User login
Candidiasis: The essentials of diagnosis and treatment
CASE Woman with vulvar itch and white vaginal discharge
A 26-year-old sexually active nulligravid woman requests evaluation for moderately intense “itching in the vagina and on the vulva.” She uses combination oral contraceptives and has 2 current sexual partners. On physical examination, you note a thick, white, curd-like discharge that is adherent to the vaginal epithelium. The vulva is erythematous, and small “satellite lesions” are evident in the intertriginous folds.
- What is the most likely diagnosis?
- How should you treat this patient?
Approximately 75% of all women will have at least 1 episode of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) in their lifetime.1 Candida albicans, the most commonly identified organism in these infections, colonizes the vagina of many individuals commensally; higher rates of colonization occur in women with diabetes, obesity, recent use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, steroid use and immunosuppression, and in women who are pregnant. Of special interest, pregnant women have an increased risk of symptomatic infection, and they respond less favorably to conventional treatment regimens.1
Deconstructing C albicans and other species
Historically, in more than 90% of cases, C albicans is the principal cause of VVC. While it remains the most prevalent Candida species in the United States, over the last 15 years studies have demonstrated that in some countries, such as India and Nigeria, C albicans constitutes less than half of the cultured species in women with VVC. This observation may be due to the widespread availability and use of common antifungal medications, which leads to resistance and selection for resistant species.1,2
In asymptomatic women, vaginal colonies of C albicans grow in the yeast form. This condition is usually well tolerated by the host and does not cause a major immune response. In periods of stress for the host micro- and mycobiomes, however (dysbiosis, immune suppression, trauma), C albicans is induced into morphogenesis, proliferating and forming hyphae that are thought to activate the host immune response. The vaginal epithelium becomes sensitized to the presence of C albicans and recruits large numbers of neutrophils that, in turn, drive the pathophysiology of VVC.3
There is a theory that the separation of the urethra and anus by the vagina has exerted evolutionary pressure to maintain the presence of commensal C albicans yeast colonies in the vagina. C albicans exerts an antagonistic effect on many bacteria and, therefore, may act as a “microbiologic barrier” between the anus and the urethra to prevent urinary tract infections that, before the modern antibiotic era, may have caused serious morbidity and even mortality.3
Other organisms that cause VVC include C glabrata, C parapsilosis, and C tropicalis. Ex vivo experiments have shown that co-infection of C albicans with C glabrata enhances the ability of C glabrata to invade tissue.2 C glabrata is more frequently resistant to commonly used antifungal compounds than C albicans,2,4 which suggests that identifying the specific fungal pathogen is becoming increasingly important in planning targeted therapy.
Continue to: A common infection...
A common infection
While three-quarters of women will experience VVC at least once in their lifetime, between 40% and 45% will experience it more than once, and 5% to 8% will develop recurrent VVC. Among pregnant women, 15% will develop symptomatic VVC.1,2
However, because VVC is not a reportable disease and antifungal medication is available over the counter without physician consultation, these numbers likely underestimate the true incidence of the infection.4
Complications in pregnancy
Vaginal infections, including VVC, bacterial vaginosis (BV), and trichomoniasis, may be associated with 40% of preterm deliveries.5 The high concentrations of estrogen and progesterone during pregnancy create a uniquely glycogen-rich vaginal environment in which Candida species can flourish.2,4 Even asymptomatic colonization of the vagina with Candida species has been associated with preterm labor, preterm birth, and low birth weight.1,6 This association appears to have more severe consequences if VVC occurs in the second trimester compared with the first trimester.6
Additionally, congenital candidiasis of the newborn may result from intrauterine Candida infection or heavy maternal vaginal colonization at delivery, and the infection is evident within 24 hours of birth. It presents typically as oropharyngeal candidiasis (thrush) of the newborn.1
Clinical manifestations of infection
The classic manifestations of Candida infection are similar in both the pregnant and nonpregnant patient: acute vaginal and vulvar pruritus and thick, white, malodorous “cottage cheese” vaginal discharge.1,4 Exercise caution, however, in treating presumptively based on these symptoms alone, especially in pregnancy, because they are not specific to candidiasis.4 Vaginal discharge is not always present, and it may vary in appearance and odor. Pruritus is the most specific symptom of Candida infection, but studies show that it is an accurate predictor in only 38% of cases.7
Other common signs and symptoms include the sensation of burning, dysuria, dyspareunia, fissures, excoriations, and pruritus ani. Physical examination demonstrates erythema and swelling of labial, vulvar, and vaginal structures, with a normal cervix and an adherent white or off-white discharge. When the discharge is removed from the vaginal wall, small bleeding points may appear.1,4
Making the diagnosis
As mentioned, history alone is not sufficient to make a definitive diagnosis of candidiasis. The diagnosis should be made by examining vaginal secretions under a microscope or by culture.4 A wet mount and KOH (potassium hydroxide) prep help differentiate VVC, BV, and trichomoniasis. Culture is particularly valuable in identifying less common fungal organisms, such as C glabrata and C tropicalis.
Vaginal pH testing is not conclusive for Candida because vaginal pH is normal in VVC. However, pH assessment can rule in other causative organisms if the value is abnormal (that is, elevated pH of 4.5 or greater with BV and trichomoniasis).1
Treatment options
Acute infection. A pregnant woman who tests positive for VVC may safely be treated in any trimester with a 7-day course of a topical azole.8 If the patient prefers the convenience of oral therapy, after the first trimester, oral fluconazole, 150 mg on day 1 and day 3, may be used for treatment. Note that fluconazole has been associated with an increased risk of spontaneous abortion and cardiac septal defects when used in the first trimester.1
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a number of topical treatments for VVC (TABLE).8 Several of these drugs are available over the counter without a prescription. Topical azoles are more effective than nystatin in treating VVC, and posttreatment cultures are negative in up to 90% of treated patients.8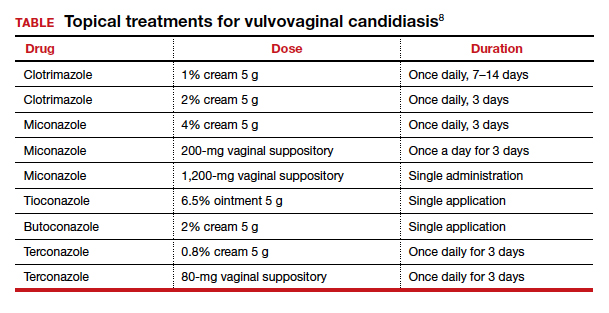
Recurrent infections. Recurrent VVC is defined as 4 or more episodes of symptomatic VVC within 12 months.8 Typical first-line treatment of recurrent infections in nonpregnant patients is a 6-month course of fluconazole, 150 mg weekly.9,10 As noted, however, fluconazole should not be used in the first trimester of pregnancy. It is acceptable therapy thereafter for patients who have troublesome recurrent or persistent infections.
Continue to: Strategies for preventing recurrence...
Strategies for preventing recurrence
While it is logical to consider antimycotic prophylaxis in women with a history of recurring VVC and/or a significant number of known risk factors, data suggest that extended prophylaxis with an azole does not consistently achieve long-term elimination of vaginal Candida organisms after cessation of the azole.9
At-risk women should be counseled to make lifestyle adjustments, such as wearing breathable cotton clothing, particularly undergarments; promptly changing out of damp clothing; and forgoing the use of commercial intravaginal feminine hygiene products.
Recent research has shown that the use of Saccharomyces cerevisiae–based probiotics has promise for controlling the burden of C albicans in women receiving antifungal drugs for VVC and also for preventing recurrence; however, this approach has undergone limited testing in humans, and its efficacy and safety in pregnancy is unknown.11 ●
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infection. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, et al, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:862.
- Goncalves B, Ferreira C, Alves CT, et al. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: epidemiology, microbiology and risk factors. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016;42:905-927.
- Hall RA, Noverr MC. Fungal interactions with the human host: exploring the spectrum of symbiosis. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2017;40:58-64.
- Sobel JD. Vulvovaginal candidosis. Lancet. 2007;369:1961-1971.
- Holzer I, Farr A, Kiss H; et al. The colonization with Candida species is more harmful in the second trimester of pregnancy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017;295:891-895.
- Farr A, Kiss H, Holzer I, et al. Effect of asymptomatic vaginal colonization with Candida albicans on pregnancy outcome. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2015;94:989-996.
- Anderson MR, Klink K, Cohrssen A. Evaluation of vaginal complaints. JAMA. 2004;291:1368-1379.
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2015;64(RR-03):1-137.
- Sobel JD, Wiesenfeld HC, Martens M, et al. Maintenance fluconazole therapy for recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:876-883.
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: Use of long-term, high-dose Diflucan (fluconazole) during pregnancy may be associated with birth defects in infants. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-drug-safety-communicationuse-long-term-high-dose-diflucan-fluconazole-during-pregnancy-may-be#. Updated August 4, 2017. Accessed July 6, 2020.
- Gaziano R, Sabbatini S, Roselletti E, et al. Saccharomyces cerevisiae-based probiotics as novel antimicrobial agents to prevent and treat vaginal infections. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:718.
CASE Woman with vulvar itch and white vaginal discharge
A 26-year-old sexually active nulligravid woman requests evaluation for moderately intense “itching in the vagina and on the vulva.” She uses combination oral contraceptives and has 2 current sexual partners. On physical examination, you note a thick, white, curd-like discharge that is adherent to the vaginal epithelium. The vulva is erythematous, and small “satellite lesions” are evident in the intertriginous folds.
- What is the most likely diagnosis?
- How should you treat this patient?
Approximately 75% of all women will have at least 1 episode of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) in their lifetime.1 Candida albicans, the most commonly identified organism in these infections, colonizes the vagina of many individuals commensally; higher rates of colonization occur in women with diabetes, obesity, recent use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, steroid use and immunosuppression, and in women who are pregnant. Of special interest, pregnant women have an increased risk of symptomatic infection, and they respond less favorably to conventional treatment regimens.1
Deconstructing C albicans and other species
Historically, in more than 90% of cases, C albicans is the principal cause of VVC. While it remains the most prevalent Candida species in the United States, over the last 15 years studies have demonstrated that in some countries, such as India and Nigeria, C albicans constitutes less than half of the cultured species in women with VVC. This observation may be due to the widespread availability and use of common antifungal medications, which leads to resistance and selection for resistant species.1,2
In asymptomatic women, vaginal colonies of C albicans grow in the yeast form. This condition is usually well tolerated by the host and does not cause a major immune response. In periods of stress for the host micro- and mycobiomes, however (dysbiosis, immune suppression, trauma), C albicans is induced into morphogenesis, proliferating and forming hyphae that are thought to activate the host immune response. The vaginal epithelium becomes sensitized to the presence of C albicans and recruits large numbers of neutrophils that, in turn, drive the pathophysiology of VVC.3
There is a theory that the separation of the urethra and anus by the vagina has exerted evolutionary pressure to maintain the presence of commensal C albicans yeast colonies in the vagina. C albicans exerts an antagonistic effect on many bacteria and, therefore, may act as a “microbiologic barrier” between the anus and the urethra to prevent urinary tract infections that, before the modern antibiotic era, may have caused serious morbidity and even mortality.3
Other organisms that cause VVC include C glabrata, C parapsilosis, and C tropicalis. Ex vivo experiments have shown that co-infection of C albicans with C glabrata enhances the ability of C glabrata to invade tissue.2 C glabrata is more frequently resistant to commonly used antifungal compounds than C albicans,2,4 which suggests that identifying the specific fungal pathogen is becoming increasingly important in planning targeted therapy.
Continue to: A common infection...
A common infection
While three-quarters of women will experience VVC at least once in their lifetime, between 40% and 45% will experience it more than once, and 5% to 8% will develop recurrent VVC. Among pregnant women, 15% will develop symptomatic VVC.1,2
However, because VVC is not a reportable disease and antifungal medication is available over the counter without physician consultation, these numbers likely underestimate the true incidence of the infection.4
Complications in pregnancy
Vaginal infections, including VVC, bacterial vaginosis (BV), and trichomoniasis, may be associated with 40% of preterm deliveries.5 The high concentrations of estrogen and progesterone during pregnancy create a uniquely glycogen-rich vaginal environment in which Candida species can flourish.2,4 Even asymptomatic colonization of the vagina with Candida species has been associated with preterm labor, preterm birth, and low birth weight.1,6 This association appears to have more severe consequences if VVC occurs in the second trimester compared with the first trimester.6
Additionally, congenital candidiasis of the newborn may result from intrauterine Candida infection or heavy maternal vaginal colonization at delivery, and the infection is evident within 24 hours of birth. It presents typically as oropharyngeal candidiasis (thrush) of the newborn.1
Clinical manifestations of infection
The classic manifestations of Candida infection are similar in both the pregnant and nonpregnant patient: acute vaginal and vulvar pruritus and thick, white, malodorous “cottage cheese” vaginal discharge.1,4 Exercise caution, however, in treating presumptively based on these symptoms alone, especially in pregnancy, because they are not specific to candidiasis.4 Vaginal discharge is not always present, and it may vary in appearance and odor. Pruritus is the most specific symptom of Candida infection, but studies show that it is an accurate predictor in only 38% of cases.7
Other common signs and symptoms include the sensation of burning, dysuria, dyspareunia, fissures, excoriations, and pruritus ani. Physical examination demonstrates erythema and swelling of labial, vulvar, and vaginal structures, with a normal cervix and an adherent white or off-white discharge. When the discharge is removed from the vaginal wall, small bleeding points may appear.1,4
Making the diagnosis
As mentioned, history alone is not sufficient to make a definitive diagnosis of candidiasis. The diagnosis should be made by examining vaginal secretions under a microscope or by culture.4 A wet mount and KOH (potassium hydroxide) prep help differentiate VVC, BV, and trichomoniasis. Culture is particularly valuable in identifying less common fungal organisms, such as C glabrata and C tropicalis.
Vaginal pH testing is not conclusive for Candida because vaginal pH is normal in VVC. However, pH assessment can rule in other causative organisms if the value is abnormal (that is, elevated pH of 4.5 or greater with BV and trichomoniasis).1
Treatment options
Acute infection. A pregnant woman who tests positive for VVC may safely be treated in any trimester with a 7-day course of a topical azole.8 If the patient prefers the convenience of oral therapy, after the first trimester, oral fluconazole, 150 mg on day 1 and day 3, may be used for treatment. Note that fluconazole has been associated with an increased risk of spontaneous abortion and cardiac septal defects when used in the first trimester.1
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a number of topical treatments for VVC (TABLE).8 Several of these drugs are available over the counter without a prescription. Topical azoles are more effective than nystatin in treating VVC, and posttreatment cultures are negative in up to 90% of treated patients.8
Recurrent infections. Recurrent VVC is defined as 4 or more episodes of symptomatic VVC within 12 months.8 Typical first-line treatment of recurrent infections in nonpregnant patients is a 6-month course of fluconazole, 150 mg weekly.9,10 As noted, however, fluconazole should not be used in the first trimester of pregnancy. It is acceptable therapy thereafter for patients who have troublesome recurrent or persistent infections.
Continue to: Strategies for preventing recurrence...
Strategies for preventing recurrence
While it is logical to consider antimycotic prophylaxis in women with a history of recurring VVC and/or a significant number of known risk factors, data suggest that extended prophylaxis with an azole does not consistently achieve long-term elimination of vaginal Candida organisms after cessation of the azole.9
At-risk women should be counseled to make lifestyle adjustments, such as wearing breathable cotton clothing, particularly undergarments; promptly changing out of damp clothing; and forgoing the use of commercial intravaginal feminine hygiene products.
Recent research has shown that the use of Saccharomyces cerevisiae–based probiotics has promise for controlling the burden of C albicans in women receiving antifungal drugs for VVC and also for preventing recurrence; however, this approach has undergone limited testing in humans, and its efficacy and safety in pregnancy is unknown.11 ●
CASE Woman with vulvar itch and white vaginal discharge
A 26-year-old sexually active nulligravid woman requests evaluation for moderately intense “itching in the vagina and on the vulva.” She uses combination oral contraceptives and has 2 current sexual partners. On physical examination, you note a thick, white, curd-like discharge that is adherent to the vaginal epithelium. The vulva is erythematous, and small “satellite lesions” are evident in the intertriginous folds.
- What is the most likely diagnosis?
- How should you treat this patient?
Approximately 75% of all women will have at least 1 episode of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) in their lifetime.1 Candida albicans, the most commonly identified organism in these infections, colonizes the vagina of many individuals commensally; higher rates of colonization occur in women with diabetes, obesity, recent use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, steroid use and immunosuppression, and in women who are pregnant. Of special interest, pregnant women have an increased risk of symptomatic infection, and they respond less favorably to conventional treatment regimens.1
Deconstructing C albicans and other species
Historically, in more than 90% of cases, C albicans is the principal cause of VVC. While it remains the most prevalent Candida species in the United States, over the last 15 years studies have demonstrated that in some countries, such as India and Nigeria, C albicans constitutes less than half of the cultured species in women with VVC. This observation may be due to the widespread availability and use of common antifungal medications, which leads to resistance and selection for resistant species.1,2
In asymptomatic women, vaginal colonies of C albicans grow in the yeast form. This condition is usually well tolerated by the host and does not cause a major immune response. In periods of stress for the host micro- and mycobiomes, however (dysbiosis, immune suppression, trauma), C albicans is induced into morphogenesis, proliferating and forming hyphae that are thought to activate the host immune response. The vaginal epithelium becomes sensitized to the presence of C albicans and recruits large numbers of neutrophils that, in turn, drive the pathophysiology of VVC.3
There is a theory that the separation of the urethra and anus by the vagina has exerted evolutionary pressure to maintain the presence of commensal C albicans yeast colonies in the vagina. C albicans exerts an antagonistic effect on many bacteria and, therefore, may act as a “microbiologic barrier” between the anus and the urethra to prevent urinary tract infections that, before the modern antibiotic era, may have caused serious morbidity and even mortality.3
Other organisms that cause VVC include C glabrata, C parapsilosis, and C tropicalis. Ex vivo experiments have shown that co-infection of C albicans with C glabrata enhances the ability of C glabrata to invade tissue.2 C glabrata is more frequently resistant to commonly used antifungal compounds than C albicans,2,4 which suggests that identifying the specific fungal pathogen is becoming increasingly important in planning targeted therapy.
Continue to: A common infection...
A common infection
While three-quarters of women will experience VVC at least once in their lifetime, between 40% and 45% will experience it more than once, and 5% to 8% will develop recurrent VVC. Among pregnant women, 15% will develop symptomatic VVC.1,2
However, because VVC is not a reportable disease and antifungal medication is available over the counter without physician consultation, these numbers likely underestimate the true incidence of the infection.4
Complications in pregnancy
Vaginal infections, including VVC, bacterial vaginosis (BV), and trichomoniasis, may be associated with 40% of preterm deliveries.5 The high concentrations of estrogen and progesterone during pregnancy create a uniquely glycogen-rich vaginal environment in which Candida species can flourish.2,4 Even asymptomatic colonization of the vagina with Candida species has been associated with preterm labor, preterm birth, and low birth weight.1,6 This association appears to have more severe consequences if VVC occurs in the second trimester compared with the first trimester.6
Additionally, congenital candidiasis of the newborn may result from intrauterine Candida infection or heavy maternal vaginal colonization at delivery, and the infection is evident within 24 hours of birth. It presents typically as oropharyngeal candidiasis (thrush) of the newborn.1
Clinical manifestations of infection
The classic manifestations of Candida infection are similar in both the pregnant and nonpregnant patient: acute vaginal and vulvar pruritus and thick, white, malodorous “cottage cheese” vaginal discharge.1,4 Exercise caution, however, in treating presumptively based on these symptoms alone, especially in pregnancy, because they are not specific to candidiasis.4 Vaginal discharge is not always present, and it may vary in appearance and odor. Pruritus is the most specific symptom of Candida infection, but studies show that it is an accurate predictor in only 38% of cases.7
Other common signs and symptoms include the sensation of burning, dysuria, dyspareunia, fissures, excoriations, and pruritus ani. Physical examination demonstrates erythema and swelling of labial, vulvar, and vaginal structures, with a normal cervix and an adherent white or off-white discharge. When the discharge is removed from the vaginal wall, small bleeding points may appear.1,4
Making the diagnosis
As mentioned, history alone is not sufficient to make a definitive diagnosis of candidiasis. The diagnosis should be made by examining vaginal secretions under a microscope or by culture.4 A wet mount and KOH (potassium hydroxide) prep help differentiate VVC, BV, and trichomoniasis. Culture is particularly valuable in identifying less common fungal organisms, such as C glabrata and C tropicalis.
Vaginal pH testing is not conclusive for Candida because vaginal pH is normal in VVC. However, pH assessment can rule in other causative organisms if the value is abnormal (that is, elevated pH of 4.5 or greater with BV and trichomoniasis).1
Treatment options
Acute infection. A pregnant woman who tests positive for VVC may safely be treated in any trimester with a 7-day course of a topical azole.8 If the patient prefers the convenience of oral therapy, after the first trimester, oral fluconazole, 150 mg on day 1 and day 3, may be used for treatment. Note that fluconazole has been associated with an increased risk of spontaneous abortion and cardiac septal defects when used in the first trimester.1
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a number of topical treatments for VVC (TABLE).8 Several of these drugs are available over the counter without a prescription. Topical azoles are more effective than nystatin in treating VVC, and posttreatment cultures are negative in up to 90% of treated patients.8
Recurrent infections. Recurrent VVC is defined as 4 or more episodes of symptomatic VVC within 12 months.8 Typical first-line treatment of recurrent infections in nonpregnant patients is a 6-month course of fluconazole, 150 mg weekly.9,10 As noted, however, fluconazole should not be used in the first trimester of pregnancy. It is acceptable therapy thereafter for patients who have troublesome recurrent or persistent infections.
Continue to: Strategies for preventing recurrence...
Strategies for preventing recurrence
While it is logical to consider antimycotic prophylaxis in women with a history of recurring VVC and/or a significant number of known risk factors, data suggest that extended prophylaxis with an azole does not consistently achieve long-term elimination of vaginal Candida organisms after cessation of the azole.9
At-risk women should be counseled to make lifestyle adjustments, such as wearing breathable cotton clothing, particularly undergarments; promptly changing out of damp clothing; and forgoing the use of commercial intravaginal feminine hygiene products.
Recent research has shown that the use of Saccharomyces cerevisiae–based probiotics has promise for controlling the burden of C albicans in women receiving antifungal drugs for VVC and also for preventing recurrence; however, this approach has undergone limited testing in humans, and its efficacy and safety in pregnancy is unknown.11 ●
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infection. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, et al, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:862.
- Goncalves B, Ferreira C, Alves CT, et al. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: epidemiology, microbiology and risk factors. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016;42:905-927.
- Hall RA, Noverr MC. Fungal interactions with the human host: exploring the spectrum of symbiosis. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2017;40:58-64.
- Sobel JD. Vulvovaginal candidosis. Lancet. 2007;369:1961-1971.
- Holzer I, Farr A, Kiss H; et al. The colonization with Candida species is more harmful in the second trimester of pregnancy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017;295:891-895.
- Farr A, Kiss H, Holzer I, et al. Effect of asymptomatic vaginal colonization with Candida albicans on pregnancy outcome. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2015;94:989-996.
- Anderson MR, Klink K, Cohrssen A. Evaluation of vaginal complaints. JAMA. 2004;291:1368-1379.
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2015;64(RR-03):1-137.
- Sobel JD, Wiesenfeld HC, Martens M, et al. Maintenance fluconazole therapy for recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:876-883.
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: Use of long-term, high-dose Diflucan (fluconazole) during pregnancy may be associated with birth defects in infants. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-drug-safety-communicationuse-long-term-high-dose-diflucan-fluconazole-during-pregnancy-may-be#. Updated August 4, 2017. Accessed July 6, 2020.
- Gaziano R, Sabbatini S, Roselletti E, et al. Saccharomyces cerevisiae-based probiotics as novel antimicrobial agents to prevent and treat vaginal infections. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:718.
- Duff P. Maternal and fetal infection. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, et al, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:862.
- Goncalves B, Ferreira C, Alves CT, et al. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: epidemiology, microbiology and risk factors. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016;42:905-927.
- Hall RA, Noverr MC. Fungal interactions with the human host: exploring the spectrum of symbiosis. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2017;40:58-64.
- Sobel JD. Vulvovaginal candidosis. Lancet. 2007;369:1961-1971.
- Holzer I, Farr A, Kiss H; et al. The colonization with Candida species is more harmful in the second trimester of pregnancy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017;295:891-895.
- Farr A, Kiss H, Holzer I, et al. Effect of asymptomatic vaginal colonization with Candida albicans on pregnancy outcome. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2015;94:989-996.
- Anderson MR, Klink K, Cohrssen A. Evaluation of vaginal complaints. JAMA. 2004;291:1368-1379.
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2015;64(RR-03):1-137.
- Sobel JD, Wiesenfeld HC, Martens M, et al. Maintenance fluconazole therapy for recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:876-883.
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: Use of long-term, high-dose Diflucan (fluconazole) during pregnancy may be associated with birth defects in infants. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-drug-safety-communicationuse-long-term-high-dose-diflucan-fluconazole-during-pregnancy-may-be#. Updated August 4, 2017. Accessed July 6, 2020.
- Gaziano R, Sabbatini S, Roselletti E, et al. Saccharomyces cerevisiae-based probiotics as novel antimicrobial agents to prevent and treat vaginal infections. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:718.

