User login
Learning Experiences in LGBT Health During Dermatology Residency
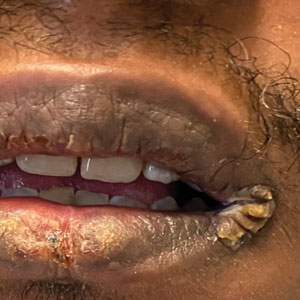
Approximately 4.5% of adults within the United States identify as members of the lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender (LGBT) community.1 This is an umbrella term inclusive of all individuals identifying as nonheterosexual or noncisgender. Although the LGBT community has increasingly become more recognized and accepted by society over time, health care disparities persist and have been well documented in the literature.2-4 Dermatologists have the potential to greatly impact LGBT health, as many health concerns in this population are cutaneous, such as sun-protection behaviors, side effects of gender-affirming hormone therapy and gender-affirming procedures, and cutaneous manifestations of sexually transmitted infections.5-7
An education gap has been demonstrated in both medical students and resident physicians regarding LGBT health and cultural competency. In a large-scale, multi-institutional survey study published in 2015, approximately two-thirds of medical students rated their schools’ LGBT curriculum as fair, poor, or very poor.8 Additional studies have echoed these results and have demonstrated not only the need but the desire for additional training on LGBT issues in medical school.9-11 The Association of American Medical Colleges has begun implementing curricular and institutional changes to fulfill this need.12,13
The LGBT education gap has been shown to extend into residency training. Multiple studies performed within a variety of medical specialties have demonstrated that resident physicians receive insufficient training in LGBT health issues, lack comfort in caring for LGBT patients, and would benefit from dedicated curricula on these topics.14-18 Currently, the 2022 Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) guidelines related to LGBT health are minimal and nonspecific.19
Ensuring that dermatology trainees are well equipped to manage these issues while providing culturally competent care to LGBT patients is paramount. However, research suggests that dedicated training on these topics likely is insufficient. A survey study of dermatology residency program directors (N=90) revealed that although 81% (72/89) viewed training in LGBT health as either very important or somewhat important, 46% (41/90) of programs did not dedicate any time to this content and 37% (33/90) only dedicated 1 to 2 hours per year.20
To further explore this potential education gap, we surveyed dermatology residents directly to better understand LGBT education within residency training, resident preparedness to care for LGBT patients, and outness/discrimination of LGBT-identifying residents. We believe this study should drive future research on the development and implementation of LGBT-specific curricula in dermatology training programs.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey study of dermatology residents in the United States was conducted. The study was deemed exempt from review by The Ohio State University (Columbus, Ohio) institutional review board. Survey responses were collected from October 7, 2020, to November 13, 2020. Qualtrics software was used to create the 20-question survey, which included a combination of categorical, dichotomous, and optional free-text questions related to patient demographics, LGBT training experiences, perceived areas of curriculum improvement, comfort level managing LGBT health issues, and personal experiences. Some questions were adapted from prior surveys.15,21 Validated survey tools used included the 2020 US Census to collect information regarding race and ethnicity, the Mohr and Fassinger Outness Inventory to measure outness regarding sexual orientation, and select questions from the 2020 Association of American Medical Colleges Medical School Graduation Questionnaire regarding discrimination.22-24
The survey was distributed to current allopathic and osteopathic dermatology residents by a variety of methods, including emails to program director and program coordinator listserves. The survey also was posted in the American Academy of Dermatology Expert Resource Group on LGBTQ Health October 2020 newsletter, as well as dermatology social media groups, including a messaging forum limited to dermatology residents, a Facebook group open to dermatologists and dermatology residents, and the Facebook group of the Gay and Lesbian Dermatology Association. Current dermatology residents, including those in combined dermatology and internal medicine programs, were included. Individuals who had been accepted to dermatology training programs but had not yet started were excluded. A follow-up email was sent to the program director listserve approximately 3 weeks after the initial distribution.
Statistical Analysis—The data were analyzed in Qualtrics and Microsoft Excel using descriptive statistics. Stata software (Stata 15.1, StataCorp) was used to perform a Kruskal-Wallis equality-of-populations rank test to compare the means of education level and feelings of preparedness.
Results
Demographics of Respondents—A total of 126 responses were recorded, 12 of which were blank and were removed from the database. A total of 114 dermatology residents’ responses were collected in Qualtrics and analyzed; 91 completed the entire survey (an 80% completion rate). Based on the 2020-2021 ACGME data listing, there were 1612 dermatology residents in the United States, which is an estimated response rate of 7% (114/1612).25 The eTable outlines the demographics of the survey respondents. Most were cisgender females (60%), followed by cisgender males (35%); the remainder preferred not to answer. Regarding sexual orientation, 77% identified as straight or heterosexual; 17% as gay, lesbian, or homosexual; 1% as queer; and 1% as bisexual. The training programs were in 26 states, the majority of which were in the Midwest (34%) and in urban settings (69%). A wide range of postgraduate levels and residency sizes were represented in the survey.
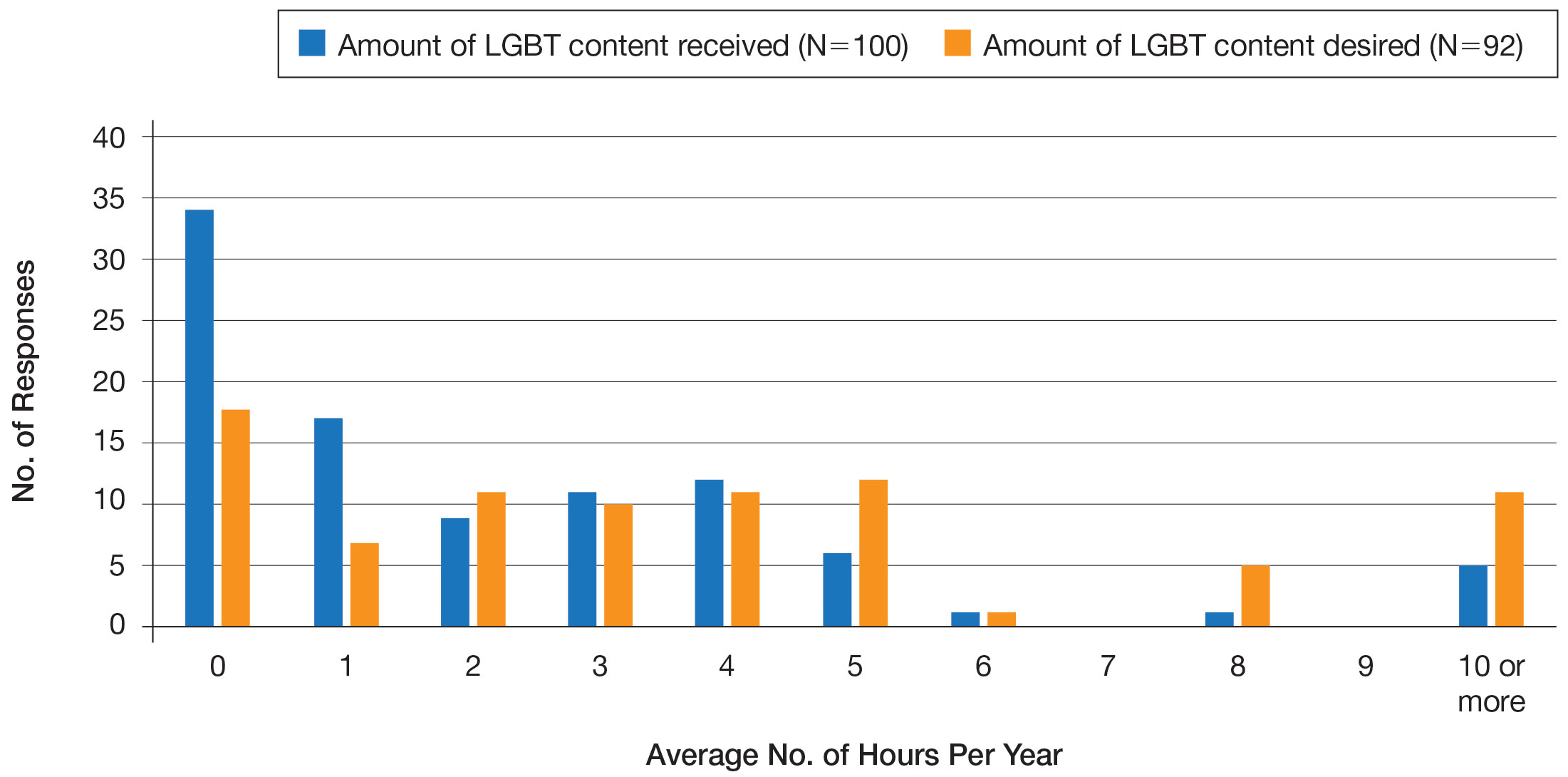
LGBT Education—Fifty-one percent of respondents reported that their programs offer 1 hour or less of LGBT-related curricula per year; 34% reported no time dedicated to this topic. A small portion of residents (5%) reported 10 or more hours of LGBT education per year. Residents also were asked the average number of hours of LGBT education they thought they should receive. The discrepancy between these measures can be visualized in Figure 1. The median hours of education received was 1 hour (IQR, 0–4 hours), whereas the median hours of education desired was 4 hours (IQR, 2–5 hours). The most common and most helpful methods of education reported were clinical experiences with faculty or patients and live lectures.
Overall, 45% of survey respondents felt that LGBT topics were covered poorly or not at all in dermatology residency, whereas 26% thought the coverage was good or excellent. The topics that residents were most likely to report receiving good or excellent coverage were dermatologic manifestations of HIV/AIDS (70%) and sexually transmitted diseases in LGBT patients (48%). The topics that were most likely to be reported as not taught or poorly taught included dermatologic concerns associated with puberty blockers (71%), body image (58%), dermatologic concerns associated with gender-affirming surgery (55%), skin cancer risk (53%), taking an LGBT-oriented history and physical examination (52%), and effects of gender-affirming hormone therapy on the skin (50%). A detailed breakdown of coverage level by topic can be found in Figure 2.
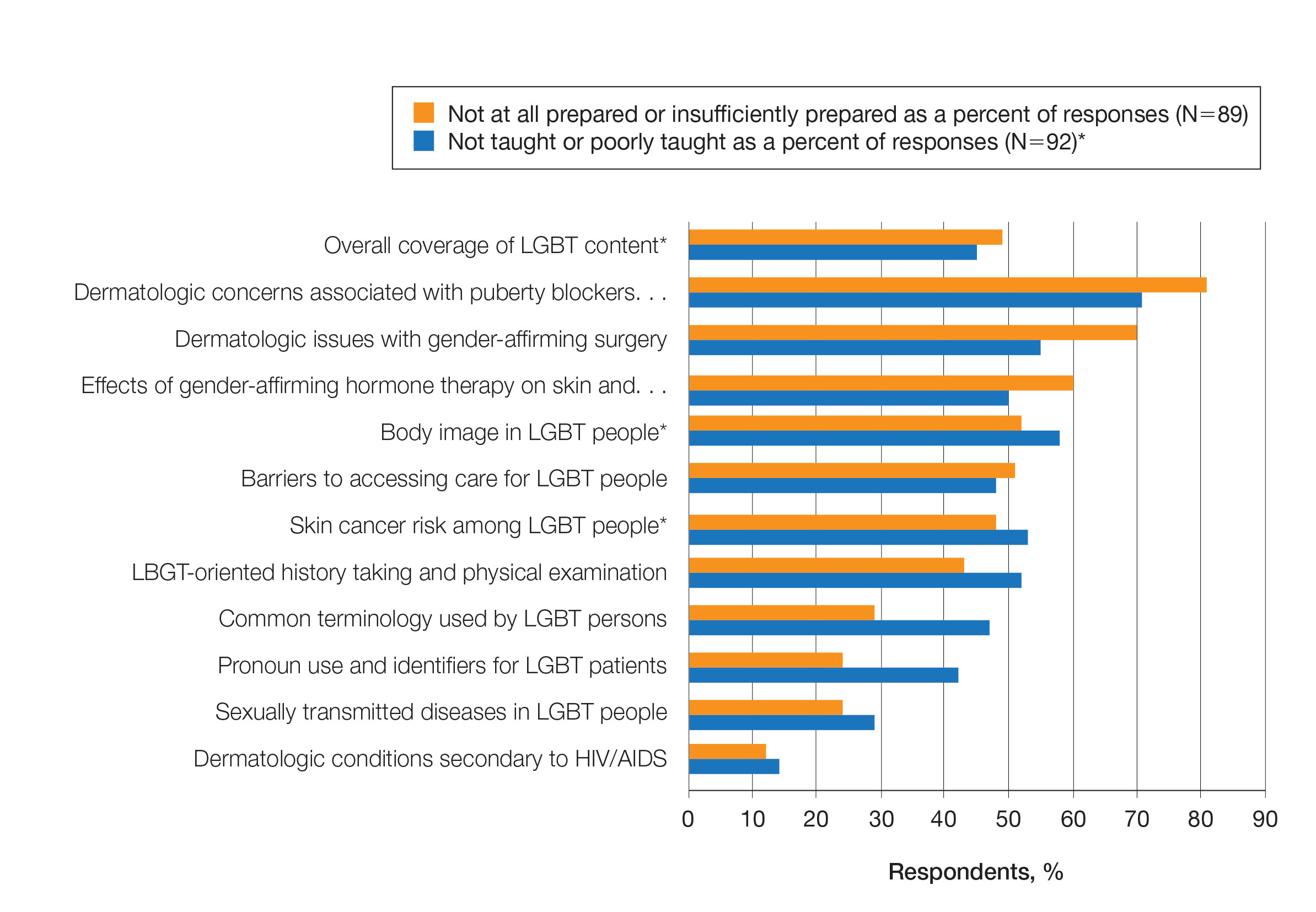
Preparedness to Care for LGBT Patients—Only 68% of survey respondents agreed or strongly agreed that they feel comfortable treating LGBT patients. Furthermore, 49% of dermatology residents reported that they feel not at all prepared or insufficiently prepared to provide care to LGBT individuals (Figure 2), and 60% believed that LGBT training needed to be improved at their residency programs.
There was a significant association between reported level of education and feelings of preparedness. A high ranking of provided education was associated with higher levels of feeling prepared to care for LGBT patients (Kruskal-Wallis rank test, P<.001).
Discrimination/Outness—Approximately one-fourth (24%; 4/17) of nonheterosexual dermatology residents reported that they had been subjected to offensive remarks about their sexual orientation in the workplace. One respondent commented that they were less “out” at their residency program due to fear of discrimination. Nearly one-third of the overall group of dermatology residents surveyed (29%; 27/92) reported that they had witnessed inappropriate or discriminatory comments about LGBT persons made by employees or staff at their programs. Most residents surveyed (96%; 88/92) agreed or strongly agreed that they feel comfortable working alongside LGBT physicians.
There were 18 nonheterosexual dermatologyresidents who completed the Mohr and Fassinger Outness Inventory.23 In general, respondents reported that they were more “out” with friends and family than work peers and were least “out” with work supervisors and strangers.
Comment
Dermatology Residents Desire More Time on LGBT Health—This cross-sectional survey study explored dermatology residents’ educational experiences with LGBT health during residency training. Similar studies have been performed in other specialties, including a study from 2019 surveying emergency medicine residents that demonstrated residents find caring for LGBT patients more challenging.15 Another 2019 study surveying psychiatry residents found that 42.4% (N=99) reported no coverage of LGBT topics.18 Our study is unique in that it surveyed dermatology residents directly regarding this topic. Although most dermatology program directors view LGBT dermatologic health as an important topic, a prior study revealed that many programs are lacking dedicated LGBT educational experiences. The most common barriers reported were insufficient time in the didactic schedule and lack of experienced faculty.20
Our study revealed that dermatology residents overall tend to agree with residents from other specialties and dermatology program directors. Most of the dermatology residents surveyed reported desiring more time per year spent on LGBT health education than they receive, and 60% expressed that LGBT educational experiences need to be improved at their residency programs. Education on and subsequent comfort level with LGBT health issues varied by subtopic, with most residents feeling comfortable dealing with dermatologic manifestations of HIV/AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases and less comfortable with topics such as puberty blockers, gender-affirming surgery and hormone therapy, body image, and skin cancer risk.
Overall, LGBT health training is viewed as important and in need of improvement by both program directors and residents, yet implementation lags at many programs. A small proportion of the represented programs are excelling in this area—just over 5% of respondents reported receiving 10 or more hours of LGBT-relevant education per year, and approximately 26% of residents felt that LGBT coverage was good or excellent at their programs. Our study showed a clear relationship between feelings of preparedness and education level. The lack of LGBT education at some dermatology residency programs translated into a large portion of dermatology residents feeling ill equipped to care for LGBT patients after graduation—nearly 50% of those surveyed reported feeling insufficiently prepared to care for the LGBT community.
Discrimination in Residency Programs—Dermatology residency programs also are not free from sexual orientation–related and gender identity–related workplace discrimination. Although 96% of dermatology residents reported that they feel comfortable working alongside LGBT physicians, 24% of nonheterosexual respondents stated they had been subjected to offensive remarks about their sexual orientation, and 29% of the overall group of dermatology residents had witnessed discriminatory comments to LGBT individuals at their programs. In addition, some nonheterosexual dermatology residents reported being less “out” with their workplace supervisors and strangers, such as patients, than with their family and friends, and 50% of this group reported that their sexual identity was not openly discussed with their workplace supervisors. It has been demonstrated that individuals are more likely to “come out” in perceived LGBT-friendly workplace environments and that being “out” positively impacts psychological health because of the effects of perceived social support and self-coherence.26,27
Study Strengths and Limitations—Strengths of this study include the modest sample size of dermatology residents that participated, high completion rate, and the anonymity of the survey. Limitations include the risk of sampling bias by posting the survey on LGBT-specific groups. The survey also took place in the fall, so the results may not accurately reflect programs that cover this material later in the academic year. Lastly, not all survey questions were validated.
Implementing Change in Residency Programs—Although the results of this study exposed the need for increasing LGBT education in dermatology residency, they do not provide guidelines for the best strategy to begin implementing change. A study from 2020 provides some guidance for incorporating LGBT health training into dermatology residency programs through a combination of curricular modifications and climate optimization.28 Additional future research should focus on the best methods for preparing dermatology residents to care for this population. In this study, residents reported that the most effective teaching methods were real encounters with LGBT patients or faculty educated on LGBT health as well as live lectures from experts. There also appeared to be a correlation between hours spent on LGBT health, including various subtopics, and residents’ perceived preparedness in these areas. Potential actionable items include clarifying the ACGME guidelines on LGBT health topics; increasing the sexual and gender diversity of the faculty, staff, residents, and patients; and dedicating additional didactic and clinical time to LGBT topics and experiences.
Conclusion
This survey study of dermatology residents regarding LGBT learning experiences in residency training provided evidence that dermatology residents as a whole are not adequately taught LGBT health topics and therefore feel unprepared to take care of this patient population. Additionally, most residents desire improvement of LGBT health education and training. Further studies focusing on the best methods for implementing LGBT-specific curricula are needed.
- Newport F. In U.S., estimate of LGBT population rises to 4.5%. Gallup. May 22, 2018. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://news.gallup.com/poll/234863/estimate-lgbt-population-rises.aspx
- Hafeez H, Zeshan M, Tahir MA, et al. Health care disparities among lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth: a literature review. Cureus. 2017;9:E1184.
- Gonzales G, Henning-Smith C. Barriers to care among transgender and gender nonconforming adults. Millbank Q. 2017;95:726-748.
- Quinn GP, Sanchez JA, Sutton SK, et al. Cancer and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender/transsexual, and queer/questioning (LGBTQ) populations. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:384-400.
- Sullivan P, Trinidad J, Hamann D. Issues in transgender dermatology: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:438-447.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: epidemiology, screening, and disease prevention. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:591-602.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: terminology, demographics, health disparities, and approaches to care. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:581-589.
- White W, Brenman S, Paradis E, et al. Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender patient care: medical students’ preparedness and comfort. Teach Learn Med. 2015;27:254-263.
- Nama N, MacPherson P, Sampson M, et al. Medical students’ perception of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) discrimination in their learning environment and their self-reported comfort level for caring for LGBT patients: a survey study. Med Educ Online. 2017;22:1-8.
- Phelan SM, Burke SE, Hardeman RR, et al. Medical school factors associated with changes in implicit and explicit bias against gay and lesbian people among 3492 graduating medical students. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:1193-1201.
- Cherabie J, Nilsen K, Houssayni S. Transgender health medical education intervention and its effects on beliefs, attitudes, comfort, and knowledge. Kans J Med. 2018;11:106-109.
- Integrating LGBT and DSD content into medical school curricula. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Published November 2015. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/equity-diversity-inclusion/lgbt-health-resources/videos/curricula-integration
- Cooper MB, Chacko M, Christner J. Incorporating LGBT health in an undergraduate medical education curriculum through the construct of social determinants of health. MedEdPORTAL. 2018;14:10781.
- Moll J, Krieger P, Moreno-Walton L, et al. The prevalence of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender health education and training in emergency medicine residency programs: what do we know? Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21:608-611.
- Moll J, Krieger P, Heron SL, et al. Attitudes, behavior, and comfort of emergency medicine residents in caring for LGBT patients: what do we know? AEM Educ Train. 2019;3:129-135.
- Hirschtritt ME, Noy G, Haller E, et al. LGBT-specific education in general psychiatry residency programs: a survey of program directors. Acad Psychiatry. 2019;43:41-45.
- Ufomata E, Eckstrand KL, Spagnoletti C, et al. Comprehensive curriculum for internal medicine residents on primary care of patients identifying as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender. MedEdPORTAL. 2020;16:10875.
- Zonana J, Batchelder S, Pula J, et al. Comment on: LGBT-specific education in general psychiatry residency programs: a survey of program directors. Acad Psychiatry. 2019;43:547-548.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Dermatology. Revised June 12, 2022. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/080_dermatology_2022.pdf
- Jia JL, Nord KM, Sarin KY, et al. Sexual and gender minority curricula within US dermatology residency programs. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:593-594.
- Mansh M, White W, Gee-Tong L, et al. Sexual and gender minority identity disclosure during undergraduate medical education: “in the closet” in medical school. Acad Med. 2015;90:634-644.
- US Census Bureau. 2020 Census Informational Questionnaire. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www2.census.gov/programs-surveys/decennial/2020/technical-documentation/questionnaires-and-instructions/questionnaires/2020-informational-questionnaire-english_DI-Q1.pdf
- Mohr JJ, Fassinger RE. Measuring dimensions of lesbian and gay male experience. Meas Eval Couns Dev. 2000;33:66-90.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Medical School Graduation Questionnaire: 2020 All Schools Summary Report. Published July 2020. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/media/46851/download
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Data Resource Book: Academic Year 2019-2020. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/publicationsbooks/2019-2020_acgme_databook_document.pdf
- Mohr JJ, Jackson SD, Sheets RL. Sexual orientation self-presentation among bisexual-identified women and men: patterns and predictors. Arch Sex Behav. 2017;46:1465-1479.
- Tatum AK. Workplace climate and job satisfaction: a test of social cognitive career theory (SCCT)’s workplace self-management model with sexual minority employees. Semantic Scholar. 2018. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Workplace-Climate-and-Job-Satisfaction%3A-A-Test-of-Tatum/5af75ab70acfb73c54e34b95597576d30e07df12
- Fakhoury JW, Daveluy S. Incorporating lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender training into a residency program. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:285-292.
Approximately 4.5% of adults within the United States identify as members of the lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender (LGBT) community.1 This is an umbrella term inclusive of all individuals identifying as nonheterosexual or noncisgender. Although the LGBT community has increasingly become more recognized and accepted by society over time, health care disparities persist and have been well documented in the literature.2-4 Dermatologists have the potential to greatly impact LGBT health, as many health concerns in this population are cutaneous, such as sun-protection behaviors, side effects of gender-affirming hormone therapy and gender-affirming procedures, and cutaneous manifestations of sexually transmitted infections.5-7
An education gap has been demonstrated in both medical students and resident physicians regarding LGBT health and cultural competency. In a large-scale, multi-institutional survey study published in 2015, approximately two-thirds of medical students rated their schools’ LGBT curriculum as fair, poor, or very poor.8 Additional studies have echoed these results and have demonstrated not only the need but the desire for additional training on LGBT issues in medical school.9-11 The Association of American Medical Colleges has begun implementing curricular and institutional changes to fulfill this need.12,13
The LGBT education gap has been shown to extend into residency training. Multiple studies performed within a variety of medical specialties have demonstrated that resident physicians receive insufficient training in LGBT health issues, lack comfort in caring for LGBT patients, and would benefit from dedicated curricula on these topics.14-18 Currently, the 2022 Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) guidelines related to LGBT health are minimal and nonspecific.19
Ensuring that dermatology trainees are well equipped to manage these issues while providing culturally competent care to LGBT patients is paramount. However, research suggests that dedicated training on these topics likely is insufficient. A survey study of dermatology residency program directors (N=90) revealed that although 81% (72/89) viewed training in LGBT health as either very important or somewhat important, 46% (41/90) of programs did not dedicate any time to this content and 37% (33/90) only dedicated 1 to 2 hours per year.20
To further explore this potential education gap, we surveyed dermatology residents directly to better understand LGBT education within residency training, resident preparedness to care for LGBT patients, and outness/discrimination of LGBT-identifying residents. We believe this study should drive future research on the development and implementation of LGBT-specific curricula in dermatology training programs.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey study of dermatology residents in the United States was conducted. The study was deemed exempt from review by The Ohio State University (Columbus, Ohio) institutional review board. Survey responses were collected from October 7, 2020, to November 13, 2020. Qualtrics software was used to create the 20-question survey, which included a combination of categorical, dichotomous, and optional free-text questions related to patient demographics, LGBT training experiences, perceived areas of curriculum improvement, comfort level managing LGBT health issues, and personal experiences. Some questions were adapted from prior surveys.15,21 Validated survey tools used included the 2020 US Census to collect information regarding race and ethnicity, the Mohr and Fassinger Outness Inventory to measure outness regarding sexual orientation, and select questions from the 2020 Association of American Medical Colleges Medical School Graduation Questionnaire regarding discrimination.22-24
The survey was distributed to current allopathic and osteopathic dermatology residents by a variety of methods, including emails to program director and program coordinator listserves. The survey also was posted in the American Academy of Dermatology Expert Resource Group on LGBTQ Health October 2020 newsletter, as well as dermatology social media groups, including a messaging forum limited to dermatology residents, a Facebook group open to dermatologists and dermatology residents, and the Facebook group of the Gay and Lesbian Dermatology Association. Current dermatology residents, including those in combined dermatology and internal medicine programs, were included. Individuals who had been accepted to dermatology training programs but had not yet started were excluded. A follow-up email was sent to the program director listserve approximately 3 weeks after the initial distribution.
Statistical Analysis—The data were analyzed in Qualtrics and Microsoft Excel using descriptive statistics. Stata software (Stata 15.1, StataCorp) was used to perform a Kruskal-Wallis equality-of-populations rank test to compare the means of education level and feelings of preparedness.
Results
Demographics of Respondents—A total of 126 responses were recorded, 12 of which were blank and were removed from the database. A total of 114 dermatology residents’ responses were collected in Qualtrics and analyzed; 91 completed the entire survey (an 80% completion rate). Based on the 2020-2021 ACGME data listing, there were 1612 dermatology residents in the United States, which is an estimated response rate of 7% (114/1612).25 The eTable outlines the demographics of the survey respondents. Most were cisgender females (60%), followed by cisgender males (35%); the remainder preferred not to answer. Regarding sexual orientation, 77% identified as straight or heterosexual; 17% as gay, lesbian, or homosexual; 1% as queer; and 1% as bisexual. The training programs were in 26 states, the majority of which were in the Midwest (34%) and in urban settings (69%). A wide range of postgraduate levels and residency sizes were represented in the survey.

LGBT Education—Fifty-one percent of respondents reported that their programs offer 1 hour or less of LGBT-related curricula per year; 34% reported no time dedicated to this topic. A small portion of residents (5%) reported 10 or more hours of LGBT education per year. Residents also were asked the average number of hours of LGBT education they thought they should receive. The discrepancy between these measures can be visualized in Figure 1. The median hours of education received was 1 hour (IQR, 0–4 hours), whereas the median hours of education desired was 4 hours (IQR, 2–5 hours). The most common and most helpful methods of education reported were clinical experiences with faculty or patients and live lectures.

Overall, 45% of survey respondents felt that LGBT topics were covered poorly or not at all in dermatology residency, whereas 26% thought the coverage was good or excellent. The topics that residents were most likely to report receiving good or excellent coverage were dermatologic manifestations of HIV/AIDS (70%) and sexually transmitted diseases in LGBT patients (48%). The topics that were most likely to be reported as not taught or poorly taught included dermatologic concerns associated with puberty blockers (71%), body image (58%), dermatologic concerns associated with gender-affirming surgery (55%), skin cancer risk (53%), taking an LGBT-oriented history and physical examination (52%), and effects of gender-affirming hormone therapy on the skin (50%). A detailed breakdown of coverage level by topic can be found in Figure 2.

Preparedness to Care for LGBT Patients—Only 68% of survey respondents agreed or strongly agreed that they feel comfortable treating LGBT patients. Furthermore, 49% of dermatology residents reported that they feel not at all prepared or insufficiently prepared to provide care to LGBT individuals (Figure 2), and 60% believed that LGBT training needed to be improved at their residency programs.
There was a significant association between reported level of education and feelings of preparedness. A high ranking of provided education was associated with higher levels of feeling prepared to care for LGBT patients (Kruskal-Wallis rank test, P<.001).
Discrimination/Outness—Approximately one-fourth (24%; 4/17) of nonheterosexual dermatology residents reported that they had been subjected to offensive remarks about their sexual orientation in the workplace. One respondent commented that they were less “out” at their residency program due to fear of discrimination. Nearly one-third of the overall group of dermatology residents surveyed (29%; 27/92) reported that they had witnessed inappropriate or discriminatory comments about LGBT persons made by employees or staff at their programs. Most residents surveyed (96%; 88/92) agreed or strongly agreed that they feel comfortable working alongside LGBT physicians.
There were 18 nonheterosexual dermatologyresidents who completed the Mohr and Fassinger Outness Inventory.23 In general, respondents reported that they were more “out” with friends and family than work peers and were least “out” with work supervisors and strangers.
Comment
Dermatology Residents Desire More Time on LGBT Health—This cross-sectional survey study explored dermatology residents’ educational experiences with LGBT health during residency training. Similar studies have been performed in other specialties, including a study from 2019 surveying emergency medicine residents that demonstrated residents find caring for LGBT patients more challenging.15 Another 2019 study surveying psychiatry residents found that 42.4% (N=99) reported no coverage of LGBT topics.18 Our study is unique in that it surveyed dermatology residents directly regarding this topic. Although most dermatology program directors view LGBT dermatologic health as an important topic, a prior study revealed that many programs are lacking dedicated LGBT educational experiences. The most common barriers reported were insufficient time in the didactic schedule and lack of experienced faculty.20
Our study revealed that dermatology residents overall tend to agree with residents from other specialties and dermatology program directors. Most of the dermatology residents surveyed reported desiring more time per year spent on LGBT health education than they receive, and 60% expressed that LGBT educational experiences need to be improved at their residency programs. Education on and subsequent comfort level with LGBT health issues varied by subtopic, with most residents feeling comfortable dealing with dermatologic manifestations of HIV/AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases and less comfortable with topics such as puberty blockers, gender-affirming surgery and hormone therapy, body image, and skin cancer risk.
Overall, LGBT health training is viewed as important and in need of improvement by both program directors and residents, yet implementation lags at many programs. A small proportion of the represented programs are excelling in this area—just over 5% of respondents reported receiving 10 or more hours of LGBT-relevant education per year, and approximately 26% of residents felt that LGBT coverage was good or excellent at their programs. Our study showed a clear relationship between feelings of preparedness and education level. The lack of LGBT education at some dermatology residency programs translated into a large portion of dermatology residents feeling ill equipped to care for LGBT patients after graduation—nearly 50% of those surveyed reported feeling insufficiently prepared to care for the LGBT community.
Discrimination in Residency Programs—Dermatology residency programs also are not free from sexual orientation–related and gender identity–related workplace discrimination. Although 96% of dermatology residents reported that they feel comfortable working alongside LGBT physicians, 24% of nonheterosexual respondents stated they had been subjected to offensive remarks about their sexual orientation, and 29% of the overall group of dermatology residents had witnessed discriminatory comments to LGBT individuals at their programs. In addition, some nonheterosexual dermatology residents reported being less “out” with their workplace supervisors and strangers, such as patients, than with their family and friends, and 50% of this group reported that their sexual identity was not openly discussed with their workplace supervisors. It has been demonstrated that individuals are more likely to “come out” in perceived LGBT-friendly workplace environments and that being “out” positively impacts psychological health because of the effects of perceived social support and self-coherence.26,27
Study Strengths and Limitations—Strengths of this study include the modest sample size of dermatology residents that participated, high completion rate, and the anonymity of the survey. Limitations include the risk of sampling bias by posting the survey on LGBT-specific groups. The survey also took place in the fall, so the results may not accurately reflect programs that cover this material later in the academic year. Lastly, not all survey questions were validated.
Implementing Change in Residency Programs—Although the results of this study exposed the need for increasing LGBT education in dermatology residency, they do not provide guidelines for the best strategy to begin implementing change. A study from 2020 provides some guidance for incorporating LGBT health training into dermatology residency programs through a combination of curricular modifications and climate optimization.28 Additional future research should focus on the best methods for preparing dermatology residents to care for this population. In this study, residents reported that the most effective teaching methods were real encounters with LGBT patients or faculty educated on LGBT health as well as live lectures from experts. There also appeared to be a correlation between hours spent on LGBT health, including various subtopics, and residents’ perceived preparedness in these areas. Potential actionable items include clarifying the ACGME guidelines on LGBT health topics; increasing the sexual and gender diversity of the faculty, staff, residents, and patients; and dedicating additional didactic and clinical time to LGBT topics and experiences.
Conclusion
This survey study of dermatology residents regarding LGBT learning experiences in residency training provided evidence that dermatology residents as a whole are not adequately taught LGBT health topics and therefore feel unprepared to take care of this patient population. Additionally, most residents desire improvement of LGBT health education and training. Further studies focusing on the best methods for implementing LGBT-specific curricula are needed.
Approximately 4.5% of adults within the United States identify as members of the lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender (LGBT) community.1 This is an umbrella term inclusive of all individuals identifying as nonheterosexual or noncisgender. Although the LGBT community has increasingly become more recognized and accepted by society over time, health care disparities persist and have been well documented in the literature.2-4 Dermatologists have the potential to greatly impact LGBT health, as many health concerns in this population are cutaneous, such as sun-protection behaviors, side effects of gender-affirming hormone therapy and gender-affirming procedures, and cutaneous manifestations of sexually transmitted infections.5-7
An education gap has been demonstrated in both medical students and resident physicians regarding LGBT health and cultural competency. In a large-scale, multi-institutional survey study published in 2015, approximately two-thirds of medical students rated their schools’ LGBT curriculum as fair, poor, or very poor.8 Additional studies have echoed these results and have demonstrated not only the need but the desire for additional training on LGBT issues in medical school.9-11 The Association of American Medical Colleges has begun implementing curricular and institutional changes to fulfill this need.12,13
The LGBT education gap has been shown to extend into residency training. Multiple studies performed within a variety of medical specialties have demonstrated that resident physicians receive insufficient training in LGBT health issues, lack comfort in caring for LGBT patients, and would benefit from dedicated curricula on these topics.14-18 Currently, the 2022 Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) guidelines related to LGBT health are minimal and nonspecific.19
Ensuring that dermatology trainees are well equipped to manage these issues while providing culturally competent care to LGBT patients is paramount. However, research suggests that dedicated training on these topics likely is insufficient. A survey study of dermatology residency program directors (N=90) revealed that although 81% (72/89) viewed training in LGBT health as either very important or somewhat important, 46% (41/90) of programs did not dedicate any time to this content and 37% (33/90) only dedicated 1 to 2 hours per year.20
To further explore this potential education gap, we surveyed dermatology residents directly to better understand LGBT education within residency training, resident preparedness to care for LGBT patients, and outness/discrimination of LGBT-identifying residents. We believe this study should drive future research on the development and implementation of LGBT-specific curricula in dermatology training programs.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey study of dermatology residents in the United States was conducted. The study was deemed exempt from review by The Ohio State University (Columbus, Ohio) institutional review board. Survey responses were collected from October 7, 2020, to November 13, 2020. Qualtrics software was used to create the 20-question survey, which included a combination of categorical, dichotomous, and optional free-text questions related to patient demographics, LGBT training experiences, perceived areas of curriculum improvement, comfort level managing LGBT health issues, and personal experiences. Some questions were adapted from prior surveys.15,21 Validated survey tools used included the 2020 US Census to collect information regarding race and ethnicity, the Mohr and Fassinger Outness Inventory to measure outness regarding sexual orientation, and select questions from the 2020 Association of American Medical Colleges Medical School Graduation Questionnaire regarding discrimination.22-24
The survey was distributed to current allopathic and osteopathic dermatology residents by a variety of methods, including emails to program director and program coordinator listserves. The survey also was posted in the American Academy of Dermatology Expert Resource Group on LGBTQ Health October 2020 newsletter, as well as dermatology social media groups, including a messaging forum limited to dermatology residents, a Facebook group open to dermatologists and dermatology residents, and the Facebook group of the Gay and Lesbian Dermatology Association. Current dermatology residents, including those in combined dermatology and internal medicine programs, were included. Individuals who had been accepted to dermatology training programs but had not yet started were excluded. A follow-up email was sent to the program director listserve approximately 3 weeks after the initial distribution.
Statistical Analysis—The data were analyzed in Qualtrics and Microsoft Excel using descriptive statistics. Stata software (Stata 15.1, StataCorp) was used to perform a Kruskal-Wallis equality-of-populations rank test to compare the means of education level and feelings of preparedness.
Results
Demographics of Respondents—A total of 126 responses were recorded, 12 of which were blank and were removed from the database. A total of 114 dermatology residents’ responses were collected in Qualtrics and analyzed; 91 completed the entire survey (an 80% completion rate). Based on the 2020-2021 ACGME data listing, there were 1612 dermatology residents in the United States, which is an estimated response rate of 7% (114/1612).25 The eTable outlines the demographics of the survey respondents. Most were cisgender females (60%), followed by cisgender males (35%); the remainder preferred not to answer. Regarding sexual orientation, 77% identified as straight or heterosexual; 17% as gay, lesbian, or homosexual; 1% as queer; and 1% as bisexual. The training programs were in 26 states, the majority of which were in the Midwest (34%) and in urban settings (69%). A wide range of postgraduate levels and residency sizes were represented in the survey.

LGBT Education—Fifty-one percent of respondents reported that their programs offer 1 hour or less of LGBT-related curricula per year; 34% reported no time dedicated to this topic. A small portion of residents (5%) reported 10 or more hours of LGBT education per year. Residents also were asked the average number of hours of LGBT education they thought they should receive. The discrepancy between these measures can be visualized in Figure 1. The median hours of education received was 1 hour (IQR, 0–4 hours), whereas the median hours of education desired was 4 hours (IQR, 2–5 hours). The most common and most helpful methods of education reported were clinical experiences with faculty or patients and live lectures.

Overall, 45% of survey respondents felt that LGBT topics were covered poorly or not at all in dermatology residency, whereas 26% thought the coverage was good or excellent. The topics that residents were most likely to report receiving good or excellent coverage were dermatologic manifestations of HIV/AIDS (70%) and sexually transmitted diseases in LGBT patients (48%). The topics that were most likely to be reported as not taught or poorly taught included dermatologic concerns associated with puberty blockers (71%), body image (58%), dermatologic concerns associated with gender-affirming surgery (55%), skin cancer risk (53%), taking an LGBT-oriented history and physical examination (52%), and effects of gender-affirming hormone therapy on the skin (50%). A detailed breakdown of coverage level by topic can be found in Figure 2.

Preparedness to Care for LGBT Patients—Only 68% of survey respondents agreed or strongly agreed that they feel comfortable treating LGBT patients. Furthermore, 49% of dermatology residents reported that they feel not at all prepared or insufficiently prepared to provide care to LGBT individuals (Figure 2), and 60% believed that LGBT training needed to be improved at their residency programs.
There was a significant association between reported level of education and feelings of preparedness. A high ranking of provided education was associated with higher levels of feeling prepared to care for LGBT patients (Kruskal-Wallis rank test, P<.001).
Discrimination/Outness—Approximately one-fourth (24%; 4/17) of nonheterosexual dermatology residents reported that they had been subjected to offensive remarks about their sexual orientation in the workplace. One respondent commented that they were less “out” at their residency program due to fear of discrimination. Nearly one-third of the overall group of dermatology residents surveyed (29%; 27/92) reported that they had witnessed inappropriate or discriminatory comments about LGBT persons made by employees or staff at their programs. Most residents surveyed (96%; 88/92) agreed or strongly agreed that they feel comfortable working alongside LGBT physicians.
There were 18 nonheterosexual dermatologyresidents who completed the Mohr and Fassinger Outness Inventory.23 In general, respondents reported that they were more “out” with friends and family than work peers and were least “out” with work supervisors and strangers.
Comment
Dermatology Residents Desire More Time on LGBT Health—This cross-sectional survey study explored dermatology residents’ educational experiences with LGBT health during residency training. Similar studies have been performed in other specialties, including a study from 2019 surveying emergency medicine residents that demonstrated residents find caring for LGBT patients more challenging.15 Another 2019 study surveying psychiatry residents found that 42.4% (N=99) reported no coverage of LGBT topics.18 Our study is unique in that it surveyed dermatology residents directly regarding this topic. Although most dermatology program directors view LGBT dermatologic health as an important topic, a prior study revealed that many programs are lacking dedicated LGBT educational experiences. The most common barriers reported were insufficient time in the didactic schedule and lack of experienced faculty.20
Our study revealed that dermatology residents overall tend to agree with residents from other specialties and dermatology program directors. Most of the dermatology residents surveyed reported desiring more time per year spent on LGBT health education than they receive, and 60% expressed that LGBT educational experiences need to be improved at their residency programs. Education on and subsequent comfort level with LGBT health issues varied by subtopic, with most residents feeling comfortable dealing with dermatologic manifestations of HIV/AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases and less comfortable with topics such as puberty blockers, gender-affirming surgery and hormone therapy, body image, and skin cancer risk.
Overall, LGBT health training is viewed as important and in need of improvement by both program directors and residents, yet implementation lags at many programs. A small proportion of the represented programs are excelling in this area—just over 5% of respondents reported receiving 10 or more hours of LGBT-relevant education per year, and approximately 26% of residents felt that LGBT coverage was good or excellent at their programs. Our study showed a clear relationship between feelings of preparedness and education level. The lack of LGBT education at some dermatology residency programs translated into a large portion of dermatology residents feeling ill equipped to care for LGBT patients after graduation—nearly 50% of those surveyed reported feeling insufficiently prepared to care for the LGBT community.
Discrimination in Residency Programs—Dermatology residency programs also are not free from sexual orientation–related and gender identity–related workplace discrimination. Although 96% of dermatology residents reported that they feel comfortable working alongside LGBT physicians, 24% of nonheterosexual respondents stated they had been subjected to offensive remarks about their sexual orientation, and 29% of the overall group of dermatology residents had witnessed discriminatory comments to LGBT individuals at their programs. In addition, some nonheterosexual dermatology residents reported being less “out” with their workplace supervisors and strangers, such as patients, than with their family and friends, and 50% of this group reported that their sexual identity was not openly discussed with their workplace supervisors. It has been demonstrated that individuals are more likely to “come out” in perceived LGBT-friendly workplace environments and that being “out” positively impacts psychological health because of the effects of perceived social support and self-coherence.26,27
Study Strengths and Limitations—Strengths of this study include the modest sample size of dermatology residents that participated, high completion rate, and the anonymity of the survey. Limitations include the risk of sampling bias by posting the survey on LGBT-specific groups. The survey also took place in the fall, so the results may not accurately reflect programs that cover this material later in the academic year. Lastly, not all survey questions were validated.
Implementing Change in Residency Programs—Although the results of this study exposed the need for increasing LGBT education in dermatology residency, they do not provide guidelines for the best strategy to begin implementing change. A study from 2020 provides some guidance for incorporating LGBT health training into dermatology residency programs through a combination of curricular modifications and climate optimization.28 Additional future research should focus on the best methods for preparing dermatology residents to care for this population. In this study, residents reported that the most effective teaching methods were real encounters with LGBT patients or faculty educated on LGBT health as well as live lectures from experts. There also appeared to be a correlation between hours spent on LGBT health, including various subtopics, and residents’ perceived preparedness in these areas. Potential actionable items include clarifying the ACGME guidelines on LGBT health topics; increasing the sexual and gender diversity of the faculty, staff, residents, and patients; and dedicating additional didactic and clinical time to LGBT topics and experiences.
Conclusion
This survey study of dermatology residents regarding LGBT learning experiences in residency training provided evidence that dermatology residents as a whole are not adequately taught LGBT health topics and therefore feel unprepared to take care of this patient population. Additionally, most residents desire improvement of LGBT health education and training. Further studies focusing on the best methods for implementing LGBT-specific curricula are needed.
- Newport F. In U.S., estimate of LGBT population rises to 4.5%. Gallup. May 22, 2018. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://news.gallup.com/poll/234863/estimate-lgbt-population-rises.aspx
- Hafeez H, Zeshan M, Tahir MA, et al. Health care disparities among lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth: a literature review. Cureus. 2017;9:E1184.
- Gonzales G, Henning-Smith C. Barriers to care among transgender and gender nonconforming adults. Millbank Q. 2017;95:726-748.
- Quinn GP, Sanchez JA, Sutton SK, et al. Cancer and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender/transsexual, and queer/questioning (LGBTQ) populations. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:384-400.
- Sullivan P, Trinidad J, Hamann D. Issues in transgender dermatology: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:438-447.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: epidemiology, screening, and disease prevention. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:591-602.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: terminology, demographics, health disparities, and approaches to care. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:581-589.
- White W, Brenman S, Paradis E, et al. Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender patient care: medical students’ preparedness and comfort. Teach Learn Med. 2015;27:254-263.
- Nama N, MacPherson P, Sampson M, et al. Medical students’ perception of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) discrimination in their learning environment and their self-reported comfort level for caring for LGBT patients: a survey study. Med Educ Online. 2017;22:1-8.
- Phelan SM, Burke SE, Hardeman RR, et al. Medical school factors associated with changes in implicit and explicit bias against gay and lesbian people among 3492 graduating medical students. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:1193-1201.
- Cherabie J, Nilsen K, Houssayni S. Transgender health medical education intervention and its effects on beliefs, attitudes, comfort, and knowledge. Kans J Med. 2018;11:106-109.
- Integrating LGBT and DSD content into medical school curricula. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Published November 2015. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/equity-diversity-inclusion/lgbt-health-resources/videos/curricula-integration
- Cooper MB, Chacko M, Christner J. Incorporating LGBT health in an undergraduate medical education curriculum through the construct of social determinants of health. MedEdPORTAL. 2018;14:10781.
- Moll J, Krieger P, Moreno-Walton L, et al. The prevalence of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender health education and training in emergency medicine residency programs: what do we know? Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21:608-611.
- Moll J, Krieger P, Heron SL, et al. Attitudes, behavior, and comfort of emergency medicine residents in caring for LGBT patients: what do we know? AEM Educ Train. 2019;3:129-135.
- Hirschtritt ME, Noy G, Haller E, et al. LGBT-specific education in general psychiatry residency programs: a survey of program directors. Acad Psychiatry. 2019;43:41-45.
- Ufomata E, Eckstrand KL, Spagnoletti C, et al. Comprehensive curriculum for internal medicine residents on primary care of patients identifying as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender. MedEdPORTAL. 2020;16:10875.
- Zonana J, Batchelder S, Pula J, et al. Comment on: LGBT-specific education in general psychiatry residency programs: a survey of program directors. Acad Psychiatry. 2019;43:547-548.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Dermatology. Revised June 12, 2022. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/080_dermatology_2022.pdf
- Jia JL, Nord KM, Sarin KY, et al. Sexual and gender minority curricula within US dermatology residency programs. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:593-594.
- Mansh M, White W, Gee-Tong L, et al. Sexual and gender minority identity disclosure during undergraduate medical education: “in the closet” in medical school. Acad Med. 2015;90:634-644.
- US Census Bureau. 2020 Census Informational Questionnaire. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www2.census.gov/programs-surveys/decennial/2020/technical-documentation/questionnaires-and-instructions/questionnaires/2020-informational-questionnaire-english_DI-Q1.pdf
- Mohr JJ, Fassinger RE. Measuring dimensions of lesbian and gay male experience. Meas Eval Couns Dev. 2000;33:66-90.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Medical School Graduation Questionnaire: 2020 All Schools Summary Report. Published July 2020. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/media/46851/download
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Data Resource Book: Academic Year 2019-2020. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/publicationsbooks/2019-2020_acgme_databook_document.pdf
- Mohr JJ, Jackson SD, Sheets RL. Sexual orientation self-presentation among bisexual-identified women and men: patterns and predictors. Arch Sex Behav. 2017;46:1465-1479.
- Tatum AK. Workplace climate and job satisfaction: a test of social cognitive career theory (SCCT)’s workplace self-management model with sexual minority employees. Semantic Scholar. 2018. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Workplace-Climate-and-Job-Satisfaction%3A-A-Test-of-Tatum/5af75ab70acfb73c54e34b95597576d30e07df12
- Fakhoury JW, Daveluy S. Incorporating lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender training into a residency program. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:285-292.
- Newport F. In U.S., estimate of LGBT population rises to 4.5%. Gallup. May 22, 2018. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://news.gallup.com/poll/234863/estimate-lgbt-population-rises.aspx
- Hafeez H, Zeshan M, Tahir MA, et al. Health care disparities among lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender youth: a literature review. Cureus. 2017;9:E1184.
- Gonzales G, Henning-Smith C. Barriers to care among transgender and gender nonconforming adults. Millbank Q. 2017;95:726-748.
- Quinn GP, Sanchez JA, Sutton SK, et al. Cancer and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender/transsexual, and queer/questioning (LGBTQ) populations. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:384-400.
- Sullivan P, Trinidad J, Hamann D. Issues in transgender dermatology: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:438-447.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: epidemiology, screening, and disease prevention. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:591-602.
- Yeung H, Luk KM, Chen SC, et al. Dermatologic care for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons: terminology, demographics, health disparities, and approaches to care. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:581-589.
- White W, Brenman S, Paradis E, et al. Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender patient care: medical students’ preparedness and comfort. Teach Learn Med. 2015;27:254-263.
- Nama N, MacPherson P, Sampson M, et al. Medical students’ perception of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) discrimination in their learning environment and their self-reported comfort level for caring for LGBT patients: a survey study. Med Educ Online. 2017;22:1-8.
- Phelan SM, Burke SE, Hardeman RR, et al. Medical school factors associated with changes in implicit and explicit bias against gay and lesbian people among 3492 graduating medical students. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:1193-1201.
- Cherabie J, Nilsen K, Houssayni S. Transgender health medical education intervention and its effects on beliefs, attitudes, comfort, and knowledge. Kans J Med. 2018;11:106-109.
- Integrating LGBT and DSD content into medical school curricula. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Published November 2015. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/equity-diversity-inclusion/lgbt-health-resources/videos/curricula-integration
- Cooper MB, Chacko M, Christner J. Incorporating LGBT health in an undergraduate medical education curriculum through the construct of social determinants of health. MedEdPORTAL. 2018;14:10781.
- Moll J, Krieger P, Moreno-Walton L, et al. The prevalence of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender health education and training in emergency medicine residency programs: what do we know? Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21:608-611.
- Moll J, Krieger P, Heron SL, et al. Attitudes, behavior, and comfort of emergency medicine residents in caring for LGBT patients: what do we know? AEM Educ Train. 2019;3:129-135.
- Hirschtritt ME, Noy G, Haller E, et al. LGBT-specific education in general psychiatry residency programs: a survey of program directors. Acad Psychiatry. 2019;43:41-45.
- Ufomata E, Eckstrand KL, Spagnoletti C, et al. Comprehensive curriculum for internal medicine residents on primary care of patients identifying as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender. MedEdPORTAL. 2020;16:10875.
- Zonana J, Batchelder S, Pula J, et al. Comment on: LGBT-specific education in general psychiatry residency programs: a survey of program directors. Acad Psychiatry. 2019;43:547-548.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Dermatology. Revised June 12, 2022. Accessed September 23, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/080_dermatology_2022.pdf
- Jia JL, Nord KM, Sarin KY, et al. Sexual and gender minority curricula within US dermatology residency programs. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:593-594.
- Mansh M, White W, Gee-Tong L, et al. Sexual and gender minority identity disclosure during undergraduate medical education: “in the closet” in medical school. Acad Med. 2015;90:634-644.
- US Census Bureau. 2020 Census Informational Questionnaire. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www2.census.gov/programs-surveys/decennial/2020/technical-documentation/questionnaires-and-instructions/questionnaires/2020-informational-questionnaire-english_DI-Q1.pdf
- Mohr JJ, Fassinger RE. Measuring dimensions of lesbian and gay male experience. Meas Eval Couns Dev. 2000;33:66-90.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Medical School Graduation Questionnaire: 2020 All Schools Summary Report. Published July 2020. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/media/46851/download
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Data Resource Book: Academic Year 2019-2020. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/publicationsbooks/2019-2020_acgme_databook_document.pdf
- Mohr JJ, Jackson SD, Sheets RL. Sexual orientation self-presentation among bisexual-identified women and men: patterns and predictors. Arch Sex Behav. 2017;46:1465-1479.
- Tatum AK. Workplace climate and job satisfaction: a test of social cognitive career theory (SCCT)’s workplace self-management model with sexual minority employees. Semantic Scholar. 2018. Accessed September 19, 2022. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Workplace-Climate-and-Job-Satisfaction%3A-A-Test-of-Tatum/5af75ab70acfb73c54e34b95597576d30e07df12
- Fakhoury JW, Daveluy S. Incorporating lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender training into a residency program. Dermatol Clin. 2020;38:285-292.
Practice Points
- Dermatologists have the potential to greatly impact lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender (LGBT) health since many health concerns in this population are cutaneous.
- Improving LGBT health education and training in dermatology residency likely will increase dermatology residents' comfort level in treating this population.
Highlights in Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer From ESMO 2022
Highlights in advanced non–small lung cancer (NSCLC) from the 2022 European Society for Medical Oncology Congress are presented by Dr Jack West of City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center in Duarte, California.
Dr West begins by discussing CodeBreak 200, a study comparing sotorasib with docetaxel in previously treated patients with a KRAS G12C mutation. Sotorasib improved progression-free survival, but overall survival data are awaited.
Next, Dr West examines 5-year updates from KEYNOTE-189 and KEYNOTE-407, comparing pembrolizumab with chemotherapy in nonsquamous and squamous disease, respectively. Around two fifths of patients remained alive and disease-free 5 years after stopping treatment.
Dr West then reports on the IPSOS trial, which compared atezolizumab with single-agent chemotherapy in patients who were ineligible for standard chemotherapy. The results suggested that immunotherapy could be used in patients who are usually excluded from trials.
He finishes with two studies in EGFR-mutated disease. ORIENT-3 indicated that the effect of sintilimab could be boosted with a bevacizumab biosimilar. INSIGHT 2 suggested that adding tepotinib to osimertinib may be effective in patients with MET amplification.
--
Associate Professor, Department of Medical Oncology, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Care, Duarte, California; Medical Director, AccessHope, Los Angeles, California
Howard (Jack) West, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Amgen; AstraZeneca; Eli Lilly; EQRx; Genentech/Roche; Merck; Mirati; Pfizer; Regeneron; Takeda
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Merck
Highlights in advanced non–small lung cancer (NSCLC) from the 2022 European Society for Medical Oncology Congress are presented by Dr Jack West of City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center in Duarte, California.
Dr West begins by discussing CodeBreak 200, a study comparing sotorasib with docetaxel in previously treated patients with a KRAS G12C mutation. Sotorasib improved progression-free survival, but overall survival data are awaited.
Next, Dr West examines 5-year updates from KEYNOTE-189 and KEYNOTE-407, comparing pembrolizumab with chemotherapy in nonsquamous and squamous disease, respectively. Around two fifths of patients remained alive and disease-free 5 years after stopping treatment.
Dr West then reports on the IPSOS trial, which compared atezolizumab with single-agent chemotherapy in patients who were ineligible for standard chemotherapy. The results suggested that immunotherapy could be used in patients who are usually excluded from trials.
He finishes with two studies in EGFR-mutated disease. ORIENT-3 indicated that the effect of sintilimab could be boosted with a bevacizumab biosimilar. INSIGHT 2 suggested that adding tepotinib to osimertinib may be effective in patients with MET amplification.
--
Associate Professor, Department of Medical Oncology, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Care, Duarte, California; Medical Director, AccessHope, Los Angeles, California
Howard (Jack) West, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Amgen; AstraZeneca; Eli Lilly; EQRx; Genentech/Roche; Merck; Mirati; Pfizer; Regeneron; Takeda
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Merck
Highlights in advanced non–small lung cancer (NSCLC) from the 2022 European Society for Medical Oncology Congress are presented by Dr Jack West of City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center in Duarte, California.
Dr West begins by discussing CodeBreak 200, a study comparing sotorasib with docetaxel in previously treated patients with a KRAS G12C mutation. Sotorasib improved progression-free survival, but overall survival data are awaited.
Next, Dr West examines 5-year updates from KEYNOTE-189 and KEYNOTE-407, comparing pembrolizumab with chemotherapy in nonsquamous and squamous disease, respectively. Around two fifths of patients remained alive and disease-free 5 years after stopping treatment.
Dr West then reports on the IPSOS trial, which compared atezolizumab with single-agent chemotherapy in patients who were ineligible for standard chemotherapy. The results suggested that immunotherapy could be used in patients who are usually excluded from trials.
He finishes with two studies in EGFR-mutated disease. ORIENT-3 indicated that the effect of sintilimab could be boosted with a bevacizumab biosimilar. INSIGHT 2 suggested that adding tepotinib to osimertinib may be effective in patients with MET amplification.
--
Associate Professor, Department of Medical Oncology, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Care, Duarte, California; Medical Director, AccessHope, Los Angeles, California
Howard (Jack) West, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Amgen; AstraZeneca; Eli Lilly; EQRx; Genentech/Roche; Merck; Mirati; Pfizer; Regeneron; Takeda
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Merck

Key Data on Early Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer From ESMO 2022
Dr Jack West of City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center in Duarte, California, discusses key presentations on early-stage non–small lung cancer (NSCLC) from the 2022 European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
He begins by reporting on 2 years of additional follow-up from the ADAURA trial, which looked at osimertinib as adjuvant therapy in patients with resected EGFR-mutated disease. The results raise the question of whether the drug needs to be given indefinitely.
Next, he discusses an analysis of data from the ADAURA trial that looked at longitudinal monitoring of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) levels. This revealed that both baseline ctDNA and ctDNA clearance were predictive of later recurrence.
Dr West moves on to a large global study that demonstrated a clear link between air pollution and lung cancer. Pollution was shown to be a tumor promoter of rare driver mutations in normal lung tissue.
After discussing disappointing data from CANOPY-A indicating that adjuvant canakinumab does not improve survival outcomes, he closes with an examination of the PATHFINDER study. This involved more than 6600 patients who were screened for cancer after a single blood test. Although the study identified cancer in 1.4% of participants, the low positive predictive value raises questions over the wider application of this test.
--
Associate Professor, Department of Medical Oncology, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Care, Duarte, California; Medical Director, AccessHope, Los Angeles, California
Howard (Jack) West, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Amgen; AstraZeneca; Eli Lilly; EQRx; Genentech/Roche; Merck; Mirati; Pfizer; Regeneron; Takeda
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Merck
Dr Jack West of City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center in Duarte, California, discusses key presentations on early-stage non–small lung cancer (NSCLC) from the 2022 European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
He begins by reporting on 2 years of additional follow-up from the ADAURA trial, which looked at osimertinib as adjuvant therapy in patients with resected EGFR-mutated disease. The results raise the question of whether the drug needs to be given indefinitely.
Next, he discusses an analysis of data from the ADAURA trial that looked at longitudinal monitoring of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) levels. This revealed that both baseline ctDNA and ctDNA clearance were predictive of later recurrence.
Dr West moves on to a large global study that demonstrated a clear link between air pollution and lung cancer. Pollution was shown to be a tumor promoter of rare driver mutations in normal lung tissue.
After discussing disappointing data from CANOPY-A indicating that adjuvant canakinumab does not improve survival outcomes, he closes with an examination of the PATHFINDER study. This involved more than 6600 patients who were screened for cancer after a single blood test. Although the study identified cancer in 1.4% of participants, the low positive predictive value raises questions over the wider application of this test.
--
Associate Professor, Department of Medical Oncology, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Care, Duarte, California; Medical Director, AccessHope, Los Angeles, California
Howard (Jack) West, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Amgen; AstraZeneca; Eli Lilly; EQRx; Genentech/Roche; Merck; Mirati; Pfizer; Regeneron; Takeda
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Merck
Dr Jack West of City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center in Duarte, California, discusses key presentations on early-stage non–small lung cancer (NSCLC) from the 2022 European Society for Medical Oncology Congress.
He begins by reporting on 2 years of additional follow-up from the ADAURA trial, which looked at osimertinib as adjuvant therapy in patients with resected EGFR-mutated disease. The results raise the question of whether the drug needs to be given indefinitely.
Next, he discusses an analysis of data from the ADAURA trial that looked at longitudinal monitoring of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) levels. This revealed that both baseline ctDNA and ctDNA clearance were predictive of later recurrence.
Dr West moves on to a large global study that demonstrated a clear link between air pollution and lung cancer. Pollution was shown to be a tumor promoter of rare driver mutations in normal lung tissue.
After discussing disappointing data from CANOPY-A indicating that adjuvant canakinumab does not improve survival outcomes, he closes with an examination of the PATHFINDER study. This involved more than 6600 patients who were screened for cancer after a single blood test. Although the study identified cancer in 1.4% of participants, the low positive predictive value raises questions over the wider application of this test.
--
Associate Professor, Department of Medical Oncology, City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Care, Duarte, California; Medical Director, AccessHope, Los Angeles, California
Howard (Jack) West, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: Amgen; AstraZeneca; Eli Lilly; EQRx; Genentech/Roche; Merck; Mirati; Pfizer; Regeneron; Takeda
Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: AstraZeneca; Merck

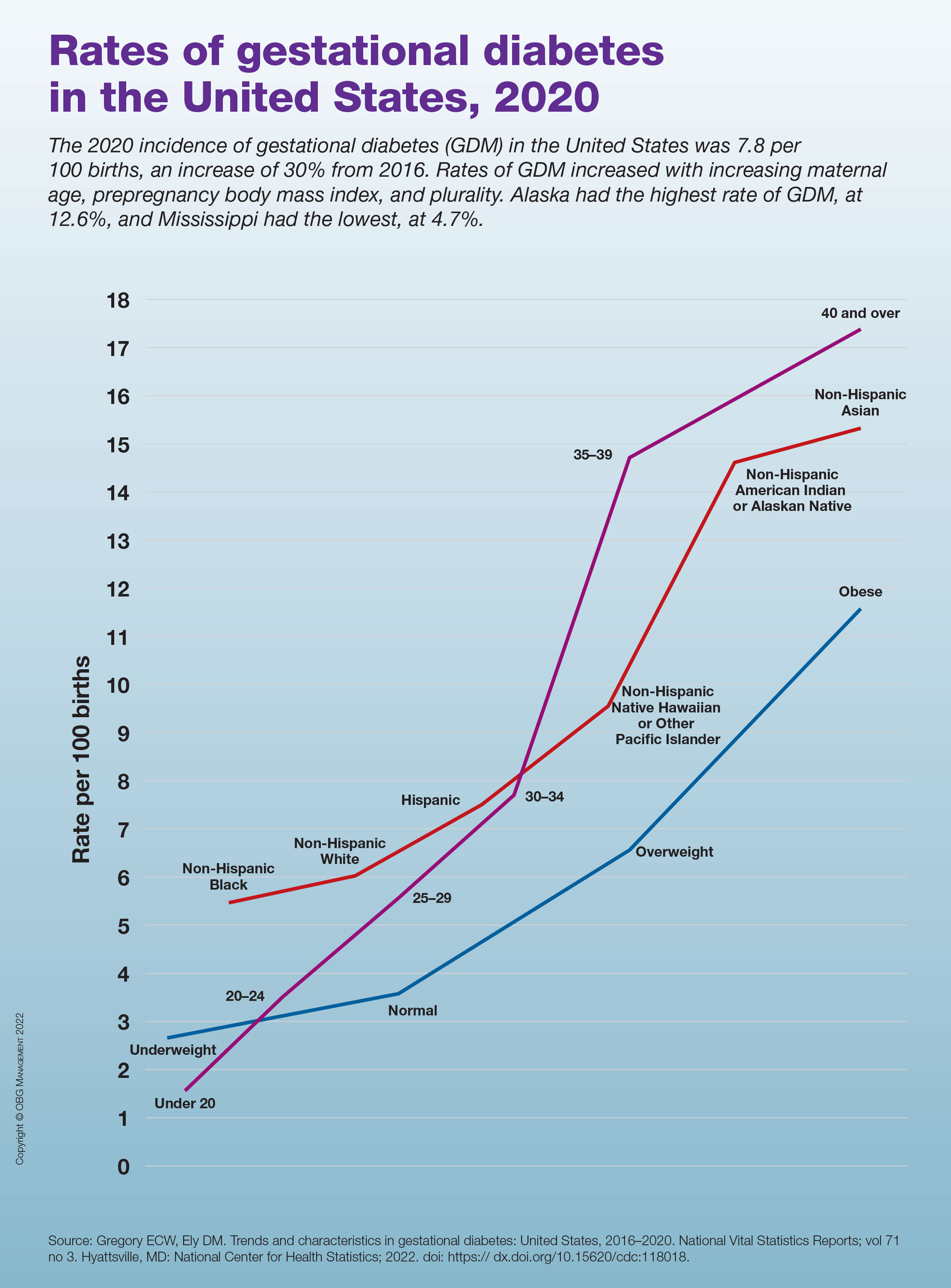
Rates of gestational diabetes in the United States, 2020


Commentary: Menstruation, sleep, and visual disturbances in migraine, October 2022
Lasmiditan—the first migraine treatment in the new ditan class— is a serotonin receptor agonist, similar to triptan medications. However, it is specific for the 5HT1F receptor rather than the 5HT1B/1D receptor. The main purpose of this specificity is that it leads to less vascular risk; specifically, this medication should be safer for populations at higher risk for vascular events, such as myocardial infarction and stroke.
Only one triptan, naratriptan, had previously been studied for the treatment of menstrual migraine, at a recommended dose of 2.5 mg twice daily as a bridge. A new study by MacGregor and colleagues looked at taking 50, 100, or 200 mg of lasmiditan vs placebo for an individual premenstrual attack.
The participants in the study were recruited from the intention-to-treat population of two prior studies for this drug, a phase 2 trial and a phase 3 trial. The menstrual calendars of the female participants were reviewed, followed by randomization into one of the four groups. Patients with chronic migraine were excluded from the study. The primary outcome was freedom from pain at 2 hours; secondary outcomes were freedom from the most bothersome symptom and reduction in pain severity.
Of the four populations followed, all three intervention groups noted significant results in freedom from pain at 2 hours compared with placebo. The 2-hour responder rate was 33.6% for the 200 mg group, 16.7% for the 50 mg and 100 mg groups, and 7.6% for the placebo group. Freedom from the most bothersome symptom and pain reduction were also significant in these populations.
Menstruation-associated migraine and worsening headache attacks due to patients' hormonal fluctuations are some of the most common issues and triggers that neurologists and headache specialists confront. Although the responder rates for freedom from pain at 2 hours were not very robust, lasmiditan does appear to be significantly effective in this population, and in those with menstrual triggers specifically. The field of headache medicine would be even better served by additional studies on both preventive and more acute medications in association with hormonal triggers.
Another very common trigger for migraine is changes in sleep patterns. An astute headache specialist will always ask about sleep quantity and quality during an initial assessment of a patient. Many headache centers have sleep-specific questionnaires that patients fill out during intake. The precise association between migraine and sleep deserves more elucidation. Duan and colleagues specifically set out to reveal whether differences in sleep quality affect migraine frequency; whether this is the same among different gender and age groups; and whether headache disability, severity, mood, and quality of life are related to underlying sleep changes independent of other factors.
A total of 134 participants with migraine and 70 without migraine or any other headache disorder were enrolled in the study. Sleep quality was assessed through The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) questionnaire. This is a commonly used self-reported questionnaire for assessing quality and quantity of sleep over the past month and is considered the standard of care in most sleep centers. The investigators here sought to determine the predictive value of the PSQI in regard to migraine. Migraine disability was assessed via the Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) scale as well as the Headache Impact Test (HIT-6). Statistical analysis was performed with logistical regression, t test, and χ2 squared test.
There strongest correlations between poor sleep quality and risk of migraine were found in women, patients over 35 years old, and those with lower education levels. The results revealed that the migraine group had poorer sleep quality, as well as higher anxiety and depression scores, compared with the control group. A low PSQI score (eg, poorer sleep quality) was associated with higher migraine frequency; this was independent of body mass index (BMI), weekly exercise time, and smoking or drinking history. After participants were divided into good and poor sleep quality subgroups, the PSQI score was found to increase the odds ratio of migraine by a factor of 6.
The investigators were able to show the predictive quality of the PSQI score. Worse sleep quality was found to be associated with a higher MIDAS score and HIT-6 score as well as total pain burden, pain severity, decreased quality of life, depression, and anxiety. Although most headache specialists spend a significant amount of time discussing sleep as it relates to migraine, it may be worth considering following a sleep quality scale, such as the PSQI, over time as we monitor our patients. This may allow us to take a more proactive role and be able to prognosticate our patients' migraine journey somewhat better. Although sleep triggers and associations with migraine can be very difficult to discuss and treat, this study very clearly argues for the importance of focusing on sleep with our patients.
Although the most common aura our patients with migraine experience is visual, many patients with migraine will also experience non-aura visual changes. These can range from short-lasting episodes of blurred vision, such as transient visual obscurations, or other transient visual disturbances that do not fit the criteria of aura as defined by the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD).
A prior study by Tsao and colleagues had revealed that almost half of headache patients experienced some headache-related visual change, the most common of which were short-lasting flickering lights or a movable, monochromatic scotoma. As opposed to visual aura, these transient disturbances were shorter in onset and duration and typically occurred during the headache phase of a migraine attack. In the current study, Tsao and colleagues sought to determine whether the presence of these findings was associated with a different headache burden from that typically found in migraine with aura.
The participants in this study were enrolled over a 10-year period from May 2010 to July 2020. They initially underwent a visual phenomenon questionnaire and then a thorough clinical interview to determine their headache diagnosis per ICHD criteria — specifically whether they had an underlying diagnosis of migraine with aura or migraine without aura. Participants were also separately diagnosed with chronic migraine or medication overuse headache. A visual rating scale was used in the initial questionnaires. This scale posed questions about the duration of symptoms; whether the symptoms develop gradually or suddenly; and whether the visual change was a scotoma, zigzag lines, or in a unilateral or bilateral visual field. A prior study by these investigators determined this visual rating scale to be highly sensitive and specific for diagnosing migraine with aura.
Participants were also given the MIDAS questionnaire and were assessed with the HIT-6 scale, a migraine photophobia score, and the Beck Depression Inventory. A total of 12,255 patients were enrolled, 9946 with migraine, who were subdivided on the basis of diagnosis of migraine with or without aura. Blurred vision was the most common visual complaint among all migraine patients. Patients who had transient visual disturbances that did not fit the criteria of migraine with aura were noted to have a statistically significant higher headache frequency, more severe headache-related disability, a higher likelihood of developing medication overuse headache, and a greater incidence of anxiety and depression.
An important distinction that all headache specialists make is whether their patients experience migraine with or without aura. The primary purpose for this distinction is to determine the appropriateness of specific medications (estrogen or vasoconstrictive medications), as migraine aura relates to vascular risk. We usually delve deeply into whether the visual symptoms that our patients experience do or do not fit into the ICHD criteria of migraine aura. We should not discard or think less of non-aura visual disturbances; these authors argue very clearly that these kinds of visual changes can be very relevant prognostically.
Lasmiditan—the first migraine treatment in the new ditan class— is a serotonin receptor agonist, similar to triptan medications. However, it is specific for the 5HT1F receptor rather than the 5HT1B/1D receptor. The main purpose of this specificity is that it leads to less vascular risk; specifically, this medication should be safer for populations at higher risk for vascular events, such as myocardial infarction and stroke.
Only one triptan, naratriptan, had previously been studied for the treatment of menstrual migraine, at a recommended dose of 2.5 mg twice daily as a bridge. A new study by MacGregor and colleagues looked at taking 50, 100, or 200 mg of lasmiditan vs placebo for an individual premenstrual attack.
The participants in the study were recruited from the intention-to-treat population of two prior studies for this drug, a phase 2 trial and a phase 3 trial. The menstrual calendars of the female participants were reviewed, followed by randomization into one of the four groups. Patients with chronic migraine were excluded from the study. The primary outcome was freedom from pain at 2 hours; secondary outcomes were freedom from the most bothersome symptom and reduction in pain severity.
Of the four populations followed, all three intervention groups noted significant results in freedom from pain at 2 hours compared with placebo. The 2-hour responder rate was 33.6% for the 200 mg group, 16.7% for the 50 mg and 100 mg groups, and 7.6% for the placebo group. Freedom from the most bothersome symptom and pain reduction were also significant in these populations.
Menstruation-associated migraine and worsening headache attacks due to patients' hormonal fluctuations are some of the most common issues and triggers that neurologists and headache specialists confront. Although the responder rates for freedom from pain at 2 hours were not very robust, lasmiditan does appear to be significantly effective in this population, and in those with menstrual triggers specifically. The field of headache medicine would be even better served by additional studies on both preventive and more acute medications in association with hormonal triggers.
Another very common trigger for migraine is changes in sleep patterns. An astute headache specialist will always ask about sleep quantity and quality during an initial assessment of a patient. Many headache centers have sleep-specific questionnaires that patients fill out during intake. The precise association between migraine and sleep deserves more elucidation. Duan and colleagues specifically set out to reveal whether differences in sleep quality affect migraine frequency; whether this is the same among different gender and age groups; and whether headache disability, severity, mood, and quality of life are related to underlying sleep changes independent of other factors.
A total of 134 participants with migraine and 70 without migraine or any other headache disorder were enrolled in the study. Sleep quality was assessed through The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) questionnaire. This is a commonly used self-reported questionnaire for assessing quality and quantity of sleep over the past month and is considered the standard of care in most sleep centers. The investigators here sought to determine the predictive value of the PSQI in regard to migraine. Migraine disability was assessed via the Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) scale as well as the Headache Impact Test (HIT-6). Statistical analysis was performed with logistical regression, t test, and χ2 squared test.
There strongest correlations between poor sleep quality and risk of migraine were found in women, patients over 35 years old, and those with lower education levels. The results revealed that the migraine group had poorer sleep quality, as well as higher anxiety and depression scores, compared with the control group. A low PSQI score (eg, poorer sleep quality) was associated with higher migraine frequency; this was independent of body mass index (BMI), weekly exercise time, and smoking or drinking history. After participants were divided into good and poor sleep quality subgroups, the PSQI score was found to increase the odds ratio of migraine by a factor of 6.
The investigators were able to show the predictive quality of the PSQI score. Worse sleep quality was found to be associated with a higher MIDAS score and HIT-6 score as well as total pain burden, pain severity, decreased quality of life, depression, and anxiety. Although most headache specialists spend a significant amount of time discussing sleep as it relates to migraine, it may be worth considering following a sleep quality scale, such as the PSQI, over time as we monitor our patients. This may allow us to take a more proactive role and be able to prognosticate our patients' migraine journey somewhat better. Although sleep triggers and associations with migraine can be very difficult to discuss and treat, this study very clearly argues for the importance of focusing on sleep with our patients.
Although the most common aura our patients with migraine experience is visual, many patients with migraine will also experience non-aura visual changes. These can range from short-lasting episodes of blurred vision, such as transient visual obscurations, or other transient visual disturbances that do not fit the criteria of aura as defined by the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD).
A prior study by Tsao and colleagues had revealed that almost half of headache patients experienced some headache-related visual change, the most common of which were short-lasting flickering lights or a movable, monochromatic scotoma. As opposed to visual aura, these transient disturbances were shorter in onset and duration and typically occurred during the headache phase of a migraine attack. In the current study, Tsao and colleagues sought to determine whether the presence of these findings was associated with a different headache burden from that typically found in migraine with aura.
The participants in this study were enrolled over a 10-year period from May 2010 to July 2020. They initially underwent a visual phenomenon questionnaire and then a thorough clinical interview to determine their headache diagnosis per ICHD criteria — specifically whether they had an underlying diagnosis of migraine with aura or migraine without aura. Participants were also separately diagnosed with chronic migraine or medication overuse headache. A visual rating scale was used in the initial questionnaires. This scale posed questions about the duration of symptoms; whether the symptoms develop gradually or suddenly; and whether the visual change was a scotoma, zigzag lines, or in a unilateral or bilateral visual field. A prior study by these investigators determined this visual rating scale to be highly sensitive and specific for diagnosing migraine with aura.
Participants were also given the MIDAS questionnaire and were assessed with the HIT-6 scale, a migraine photophobia score, and the Beck Depression Inventory. A total of 12,255 patients were enrolled, 9946 with migraine, who were subdivided on the basis of diagnosis of migraine with or without aura. Blurred vision was the most common visual complaint among all migraine patients. Patients who had transient visual disturbances that did not fit the criteria of migraine with aura were noted to have a statistically significant higher headache frequency, more severe headache-related disability, a higher likelihood of developing medication overuse headache, and a greater incidence of anxiety and depression.
An important distinction that all headache specialists make is whether their patients experience migraine with or without aura. The primary purpose for this distinction is to determine the appropriateness of specific medications (estrogen or vasoconstrictive medications), as migraine aura relates to vascular risk. We usually delve deeply into whether the visual symptoms that our patients experience do or do not fit into the ICHD criteria of migraine aura. We should not discard or think less of non-aura visual disturbances; these authors argue very clearly that these kinds of visual changes can be very relevant prognostically.
Lasmiditan—the first migraine treatment in the new ditan class— is a serotonin receptor agonist, similar to triptan medications. However, it is specific for the 5HT1F receptor rather than the 5HT1B/1D receptor. The main purpose of this specificity is that it leads to less vascular risk; specifically, this medication should be safer for populations at higher risk for vascular events, such as myocardial infarction and stroke.
Only one triptan, naratriptan, had previously been studied for the treatment of menstrual migraine, at a recommended dose of 2.5 mg twice daily as a bridge. A new study by MacGregor and colleagues looked at taking 50, 100, or 200 mg of lasmiditan vs placebo for an individual premenstrual attack.
The participants in the study were recruited from the intention-to-treat population of two prior studies for this drug, a phase 2 trial and a phase 3 trial. The menstrual calendars of the female participants were reviewed, followed by randomization into one of the four groups. Patients with chronic migraine were excluded from the study. The primary outcome was freedom from pain at 2 hours; secondary outcomes were freedom from the most bothersome symptom and reduction in pain severity.
Of the four populations followed, all three intervention groups noted significant results in freedom from pain at 2 hours compared with placebo. The 2-hour responder rate was 33.6% for the 200 mg group, 16.7% for the 50 mg and 100 mg groups, and 7.6% for the placebo group. Freedom from the most bothersome symptom and pain reduction were also significant in these populations.
Menstruation-associated migraine and worsening headache attacks due to patients' hormonal fluctuations are some of the most common issues and triggers that neurologists and headache specialists confront. Although the responder rates for freedom from pain at 2 hours were not very robust, lasmiditan does appear to be significantly effective in this population, and in those with menstrual triggers specifically. The field of headache medicine would be even better served by additional studies on both preventive and more acute medications in association with hormonal triggers.
Another very common trigger for migraine is changes in sleep patterns. An astute headache specialist will always ask about sleep quantity and quality during an initial assessment of a patient. Many headache centers have sleep-specific questionnaires that patients fill out during intake. The precise association between migraine and sleep deserves more elucidation. Duan and colleagues specifically set out to reveal whether differences in sleep quality affect migraine frequency; whether this is the same among different gender and age groups; and whether headache disability, severity, mood, and quality of life are related to underlying sleep changes independent of other factors.
A total of 134 participants with migraine and 70 without migraine or any other headache disorder were enrolled in the study. Sleep quality was assessed through The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) questionnaire. This is a commonly used self-reported questionnaire for assessing quality and quantity of sleep over the past month and is considered the standard of care in most sleep centers. The investigators here sought to determine the predictive value of the PSQI in regard to migraine. Migraine disability was assessed via the Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) scale as well as the Headache Impact Test (HIT-6). Statistical analysis was performed with logistical regression, t test, and χ2 squared test.
There strongest correlations between poor sleep quality and risk of migraine were found in women, patients over 35 years old, and those with lower education levels. The results revealed that the migraine group had poorer sleep quality, as well as higher anxiety and depression scores, compared with the control group. A low PSQI score (eg, poorer sleep quality) was associated with higher migraine frequency; this was independent of body mass index (BMI), weekly exercise time, and smoking or drinking history. After participants were divided into good and poor sleep quality subgroups, the PSQI score was found to increase the odds ratio of migraine by a factor of 6.
The investigators were able to show the predictive quality of the PSQI score. Worse sleep quality was found to be associated with a higher MIDAS score and HIT-6 score as well as total pain burden, pain severity, decreased quality of life, depression, and anxiety. Although most headache specialists spend a significant amount of time discussing sleep as it relates to migraine, it may be worth considering following a sleep quality scale, such as the PSQI, over time as we monitor our patients. This may allow us to take a more proactive role and be able to prognosticate our patients' migraine journey somewhat better. Although sleep triggers and associations with migraine can be very difficult to discuss and treat, this study very clearly argues for the importance of focusing on sleep with our patients.
Although the most common aura our patients with migraine experience is visual, many patients with migraine will also experience non-aura visual changes. These can range from short-lasting episodes of blurred vision, such as transient visual obscurations, or other transient visual disturbances that do not fit the criteria of aura as defined by the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD).
A prior study by Tsao and colleagues had revealed that almost half of headache patients experienced some headache-related visual change, the most common of which were short-lasting flickering lights or a movable, monochromatic scotoma. As opposed to visual aura, these transient disturbances were shorter in onset and duration and typically occurred during the headache phase of a migraine attack. In the current study, Tsao and colleagues sought to determine whether the presence of these findings was associated with a different headache burden from that typically found in migraine with aura.
The participants in this study were enrolled over a 10-year period from May 2010 to July 2020. They initially underwent a visual phenomenon questionnaire and then a thorough clinical interview to determine their headache diagnosis per ICHD criteria — specifically whether they had an underlying diagnosis of migraine with aura or migraine without aura. Participants were also separately diagnosed with chronic migraine or medication overuse headache. A visual rating scale was used in the initial questionnaires. This scale posed questions about the duration of symptoms; whether the symptoms develop gradually or suddenly; and whether the visual change was a scotoma, zigzag lines, or in a unilateral or bilateral visual field. A prior study by these investigators determined this visual rating scale to be highly sensitive and specific for diagnosing migraine with aura.
Participants were also given the MIDAS questionnaire and were assessed with the HIT-6 scale, a migraine photophobia score, and the Beck Depression Inventory. A total of 12,255 patients were enrolled, 9946 with migraine, who were subdivided on the basis of diagnosis of migraine with or without aura. Blurred vision was the most common visual complaint among all migraine patients. Patients who had transient visual disturbances that did not fit the criteria of migraine with aura were noted to have a statistically significant higher headache frequency, more severe headache-related disability, a higher likelihood of developing medication overuse headache, and a greater incidence of anxiety and depression.
An important distinction that all headache specialists make is whether their patients experience migraine with or without aura. The primary purpose for this distinction is to determine the appropriateness of specific medications (estrogen or vasoconstrictive medications), as migraine aura relates to vascular risk. We usually delve deeply into whether the visual symptoms that our patients experience do or do not fit into the ICHD criteria of migraine aura. We should not discard or think less of non-aura visual disturbances; these authors argue very clearly that these kinds of visual changes can be very relevant prognostically.
Cutaneous Eruption in an Immunocompromised Patient
The Diagnosis: Secondary Syphilis
Histopathology revealed a lichenoid interface dermatitis with psoriasiform hyperplasia (Figure 1A). A single spirochete was identified using immunohistochemical staining (Figure 1B). Laboratory workup revealed positive IgG and IgM treponemal antibodies and reactive rapid plasma reagin titer of 1:2048. A VDRL test performed on a cerebrospinal fluid specimen also was reactive at 1:8. A diagnosis of secondary syphilis with neurologic involvement was made, and the patient was treated with intravenous penicillin G for 14 days. Following treatment, his rapid plasma reagin decreased 4-fold with an improvement in his ocular and cutaneous symptoms.
Mucocutaneus manifestations of secondary syphilis are multitudinous. As in our patient, the classic presentation is a generalized morbilliform and papulosquamous eruption involving the palms (Figure 2) and soles. Split papules at the oral commissures, mucosal patches, and condyloma lata are the characteristic mucosal lesions of secondary syphilis.1 Patchy nonscarring alopecia is not uncommon and can be the only manifestation of secondary syphilis.2 The histopathologic features of secondary syphilis vary depending on the location and type of the skin eruption. Psoriasiform or lichenoid changes commonly occur in the epidermis and dermoepidermal junction.3 The dermal inflammatory patterns that have been described include granulomatous, nodular, and superficial and deep perivascular inflammation. The infiltrate often is composed of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and histocytes. Reactive endothelial cells and perineural plasma cell infiltrates also are common histologic features.3,4 Spirochetes can be identified in most cases using immunohistochemical staining; however, the absence of spirochetes does not exclude syphilis.3 The sensitivity of immunohistochemical staining in secondary syphilis is reported to be 71% to 100% with a very high specificity.5 The treatment for all stages of syphilis is benzathine penicillin G, and the route of administration and duration of treatment depend on the stage of disease.6

A broad differential diagnosis must be considered when encountering skin eruptions in patients with HIV. Psoriasis usually presents as circumscribed erythematous plaques with dry and silvery scaling and a predilection for the extensor surfaces of the limbs, sacrum, scalp, and nails. Nail manifestations include distal onycholysis, irregular pitting, oil spots, salmon patches, and subungual hyperkeratosis. Alopecia occasionally may be seen within scalp lesions7; however, the constellation of alopecia with a moth-eaten appearance, subungual hyperkeratosis, papulosquamous eruption, and split papules was more suggestive of secondary syphilis in our patient. In immunocompromised patients, crusted scabies can be considered for the diagnosis of papulosquamous eruptions involving the palms and soles. It often presents with symmetric, mildly pruritic, psoriasiform dermatitis that favors acral sites, but widespread involvement can be observed.8 Areas of the scalp and face can be affected in infants, elderly patients, and immunocompromised individuals. Unlike in secondary syphilis, patchy alopecia, split papules, and ocular symptoms typically are not observed in scabies.
Sarcoidosis is common in Black individuals, and similar to syphilis, it is considered a great imitator of other dermatologic diseases. Frequently, it presents as redviolaceous papules, nodules, or plaques; however, rare variants including psoriasiform, ichthyosiform, verrucous, and lichenoid skin eruptions can occur. Nail dystrophy, split papules, and alopecia also have been observed.9 Ocular involvement is common and frequently presents as uveitis.10 The pathologic hallmark of sarcoidosis is noncaseating granulomatous inflammation, which also may occur in syphilitic lesions9; however, a papulosquamous eruption involving the palms and soles, positive serology, and the finding of interface lichenoid dermatitis with psoriasiform hyperplasia confirmed the diagnosis of secondary syphilis in our patient. Pityriasis rubra pilaris is a rare papulosquamous disorder that can be associated with HIV (type VI/HIVassociated follicular syndrome). It presents with generalized red-orange keratotic papules and often is associated with acne conglobata, hidradenitis suppurativa, and lichen spinulosus.11 Unlike in secondary syphilis, patchy alopecia, split papules, and ocular symptoms typically are not observed in pityriasis rubra pilaris.
This case highlights many classical findings of secondary syphilis and demonstrates that, while helpful, routine skin biopsy may not be required. Treatment should be guided by clinical presentation and serologic testing while reserving skin biopsy for equivocal cases.
- Forrestel AK, Kovarik CL, Katz KA. Sexually acquired syphilis: historical aspects, microbiology, epidemiology, and clinical manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1-14.
- Balagula Y, Mattei PL, Wisco OJ, et al. The great imitator revisited: the spectrum of atypical cutaneous manifestations of secondary syphilis. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1434-1441.
- Hoang MP, High WA, Molberg KH. Secondary syphilis: a histologic and immunohistochemical evaluation. J Cutan Pathol. 2004; 31:595-599.
- Flamm A, Parikh K, Xie Q, et al. Histologic features of secondary syphilis: a multicenter retrospective review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:1025-1030.
- Forrestel AK, Kovarik CL, Katz KA. Sexually acquired syphilis: laboratory diagnosis, management, and prevention [published online February 8, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:17-28.
- Ghanem KG, Ram S, Rice PA. The modern epidemic of syphilis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:845-854.
- Boehncke WH, Schön MP. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2015;386:983-994.
- Karthikeyan K. Crusted scabies. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75:340-347.
- Haimovic A, Sanchez M, Judson MA, et al. Sarcoidosis: a comprehensive review and update for the dermatologist: part I. cutaneous disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:699.e1-718.
- Haimovic A, Sanchez M, Judson MA, et al. Sarcoidosis: a comprehensive review and update for the dermatologist: part II. extracutaneous disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:719.e1-730.
- Miralles E, Núñez M, De Las Heras M, et al. Pityriasis rubra pilaris and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Br J Dermatol. 1995;133:990-993.
The Diagnosis: Secondary Syphilis
Histopathology revealed a lichenoid interface dermatitis with psoriasiform hyperplasia (Figure 1A). A single spirochete was identified using immunohistochemical staining (Figure 1B). Laboratory workup revealed positive IgG and IgM treponemal antibodies and reactive rapid plasma reagin titer of 1:2048. A VDRL test performed on a cerebrospinal fluid specimen also was reactive at 1:8. A diagnosis of secondary syphilis with neurologic involvement was made, and the patient was treated with intravenous penicillin G for 14 days. Following treatment, his rapid plasma reagin decreased 4-fold with an improvement in his ocular and cutaneous symptoms.

Mucocutaneus manifestations of secondary syphilis are multitudinous. As in our patient, the classic presentation is a generalized morbilliform and papulosquamous eruption involving the palms (Figure 2) and soles. Split papules at the oral commissures, mucosal patches, and condyloma lata are the characteristic mucosal lesions of secondary syphilis.1 Patchy nonscarring alopecia is not uncommon and can be the only manifestation of secondary syphilis.2 The histopathologic features of secondary syphilis vary depending on the location and type of the skin eruption. Psoriasiform or lichenoid changes commonly occur in the epidermis and dermoepidermal junction.3 The dermal inflammatory patterns that have been described include granulomatous, nodular, and superficial and deep perivascular inflammation. The infiltrate often is composed of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and histocytes. Reactive endothelial cells and perineural plasma cell infiltrates also are common histologic features.3,4 Spirochetes can be identified in most cases using immunohistochemical staining; however, the absence of spirochetes does not exclude syphilis.3 The sensitivity of immunohistochemical staining in secondary syphilis is reported to be 71% to 100% with a very high specificity.5 The treatment for all stages of syphilis is benzathine penicillin G, and the route of administration and duration of treatment depend on the stage of disease.6

A broad differential diagnosis must be considered when encountering skin eruptions in patients with HIV. Psoriasis usually presents as circumscribed erythematous plaques with dry and silvery scaling and a predilection for the extensor surfaces of the limbs, sacrum, scalp, and nails. Nail manifestations include distal onycholysis, irregular pitting, oil spots, salmon patches, and subungual hyperkeratosis. Alopecia occasionally may be seen within scalp lesions7; however, the constellation of alopecia with a moth-eaten appearance, subungual hyperkeratosis, papulosquamous eruption, and split papules was more suggestive of secondary syphilis in our patient. In immunocompromised patients, crusted scabies can be considered for the diagnosis of papulosquamous eruptions involving the palms and soles. It often presents with symmetric, mildly pruritic, psoriasiform dermatitis that favors acral sites, but widespread involvement can be observed.8 Areas of the scalp and face can be affected in infants, elderly patients, and immunocompromised individuals. Unlike in secondary syphilis, patchy alopecia, split papules, and ocular symptoms typically are not observed in scabies.
Sarcoidosis is common in Black individuals, and similar to syphilis, it is considered a great imitator of other dermatologic diseases. Frequently, it presents as redviolaceous papules, nodules, or plaques; however, rare variants including psoriasiform, ichthyosiform, verrucous, and lichenoid skin eruptions can occur. Nail dystrophy, split papules, and alopecia also have been observed.9 Ocular involvement is common and frequently presents as uveitis.10 The pathologic hallmark of sarcoidosis is noncaseating granulomatous inflammation, which also may occur in syphilitic lesions9; however, a papulosquamous eruption involving the palms and soles, positive serology, and the finding of interface lichenoid dermatitis with psoriasiform hyperplasia confirmed the diagnosis of secondary syphilis in our patient. Pityriasis rubra pilaris is a rare papulosquamous disorder that can be associated with HIV (type VI/HIVassociated follicular syndrome). It presents with generalized red-orange keratotic papules and often is associated with acne conglobata, hidradenitis suppurativa, and lichen spinulosus.11 Unlike in secondary syphilis, patchy alopecia, split papules, and ocular symptoms typically are not observed in pityriasis rubra pilaris.
This case highlights many classical findings of secondary syphilis and demonstrates that, while helpful, routine skin biopsy may not be required. Treatment should be guided by clinical presentation and serologic testing while reserving skin biopsy for equivocal cases.
The Diagnosis: Secondary Syphilis
Histopathology revealed a lichenoid interface dermatitis with psoriasiform hyperplasia (Figure 1A). A single spirochete was identified using immunohistochemical staining (Figure 1B). Laboratory workup revealed positive IgG and IgM treponemal antibodies and reactive rapid plasma reagin titer of 1:2048. A VDRL test performed on a cerebrospinal fluid specimen also was reactive at 1:8. A diagnosis of secondary syphilis with neurologic involvement was made, and the patient was treated with intravenous penicillin G for 14 days. Following treatment, his rapid plasma reagin decreased 4-fold with an improvement in his ocular and cutaneous symptoms.

Mucocutaneus manifestations of secondary syphilis are multitudinous. As in our patient, the classic presentation is a generalized morbilliform and papulosquamous eruption involving the palms (Figure 2) and soles. Split papules at the oral commissures, mucosal patches, and condyloma lata are the characteristic mucosal lesions of secondary syphilis.1 Patchy nonscarring alopecia is not uncommon and can be the only manifestation of secondary syphilis.2 The histopathologic features of secondary syphilis vary depending on the location and type of the skin eruption. Psoriasiform or lichenoid changes commonly occur in the epidermis and dermoepidermal junction.3 The dermal inflammatory patterns that have been described include granulomatous, nodular, and superficial and deep perivascular inflammation. The infiltrate often is composed of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and histocytes. Reactive endothelial cells and perineural plasma cell infiltrates also are common histologic features.3,4 Spirochetes can be identified in most cases using immunohistochemical staining; however, the absence of spirochetes does not exclude syphilis.3 The sensitivity of immunohistochemical staining in secondary syphilis is reported to be 71% to 100% with a very high specificity.5 The treatment for all stages of syphilis is benzathine penicillin G, and the route of administration and duration of treatment depend on the stage of disease.6

A broad differential diagnosis must be considered when encountering skin eruptions in patients with HIV. Psoriasis usually presents as circumscribed erythematous plaques with dry and silvery scaling and a predilection for the extensor surfaces of the limbs, sacrum, scalp, and nails. Nail manifestations include distal onycholysis, irregular pitting, oil spots, salmon patches, and subungual hyperkeratosis. Alopecia occasionally may be seen within scalp lesions7; however, the constellation of alopecia with a moth-eaten appearance, subungual hyperkeratosis, papulosquamous eruption, and split papules was more suggestive of secondary syphilis in our patient. In immunocompromised patients, crusted scabies can be considered for the diagnosis of papulosquamous eruptions involving the palms and soles. It often presents with symmetric, mildly pruritic, psoriasiform dermatitis that favors acral sites, but widespread involvement can be observed.8 Areas of the scalp and face can be affected in infants, elderly patients, and immunocompromised individuals. Unlike in secondary syphilis, patchy alopecia, split papules, and ocular symptoms typically are not observed in scabies.
Sarcoidosis is common in Black individuals, and similar to syphilis, it is considered a great imitator of other dermatologic diseases. Frequently, it presents as redviolaceous papules, nodules, or plaques; however, rare variants including psoriasiform, ichthyosiform, verrucous, and lichenoid skin eruptions can occur. Nail dystrophy, split papules, and alopecia also have been observed.9 Ocular involvement is common and frequently presents as uveitis.10 The pathologic hallmark of sarcoidosis is noncaseating granulomatous inflammation, which also may occur in syphilitic lesions9; however, a papulosquamous eruption involving the palms and soles, positive serology, and the finding of interface lichenoid dermatitis with psoriasiform hyperplasia confirmed the diagnosis of secondary syphilis in our patient. Pityriasis rubra pilaris is a rare papulosquamous disorder that can be associated with HIV (type VI/HIVassociated follicular syndrome). It presents with generalized red-orange keratotic papules and often is associated with acne conglobata, hidradenitis suppurativa, and lichen spinulosus.11 Unlike in secondary syphilis, patchy alopecia, split papules, and ocular symptoms typically are not observed in pityriasis rubra pilaris.
This case highlights many classical findings of secondary syphilis and demonstrates that, while helpful, routine skin biopsy may not be required. Treatment should be guided by clinical presentation and serologic testing while reserving skin biopsy for equivocal cases.
- Forrestel AK, Kovarik CL, Katz KA. Sexually acquired syphilis: historical aspects, microbiology, epidemiology, and clinical manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1-14.
- Balagula Y, Mattei PL, Wisco OJ, et al. The great imitator revisited: the spectrum of atypical cutaneous manifestations of secondary syphilis. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1434-1441.
- Hoang MP, High WA, Molberg KH. Secondary syphilis: a histologic and immunohistochemical evaluation. J Cutan Pathol. 2004; 31:595-599.
- Flamm A, Parikh K, Xie Q, et al. Histologic features of secondary syphilis: a multicenter retrospective review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:1025-1030.
- Forrestel AK, Kovarik CL, Katz KA. Sexually acquired syphilis: laboratory diagnosis, management, and prevention [published online February 8, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:17-28.
- Ghanem KG, Ram S, Rice PA. The modern epidemic of syphilis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:845-854.
- Boehncke WH, Schön MP. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2015;386:983-994.
- Karthikeyan K. Crusted scabies. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75:340-347.
- Haimovic A, Sanchez M, Judson MA, et al. Sarcoidosis: a comprehensive review and update for the dermatologist: part I. cutaneous disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:699.e1-718.
- Haimovic A, Sanchez M, Judson MA, et al. Sarcoidosis: a comprehensive review and update for the dermatologist: part II. extracutaneous disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:719.e1-730.
- Miralles E, Núñez M, De Las Heras M, et al. Pityriasis rubra pilaris and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Br J Dermatol. 1995;133:990-993.
- Forrestel AK, Kovarik CL, Katz KA. Sexually acquired syphilis: historical aspects, microbiology, epidemiology, and clinical manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:1-14.
- Balagula Y, Mattei PL, Wisco OJ, et al. The great imitator revisited: the spectrum of atypical cutaneous manifestations of secondary syphilis. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1434-1441.
- Hoang MP, High WA, Molberg KH. Secondary syphilis: a histologic and immunohistochemical evaluation. J Cutan Pathol. 2004; 31:595-599.
- Flamm A, Parikh K, Xie Q, et al. Histologic features of secondary syphilis: a multicenter retrospective review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:1025-1030.
- Forrestel AK, Kovarik CL, Katz KA. Sexually acquired syphilis: laboratory diagnosis, management, and prevention [published online February 8, 2020]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:17-28.
- Ghanem KG, Ram S, Rice PA. The modern epidemic of syphilis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:845-854.
- Boehncke WH, Schön MP. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2015;386:983-994.
- Karthikeyan K. Crusted scabies. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75:340-347.
- Haimovic A, Sanchez M, Judson MA, et al. Sarcoidosis: a comprehensive review and update for the dermatologist: part I. cutaneous disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:699.e1-718.
- Haimovic A, Sanchez M, Judson MA, et al. Sarcoidosis: a comprehensive review and update for the dermatologist: part II. extracutaneous disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:719.e1-730.
- Miralles E, Núñez M, De Las Heras M, et al. Pityriasis rubra pilaris and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Br J Dermatol. 1995;133:990-993.
A 29-year-old Black man with long-standing untreated HIV presented with mildly pruritic, scaly plaques on the palms and soles of 2 weeks’ duration. His medical history was notable for primary syphilis treated approximately 1 year prior. A review of symptoms was positive for blurry vision and floaters but negative for constitutional symptoms. Physical examination revealed well-defined scaly plaques over the palms, soles, and elbows with subungual hyperkeratosis. Patches of nonscarring alopecia over the scalp and split papules at the oral commissures also were noted. There were no palpable lymph nodes or genital involvement. Eye examination showed conjunctival injection and 20 cells per field in the vitreous humor. Laboratory evaluation revealed an HIV viral load of 31,623 copies/mL and a CD4 count of 47 cells/μL (reference range, 362–1531 cells/μL). A shave biopsy of the left elbow was performed for histopathologic evaluation.
High Risk of Long COVID Neurologic Sequelae in Veterans
We now know that the effects of COVID-19 don’t always end when the infection seems over. Long COVID—the postacute sequelae—can encompass a wide range of extrapulmonary organ dysfunctions. Most studies on COVID-19 have had follow-ups of 6 months or less with a narrow selection of neurologic outcomes, say Evan Xu, Yan Xie, PhD, and Ziyad Al-Aly, MD of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) St. Louis Health Care System in Missouri. The 12-month study of 11,652,484 people published in Nature Medicine sounds an alert: Get ready to care for more patients with long-term, even chronic, neurologic disorders from migraine to stroke.
The researchers “leveraged the breadth and depth” of the VA’s national health care databases to build 3 groups: 154,068 people who survived the first 30 days of COVID-19; 5,638,795 VA users with no evidence of COVID-19 infection; and 5,859,621 VA users during 2017 (ie, prepandemic). Altogether, the groups corresponded to 14,064,985 person-years of follow-up.
The findings, which the researchers termed robust, revealed substantial risks and burdens beyond the first 30 days of COVID-19 infection, including “an array of neurologic disorders spanning several disease categories.”
Patients were at greater risk for stroke (both ischemic and hemorrhagic), cognition and memory disorders, peripheral nervous system disorders, episodic disorders like migraine and seizures, extrapyramidal and movement disorders, mental health disorders, musculoskeletal disorders, sensory disorders, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and encephalitis or encephalopathy.
The researchers estimated the hazard ratio of any neurological sequelae as 1.42. The risks were elevated even in people who did not require hospitalization during acute COVID-19 and increased according to the care setting of the acute phase of the disease from nonhospitalized to hospitalized and admitted to intensive care.
“Given the colossal scale of the pandemic,” the researchers say, governments and health systems should consider these findings when devising policy for continued management and developing plans for a postpandemic world. Some of the disorders they report on, they note, “are serious chronic conditions that will impact some people for a lifetime.” They point to 2 key findings: first, regardless of age, people with COVID-19 had a higher risk of all the neurologic outcomes examined, and second, the analyses suggest that the effects on risk were stronger in younger adults.
“The effects of these disorders on younger lives are profound and cannot be overstated,” the researchers say. Equally troubling, they note, is the stronger effect of COVID-19 on mental health, musculoskeletal, and episodic disorders in older adults, “highlighting their vulnerability” to these disorders following COVID-19 infection.
“It is imperative,” the researchers conclude, “that we recognize the enormous challenges posed by long COVID and all its downstream long-term consequences” and design capacity planning and clinical care pathways to address the needs of people who make it past the acute phase of COVID-19
We now know that the effects of COVID-19 don’t always end when the infection seems over. Long COVID—the postacute sequelae—can encompass a wide range of extrapulmonary organ dysfunctions. Most studies on COVID-19 have had follow-ups of 6 months or less with a narrow selection of neurologic outcomes, say Evan Xu, Yan Xie, PhD, and Ziyad Al-Aly, MD of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) St. Louis Health Care System in Missouri. The 12-month study of 11,652,484 people published in Nature Medicine sounds an alert: Get ready to care for more patients with long-term, even chronic, neurologic disorders from migraine to stroke.
The researchers “leveraged the breadth and depth” of the VA’s national health care databases to build 3 groups: 154,068 people who survived the first 30 days of COVID-19; 5,638,795 VA users with no evidence of COVID-19 infection; and 5,859,621 VA users during 2017 (ie, prepandemic). Altogether, the groups corresponded to 14,064,985 person-years of follow-up.
The findings, which the researchers termed robust, revealed substantial risks and burdens beyond the first 30 days of COVID-19 infection, including “an array of neurologic disorders spanning several disease categories.”
Patients were at greater risk for stroke (both ischemic and hemorrhagic), cognition and memory disorders, peripheral nervous system disorders, episodic disorders like migraine and seizures, extrapyramidal and movement disorders, mental health disorders, musculoskeletal disorders, sensory disorders, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and encephalitis or encephalopathy.
The researchers estimated the hazard ratio of any neurological sequelae as 1.42. The risks were elevated even in people who did not require hospitalization during acute COVID-19 and increased according to the care setting of the acute phase of the disease from nonhospitalized to hospitalized and admitted to intensive care.
“Given the colossal scale of the pandemic,” the researchers say, governments and health systems should consider these findings when devising policy for continued management and developing plans for a postpandemic world. Some of the disorders they report on, they note, “are serious chronic conditions that will impact some people for a lifetime.” They point to 2 key findings: first, regardless of age, people with COVID-19 had a higher risk of all the neurologic outcomes examined, and second, the analyses suggest that the effects on risk were stronger in younger adults.
“The effects of these disorders on younger lives are profound and cannot be overstated,” the researchers say. Equally troubling, they note, is the stronger effect of COVID-19 on mental health, musculoskeletal, and episodic disorders in older adults, “highlighting their vulnerability” to these disorders following COVID-19 infection.
“It is imperative,” the researchers conclude, “that we recognize the enormous challenges posed by long COVID and all its downstream long-term consequences” and design capacity planning and clinical care pathways to address the needs of people who make it past the acute phase of COVID-19
We now know that the effects of COVID-19 don’t always end when the infection seems over. Long COVID—the postacute sequelae—can encompass a wide range of extrapulmonary organ dysfunctions. Most studies on COVID-19 have had follow-ups of 6 months or less with a narrow selection of neurologic outcomes, say Evan Xu, Yan Xie, PhD, and Ziyad Al-Aly, MD of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) St. Louis Health Care System in Missouri. The 12-month study of 11,652,484 people published in Nature Medicine sounds an alert: Get ready to care for more patients with long-term, even chronic, neurologic disorders from migraine to stroke.
The researchers “leveraged the breadth and depth” of the VA’s national health care databases to build 3 groups: 154,068 people who survived the first 30 days of COVID-19; 5,638,795 VA users with no evidence of COVID-19 infection; and 5,859,621 VA users during 2017 (ie, prepandemic). Altogether, the groups corresponded to 14,064,985 person-years of follow-up.
The findings, which the researchers termed robust, revealed substantial risks and burdens beyond the first 30 days of COVID-19 infection, including “an array of neurologic disorders spanning several disease categories.”
Patients were at greater risk for stroke (both ischemic and hemorrhagic), cognition and memory disorders, peripheral nervous system disorders, episodic disorders like migraine and seizures, extrapyramidal and movement disorders, mental health disorders, musculoskeletal disorders, sensory disorders, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and encephalitis or encephalopathy.
The researchers estimated the hazard ratio of any neurological sequelae as 1.42. The risks were elevated even in people who did not require hospitalization during acute COVID-19 and increased according to the care setting of the acute phase of the disease from nonhospitalized to hospitalized and admitted to intensive care.
“Given the colossal scale of the pandemic,” the researchers say, governments and health systems should consider these findings when devising policy for continued management and developing plans for a postpandemic world. Some of the disorders they report on, they note, “are serious chronic conditions that will impact some people for a lifetime.” They point to 2 key findings: first, regardless of age, people with COVID-19 had a higher risk of all the neurologic outcomes examined, and second, the analyses suggest that the effects on risk were stronger in younger adults.
“The effects of these disorders on younger lives are profound and cannot be overstated,” the researchers say. Equally troubling, they note, is the stronger effect of COVID-19 on mental health, musculoskeletal, and episodic disorders in older adults, “highlighting their vulnerability” to these disorders following COVID-19 infection.
“It is imperative,” the researchers conclude, “that we recognize the enormous challenges posed by long COVID and all its downstream long-term consequences” and design capacity planning and clinical care pathways to address the needs of people who make it past the acute phase of COVID-19
Positive psychiatry: An introduction
Historically, psychology and psychiatry have mostly focused on negative emotions and pathological states. However, during the last few decades, new developments in both disciplines have created novel vistas for a more comprehensive understanding of human behavior.1,2 These developments have taken on the names of positive psychology and positive psychiatry, respectively. Positive psychiatry is the science and practice of psychiatry that focuses on psycho-bio-social study and promotion of well-being and health through enhancement of positive psychosocial factors (eg, resilience, optimism, wisdom, social support) in people with illnesses or disabilities as well as in the community at large.3 This new perspective is aimed at enhancing and enriching psychiatric practice and research rather than replacing our stated aim of providing reliable and valid diagnostic categories along with effective therapeutic interventions.
In this issue of
In Part 1, Boardman et al describe positive psychiatry tools to enhance clinical practice through positive interventions in several categories: adopting a positive orientation, harnessing strengths, mobilizing values, cultivating social connections, and optimizing health habits. The authors show how positive psychiatry aims to create a balance between pathogenesis (the study and understanding of diseases) and salutogenesis (the study and creation of health).4
In Part 2, Rettew discusses applying positive psychiatry principles and practices when working with children, adolescents, and their families. The author demonstrates how the principles and practices associated with positive psychiatry represent a natural and highly needed extension of the traditional work within child and adolescent psychiatry, and not a radical transformation of thought or effort. Rettew provides a case example in which he compares traditional and positive psychiatry approaches.
In Part 3, Oughli et al describe resilience in older adults with late-life depression, its clinical and neurocognitive correlates, and associated neurobiological and immunological biomarkers. The authors also narrate resilience-building interventions such as mind-body therapies, which have been reported to enhance resilience through promoting positive perceptions of various experiences and challenges. Evidence suggests that stress reduction, decreased inflammation, and improved emotional regulation may have direct neuroplastic effects on the brain, resulting in greater resilience.
Finally, in Part 4, Hamid Peseschkian summarizes the ideas and practices of positive psychotherapy (PPT) as practiced in Germany since its introduction by Nossrat Peseschkian in 1977. Based on a resource-oriented conception of human beings, PPT combines humanistic, systemic, psychodynamic, and cognitive-behavioral aspects. This short-term method can be readily understood by patients from diverse cultures and social backgrounds.
Taken together, these articles present recent advances in positive psychiatry, especially from an intervention perspective. This is a timely development in view of the evidence of rising global rates of suicide, substance use, anxiety, depression, and perceived stress. By uniting a positive perspective, along with studying its neurobiological underpinnings, and taking a life-long approach, we can now apply these innovations to children, young adults, and older adults, thus providing clinicians with tools to enhance well-being and promote mental health in people with and without mental or physical illnesses.
1. Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
2. Jeste DV. A fulfilling year of APA presidency: from DSM-5 to positive psychiatry. Am J Psychiatry. 2013;170(10):1102-1105.
3. Jeste DV. Positive psychiatry comes of age. Int Psychogeriatr. 2018;30(12):1735-1738.
4. Mittelmark MB, Sagy S, Eriksson M, et al (eds). The Handbook of Salutogenesis [Internet]. Springer; 2017.
Historically, psychology and psychiatry have mostly focused on negative emotions and pathological states. However, during the last few decades, new developments in both disciplines have created novel vistas for a more comprehensive understanding of human behavior.1,2 These developments have taken on the names of positive psychology and positive psychiatry, respectively. Positive psychiatry is the science and practice of psychiatry that focuses on psycho-bio-social study and promotion of well-being and health through enhancement of positive psychosocial factors (eg, resilience, optimism, wisdom, social support) in people with illnesses or disabilities as well as in the community at large.3 This new perspective is aimed at enhancing and enriching psychiatric practice and research rather than replacing our stated aim of providing reliable and valid diagnostic categories along with effective therapeutic interventions.
In this issue of
In Part 1, Boardman et al describe positive psychiatry tools to enhance clinical practice through positive interventions in several categories: adopting a positive orientation, harnessing strengths, mobilizing values, cultivating social connections, and optimizing health habits. The authors show how positive psychiatry aims to create a balance between pathogenesis (the study and understanding of diseases) and salutogenesis (the study and creation of health).4
In Part 2, Rettew discusses applying positive psychiatry principles and practices when working with children, adolescents, and their families. The author demonstrates how the principles and practices associated with positive psychiatry represent a natural and highly needed extension of the traditional work within child and adolescent psychiatry, and not a radical transformation of thought or effort. Rettew provides a case example in which he compares traditional and positive psychiatry approaches.
In Part 3, Oughli et al describe resilience in older adults with late-life depression, its clinical and neurocognitive correlates, and associated neurobiological and immunological biomarkers. The authors also narrate resilience-building interventions such as mind-body therapies, which have been reported to enhance resilience through promoting positive perceptions of various experiences and challenges. Evidence suggests that stress reduction, decreased inflammation, and improved emotional regulation may have direct neuroplastic effects on the brain, resulting in greater resilience.
Finally, in Part 4, Hamid Peseschkian summarizes the ideas and practices of positive psychotherapy (PPT) as practiced in Germany since its introduction by Nossrat Peseschkian in 1977. Based on a resource-oriented conception of human beings, PPT combines humanistic, systemic, psychodynamic, and cognitive-behavioral aspects. This short-term method can be readily understood by patients from diverse cultures and social backgrounds.
Taken together, these articles present recent advances in positive psychiatry, especially from an intervention perspective. This is a timely development in view of the evidence of rising global rates of suicide, substance use, anxiety, depression, and perceived stress. By uniting a positive perspective, along with studying its neurobiological underpinnings, and taking a life-long approach, we can now apply these innovations to children, young adults, and older adults, thus providing clinicians with tools to enhance well-being and promote mental health in people with and without mental or physical illnesses.
Historically, psychology and psychiatry have mostly focused on negative emotions and pathological states. However, during the last few decades, new developments in both disciplines have created novel vistas for a more comprehensive understanding of human behavior.1,2 These developments have taken on the names of positive psychology and positive psychiatry, respectively. Positive psychiatry is the science and practice of psychiatry that focuses on psycho-bio-social study and promotion of well-being and health through enhancement of positive psychosocial factors (eg, resilience, optimism, wisdom, social support) in people with illnesses or disabilities as well as in the community at large.3 This new perspective is aimed at enhancing and enriching psychiatric practice and research rather than replacing our stated aim of providing reliable and valid diagnostic categories along with effective therapeutic interventions.
In this issue of
In Part 1, Boardman et al describe positive psychiatry tools to enhance clinical practice through positive interventions in several categories: adopting a positive orientation, harnessing strengths, mobilizing values, cultivating social connections, and optimizing health habits. The authors show how positive psychiatry aims to create a balance between pathogenesis (the study and understanding of diseases) and salutogenesis (the study and creation of health).4
In Part 2, Rettew discusses applying positive psychiatry principles and practices when working with children, adolescents, and their families. The author demonstrates how the principles and practices associated with positive psychiatry represent a natural and highly needed extension of the traditional work within child and adolescent psychiatry, and not a radical transformation of thought or effort. Rettew provides a case example in which he compares traditional and positive psychiatry approaches.
In Part 3, Oughli et al describe resilience in older adults with late-life depression, its clinical and neurocognitive correlates, and associated neurobiological and immunological biomarkers. The authors also narrate resilience-building interventions such as mind-body therapies, which have been reported to enhance resilience through promoting positive perceptions of various experiences and challenges. Evidence suggests that stress reduction, decreased inflammation, and improved emotional regulation may have direct neuroplastic effects on the brain, resulting in greater resilience.
Finally, in Part 4, Hamid Peseschkian summarizes the ideas and practices of positive psychotherapy (PPT) as practiced in Germany since its introduction by Nossrat Peseschkian in 1977. Based on a resource-oriented conception of human beings, PPT combines humanistic, systemic, psychodynamic, and cognitive-behavioral aspects. This short-term method can be readily understood by patients from diverse cultures and social backgrounds.
Taken together, these articles present recent advances in positive psychiatry, especially from an intervention perspective. This is a timely development in view of the evidence of rising global rates of suicide, substance use, anxiety, depression, and perceived stress. By uniting a positive perspective, along with studying its neurobiological underpinnings, and taking a life-long approach, we can now apply these innovations to children, young adults, and older adults, thus providing clinicians with tools to enhance well-being and promote mental health in people with and without mental or physical illnesses.
1. Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
2. Jeste DV. A fulfilling year of APA presidency: from DSM-5 to positive psychiatry. Am J Psychiatry. 2013;170(10):1102-1105.
3. Jeste DV. Positive psychiatry comes of age. Int Psychogeriatr. 2018;30(12):1735-1738.
4. Mittelmark MB, Sagy S, Eriksson M, et al (eds). The Handbook of Salutogenesis [Internet]. Springer; 2017.
1. Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
2. Jeste DV. A fulfilling year of APA presidency: from DSM-5 to positive psychiatry. Am J Psychiatry. 2013;170(10):1102-1105.
3. Jeste DV. Positive psychiatry comes of age. Int Psychogeriatr. 2018;30(12):1735-1738.
4. Mittelmark MB, Sagy S, Eriksson M, et al (eds). The Handbook of Salutogenesis [Internet]. Springer; 2017.
Using the tools of positive psychiatry to improve clinical practice
FIRST OF 4 PARTS
What does wellness mean to you? A 2018 survey posed this question to more than 6,000 people living with depression and bipolar disorder. In addition to better treatment and greater understanding of their illnesses, other priorities emerged: a longing for better days, a sense of purpose, and a longing to function well and be happy.1 As one respondent explained, “Wellness means stability; well enough to hold a job, well enough to enjoy activities, well enough to feel joy and hope.” Traditional treatment that focuses on alleviating symptoms may not sufficiently address outcomes patients value. When the focus is primarily deficit-based, clinicians and patients may miss opportunities for optimization and transformation.
Positive psychiatry is the science and practice of psychiatry that seeks to enhance and promote well-being and health through the enhancement of positive psychosocial factors such as resilience, optimism, wisdom, and social support in people with illnesses or disabilities as well as those in the community at large.2 It is based on the principles that there is no health without mental health, and that mental health can improve through preventive, therapeutic, and rehabilitative interventions.3
Positive interventions are defined as “treatment methods or intentional activities that aim to cultivate positive feelings, behaviors, or cognitions.”4 They are evidence-based intentional exercises designed to increase well-being and enhance flourishing. Although positive interventions were originally studied as activities for nonclinical populations and for helping healthy people thrive, they are increasingly being valued for their therapeutic role in treating psychopathology.5 By adding positive interventions to their toolbox, psychiatrists can expand the range of treatment options, better engage patients during the treatment process, and bolster positive mental health.
In this article, we provide practical ways to integrate the tools and principles of positive psychiatry into everyday clinical practice. The goal is to broaden how clinicians think about mental health and therapeutic options and, above all, enhance our patients’ everyday well-being. Teaching patients to adopt a positive orientation, harness strengths, mobilize values, cultivate social connections, and optimize healthy habits are strategies clinicians can apply not only to provide a counterweight to the traditional emphasis on illness, but also to enhance the range and richness of their patients’ everyday experience.
Adopt a positive orientation
When a clinician first meets a patient, “What’s wrong?” is a typical conversation starter, and conversations tend to revolve around problems, failures, and negative experiences. Positive psychiatry posits that there is therapeutic benefit to emphasizing and exploring a patient’s positive emotions, experiences, and aspirations. Questions such as “What was your sense of well-being this week? What is your goal for today’s session? What is your goal for the coming week?” can reorient a session towards an individual’s potential and promote exploration of what’s possible.
To promote a positive orientation, clinicians may consider integrating the Savoring and Three Good Things exercises—2 well-studied interventions—into their repertoire to activate and enhance positive emotional states such as gratitude and joy.6 An example of a Savoring activity is taking a 20-minute daily walk while trying to notice as many positive elements as possible. Similarly, the Three Good Things exercise, in which patients are asked to notice and write down 3 positive events and reflect on why they happened, promotes positive reflection and gratitude. A 14-day daily diary study conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic found that higher levels of gratitude were associated with higher levels of positive affect, lower levels of perceived stress related to COVID-19, and better subjective health.7 In addition to coping with life’s negative events, deliberately enhancing the impact of good things is a positive emotion amplifier. As French writer François de La Rochefoucauld argued, “Happiness does not consist in things themselves but in the relish we have of them.”8
Continue to: Harness strengths
Harness strengths
A growing body of evidence suggests that in addition to focusing on a patient’s chief concern, identifying and cultivating an individual’s signature strengths can mitigate stress and enhance well-being. Signature strengths are positive personality qualities that reflect our core identity and are morally valued. The VIA Character Strengths Survey is the most used and validated psychometric instrument to measure and identify signature strengths such as curiosity, self-regulation, honesty, and teamwork.9
To incorporate this tool into clinical practice, ask patients to complete a strengths survey using a validated assessment tool such as the VIA survey (www.viacharacter.org). After a patient identifies their signature strengths, encourage them to explore and apply these strengths in everyday life and in new ways. In addition to becoming aware of and using their signature strengths, encourage patients to “strengths spot” in others. “What strengths did you notice your coworker, family, or friend using today?” is a potential question to explore with patients. A strengths-based approach may be particularly helpful in uncovering motivation and fully engaging patients in treatment. Moreover, integrating strengths into the typically negatively skewed narrative underscores to patients that therapy isn’t only about untwisting distorted thinking, but also about harnessing one’s strengths, talents, and abilities. Strengths expressed through pragmatic actions can boost coping skills as well as enhance well-being.
Mobilize values
Value affirmation exercises have been shown to generate lasting benefits in creating positive feelings and behaviors.10 Encouraging patients to think about what they genuinely value redirects their gaze towards possibility and diverts self-focus. For instance, ask a patient to identify 2 or 3 values and write about why they are important. By reflecting on their values in writing, they affirm their identity and self-worth, thus creating a virtuous cycle of confidence, effort, and achievement. People who put their values front and center are more attuned to the needs of others as well as their own needs, and they make better connections.11 Including a patient’s values in the treatment plan may increase problem-solving skills, boost motivation, and build better stress management skills.
The “life review” is another intervention that facilitates exploration of a patient’s values. This exercise involves asking patients to recount the story of their life and the experiences that were most meaningful to them. This process allows clinicians to gain a deeper understanding of the patient’s values, which can help guide treatment. Meta-analytic evidence has demonstrated these reminiscence-based interventions have significant effects on well-being.6 As Mahatma Gandhi famously said, “Happiness is when what you think, what you say, and what you do are in harmony.” Creating more overlap between a patient’s values and their everyday actions and behaviors bolsters resilience, buffers against stress, and can restore a healthier self-concept.
Cultivate social connections
Social connection is recognized as a core psychological need and essential for well-being. The opposite of connection—social isolation—has negative effects on overall health, including increases in inflammatory markers, depression rates, and even all-cause mortality.12 A 2015 meta-analytic review demonstrated that loneliness increased the likelihood of mortality by 26%—a similar increase as seen with smoking 15 cigarettes a day.13
Continue to: As with any vital sign...
As with any vital sign, exploring a patient’s number of social contacts, quantity of social visits per week, and quality of relationships is an important indicator of health. Giving patients tools to cultivate social connection and deepen their relationships can enhance therapeutic outcomes. Asking patients to perform acts of kindness is one example of a “social prescription.” Feeding a stranger’s parking meter, picking up litter, helping a friend with a chore, providing a meal to a person in need, and volunteering are potential ways for patients to engage in kind deeds. After each act, encourage the patient to write down what they did and how it made them feel.
“Prescribing” positive communication is another way to enhance a patient’s social connections. For instance, teaching them about active constructive responding (ACR)—responding with enthusiasm when another person shares information or good news—has been shown to strengthen bonds with friends and family.14 Making eye contact, giving the other person one’s full attention, inquiring about details, and responding with enthusiasm and interest are simple ways patients can apply ACR in their daily lives. Counseling a patient on increasing social connections, prescribing connections, and inquiring about quantity and quality of social interactions can help them not only add years to their life but also add health and well-being to those years.
Optimize healthy habits
Mounting research demonstrates that exercise, sleep, and nutrition are important for well-being. Evidence shows that therapeutic lifestyle changes can reduce depressive symptoms and boost positive feelings. Numerous meta-analyses have demonstrated the benefits of sleep and exercise interventions for reducing depressive symptoms in psychiatric patients.15,16 Longitudinal studies have provided evidence that healthy diets increase happiness, even after controlling for potential confounders such as socioeconomic factors.17 Other lifestyle factors—including financial stability, pet ownership, decreased social media use, and spending time in nature—have been shown to contribute to well-being.18
Despite the substantial evidence that lifestyle factors can improve health outcomes, few clinicians ask about, focus on, or promote positive habits.19 Positive psychiatry seeks to reorient clinicians towards lifestyle factors that enhance well-being. Clinicians can deploy a variety of strategies to support patients in making healthy and sustainable changes. Assessing readiness for change, motivational interviewing, setting SMART (specific, measurable, assignable, realistic, and time-related) goals, and referring patients to relevant community resources are ways to encourage and promote therapeutic lifestyle changes. Inquiring about a patient’s typical day—such as how they spend their free time, what they eat, when they go to bed, and how much time they spend outdoors—opens conversations about general well-being and shows the patient that therapy is about the whole person, and not only symptom management. Helping patients have better days can empower them to lead more satisfied lives.20
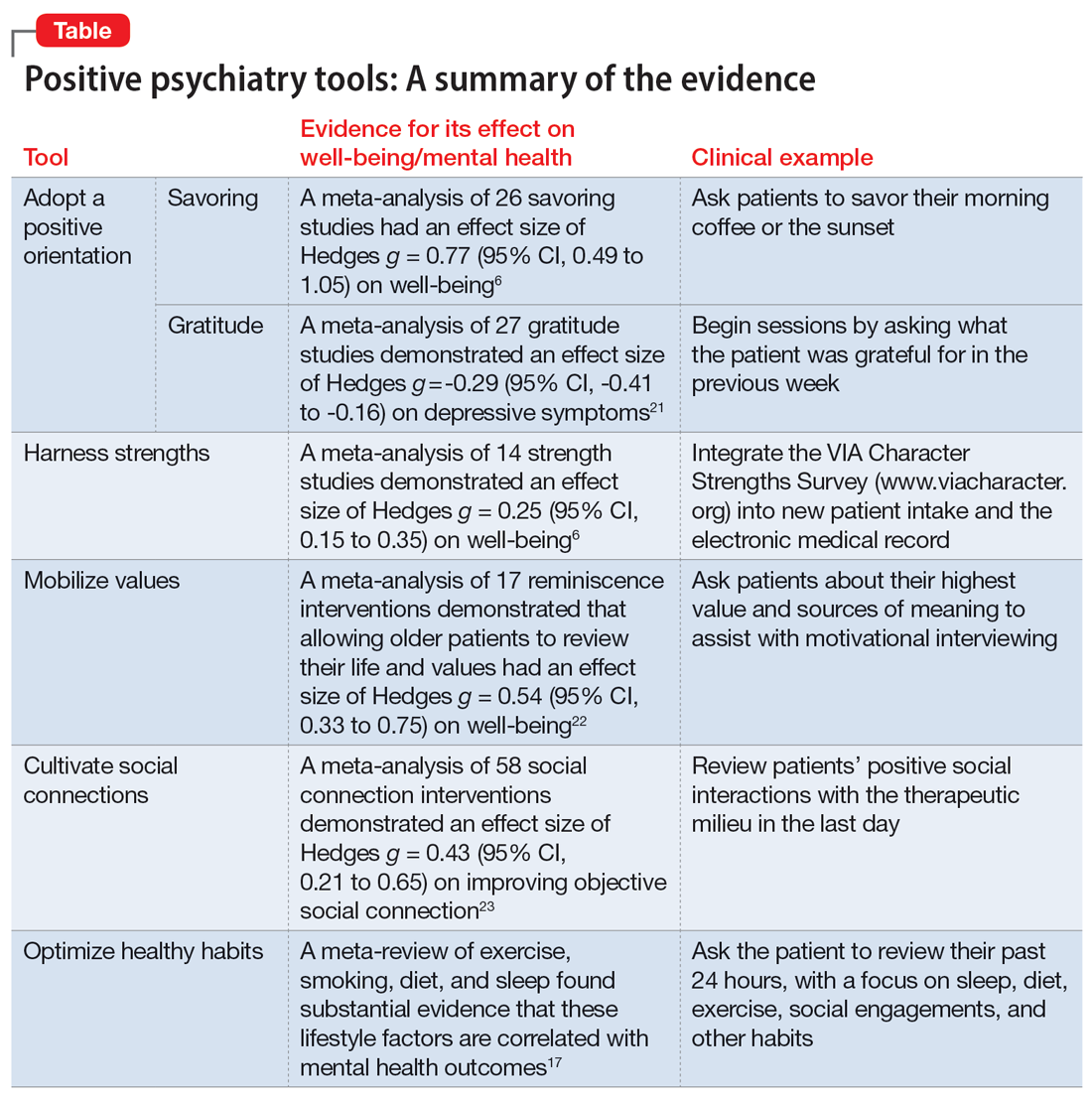
The Table6,17,21-23 summarizes the scientific evidence for the strategies described in this article. The Figure provides a flowchart for using these strategies in clinical practice.
Continue to: Balancing pathogenesis with salutogenesis
Balancing pathogenesis with salutogenesis
By exploring and emphasizing potential and possibility, positive psychiatry aims to create a balance between pathogenesis (the study and understanding of disease) with salutogenesis (the study and creation of health24). Clinicians are well positioned to manage symptoms and bolster positive states. Rather than an either/or approach to well-being, positive psychiatry strives for a both/and approach to well-being. By adding positive interventions to their toolbox, clinicians can expand the range of treatment options, better engage patients in the treatment process, and bolster mental health.
Bottom Line
Clinicians can integrate the tools and principles of positive psychiatry into clinical practice. Teaching patients to adopt a positive orientation, harness strengths, mobilize values, cultivate social connections, and optimize healthy habits can not only provide a counterweight to the traditional emphasis on illness, but also can enhance the range and richness of patients’ everyday experience.
Related Resources
- University of Pennsylvania. Authentic happiness. https://www.authentichappiness.sas.upenn.edu
- Jeste DV, Palmer BW (eds). Positive Psychiatry: A Clinical Handbook. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2015.
- Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
1. Morton E, Foxworth P, Dardess P, et al. “Supporting Wellness”: a depression and bipolar support alliance mixed-methods investigation of lived experience perspectives and priorities for mood disorder treatment. J Affect Disord. 2022;299:575-584.
2. Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
3. Jeste DV. Positive psychiatry comes of age. Int Psychogeriatr. 2018;30(12):1735-1738.
4. Sin NL, Lyubomirsky S. Enhancing well-being and alleviating depressive symptoms with positive psychology interventions: a practice-friendly meta-analysis. J Clin Psychol. 2009;65(5):467-487.
5. Seligman MEP, Rashid T, Parks AC. Positive psychotherapy. Am Psychol. 2006;61(8):774-788.
6. Carr A, Cullen K, Keeney C, et al. Effectiveness of positive psychology interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Posit Psychol. 2021;16(6):749-769.
7. Jiang D. Feeling gratitude is associated with better well-being across the life span: a daily diary study during the COVID-19 outbreak. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2022;77(4):e36-e45.
8. de La Rochefoucauld F. Maxims and moral reflections (1796). Gale ECCO: 2010.
9. Niemiec RM. VIA character strengths: Research and practice (The first 10 years). In: Knoop HH, Fave AD (eds). Well-being and Cultures. Springer;2013:11-29.
10. Cohen GL, Sherman DK. The psychology of change: self-affirmation and social psychological intervention. Annu Rev Psychol. 2014;65:333-371.
11. Thomaes S, Bushman BJ, de Castro BO, et al. Arousing “gentle passions” in young adolescents: sustained experimental effects of value affirmations on prosocial feelings and behaviors. Dev Psychol. 2012;48(1):103-110.
12. Cacioppo JT, Cacioppo S, Capitanio JP, et al. The neuroendocrinology of social isolation. Annu Rev Psychol. 2015;66:733-767.
13. Holt-Lunstad J, Smith TB, Baker M, et al. Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for mortality: a meta-analytic review. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2015;10(2):227-237.
14. Gable SL, Reis HT, Impett EA, et al. What do you do when things go right? The intrapersonal and interpersonal benefits of sharing positive events. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2004;87(2):228-245.
15. Gee B, Orchard F, Clarke E, et al. The effect of non-pharmacological sleep interventions on depression symptoms: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sleep Med Rev. 2019;43:118-128.
16. Krogh J, Hjorthøj C, Speyer H, et al. Exercise for patients with major depression: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. BMJ Open. 2017;7(9):e014820. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014820
17. Firth J, Solmi M, Wootton RE, et al. A meta-review of “lifestyle psychiatry”: the role of exercise, smoking, diet and sleep in the prevention and treatment of mental disorders. World Psychiatry. 2020;19(3):360-380.
18. Piotrowski MC, Lunsford J, Gaynes BN. Lifestyle psychiatry for depression and anxiety: beyond diet and exercise. Lifestyle Med. 2021;2(1):e21. doi:10.1002/lim2.21
19. Janney CA, Brzoznowski KF, Richardson Cret al. Moving towards wellness: physical activity practices, perspectives, and preferences of users of outpatient mental health service. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2017;49:63-66.
20. Walsh R. Lifestyle and mental health. Am Psychol. 2011;66(7):579-592.
21. Cregg DR, Cheavens JS. Gratitude interventions: effective self-help? A meta-analysis of the impact on symptoms of depression and anxiety. J Happiness Stud. 2021;22(1):413-445.
22. Bohlmeijer E, Roemer M, Cuijpers P, et al. The effects of reminiscence on psychological well-being in older adults: a meta-analysis. Aging Ment Health. 2007;11(3):291-300.
23. Zagic D, Wuthrich VM, Rapee RM, et al. Interventions to improve social connections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2022;57(5):885-906.
24. Mittelmark MB, Sagy S, Eriksson M, et al (eds). The Handbook of Salutogenesis [Internet]. Springer; 2017.
FIRST OF 4 PARTS
What does wellness mean to you? A 2018 survey posed this question to more than 6,000 people living with depression and bipolar disorder. In addition to better treatment and greater understanding of their illnesses, other priorities emerged: a longing for better days, a sense of purpose, and a longing to function well and be happy.1 As one respondent explained, “Wellness means stability; well enough to hold a job, well enough to enjoy activities, well enough to feel joy and hope.” Traditional treatment that focuses on alleviating symptoms may not sufficiently address outcomes patients value. When the focus is primarily deficit-based, clinicians and patients may miss opportunities for optimization and transformation.
Positive psychiatry is the science and practice of psychiatry that seeks to enhance and promote well-being and health through the enhancement of positive psychosocial factors such as resilience, optimism, wisdom, and social support in people with illnesses or disabilities as well as those in the community at large.2 It is based on the principles that there is no health without mental health, and that mental health can improve through preventive, therapeutic, and rehabilitative interventions.3
Positive interventions are defined as “treatment methods or intentional activities that aim to cultivate positive feelings, behaviors, or cognitions.”4 They are evidence-based intentional exercises designed to increase well-being and enhance flourishing. Although positive interventions were originally studied as activities for nonclinical populations and for helping healthy people thrive, they are increasingly being valued for their therapeutic role in treating psychopathology.5 By adding positive interventions to their toolbox, psychiatrists can expand the range of treatment options, better engage patients during the treatment process, and bolster positive mental health.
In this article, we provide practical ways to integrate the tools and principles of positive psychiatry into everyday clinical practice. The goal is to broaden how clinicians think about mental health and therapeutic options and, above all, enhance our patients’ everyday well-being. Teaching patients to adopt a positive orientation, harness strengths, mobilize values, cultivate social connections, and optimize healthy habits are strategies clinicians can apply not only to provide a counterweight to the traditional emphasis on illness, but also to enhance the range and richness of their patients’ everyday experience.
Adopt a positive orientation
When a clinician first meets a patient, “What’s wrong?” is a typical conversation starter, and conversations tend to revolve around problems, failures, and negative experiences. Positive psychiatry posits that there is therapeutic benefit to emphasizing and exploring a patient’s positive emotions, experiences, and aspirations. Questions such as “What was your sense of well-being this week? What is your goal for today’s session? What is your goal for the coming week?” can reorient a session towards an individual’s potential and promote exploration of what’s possible.
To promote a positive orientation, clinicians may consider integrating the Savoring and Three Good Things exercises—2 well-studied interventions—into their repertoire to activate and enhance positive emotional states such as gratitude and joy.6 An example of a Savoring activity is taking a 20-minute daily walk while trying to notice as many positive elements as possible. Similarly, the Three Good Things exercise, in which patients are asked to notice and write down 3 positive events and reflect on why they happened, promotes positive reflection and gratitude. A 14-day daily diary study conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic found that higher levels of gratitude were associated with higher levels of positive affect, lower levels of perceived stress related to COVID-19, and better subjective health.7 In addition to coping with life’s negative events, deliberately enhancing the impact of good things is a positive emotion amplifier. As French writer François de La Rochefoucauld argued, “Happiness does not consist in things themselves but in the relish we have of them.”8
Continue to: Harness strengths
Harness strengths
A growing body of evidence suggests that in addition to focusing on a patient’s chief concern, identifying and cultivating an individual’s signature strengths can mitigate stress and enhance well-being. Signature strengths are positive personality qualities that reflect our core identity and are morally valued. The VIA Character Strengths Survey is the most used and validated psychometric instrument to measure and identify signature strengths such as curiosity, self-regulation, honesty, and teamwork.9
To incorporate this tool into clinical practice, ask patients to complete a strengths survey using a validated assessment tool such as the VIA survey (www.viacharacter.org). After a patient identifies their signature strengths, encourage them to explore and apply these strengths in everyday life and in new ways. In addition to becoming aware of and using their signature strengths, encourage patients to “strengths spot” in others. “What strengths did you notice your coworker, family, or friend using today?” is a potential question to explore with patients. A strengths-based approach may be particularly helpful in uncovering motivation and fully engaging patients in treatment. Moreover, integrating strengths into the typically negatively skewed narrative underscores to patients that therapy isn’t only about untwisting distorted thinking, but also about harnessing one’s strengths, talents, and abilities. Strengths expressed through pragmatic actions can boost coping skills as well as enhance well-being.
Mobilize values
Value affirmation exercises have been shown to generate lasting benefits in creating positive feelings and behaviors.10 Encouraging patients to think about what they genuinely value redirects their gaze towards possibility and diverts self-focus. For instance, ask a patient to identify 2 or 3 values and write about why they are important. By reflecting on their values in writing, they affirm their identity and self-worth, thus creating a virtuous cycle of confidence, effort, and achievement. People who put their values front and center are more attuned to the needs of others as well as their own needs, and they make better connections.11 Including a patient’s values in the treatment plan may increase problem-solving skills, boost motivation, and build better stress management skills.
The “life review” is another intervention that facilitates exploration of a patient’s values. This exercise involves asking patients to recount the story of their life and the experiences that were most meaningful to them. This process allows clinicians to gain a deeper understanding of the patient’s values, which can help guide treatment. Meta-analytic evidence has demonstrated these reminiscence-based interventions have significant effects on well-being.6 As Mahatma Gandhi famously said, “Happiness is when what you think, what you say, and what you do are in harmony.” Creating more overlap between a patient’s values and their everyday actions and behaviors bolsters resilience, buffers against stress, and can restore a healthier self-concept.
Cultivate social connections
Social connection is recognized as a core psychological need and essential for well-being. The opposite of connection—social isolation—has negative effects on overall health, including increases in inflammatory markers, depression rates, and even all-cause mortality.12 A 2015 meta-analytic review demonstrated that loneliness increased the likelihood of mortality by 26%—a similar increase as seen with smoking 15 cigarettes a day.13
Continue to: As with any vital sign...
As with any vital sign, exploring a patient’s number of social contacts, quantity of social visits per week, and quality of relationships is an important indicator of health. Giving patients tools to cultivate social connection and deepen their relationships can enhance therapeutic outcomes. Asking patients to perform acts of kindness is one example of a “social prescription.” Feeding a stranger’s parking meter, picking up litter, helping a friend with a chore, providing a meal to a person in need, and volunteering are potential ways for patients to engage in kind deeds. After each act, encourage the patient to write down what they did and how it made them feel.
“Prescribing” positive communication is another way to enhance a patient’s social connections. For instance, teaching them about active constructive responding (ACR)—responding with enthusiasm when another person shares information or good news—has been shown to strengthen bonds with friends and family.14 Making eye contact, giving the other person one’s full attention, inquiring about details, and responding with enthusiasm and interest are simple ways patients can apply ACR in their daily lives. Counseling a patient on increasing social connections, prescribing connections, and inquiring about quantity and quality of social interactions can help them not only add years to their life but also add health and well-being to those years.
Optimize healthy habits
Mounting research demonstrates that exercise, sleep, and nutrition are important for well-being. Evidence shows that therapeutic lifestyle changes can reduce depressive symptoms and boost positive feelings. Numerous meta-analyses have demonstrated the benefits of sleep and exercise interventions for reducing depressive symptoms in psychiatric patients.15,16 Longitudinal studies have provided evidence that healthy diets increase happiness, even after controlling for potential confounders such as socioeconomic factors.17 Other lifestyle factors—including financial stability, pet ownership, decreased social media use, and spending time in nature—have been shown to contribute to well-being.18
Despite the substantial evidence that lifestyle factors can improve health outcomes, few clinicians ask about, focus on, or promote positive habits.19 Positive psychiatry seeks to reorient clinicians towards lifestyle factors that enhance well-being. Clinicians can deploy a variety of strategies to support patients in making healthy and sustainable changes. Assessing readiness for change, motivational interviewing, setting SMART (specific, measurable, assignable, realistic, and time-related) goals, and referring patients to relevant community resources are ways to encourage and promote therapeutic lifestyle changes. Inquiring about a patient’s typical day—such as how they spend their free time, what they eat, when they go to bed, and how much time they spend outdoors—opens conversations about general well-being and shows the patient that therapy is about the whole person, and not only symptom management. Helping patients have better days can empower them to lead more satisfied lives.20

The Table6,17,21-23 summarizes the scientific evidence for the strategies described in this article. The Figure provides a flowchart for using these strategies in clinical practice.

Continue to: Balancing pathogenesis with salutogenesis
Balancing pathogenesis with salutogenesis
By exploring and emphasizing potential and possibility, positive psychiatry aims to create a balance between pathogenesis (the study and understanding of disease) with salutogenesis (the study and creation of health24). Clinicians are well positioned to manage symptoms and bolster positive states. Rather than an either/or approach to well-being, positive psychiatry strives for a both/and approach to well-being. By adding positive interventions to their toolbox, clinicians can expand the range of treatment options, better engage patients in the treatment process, and bolster mental health.
Bottom Line
Clinicians can integrate the tools and principles of positive psychiatry into clinical practice. Teaching patients to adopt a positive orientation, harness strengths, mobilize values, cultivate social connections, and optimize healthy habits can not only provide a counterweight to the traditional emphasis on illness, but also can enhance the range and richness of patients’ everyday experience.
Related Resources
- University of Pennsylvania. Authentic happiness. https://www.authentichappiness.sas.upenn.edu
- Jeste DV, Palmer BW (eds). Positive Psychiatry: A Clinical Handbook. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2015.
- Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
FIRST OF 4 PARTS
What does wellness mean to you? A 2018 survey posed this question to more than 6,000 people living with depression and bipolar disorder. In addition to better treatment and greater understanding of their illnesses, other priorities emerged: a longing for better days, a sense of purpose, and a longing to function well and be happy.1 As one respondent explained, “Wellness means stability; well enough to hold a job, well enough to enjoy activities, well enough to feel joy and hope.” Traditional treatment that focuses on alleviating symptoms may not sufficiently address outcomes patients value. When the focus is primarily deficit-based, clinicians and patients may miss opportunities for optimization and transformation.
Positive psychiatry is the science and practice of psychiatry that seeks to enhance and promote well-being and health through the enhancement of positive psychosocial factors such as resilience, optimism, wisdom, and social support in people with illnesses or disabilities as well as those in the community at large.2 It is based on the principles that there is no health without mental health, and that mental health can improve through preventive, therapeutic, and rehabilitative interventions.3
Positive interventions are defined as “treatment methods or intentional activities that aim to cultivate positive feelings, behaviors, or cognitions.”4 They are evidence-based intentional exercises designed to increase well-being and enhance flourishing. Although positive interventions were originally studied as activities for nonclinical populations and for helping healthy people thrive, they are increasingly being valued for their therapeutic role in treating psychopathology.5 By adding positive interventions to their toolbox, psychiatrists can expand the range of treatment options, better engage patients during the treatment process, and bolster positive mental health.
In this article, we provide practical ways to integrate the tools and principles of positive psychiatry into everyday clinical practice. The goal is to broaden how clinicians think about mental health and therapeutic options and, above all, enhance our patients’ everyday well-being. Teaching patients to adopt a positive orientation, harness strengths, mobilize values, cultivate social connections, and optimize healthy habits are strategies clinicians can apply not only to provide a counterweight to the traditional emphasis on illness, but also to enhance the range and richness of their patients’ everyday experience.
Adopt a positive orientation
When a clinician first meets a patient, “What’s wrong?” is a typical conversation starter, and conversations tend to revolve around problems, failures, and negative experiences. Positive psychiatry posits that there is therapeutic benefit to emphasizing and exploring a patient’s positive emotions, experiences, and aspirations. Questions such as “What was your sense of well-being this week? What is your goal for today’s session? What is your goal for the coming week?” can reorient a session towards an individual’s potential and promote exploration of what’s possible.
To promote a positive orientation, clinicians may consider integrating the Savoring and Three Good Things exercises—2 well-studied interventions—into their repertoire to activate and enhance positive emotional states such as gratitude and joy.6 An example of a Savoring activity is taking a 20-minute daily walk while trying to notice as many positive elements as possible. Similarly, the Three Good Things exercise, in which patients are asked to notice and write down 3 positive events and reflect on why they happened, promotes positive reflection and gratitude. A 14-day daily diary study conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic found that higher levels of gratitude were associated with higher levels of positive affect, lower levels of perceived stress related to COVID-19, and better subjective health.7 In addition to coping with life’s negative events, deliberately enhancing the impact of good things is a positive emotion amplifier. As French writer François de La Rochefoucauld argued, “Happiness does not consist in things themselves but in the relish we have of them.”8
Continue to: Harness strengths
Harness strengths
A growing body of evidence suggests that in addition to focusing on a patient’s chief concern, identifying and cultivating an individual’s signature strengths can mitigate stress and enhance well-being. Signature strengths are positive personality qualities that reflect our core identity and are morally valued. The VIA Character Strengths Survey is the most used and validated psychometric instrument to measure and identify signature strengths such as curiosity, self-regulation, honesty, and teamwork.9
To incorporate this tool into clinical practice, ask patients to complete a strengths survey using a validated assessment tool such as the VIA survey (www.viacharacter.org). After a patient identifies their signature strengths, encourage them to explore and apply these strengths in everyday life and in new ways. In addition to becoming aware of and using their signature strengths, encourage patients to “strengths spot” in others. “What strengths did you notice your coworker, family, or friend using today?” is a potential question to explore with patients. A strengths-based approach may be particularly helpful in uncovering motivation and fully engaging patients in treatment. Moreover, integrating strengths into the typically negatively skewed narrative underscores to patients that therapy isn’t only about untwisting distorted thinking, but also about harnessing one’s strengths, talents, and abilities. Strengths expressed through pragmatic actions can boost coping skills as well as enhance well-being.
Mobilize values
Value affirmation exercises have been shown to generate lasting benefits in creating positive feelings and behaviors.10 Encouraging patients to think about what they genuinely value redirects their gaze towards possibility and diverts self-focus. For instance, ask a patient to identify 2 or 3 values and write about why they are important. By reflecting on their values in writing, they affirm their identity and self-worth, thus creating a virtuous cycle of confidence, effort, and achievement. People who put their values front and center are more attuned to the needs of others as well as their own needs, and they make better connections.11 Including a patient’s values in the treatment plan may increase problem-solving skills, boost motivation, and build better stress management skills.
The “life review” is another intervention that facilitates exploration of a patient’s values. This exercise involves asking patients to recount the story of their life and the experiences that were most meaningful to them. This process allows clinicians to gain a deeper understanding of the patient’s values, which can help guide treatment. Meta-analytic evidence has demonstrated these reminiscence-based interventions have significant effects on well-being.6 As Mahatma Gandhi famously said, “Happiness is when what you think, what you say, and what you do are in harmony.” Creating more overlap between a patient’s values and their everyday actions and behaviors bolsters resilience, buffers against stress, and can restore a healthier self-concept.
Cultivate social connections
Social connection is recognized as a core psychological need and essential for well-being. The opposite of connection—social isolation—has negative effects on overall health, including increases in inflammatory markers, depression rates, and even all-cause mortality.12 A 2015 meta-analytic review demonstrated that loneliness increased the likelihood of mortality by 26%—a similar increase as seen with smoking 15 cigarettes a day.13
Continue to: As with any vital sign...
As with any vital sign, exploring a patient’s number of social contacts, quantity of social visits per week, and quality of relationships is an important indicator of health. Giving patients tools to cultivate social connection and deepen their relationships can enhance therapeutic outcomes. Asking patients to perform acts of kindness is one example of a “social prescription.” Feeding a stranger’s parking meter, picking up litter, helping a friend with a chore, providing a meal to a person in need, and volunteering are potential ways for patients to engage in kind deeds. After each act, encourage the patient to write down what they did and how it made them feel.
“Prescribing” positive communication is another way to enhance a patient’s social connections. For instance, teaching them about active constructive responding (ACR)—responding with enthusiasm when another person shares information or good news—has been shown to strengthen bonds with friends and family.14 Making eye contact, giving the other person one’s full attention, inquiring about details, and responding with enthusiasm and interest are simple ways patients can apply ACR in their daily lives. Counseling a patient on increasing social connections, prescribing connections, and inquiring about quantity and quality of social interactions can help them not only add years to their life but also add health and well-being to those years.
Optimize healthy habits
Mounting research demonstrates that exercise, sleep, and nutrition are important for well-being. Evidence shows that therapeutic lifestyle changes can reduce depressive symptoms and boost positive feelings. Numerous meta-analyses have demonstrated the benefits of sleep and exercise interventions for reducing depressive symptoms in psychiatric patients.15,16 Longitudinal studies have provided evidence that healthy diets increase happiness, even after controlling for potential confounders such as socioeconomic factors.17 Other lifestyle factors—including financial stability, pet ownership, decreased social media use, and spending time in nature—have been shown to contribute to well-being.18
Despite the substantial evidence that lifestyle factors can improve health outcomes, few clinicians ask about, focus on, or promote positive habits.19 Positive psychiatry seeks to reorient clinicians towards lifestyle factors that enhance well-being. Clinicians can deploy a variety of strategies to support patients in making healthy and sustainable changes. Assessing readiness for change, motivational interviewing, setting SMART (specific, measurable, assignable, realistic, and time-related) goals, and referring patients to relevant community resources are ways to encourage and promote therapeutic lifestyle changes. Inquiring about a patient’s typical day—such as how they spend their free time, what they eat, when they go to bed, and how much time they spend outdoors—opens conversations about general well-being and shows the patient that therapy is about the whole person, and not only symptom management. Helping patients have better days can empower them to lead more satisfied lives.20

The Table6,17,21-23 summarizes the scientific evidence for the strategies described in this article. The Figure provides a flowchart for using these strategies in clinical practice.

Continue to: Balancing pathogenesis with salutogenesis
Balancing pathogenesis with salutogenesis
By exploring and emphasizing potential and possibility, positive psychiatry aims to create a balance between pathogenesis (the study and understanding of disease) with salutogenesis (the study and creation of health24). Clinicians are well positioned to manage symptoms and bolster positive states. Rather than an either/or approach to well-being, positive psychiatry strives for a both/and approach to well-being. By adding positive interventions to their toolbox, clinicians can expand the range of treatment options, better engage patients in the treatment process, and bolster mental health.
Bottom Line
Clinicians can integrate the tools and principles of positive psychiatry into clinical practice. Teaching patients to adopt a positive orientation, harness strengths, mobilize values, cultivate social connections, and optimize healthy habits can not only provide a counterweight to the traditional emphasis on illness, but also can enhance the range and richness of patients’ everyday experience.
Related Resources
- University of Pennsylvania. Authentic happiness. https://www.authentichappiness.sas.upenn.edu
- Jeste DV, Palmer BW (eds). Positive Psychiatry: A Clinical Handbook. American Psychiatric Publishing; 2015.
- Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
1. Morton E, Foxworth P, Dardess P, et al. “Supporting Wellness”: a depression and bipolar support alliance mixed-methods investigation of lived experience perspectives and priorities for mood disorder treatment. J Affect Disord. 2022;299:575-584.
2. Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
3. Jeste DV. Positive psychiatry comes of age. Int Psychogeriatr. 2018;30(12):1735-1738.
4. Sin NL, Lyubomirsky S. Enhancing well-being and alleviating depressive symptoms with positive psychology interventions: a practice-friendly meta-analysis. J Clin Psychol. 2009;65(5):467-487.
5. Seligman MEP, Rashid T, Parks AC. Positive psychotherapy. Am Psychol. 2006;61(8):774-788.
6. Carr A, Cullen K, Keeney C, et al. Effectiveness of positive psychology interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Posit Psychol. 2021;16(6):749-769.
7. Jiang D. Feeling gratitude is associated with better well-being across the life span: a daily diary study during the COVID-19 outbreak. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2022;77(4):e36-e45.
8. de La Rochefoucauld F. Maxims and moral reflections (1796). Gale ECCO: 2010.
9. Niemiec RM. VIA character strengths: Research and practice (The first 10 years). In: Knoop HH, Fave AD (eds). Well-being and Cultures. Springer;2013:11-29.
10. Cohen GL, Sherman DK. The psychology of change: self-affirmation and social psychological intervention. Annu Rev Psychol. 2014;65:333-371.
11. Thomaes S, Bushman BJ, de Castro BO, et al. Arousing “gentle passions” in young adolescents: sustained experimental effects of value affirmations on prosocial feelings and behaviors. Dev Psychol. 2012;48(1):103-110.
12. Cacioppo JT, Cacioppo S, Capitanio JP, et al. The neuroendocrinology of social isolation. Annu Rev Psychol. 2015;66:733-767.
13. Holt-Lunstad J, Smith TB, Baker M, et al. Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for mortality: a meta-analytic review. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2015;10(2):227-237.
14. Gable SL, Reis HT, Impett EA, et al. What do you do when things go right? The intrapersonal and interpersonal benefits of sharing positive events. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2004;87(2):228-245.
15. Gee B, Orchard F, Clarke E, et al. The effect of non-pharmacological sleep interventions on depression symptoms: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sleep Med Rev. 2019;43:118-128.
16. Krogh J, Hjorthøj C, Speyer H, et al. Exercise for patients with major depression: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. BMJ Open. 2017;7(9):e014820. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014820
17. Firth J, Solmi M, Wootton RE, et al. A meta-review of “lifestyle psychiatry”: the role of exercise, smoking, diet and sleep in the prevention and treatment of mental disorders. World Psychiatry. 2020;19(3):360-380.
18. Piotrowski MC, Lunsford J, Gaynes BN. Lifestyle psychiatry for depression and anxiety: beyond diet and exercise. Lifestyle Med. 2021;2(1):e21. doi:10.1002/lim2.21
19. Janney CA, Brzoznowski KF, Richardson Cret al. Moving towards wellness: physical activity practices, perspectives, and preferences of users of outpatient mental health service. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2017;49:63-66.
20. Walsh R. Lifestyle and mental health. Am Psychol. 2011;66(7):579-592.
21. Cregg DR, Cheavens JS. Gratitude interventions: effective self-help? A meta-analysis of the impact on symptoms of depression and anxiety. J Happiness Stud. 2021;22(1):413-445.
22. Bohlmeijer E, Roemer M, Cuijpers P, et al. The effects of reminiscence on psychological well-being in older adults: a meta-analysis. Aging Ment Health. 2007;11(3):291-300.
23. Zagic D, Wuthrich VM, Rapee RM, et al. Interventions to improve social connections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2022;57(5):885-906.
24. Mittelmark MB, Sagy S, Eriksson M, et al (eds). The Handbook of Salutogenesis [Internet]. Springer; 2017.
1. Morton E, Foxworth P, Dardess P, et al. “Supporting Wellness”: a depression and bipolar support alliance mixed-methods investigation of lived experience perspectives and priorities for mood disorder treatment. J Affect Disord. 2022;299:575-584.
2. Jeste DV, Palmer BW, Rettew DC, et al. Positive psychiatry: its time has come. J Clin Psychiatry. 2015;76(6):675-683.
3. Jeste DV. Positive psychiatry comes of age. Int Psychogeriatr. 2018;30(12):1735-1738.
4. Sin NL, Lyubomirsky S. Enhancing well-being and alleviating depressive symptoms with positive psychology interventions: a practice-friendly meta-analysis. J Clin Psychol. 2009;65(5):467-487.
5. Seligman MEP, Rashid T, Parks AC. Positive psychotherapy. Am Psychol. 2006;61(8):774-788.
6. Carr A, Cullen K, Keeney C, et al. Effectiveness of positive psychology interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Posit Psychol. 2021;16(6):749-769.
7. Jiang D. Feeling gratitude is associated with better well-being across the life span: a daily diary study during the COVID-19 outbreak. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2022;77(4):e36-e45.
8. de La Rochefoucauld F. Maxims and moral reflections (1796). Gale ECCO: 2010.
9. Niemiec RM. VIA character strengths: Research and practice (The first 10 years). In: Knoop HH, Fave AD (eds). Well-being and Cultures. Springer;2013:11-29.
10. Cohen GL, Sherman DK. The psychology of change: self-affirmation and social psychological intervention. Annu Rev Psychol. 2014;65:333-371.
11. Thomaes S, Bushman BJ, de Castro BO, et al. Arousing “gentle passions” in young adolescents: sustained experimental effects of value affirmations on prosocial feelings and behaviors. Dev Psychol. 2012;48(1):103-110.
12. Cacioppo JT, Cacioppo S, Capitanio JP, et al. The neuroendocrinology of social isolation. Annu Rev Psychol. 2015;66:733-767.
13. Holt-Lunstad J, Smith TB, Baker M, et al. Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for mortality: a meta-analytic review. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2015;10(2):227-237.
14. Gable SL, Reis HT, Impett EA, et al. What do you do when things go right? The intrapersonal and interpersonal benefits of sharing positive events. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2004;87(2):228-245.
15. Gee B, Orchard F, Clarke E, et al. The effect of non-pharmacological sleep interventions on depression symptoms: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sleep Med Rev. 2019;43:118-128.
16. Krogh J, Hjorthøj C, Speyer H, et al. Exercise for patients with major depression: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. BMJ Open. 2017;7(9):e014820. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014820
17. Firth J, Solmi M, Wootton RE, et al. A meta-review of “lifestyle psychiatry”: the role of exercise, smoking, diet and sleep in the prevention and treatment of mental disorders. World Psychiatry. 2020;19(3):360-380.
18. Piotrowski MC, Lunsford J, Gaynes BN. Lifestyle psychiatry for depression and anxiety: beyond diet and exercise. Lifestyle Med. 2021;2(1):e21. doi:10.1002/lim2.21
19. Janney CA, Brzoznowski KF, Richardson Cret al. Moving towards wellness: physical activity practices, perspectives, and preferences of users of outpatient mental health service. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2017;49:63-66.
20. Walsh R. Lifestyle and mental health. Am Psychol. 2011;66(7):579-592.
21. Cregg DR, Cheavens JS. Gratitude interventions: effective self-help? A meta-analysis of the impact on symptoms of depression and anxiety. J Happiness Stud. 2021;22(1):413-445.
22. Bohlmeijer E, Roemer M, Cuijpers P, et al. The effects of reminiscence on psychological well-being in older adults: a meta-analysis. Aging Ment Health. 2007;11(3):291-300.
23. Zagic D, Wuthrich VM, Rapee RM, et al. Interventions to improve social connections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2022;57(5):885-906.
24. Mittelmark MB, Sagy S, Eriksson M, et al (eds). The Handbook of Salutogenesis [Internet]. Springer; 2017.
The accelerating societal entropy undermines mental health
According to the second law of thermodynamics, it is inevitable that entropy will continue to increase over time.1 Entropy is a measure of disorder, which can eventuate in chaos and lead to profound uncertainty, with serious psychological consequences.
The increase in entropy is usually gradual. It took hundreds of years for powerful empires and civilizations to collapse and disappear. Inanimate objects such as a house, a piece of furniture, or a piece of equipment eventually deteriorate and break down over time. Tidy offices will become messy, cluttered, and dirty unless attended to regularly. Living organisms, including humans, inevitably undergo an aging process with cellular senescence, atrophy, and loss of cerebral, muscle, and bone tissue, ending in death. Even human relationships will eventually fracture, wither, and end. The passage of time ruthlessly increases the entropy of everything in life. Even the 13-billion-year-old universe, which currently looks formidable and permanent to us, is inexorably expanding and hurtling towards a calamitous end a few billion years from now.
To slow down, halt, or reverse entropy, work and energy must be invested. A house requires regular maintenance for all its components to avoid deteriorating and becoming uninhabitable (very high entropy). Humans require massive amounts of work during fetal life, infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and throughout old age. This includes work by parents, teachers, friends, physicians, farmers, and manufacturers of food, clothing, and sundry supplies, all targeted to maintain an individual and slow the rate of entropy. But death is inevitable as the final stage of human entropy.
The brain is an entropic organ.2 Psychiatric disorders can be conceptualized as a neurobiologic consequence of a major rise in brain entropy. The chaos created by high brain entropy will lead to a disruption of basic mental functions such as thought, mood, affect, impulses, behavior, and cognition. Brain entropy increases can be due to genetics or the environment, but most often are due an interaction of both (G x E).
Societal entropy and our patients
Psychiatric patients are deeply influenced by the context in which they live (society). The entropy of contemporary society is rising at an alarming rate, which means that order is rapidly degenerating into disorder at an unprecedented pace. When the COVID-19 pandemic abruptly emerged in early 2020, it was a major public health shock that drastically changed the lives of all citizens and dramatically increased societal entropy. The pandemic led to lockdowns, fear of death, gut-wrenching uncertainty (especially for a whole year before vaccines were developed, but even after), loss of socialization and sexual intimacy, loss of employment, financial straits, and an inability to access routine medical or surgical procedures. Everyone in society developed anxiety and acute stress reaction, but those with pre-existing psychiatric disorders suffered the most with an intensification of their symptoms.
The unforeseen, sudden, and traumatically life-altering pandemic triggered various degrees of posttraumatic stress disorder across all age groups, and painful death in medically compromised individuals and older adults. Both physical and psychological entropy skyrocketed and the “order” of life as we knew it rapidly disintegrated into shambles and disorder. The abrupt traumatic jolt triggered various degrees of deleterious impacts on the brains of all who experienced it in real time. The rise in the psychobiological entropy was unprecedented across the structures of society, especially the population, its vulnerable human component.
But even as the worst of the pandemic is in our rearview mirror and life again has a semblance of normality, the rise of entropy continues to accelerate because we continue to be surrounded and engulfed by countless stressful events in contemporary society. Those nagging stresses continue to transmute order to chaos and metamorphose comforting predictability to entrenched uncertainty:
- Toxic political hyperpartisanship, with intense animus and visceral bidirectional hatred
- Racial tensions, with overt bias across groups
- Economic turmoil, with inflation and threats of recession
- Actual wars and threats of war
- Social media that spreads bad news and distorts facts
- An opioid crisis, with hundreds of thousands of deaths
- Skyrocketing crime, with a decline in policing and quick release of criminals without bail
- A ruthless and arbitrary “cancel culture” that doesn’t even spare the previously revered founders of the republic
- Cognitive dissonance of disparaging Abraham Lincoln despite his major achievement of eliminating slavery by waging a civil war
- The social and medical strife regarding access to abortion.
Continue to: I also would include...
(I also would include some “entropy pet peeves” of mine: Torn clothes as a fashion statement, transforming tattoos from an oddity to a fad, nose rings that disfigure pretty faces, and banishing neckties for men.)
Our role in this scenario
As psychiatrists, we must step up to intensify the work needed to slow down and even reverse the dangerously rising brain entropy in our patients. But that is not an easy task given the implosion of societal norms and traditional values, along with the radicalization of beliefs, with utter intolerance of others’ beliefs. We also face the challenge of maintaining a modicum of resilience and wellness in ourselves, which can be antidotes to entropy.
It’s impossible to stop the inevitability of rising entropy, both physical and psychological, but psychiatrists and other mental health professionals must invest their skills and talents now more than ever to at least slow down the pace of entropy among our patients. Otherwise, psychological chaos and disorder will be quite damaging to their lives, and worsen their outcomes.
1. Ben-Naim A. Entropy Demystified. World Scientific; 2007.
2. Carhart-Harris RL. The entropic brain - revisited. Neuropharmacology. 2018;142:167-178. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.03.010
According to the second law of thermodynamics, it is inevitable that entropy will continue to increase over time.1 Entropy is a measure of disorder, which can eventuate in chaos and lead to profound uncertainty, with serious psychological consequences.
The increase in entropy is usually gradual. It took hundreds of years for powerful empires and civilizations to collapse and disappear. Inanimate objects such as a house, a piece of furniture, or a piece of equipment eventually deteriorate and break down over time. Tidy offices will become messy, cluttered, and dirty unless attended to regularly. Living organisms, including humans, inevitably undergo an aging process with cellular senescence, atrophy, and loss of cerebral, muscle, and bone tissue, ending in death. Even human relationships will eventually fracture, wither, and end. The passage of time ruthlessly increases the entropy of everything in life. Even the 13-billion-year-old universe, which currently looks formidable and permanent to us, is inexorably expanding and hurtling towards a calamitous end a few billion years from now.
To slow down, halt, or reverse entropy, work and energy must be invested. A house requires regular maintenance for all its components to avoid deteriorating and becoming uninhabitable (very high entropy). Humans require massive amounts of work during fetal life, infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and throughout old age. This includes work by parents, teachers, friends, physicians, farmers, and manufacturers of food, clothing, and sundry supplies, all targeted to maintain an individual and slow the rate of entropy. But death is inevitable as the final stage of human entropy.
The brain is an entropic organ.2 Psychiatric disorders can be conceptualized as a neurobiologic consequence of a major rise in brain entropy. The chaos created by high brain entropy will lead to a disruption of basic mental functions such as thought, mood, affect, impulses, behavior, and cognition. Brain entropy increases can be due to genetics or the environment, but most often are due an interaction of both (G x E).
Societal entropy and our patients
Psychiatric patients are deeply influenced by the context in which they live (society). The entropy of contemporary society is rising at an alarming rate, which means that order is rapidly degenerating into disorder at an unprecedented pace. When the COVID-19 pandemic abruptly emerged in early 2020, it was a major public health shock that drastically changed the lives of all citizens and dramatically increased societal entropy. The pandemic led to lockdowns, fear of death, gut-wrenching uncertainty (especially for a whole year before vaccines were developed, but even after), loss of socialization and sexual intimacy, loss of employment, financial straits, and an inability to access routine medical or surgical procedures. Everyone in society developed anxiety and acute stress reaction, but those with pre-existing psychiatric disorders suffered the most with an intensification of their symptoms.
The unforeseen, sudden, and traumatically life-altering pandemic triggered various degrees of posttraumatic stress disorder across all age groups, and painful death in medically compromised individuals and older adults. Both physical and psychological entropy skyrocketed and the “order” of life as we knew it rapidly disintegrated into shambles and disorder. The abrupt traumatic jolt triggered various degrees of deleterious impacts on the brains of all who experienced it in real time. The rise in the psychobiological entropy was unprecedented across the structures of society, especially the population, its vulnerable human component.
But even as the worst of the pandemic is in our rearview mirror and life again has a semblance of normality, the rise of entropy continues to accelerate because we continue to be surrounded and engulfed by countless stressful events in contemporary society. Those nagging stresses continue to transmute order to chaos and metamorphose comforting predictability to entrenched uncertainty:
- Toxic political hyperpartisanship, with intense animus and visceral bidirectional hatred
- Racial tensions, with overt bias across groups
- Economic turmoil, with inflation and threats of recession
- Actual wars and threats of war
- Social media that spreads bad news and distorts facts
- An opioid crisis, with hundreds of thousands of deaths
- Skyrocketing crime, with a decline in policing and quick release of criminals without bail
- A ruthless and arbitrary “cancel culture” that doesn’t even spare the previously revered founders of the republic
- Cognitive dissonance of disparaging Abraham Lincoln despite his major achievement of eliminating slavery by waging a civil war
- The social and medical strife regarding access to abortion.
Continue to: I also would include...
(I also would include some “entropy pet peeves” of mine: Torn clothes as a fashion statement, transforming tattoos from an oddity to a fad, nose rings that disfigure pretty faces, and banishing neckties for men.)
Our role in this scenario
As psychiatrists, we must step up to intensify the work needed to slow down and even reverse the dangerously rising brain entropy in our patients. But that is not an easy task given the implosion of societal norms and traditional values, along with the radicalization of beliefs, with utter intolerance of others’ beliefs. We also face the challenge of maintaining a modicum of resilience and wellness in ourselves, which can be antidotes to entropy.
It’s impossible to stop the inevitability of rising entropy, both physical and psychological, but psychiatrists and other mental health professionals must invest their skills and talents now more than ever to at least slow down the pace of entropy among our patients. Otherwise, psychological chaos and disorder will be quite damaging to their lives, and worsen their outcomes.
According to the second law of thermodynamics, it is inevitable that entropy will continue to increase over time.1 Entropy is a measure of disorder, which can eventuate in chaos and lead to profound uncertainty, with serious psychological consequences.
The increase in entropy is usually gradual. It took hundreds of years for powerful empires and civilizations to collapse and disappear. Inanimate objects such as a house, a piece of furniture, or a piece of equipment eventually deteriorate and break down over time. Tidy offices will become messy, cluttered, and dirty unless attended to regularly. Living organisms, including humans, inevitably undergo an aging process with cellular senescence, atrophy, and loss of cerebral, muscle, and bone tissue, ending in death. Even human relationships will eventually fracture, wither, and end. The passage of time ruthlessly increases the entropy of everything in life. Even the 13-billion-year-old universe, which currently looks formidable and permanent to us, is inexorably expanding and hurtling towards a calamitous end a few billion years from now.
To slow down, halt, or reverse entropy, work and energy must be invested. A house requires regular maintenance for all its components to avoid deteriorating and becoming uninhabitable (very high entropy). Humans require massive amounts of work during fetal life, infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and throughout old age. This includes work by parents, teachers, friends, physicians, farmers, and manufacturers of food, clothing, and sundry supplies, all targeted to maintain an individual and slow the rate of entropy. But death is inevitable as the final stage of human entropy.
The brain is an entropic organ.2 Psychiatric disorders can be conceptualized as a neurobiologic consequence of a major rise in brain entropy. The chaos created by high brain entropy will lead to a disruption of basic mental functions such as thought, mood, affect, impulses, behavior, and cognition. Brain entropy increases can be due to genetics or the environment, but most often are due an interaction of both (G x E).
Societal entropy and our patients
Psychiatric patients are deeply influenced by the context in which they live (society). The entropy of contemporary society is rising at an alarming rate, which means that order is rapidly degenerating into disorder at an unprecedented pace. When the COVID-19 pandemic abruptly emerged in early 2020, it was a major public health shock that drastically changed the lives of all citizens and dramatically increased societal entropy. The pandemic led to lockdowns, fear of death, gut-wrenching uncertainty (especially for a whole year before vaccines were developed, but even after), loss of socialization and sexual intimacy, loss of employment, financial straits, and an inability to access routine medical or surgical procedures. Everyone in society developed anxiety and acute stress reaction, but those with pre-existing psychiatric disorders suffered the most with an intensification of their symptoms.
The unforeseen, sudden, and traumatically life-altering pandemic triggered various degrees of posttraumatic stress disorder across all age groups, and painful death in medically compromised individuals and older adults. Both physical and psychological entropy skyrocketed and the “order” of life as we knew it rapidly disintegrated into shambles and disorder. The abrupt traumatic jolt triggered various degrees of deleterious impacts on the brains of all who experienced it in real time. The rise in the psychobiological entropy was unprecedented across the structures of society, especially the population, its vulnerable human component.
But even as the worst of the pandemic is in our rearview mirror and life again has a semblance of normality, the rise of entropy continues to accelerate because we continue to be surrounded and engulfed by countless stressful events in contemporary society. Those nagging stresses continue to transmute order to chaos and metamorphose comforting predictability to entrenched uncertainty:
- Toxic political hyperpartisanship, with intense animus and visceral bidirectional hatred
- Racial tensions, with overt bias across groups
- Economic turmoil, with inflation and threats of recession
- Actual wars and threats of war
- Social media that spreads bad news and distorts facts
- An opioid crisis, with hundreds of thousands of deaths
- Skyrocketing crime, with a decline in policing and quick release of criminals without bail
- A ruthless and arbitrary “cancel culture” that doesn’t even spare the previously revered founders of the republic
- Cognitive dissonance of disparaging Abraham Lincoln despite his major achievement of eliminating slavery by waging a civil war
- The social and medical strife regarding access to abortion.
Continue to: I also would include...
(I also would include some “entropy pet peeves” of mine: Torn clothes as a fashion statement, transforming tattoos from an oddity to a fad, nose rings that disfigure pretty faces, and banishing neckties for men.)
Our role in this scenario
As psychiatrists, we must step up to intensify the work needed to slow down and even reverse the dangerously rising brain entropy in our patients. But that is not an easy task given the implosion of societal norms and traditional values, along with the radicalization of beliefs, with utter intolerance of others’ beliefs. We also face the challenge of maintaining a modicum of resilience and wellness in ourselves, which can be antidotes to entropy.
It’s impossible to stop the inevitability of rising entropy, both physical and psychological, but psychiatrists and other mental health professionals must invest their skills and talents now more than ever to at least slow down the pace of entropy among our patients. Otherwise, psychological chaos and disorder will be quite damaging to their lives, and worsen their outcomes.
1. Ben-Naim A. Entropy Demystified. World Scientific; 2007.
2. Carhart-Harris RL. The entropic brain - revisited. Neuropharmacology. 2018;142:167-178. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.03.010
1. Ben-Naim A. Entropy Demystified. World Scientific; 2007.
2. Carhart-Harris RL. The entropic brain - revisited. Neuropharmacology. 2018;142:167-178. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.03.010