User login
Doug Brunk is a San Diego-based award-winning reporter who began covering health care in 1991. Before joining the company, he wrote for the health sciences division of Columbia University and was an associate editor at Contemporary Long Term Care magazine when it won a Jesse H. Neal Award. His work has been syndicated by the Los Angeles Times and he is the author of two books related to the University of Kentucky Wildcats men's basketball program. Doug has a master’s degree in magazine journalism from the S.I. Newhouse School of Public Communications at Syracuse University. Follow him on Twitter @dougbrunk.
Certain opioids hold promise for treating itch
Certain opioids are proving to be effective in treating a variety of itch conditions, according to Brian S. Kim, MD.
“We know that opioids or opiates do cause itch in a significant number of patients,” Dr. Kim, a dermatologist who is codirector of the Center for the Study of Itch & Sensory Disorders at Washington University, St. Louis, said during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “It’s thought to do this by way of acting as a pruritogen at times and stimulating sensory neurons [that] then activate the itch cascade. But it’s also been well known that endogenous kappa opioids can activate sensory neurons that can then suppress itch and gate out signals from these opiates, but perhaps other pruritogens as well.”
Multiple drugs differentially target kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) and mu-opioid receptor (MOR) pathways, he continued. For example, oral naltrexone is a MOR antagonist, oral nalfurafine and intravenous difelikefalin are KOR agonists, while intranasal butorphanol and oral nalbuphine have a dual mechanism.
Difelikefalin is the first Food and Drug Administration–approved treatment for uremic pruritus associated with dialysis, approved in August 2021 for moderate-to-severe pruritus associated with chronic kidney disease in adults undergoing hemodialysis; it is administered intravenously. During the 2021 annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, Dr. Kim and colleagues presented findings from a phase 2 trial of 401 people with atopic dermatitis (AD) and moderate to severe pruritus, who were randomized to receive oral difelikefalin at a dose of 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, or 1.0 mg, or placebo over a 12-week treatment period. The primary endpoint, change from baseline in Itch Numerical Rating Scale score, was not met in any of the difelikefalin dose groups in the overall study population, but patients with a body surface area of less than 10% experienced a significant improvement in itch at week 12 in the combined difelikefalin dose group in (P = .039). A significant reduction in itch with difelikefalin was seen in this group of patients with itch-dominant AD, as early as the second day of treatment.
In another trial, 373 hemodialysis patients with moderate or severe uremic pruritus were randomized in a 1: 1:1 ratio to nalbuphine extended-release tablets 120 mg, 60 mg, or placebo and treated for 8 weeks. The researchers found that nalbuphine 120 mg significantly reduced the itching intensity. Specifically, from a baseline numerical rate scale (NRS) of 6.9, the mean NRS declined by 3.5 and by 2.8 in the nalbuphine 120-mg and the placebo groups, respectively (P = .017).
In a separate, unpublished multicenter, randomized, phase 2/3 trial, researchers evaluated the safety and antipruritic efficacy of nalbuphine extended-release tablets dosed twice daily at 90 mg and 180 mg in 62 patients in the United States and Europe. The proportion of patients in the nalbuphine 180-mg arm who met 50% responder criteria at week 10 or last observed visit approached statistical significance (P = .083), and this arm met statistical significance for patients who completed treatment (P = .028).
Dr. Kim disclosed that he has served as a consultant for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Cara Therapeutics, Galderma, GlaxoSmithKline, LEO Pharma, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Trevi Therapeutics. He also has conducted contracted research for Cara Therapeutics and LEO Pharma.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Certain opioids are proving to be effective in treating a variety of itch conditions, according to Brian S. Kim, MD.
“We know that opioids or opiates do cause itch in a significant number of patients,” Dr. Kim, a dermatologist who is codirector of the Center for the Study of Itch & Sensory Disorders at Washington University, St. Louis, said during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “It’s thought to do this by way of acting as a pruritogen at times and stimulating sensory neurons [that] then activate the itch cascade. But it’s also been well known that endogenous kappa opioids can activate sensory neurons that can then suppress itch and gate out signals from these opiates, but perhaps other pruritogens as well.”
Multiple drugs differentially target kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) and mu-opioid receptor (MOR) pathways, he continued. For example, oral naltrexone is a MOR antagonist, oral nalfurafine and intravenous difelikefalin are KOR agonists, while intranasal butorphanol and oral nalbuphine have a dual mechanism.
Difelikefalin is the first Food and Drug Administration–approved treatment for uremic pruritus associated with dialysis, approved in August 2021 for moderate-to-severe pruritus associated with chronic kidney disease in adults undergoing hemodialysis; it is administered intravenously. During the 2021 annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, Dr. Kim and colleagues presented findings from a phase 2 trial of 401 people with atopic dermatitis (AD) and moderate to severe pruritus, who were randomized to receive oral difelikefalin at a dose of 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, or 1.0 mg, or placebo over a 12-week treatment period. The primary endpoint, change from baseline in Itch Numerical Rating Scale score, was not met in any of the difelikefalin dose groups in the overall study population, but patients with a body surface area of less than 10% experienced a significant improvement in itch at week 12 in the combined difelikefalin dose group in (P = .039). A significant reduction in itch with difelikefalin was seen in this group of patients with itch-dominant AD, as early as the second day of treatment.
In another trial, 373 hemodialysis patients with moderate or severe uremic pruritus were randomized in a 1: 1:1 ratio to nalbuphine extended-release tablets 120 mg, 60 mg, or placebo and treated for 8 weeks. The researchers found that nalbuphine 120 mg significantly reduced the itching intensity. Specifically, from a baseline numerical rate scale (NRS) of 6.9, the mean NRS declined by 3.5 and by 2.8 in the nalbuphine 120-mg and the placebo groups, respectively (P = .017).
In a separate, unpublished multicenter, randomized, phase 2/3 trial, researchers evaluated the safety and antipruritic efficacy of nalbuphine extended-release tablets dosed twice daily at 90 mg and 180 mg in 62 patients in the United States and Europe. The proportion of patients in the nalbuphine 180-mg arm who met 50% responder criteria at week 10 or last observed visit approached statistical significance (P = .083), and this arm met statistical significance for patients who completed treatment (P = .028).
Dr. Kim disclosed that he has served as a consultant for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Cara Therapeutics, Galderma, GlaxoSmithKline, LEO Pharma, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Trevi Therapeutics. He also has conducted contracted research for Cara Therapeutics and LEO Pharma.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Certain opioids are proving to be effective in treating a variety of itch conditions, according to Brian S. Kim, MD.
“We know that opioids or opiates do cause itch in a significant number of patients,” Dr. Kim, a dermatologist who is codirector of the Center for the Study of Itch & Sensory Disorders at Washington University, St. Louis, said during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “It’s thought to do this by way of acting as a pruritogen at times and stimulating sensory neurons [that] then activate the itch cascade. But it’s also been well known that endogenous kappa opioids can activate sensory neurons that can then suppress itch and gate out signals from these opiates, but perhaps other pruritogens as well.”
Multiple drugs differentially target kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) and mu-opioid receptor (MOR) pathways, he continued. For example, oral naltrexone is a MOR antagonist, oral nalfurafine and intravenous difelikefalin are KOR agonists, while intranasal butorphanol and oral nalbuphine have a dual mechanism.
Difelikefalin is the first Food and Drug Administration–approved treatment for uremic pruritus associated with dialysis, approved in August 2021 for moderate-to-severe pruritus associated with chronic kidney disease in adults undergoing hemodialysis; it is administered intravenously. During the 2021 annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, Dr. Kim and colleagues presented findings from a phase 2 trial of 401 people with atopic dermatitis (AD) and moderate to severe pruritus, who were randomized to receive oral difelikefalin at a dose of 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, or 1.0 mg, or placebo over a 12-week treatment period. The primary endpoint, change from baseline in Itch Numerical Rating Scale score, was not met in any of the difelikefalin dose groups in the overall study population, but patients with a body surface area of less than 10% experienced a significant improvement in itch at week 12 in the combined difelikefalin dose group in (P = .039). A significant reduction in itch with difelikefalin was seen in this group of patients with itch-dominant AD, as early as the second day of treatment.
In another trial, 373 hemodialysis patients with moderate or severe uremic pruritus were randomized in a 1: 1:1 ratio to nalbuphine extended-release tablets 120 mg, 60 mg, or placebo and treated for 8 weeks. The researchers found that nalbuphine 120 mg significantly reduced the itching intensity. Specifically, from a baseline numerical rate scale (NRS) of 6.9, the mean NRS declined by 3.5 and by 2.8 in the nalbuphine 120-mg and the placebo groups, respectively (P = .017).
In a separate, unpublished multicenter, randomized, phase 2/3 trial, researchers evaluated the safety and antipruritic efficacy of nalbuphine extended-release tablets dosed twice daily at 90 mg and 180 mg in 62 patients in the United States and Europe. The proportion of patients in the nalbuphine 180-mg arm who met 50% responder criteria at week 10 or last observed visit approached statistical significance (P = .083), and this arm met statistical significance for patients who completed treatment (P = .028).
Dr. Kim disclosed that he has served as a consultant for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Cara Therapeutics, Galderma, GlaxoSmithKline, LEO Pharma, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Trevi Therapeutics. He also has conducted contracted research for Cara Therapeutics and LEO Pharma.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
FROM THE MEDSCAPELIVE LAS VEGAS DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Validity of commercial serologic tests for dermatomyositis still questionable
, according to Jeffrey P. Callen, MD.
That’s because the validity and reproducibility of testing in commercial laboratories remain questionable, Dr. Callen, professor of medicine and chief of the division of dermatology at the University of Louisville, Ky., said during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “The testing in research laboratories is not widely available and the results are often delayed by weeks to months,” he said.
In addition, while the associations between antibody results and risks of malignancy or pulmonary disease are “statistically valid,” he said, “there are patients with disease in whom antibodies are not present and those without associated disease in whom the testing was positive.” For example, there are patients positive for anti–transition initiation factor (TIF)-1gamma but don’t have a malignancy, “and the ones with anti-MDA-5 tend to have pulmonary disease, but there are patients with anti-MDA-5 who don’t have pulmonary disease.”
Compared with patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, patients with dermatomyositis tend to have more itching and they tend of have fewer serologic abnormalities, such as anti-Ro/SS-A antibody, “but there is overlap,” Dr. Callen said. “The reason to differentiate cutaneous lupus erythematosus from dermatomyositis is because we think that patients who have amyopathic dermatomyositis still have an increased risk of having or developing an internal malignancy,” he added. Another differentiating point that is substantive is the presence of Gottron papules.
In a recent development related to antibody testing, researchers demonstrated that the IgG2 isotype of anti-TIF-1gamma antibodies is a biomarker of cancer and mortality in adult dermatomyositis.
According to population-based studies, about 20%-25% of dermatomyositis patients have had, have, or will develop a cancer (Lancet 2001;357: 96-100). Amyopathic dermatomyositis patients may also have cancer. Polymyositis patients generally have lower rates and their risk of subsequent malignancy is much closer to that of the general population, suggesting that the presence of the association is due to a “diagnostic suspicion bias,” Dr. Callen said.
A large-scale multicenter cohort study that set out to identify the risk factors and prognosis of patients with cancer-associated myositis found that ovarian cancer seems to be overrepresented. The only serologic abnormality that was statistically significant was anti-TIF-1gamma antibody (P less than .001). Patients with cancer-associated myositis also have less overall survival compared with those with non–cancer-associated myositis (P = .004), with malignancy being the primary cause of death (P less than .001).
In what is believed to be the largest study of its kind, Dr. Callen and colleagues retrospectively examined the prevalence of malignancy and screening practices in 400 dermatomyositis patients. Of the 400 patients, 48 (12%) had malignancies, and 21 cancers (40%) were diagnosed within 1 year of the dermatomyositis diagnosis. Both classic dermatomyositis and amyopathic dermatomyositis were associated with cancer, and 27 patients (6.8%) had a cancer at the time of diagnosis. Of those, 59% were asymptomatic; their cancers were discovered with CT scans, suggesting that “blind” screening is effective in identifying cancers in DM patients.
Dr. Callen’s malignancy evaluation includes chest x-ray, CT of the chest and abdomen, stool Hematest in all dermatomyositis patients; a mammogram, pelvic ultrasound and/or CT of the pelvis in women; and age, race or ethnicity-related testing. “I generally reevaluate patients annually for 3 years, because data from epidemiologic studies suggest that after 3 years [from the initial diagnosis], the rates of malignancy return toward normal,” he said. “I also evaluate any new symptom that might be suggestive of malignancy. The remaining issue is how to handle a patient in remission for several years, but who develops a relapse. What I do is perform another malignancy assessment.”
According to results from a meta-analysis of risk factors and systematic review of screening approaches, factors that increase malignancy risk include dermatomyositis subtype (risk ratio, 2.21), older age (weighted mean difference 11.19), male gender (RR, 1.53), dysphagia (RR, 2.09), cutaneous necrosis (RR, 2.73), and positive anti-TIF-1gamma (RR, 4.41).
Factors associated with a decreased risk of malignancy include polymyositis (RR, 0.49), clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis subtypes (RR, 0.44), Raynaud’s phenomenon (RR, 0.61), interstitial lung disease (RR, 0.49), very high serum creatine kinase (WMD –1189.96) or lactate dehydrogenase levels (WMD –336.53), and anti-Jo1 (RR, 0.45) or anti-EJ (RR, 0.17) positivity.
The analysis also found that CT scanning of the thorax, abdomen and pelvis appeared to yield a high proportion of underlying asymptomatic cancers. Limited evidence relating to the utility of tumor markers and 18F-FDG PET/CT was available.
As for treatment, the use of tofacitinib for cutaneous lesions of dermatomyositis has been suggested in various studies. In a recent open-label study of 10 patients with dermatomyositis who took extended release the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib 11 mg daily for 12 weeks, half experienced moderate improvement in disease activity, and the other half experienced minimal improvement. JAK inhibitors have been used in patients with juvenile dermatomyositis.
Dr. Callen’s treatment approach with dermatomyositis patients includes recommendations for sunscreens and protective clothing, plus assessment of vitamin D levels. “I will use topical emollients, corticosteroids, and calcineurin inhibitors,” he said. “Antimalarials might be used. I generally reach for methotrexate or mycophenolate mofetil relatively early. IVIG has also been studied.” Off-label therapies that have been used include dapsone, thalidomide, leflunomide, sirolimus, chlorambucil, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab, apremilast, tofacitinib, lenabasum, and low-dose naltrexone.
Dr. Callen disclosed that he is a consultant to Genentech and is a member of the safety monitoring committee for Principia Biopharma. He holds equity in Celgene, Pfizer, 3M, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Abbott Laboratories, AbbVie, Procter & Gamble, Gilead, Allergen, and Amgen.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
, according to Jeffrey P. Callen, MD.
That’s because the validity and reproducibility of testing in commercial laboratories remain questionable, Dr. Callen, professor of medicine and chief of the division of dermatology at the University of Louisville, Ky., said during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “The testing in research laboratories is not widely available and the results are often delayed by weeks to months,” he said.
In addition, while the associations between antibody results and risks of malignancy or pulmonary disease are “statistically valid,” he said, “there are patients with disease in whom antibodies are not present and those without associated disease in whom the testing was positive.” For example, there are patients positive for anti–transition initiation factor (TIF)-1gamma but don’t have a malignancy, “and the ones with anti-MDA-5 tend to have pulmonary disease, but there are patients with anti-MDA-5 who don’t have pulmonary disease.”
Compared with patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, patients with dermatomyositis tend to have more itching and they tend of have fewer serologic abnormalities, such as anti-Ro/SS-A antibody, “but there is overlap,” Dr. Callen said. “The reason to differentiate cutaneous lupus erythematosus from dermatomyositis is because we think that patients who have amyopathic dermatomyositis still have an increased risk of having or developing an internal malignancy,” he added. Another differentiating point that is substantive is the presence of Gottron papules.
In a recent development related to antibody testing, researchers demonstrated that the IgG2 isotype of anti-TIF-1gamma antibodies is a biomarker of cancer and mortality in adult dermatomyositis.
According to population-based studies, about 20%-25% of dermatomyositis patients have had, have, or will develop a cancer (Lancet 2001;357: 96-100). Amyopathic dermatomyositis patients may also have cancer. Polymyositis patients generally have lower rates and their risk of subsequent malignancy is much closer to that of the general population, suggesting that the presence of the association is due to a “diagnostic suspicion bias,” Dr. Callen said.
A large-scale multicenter cohort study that set out to identify the risk factors and prognosis of patients with cancer-associated myositis found that ovarian cancer seems to be overrepresented. The only serologic abnormality that was statistically significant was anti-TIF-1gamma antibody (P less than .001). Patients with cancer-associated myositis also have less overall survival compared with those with non–cancer-associated myositis (P = .004), with malignancy being the primary cause of death (P less than .001).
In what is believed to be the largest study of its kind, Dr. Callen and colleagues retrospectively examined the prevalence of malignancy and screening practices in 400 dermatomyositis patients. Of the 400 patients, 48 (12%) had malignancies, and 21 cancers (40%) were diagnosed within 1 year of the dermatomyositis diagnosis. Both classic dermatomyositis and amyopathic dermatomyositis were associated with cancer, and 27 patients (6.8%) had a cancer at the time of diagnosis. Of those, 59% were asymptomatic; their cancers were discovered with CT scans, suggesting that “blind” screening is effective in identifying cancers in DM patients.
Dr. Callen’s malignancy evaluation includes chest x-ray, CT of the chest and abdomen, stool Hematest in all dermatomyositis patients; a mammogram, pelvic ultrasound and/or CT of the pelvis in women; and age, race or ethnicity-related testing. “I generally reevaluate patients annually for 3 years, because data from epidemiologic studies suggest that after 3 years [from the initial diagnosis], the rates of malignancy return toward normal,” he said. “I also evaluate any new symptom that might be suggestive of malignancy. The remaining issue is how to handle a patient in remission for several years, but who develops a relapse. What I do is perform another malignancy assessment.”
According to results from a meta-analysis of risk factors and systematic review of screening approaches, factors that increase malignancy risk include dermatomyositis subtype (risk ratio, 2.21), older age (weighted mean difference 11.19), male gender (RR, 1.53), dysphagia (RR, 2.09), cutaneous necrosis (RR, 2.73), and positive anti-TIF-1gamma (RR, 4.41).
Factors associated with a decreased risk of malignancy include polymyositis (RR, 0.49), clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis subtypes (RR, 0.44), Raynaud’s phenomenon (RR, 0.61), interstitial lung disease (RR, 0.49), very high serum creatine kinase (WMD –1189.96) or lactate dehydrogenase levels (WMD –336.53), and anti-Jo1 (RR, 0.45) or anti-EJ (RR, 0.17) positivity.
The analysis also found that CT scanning of the thorax, abdomen and pelvis appeared to yield a high proportion of underlying asymptomatic cancers. Limited evidence relating to the utility of tumor markers and 18F-FDG PET/CT was available.
As for treatment, the use of tofacitinib for cutaneous lesions of dermatomyositis has been suggested in various studies. In a recent open-label study of 10 patients with dermatomyositis who took extended release the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib 11 mg daily for 12 weeks, half experienced moderate improvement in disease activity, and the other half experienced minimal improvement. JAK inhibitors have been used in patients with juvenile dermatomyositis.
Dr. Callen’s treatment approach with dermatomyositis patients includes recommendations for sunscreens and protective clothing, plus assessment of vitamin D levels. “I will use topical emollients, corticosteroids, and calcineurin inhibitors,” he said. “Antimalarials might be used. I generally reach for methotrexate or mycophenolate mofetil relatively early. IVIG has also been studied.” Off-label therapies that have been used include dapsone, thalidomide, leflunomide, sirolimus, chlorambucil, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab, apremilast, tofacitinib, lenabasum, and low-dose naltrexone.
Dr. Callen disclosed that he is a consultant to Genentech and is a member of the safety monitoring committee for Principia Biopharma. He holds equity in Celgene, Pfizer, 3M, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Abbott Laboratories, AbbVie, Procter & Gamble, Gilead, Allergen, and Amgen.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
, according to Jeffrey P. Callen, MD.
That’s because the validity and reproducibility of testing in commercial laboratories remain questionable, Dr. Callen, professor of medicine and chief of the division of dermatology at the University of Louisville, Ky., said during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “The testing in research laboratories is not widely available and the results are often delayed by weeks to months,” he said.
In addition, while the associations between antibody results and risks of malignancy or pulmonary disease are “statistically valid,” he said, “there are patients with disease in whom antibodies are not present and those without associated disease in whom the testing was positive.” For example, there are patients positive for anti–transition initiation factor (TIF)-1gamma but don’t have a malignancy, “and the ones with anti-MDA-5 tend to have pulmonary disease, but there are patients with anti-MDA-5 who don’t have pulmonary disease.”
Compared with patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, patients with dermatomyositis tend to have more itching and they tend of have fewer serologic abnormalities, such as anti-Ro/SS-A antibody, “but there is overlap,” Dr. Callen said. “The reason to differentiate cutaneous lupus erythematosus from dermatomyositis is because we think that patients who have amyopathic dermatomyositis still have an increased risk of having or developing an internal malignancy,” he added. Another differentiating point that is substantive is the presence of Gottron papules.
In a recent development related to antibody testing, researchers demonstrated that the IgG2 isotype of anti-TIF-1gamma antibodies is a biomarker of cancer and mortality in adult dermatomyositis.
According to population-based studies, about 20%-25% of dermatomyositis patients have had, have, or will develop a cancer (Lancet 2001;357: 96-100). Amyopathic dermatomyositis patients may also have cancer. Polymyositis patients generally have lower rates and their risk of subsequent malignancy is much closer to that of the general population, suggesting that the presence of the association is due to a “diagnostic suspicion bias,” Dr. Callen said.
A large-scale multicenter cohort study that set out to identify the risk factors and prognosis of patients with cancer-associated myositis found that ovarian cancer seems to be overrepresented. The only serologic abnormality that was statistically significant was anti-TIF-1gamma antibody (P less than .001). Patients with cancer-associated myositis also have less overall survival compared with those with non–cancer-associated myositis (P = .004), with malignancy being the primary cause of death (P less than .001).
In what is believed to be the largest study of its kind, Dr. Callen and colleagues retrospectively examined the prevalence of malignancy and screening practices in 400 dermatomyositis patients. Of the 400 patients, 48 (12%) had malignancies, and 21 cancers (40%) were diagnosed within 1 year of the dermatomyositis diagnosis. Both classic dermatomyositis and amyopathic dermatomyositis were associated with cancer, and 27 patients (6.8%) had a cancer at the time of diagnosis. Of those, 59% were asymptomatic; their cancers were discovered with CT scans, suggesting that “blind” screening is effective in identifying cancers in DM patients.
Dr. Callen’s malignancy evaluation includes chest x-ray, CT of the chest and abdomen, stool Hematest in all dermatomyositis patients; a mammogram, pelvic ultrasound and/or CT of the pelvis in women; and age, race or ethnicity-related testing. “I generally reevaluate patients annually for 3 years, because data from epidemiologic studies suggest that after 3 years [from the initial diagnosis], the rates of malignancy return toward normal,” he said. “I also evaluate any new symptom that might be suggestive of malignancy. The remaining issue is how to handle a patient in remission for several years, but who develops a relapse. What I do is perform another malignancy assessment.”
According to results from a meta-analysis of risk factors and systematic review of screening approaches, factors that increase malignancy risk include dermatomyositis subtype (risk ratio, 2.21), older age (weighted mean difference 11.19), male gender (RR, 1.53), dysphagia (RR, 2.09), cutaneous necrosis (RR, 2.73), and positive anti-TIF-1gamma (RR, 4.41).
Factors associated with a decreased risk of malignancy include polymyositis (RR, 0.49), clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis subtypes (RR, 0.44), Raynaud’s phenomenon (RR, 0.61), interstitial lung disease (RR, 0.49), very high serum creatine kinase (WMD –1189.96) or lactate dehydrogenase levels (WMD –336.53), and anti-Jo1 (RR, 0.45) or anti-EJ (RR, 0.17) positivity.
The analysis also found that CT scanning of the thorax, abdomen and pelvis appeared to yield a high proportion of underlying asymptomatic cancers. Limited evidence relating to the utility of tumor markers and 18F-FDG PET/CT was available.
As for treatment, the use of tofacitinib for cutaneous lesions of dermatomyositis has been suggested in various studies. In a recent open-label study of 10 patients with dermatomyositis who took extended release the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib 11 mg daily for 12 weeks, half experienced moderate improvement in disease activity, and the other half experienced minimal improvement. JAK inhibitors have been used in patients with juvenile dermatomyositis.
Dr. Callen’s treatment approach with dermatomyositis patients includes recommendations for sunscreens and protective clothing, plus assessment of vitamin D levels. “I will use topical emollients, corticosteroids, and calcineurin inhibitors,” he said. “Antimalarials might be used. I generally reach for methotrexate or mycophenolate mofetil relatively early. IVIG has also been studied.” Off-label therapies that have been used include dapsone, thalidomide, leflunomide, sirolimus, chlorambucil, etanercept, infliximab, rituximab, apremilast, tofacitinib, lenabasum, and low-dose naltrexone.
Dr. Callen disclosed that he is a consultant to Genentech and is a member of the safety monitoring committee for Principia Biopharma. He holds equity in Celgene, Pfizer, 3M, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Abbott Laboratories, AbbVie, Procter & Gamble, Gilead, Allergen, and Amgen.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
FROM THE MEDSCAPELIVE LAS VEGAS DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
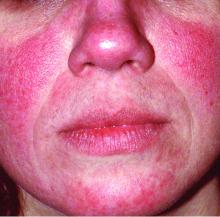
Rosacea is in the eye of the beholder, expert says
In the clinical experience of Emmy Graber, MD, MBA, rosacea is in the eye of the beholder.
“It’s not really up to us as the providers as to what’s important to the patient or how bad their rosacea is,” she said during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “It really is up to the patient,” added Dr. Graber, president of The Dermatology Institute of Boston, who recommends asking patients about how severe they consider their rosacea to be, and what about rosacea bothers them most. Their responses may be surprising.
A study published in 2017 showed that complete resolution of even mild rosacea prolongs remission of rosacea, and most importantly, improves the quality of life for patients. “So, don’t discount what you consider to be mild rosacea in patients,” she said.
Skin care recommendations
“And don’t forget about basic skin care,” she advised. A recently published Chinese study of 999 rosacea patients and 1,010 controls with healthy skin found that a high frequency of cleansing and expansive use of cleansers were positively correlated with rosacea occurrence, suggesting that overcleansing can be a risk factor for rosacea. “Ask your patient, ‘how often are you cleaning your face?’ ” Dr. Graber suggested. “You might find that they’re overdoing it by washing three or four times a day. Several studies have shown that basic skin care alone improves rosacea.”
Skin care recommendations for patients with rosacea include avoiding chemical or physical exfoliants and alcohol-based topical products, and moisturizing and washing their faces with mild, synthetic detergent-based products rather than traditional soaps, which may further alkalinize and irritate the skin. “Patients should also be counseled to use physical-based sunscreens rather than chemical-based sunscreens,” she said.
Treating erythema
For treating erythema with topicals, a systematic review published in 2019 found the most evidence for brimonidine 0.33% gel, an alpha2-adrenergic agonist, and oxymetazoline 1% cream, an alpha1-adrenergic agonist. “Both of these products functionally constrict facial blood vessels,” and are Food and Drug Administration approved for treating persistent erythema, Dr. Graber said. “These products improve erythema within 3 hours of and up to 12 hours after application and overall, they are well tolerated.”
Based on clinical trial results, about 15% of patients on brimonidine report adverse reactions such as dermatitis, burning, pruritus, and erythema, compared with 8% of patients on oxymetazoline. At the same time, up to 20% of individuals on brimonidine report rebound erythema, compared with fewer than 1% of those using oxymetazoline. Laser and light therapies such as pulse-dye lasers, potassium-titanyl-phosphate lasers, and intense-pulse light devices are also effective in treating persistent erythema but are less effective for transient flushing.
Treatment of papules and pustules
For treating papules and pustules, the 2019 systemic review also found high-certainty evidence for using azelaic acid and topical ivermectin, and moderate-certainty evidence for using topical metronidazole and topical minocycline. “Topical ivermectin was demonstrated to be the most effective topical treatment for papulopustular rosacea and to provide the greatest psychological benefit to these patients,” Dr. Graber said.
In a double-blind, multicenter 15-week trial comparing azelaic acid 15% gel with metronidazole 0.75% gel in patients with papulopustular rosacea, both agents were found to be effective. But those treated with azelaic acid 15% gel had a greater reduction in lesion counts and erythema, and improvement in global assessments, compared with metronidazole 0.75% gel. However, the azelaic acid 15% gel was associated with more stinging compared with metronidazole 0.75% gel, although it was usually transient.
Another study, a double-blind, single-center, 15-week trial, compared the efficacy of azelaic acid 20% cream with metronidazole 0.75% cream. Both agents were found to be effective and had similar levels of reductions in papules and pustules. However, patients in the azelaic acid 20% cream arm had significantly higher physician ratings of global improvement, as well as overall higher patient satisfaction.
More recently, a phase 3 study of 962 patients found that ivermectin 1% cream once daily improved quality of life slightly more than metronidazole 0.75% cream twice daily. No difference in adverse events were noted between the two agents.
Other options for treating papules and pustules include topical minocycline 1.5% foam, which is FDA approved for rosacea, as well as second-line agents topical sodium sulfacetamide with sulfur cleanser (cream or lotion), and permethrin, Dr. Graber said.
As for treating papules and pustules with oral agents, the strongest evidence favors oral tetracyclines and isotretinoin, she noted.
Doxycycline, minocycline, tetracycline, and sarecycline can be used as monotherapy or coadministered with topical agents. “The addition of topical agents may also help to shorten the duration of antibiotic use, which is very important,” Dr. Graber said.
She noted that oral beta-blockers might be useful to treat persistent erythema and flushing because they antagonize the effects of sympathetic nerve stimulation and circulating catecholamines at b-adrenoceptors. Carvedilol and propranolol have been the most studied. The most common potential side effects are hypotension and bradycardia.
Dr. Graber disclosed that she is a consultant/adviser for Digital Diagnostics, Almirall, Hovione, Keratin Biosciences, La Roche Posay, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, Sol-Gel, Verrica, and WebMD. She is also a research investigator for Hovione, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, and she receives royalties from Wolters Kluwer Health.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
In the clinical experience of Emmy Graber, MD, MBA, rosacea is in the eye of the beholder.
“It’s not really up to us as the providers as to what’s important to the patient or how bad their rosacea is,” she said during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “It really is up to the patient,” added Dr. Graber, president of The Dermatology Institute of Boston, who recommends asking patients about how severe they consider their rosacea to be, and what about rosacea bothers them most. Their responses may be surprising.
A study published in 2017 showed that complete resolution of even mild rosacea prolongs remission of rosacea, and most importantly, improves the quality of life for patients. “So, don’t discount what you consider to be mild rosacea in patients,” she said.
Skin care recommendations
“And don’t forget about basic skin care,” she advised. A recently published Chinese study of 999 rosacea patients and 1,010 controls with healthy skin found that a high frequency of cleansing and expansive use of cleansers were positively correlated with rosacea occurrence, suggesting that overcleansing can be a risk factor for rosacea. “Ask your patient, ‘how often are you cleaning your face?’ ” Dr. Graber suggested. “You might find that they’re overdoing it by washing three or four times a day. Several studies have shown that basic skin care alone improves rosacea.”
Skin care recommendations for patients with rosacea include avoiding chemical or physical exfoliants and alcohol-based topical products, and moisturizing and washing their faces with mild, synthetic detergent-based products rather than traditional soaps, which may further alkalinize and irritate the skin. “Patients should also be counseled to use physical-based sunscreens rather than chemical-based sunscreens,” she said.
Treating erythema
For treating erythema with topicals, a systematic review published in 2019 found the most evidence for brimonidine 0.33% gel, an alpha2-adrenergic agonist, and oxymetazoline 1% cream, an alpha1-adrenergic agonist. “Both of these products functionally constrict facial blood vessels,” and are Food and Drug Administration approved for treating persistent erythema, Dr. Graber said. “These products improve erythema within 3 hours of and up to 12 hours after application and overall, they are well tolerated.”
Based on clinical trial results, about 15% of patients on brimonidine report adverse reactions such as dermatitis, burning, pruritus, and erythema, compared with 8% of patients on oxymetazoline. At the same time, up to 20% of individuals on brimonidine report rebound erythema, compared with fewer than 1% of those using oxymetazoline. Laser and light therapies such as pulse-dye lasers, potassium-titanyl-phosphate lasers, and intense-pulse light devices are also effective in treating persistent erythema but are less effective for transient flushing.
Treatment of papules and pustules
For treating papules and pustules, the 2019 systemic review also found high-certainty evidence for using azelaic acid and topical ivermectin, and moderate-certainty evidence for using topical metronidazole and topical minocycline. “Topical ivermectin was demonstrated to be the most effective topical treatment for papulopustular rosacea and to provide the greatest psychological benefit to these patients,” Dr. Graber said.
In a double-blind, multicenter 15-week trial comparing azelaic acid 15% gel with metronidazole 0.75% gel in patients with papulopustular rosacea, both agents were found to be effective. But those treated with azelaic acid 15% gel had a greater reduction in lesion counts and erythema, and improvement in global assessments, compared with metronidazole 0.75% gel. However, the azelaic acid 15% gel was associated with more stinging compared with metronidazole 0.75% gel, although it was usually transient.
Another study, a double-blind, single-center, 15-week trial, compared the efficacy of azelaic acid 20% cream with metronidazole 0.75% cream. Both agents were found to be effective and had similar levels of reductions in papules and pustules. However, patients in the azelaic acid 20% cream arm had significantly higher physician ratings of global improvement, as well as overall higher patient satisfaction.
More recently, a phase 3 study of 962 patients found that ivermectin 1% cream once daily improved quality of life slightly more than metronidazole 0.75% cream twice daily. No difference in adverse events were noted between the two agents.
Other options for treating papules and pustules include topical minocycline 1.5% foam, which is FDA approved for rosacea, as well as second-line agents topical sodium sulfacetamide with sulfur cleanser (cream or lotion), and permethrin, Dr. Graber said.
As for treating papules and pustules with oral agents, the strongest evidence favors oral tetracyclines and isotretinoin, she noted.
Doxycycline, minocycline, tetracycline, and sarecycline can be used as monotherapy or coadministered with topical agents. “The addition of topical agents may also help to shorten the duration of antibiotic use, which is very important,” Dr. Graber said.
She noted that oral beta-blockers might be useful to treat persistent erythema and flushing because they antagonize the effects of sympathetic nerve stimulation and circulating catecholamines at b-adrenoceptors. Carvedilol and propranolol have been the most studied. The most common potential side effects are hypotension and bradycardia.
Dr. Graber disclosed that she is a consultant/adviser for Digital Diagnostics, Almirall, Hovione, Keratin Biosciences, La Roche Posay, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, Sol-Gel, Verrica, and WebMD. She is also a research investigator for Hovione, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, and she receives royalties from Wolters Kluwer Health.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
In the clinical experience of Emmy Graber, MD, MBA, rosacea is in the eye of the beholder.
“It’s not really up to us as the providers as to what’s important to the patient or how bad their rosacea is,” she said during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “It really is up to the patient,” added Dr. Graber, president of The Dermatology Institute of Boston, who recommends asking patients about how severe they consider their rosacea to be, and what about rosacea bothers them most. Their responses may be surprising.
A study published in 2017 showed that complete resolution of even mild rosacea prolongs remission of rosacea, and most importantly, improves the quality of life for patients. “So, don’t discount what you consider to be mild rosacea in patients,” she said.
Skin care recommendations
“And don’t forget about basic skin care,” she advised. A recently published Chinese study of 999 rosacea patients and 1,010 controls with healthy skin found that a high frequency of cleansing and expansive use of cleansers were positively correlated with rosacea occurrence, suggesting that overcleansing can be a risk factor for rosacea. “Ask your patient, ‘how often are you cleaning your face?’ ” Dr. Graber suggested. “You might find that they’re overdoing it by washing three or four times a day. Several studies have shown that basic skin care alone improves rosacea.”
Skin care recommendations for patients with rosacea include avoiding chemical or physical exfoliants and alcohol-based topical products, and moisturizing and washing their faces with mild, synthetic detergent-based products rather than traditional soaps, which may further alkalinize and irritate the skin. “Patients should also be counseled to use physical-based sunscreens rather than chemical-based sunscreens,” she said.
Treating erythema
For treating erythema with topicals, a systematic review published in 2019 found the most evidence for brimonidine 0.33% gel, an alpha2-adrenergic agonist, and oxymetazoline 1% cream, an alpha1-adrenergic agonist. “Both of these products functionally constrict facial blood vessels,” and are Food and Drug Administration approved for treating persistent erythema, Dr. Graber said. “These products improve erythema within 3 hours of and up to 12 hours after application and overall, they are well tolerated.”
Based on clinical trial results, about 15% of patients on brimonidine report adverse reactions such as dermatitis, burning, pruritus, and erythema, compared with 8% of patients on oxymetazoline. At the same time, up to 20% of individuals on brimonidine report rebound erythema, compared with fewer than 1% of those using oxymetazoline. Laser and light therapies such as pulse-dye lasers, potassium-titanyl-phosphate lasers, and intense-pulse light devices are also effective in treating persistent erythema but are less effective for transient flushing.
Treatment of papules and pustules
For treating papules and pustules, the 2019 systemic review also found high-certainty evidence for using azelaic acid and topical ivermectin, and moderate-certainty evidence for using topical metronidazole and topical minocycline. “Topical ivermectin was demonstrated to be the most effective topical treatment for papulopustular rosacea and to provide the greatest psychological benefit to these patients,” Dr. Graber said.
In a double-blind, multicenter 15-week trial comparing azelaic acid 15% gel with metronidazole 0.75% gel in patients with papulopustular rosacea, both agents were found to be effective. But those treated with azelaic acid 15% gel had a greater reduction in lesion counts and erythema, and improvement in global assessments, compared with metronidazole 0.75% gel. However, the azelaic acid 15% gel was associated with more stinging compared with metronidazole 0.75% gel, although it was usually transient.
Another study, a double-blind, single-center, 15-week trial, compared the efficacy of azelaic acid 20% cream with metronidazole 0.75% cream. Both agents were found to be effective and had similar levels of reductions in papules and pustules. However, patients in the azelaic acid 20% cream arm had significantly higher physician ratings of global improvement, as well as overall higher patient satisfaction.
More recently, a phase 3 study of 962 patients found that ivermectin 1% cream once daily improved quality of life slightly more than metronidazole 0.75% cream twice daily. No difference in adverse events were noted between the two agents.
Other options for treating papules and pustules include topical minocycline 1.5% foam, which is FDA approved for rosacea, as well as second-line agents topical sodium sulfacetamide with sulfur cleanser (cream or lotion), and permethrin, Dr. Graber said.
As for treating papules and pustules with oral agents, the strongest evidence favors oral tetracyclines and isotretinoin, she noted.
Doxycycline, minocycline, tetracycline, and sarecycline can be used as monotherapy or coadministered with topical agents. “The addition of topical agents may also help to shorten the duration of antibiotic use, which is very important,” Dr. Graber said.
She noted that oral beta-blockers might be useful to treat persistent erythema and flushing because they antagonize the effects of sympathetic nerve stimulation and circulating catecholamines at b-adrenoceptors. Carvedilol and propranolol have been the most studied. The most common potential side effects are hypotension and bradycardia.
Dr. Graber disclosed that she is a consultant/adviser for Digital Diagnostics, Almirall, Hovione, Keratin Biosciences, La Roche Posay, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, Sol-Gel, Verrica, and WebMD. She is also a research investigator for Hovione, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, and she receives royalties from Wolters Kluwer Health.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
FROM MEDSCAPELIVE LAS VEGAS DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
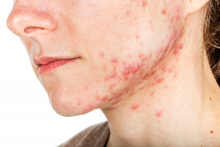
Topical options for acne patients continue to expand
yet they are likely underused in today’s clinical practice.
A study of prescribing practices from 2012 to 2014 indicated that dermatologists prescribed retinoids for just 58.8% of acne cases, while nondermatologists prescribed them for only 32.4% of cases. “If the guidelines are telling us that we should use topical retinoids for almost all of our acne patients, why are we using them for half of the patients?” Emmy Graber, MD, MBA, asked during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “We have a lot of options today for topical retinoids,” she added, noting that, in the past few years, trifarotene cream 0.005% and new formulations of tazarotene lotion (0.045%) and tretinoin lotion (0.05%) have become available.
According to Dr. Graber, president of The Dermatology Institute of Boston, tazarotene has been considered the most efficacious topical retinoid but is generally the least well tolerated, while adapalene has often been considered to be one of the better-tolerated topical retinoids. “This is a broad generalization,” she said. “One should also take into account the concentration and formulation of the retinoid. Cutaneous adverse events increase in severity as the concentration increases regardless of the vehicle.” There are no studies comparing trifarotene with other topical retinoids, she added.
In two phase 2, double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies (PERFECT 1 and PERFECT 2), researchers randomized more than 2,400 patients with moderate facial or truncal acne to receive trifarotene cream or a vehicle for 12 weeks. The mean percent change from baseline in facial inflammatory lesions in the trifarotene-treated group was –54.4% and –66.2% in PERFECT 1, and PERFECT 2, respectively, while the mean percent change from baseline in facial noninflammatory lesions was –49.7% and –57.7%, respectively.
In addition, the mean percent change from baseline in truncal inflammatory lesions in the trifarotene-treated groups was –57.4% and –65.4%, respectively, while the mean percent change from baseline in truncal noninflammatory lesions was –49.1% and –55.2%, respectively.
The choice of vehicle may affect absorption of topical retinoids, and some formulations may increase skin hydration and decrease transepidermal water loss, “which is a good thing,” Dr. Graber said. “Also, vehicles aim to slow drug delivery over time while also making sure that the drug penetrates into the pilosebaceous unit.”
One recent advance is the honeycomb-like polymeric emulsion technology found in tretinoin 0.05% lotion and tazarotene 0.045% lotion. These formulations contain droplets of the tretinoin and tazarotene embedded in a honeycomb matrix with hydrating agents. “I think this is exciting and could enhance our patient compliance and tolerability,” she said. Another unique feature about these two products, especially the tretinoin product, is the very small particle size with this new formulation. “It’s small enough that it can penetrate down into the pilosebaceous unit,” which is different than with older formulations, in which the tretinoin “largely just sat on the surface of the skin and didn’t penetrate into the pilosebaceous unit.” In addition, she said, “there’s only 9% degradation of the tretinoin in UV light, compared to 72% degradation of standard tretinoin 0.025% gel, and with the new tretinoin formulation, there’s no degradation when used with benzoyl peroxide.”
Another new topical retinoid to consider is a fixed-dose combination of encapsulated benzoyl peroxide 3% and encapsulated tretinoin 0.1% cream (Twyneo), which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in July 2021 for the treatment of acne in adults and children aged 9 years and older. “Typically, benzoyl peroxide and tretinoin cannot be mixed in the same tube to stability issues,” she said. “Here, each product is individually encapsulated in a silica shell so that they can be applied together.”
The approval was supported by positive results from two phase 3, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, multicenter studies (NCT03761784 and NCT03761810), in which Twyneo demonstrated efficacy and a favorable tolerability profile in patients aged 9 years and older with facial acne.
Another topical treatment option, dapsone, is now FDA approved for ages 9 and up, expanded from its initial indication for ages 12 and up. The new indication is based on a phase 4, multicenter, open-label study in which acne patients aged 9-11 years applied dapsone 7.5% gel once daily to the face and acne-affected areas on the upper chest, upper back, and shoulders for 12 weeks. After 12 weeks, facial acne was clear or almost clear in about 47% of patients. “Inflammatory, noninflammatory, and total lesions decreased from baseline, but there was a greater reduction in noninflammatory lesions, so if you have a very young patient with acne, now you can consider dapsone gel,” Dr. Graber said.
In August 2020, clascoterone cream became the first topical androgen receptor inhibitor approved for the treatment of acne in patients 12 years of age and older. It is a drug believed to address sebum and inflammation directly in the sebaceous gland and is structurally similar to dihydrotestosterone and spironolactone.
“This is a completely new drug category in acne,” she said. “Unlike all oral antiandrogen therapies, clascoterone cream can be used in both males and females with acne. It’s the first acne drug to have a new mechanism of action in almost 40 years, since isotretinoin was approved in 1982.”
In vitro, she continued, clascoterone competes with dihydrotestosterone for binding to the androgen receptor, inhibiting downstream signaling and leading to inhibited sebum production, reduced secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and inhibition of inflammatory pathways. Two phase 3 studies that led to its approval involved 1,440 patients with moderate to severe facial acne aged 9-58 years. The cream was applied twice a day for 12 weeks and treatment adherence was approximately 90%. The researchers found that clascoterone cream was significantly more effective than vehicle cream at achieving Investigator’s Global Assessment scores of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear), the definition of treatment success in the study, and reducing noninflammatory lesion and inflammatory lesion counts at week 12. “There were no safety issues noted during these studies, and clascoterone cream was well tolerated,” Dr. Graber said.
Dr. Graber disclosed that she is a consultant/adviser for Digital Diagnostics, Almirall, Hovione, Keratin Biosciences, La Roche Posay, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, Sol-Gel, Verrica, and WebMD. She is also a research investigator for Hovione, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, and she receives royalties from Wolters Kluwer Health.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Commentary by Lawrence W. Eichenfield, MD
Acne vulgaris remains an issue of tremendous importance to preteens, teens, and young adults, with approximately 85% of individuals aged 12-24 being affected. Expanding options for topical treatments may help bring effective disease control. Dr. Graber pointed out that historically, pediatricians and other primary care practitioners utilize topical retinoids less often for acne care as compared with dermatologists or guidelines recommendations (either the AAP’s or AAD’s). There are now expanded options, including over-the-counter retinoids (adapalene 0.1% gel), generic and trade brand topical tretinoin products, prescription adapalene medications, older and recently approved tazarotene products, and a newer type of topical retinoid, trifarotene. Novel formulations and emulsion technology, as well as retinoid developed in combination products, give more options in patients down to 9 years of age. A novel topical anti-androgen, clascoterone, is in its own category, as the first topical “hormonal agent,” allowing hormonal therapy to be used for males as well as females (aged 12 years and up). A recent review in JAMA (2021 Nov 23;326[20]:2055-67) incorporates many of these newer medications into management suggestions, emphasizing that first-line therapies are topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, or combinations of topicals, whereas in more severe disease, oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or minocycline, hormonal therapies such as combination oral conceptive agents or spironolactone, or isotretinoin are most effective.
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children's Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. He disclosed that he has served as an investigator and/or consultant to AbbVie, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Verrica.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 6/18/22.
yet they are likely underused in today’s clinical practice.
A study of prescribing practices from 2012 to 2014 indicated that dermatologists prescribed retinoids for just 58.8% of acne cases, while nondermatologists prescribed them for only 32.4% of cases. “If the guidelines are telling us that we should use topical retinoids for almost all of our acne patients, why are we using them for half of the patients?” Emmy Graber, MD, MBA, asked during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “We have a lot of options today for topical retinoids,” she added, noting that, in the past few years, trifarotene cream 0.005% and new formulations of tazarotene lotion (0.045%) and tretinoin lotion (0.05%) have become available.
According to Dr. Graber, president of The Dermatology Institute of Boston, tazarotene has been considered the most efficacious topical retinoid but is generally the least well tolerated, while adapalene has often been considered to be one of the better-tolerated topical retinoids. “This is a broad generalization,” she said. “One should also take into account the concentration and formulation of the retinoid. Cutaneous adverse events increase in severity as the concentration increases regardless of the vehicle.” There are no studies comparing trifarotene with other topical retinoids, she added.
In two phase 2, double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies (PERFECT 1 and PERFECT 2), researchers randomized more than 2,400 patients with moderate facial or truncal acne to receive trifarotene cream or a vehicle for 12 weeks. The mean percent change from baseline in facial inflammatory lesions in the trifarotene-treated group was –54.4% and –66.2% in PERFECT 1, and PERFECT 2, respectively, while the mean percent change from baseline in facial noninflammatory lesions was –49.7% and –57.7%, respectively.
In addition, the mean percent change from baseline in truncal inflammatory lesions in the trifarotene-treated groups was –57.4% and –65.4%, respectively, while the mean percent change from baseline in truncal noninflammatory lesions was –49.1% and –55.2%, respectively.
The choice of vehicle may affect absorption of topical retinoids, and some formulations may increase skin hydration and decrease transepidermal water loss, “which is a good thing,” Dr. Graber said. “Also, vehicles aim to slow drug delivery over time while also making sure that the drug penetrates into the pilosebaceous unit.”
One recent advance is the honeycomb-like polymeric emulsion technology found in tretinoin 0.05% lotion and tazarotene 0.045% lotion. These formulations contain droplets of the tretinoin and tazarotene embedded in a honeycomb matrix with hydrating agents. “I think this is exciting and could enhance our patient compliance and tolerability,” she said. Another unique feature about these two products, especially the tretinoin product, is the very small particle size with this new formulation. “It’s small enough that it can penetrate down into the pilosebaceous unit,” which is different than with older formulations, in which the tretinoin “largely just sat on the surface of the skin and didn’t penetrate into the pilosebaceous unit.” In addition, she said, “there’s only 9% degradation of the tretinoin in UV light, compared to 72% degradation of standard tretinoin 0.025% gel, and with the new tretinoin formulation, there’s no degradation when used with benzoyl peroxide.”
Another new topical retinoid to consider is a fixed-dose combination of encapsulated benzoyl peroxide 3% and encapsulated tretinoin 0.1% cream (Twyneo), which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in July 2021 for the treatment of acne in adults and children aged 9 years and older. “Typically, benzoyl peroxide and tretinoin cannot be mixed in the same tube to stability issues,” she said. “Here, each product is individually encapsulated in a silica shell so that they can be applied together.”
The approval was supported by positive results from two phase 3, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, multicenter studies (NCT03761784 and NCT03761810), in which Twyneo demonstrated efficacy and a favorable tolerability profile in patients aged 9 years and older with facial acne.
Another topical treatment option, dapsone, is now FDA approved for ages 9 and up, expanded from its initial indication for ages 12 and up. The new indication is based on a phase 4, multicenter, open-label study in which acne patients aged 9-11 years applied dapsone 7.5% gel once daily to the face and acne-affected areas on the upper chest, upper back, and shoulders for 12 weeks. After 12 weeks, facial acne was clear or almost clear in about 47% of patients. “Inflammatory, noninflammatory, and total lesions decreased from baseline, but there was a greater reduction in noninflammatory lesions, so if you have a very young patient with acne, now you can consider dapsone gel,” Dr. Graber said.
In August 2020, clascoterone cream became the first topical androgen receptor inhibitor approved for the treatment of acne in patients 12 years of age and older. It is a drug believed to address sebum and inflammation directly in the sebaceous gland and is structurally similar to dihydrotestosterone and spironolactone.
“This is a completely new drug category in acne,” she said. “Unlike all oral antiandrogen therapies, clascoterone cream can be used in both males and females with acne. It’s the first acne drug to have a new mechanism of action in almost 40 years, since isotretinoin was approved in 1982.”
In vitro, she continued, clascoterone competes with dihydrotestosterone for binding to the androgen receptor, inhibiting downstream signaling and leading to inhibited sebum production, reduced secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and inhibition of inflammatory pathways. Two phase 3 studies that led to its approval involved 1,440 patients with moderate to severe facial acne aged 9-58 years. The cream was applied twice a day for 12 weeks and treatment adherence was approximately 90%. The researchers found that clascoterone cream was significantly more effective than vehicle cream at achieving Investigator’s Global Assessment scores of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear), the definition of treatment success in the study, and reducing noninflammatory lesion and inflammatory lesion counts at week 12. “There were no safety issues noted during these studies, and clascoterone cream was well tolerated,” Dr. Graber said.
Dr. Graber disclosed that she is a consultant/adviser for Digital Diagnostics, Almirall, Hovione, Keratin Biosciences, La Roche Posay, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, Sol-Gel, Verrica, and WebMD. She is also a research investigator for Hovione, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, and she receives royalties from Wolters Kluwer Health.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Commentary by Lawrence W. Eichenfield, MD
Acne vulgaris remains an issue of tremendous importance to preteens, teens, and young adults, with approximately 85% of individuals aged 12-24 being affected. Expanding options for topical treatments may help bring effective disease control. Dr. Graber pointed out that historically, pediatricians and other primary care practitioners utilize topical retinoids less often for acne care as compared with dermatologists or guidelines recommendations (either the AAP’s or AAD’s). There are now expanded options, including over-the-counter retinoids (adapalene 0.1% gel), generic and trade brand topical tretinoin products, prescription adapalene medications, older and recently approved tazarotene products, and a newer type of topical retinoid, trifarotene. Novel formulations and emulsion technology, as well as retinoid developed in combination products, give more options in patients down to 9 years of age. A novel topical anti-androgen, clascoterone, is in its own category, as the first topical “hormonal agent,” allowing hormonal therapy to be used for males as well as females (aged 12 years and up). A recent review in JAMA (2021 Nov 23;326[20]:2055-67) incorporates many of these newer medications into management suggestions, emphasizing that first-line therapies are topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, or combinations of topicals, whereas in more severe disease, oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or minocycline, hormonal therapies such as combination oral conceptive agents or spironolactone, or isotretinoin are most effective.
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children's Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. He disclosed that he has served as an investigator and/or consultant to AbbVie, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Verrica.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 6/18/22.
yet they are likely underused in today’s clinical practice.
A study of prescribing practices from 2012 to 2014 indicated that dermatologists prescribed retinoids for just 58.8% of acne cases, while nondermatologists prescribed them for only 32.4% of cases. “If the guidelines are telling us that we should use topical retinoids for almost all of our acne patients, why are we using them for half of the patients?” Emmy Graber, MD, MBA, asked during MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “We have a lot of options today for topical retinoids,” she added, noting that, in the past few years, trifarotene cream 0.005% and new formulations of tazarotene lotion (0.045%) and tretinoin lotion (0.05%) have become available.
According to Dr. Graber, president of The Dermatology Institute of Boston, tazarotene has been considered the most efficacious topical retinoid but is generally the least well tolerated, while adapalene has often been considered to be one of the better-tolerated topical retinoids. “This is a broad generalization,” she said. “One should also take into account the concentration and formulation of the retinoid. Cutaneous adverse events increase in severity as the concentration increases regardless of the vehicle.” There are no studies comparing trifarotene with other topical retinoids, she added.
In two phase 2, double-blind, vehicle-controlled studies (PERFECT 1 and PERFECT 2), researchers randomized more than 2,400 patients with moderate facial or truncal acne to receive trifarotene cream or a vehicle for 12 weeks. The mean percent change from baseline in facial inflammatory lesions in the trifarotene-treated group was –54.4% and –66.2% in PERFECT 1, and PERFECT 2, respectively, while the mean percent change from baseline in facial noninflammatory lesions was –49.7% and –57.7%, respectively.
In addition, the mean percent change from baseline in truncal inflammatory lesions in the trifarotene-treated groups was –57.4% and –65.4%, respectively, while the mean percent change from baseline in truncal noninflammatory lesions was –49.1% and –55.2%, respectively.
The choice of vehicle may affect absorption of topical retinoids, and some formulations may increase skin hydration and decrease transepidermal water loss, “which is a good thing,” Dr. Graber said. “Also, vehicles aim to slow drug delivery over time while also making sure that the drug penetrates into the pilosebaceous unit.”
One recent advance is the honeycomb-like polymeric emulsion technology found in tretinoin 0.05% lotion and tazarotene 0.045% lotion. These formulations contain droplets of the tretinoin and tazarotene embedded in a honeycomb matrix with hydrating agents. “I think this is exciting and could enhance our patient compliance and tolerability,” she said. Another unique feature about these two products, especially the tretinoin product, is the very small particle size with this new formulation. “It’s small enough that it can penetrate down into the pilosebaceous unit,” which is different than with older formulations, in which the tretinoin “largely just sat on the surface of the skin and didn’t penetrate into the pilosebaceous unit.” In addition, she said, “there’s only 9% degradation of the tretinoin in UV light, compared to 72% degradation of standard tretinoin 0.025% gel, and with the new tretinoin formulation, there’s no degradation when used with benzoyl peroxide.”
Another new topical retinoid to consider is a fixed-dose combination of encapsulated benzoyl peroxide 3% and encapsulated tretinoin 0.1% cream (Twyneo), which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in July 2021 for the treatment of acne in adults and children aged 9 years and older. “Typically, benzoyl peroxide and tretinoin cannot be mixed in the same tube to stability issues,” she said. “Here, each product is individually encapsulated in a silica shell so that they can be applied together.”
The approval was supported by positive results from two phase 3, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, multicenter studies (NCT03761784 and NCT03761810), in which Twyneo demonstrated efficacy and a favorable tolerability profile in patients aged 9 years and older with facial acne.
Another topical treatment option, dapsone, is now FDA approved for ages 9 and up, expanded from its initial indication for ages 12 and up. The new indication is based on a phase 4, multicenter, open-label study in which acne patients aged 9-11 years applied dapsone 7.5% gel once daily to the face and acne-affected areas on the upper chest, upper back, and shoulders for 12 weeks. After 12 weeks, facial acne was clear or almost clear in about 47% of patients. “Inflammatory, noninflammatory, and total lesions decreased from baseline, but there was a greater reduction in noninflammatory lesions, so if you have a very young patient with acne, now you can consider dapsone gel,” Dr. Graber said.
In August 2020, clascoterone cream became the first topical androgen receptor inhibitor approved for the treatment of acne in patients 12 years of age and older. It is a drug believed to address sebum and inflammation directly in the sebaceous gland and is structurally similar to dihydrotestosterone and spironolactone.
“This is a completely new drug category in acne,” she said. “Unlike all oral antiandrogen therapies, clascoterone cream can be used in both males and females with acne. It’s the first acne drug to have a new mechanism of action in almost 40 years, since isotretinoin was approved in 1982.”
In vitro, she continued, clascoterone competes with dihydrotestosterone for binding to the androgen receptor, inhibiting downstream signaling and leading to inhibited sebum production, reduced secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and inhibition of inflammatory pathways. Two phase 3 studies that led to its approval involved 1,440 patients with moderate to severe facial acne aged 9-58 years. The cream was applied twice a day for 12 weeks and treatment adherence was approximately 90%. The researchers found that clascoterone cream was significantly more effective than vehicle cream at achieving Investigator’s Global Assessment scores of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear), the definition of treatment success in the study, and reducing noninflammatory lesion and inflammatory lesion counts at week 12. “There were no safety issues noted during these studies, and clascoterone cream was well tolerated,” Dr. Graber said.
Dr. Graber disclosed that she is a consultant/adviser for Digital Diagnostics, Almirall, Hovione, Keratin Biosciences, La Roche Posay, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, Sol-Gel, Verrica, and WebMD. She is also a research investigator for Hovione, Ortho Dermatologics, Sebacia, and she receives royalties from Wolters Kluwer Health.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Commentary by Lawrence W. Eichenfield, MD
Acne vulgaris remains an issue of tremendous importance to preteens, teens, and young adults, with approximately 85% of individuals aged 12-24 being affected. Expanding options for topical treatments may help bring effective disease control. Dr. Graber pointed out that historically, pediatricians and other primary care practitioners utilize topical retinoids less often for acne care as compared with dermatologists or guidelines recommendations (either the AAP’s or AAD’s). There are now expanded options, including over-the-counter retinoids (adapalene 0.1% gel), generic and trade brand topical tretinoin products, prescription adapalene medications, older and recently approved tazarotene products, and a newer type of topical retinoid, trifarotene. Novel formulations and emulsion technology, as well as retinoid developed in combination products, give more options in patients down to 9 years of age. A novel topical anti-androgen, clascoterone, is in its own category, as the first topical “hormonal agent,” allowing hormonal therapy to be used for males as well as females (aged 12 years and up). A recent review in JAMA (2021 Nov 23;326[20]:2055-67) incorporates many of these newer medications into management suggestions, emphasizing that first-line therapies are topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, or combinations of topicals, whereas in more severe disease, oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or minocycline, hormonal therapies such as combination oral conceptive agents or spironolactone, or isotretinoin are most effective.
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children's Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. He disclosed that he has served as an investigator and/or consultant to AbbVie, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Verrica.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 6/18/22.
FROM THE MEDSCAPELIVE LAS VEGAS DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Cannabinoids being studied for a variety of dermatologic conditions
.
“When you walk into places like CVS or Walgreens, you see lots of displays for CBD creams and oils,” Todd S. Anhalt, MD, said during the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. “The problem is, we don’t know what’s in them or who made them or how good they are. That’s going to be a problem for a while.”
According to Dr. Anhalt, clinical professor emeritus of dermatology at Stanford (Calif.) University, there are about 140 active cannabinoid compounds in cannabis, but the most important ones are THC and cannabidiol (CBD). There are three types of cannabinoids, based on where the cannabidiol is produced: endocannabinoids, which are produced in the human body; phytocannabinoids, which are derived from plants such as marijuana and hemp; and synthetic cannabinoids, which are derived in labs.
Dr. Anhalt described the endocannabinoid system as a conserved network of molecular signaling made of several components: signaling molecules (endocannabinoids), endocannabinoid receptors (CB-1 and CB-2), enzymes, and transporters. There is also overlap between cannabinoids and terpenes, which are responsible for flavor and aroma in plants and marijuana and can enhance the effects of CBD.
“For the most part, CB-1 receptors are in the central nervous system and CB-2 [receptors] are mostly in the periphery,” including the skin and digestive system, said Dr. Anhalt, who practices at the California Skin Institute in Los Altos, Calif. “This is interesting because one of the main conditions I recommend cannabidiol for is in patients with peripheral neuropathy, despite the fact they may be on all sorts of medications such as Neurontin and Lyrica or tricyclic antidepressants. Sometimes they don’t get much relief from those. I have had many patients tell me that they have had reduction of pain and increased functionality using the CBD creams.” CB-2 receptors, he noted, are located in keratinocytes, sensory receptors, sweat glands, fibroblasts, Langerhans cells, melanocytes, and sebaceous glands.
Recent research shows that the endocannabinoid system is involved in modulation of the CNS and in immune function, particularly skin homeostasis and barrier function. “We know that barrier function can be affected by the generation of oxidative species,” he said. “The stress that it causes can decrease barrier function and lead to cytokine release and itch. CBDs have been shown to enter cells, target and upregulate genes with decreased oxidation and inflammation, and protect membrane integrity in skin cells. Therefore, this might be helpful in atopic dermatitis.” Other potential uses in dermatology include wound healing, acne, hair growth modulation, skin and hair pigmentation, skin infections, psoriasis, and cutaneous malignancies, as well as neuropathic pain.
Evidence is strongest for neuropathic pain, he said, which is mediated by CB-1 receptors peripherally, followed by itch and atopic dermatitis. The authors of a 2017 systematic review concluded that “low-strength” evidence exists to suggest that cannabis alleviates neuropathic pain, with insufficient evidence for other types of pain.
Topical CBD comes in various forms: oils (usually hemp oil), creams, and lotions, Dr. Anhalt said. “I advise patients to apply it 2-4 times per day depending on how anxious or uncomfortable they are. It takes my patients 10 days to 2 weeks before they notice anything at all.”
For atopic dermatitis, it could be useful “not to use it instead of a moisturizer, but as a moisturizer,” Dr. Anhalt advised. “You can have a patient get big jars of CBD creams and lotions. They may have to try a few before they find one that they really like, but you can replace all of the other moisturizers that you’re using right now in patients who have a lot of itch.”
As for CBD’s effect on peripheral neuropathy, the medical literature is lacking, but some studies show low to moderate evidence of efficacy. For example, a Cochrane Review found that a 30% or greater pain reduction was achieved by 39% of patients who used cannabis-based treatments, vs. 33% of those on placebo.
“I would not suggest CBD as a first-line drug unless it’s very mild peripheral neuropathy, but for patients who are on gabapentin who are better but not better enough, this is an excellent adjunct,” Dr. Anhalt said. “It’s worth trying. It’s not too expensive and it’s really safe.”
The application of topical CBD to treat cutaneous malignancies has not yet shown evidence of significant efficacy, while using CBDs for acne holds promise. “The endogenous cannabinoid system is involved in the production of lipids,” he said. “Cannabinoids have an antilipogenic activity, so they decrease sebum production. CBD could help patients with mild acne who are reluctant to use other types of medications. For this and other potential dermatologic applications, lots more studies need to be done.”
Dr. Anhalt reported having no financial disclosures.
.
“When you walk into places like CVS or Walgreens, you see lots of displays for CBD creams and oils,” Todd S. Anhalt, MD, said during the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. “The problem is, we don’t know what’s in them or who made them or how good they are. That’s going to be a problem for a while.”
According to Dr. Anhalt, clinical professor emeritus of dermatology at Stanford (Calif.) University, there are about 140 active cannabinoid compounds in cannabis, but the most important ones are THC and cannabidiol (CBD). There are three types of cannabinoids, based on where the cannabidiol is produced: endocannabinoids, which are produced in the human body; phytocannabinoids, which are derived from plants such as marijuana and hemp; and synthetic cannabinoids, which are derived in labs.
Dr. Anhalt described the endocannabinoid system as a conserved network of molecular signaling made of several components: signaling molecules (endocannabinoids), endocannabinoid receptors (CB-1 and CB-2), enzymes, and transporters. There is also overlap between cannabinoids and terpenes, which are responsible for flavor and aroma in plants and marijuana and can enhance the effects of CBD.
“For the most part, CB-1 receptors are in the central nervous system and CB-2 [receptors] are mostly in the periphery,” including the skin and digestive system, said Dr. Anhalt, who practices at the California Skin Institute in Los Altos, Calif. “This is interesting because one of the main conditions I recommend cannabidiol for is in patients with peripheral neuropathy, despite the fact they may be on all sorts of medications such as Neurontin and Lyrica or tricyclic antidepressants. Sometimes they don’t get much relief from those. I have had many patients tell me that they have had reduction of pain and increased functionality using the CBD creams.” CB-2 receptors, he noted, are located in keratinocytes, sensory receptors, sweat glands, fibroblasts, Langerhans cells, melanocytes, and sebaceous glands.
Recent research shows that the endocannabinoid system is involved in modulation of the CNS and in immune function, particularly skin homeostasis and barrier function. “We know that barrier function can be affected by the generation of oxidative species,” he said. “The stress that it causes can decrease barrier function and lead to cytokine release and itch. CBDs have been shown to enter cells, target and upregulate genes with decreased oxidation and inflammation, and protect membrane integrity in skin cells. Therefore, this might be helpful in atopic dermatitis.” Other potential uses in dermatology include wound healing, acne, hair growth modulation, skin and hair pigmentation, skin infections, psoriasis, and cutaneous malignancies, as well as neuropathic pain.
Evidence is strongest for neuropathic pain, he said, which is mediated by CB-1 receptors peripherally, followed by itch and atopic dermatitis. The authors of a 2017 systematic review concluded that “low-strength” evidence exists to suggest that cannabis alleviates neuropathic pain, with insufficient evidence for other types of pain.
Topical CBD comes in various forms: oils (usually hemp oil), creams, and lotions, Dr. Anhalt said. “I advise patients to apply it 2-4 times per day depending on how anxious or uncomfortable they are. It takes my patients 10 days to 2 weeks before they notice anything at all.”
For atopic dermatitis, it could be useful “not to use it instead of a moisturizer, but as a moisturizer,” Dr. Anhalt advised. “You can have a patient get big jars of CBD creams and lotions. They may have to try a few before they find one that they really like, but you can replace all of the other moisturizers that you’re using right now in patients who have a lot of itch.”
As for CBD’s effect on peripheral neuropathy, the medical literature is lacking, but some studies show low to moderate evidence of efficacy. For example, a Cochrane Review found that a 30% or greater pain reduction was achieved by 39% of patients who used cannabis-based treatments, vs. 33% of those on placebo.
“I would not suggest CBD as a first-line drug unless it’s very mild peripheral neuropathy, but for patients who are on gabapentin who are better but not better enough, this is an excellent adjunct,” Dr. Anhalt said. “It’s worth trying. It’s not too expensive and it’s really safe.”
The application of topical CBD to treat cutaneous malignancies has not yet shown evidence of significant efficacy, while using CBDs for acne holds promise. “The endogenous cannabinoid system is involved in the production of lipids,” he said. “Cannabinoids have an antilipogenic activity, so they decrease sebum production. CBD could help patients with mild acne who are reluctant to use other types of medications. For this and other potential dermatologic applications, lots more studies need to be done.”
Dr. Anhalt reported having no financial disclosures.
.
“When you walk into places like CVS or Walgreens, you see lots of displays for CBD creams and oils,” Todd S. Anhalt, MD, said during the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. “The problem is, we don’t know what’s in them or who made them or how good they are. That’s going to be a problem for a while.”
According to Dr. Anhalt, clinical professor emeritus of dermatology at Stanford (Calif.) University, there are about 140 active cannabinoid compounds in cannabis, but the most important ones are THC and cannabidiol (CBD). There are three types of cannabinoids, based on where the cannabidiol is produced: endocannabinoids, which are produced in the human body; phytocannabinoids, which are derived from plants such as marijuana and hemp; and synthetic cannabinoids, which are derived in labs.
Dr. Anhalt described the endocannabinoid system as a conserved network of molecular signaling made of several components: signaling molecules (endocannabinoids), endocannabinoid receptors (CB-1 and CB-2), enzymes, and transporters. There is also overlap between cannabinoids and terpenes, which are responsible for flavor and aroma in plants and marijuana and can enhance the effects of CBD.
“For the most part, CB-1 receptors are in the central nervous system and CB-2 [receptors] are mostly in the periphery,” including the skin and digestive system, said Dr. Anhalt, who practices at the California Skin Institute in Los Altos, Calif. “This is interesting because one of the main conditions I recommend cannabidiol for is in patients with peripheral neuropathy, despite the fact they may be on all sorts of medications such as Neurontin and Lyrica or tricyclic antidepressants. Sometimes they don’t get much relief from those. I have had many patients tell me that they have had reduction of pain and increased functionality using the CBD creams.” CB-2 receptors, he noted, are located in keratinocytes, sensory receptors, sweat glands, fibroblasts, Langerhans cells, melanocytes, and sebaceous glands.
Recent research shows that the endocannabinoid system is involved in modulation of the CNS and in immune function, particularly skin homeostasis and barrier function. “We know that barrier function can be affected by the generation of oxidative species,” he said. “The stress that it causes can decrease barrier function and lead to cytokine release and itch. CBDs have been shown to enter cells, target and upregulate genes with decreased oxidation and inflammation, and protect membrane integrity in skin cells. Therefore, this might be helpful in atopic dermatitis.” Other potential uses in dermatology include wound healing, acne, hair growth modulation, skin and hair pigmentation, skin infections, psoriasis, and cutaneous malignancies, as well as neuropathic pain.
Evidence is strongest for neuropathic pain, he said, which is mediated by CB-1 receptors peripherally, followed by itch and atopic dermatitis. The authors of a 2017 systematic review concluded that “low-strength” evidence exists to suggest that cannabis alleviates neuropathic pain, with insufficient evidence for other types of pain.
Topical CBD comes in various forms: oils (usually hemp oil), creams, and lotions, Dr. Anhalt said. “I advise patients to apply it 2-4 times per day depending on how anxious or uncomfortable they are. It takes my patients 10 days to 2 weeks before they notice anything at all.”
For atopic dermatitis, it could be useful “not to use it instead of a moisturizer, but as a moisturizer,” Dr. Anhalt advised. “You can have a patient get big jars of CBD creams and lotions. They may have to try a few before they find one that they really like, but you can replace all of the other moisturizers that you’re using right now in patients who have a lot of itch.”
As for CBD’s effect on peripheral neuropathy, the medical literature is lacking, but some studies show low to moderate evidence of efficacy. For example, a Cochrane Review found that a 30% or greater pain reduction was achieved by 39% of patients who used cannabis-based treatments, vs. 33% of those on placebo.
“I would not suggest CBD as a first-line drug unless it’s very mild peripheral neuropathy, but for patients who are on gabapentin who are better but not better enough, this is an excellent adjunct,” Dr. Anhalt said. “It’s worth trying. It’s not too expensive and it’s really safe.”
The application of topical CBD to treat cutaneous malignancies has not yet shown evidence of significant efficacy, while using CBDs for acne holds promise. “The endogenous cannabinoid system is involved in the production of lipids,” he said. “Cannabinoids have an antilipogenic activity, so they decrease sebum production. CBD could help patients with mild acne who are reluctant to use other types of medications. For this and other potential dermatologic applications, lots more studies need to be done.”
Dr. Anhalt reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM PDA 2021
What are the legal risks of practicing laser cutaneous surgery?
The physician-patient relationship is a key factor in preventing litigation following cutaneous laser surgery, according to Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD.
“Numerous studies indicate that good communication and rapport are the most important means to avoid a lawsuit,” Dr. Avram, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “It is helpful to say that the outcome was not optimal or what you were anticipating. Communicate your plan [for the complication] clearly and honestly to your patient. The patient may not understand the severity of the complication. If they don’t, they will either leave it alone or they will go elsewhere and may receive poor care.” He added that in New England, “we have some stoic patients who may say ‘I don’t want to bother the doctor’ or ‘It’s my fault for having the procedure done.’ ”
Establishing effective communication with patients from the outset is good practice, he continued, because 75% of physicians in low-risk specialties will face a malpractice claim by age 65. Nearly a decade ago Dr. Avram, H. Ray Jalian, MD, and Chris Jalian, JD, published results from a national legal database analysis identifying common errors and risk factors for litigation in cutaneous surgery. Their search yielded 1,807 documents with 174 unique legal claims involving injury from a cutaneous laser treatment, from 1985 to 2012. The most common litigated procedures were laser hair removal, rejuvenation (mostly related to intense pulsed-light treatments), and laser treatment of leg veins, while the most common injuries sustained were burns, scars, and pigmentary changes. The most common causes of legal action were lack of informed consent and fraud.
Among the 120 cases with public decisions, cases favored the plaintiff 51% of the time. “That’s unusual,” said Dr. Avram, president of American Society for Dermatologic Surgery. “Usually, physicians do better, but I think the fact that they’re cosmetic cases probably shades things a little bit.” The median monetary award was $350,000 and ranged from $5,000 to $2,145,000. The two largest judgments were for improper use of topical anesthesia that led to deaths of patients in laser hair removal cases.
In a separate analysis, the same authors searched an online national database to identify the incidence of medical professional liability claims resulting from cutaneous laser surgery performed by nonphysician operators (NPOs) from 1999 to 2012. Among the 175 cases identified, 43% involved an NPO. “In fact, the cases involving NPOs exploded over a 4-year period; they grew from 36% in 2008 of cases to 78% in 2011,” Dr. Avram said. “This was even more true for laser hair removal.”
The practice setting turned out to be a factor. Only 23% of NPO litigation involving laser procedures arose in medical office settings, while 77% of cases involving NPOs were performed outside of traditional medical settings such as in salons and medical spas – mostly for laser hair removal. “We updated this information by examining the setting for nonphysician operator litigation between 2012 and 2017 and found that 66% of cases involving NPOs were performed outside of a traditional medical setting, while 34% of NPO litigation arose in medical office settings,” Dr. Avram said during the meeting, which was named What’s the Truth? and sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s close to a 2 to 1 ratio.”
In an analysis of medical professional liability claims involving Mohs surgery from 1989 to 2011, 26 of the 42 cases identified involved a primary defendant who was not a Mohs surgeon. In the 26 cases, the most common reasons for lawsuits were failure or delay of diagnosis of a skin cancer, cosmetic outcome issues, lack of informed consent, and delay or failure to refer to a Mohs surgeon. Of the cases that involved Mohs surgeons, the most common causes were lack of proper informed consent and cosmetic outcome issues, but “these cases were overwhelmingly decided in favor of the surgeons,” said Dr. Avram, one of the study authors.
On a related note, Dr. Avram underscored the importance of biopsy-site photography, “because patients and physicians misidentify biopsy sites too commonly,” he said. In a single-center study of 34 biopsy sites of cutaneous head and neck malignancies, patients misidentified the biopsy site 4-7 weeks out in 29% of the cases. Blinded dermatologists and the patient misidentified the biopsy site in 12% of the cases. “Good biopsy site photography should be mandatory in your practice,” he advised.
Clinicians can avoid cutaneous laser surgery complications only by not treating patients. “Complications and side effects are inevitable; you need to know your limits,” he said. “Even in skilled hands, if you treat enough patients, you will encounter challenging side effects. Do not perform a procedure that might produce a side effect that you cannot recognize and treat.”
The best way to avoid complications is to trust your eyes – not the laser – since the same device made by the same manufacturer may produce highly different outputs at the same setting (see J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74[5]:807-19).
“Moreover, lasers can produce much different energies after they have been serviced,” Dr. Avram said. “Do not memorize settings. Do not blindly replicate recommended settings from a colleague or a device manufacturer,” he advised. “Some devices are not externally calibrated. Therefore, the settings on one device may not translate the same way to yours. Often, device manufacturers underplay the settings. Safe and unsafe laser endpoints and close observation are the best means to avoiding clinical complications. That means you follow clinical endpoints, not fluences. The key clinical finding is the endpoint, not the energy setting.”
Temporary and expected side effects include erythema, edema, and purpura. “With these it’s just handholding and unlikely to lead to any legal consequences,” he continued. “With temporary hyperpigmentation that can occur with laser hair removal, time is one your side, because typically this will resolve before any litigation progresses. Permanent side effects from lasers and light sources and injectables are a different issue, things like permanent hypopigmentation, depigmentation, and scarring. These are most likely to produce liability.”
In Dr. Avram’s opinion, complications are best handled with widespread communication. “There is a temptation to avoid a patient with a poor outcome or side effect,” he said. “This is bad medicine and rightfully angers your patient and increases the risk of a lawsuit. [Resist] the temptation to avoid showing a poor outcome to a colleague. Many complications can be significantly improved or cleared with timely and appropriate interventions. You should always document your efforts.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan and Galderma. He is a member of the scientific advisory board for Allergan and Soliton, is an investigator for Endo, and holds stock options in La Jolla NanoMedical Inc.
The physician-patient relationship is a key factor in preventing litigation following cutaneous laser surgery, according to Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD.
“Numerous studies indicate that good communication and rapport are the most important means to avoid a lawsuit,” Dr. Avram, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “It is helpful to say that the outcome was not optimal or what you were anticipating. Communicate your plan [for the complication] clearly and honestly to your patient. The patient may not understand the severity of the complication. If they don’t, they will either leave it alone or they will go elsewhere and may receive poor care.” He added that in New England, “we have some stoic patients who may say ‘I don’t want to bother the doctor’ or ‘It’s my fault for having the procedure done.’ ”
Establishing effective communication with patients from the outset is good practice, he continued, because 75% of physicians in low-risk specialties will face a malpractice claim by age 65. Nearly a decade ago Dr. Avram, H. Ray Jalian, MD, and Chris Jalian, JD, published results from a national legal database analysis identifying common errors and risk factors for litigation in cutaneous surgery. Their search yielded 1,807 documents with 174 unique legal claims involving injury from a cutaneous laser treatment, from 1985 to 2012. The most common litigated procedures were laser hair removal, rejuvenation (mostly related to intense pulsed-light treatments), and laser treatment of leg veins, while the most common injuries sustained were burns, scars, and pigmentary changes. The most common causes of legal action were lack of informed consent and fraud.
Among the 120 cases with public decisions, cases favored the plaintiff 51% of the time. “That’s unusual,” said Dr. Avram, president of American Society for Dermatologic Surgery. “Usually, physicians do better, but I think the fact that they’re cosmetic cases probably shades things a little bit.” The median monetary award was $350,000 and ranged from $5,000 to $2,145,000. The two largest judgments were for improper use of topical anesthesia that led to deaths of patients in laser hair removal cases.
In a separate analysis, the same authors searched an online national database to identify the incidence of medical professional liability claims resulting from cutaneous laser surgery performed by nonphysician operators (NPOs) from 1999 to 2012. Among the 175 cases identified, 43% involved an NPO. “In fact, the cases involving NPOs exploded over a 4-year period; they grew from 36% in 2008 of cases to 78% in 2011,” Dr. Avram said. “This was even more true for laser hair removal.”
The practice setting turned out to be a factor. Only 23% of NPO litigation involving laser procedures arose in medical office settings, while 77% of cases involving NPOs were performed outside of traditional medical settings such as in salons and medical spas – mostly for laser hair removal. “We updated this information by examining the setting for nonphysician operator litigation between 2012 and 2017 and found that 66% of cases involving NPOs were performed outside of a traditional medical setting, while 34% of NPO litigation arose in medical office settings,” Dr. Avram said during the meeting, which was named What’s the Truth? and sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s close to a 2 to 1 ratio.”
In an analysis of medical professional liability claims involving Mohs surgery from 1989 to 2011, 26 of the 42 cases identified involved a primary defendant who was not a Mohs surgeon. In the 26 cases, the most common reasons for lawsuits were failure or delay of diagnosis of a skin cancer, cosmetic outcome issues, lack of informed consent, and delay or failure to refer to a Mohs surgeon. Of the cases that involved Mohs surgeons, the most common causes were lack of proper informed consent and cosmetic outcome issues, but “these cases were overwhelmingly decided in favor of the surgeons,” said Dr. Avram, one of the study authors.
On a related note, Dr. Avram underscored the importance of biopsy-site photography, “because patients and physicians misidentify biopsy sites too commonly,” he said. In a single-center study of 34 biopsy sites of cutaneous head and neck malignancies, patients misidentified the biopsy site 4-7 weeks out in 29% of the cases. Blinded dermatologists and the patient misidentified the biopsy site in 12% of the cases. “Good biopsy site photography should be mandatory in your practice,” he advised.
Clinicians can avoid cutaneous laser surgery complications only by not treating patients. “Complications and side effects are inevitable; you need to know your limits,” he said. “Even in skilled hands, if you treat enough patients, you will encounter challenging side effects. Do not perform a procedure that might produce a side effect that you cannot recognize and treat.”
The best way to avoid complications is to trust your eyes – not the laser – since the same device made by the same manufacturer may produce highly different outputs at the same setting (see J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74[5]:807-19).
“Moreover, lasers can produce much different energies after they have been serviced,” Dr. Avram said. “Do not memorize settings. Do not blindly replicate recommended settings from a colleague or a device manufacturer,” he advised. “Some devices are not externally calibrated. Therefore, the settings on one device may not translate the same way to yours. Often, device manufacturers underplay the settings. Safe and unsafe laser endpoints and close observation are the best means to avoiding clinical complications. That means you follow clinical endpoints, not fluences. The key clinical finding is the endpoint, not the energy setting.”
Temporary and expected side effects include erythema, edema, and purpura. “With these it’s just handholding and unlikely to lead to any legal consequences,” he continued. “With temporary hyperpigmentation that can occur with laser hair removal, time is one your side, because typically this will resolve before any litigation progresses. Permanent side effects from lasers and light sources and injectables are a different issue, things like permanent hypopigmentation, depigmentation, and scarring. These are most likely to produce liability.”
In Dr. Avram’s opinion, complications are best handled with widespread communication. “There is a temptation to avoid a patient with a poor outcome or side effect,” he said. “This is bad medicine and rightfully angers your patient and increases the risk of a lawsuit. [Resist] the temptation to avoid showing a poor outcome to a colleague. Many complications can be significantly improved or cleared with timely and appropriate interventions. You should always document your efforts.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan and Galderma. He is a member of the scientific advisory board for Allergan and Soliton, is an investigator for Endo, and holds stock options in La Jolla NanoMedical Inc.
The physician-patient relationship is a key factor in preventing litigation following cutaneous laser surgery, according to Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD.
“Numerous studies indicate that good communication and rapport are the most important means to avoid a lawsuit,” Dr. Avram, director of laser, cosmetics, and dermatologic surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “It is helpful to say that the outcome was not optimal or what you were anticipating. Communicate your plan [for the complication] clearly and honestly to your patient. The patient may not understand the severity of the complication. If they don’t, they will either leave it alone or they will go elsewhere and may receive poor care.” He added that in New England, “we have some stoic patients who may say ‘I don’t want to bother the doctor’ or ‘It’s my fault for having the procedure done.’ ”
Establishing effective communication with patients from the outset is good practice, he continued, because 75% of physicians in low-risk specialties will face a malpractice claim by age 65. Nearly a decade ago Dr. Avram, H. Ray Jalian, MD, and Chris Jalian, JD, published results from a national legal database analysis identifying common errors and risk factors for litigation in cutaneous surgery. Their search yielded 1,807 documents with 174 unique legal claims involving injury from a cutaneous laser treatment, from 1985 to 2012. The most common litigated procedures were laser hair removal, rejuvenation (mostly related to intense pulsed-light treatments), and laser treatment of leg veins, while the most common injuries sustained were burns, scars, and pigmentary changes. The most common causes of legal action were lack of informed consent and fraud.
Among the 120 cases with public decisions, cases favored the plaintiff 51% of the time. “That’s unusual,” said Dr. Avram, president of American Society for Dermatologic Surgery. “Usually, physicians do better, but I think the fact that they’re cosmetic cases probably shades things a little bit.” The median monetary award was $350,000 and ranged from $5,000 to $2,145,000. The two largest judgments were for improper use of topical anesthesia that led to deaths of patients in laser hair removal cases.
In a separate analysis, the same authors searched an online national database to identify the incidence of medical professional liability claims resulting from cutaneous laser surgery performed by nonphysician operators (NPOs) from 1999 to 2012. Among the 175 cases identified, 43% involved an NPO. “In fact, the cases involving NPOs exploded over a 4-year period; they grew from 36% in 2008 of cases to 78% in 2011,” Dr. Avram said. “This was even more true for laser hair removal.”
The practice setting turned out to be a factor. Only 23% of NPO litigation involving laser procedures arose in medical office settings, while 77% of cases involving NPOs were performed outside of traditional medical settings such as in salons and medical spas – mostly for laser hair removal. “We updated this information by examining the setting for nonphysician operator litigation between 2012 and 2017 and found that 66% of cases involving NPOs were performed outside of a traditional medical setting, while 34% of NPO litigation arose in medical office settings,” Dr. Avram said during the meeting, which was named What’s the Truth? and sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s close to a 2 to 1 ratio.”
In an analysis of medical professional liability claims involving Mohs surgery from 1989 to 2011, 26 of the 42 cases identified involved a primary defendant who was not a Mohs surgeon. In the 26 cases, the most common reasons for lawsuits were failure or delay of diagnosis of a skin cancer, cosmetic outcome issues, lack of informed consent, and delay or failure to refer to a Mohs surgeon. Of the cases that involved Mohs surgeons, the most common causes were lack of proper informed consent and cosmetic outcome issues, but “these cases were overwhelmingly decided in favor of the surgeons,” said Dr. Avram, one of the study authors.
On a related note, Dr. Avram underscored the importance of biopsy-site photography, “because patients and physicians misidentify biopsy sites too commonly,” he said. In a single-center study of 34 biopsy sites of cutaneous head and neck malignancies, patients misidentified the biopsy site 4-7 weeks out in 29% of the cases. Blinded dermatologists and the patient misidentified the biopsy site in 12% of the cases. “Good biopsy site photography should be mandatory in your practice,” he advised.
Clinicians can avoid cutaneous laser surgery complications only by not treating patients. “Complications and side effects are inevitable; you need to know your limits,” he said. “Even in skilled hands, if you treat enough patients, you will encounter challenging side effects. Do not perform a procedure that might produce a side effect that you cannot recognize and treat.”
The best way to avoid complications is to trust your eyes – not the laser – since the same device made by the same manufacturer may produce highly different outputs at the same setting (see J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74[5]:807-19).
“Moreover, lasers can produce much different energies after they have been serviced,” Dr. Avram said. “Do not memorize settings. Do not blindly replicate recommended settings from a colleague or a device manufacturer,” he advised. “Some devices are not externally calibrated. Therefore, the settings on one device may not translate the same way to yours. Often, device manufacturers underplay the settings. Safe and unsafe laser endpoints and close observation are the best means to avoiding clinical complications. That means you follow clinical endpoints, not fluences. The key clinical finding is the endpoint, not the energy setting.”
Temporary and expected side effects include erythema, edema, and purpura. “With these it’s just handholding and unlikely to lead to any legal consequences,” he continued. “With temporary hyperpigmentation that can occur with laser hair removal, time is one your side, because typically this will resolve before any litigation progresses. Permanent side effects from lasers and light sources and injectables are a different issue, things like permanent hypopigmentation, depigmentation, and scarring. These are most likely to produce liability.”
In Dr. Avram’s opinion, complications are best handled with widespread communication. “There is a temptation to avoid a patient with a poor outcome or side effect,” he said. “This is bad medicine and rightfully angers your patient and increases the risk of a lawsuit. [Resist] the temptation to avoid showing a poor outcome to a colleague. Many complications can be significantly improved or cleared with timely and appropriate interventions. You should always document your efforts.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan and Galderma. He is a member of the scientific advisory board for Allergan and Soliton, is an investigator for Endo, and holds stock options in La Jolla NanoMedical Inc.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
Expert shares eye protection tips for cutaneous laser surgery
Suzanne L. Kilmer, MD, will never forget the day when the center of her vision became blurry after performing cutaneous laser surgery.
The laser light reflected off the patient’s protective eye shield and caused a photo-induced foveal injury to Dr. Kilmer’s eye even though she was wearing protective goggles. “It was like the central part of my vision was browned out,” Dr. Kilmer, director of the Laser and Skin Surgery Center of Northern California, Sacramento, recalled during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “My injury completely resolved, but you may not get so lucky. You can really get into trouble with longer pulse widths and higher-energy lasers.”
The injury occurred, she said, because the goggles she wore were sufficient for 1,064-nm wavelengths, but she was treating the patient with a 532 nm–wavelength laser. “I did not have the protection I needed,” she said. “You have to make sure to check the glasses yourself before you treat so that what happened to me doesn’t happen to you.”
Dr. Kilmer, who is also a clinical professor of dermatology at the University of California, Davis, said that during cutaneous laser surgery, “we want to pay attention all the time to minimize our risk.” She also recommended to make sure “all personnel in the room have had good safety training and have baseline eye exams. The door needs to be closed. The windows need to be covered, and you need a warning sign on the door that contains the specific wavelength, pulse width, and energy being used.”
The most important element of the sign, she added, pertains to the wavelength, because that determines the most appropriate goggles or eyewear to use “to ensure that you have an optical density high enough to protect your eyes.”
She advised using only eyewear designed for the specific laser wavelength being used, and to check the optical density prior to firing the laser. “You want the optical density to be greater than 4-6; you want as much protection as possible,” Dr. Kilmer said. “If you’re using a 1,064-nm laser and a 532-nm laser, you want glasses that protect you from both of those wavelengths. Multi- and dual-wavelength glasses are now available. The newer eyewear also allows you to see much better so there’s less risk with you taking it off the goggles [during the procedure].”
Dr. Kilmer recommends keeping a set of goggles outside of the procedure room door that matches every set of goggles being used in the room. “In one room, you may have several different lasers,” she said. “So you want some way to ‘attach’ the goggles to that particular laser, whether it’s a tray or some type of a coding system – some way to keep those together.”
For eye shield protection, the David-Baker lid clamp and the Jaeger plate are appropriate for ablative laser resurfacing, but most dermatologists use individual steel eye shields that are placed externally or internally. “Make sure you have different-sized eye shields on hand,” she advised during the meeting, which was named What’s the Truth? and sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine.
“Depending on what you’re performing, you will need anywhere from neonate size to larger adult size. Some adults may require child-size shields,” she said, noting that there are external eye shields that can be cleaned after each use. “But we tend to use LASER-Aid disposable eye shields, which have metal in the middle and stick over the eyelid. You only use these when you’re working outside of the orbital rim. If you’re treating within the orbital rim, you have to use an internal eye shield.”
She reported having no relevant financial disclosures related to her presentation.
Suzanne L. Kilmer, MD, will never forget the day when the center of her vision became blurry after performing cutaneous laser surgery.
The laser light reflected off the patient’s protective eye shield and caused a photo-induced foveal injury to Dr. Kilmer’s eye even though she was wearing protective goggles. “It was like the central part of my vision was browned out,” Dr. Kilmer, director of the Laser and Skin Surgery Center of Northern California, Sacramento, recalled during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “My injury completely resolved, but you may not get so lucky. You can really get into trouble with longer pulse widths and higher-energy lasers.”
The injury occurred, she said, because the goggles she wore were sufficient for 1,064-nm wavelengths, but she was treating the patient with a 532 nm–wavelength laser. “I did not have the protection I needed,” she said. “You have to make sure to check the glasses yourself before you treat so that what happened to me doesn’t happen to you.”
Dr. Kilmer, who is also a clinical professor of dermatology at the University of California, Davis, said that during cutaneous laser surgery, “we want to pay attention all the time to minimize our risk.” She also recommended to make sure “all personnel in the room have had good safety training and have baseline eye exams. The door needs to be closed. The windows need to be covered, and you need a warning sign on the door that contains the specific wavelength, pulse width, and energy being used.”
The most important element of the sign, she added, pertains to the wavelength, because that determines the most appropriate goggles or eyewear to use “to ensure that you have an optical density high enough to protect your eyes.”
She advised using only eyewear designed for the specific laser wavelength being used, and to check the optical density prior to firing the laser. “You want the optical density to be greater than 4-6; you want as much protection as possible,” Dr. Kilmer said. “If you’re using a 1,064-nm laser and a 532-nm laser, you want glasses that protect you from both of those wavelengths. Multi- and dual-wavelength glasses are now available. The newer eyewear also allows you to see much better so there’s less risk with you taking it off the goggles [during the procedure].”
Dr. Kilmer recommends keeping a set of goggles outside of the procedure room door that matches every set of goggles being used in the room. “In one room, you may have several different lasers,” she said. “So you want some way to ‘attach’ the goggles to that particular laser, whether it’s a tray or some type of a coding system – some way to keep those together.”
For eye shield protection, the David-Baker lid clamp and the Jaeger plate are appropriate for ablative laser resurfacing, but most dermatologists use individual steel eye shields that are placed externally or internally. “Make sure you have different-sized eye shields on hand,” she advised during the meeting, which was named What’s the Truth? and sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine.
“Depending on what you’re performing, you will need anywhere from neonate size to larger adult size. Some adults may require child-size shields,” she said, noting that there are external eye shields that can be cleaned after each use. “But we tend to use LASER-Aid disposable eye shields, which have metal in the middle and stick over the eyelid. You only use these when you’re working outside of the orbital rim. If you’re treating within the orbital rim, you have to use an internal eye shield.”
She reported having no relevant financial disclosures related to her presentation.
Suzanne L. Kilmer, MD, will never forget the day when the center of her vision became blurry after performing cutaneous laser surgery.
The laser light reflected off the patient’s protective eye shield and caused a photo-induced foveal injury to Dr. Kilmer’s eye even though she was wearing protective goggles. “It was like the central part of my vision was browned out,” Dr. Kilmer, director of the Laser and Skin Surgery Center of Northern California, Sacramento, recalled during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “My injury completely resolved, but you may not get so lucky. You can really get into trouble with longer pulse widths and higher-energy lasers.”
The injury occurred, she said, because the goggles she wore were sufficient for 1,064-nm wavelengths, but she was treating the patient with a 532 nm–wavelength laser. “I did not have the protection I needed,” she said. “You have to make sure to check the glasses yourself before you treat so that what happened to me doesn’t happen to you.”
Dr. Kilmer, who is also a clinical professor of dermatology at the University of California, Davis, said that during cutaneous laser surgery, “we want to pay attention all the time to minimize our risk.” She also recommended to make sure “all personnel in the room have had good safety training and have baseline eye exams. The door needs to be closed. The windows need to be covered, and you need a warning sign on the door that contains the specific wavelength, pulse width, and energy being used.”
The most important element of the sign, she added, pertains to the wavelength, because that determines the most appropriate goggles or eyewear to use “to ensure that you have an optical density high enough to protect your eyes.”
She advised using only eyewear designed for the specific laser wavelength being used, and to check the optical density prior to firing the laser. “You want the optical density to be greater than 4-6; you want as much protection as possible,” Dr. Kilmer said. “If you’re using a 1,064-nm laser and a 532-nm laser, you want glasses that protect you from both of those wavelengths. Multi- and dual-wavelength glasses are now available. The newer eyewear also allows you to see much better so there’s less risk with you taking it off the goggles [during the procedure].”
Dr. Kilmer recommends keeping a set of goggles outside of the procedure room door that matches every set of goggles being used in the room. “In one room, you may have several different lasers,” she said. “So you want some way to ‘attach’ the goggles to that particular laser, whether it’s a tray or some type of a coding system – some way to keep those together.”
For eye shield protection, the David-Baker lid clamp and the Jaeger plate are appropriate for ablative laser resurfacing, but most dermatologists use individual steel eye shields that are placed externally or internally. “Make sure you have different-sized eye shields on hand,” she advised during the meeting, which was named What’s the Truth? and sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine.
“Depending on what you’re performing, you will need anywhere from neonate size to larger adult size. Some adults may require child-size shields,” she said, noting that there are external eye shields that can be cleaned after each use. “But we tend to use LASER-Aid disposable eye shields, which have metal in the middle and stick over the eyelid. You only use these when you’re working outside of the orbital rim. If you’re treating within the orbital rim, you have to use an internal eye shield.”
She reported having no relevant financial disclosures related to her presentation.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
Evaluations of novel approaches to treating NF-1 tumors are underway
In the clinical experience of R. Rox Anderson, MD, currently available treatment options for benign tumors caused by neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1) are not acceptable.
“Simply removing the tumors with surgery is not the answer,” Dr. Anderson, a dermatologist who is the director of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “We need a way to inhibit the cutaneous neurofibromatosis early in life and prevent disfigurement that occurs when kids become adults.
“Kids with NF-1 are born looking normal,” he said. “They have café au lait macules and Lisch nodules in their eye, but they’re normal-looking kids. By early adulthood, many will grow hundreds of tumors that are disfiguring.”
In patients with NF-1, surgical excision works for cutaneous tumors but is expensive and not widely available, and is usually not covered by health insurance. “Plus, you have these adults who have already been through a lot of trauma, with the disfigurement in their lives, who have to be put under general anesthesia to remove a large number of tumors,” Dr. Anderson said at the meeting, which was named What’s the Truth and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. Cryotherapy is a minimally invasive way to treat cutaneous neurofibroma tumors, “but this destroys the overlying skin, so you get unwanted destruction,” he said. “I like the idea of selecting heating, but we don’t know yet by what method.”
Dr. Anderson and his colleagues just launched a comparative clinical They plan to perform one or more treatment methods per patient in a single treatment session, then follow up at least 6 months later. Baseline and untreated cutaneous NF lesions will serve as controls. The researchers plan to conduct three-dimensional imaging, clinical assessments, and evaluate pain and other subjective measures.
Use of deoxycholate in a pilot trial was well tolerated and induced tumor regression in adults with cutaneous NF, he said.
Dr. Anderson noted that other researchers are studying the potential role of topical or local mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK) inhibitors for these tumors. “Systemic MEK inhibitors are effective for plexiform neuromas, but cause significant cutaneous side effects,” he said. A “soft” MEK inhibitor, NFX-179 is rapidly metabolized such that high drug levels are achieved in skin without systemic drug levels. However, Dr. Anderson said that it remains unclear if this approach will prevent cutaneous NF tumors from forming, arrest their growth, or induce their regression.
Dr. Anderson reported having received research funding and/or consulting fees from numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
Commentary by Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a common genodermatosis, associated with the development of neurofibromas derived from nerves, soft tissue, and skin. Cutaneous NFs often develop in later childhood onward and may be deforming, associated with pruritus, pain, and significant effect on quality of life. Dr. Anderson is a world leader in laser treatment, having developed the theories behind laser development for medical usage, as well as the laser technology used for vascular birthmarks and hair removal, laser and cooling techniques targeting fat, and “fractionating” laser energy, which has revolutionized scar management. We look forward to his group’s insights into better management of NF1 lesions!
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children's Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. He disclosed that he has served as an investigator and/or consultant to AbbVie, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Verrica.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 6/18/22.
In the clinical experience of R. Rox Anderson, MD, currently available treatment options for benign tumors caused by neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1) are not acceptable.
“Simply removing the tumors with surgery is not the answer,” Dr. Anderson, a dermatologist who is the director of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “We need a way to inhibit the cutaneous neurofibromatosis early in life and prevent disfigurement that occurs when kids become adults.
“Kids with NF-1 are born looking normal,” he said. “They have café au lait macules and Lisch nodules in their eye, but they’re normal-looking kids. By early adulthood, many will grow hundreds of tumors that are disfiguring.”
In patients with NF-1, surgical excision works for cutaneous tumors but is expensive and not widely available, and is usually not covered by health insurance. “Plus, you have these adults who have already been through a lot of trauma, with the disfigurement in their lives, who have to be put under general anesthesia to remove a large number of tumors,” Dr. Anderson said at the meeting, which was named What’s the Truth and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. Cryotherapy is a minimally invasive way to treat cutaneous neurofibroma tumors, “but this destroys the overlying skin, so you get unwanted destruction,” he said. “I like the idea of selecting heating, but we don’t know yet by what method.”
Dr. Anderson and his colleagues just launched a comparative clinical They plan to perform one or more treatment methods per patient in a single treatment session, then follow up at least 6 months later. Baseline and untreated cutaneous NF lesions will serve as controls. The researchers plan to conduct three-dimensional imaging, clinical assessments, and evaluate pain and other subjective measures.
Use of deoxycholate in a pilot trial was well tolerated and induced tumor regression in adults with cutaneous NF, he said.
Dr. Anderson noted that other researchers are studying the potential role of topical or local mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK) inhibitors for these tumors. “Systemic MEK inhibitors are effective for plexiform neuromas, but cause significant cutaneous side effects,” he said. A “soft” MEK inhibitor, NFX-179 is rapidly metabolized such that high drug levels are achieved in skin without systemic drug levels. However, Dr. Anderson said that it remains unclear if this approach will prevent cutaneous NF tumors from forming, arrest their growth, or induce their regression.
Dr. Anderson reported having received research funding and/or consulting fees from numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
Commentary by Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a common genodermatosis, associated with the development of neurofibromas derived from nerves, soft tissue, and skin. Cutaneous NFs often develop in later childhood onward and may be deforming, associated with pruritus, pain, and significant effect on quality of life. Dr. Anderson is a world leader in laser treatment, having developed the theories behind laser development for medical usage, as well as the laser technology used for vascular birthmarks and hair removal, laser and cooling techniques targeting fat, and “fractionating” laser energy, which has revolutionized scar management. We look forward to his group’s insights into better management of NF1 lesions!
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children's Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. He disclosed that he has served as an investigator and/or consultant to AbbVie, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Verrica.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 6/18/22.
In the clinical experience of R. Rox Anderson, MD, currently available treatment options for benign tumors caused by neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1) are not acceptable.
“Simply removing the tumors with surgery is not the answer,” Dr. Anderson, a dermatologist who is the director of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “We need a way to inhibit the cutaneous neurofibromatosis early in life and prevent disfigurement that occurs when kids become adults.
“Kids with NF-1 are born looking normal,” he said. “They have café au lait macules and Lisch nodules in their eye, but they’re normal-looking kids. By early adulthood, many will grow hundreds of tumors that are disfiguring.”
In patients with NF-1, surgical excision works for cutaneous tumors but is expensive and not widely available, and is usually not covered by health insurance. “Plus, you have these adults who have already been through a lot of trauma, with the disfigurement in their lives, who have to be put under general anesthesia to remove a large number of tumors,” Dr. Anderson said at the meeting, which was named What’s the Truth and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. Cryotherapy is a minimally invasive way to treat cutaneous neurofibroma tumors, “but this destroys the overlying skin, so you get unwanted destruction,” he said. “I like the idea of selecting heating, but we don’t know yet by what method.”
Dr. Anderson and his colleagues just launched a comparative clinical They plan to perform one or more treatment methods per patient in a single treatment session, then follow up at least 6 months later. Baseline and untreated cutaneous NF lesions will serve as controls. The researchers plan to conduct three-dimensional imaging, clinical assessments, and evaluate pain and other subjective measures.
Use of deoxycholate in a pilot trial was well tolerated and induced tumor regression in adults with cutaneous NF, he said.
Dr. Anderson noted that other researchers are studying the potential role of topical or local mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK) inhibitors for these tumors. “Systemic MEK inhibitors are effective for plexiform neuromas, but cause significant cutaneous side effects,” he said. A “soft” MEK inhibitor, NFX-179 is rapidly metabolized such that high drug levels are achieved in skin without systemic drug levels. However, Dr. Anderson said that it remains unclear if this approach will prevent cutaneous NF tumors from forming, arrest their growth, or induce their regression.
Dr. Anderson reported having received research funding and/or consulting fees from numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
Commentary by Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a common genodermatosis, associated with the development of neurofibromas derived from nerves, soft tissue, and skin. Cutaneous NFs often develop in later childhood onward and may be deforming, associated with pruritus, pain, and significant effect on quality of life. Dr. Anderson is a world leader in laser treatment, having developed the theories behind laser development for medical usage, as well as the laser technology used for vascular birthmarks and hair removal, laser and cooling techniques targeting fat, and “fractionating” laser energy, which has revolutionized scar management. We look forward to his group’s insights into better management of NF1 lesions!
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children's Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. He disclosed that he has served as an investigator and/or consultant to AbbVie, Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Verrica.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 6/18/22.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
One of the keys to success on social media? Entertain and educate the public
Social media isn’t everyone’s cup of tea, but
“I admit that I’m somewhat obsessed with it. I kind of blame it on my work as a dermatologist, that I’m trying to grow my social media as well. It’s interesting to me, fascinating, and I want to understand it more. I think that’s the mindset you need to approach it with.”
Perhaps no other public figure in dermatology has enjoyed success in social media more than Dr. Lee, a board-certified dermatologist who practices in Upland, Calif. In the fall of 2014, she started using Instagram to provide followers a glimpse into her life as a dermatologist, everything from Mohs surgery and Botox to keloid removals and ear lobe repair surgeries. From this she formed her alter ego, “Dr. Pimple Popper,” and became a YouTube sensation, building 7.1 million subscribers over the course of a few years, amounting to 4.5 billion lifetime views. She also grew 12 million followers on TikTok, 4.4 million followers on Instagram, 3 million on Facebook, and more than 139,000 on Twitter. About 80% of her followers are women who range between 18 and 40 years of age.
During the meeting she offered five social media marketing tips for busy clinicians:
You have to ‘play’ to ‘win.’ Active participation in social media is required to develop followers. “You cannot delegate this content,” Dr. Lee said. “You can hire people to help you or leave the task to a social media-savvy medical assistant in your office, but the content should be your responsibility ultimately, because you are the physician,” she added. Not everyone chooses to participate in social media, but it’s also something not to shy away from out of intimidation. “There is some talent associated with it, but it takes a lot of persistence as well,” she said.
Patients come first. Protect them at all costs. Dr. Lee rarely posts the faces of patients she cares for unless they grant consent in advance. “I try to show the work that I do and the beauty of dermatology,” she said during the meeting, which was named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth?” and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. She added that taking part in social media can help you improve communication skills by engaging with followers who like, share, or respond to the material posted. “When you look back at your posts objectively, you learn about yourself and how you relate to your patients,” she said. “It helps to hone my bedside manner and my skills as a dermatologist.”
Show that you are human. Many dermatologists and other “skin influencers” have established their presence on the Internet and may be direct competitors for patients, but that doesn’t mean you can’t establish your own identity. One way to stand out is by posting content related to your authentic self, such as a photo or video that shows you engaged in a hobby, dining at a favorite restaurant, or visiting a beloved vacation spot. “Your followers don’t want a robot, someone who thinks they’re amazing and can do everything,” said Dr. Lee, who stars in her own TV reality show on TLC. “Show that you have a funny side. You want them to fall in love with you and see a little bit of your world, whatever it might be. Charm the socks off of them.”
Entertain first, educate a close second. The main way you’re going to get people to follow and watch you is to provide some entertainment, “not at the expense of a patient or your practice, though,” she said. “Then you’re going to educate people. We dermatologists have something to teach the world because we are experts on skin, hair, and nails. You want to impart this knowledge in a way that captivates people.” It’s like the sense of accomplishment that comes from learning something new after reading a book or watching a movie, she explained. “You feel good about it, and you can take that knowledge with you somewhere else. I love it when kids come up to me and tell me they know what a lipoma is, what a cyst is, and what psoriasis is because they’ve seen my show, or because they follow me on social media. It’s wonderful because I can see that I’ve educated them.”
Be kind and don’t activate the trolls. Dr. Lee allows positivity and kindness to rule the day on her social media content. “This is what I try to relay to followers, but I also do not engage with the negativity,” she said. “Every now and then, there will be someone who tries to insult what you do or who insults you personally. If you engage with them, it almost invites them to do it more. It almost gives them the ability to fight with you. Try to stay above that; just put out goodness and kindness.”
Several years ago, YouTube and Instagram temporarily shut down Dr. Lee’s accounts because she posted graphic images of skin lesions and procedures – a practice that wasn’t so commonplace at the time. “Don’t just post a graphic image just to be graphic,” she advised. “Make sure it has an educational message associated with it. That will help to validate your content. Posting a warning sign that some images may be graphic could help, too.”
Dr. Lee reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Social media isn’t everyone’s cup of tea, but
“I admit that I’m somewhat obsessed with it. I kind of blame it on my work as a dermatologist, that I’m trying to grow my social media as well. It’s interesting to me, fascinating, and I want to understand it more. I think that’s the mindset you need to approach it with.”
Perhaps no other public figure in dermatology has enjoyed success in social media more than Dr. Lee, a board-certified dermatologist who practices in Upland, Calif. In the fall of 2014, she started using Instagram to provide followers a glimpse into her life as a dermatologist, everything from Mohs surgery and Botox to keloid removals and ear lobe repair surgeries. From this she formed her alter ego, “Dr. Pimple Popper,” and became a YouTube sensation, building 7.1 million subscribers over the course of a few years, amounting to 4.5 billion lifetime views. She also grew 12 million followers on TikTok, 4.4 million followers on Instagram, 3 million on Facebook, and more than 139,000 on Twitter. About 80% of her followers are women who range between 18 and 40 years of age.
During the meeting she offered five social media marketing tips for busy clinicians:
You have to ‘play’ to ‘win.’ Active participation in social media is required to develop followers. “You cannot delegate this content,” Dr. Lee said. “You can hire people to help you or leave the task to a social media-savvy medical assistant in your office, but the content should be your responsibility ultimately, because you are the physician,” she added. Not everyone chooses to participate in social media, but it’s also something not to shy away from out of intimidation. “There is some talent associated with it, but it takes a lot of persistence as well,” she said.
Patients come first. Protect them at all costs. Dr. Lee rarely posts the faces of patients she cares for unless they grant consent in advance. “I try to show the work that I do and the beauty of dermatology,” she said during the meeting, which was named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth?” and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. She added that taking part in social media can help you improve communication skills by engaging with followers who like, share, or respond to the material posted. “When you look back at your posts objectively, you learn about yourself and how you relate to your patients,” she said. “It helps to hone my bedside manner and my skills as a dermatologist.”
Show that you are human. Many dermatologists and other “skin influencers” have established their presence on the Internet and may be direct competitors for patients, but that doesn’t mean you can’t establish your own identity. One way to stand out is by posting content related to your authentic self, such as a photo or video that shows you engaged in a hobby, dining at a favorite restaurant, or visiting a beloved vacation spot. “Your followers don’t want a robot, someone who thinks they’re amazing and can do everything,” said Dr. Lee, who stars in her own TV reality show on TLC. “Show that you have a funny side. You want them to fall in love with you and see a little bit of your world, whatever it might be. Charm the socks off of them.”
Entertain first, educate a close second. The main way you’re going to get people to follow and watch you is to provide some entertainment, “not at the expense of a patient or your practice, though,” she said. “Then you’re going to educate people. We dermatologists have something to teach the world because we are experts on skin, hair, and nails. You want to impart this knowledge in a way that captivates people.” It’s like the sense of accomplishment that comes from learning something new after reading a book or watching a movie, she explained. “You feel good about it, and you can take that knowledge with you somewhere else. I love it when kids come up to me and tell me they know what a lipoma is, what a cyst is, and what psoriasis is because they’ve seen my show, or because they follow me on social media. It’s wonderful because I can see that I’ve educated them.”
Be kind and don’t activate the trolls. Dr. Lee allows positivity and kindness to rule the day on her social media content. “This is what I try to relay to followers, but I also do not engage with the negativity,” she said. “Every now and then, there will be someone who tries to insult what you do or who insults you personally. If you engage with them, it almost invites them to do it more. It almost gives them the ability to fight with you. Try to stay above that; just put out goodness and kindness.”
Several years ago, YouTube and Instagram temporarily shut down Dr. Lee’s accounts because she posted graphic images of skin lesions and procedures – a practice that wasn’t so commonplace at the time. “Don’t just post a graphic image just to be graphic,” she advised. “Make sure it has an educational message associated with it. That will help to validate your content. Posting a warning sign that some images may be graphic could help, too.”
Dr. Lee reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Social media isn’t everyone’s cup of tea, but
“I admit that I’m somewhat obsessed with it. I kind of blame it on my work as a dermatologist, that I’m trying to grow my social media as well. It’s interesting to me, fascinating, and I want to understand it more. I think that’s the mindset you need to approach it with.”
Perhaps no other public figure in dermatology has enjoyed success in social media more than Dr. Lee, a board-certified dermatologist who practices in Upland, Calif. In the fall of 2014, she started using Instagram to provide followers a glimpse into her life as a dermatologist, everything from Mohs surgery and Botox to keloid removals and ear lobe repair surgeries. From this she formed her alter ego, “Dr. Pimple Popper,” and became a YouTube sensation, building 7.1 million subscribers over the course of a few years, amounting to 4.5 billion lifetime views. She also grew 12 million followers on TikTok, 4.4 million followers on Instagram, 3 million on Facebook, and more than 139,000 on Twitter. About 80% of her followers are women who range between 18 and 40 years of age.
During the meeting she offered five social media marketing tips for busy clinicians:
You have to ‘play’ to ‘win.’ Active participation in social media is required to develop followers. “You cannot delegate this content,” Dr. Lee said. “You can hire people to help you or leave the task to a social media-savvy medical assistant in your office, but the content should be your responsibility ultimately, because you are the physician,” she added. Not everyone chooses to participate in social media, but it’s also something not to shy away from out of intimidation. “There is some talent associated with it, but it takes a lot of persistence as well,” she said.
Patients come first. Protect them at all costs. Dr. Lee rarely posts the faces of patients she cares for unless they grant consent in advance. “I try to show the work that I do and the beauty of dermatology,” she said during the meeting, which was named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth?” and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. She added that taking part in social media can help you improve communication skills by engaging with followers who like, share, or respond to the material posted. “When you look back at your posts objectively, you learn about yourself and how you relate to your patients,” she said. “It helps to hone my bedside manner and my skills as a dermatologist.”
Show that you are human. Many dermatologists and other “skin influencers” have established their presence on the Internet and may be direct competitors for patients, but that doesn’t mean you can’t establish your own identity. One way to stand out is by posting content related to your authentic self, such as a photo or video that shows you engaged in a hobby, dining at a favorite restaurant, or visiting a beloved vacation spot. “Your followers don’t want a robot, someone who thinks they’re amazing and can do everything,” said Dr. Lee, who stars in her own TV reality show on TLC. “Show that you have a funny side. You want them to fall in love with you and see a little bit of your world, whatever it might be. Charm the socks off of them.”
Entertain first, educate a close second. The main way you’re going to get people to follow and watch you is to provide some entertainment, “not at the expense of a patient or your practice, though,” she said. “Then you’re going to educate people. We dermatologists have something to teach the world because we are experts on skin, hair, and nails. You want to impart this knowledge in a way that captivates people.” It’s like the sense of accomplishment that comes from learning something new after reading a book or watching a movie, she explained. “You feel good about it, and you can take that knowledge with you somewhere else. I love it when kids come up to me and tell me they know what a lipoma is, what a cyst is, and what psoriasis is because they’ve seen my show, or because they follow me on social media. It’s wonderful because I can see that I’ve educated them.”
Be kind and don’t activate the trolls. Dr. Lee allows positivity and kindness to rule the day on her social media content. “This is what I try to relay to followers, but I also do not engage with the negativity,” she said. “Every now and then, there will be someone who tries to insult what you do or who insults you personally. If you engage with them, it almost invites them to do it more. It almost gives them the ability to fight with you. Try to stay above that; just put out goodness and kindness.”
Several years ago, YouTube and Instagram temporarily shut down Dr. Lee’s accounts because she posted graphic images of skin lesions and procedures – a practice that wasn’t so commonplace at the time. “Don’t just post a graphic image just to be graphic,” she advised. “Make sure it has an educational message associated with it. That will help to validate your content. Posting a warning sign that some images may be graphic could help, too.”
Dr. Lee reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
Treatment with novel laser in acne studies targets sebaceous glands
at 12 months, a development that indicates the promise this has a treatment for acne in the future.
Currently, “there is no strong evidence that lasers are better than conventional treatments for acne,” Fernanda H. Sakamoto, MD, PhD, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. Some patients struggling with acne “search for so many different options and they end up spending a lot of money,” which, she said, includes an estimated $222 million for laser treatment alone in 2019.
Unlike other existing laser and light options for acne treatment, however, Accure is the first light-based platform to selectively target and injure sebaceous glands, the main source of sebum production and the key to a durable solution for acne. The laser, which uses a 1,726-nm wavelength, is being developed by researchers at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston and was granted the European CE mark, which allows marketing of the product in Europe, in May of 2020.
In 2012, Dr. Sakamoto, a dermatologist at the center, and her Wellman colleagues were the first to describe the use of selective photothermolysis to target sebaceous glands. “We found that the peak absorption of lipids in sebaceous glands occurs between 1,700 and 1,720 nm,” she said. “Compared to water, the contrast is not high, so for us to develop a laser that is selective for acne, we needed to develop a strong cooling system and we had to create different methods to make it more selective.” She said that it took about 10 years to develop this laser.
The latest Accure prototype features a smart laser handpiece for real time thermal monitoring and precise delivery of laser emissions. “We have developed a mathematical model which permits us to predict safe and effective treatment patterns,” Dr. Sakamoto said at the meeting, which was named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth?” and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “It has a unique cooling system that can control and protect the skin.”
The clinical trial for Food and Drug Administration clearance, which was delayed because of the COVID-19 pandemic, is still underway, she said, and the hope is that the laser will cleared by the FDA by next year. She and her Wellman colleagues have been working with four veteran dermatologists to conduct clinical trials of the device: Emil Tanghetti, MD, in California; Roy Geronemus, MD, in New York; Joel Cohen, MD, in Colorado; and Daniel Friedmann, MD, in Texas. As of Oct. 2, 2021, more than 50 patients were enrolled in four IRB-approved studies and an additional 30 are enrolled in a pilot facial acne trial, Dr. Sakamoto said. In the trials, patients are followed at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment.
Among patients enrolled in the pilot facial acne trial, researchers have observed a 100% responder rate for patients with more than five acne lesions at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment. The average lesion reduction at week 12 was 82% and the mean Visual Analog Scale score immediately after treatment was 2.10 out of 10. Each patient received more than 12,000 trigger pulls of energy from the device with no adverse events.
“This laser is absorbed in the near-infrared spectrum, so there is no melanin absorption,” Dr. Sakamoto explained. “It’s pretty much a color-blind laser, so we can treat darker skin types safely, with no side effects.” In other findings, researchers observed a 45% reduction in acne lesions after one treatment session, which “keeps improving over time,” she said. “At 12 weeks, we have clearance of over 80% of the lesions.”
At 12 months, they observed a 90% inflammatory lesion count reduction from baseline and a rapid response to treatment: a 73% reduction achieved after the first two treatment sessions. Histological studies revealed selective sebaceous gland destruction with no damage to the epidermis, surrounding dermis, or other follicular structures.
Dr. Sakamoto disclosed that she has received portions of patent royalties from Massachusetts General Hospital. Accure was cofounded by R. Rox Anderson, MD, the director of the Wellman Center.
at 12 months, a development that indicates the promise this has a treatment for acne in the future.
Currently, “there is no strong evidence that lasers are better than conventional treatments for acne,” Fernanda H. Sakamoto, MD, PhD, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. Some patients struggling with acne “search for so many different options and they end up spending a lot of money,” which, she said, includes an estimated $222 million for laser treatment alone in 2019.
Unlike other existing laser and light options for acne treatment, however, Accure is the first light-based platform to selectively target and injure sebaceous glands, the main source of sebum production and the key to a durable solution for acne. The laser, which uses a 1,726-nm wavelength, is being developed by researchers at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston and was granted the European CE mark, which allows marketing of the product in Europe, in May of 2020.
In 2012, Dr. Sakamoto, a dermatologist at the center, and her Wellman colleagues were the first to describe the use of selective photothermolysis to target sebaceous glands. “We found that the peak absorption of lipids in sebaceous glands occurs between 1,700 and 1,720 nm,” she said. “Compared to water, the contrast is not high, so for us to develop a laser that is selective for acne, we needed to develop a strong cooling system and we had to create different methods to make it more selective.” She said that it took about 10 years to develop this laser.
The latest Accure prototype features a smart laser handpiece for real time thermal monitoring and precise delivery of laser emissions. “We have developed a mathematical model which permits us to predict safe and effective treatment patterns,” Dr. Sakamoto said at the meeting, which was named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth?” and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “It has a unique cooling system that can control and protect the skin.”
The clinical trial for Food and Drug Administration clearance, which was delayed because of the COVID-19 pandemic, is still underway, she said, and the hope is that the laser will cleared by the FDA by next year. She and her Wellman colleagues have been working with four veteran dermatologists to conduct clinical trials of the device: Emil Tanghetti, MD, in California; Roy Geronemus, MD, in New York; Joel Cohen, MD, in Colorado; and Daniel Friedmann, MD, in Texas. As of Oct. 2, 2021, more than 50 patients were enrolled in four IRB-approved studies and an additional 30 are enrolled in a pilot facial acne trial, Dr. Sakamoto said. In the trials, patients are followed at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment.
Among patients enrolled in the pilot facial acne trial, researchers have observed a 100% responder rate for patients with more than five acne lesions at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment. The average lesion reduction at week 12 was 82% and the mean Visual Analog Scale score immediately after treatment was 2.10 out of 10. Each patient received more than 12,000 trigger pulls of energy from the device with no adverse events.
“This laser is absorbed in the near-infrared spectrum, so there is no melanin absorption,” Dr. Sakamoto explained. “It’s pretty much a color-blind laser, so we can treat darker skin types safely, with no side effects.” In other findings, researchers observed a 45% reduction in acne lesions after one treatment session, which “keeps improving over time,” she said. “At 12 weeks, we have clearance of over 80% of the lesions.”
At 12 months, they observed a 90% inflammatory lesion count reduction from baseline and a rapid response to treatment: a 73% reduction achieved after the first two treatment sessions. Histological studies revealed selective sebaceous gland destruction with no damage to the epidermis, surrounding dermis, or other follicular structures.
Dr. Sakamoto disclosed that she has received portions of patent royalties from Massachusetts General Hospital. Accure was cofounded by R. Rox Anderson, MD, the director of the Wellman Center.
at 12 months, a development that indicates the promise this has a treatment for acne in the future.
Currently, “there is no strong evidence that lasers are better than conventional treatments for acne,” Fernanda H. Sakamoto, MD, PhD, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. Some patients struggling with acne “search for so many different options and they end up spending a lot of money,” which, she said, includes an estimated $222 million for laser treatment alone in 2019.
Unlike other existing laser and light options for acne treatment, however, Accure is the first light-based platform to selectively target and injure sebaceous glands, the main source of sebum production and the key to a durable solution for acne. The laser, which uses a 1,726-nm wavelength, is being developed by researchers at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston and was granted the European CE mark, which allows marketing of the product in Europe, in May of 2020.
In 2012, Dr. Sakamoto, a dermatologist at the center, and her Wellman colleagues were the first to describe the use of selective photothermolysis to target sebaceous glands. “We found that the peak absorption of lipids in sebaceous glands occurs between 1,700 and 1,720 nm,” she said. “Compared to water, the contrast is not high, so for us to develop a laser that is selective for acne, we needed to develop a strong cooling system and we had to create different methods to make it more selective.” She said that it took about 10 years to develop this laser.
The latest Accure prototype features a smart laser handpiece for real time thermal monitoring and precise delivery of laser emissions. “We have developed a mathematical model which permits us to predict safe and effective treatment patterns,” Dr. Sakamoto said at the meeting, which was named “Laser & Aesthetic Skin Therapy: What’s the Truth?” and was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “It has a unique cooling system that can control and protect the skin.”
The clinical trial for Food and Drug Administration clearance, which was delayed because of the COVID-19 pandemic, is still underway, she said, and the hope is that the laser will cleared by the FDA by next year. She and her Wellman colleagues have been working with four veteran dermatologists to conduct clinical trials of the device: Emil Tanghetti, MD, in California; Roy Geronemus, MD, in New York; Joel Cohen, MD, in Colorado; and Daniel Friedmann, MD, in Texas. As of Oct. 2, 2021, more than 50 patients were enrolled in four IRB-approved studies and an additional 30 are enrolled in a pilot facial acne trial, Dr. Sakamoto said. In the trials, patients are followed at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment.
Among patients enrolled in the pilot facial acne trial, researchers have observed a 100% responder rate for patients with more than five acne lesions at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment. The average lesion reduction at week 12 was 82% and the mean Visual Analog Scale score immediately after treatment was 2.10 out of 10. Each patient received more than 12,000 trigger pulls of energy from the device with no adverse events.
“This laser is absorbed in the near-infrared spectrum, so there is no melanin absorption,” Dr. Sakamoto explained. “It’s pretty much a color-blind laser, so we can treat darker skin types safely, with no side effects.” In other findings, researchers observed a 45% reduction in acne lesions after one treatment session, which “keeps improving over time,” she said. “At 12 weeks, we have clearance of over 80% of the lesions.”
At 12 months, they observed a 90% inflammatory lesion count reduction from baseline and a rapid response to treatment: a 73% reduction achieved after the first two treatment sessions. Histological studies revealed selective sebaceous gland destruction with no damage to the epidermis, surrounding dermis, or other follicular structures.
Dr. Sakamoto disclosed that she has received portions of patent royalties from Massachusetts General Hospital. Accure was cofounded by R. Rox Anderson, MD, the director of the Wellman Center.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE