more and to refer women with IBD surgery for IVF after trying to get pregnant for 6 months. Dr. Friedman coauthored two studies of the Danish National Birth Cohort of ART in women with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) along with controls (Gut. 2016;65:767-76; Gut. 2017;66:556-58). “We found that women with Crohn’s and UC had a decreased chance of having a clinical pregnancy, but they had no problem carrying the pregnancy to term,” she said.
Those findings raised questions about the etiology of decreased fertility in IBD patients, which could include factors such as IVF technique, reproductive hormone and microbiome changes, or IBD medications. “How can we carry that forward to all women with IBD?” she said. Women with IBD have less chance of conceiving with each IVF treatment cycle than do women without IBD, she said. “The most interesting thing is that the reduced chance of live birth after IVF treatment in Crohn’s and UC is related to the stages of implantation and not to the ability to maintain the fetus throughout pregnancy,” she said.
Dr. Friedman has no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Friedman S. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, Session Sp86.
AUSTIN, TEX. – Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who want to have children can benefit from better education about recent findings that disease control, laparoscopic surgery, and in vitro fertilization (IVF) have improved their chances of conceiving, according to a review of published reports presented here at the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, a partnership of the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“Decreased fertility in IBD is due to voluntary childlessness, which we can change with education; surgery for IBD, which we can improve with laparoscopic surgery; and increased disease activity, which we can also make a difference in,” Sonia Friedman, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
Dr. Friedman and coauthors last year published an analysis of the Danish National Birth Cohort, which showed women with IBD had an 28% greater relative risk of taking a year or more to get pregnant than controls without IBD, and that the relative risk was even higher in women with Crohn’s disease — 54% (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.08.031). “We found that women with Crohn’s surgery had decreased fertility by 2.54 times greater relative risk,” she said.
“Fertility, pregnancy is the most important thing to patients,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “That’s what people ask me about the most. In the population of IBD patients, the onset is age 15-35, and these people are in the prime of their reproductive years.” Sexual function, known to be decreased in men and women with IBD, is also an overriding concern in these patients, she said. “There needs to be a lot more information out there about it.”
She said gastroenterologists should keep in mind that much of the evidence documenting reduced fertility after ileo-pouch anal anastomosis is dated and focused on open surgery, which caused profound scarring of the pelvis and fallopian tubes, thus hindering conception. Laparoscopic ileoanal J-pouch surgery (IPAA) has yielded much improved outcomes in women of child-bearing age, she said, citing a study late last year that reported women who had laparoscopic IPAA had a median time to pregnancy of 3.5 months versus 9 months for women who had open IPAA (Surgery. 2019;166:670-7).
“It’s really important to discuss the issues of fertility, especially for patients contemplating surgery,” Dr. Friedman said. “Emphasize that there are good outcomes with laparoscopic surgery, and they can have assisted reproductive technology [ART], or in vitro fertilization, if needed. Never withhold surgery based on fear of infertility.”
Her practice is to refer women with IBD in remission for IVF if they’ve tried to get pregnant every month for a year or more and to refer women with IBD surgery for IVF after trying to get pregnant for 6 months. Dr. Friedman coauthored two studies of the Danish National Birth Cohort of ART in women with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) along with controls (Gut. 2016;65:767-76; Gut. 2017;66:556-58). “We found that women with Crohn’s and UC had a decreased chance of having a clinical pregnancy, but they had no problem carrying the pregnancy to term,” she said.
Those findings raised questions about the etiology of decreased fertility in IBD patients, which could include factors such as IVF technique, reproductive hormone and microbiome changes, or IBD medications. “How can we carry that forward to all women with IBD?” she said. Women with IBD have less chance of conceiving with each IVF treatment cycle than do women without IBD, she said. “The most interesting thing is that the reduced chance of live birth after IVF treatment in Crohn’s and UC is related to the stages of implantation and not to the ability to maintain the fetus throughout pregnancy,” she said.
Dr. Friedman has no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Friedman S. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, Session Sp86.
AUSTIN, TEX. – Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who want to have children can benefit from better education about recent findings that disease control, laparoscopic surgery, and in vitro fertilization (IVF) have improved their chances of conceiving, according to a review of published reports presented here at the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, a partnership of the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“Decreased fertility in IBD is due to voluntary childlessness, which we can change with education; surgery for IBD, which we can improve with laparoscopic surgery; and increased disease activity, which we can also make a difference in,” Sonia Friedman, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
Dr. Friedman and coauthors last year published an analysis of the Danish National Birth Cohort, which showed women with IBD had an 28% greater relative risk of taking a year or more to get pregnant than controls without IBD, and that the relative risk was even higher in women with Crohn’s disease — 54% (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.08.031). “We found that women with Crohn’s surgery had decreased fertility by 2.54 times greater relative risk,” she said.
“Fertility, pregnancy is the most important thing to patients,” Dr. Friedman said in an interview. “That’s what people ask me about the most. In the population of IBD patients, the onset is age 15-35, and these people are in the prime of their reproductive years.” Sexual function, known to be decreased in men and women with IBD, is also an overriding concern in these patients, she said. “There needs to be a lot more information out there about it.”
She said gastroenterologists should keep in mind that much of the evidence documenting reduced fertility after ileo-pouch anal anastomosis is dated and focused on open surgery, which caused profound scarring of the pelvis and fallopian tubes, thus hindering conception. Laparoscopic ileoanal J-pouch surgery (IPAA) has yielded much improved outcomes in women of child-bearing age, she said, citing a study late last year that reported women who had laparoscopic IPAA had a median time to pregnancy of 3.5 months versus 9 months for women who had open IPAA (Surgery. 2019;166:670-7).
“It’s really important to discuss the issues of fertility, especially for patients contemplating surgery,” Dr. Friedman said. “Emphasize that there are good outcomes with laparoscopic surgery, and they can have assisted reproductive technology [ART], or in vitro fertilization, if needed. Never withhold surgery based on fear of infertility.”
Her practice is to refer women with IBD in remission for IVF if they’ve tried to get pregnant every month for a year or more and to refer women with IBD surgery for IVF after trying to get pregnant for 6 months. Dr. Friedman coauthored two studies of the Danish National Birth Cohort of ART in women with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) along with controls (Gut. 2016;65:767-76; Gut. 2017;66:556-58). “We found that women with Crohn’s and UC had a decreased chance of having a clinical pregnancy, but they had no problem carrying the pregnancy to term,” she said.
Those findings raised questions about the etiology of decreased fertility in IBD patients, which could include factors such as IVF technique, reproductive hormone and microbiome changes, or IBD medications. “How can we carry that forward to all women with IBD?” she said. Women with IBD have less chance of conceiving with each IVF treatment cycle than do women without IBD, she said. “The most interesting thing is that the reduced chance of live birth after IVF treatment in Crohn’s and UC is related to the stages of implantation and not to the ability to maintain the fetus throughout pregnancy,” she said.
Dr. Friedman has no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Friedman S. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, Session Sp86.
REPORTING FROM CROHN’S & COLITIS CONGRESS
New diet linked to reduced IBD symptoms
AUSTIN, TEX. – A customized diet developed to relieve inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) symptoms without compromising nutrition has uncovered a novel molecular mechanism of the diet-microbiome immune interaction that may allow gastroenterologists to tailor patient diets to enhance the gut microbiome, according to a poster presented at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
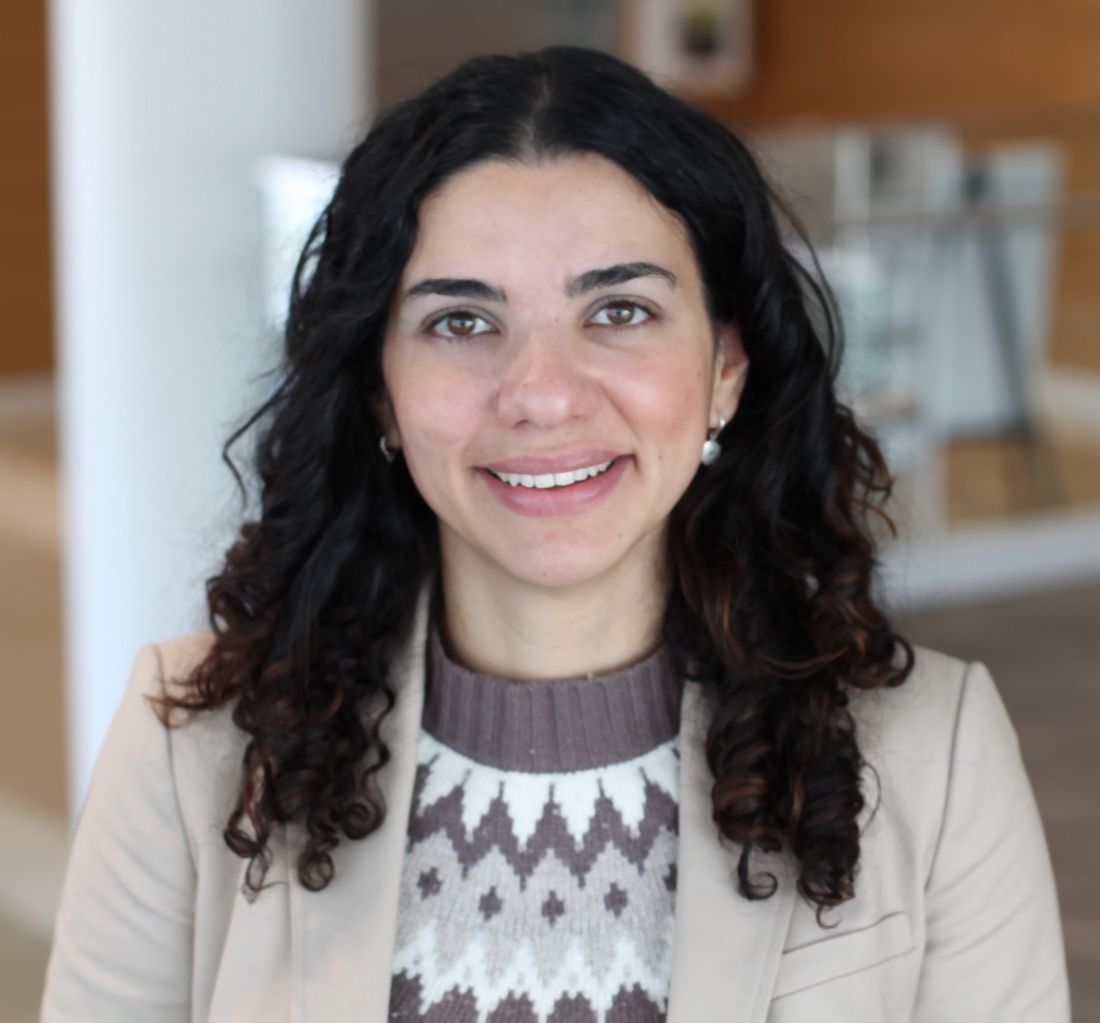
The study found that P-glycoprotein (P-gp) expression, associated with healthy gut, increased after adoption of the IBD-Anti-Inflammatory Diet (IBD-AID), said poster presenter and study leader Ana Luisa Maldonado-Contreras, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester. The study involved 19 IBD patients placed on the IBD-AID. This is reportedly the first evidence of a whole-dietary recommendation that may help patients with IBD to reduce their symptoms.
“The IBD-AID has been rationally designed to feed a health-promoting, anti-inflammatory microbiome aiming at reducing chronic inflammation” Dr. Maldonado-Contreras said in an interview. The UMass researchers, led by Barbara Olendzki, RD, MPH, director of the Center for Applied Nutrition, derived the IBD-AID diet from a specific carbohydrate diet and modified it based on their research to increase the diversity of bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and modulate the local immune response.
“SCFAs, such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate, are crucial in maintaining intestinal homeostasis by fueling colonocytes, strengthening the gut barrier function, and controlling local mucosal inflammation,” Dr. Maldonado-Contreras said. SCFAs regulate the production of proinflammatory mediators such as cytokines (tumor necrosis factor–alpha and interleukin 2, 6, and 10), eicosanoids, and chemokines, such as MCP-1 and CINC-2, by acting on macrophages and endothelial cells. High levels of SCFAs down-regulate those proinflammatory mediators.
The study found IBD-AID favored a beneficial gut microbiota. Prebiotic foods such as oats, barley, beans, and tempeh correlated with beneficial counts of Bacteroides and Parabacteroides, both capable of producing SCFAs. Probiotic foods like yogurt, fermented cabbage, and kefir correlated with high levels of Clostridium bolteae, a bacterium that plays a critical role in regulatory T-cell induction. Vegetables and nuts correlated with an abundance of Roseburia hominis, Eubacterium rectale, and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, which tend to be reduced in IBD patients and are potent butyrate-producing Clostridia with known anti-inflammatory activity. Declines in putative pathogenic strains, such as Escherichia, Alistipes, and Eggerthella accompanied the increase of SCFA-producing bacteria.
Among the study patients treated for at least 8 weeks, the 61.3% who achieved at least 50% dietary compliance reported a dramatic decrease of symptoms and disease severity.
Dr. Maldonado-Contreras explained the role P-gp has as a biomarker of gut microbiota. “P-gp is an ABC-transporter located in the apical side of intestinal epithelial cells and is responsible for suppressing neutrophil migration in healthy individuals,” she said. “Loss of P-gp expression, or a reduction in its function, correlates with inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract in both mice and humans.” The study compared P-gp expression before and after patients went on the IBD-AID diet.
Dr. Maldonado-Contreras credited the study’s reported diet compliance of 76% to adoption of the patient-centered counseling model (J Am Diet Assoc. 2001;101:332-41). “With the patient-centered counseling model, we aimed to build self-efficacy, self-management strategies and to provide cooking-skill abilities to promote long-term behavioral habits related to the IBD-AID,” she said. The IBD-AID recipes, menus, and tips are available online (https://www.umassmed.edu/nutrition/).
The Dr. Maldonado-Contreras along with researchers at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York are further evaluating an adapted version of the IBD-AID diet in pregnancy in the MELODY trial. “We are evaluating whether adherence to the modified IBD-AID during pregnancy in women with Crohn’s disease could beneficially shift the microbiome of mom and their babies, thereby promoting a healthier immune system during a critical time of the baby’s immune system development,” Dr. Maldonado-Contreras said. The trial has recruited 50 patients with Crohn’s disease and healthy controls so far.
Dr. Maldonado-Contreras has no financial relationships to disclose.
AUSTIN, TEX. – A customized diet developed to relieve inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) symptoms without compromising nutrition has uncovered a novel molecular mechanism of the diet-microbiome immune interaction that may allow gastroenterologists to tailor patient diets to enhance the gut microbiome, according to a poster presented at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
The study found that P-glycoprotein (P-gp) expression, associated with healthy gut, increased after adoption of the IBD-Anti-Inflammatory Diet (IBD-AID), said poster presenter and study leader Ana Luisa Maldonado-Contreras, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester. The study involved 19 IBD patients placed on the IBD-AID. This is reportedly the first evidence of a whole-dietary recommendation that may help patients with IBD to reduce their symptoms.
“The IBD-AID has been rationally designed to feed a health-promoting, anti-inflammatory microbiome aiming at reducing chronic inflammation” Dr. Maldonado-Contreras said in an interview. The UMass researchers, led by Barbara Olendzki, RD, MPH, director of the Center for Applied Nutrition, derived the IBD-AID diet from a specific carbohydrate diet and modified it based on their research to increase the diversity of bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and modulate the local immune response.
“SCFAs, such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate, are crucial in maintaining intestinal homeostasis by fueling colonocytes, strengthening the gut barrier function, and controlling local mucosal inflammation,” Dr. Maldonado-Contreras said. SCFAs regulate the production of proinflammatory mediators such as cytokines (tumor necrosis factor–alpha and interleukin 2, 6, and 10), eicosanoids, and chemokines, such as MCP-1 and CINC-2, by acting on macrophages and endothelial cells. High levels of SCFAs down-regulate those proinflammatory mediators.
The study found IBD-AID favored a beneficial gut microbiota. Prebiotic foods such as oats, barley, beans, and tempeh correlated with beneficial counts of Bacteroides and Parabacteroides, both capable of producing SCFAs. Probiotic foods like yogurt, fermented cabbage, and kefir correlated with high levels of Clostridium bolteae, a bacterium that plays a critical role in regulatory T-cell induction. Vegetables and nuts correlated with an abundance of Roseburia hominis, Eubacterium rectale, and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, which tend to be reduced in IBD patients and are potent butyrate-producing Clostridia with known anti-inflammatory activity. Declines in putative pathogenic strains, such as Escherichia, Alistipes, and Eggerthella accompanied the increase of SCFA-producing bacteria.
Among the study patients treated for at least 8 weeks, the 61.3% who achieved at least 50% dietary compliance reported a dramatic decrease of symptoms and disease severity.
Dr. Maldonado-Contreras explained the role P-gp has as a biomarker of gut microbiota. “P-gp is an ABC-transporter located in the apical side of intestinal epithelial cells and is responsible for suppressing neutrophil migration in healthy individuals,” she said. “Loss of P-gp expression, or a reduction in its function, correlates with inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract in both mice and humans.” The study compared P-gp expression before and after patients went on the IBD-AID diet.
Dr. Maldonado-Contreras credited the study’s reported diet compliance of 76% to adoption of the patient-centered counseling model (J Am Diet Assoc. 2001;101:332-41). “With the patient-centered counseling model, we aimed to build self-efficacy, self-management strategies and to provide cooking-skill abilities to promote long-term behavioral habits related to the IBD-AID,” she said. The IBD-AID recipes, menus, and tips are available online (https://www.umassmed.edu/nutrition/).
The Dr. Maldonado-Contreras along with researchers at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York are further evaluating an adapted version of the IBD-AID diet in pregnancy in the MELODY trial. “We are evaluating whether adherence to the modified IBD-AID during pregnancy in women with Crohn’s disease could beneficially shift the microbiome of mom and their babies, thereby promoting a healthier immune system during a critical time of the baby’s immune system development,” Dr. Maldonado-Contreras said. The trial has recruited 50 patients with Crohn’s disease and healthy controls so far.
Dr. Maldonado-Contreras has no financial relationships to disclose.
AUSTIN, TEX. – A customized diet developed to relieve inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) symptoms without compromising nutrition has uncovered a novel molecular mechanism of the diet-microbiome immune interaction that may allow gastroenterologists to tailor patient diets to enhance the gut microbiome, according to a poster presented at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
The study found that P-glycoprotein (P-gp) expression, associated with healthy gut, increased after adoption of the IBD-Anti-Inflammatory Diet (IBD-AID), said poster presenter and study leader Ana Luisa Maldonado-Contreras, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester. The study involved 19 IBD patients placed on the IBD-AID. This is reportedly the first evidence of a whole-dietary recommendation that may help patients with IBD to reduce their symptoms.
“The IBD-AID has been rationally designed to feed a health-promoting, anti-inflammatory microbiome aiming at reducing chronic inflammation” Dr. Maldonado-Contreras said in an interview. The UMass researchers, led by Barbara Olendzki, RD, MPH, director of the Center for Applied Nutrition, derived the IBD-AID diet from a specific carbohydrate diet and modified it based on their research to increase the diversity of bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and modulate the local immune response.
“SCFAs, such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate, are crucial in maintaining intestinal homeostasis by fueling colonocytes, strengthening the gut barrier function, and controlling local mucosal inflammation,” Dr. Maldonado-Contreras said. SCFAs regulate the production of proinflammatory mediators such as cytokines (tumor necrosis factor–alpha and interleukin 2, 6, and 10), eicosanoids, and chemokines, such as MCP-1 and CINC-2, by acting on macrophages and endothelial cells. High levels of SCFAs down-regulate those proinflammatory mediators.
The study found IBD-AID favored a beneficial gut microbiota. Prebiotic foods such as oats, barley, beans, and tempeh correlated with beneficial counts of Bacteroides and Parabacteroides, both capable of producing SCFAs. Probiotic foods like yogurt, fermented cabbage, and kefir correlated with high levels of Clostridium bolteae, a bacterium that plays a critical role in regulatory T-cell induction. Vegetables and nuts correlated with an abundance of Roseburia hominis, Eubacterium rectale, and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, which tend to be reduced in IBD patients and are potent butyrate-producing Clostridia with known anti-inflammatory activity. Declines in putative pathogenic strains, such as Escherichia, Alistipes, and Eggerthella accompanied the increase of SCFA-producing bacteria.
Among the study patients treated for at least 8 weeks, the 61.3% who achieved at least 50% dietary compliance reported a dramatic decrease of symptoms and disease severity.
Dr. Maldonado-Contreras explained the role P-gp has as a biomarker of gut microbiota. “P-gp is an ABC-transporter located in the apical side of intestinal epithelial cells and is responsible for suppressing neutrophil migration in healthy individuals,” she said. “Loss of P-gp expression, or a reduction in its function, correlates with inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract in both mice and humans.” The study compared P-gp expression before and after patients went on the IBD-AID diet.
Dr. Maldonado-Contreras credited the study’s reported diet compliance of 76% to adoption of the patient-centered counseling model (J Am Diet Assoc. 2001;101:332-41). “With the patient-centered counseling model, we aimed to build self-efficacy, self-management strategies and to provide cooking-skill abilities to promote long-term behavioral habits related to the IBD-AID,” she said. The IBD-AID recipes, menus, and tips are available online (https://www.umassmed.edu/nutrition/).
The Dr. Maldonado-Contreras along with researchers at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York are further evaluating an adapted version of the IBD-AID diet in pregnancy in the MELODY trial. “We are evaluating whether adherence to the modified IBD-AID during pregnancy in women with Crohn’s disease could beneficially shift the microbiome of mom and their babies, thereby promoting a healthier immune system during a critical time of the baby’s immune system development,” Dr. Maldonado-Contreras said. The trial has recruited 50 patients with Crohn’s disease and healthy controls so far.
Dr. Maldonado-Contreras has no financial relationships to disclose.
REPORTING FROM CROHN’S & COLITIS CONGRESS
Can diet, microbiome personalization reverse IBD increase?
AUSTIN, TEX. – With the increase in the prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease worldwide approaching pandemic proportions, personalized medicine targeting diet and the microbiome may contribute to a halt or even a reversal of the trend, a leading researcher from Israel and proponent of the Mediterranean diet reported at the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, a partnership of the Crohn's & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“Inflammatory bowel disease is turning into a pandemic around the world,” said Iris Dotan, MD, of the Rabin Medical Center in Petah Tikva, Israel, citing research reported at the 2015 meeting of the European Crohn’s & Colitis Organization that showed the prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in Israel increasing almost 400% from 1991 to 2015, up to 460 per 100,000. “The rising incidence highlights the role of environmental factors,” she added.
She reported on her work with the Rabin Medical Center Pouch Cohort, which is studying the ileal pouch as a man-made model of IBD to get answers. “We believe that when patients progress from having a pouch that is normal to having pouchitis it actually resembles Crohn’s disease and can be used as a model to identify processes that are ongoing in these patients,” she said.
The study is following an unspecified number of ileal pouch patients prospectively, evaluating their biomaterial with stool samples and mucosal biopsies, and tracking their diet and psychosocial status to gain insight into what sets off episodes of pouchitis.
Already, the study has provided insight into how antibiotics may contribute to IBD. “Pouch disease is a very antibiotic-responsive disease,” she said in an interview. “Antibiotics are clinically effective. However, as we dive deeper into this and understand the mechanistics of it, we see that antibiotics cause more dysbiosis, which is something that is unwanted in patients with a pouch.”
A similar response has been shown in Crohn’s disease, she said. With antibiotics, “you’re doing something that might be helpful clinically for the short term; however, it might be harmful in the long term.”
When these patients stop antibiotic therapy, their dysbiosis increases and resistance wanes, she said. “These patients are replenished by other bacteria, probably some from the oral cavity, causing this circle so they would need recurrent courses of antibiotics.”
Evidence is accumulating that the Mediterranean diet can break that cycle, Dr. Dotan said, citing unpublished findings from her group that showed pouchitis patients consumed less fruit than counterparts without the disease. Dr. Dotan also cited a study published this year that found the Mediterranean diet is associated with a lower risk of Crohn’s disease later in life (Gut. 2020 Jan 3. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319505).
Dr. Dotan’s research has shown that patients don’t have to adhere completely to the Mediterranean diet but can make less-drastic but significant changes. “You don’t need the whole program,” she said. “If you tell patients to start with something – increase fruits and vegetables – that’s not too complex. Then try to change some of the protein with legumes or other protein sources; that also would be helpful.” Another strategy is to direct patients away from processed foods with additives and preservatives.
“Microbial modifications, including antibiotics, probiotics, diet, and fecal microbial transplantation may have variable effects on specific patient populations, so we can’t be too long simplistic about these options,” she said.
Personalization of diet and microbial manipulations may do more than provide short-term treatment for patients, she said. “It might contribute to halting or even reversing the global increase we’ve seen in IBD recurrence over the past few years.”
Dr. Dotan disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Takeda, Pfizer, Genentech/Roche, Neopharm, and Gilead.
SOURCE: Dotan I. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020, Presentation Sp75.
AUSTIN, TEX. – With the increase in the prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease worldwide approaching pandemic proportions, personalized medicine targeting diet and the microbiome may contribute to a halt or even a reversal of the trend, a leading researcher from Israel and proponent of the Mediterranean diet reported at the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, a partnership of the Crohn's & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“Inflammatory bowel disease is turning into a pandemic around the world,” said Iris Dotan, MD, of the Rabin Medical Center in Petah Tikva, Israel, citing research reported at the 2015 meeting of the European Crohn’s & Colitis Organization that showed the prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in Israel increasing almost 400% from 1991 to 2015, up to 460 per 100,000. “The rising incidence highlights the role of environmental factors,” she added.
She reported on her work with the Rabin Medical Center Pouch Cohort, which is studying the ileal pouch as a man-made model of IBD to get answers. “We believe that when patients progress from having a pouch that is normal to having pouchitis it actually resembles Crohn’s disease and can be used as a model to identify processes that are ongoing in these patients,” she said.
The study is following an unspecified number of ileal pouch patients prospectively, evaluating their biomaterial with stool samples and mucosal biopsies, and tracking their diet and psychosocial status to gain insight into what sets off episodes of pouchitis.
Already, the study has provided insight into how antibiotics may contribute to IBD. “Pouch disease is a very antibiotic-responsive disease,” she said in an interview. “Antibiotics are clinically effective. However, as we dive deeper into this and understand the mechanistics of it, we see that antibiotics cause more dysbiosis, which is something that is unwanted in patients with a pouch.”
A similar response has been shown in Crohn’s disease, she said. With antibiotics, “you’re doing something that might be helpful clinically for the short term; however, it might be harmful in the long term.”
When these patients stop antibiotic therapy, their dysbiosis increases and resistance wanes, she said. “These patients are replenished by other bacteria, probably some from the oral cavity, causing this circle so they would need recurrent courses of antibiotics.”
Evidence is accumulating that the Mediterranean diet can break that cycle, Dr. Dotan said, citing unpublished findings from her group that showed pouchitis patients consumed less fruit than counterparts without the disease. Dr. Dotan also cited a study published this year that found the Mediterranean diet is associated with a lower risk of Crohn’s disease later in life (Gut. 2020 Jan 3. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319505).
Dr. Dotan’s research has shown that patients don’t have to adhere completely to the Mediterranean diet but can make less-drastic but significant changes. “You don’t need the whole program,” she said. “If you tell patients to start with something – increase fruits and vegetables – that’s not too complex. Then try to change some of the protein with legumes or other protein sources; that also would be helpful.” Another strategy is to direct patients away from processed foods with additives and preservatives.
“Microbial modifications, including antibiotics, probiotics, diet, and fecal microbial transplantation may have variable effects on specific patient populations, so we can’t be too long simplistic about these options,” she said.
Personalization of diet and microbial manipulations may do more than provide short-term treatment for patients, she said. “It might contribute to halting or even reversing the global increase we’ve seen in IBD recurrence over the past few years.”
Dr. Dotan disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Takeda, Pfizer, Genentech/Roche, Neopharm, and Gilead.
SOURCE: Dotan I. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020, Presentation Sp75.
AUSTIN, TEX. – With the increase in the prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease worldwide approaching pandemic proportions, personalized medicine targeting diet and the microbiome may contribute to a halt or even a reversal of the trend, a leading researcher from Israel and proponent of the Mediterranean diet reported at the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, a partnership of the Crohn's & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“Inflammatory bowel disease is turning into a pandemic around the world,” said Iris Dotan, MD, of the Rabin Medical Center in Petah Tikva, Israel, citing research reported at the 2015 meeting of the European Crohn’s & Colitis Organization that showed the prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in Israel increasing almost 400% from 1991 to 2015, up to 460 per 100,000. “The rising incidence highlights the role of environmental factors,” she added.
She reported on her work with the Rabin Medical Center Pouch Cohort, which is studying the ileal pouch as a man-made model of IBD to get answers. “We believe that when patients progress from having a pouch that is normal to having pouchitis it actually resembles Crohn’s disease and can be used as a model to identify processes that are ongoing in these patients,” she said.
The study is following an unspecified number of ileal pouch patients prospectively, evaluating their biomaterial with stool samples and mucosal biopsies, and tracking their diet and psychosocial status to gain insight into what sets off episodes of pouchitis.
Already, the study has provided insight into how antibiotics may contribute to IBD. “Pouch disease is a very antibiotic-responsive disease,” she said in an interview. “Antibiotics are clinically effective. However, as we dive deeper into this and understand the mechanistics of it, we see that antibiotics cause more dysbiosis, which is something that is unwanted in patients with a pouch.”
A similar response has been shown in Crohn’s disease, she said. With antibiotics, “you’re doing something that might be helpful clinically for the short term; however, it might be harmful in the long term.”
When these patients stop antibiotic therapy, their dysbiosis increases and resistance wanes, she said. “These patients are replenished by other bacteria, probably some from the oral cavity, causing this circle so they would need recurrent courses of antibiotics.”
Evidence is accumulating that the Mediterranean diet can break that cycle, Dr. Dotan said, citing unpublished findings from her group that showed pouchitis patients consumed less fruit than counterparts without the disease. Dr. Dotan also cited a study published this year that found the Mediterranean diet is associated with a lower risk of Crohn’s disease later in life (Gut. 2020 Jan 3. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319505).
Dr. Dotan’s research has shown that patients don’t have to adhere completely to the Mediterranean diet but can make less-drastic but significant changes. “You don’t need the whole program,” she said. “If you tell patients to start with something – increase fruits and vegetables – that’s not too complex. Then try to change some of the protein with legumes or other protein sources; that also would be helpful.” Another strategy is to direct patients away from processed foods with additives and preservatives.
“Microbial modifications, including antibiotics, probiotics, diet, and fecal microbial transplantation may have variable effects on specific patient populations, so we can’t be too long simplistic about these options,” she said.
Personalization of diet and microbial manipulations may do more than provide short-term treatment for patients, she said. “It might contribute to halting or even reversing the global increase we’ve seen in IBD recurrence over the past few years.”
Dr. Dotan disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie, Takeda, Pfizer, Genentech/Roche, Neopharm, and Gilead.
SOURCE: Dotan I. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020, Presentation Sp75.
REPORTING FROM THE CROHN’S & COLITIS CONGRESS
High stress linked to UC flare risk
AUSTIN, TEX. – Early results from a cohort study that aims to characterize the brain-gut relationship in ulcerative colitis (UC) have identified potential structural and functional brain changes consistent with the effect chronic bowel inflammation has on the brain and found two subgroups of patients that differed in how they respond to stress. These findings may provide further insight into the role of the brain in symptom flares, the study leader reported the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, a partnership of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
So far, the study has shown that, based on validated measures of perceived stress or neuroticism, patients with UC in clinical remission are clustered on two ends of the stress spectrum, with high and low stress responsiveness, said Emeran A. Mayer, MD, who is coprincipal investigator of the study with Jenny Sauk, MD, both of the University of California, Los Angeles.
The goal of the longitudinal follow-up study is to identify brain, gut microbiome, and stress signatures that predict the risk of flares for up to 2 years in UC patients in clinical remission, he said. Patients’ clinical, microbiome, and stress-psychological measures are evaluated quarterly. The intent is to enroll 100- 120 patients between ages 18 years and 65 years. Questionnaire and symptom data on 70 patients have been analyzed so far.
“What we found so far is that, at baseline using the questionnaire data and clustering analysis, you can identify two distinct subgroups: one characterized by stress hyperresponsiveness and one that does not have that feature,” Dr. Mayer said in an interview. “Then we found in the stress hyperresponsive group there are more flares reported and documented during a mean follow-up of 8.1 months.”
The findings so far have also determined that the differences in stress responsiveness and flare frequency don’t seem to be related to baseline fecal calprotectin levels, said Dr. Mayer, who is director of the G. Oppenheimer Center for Neurobiology of Stress and Resilience (CNSR) and codirector of the CURE: Digestive Diseases Research Center.
Early findings show the incidence of clinical flares in the high stress responsiveness group was 27.4% vs. 9.3% in the low-stress group, and the rate of symptomatic flares was 11.8% vs. 4.6%, respectively.
With regard to baseline biological measures, there were no significant differences in cardiovagal tone or morning salivary cortisol measures between the two clusters, Dr. Mayer noted, although the high stress responsiveness cluster had higher sympathetic tone before, during, and after a brief psychological stress.
He noted that the same clustering into low and high stress responsiveness was confirmed in a different data set of 66 UC subjects and that the two clusters showed significant differences in anatomical connectivity of the default mode network in the brain, a set of regions involved in chronic pain and emotion regulation.
By identifying factors that contribute to inflammatory bowel disease, the study may ultimately simplify the process of identifying IBD patients in remission who are at highest risk of flares, Dr. Mayer said. “Patients won’t need to undergo brain imaging or assessment of microbiome parameters; they can just answer a short questionnaire,” he said. Another potential benefit of the study would be to identify changes in the brain–gut microbiome interactions associated with flares, he said.
Full study results would be available in about 2 years, Dr. Mayer said, with more data on biological parameters expected next year.
The study is funded with a Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation grant. Dr. Mayer disclosed financial relationships with Amare, Axial Biotherapeutics, Bloom Science, Danone, Mahana Therapeutics, Pendulum, Ubiome, and Viome.
SOURCE: Mayer EA et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020, Session Sp74.
AUSTIN, TEX. – Early results from a cohort study that aims to characterize the brain-gut relationship in ulcerative colitis (UC) have identified potential structural and functional brain changes consistent with the effect chronic bowel inflammation has on the brain and found two subgroups of patients that differed in how they respond to stress. These findings may provide further insight into the role of the brain in symptom flares, the study leader reported the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, a partnership of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
So far, the study has shown that, based on validated measures of perceived stress or neuroticism, patients with UC in clinical remission are clustered on two ends of the stress spectrum, with high and low stress responsiveness, said Emeran A. Mayer, MD, who is coprincipal investigator of the study with Jenny Sauk, MD, both of the University of California, Los Angeles.
The goal of the longitudinal follow-up study is to identify brain, gut microbiome, and stress signatures that predict the risk of flares for up to 2 years in UC patients in clinical remission, he said. Patients’ clinical, microbiome, and stress-psychological measures are evaluated quarterly. The intent is to enroll 100- 120 patients between ages 18 years and 65 years. Questionnaire and symptom data on 70 patients have been analyzed so far.
“What we found so far is that, at baseline using the questionnaire data and clustering analysis, you can identify two distinct subgroups: one characterized by stress hyperresponsiveness and one that does not have that feature,” Dr. Mayer said in an interview. “Then we found in the stress hyperresponsive group there are more flares reported and documented during a mean follow-up of 8.1 months.”
The findings so far have also determined that the differences in stress responsiveness and flare frequency don’t seem to be related to baseline fecal calprotectin levels, said Dr. Mayer, who is director of the G. Oppenheimer Center for Neurobiology of Stress and Resilience (CNSR) and codirector of the CURE: Digestive Diseases Research Center.
Early findings show the incidence of clinical flares in the high stress responsiveness group was 27.4% vs. 9.3% in the low-stress group, and the rate of symptomatic flares was 11.8% vs. 4.6%, respectively.
With regard to baseline biological measures, there were no significant differences in cardiovagal tone or morning salivary cortisol measures between the two clusters, Dr. Mayer noted, although the high stress responsiveness cluster had higher sympathetic tone before, during, and after a brief psychological stress.
He noted that the same clustering into low and high stress responsiveness was confirmed in a different data set of 66 UC subjects and that the two clusters showed significant differences in anatomical connectivity of the default mode network in the brain, a set of regions involved in chronic pain and emotion regulation.
By identifying factors that contribute to inflammatory bowel disease, the study may ultimately simplify the process of identifying IBD patients in remission who are at highest risk of flares, Dr. Mayer said. “Patients won’t need to undergo brain imaging or assessment of microbiome parameters; they can just answer a short questionnaire,” he said. Another potential benefit of the study would be to identify changes in the brain–gut microbiome interactions associated with flares, he said.
Full study results would be available in about 2 years, Dr. Mayer said, with more data on biological parameters expected next year.
The study is funded with a Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation grant. Dr. Mayer disclosed financial relationships with Amare, Axial Biotherapeutics, Bloom Science, Danone, Mahana Therapeutics, Pendulum, Ubiome, and Viome.
SOURCE: Mayer EA et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020, Session Sp74.
AUSTIN, TEX. – Early results from a cohort study that aims to characterize the brain-gut relationship in ulcerative colitis (UC) have identified potential structural and functional brain changes consistent with the effect chronic bowel inflammation has on the brain and found two subgroups of patients that differed in how they respond to stress. These findings may provide further insight into the role of the brain in symptom flares, the study leader reported the Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, a partnership of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
So far, the study has shown that, based on validated measures of perceived stress or neuroticism, patients with UC in clinical remission are clustered on two ends of the stress spectrum, with high and low stress responsiveness, said Emeran A. Mayer, MD, who is coprincipal investigator of the study with Jenny Sauk, MD, both of the University of California, Los Angeles.
The goal of the longitudinal follow-up study is to identify brain, gut microbiome, and stress signatures that predict the risk of flares for up to 2 years in UC patients in clinical remission, he said. Patients’ clinical, microbiome, and stress-psychological measures are evaluated quarterly. The intent is to enroll 100- 120 patients between ages 18 years and 65 years. Questionnaire and symptom data on 70 patients have been analyzed so far.
“What we found so far is that, at baseline using the questionnaire data and clustering analysis, you can identify two distinct subgroups: one characterized by stress hyperresponsiveness and one that does not have that feature,” Dr. Mayer said in an interview. “Then we found in the stress hyperresponsive group there are more flares reported and documented during a mean follow-up of 8.1 months.”
The findings so far have also determined that the differences in stress responsiveness and flare frequency don’t seem to be related to baseline fecal calprotectin levels, said Dr. Mayer, who is director of the G. Oppenheimer Center for Neurobiology of Stress and Resilience (CNSR) and codirector of the CURE: Digestive Diseases Research Center.
Early findings show the incidence of clinical flares in the high stress responsiveness group was 27.4% vs. 9.3% in the low-stress group, and the rate of symptomatic flares was 11.8% vs. 4.6%, respectively.
With regard to baseline biological measures, there were no significant differences in cardiovagal tone or morning salivary cortisol measures between the two clusters, Dr. Mayer noted, although the high stress responsiveness cluster had higher sympathetic tone before, during, and after a brief psychological stress.
He noted that the same clustering into low and high stress responsiveness was confirmed in a different data set of 66 UC subjects and that the two clusters showed significant differences in anatomical connectivity of the default mode network in the brain, a set of regions involved in chronic pain and emotion regulation.
By identifying factors that contribute to inflammatory bowel disease, the study may ultimately simplify the process of identifying IBD patients in remission who are at highest risk of flares, Dr. Mayer said. “Patients won’t need to undergo brain imaging or assessment of microbiome parameters; they can just answer a short questionnaire,” he said. Another potential benefit of the study would be to identify changes in the brain–gut microbiome interactions associated with flares, he said.
Full study results would be available in about 2 years, Dr. Mayer said, with more data on biological parameters expected next year.
The study is funded with a Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation grant. Dr. Mayer disclosed financial relationships with Amare, Axial Biotherapeutics, Bloom Science, Danone, Mahana Therapeutics, Pendulum, Ubiome, and Viome.
SOURCE: Mayer EA et al. Crohn’s & Colitis Congress 2020, Session Sp74.
REPORTING FROM CROHN’S & COLITIS CONGRESS
RECOVERY: Early SAVR benefits asymptomatic severe AS patients
PHILADELPHIA – Early aortic valve replacement surgery for patients with asymptomatic, severe aortic stenosis has been a controversial strategy, but the first randomized trial comparing early surgery with conservative management found that early-surgery patients had a 17-fold improved survival at 8 years, according to trial results reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Albeit small – 145 patients randomized to early surgery or conservative therapy – the RECOVERY trial results provide important evidence to support early preemptive aortic valve replacement for patients with asymptomatic but severe aortic stenosis, said Duk-Hyun Kang, MD, of the division of cardiology, Asan Medical Center in Seoul, South Korea.
The trial randomized 73 patients to early surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) and 72 to conventional treatment. Baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups, with a mean EuroSCORE II of 0.9, peak aortic-valve jet velocity (Vmax) of 5.1 m/sec, and mean aortic-valve area of 0.63 cm2. Fifty-three conventional treatment patients went on to have SAVR when symptoms developed during follow-up. There were no operation-related deaths in either group, although one early surgery patient had a stroke and one conventional treatment patients had an MI during the operative period.
At a median follow-up of 6.2 years, 1 early-surgery patient (1.4%) and 11 conventional-therapy patients (15.3%) died from operative or cardiovascular death, Dr. Kang said (P = 0.003). “The number needed to treat to prevent one cardiovascular death within 4 years was 20 patients,” Dr. Kang said. At 4 and 8 years, the cumulative incidences of operative CV or death were 1.4% for both in the early-surgery group and 5.7% and 25.5% in the conventional-treatment group, Dr. Kang said (P = 0.003).
Rates of all-cause mortality were 6.8% and 20.8% (P = 0.030) in the respective groups. “The number needed to treat to save one life in 4 years was 16 patients,” Dr. Kang said. At 4 and 8 years, the cumulative incidence of any-cause death was 4.1% and 10.2% in the early-surgery patients and 9.7% and 31.8% in the conventional group (P = 0.018).
Among the trial limitations Dr. Kang acknowledged were that the population had severe AS with aortic velocity of 4.5 m/sec or greater. “The benefit of early surgery may be relatively smaller in asymptomatic patients with less severe aortic stenosis,” he said.
Not all patients had an exercise test to confirm their asymptomatic status, but as discussant Robert Bonow, MD, of Northwestern University in Chicago pointed out, “this is what we’re dealing with clinically.” Also the mean age of the patient population – 64.9 years – is relatively young, and they had a high incidence of bicuspid aortic valve, few comorbidities, and low operative risk, Dr. Kang said. “Thus, our study population is quite different from the populations enrolled in the TAVR [transcatheter AVR] trials, and the results of our study cannot be directly applied to early TAVR for asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis,” he said.
The mean age in both the PARTNER 3 (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1695-705) and EVOLUT (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1706-15) trials comparing TAVR and SAVR in low-risk patients was 73.6 years, and they had higher rates of comorbidities than did the RECOVERY patients.
Dr. Bonow said the RECOVERY findings add to the PARTNER 3 and EVOLUT findings and raise the question about rethinking guideline indications for AVR in asymptomatic severe AS patients. “Should we be talking about moving our Vmax threshold down to 4.5 m/sec, or maybe increasing the Class IIa indications to Class I?” he said. “I think we need to wait to see more data to support these excellent results.”
However, most of these asymptomatic patients do eventually have surgery “in a very short period of time,” Dr. Bonow said. “So from a clinical management point of view, I think we already have the data suggesting that we could move the ball forward, and now we have these excellent outcome data from Korea as well.”
Results were published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019 Nov 16. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1912846).
Dr. Kang and Dr. Bonow had no financial relationships to disclose.
PHILADELPHIA – Early aortic valve replacement surgery for patients with asymptomatic, severe aortic stenosis has been a controversial strategy, but the first randomized trial comparing early surgery with conservative management found that early-surgery patients had a 17-fold improved survival at 8 years, according to trial results reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Albeit small – 145 patients randomized to early surgery or conservative therapy – the RECOVERY trial results provide important evidence to support early preemptive aortic valve replacement for patients with asymptomatic but severe aortic stenosis, said Duk-Hyun Kang, MD, of the division of cardiology, Asan Medical Center in Seoul, South Korea.
The trial randomized 73 patients to early surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) and 72 to conventional treatment. Baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups, with a mean EuroSCORE II of 0.9, peak aortic-valve jet velocity (Vmax) of 5.1 m/sec, and mean aortic-valve area of 0.63 cm2. Fifty-three conventional treatment patients went on to have SAVR when symptoms developed during follow-up. There were no operation-related deaths in either group, although one early surgery patient had a stroke and one conventional treatment patients had an MI during the operative period.
At a median follow-up of 6.2 years, 1 early-surgery patient (1.4%) and 11 conventional-therapy patients (15.3%) died from operative or cardiovascular death, Dr. Kang said (P = 0.003). “The number needed to treat to prevent one cardiovascular death within 4 years was 20 patients,” Dr. Kang said. At 4 and 8 years, the cumulative incidences of operative CV or death were 1.4% for both in the early-surgery group and 5.7% and 25.5% in the conventional-treatment group, Dr. Kang said (P = 0.003).
Rates of all-cause mortality were 6.8% and 20.8% (P = 0.030) in the respective groups. “The number needed to treat to save one life in 4 years was 16 patients,” Dr. Kang said. At 4 and 8 years, the cumulative incidence of any-cause death was 4.1% and 10.2% in the early-surgery patients and 9.7% and 31.8% in the conventional group (P = 0.018).
Among the trial limitations Dr. Kang acknowledged were that the population had severe AS with aortic velocity of 4.5 m/sec or greater. “The benefit of early surgery may be relatively smaller in asymptomatic patients with less severe aortic stenosis,” he said.
Not all patients had an exercise test to confirm their asymptomatic status, but as discussant Robert Bonow, MD, of Northwestern University in Chicago pointed out, “this is what we’re dealing with clinically.” Also the mean age of the patient population – 64.9 years – is relatively young, and they had a high incidence of bicuspid aortic valve, few comorbidities, and low operative risk, Dr. Kang said. “Thus, our study population is quite different from the populations enrolled in the TAVR [transcatheter AVR] trials, and the results of our study cannot be directly applied to early TAVR for asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis,” he said.
The mean age in both the PARTNER 3 (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1695-705) and EVOLUT (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1706-15) trials comparing TAVR and SAVR in low-risk patients was 73.6 years, and they had higher rates of comorbidities than did the RECOVERY patients.
Dr. Bonow said the RECOVERY findings add to the PARTNER 3 and EVOLUT findings and raise the question about rethinking guideline indications for AVR in asymptomatic severe AS patients. “Should we be talking about moving our Vmax threshold down to 4.5 m/sec, or maybe increasing the Class IIa indications to Class I?” he said. “I think we need to wait to see more data to support these excellent results.”
However, most of these asymptomatic patients do eventually have surgery “in a very short period of time,” Dr. Bonow said. “So from a clinical management point of view, I think we already have the data suggesting that we could move the ball forward, and now we have these excellent outcome data from Korea as well.”
Results were published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019 Nov 16. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1912846).
Dr. Kang and Dr. Bonow had no financial relationships to disclose.
PHILADELPHIA – Early aortic valve replacement surgery for patients with asymptomatic, severe aortic stenosis has been a controversial strategy, but the first randomized trial comparing early surgery with conservative management found that early-surgery patients had a 17-fold improved survival at 8 years, according to trial results reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Albeit small – 145 patients randomized to early surgery or conservative therapy – the RECOVERY trial results provide important evidence to support early preemptive aortic valve replacement for patients with asymptomatic but severe aortic stenosis, said Duk-Hyun Kang, MD, of the division of cardiology, Asan Medical Center in Seoul, South Korea.
The trial randomized 73 patients to early surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) and 72 to conventional treatment. Baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups, with a mean EuroSCORE II of 0.9, peak aortic-valve jet velocity (Vmax) of 5.1 m/sec, and mean aortic-valve area of 0.63 cm2. Fifty-three conventional treatment patients went on to have SAVR when symptoms developed during follow-up. There were no operation-related deaths in either group, although one early surgery patient had a stroke and one conventional treatment patients had an MI during the operative period.
At a median follow-up of 6.2 years, 1 early-surgery patient (1.4%) and 11 conventional-therapy patients (15.3%) died from operative or cardiovascular death, Dr. Kang said (P = 0.003). “The number needed to treat to prevent one cardiovascular death within 4 years was 20 patients,” Dr. Kang said. At 4 and 8 years, the cumulative incidences of operative CV or death were 1.4% for both in the early-surgery group and 5.7% and 25.5% in the conventional-treatment group, Dr. Kang said (P = 0.003).
Rates of all-cause mortality were 6.8% and 20.8% (P = 0.030) in the respective groups. “The number needed to treat to save one life in 4 years was 16 patients,” Dr. Kang said. At 4 and 8 years, the cumulative incidence of any-cause death was 4.1% and 10.2% in the early-surgery patients and 9.7% and 31.8% in the conventional group (P = 0.018).
Among the trial limitations Dr. Kang acknowledged were that the population had severe AS with aortic velocity of 4.5 m/sec or greater. “The benefit of early surgery may be relatively smaller in asymptomatic patients with less severe aortic stenosis,” he said.
Not all patients had an exercise test to confirm their asymptomatic status, but as discussant Robert Bonow, MD, of Northwestern University in Chicago pointed out, “this is what we’re dealing with clinically.” Also the mean age of the patient population – 64.9 years – is relatively young, and they had a high incidence of bicuspid aortic valve, few comorbidities, and low operative risk, Dr. Kang said. “Thus, our study population is quite different from the populations enrolled in the TAVR [transcatheter AVR] trials, and the results of our study cannot be directly applied to early TAVR for asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis,” he said.
The mean age in both the PARTNER 3 (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1695-705) and EVOLUT (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1706-15) trials comparing TAVR and SAVR in low-risk patients was 73.6 years, and they had higher rates of comorbidities than did the RECOVERY patients.
Dr. Bonow said the RECOVERY findings add to the PARTNER 3 and EVOLUT findings and raise the question about rethinking guideline indications for AVR in asymptomatic severe AS patients. “Should we be talking about moving our Vmax threshold down to 4.5 m/sec, or maybe increasing the Class IIa indications to Class I?” he said. “I think we need to wait to see more data to support these excellent results.”
However, most of these asymptomatic patients do eventually have surgery “in a very short period of time,” Dr. Bonow said. “So from a clinical management point of view, I think we already have the data suggesting that we could move the ball forward, and now we have these excellent outcome data from Korea as well.”
Results were published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019 Nov 16. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1912846).
Dr. Kang and Dr. Bonow had no financial relationships to disclose.
REPORTING FROM THE AHA SCIENTIFIC SESSIONS
FUEL trial: Post-Fontan udenafil shows mixed results
PHILADELPHIA – In adolescents who have had a Fontan procedure for congenital heart disease, a randomized trial of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor udenafil showed that it achieved improved exercise performance but did not lead to significant improvement in oxygen levels or myocardial performance.
That’s according to results of the Pediatric Heart Network’s Fontan Udenafil Exercise Longitudinal Trial (FUEL) presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. “Treatment with udenafil was not associated with a statistically significant improvement in oxygen consumption at peak exercise, but it was associated with statistically significant improvements in exercise performance at the ventilatory anaerobic threshold,” said David J. Goldberg, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia in reporting the FUEL results. The results were published simultaneously in Circulation (2019 Nov 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044352).
“This is the first large clinical trial to show improvement in measures of clinically relevant exercise performance in those with single-ventricle heart disease after Fontan palliation,” he said.
FUEL enrolled 400 male and female adolescents with a single functional ventricle after Fontan surgical palliation. In these patients, pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) is critical for the efficient flow of blood through the lungs without the benefit of a ventricular pump. “While this circulation is typically stable through childhood, cardiovascular efficiency deteriorates over time, associated with a decline in exercise performance and the accrual of Fontan-associated morbidities,” Dr. Goldberg said. “Given the importance of pulmonary vascular resistance, modulators of PVR make sense as potential therapies.”
FUEL evaluated the effect of udenafil 87.5 mg twice daily versus placebo in post-Fontan patients who’d been on anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy. The treatment group had a higher percentage of female patients (44% vs. 36% on placebo), but all other baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups.
While the trial found the drug was well tolerated and safe, with side effects typical of PDE5 inhibitors, it did not lead to changes in myocardial performance index, reactive hyperemia index, or log brain natriuretic peptide, Dr. Goldberg said.
At 6 months, both groups showed a decline in exercise data, “as expected,” Dr. Goldberg said. “But that decline was attenuated in the group receiving udenafil,” he said, with peak oxygen consumption declining an average of 0.23 and 0.89 mL/kg per minute in the treatment and placebo groups, respectively (P = 0.092).
Total oxygen consumption, however, actually improved in the udenafil group and declined in the placebo group, 44 mL/min on average versus –3.7 mL/min (P = 0.071).
“There was no significant difference in the change in peak heart rate or the change in peak oxygen saturation between the groups,” Dr. Goldberg said. But three measures at the ventilatory aerobic threshold (VAT) – oxygen consumption, work rate, and ventilation/carbon dioxide output – all showed statistically significant improvement in exercise performance.
“This has important clinical implications,” Dr. Goldberg said of the study findings. “Our study extends recent findings in highlighting the importance of submaximal exercise in the understanding of Fontan physiology. And unlike peak oxygen consumption, submaximal exercise is not constrained by the physiologic ceiling of central venous pressure inherent in exercise physiology after Fontan palliation.”
Maximum oxygen consumption at VAT is likely a more relevant measure after Fontan palliation than is central venous pressure, discussant Craig A. Sable, MD, a pediatric cardiologist in Potomac, Md., noted in his comments. “This is because VAT occurs at about 70% of maximum VO2 [oxygen consumption] in Fontan as opposed to 55% in two-ventricle physiology,” Dr. Sable said.
In adults with congenital heart disease, maximal VO2 of 45%-50% of predicted levels portends increased risk of heart failure and death. “Therefore, a medication that addresses the central deficiencies of Fontan physiology and results in improved exercise performance may allow for a longer period of symptom-free survival,” he said.
In an invited commentary in Circulation (2019 Nov 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044512), Marc Gewillig, MD, and Alexander van de Bruaene, MD, of University Hospitals Leuven (Belgium) said that the findings of FUEL and other trials of pulmonary vasodilators after Fontan leave “open for debate” whether the treatment effects of a 3%-5% improvement in oxygen consumption is clinically meaningful for adolescents. “For failing Fontan patients (not studied in FUEL), these improvements are minimal but maybe relevant,” the commentators wrote. But the studies do not resolve whether that’s enough to prevent further decline.
Dr. Goldberg disclosed receiving research grants from trial sponsor Mezzion Pharmaceuticals and the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Dr. Sable, Dr. Gewillig, and Dr. van de Bruaene have no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Goldberg D. AHA 2019, Late Breaking Science Session 5.
PHILADELPHIA – In adolescents who have had a Fontan procedure for congenital heart disease, a randomized trial of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor udenafil showed that it achieved improved exercise performance but did not lead to significant improvement in oxygen levels or myocardial performance.
That’s according to results of the Pediatric Heart Network’s Fontan Udenafil Exercise Longitudinal Trial (FUEL) presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. “Treatment with udenafil was not associated with a statistically significant improvement in oxygen consumption at peak exercise, but it was associated with statistically significant improvements in exercise performance at the ventilatory anaerobic threshold,” said David J. Goldberg, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia in reporting the FUEL results. The results were published simultaneously in Circulation (2019 Nov 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044352).
“This is the first large clinical trial to show improvement in measures of clinically relevant exercise performance in those with single-ventricle heart disease after Fontan palliation,” he said.
FUEL enrolled 400 male and female adolescents with a single functional ventricle after Fontan surgical palliation. In these patients, pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) is critical for the efficient flow of blood through the lungs without the benefit of a ventricular pump. “While this circulation is typically stable through childhood, cardiovascular efficiency deteriorates over time, associated with a decline in exercise performance and the accrual of Fontan-associated morbidities,” Dr. Goldberg said. “Given the importance of pulmonary vascular resistance, modulators of PVR make sense as potential therapies.”
FUEL evaluated the effect of udenafil 87.5 mg twice daily versus placebo in post-Fontan patients who’d been on anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy. The treatment group had a higher percentage of female patients (44% vs. 36% on placebo), but all other baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups.
While the trial found the drug was well tolerated and safe, with side effects typical of PDE5 inhibitors, it did not lead to changes in myocardial performance index, reactive hyperemia index, or log brain natriuretic peptide, Dr. Goldberg said.
At 6 months, both groups showed a decline in exercise data, “as expected,” Dr. Goldberg said. “But that decline was attenuated in the group receiving udenafil,” he said, with peak oxygen consumption declining an average of 0.23 and 0.89 mL/kg per minute in the treatment and placebo groups, respectively (P = 0.092).
Total oxygen consumption, however, actually improved in the udenafil group and declined in the placebo group, 44 mL/min on average versus –3.7 mL/min (P = 0.071).
“There was no significant difference in the change in peak heart rate or the change in peak oxygen saturation between the groups,” Dr. Goldberg said. But three measures at the ventilatory aerobic threshold (VAT) – oxygen consumption, work rate, and ventilation/carbon dioxide output – all showed statistically significant improvement in exercise performance.
“This has important clinical implications,” Dr. Goldberg said of the study findings. “Our study extends recent findings in highlighting the importance of submaximal exercise in the understanding of Fontan physiology. And unlike peak oxygen consumption, submaximal exercise is not constrained by the physiologic ceiling of central venous pressure inherent in exercise physiology after Fontan palliation.”
Maximum oxygen consumption at VAT is likely a more relevant measure after Fontan palliation than is central venous pressure, discussant Craig A. Sable, MD, a pediatric cardiologist in Potomac, Md., noted in his comments. “This is because VAT occurs at about 70% of maximum VO2 [oxygen consumption] in Fontan as opposed to 55% in two-ventricle physiology,” Dr. Sable said.
In adults with congenital heart disease, maximal VO2 of 45%-50% of predicted levels portends increased risk of heart failure and death. “Therefore, a medication that addresses the central deficiencies of Fontan physiology and results in improved exercise performance may allow for a longer period of symptom-free survival,” he said.
In an invited commentary in Circulation (2019 Nov 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044512), Marc Gewillig, MD, and Alexander van de Bruaene, MD, of University Hospitals Leuven (Belgium) said that the findings of FUEL and other trials of pulmonary vasodilators after Fontan leave “open for debate” whether the treatment effects of a 3%-5% improvement in oxygen consumption is clinically meaningful for adolescents. “For failing Fontan patients (not studied in FUEL), these improvements are minimal but maybe relevant,” the commentators wrote. But the studies do not resolve whether that’s enough to prevent further decline.
Dr. Goldberg disclosed receiving research grants from trial sponsor Mezzion Pharmaceuticals and the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Dr. Sable, Dr. Gewillig, and Dr. van de Bruaene have no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Goldberg D. AHA 2019, Late Breaking Science Session 5.
PHILADELPHIA – In adolescents who have had a Fontan procedure for congenital heart disease, a randomized trial of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor udenafil showed that it achieved improved exercise performance but did not lead to significant improvement in oxygen levels or myocardial performance.
That’s according to results of the Pediatric Heart Network’s Fontan Udenafil Exercise Longitudinal Trial (FUEL) presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. “Treatment with udenafil was not associated with a statistically significant improvement in oxygen consumption at peak exercise, but it was associated with statistically significant improvements in exercise performance at the ventilatory anaerobic threshold,” said David J. Goldberg, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia in reporting the FUEL results. The results were published simultaneously in Circulation (2019 Nov 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044352).
“This is the first large clinical trial to show improvement in measures of clinically relevant exercise performance in those with single-ventricle heart disease after Fontan palliation,” he said.
FUEL enrolled 400 male and female adolescents with a single functional ventricle after Fontan surgical palliation. In these patients, pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) is critical for the efficient flow of blood through the lungs without the benefit of a ventricular pump. “While this circulation is typically stable through childhood, cardiovascular efficiency deteriorates over time, associated with a decline in exercise performance and the accrual of Fontan-associated morbidities,” Dr. Goldberg said. “Given the importance of pulmonary vascular resistance, modulators of PVR make sense as potential therapies.”
FUEL evaluated the effect of udenafil 87.5 mg twice daily versus placebo in post-Fontan patients who’d been on anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy. The treatment group had a higher percentage of female patients (44% vs. 36% on placebo), but all other baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups.
While the trial found the drug was well tolerated and safe, with side effects typical of PDE5 inhibitors, it did not lead to changes in myocardial performance index, reactive hyperemia index, or log brain natriuretic peptide, Dr. Goldberg said.
At 6 months, both groups showed a decline in exercise data, “as expected,” Dr. Goldberg said. “But that decline was attenuated in the group receiving udenafil,” he said, with peak oxygen consumption declining an average of 0.23 and 0.89 mL/kg per minute in the treatment and placebo groups, respectively (P = 0.092).
Total oxygen consumption, however, actually improved in the udenafil group and declined in the placebo group, 44 mL/min on average versus –3.7 mL/min (P = 0.071).
“There was no significant difference in the change in peak heart rate or the change in peak oxygen saturation between the groups,” Dr. Goldberg said. But three measures at the ventilatory aerobic threshold (VAT) – oxygen consumption, work rate, and ventilation/carbon dioxide output – all showed statistically significant improvement in exercise performance.
“This has important clinical implications,” Dr. Goldberg said of the study findings. “Our study extends recent findings in highlighting the importance of submaximal exercise in the understanding of Fontan physiology. And unlike peak oxygen consumption, submaximal exercise is not constrained by the physiologic ceiling of central venous pressure inherent in exercise physiology after Fontan palliation.”
Maximum oxygen consumption at VAT is likely a more relevant measure after Fontan palliation than is central venous pressure, discussant Craig A. Sable, MD, a pediatric cardiologist in Potomac, Md., noted in his comments. “This is because VAT occurs at about 70% of maximum VO2 [oxygen consumption] in Fontan as opposed to 55% in two-ventricle physiology,” Dr. Sable said.
In adults with congenital heart disease, maximal VO2 of 45%-50% of predicted levels portends increased risk of heart failure and death. “Therefore, a medication that addresses the central deficiencies of Fontan physiology and results in improved exercise performance may allow for a longer period of symptom-free survival,” he said.
In an invited commentary in Circulation (2019 Nov 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044512), Marc Gewillig, MD, and Alexander van de Bruaene, MD, of University Hospitals Leuven (Belgium) said that the findings of FUEL and other trials of pulmonary vasodilators after Fontan leave “open for debate” whether the treatment effects of a 3%-5% improvement in oxygen consumption is clinically meaningful for adolescents. “For failing Fontan patients (not studied in FUEL), these improvements are minimal but maybe relevant,” the commentators wrote. But the studies do not resolve whether that’s enough to prevent further decline.
Dr. Goldberg disclosed receiving research grants from trial sponsor Mezzion Pharmaceuticals and the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Dr. Sable, Dr. Gewillig, and Dr. van de Bruaene have no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Goldberg D. AHA 2019, Late Breaking Science Session 5.
REPORTING FROM AHA 2019















