User login
For MD-IQ on Family Practice News, but a regular topic for Rheumatology News
Prescription osteoarthritis relief gets OTC approval
The Food and Drug Administration has approved formerly prescription-only Voltaren Arthritis Pain (diclofenac sodium topical gel, 1%) for nonprescription use via a process known as a prescription to over-the-counter (Rx-to-OTC) switch, according to a news release from the agency.
“As a result of the Rx-to-OTC switch process, many products sold over the counter today use ingredients or dosage strengths that were available only by prescription 30 years ago,” Karen Mahoney, MD, acting deputy director of the Office of Nonprescription Drugs in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the release.
This switch to nonprescription status is usually initiated by the manufacturer, who must provide data that demonstrates the drug in question is both safe and effective as self-medication in accordance with the proposed labeling and that consumers can use it safely and effectively without the supervision of a health care professional.
This particular therapy is a topical NSAID gel and was first approved by the FDA in 2007 with the indication for relief of osteoarthritis pain. It can take 7 days to have an effect, but if patients find it takes longer than that or they need to use it for more than 21 days, they should seek medical attention. The gel can cause severe allergic reactions, especially in people allergic to aspirin; patients who experience such reactions are advised to stop use and seek immediate medical care. Other concerns include potential for liver damage with extended use; the possibility of severe stomach bleeds; and risk of heart attack, heart failure, and stroke.
The gel will no longer be available in prescription form.
Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website, as can the full news release regarding this approval.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved formerly prescription-only Voltaren Arthritis Pain (diclofenac sodium topical gel, 1%) for nonprescription use via a process known as a prescription to over-the-counter (Rx-to-OTC) switch, according to a news release from the agency.
“As a result of the Rx-to-OTC switch process, many products sold over the counter today use ingredients or dosage strengths that were available only by prescription 30 years ago,” Karen Mahoney, MD, acting deputy director of the Office of Nonprescription Drugs in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the release.
This switch to nonprescription status is usually initiated by the manufacturer, who must provide data that demonstrates the drug in question is both safe and effective as self-medication in accordance with the proposed labeling and that consumers can use it safely and effectively without the supervision of a health care professional.
This particular therapy is a topical NSAID gel and was first approved by the FDA in 2007 with the indication for relief of osteoarthritis pain. It can take 7 days to have an effect, but if patients find it takes longer than that or they need to use it for more than 21 days, they should seek medical attention. The gel can cause severe allergic reactions, especially in people allergic to aspirin; patients who experience such reactions are advised to stop use and seek immediate medical care. Other concerns include potential for liver damage with extended use; the possibility of severe stomach bleeds; and risk of heart attack, heart failure, and stroke.
The gel will no longer be available in prescription form.
Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website, as can the full news release regarding this approval.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved formerly prescription-only Voltaren Arthritis Pain (diclofenac sodium topical gel, 1%) for nonprescription use via a process known as a prescription to over-the-counter (Rx-to-OTC) switch, according to a news release from the agency.
“As a result of the Rx-to-OTC switch process, many products sold over the counter today use ingredients or dosage strengths that were available only by prescription 30 years ago,” Karen Mahoney, MD, acting deputy director of the Office of Nonprescription Drugs in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the release.
This switch to nonprescription status is usually initiated by the manufacturer, who must provide data that demonstrates the drug in question is both safe and effective as self-medication in accordance with the proposed labeling and that consumers can use it safely and effectively without the supervision of a health care professional.
This particular therapy is a topical NSAID gel and was first approved by the FDA in 2007 with the indication for relief of osteoarthritis pain. It can take 7 days to have an effect, but if patients find it takes longer than that or they need to use it for more than 21 days, they should seek medical attention. The gel can cause severe allergic reactions, especially in people allergic to aspirin; patients who experience such reactions are advised to stop use and seek immediate medical care. Other concerns include potential for liver damage with extended use; the possibility of severe stomach bleeds; and risk of heart attack, heart failure, and stroke.
The gel will no longer be available in prescription form.
Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website, as can the full news release regarding this approval.
Prednisolone scores for hand OA
ATLANTA – Dutch investigators at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology made a good case for 6 weeks of low-dose prednisolone to help people with hand osteoarthritis get over a particularly bad spell.
A total of 42 patients randomized to prednisolone 10 mg/day fell a mean of 21.5 mm at 6 weeks from a baseline visual analog hand pain score of 54 mm (out of a possible 100 mm), versus a drop of 5.2 mm from a baseline score of 53 mm among 46 randomized to placebo; the mean group difference was 16.5 mm. Patients taking prednisolone did better on function, quality of life, and physician global assessments, too.
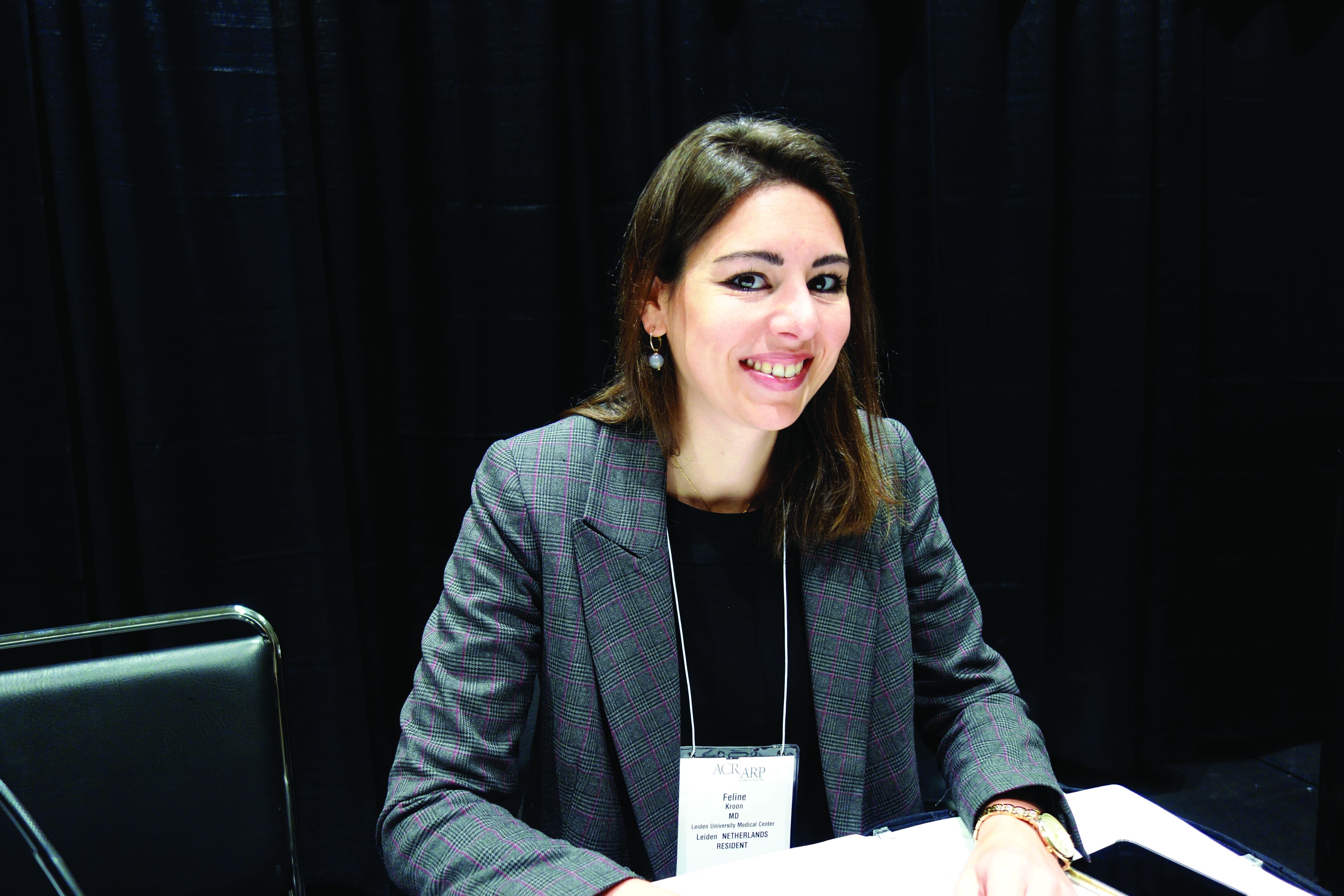
“This trial provides evidence that local inflammation is a suitable target for drug treatment in hand OA. We think this study provides clinicians with a short-term treatment option for patients who have a flare of their disease,” said lead investigator Féline Kroon, MD, a rheumatologist at Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center.
“The large beneficial effect size exceeded that of all available therapeutic options for hand osteoarthritis,” including NSAIDs, she and her team noted in the study write-up, which was published to coincide with the meeting (Lancet. 2019 Nov 30;394[10213]:1993-2001).
Many physicians already use short-course prednisolone for hand OA, but there was no clinical evidence that it helped until now. The study also adds weight to the idea that OA has an inflammatory component – an idea that has been building for a while, Dr. Kroon said.
Leiden investigators and others have previously shown that synovial inflammation is often present in hand OA and a main determinant of pain and radiographic progression.
The 92 patients in the Low-Dose Prednisolone in Patients with Painful Hand Osteoarthritis (HOPE) trial had to have at least four interphalangeal joints (IPJs) with osteoarthritic nodes, at least one IPJ with soft swelling or erythema, and at least one with a positive power Doppler signal or grade 2 or higher synovitis on ultrasound. They also had to have flared at least 20 mm on the pain scale with NSAID washout.
There were more responders in the prednisolone group at 6 weeks (72% versus 33%), and significantly greater improvement in synovial thickening. There was no difference in power Doppler score or synovitis score per joint on MRI, but bone marrow lesions appeared less severe with prednisolone.
All the between-group differences disappeared when prednisolone was tapered after 6 weeks.
Four patients discontinued the study because of an adverse event: a myocardial infarction in the prednisolone group, and, in the control arm, a bowel surgery, an infected leg hematoma, and a case of Lyme arthritis of the knee. Adverse events were otherwise mild and similar in both arms.
The mean age in the study was 64 years, and 79% of the subjects were women. Exclusion criteria included chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases, psoriasis, use of immune-modulating drugs within 90 days of baseline, and predominantly thumb base pain instead of finger pain.
The approach “is for short course. Long-term steroids can have important side effects, like osteoporosis. We do not think this study should be used to encourage prolonged prescribing of glucocorticoids in patients with hand OA,” Dr. Kroon said.
Two previous trials of glucocorticoids for hand OA were inconclusive. A dose of prednisone 5 mg/day for 4 weeks did not separate from placebo in one, and the second showed pain improvements with a combination of prednisolone and dipyridamole versus placebo, but with more adverse events, particularly dipyridamole headaches.
The work was funded by the Dutch Arthritis Society. Dr. Kroon did not have any disclosures.
SOURCE: Kroon F et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 1760.
ATLANTA – Dutch investigators at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology made a good case for 6 weeks of low-dose prednisolone to help people with hand osteoarthritis get over a particularly bad spell.
A total of 42 patients randomized to prednisolone 10 mg/day fell a mean of 21.5 mm at 6 weeks from a baseline visual analog hand pain score of 54 mm (out of a possible 100 mm), versus a drop of 5.2 mm from a baseline score of 53 mm among 46 randomized to placebo; the mean group difference was 16.5 mm. Patients taking prednisolone did better on function, quality of life, and physician global assessments, too.
“This trial provides evidence that local inflammation is a suitable target for drug treatment in hand OA. We think this study provides clinicians with a short-term treatment option for patients who have a flare of their disease,” said lead investigator Féline Kroon, MD, a rheumatologist at Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center.
“The large beneficial effect size exceeded that of all available therapeutic options for hand osteoarthritis,” including NSAIDs, she and her team noted in the study write-up, which was published to coincide with the meeting (Lancet. 2019 Nov 30;394[10213]:1993-2001).
Many physicians already use short-course prednisolone for hand OA, but there was no clinical evidence that it helped until now. The study also adds weight to the idea that OA has an inflammatory component – an idea that has been building for a while, Dr. Kroon said.
Leiden investigators and others have previously shown that synovial inflammation is often present in hand OA and a main determinant of pain and radiographic progression.
The 92 patients in the Low-Dose Prednisolone in Patients with Painful Hand Osteoarthritis (HOPE) trial had to have at least four interphalangeal joints (IPJs) with osteoarthritic nodes, at least one IPJ with soft swelling or erythema, and at least one with a positive power Doppler signal or grade 2 or higher synovitis on ultrasound. They also had to have flared at least 20 mm on the pain scale with NSAID washout.
There were more responders in the prednisolone group at 6 weeks (72% versus 33%), and significantly greater improvement in synovial thickening. There was no difference in power Doppler score or synovitis score per joint on MRI, but bone marrow lesions appeared less severe with prednisolone.
All the between-group differences disappeared when prednisolone was tapered after 6 weeks.
Four patients discontinued the study because of an adverse event: a myocardial infarction in the prednisolone group, and, in the control arm, a bowel surgery, an infected leg hematoma, and a case of Lyme arthritis of the knee. Adverse events were otherwise mild and similar in both arms.
The mean age in the study was 64 years, and 79% of the subjects were women. Exclusion criteria included chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases, psoriasis, use of immune-modulating drugs within 90 days of baseline, and predominantly thumb base pain instead of finger pain.
The approach “is for short course. Long-term steroids can have important side effects, like osteoporosis. We do not think this study should be used to encourage prolonged prescribing of glucocorticoids in patients with hand OA,” Dr. Kroon said.
Two previous trials of glucocorticoids for hand OA were inconclusive. A dose of prednisone 5 mg/day for 4 weeks did not separate from placebo in one, and the second showed pain improvements with a combination of prednisolone and dipyridamole versus placebo, but with more adverse events, particularly dipyridamole headaches.
The work was funded by the Dutch Arthritis Society. Dr. Kroon did not have any disclosures.
SOURCE: Kroon F et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 1760.
ATLANTA – Dutch investigators at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology made a good case for 6 weeks of low-dose prednisolone to help people with hand osteoarthritis get over a particularly bad spell.
A total of 42 patients randomized to prednisolone 10 mg/day fell a mean of 21.5 mm at 6 weeks from a baseline visual analog hand pain score of 54 mm (out of a possible 100 mm), versus a drop of 5.2 mm from a baseline score of 53 mm among 46 randomized to placebo; the mean group difference was 16.5 mm. Patients taking prednisolone did better on function, quality of life, and physician global assessments, too.
“This trial provides evidence that local inflammation is a suitable target for drug treatment in hand OA. We think this study provides clinicians with a short-term treatment option for patients who have a flare of their disease,” said lead investigator Féline Kroon, MD, a rheumatologist at Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center.
“The large beneficial effect size exceeded that of all available therapeutic options for hand osteoarthritis,” including NSAIDs, she and her team noted in the study write-up, which was published to coincide with the meeting (Lancet. 2019 Nov 30;394[10213]:1993-2001).
Many physicians already use short-course prednisolone for hand OA, but there was no clinical evidence that it helped until now. The study also adds weight to the idea that OA has an inflammatory component – an idea that has been building for a while, Dr. Kroon said.
Leiden investigators and others have previously shown that synovial inflammation is often present in hand OA and a main determinant of pain and radiographic progression.
The 92 patients in the Low-Dose Prednisolone in Patients with Painful Hand Osteoarthritis (HOPE) trial had to have at least four interphalangeal joints (IPJs) with osteoarthritic nodes, at least one IPJ with soft swelling or erythema, and at least one with a positive power Doppler signal or grade 2 or higher synovitis on ultrasound. They also had to have flared at least 20 mm on the pain scale with NSAID washout.
There were more responders in the prednisolone group at 6 weeks (72% versus 33%), and significantly greater improvement in synovial thickening. There was no difference in power Doppler score or synovitis score per joint on MRI, but bone marrow lesions appeared less severe with prednisolone.
All the between-group differences disappeared when prednisolone was tapered after 6 weeks.
Four patients discontinued the study because of an adverse event: a myocardial infarction in the prednisolone group, and, in the control arm, a bowel surgery, an infected leg hematoma, and a case of Lyme arthritis of the knee. Adverse events were otherwise mild and similar in both arms.
The mean age in the study was 64 years, and 79% of the subjects were women. Exclusion criteria included chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases, psoriasis, use of immune-modulating drugs within 90 days of baseline, and predominantly thumb base pain instead of finger pain.
The approach “is for short course. Long-term steroids can have important side effects, like osteoporosis. We do not think this study should be used to encourage prolonged prescribing of glucocorticoids in patients with hand OA,” Dr. Kroon said.
Two previous trials of glucocorticoids for hand OA were inconclusive. A dose of prednisone 5 mg/day for 4 weeks did not separate from placebo in one, and the second showed pain improvements with a combination of prednisolone and dipyridamole versus placebo, but with more adverse events, particularly dipyridamole headaches.
The work was funded by the Dutch Arthritis Society. Dr. Kroon did not have any disclosures.
SOURCE: Kroon F et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 1760.
REPORTING FROM ACR 2019
Well-tolerated topical capsaicin formulation reduces knee OA pain
ATLANTA – Use of high-concentration topical capsaicin was associated with reduced pain, a longer duration of clinical response, and was well tolerated in patients with knee osteoarthritis, compared with lower concentrations of capsaicin and placebo, according to recent research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
While the ACR has recommended topical capsaicin for the relief of hand and knee OA pain, there are issues with using low-dose capsaicin, including the need for multiple applications and burning, stinging sensations at applications sites. As repeat exposure to capsaicin results in depletion of pain neurotransmitters and a reduction in nerve fibers in a dose-dependent fashion, higher doses of topical capsaicin are a potential topical treatment for OA pain relief, but their tolerability is low, Tim Warneke, vice president of clinical operations at Vizuri Health Sciences in Columbia, Md., said in his presentation.
“[P]oor tolerability has limited the ability to maximize the analgesic effect of capsaicin,” Mr. Warneke said. “While [over-the-counter] preparations of capsaicin provide some pain relief, poor tolerability with higher doses has really left us wondering if we haven’t maximized capsaicin’s ability to provide pain relief.”
Mr. Warneke and colleagues conducted a phase 2, multicenter, double-blind, parallel-group, vehicle-controlled trial where 120 patients with knee OA were randomized in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive 5% capsaicin topical liquid (CGS-200-5), 1% capsaicin topical liquid (CGS-200-1), or vehicle (CGS-200-0) and then followed up to 90 days. “The CGS-200 vehicle was developed to mitigate the burning, stinging pain of capsaicin,” Mr. Warneke said. “It allows the 5% concentration to be well tolerated, which opens the door for increased efficacy, including durability of response.”
Inclusion criteria were radiographically confirmed knee OA using 1986 ACR classification criteria, a Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain score of 250 mm or greater, and more than 3 months of chronic knee pain. While patients were excluded for use of topical, oral, or injectable corticosteroids in the month prior to enrollment, they were allowed to continue using analgesics such as NSAIDs if they maintained their daily dose throughout the trial. Mr. Warneke noted the study population was typical of an OA population with a mostly female, mostly Caucasian cohort who had a median age of 60 years and a body mass index of 30 kg/m2. Patients had moderate to severe OA and were refractory to previous pain treatments.
The interventions consisted of a single 60-minute application of capsaicin or vehicle to both knees once per day for 4 consecutive days, and patients performed the applications in the clinic. The investigators compared change in WOMAC pain scores between the groups at 31 days, 60 days, and 90 days post dose.
The results at 31 days showed a 46.2% reduction in WOMAC pain scores from baseline for patients using CGS-200-5, compared with a 28.3% reduction in the vehicle group (P = .02). At 60 days, there was a 49.1% reduction in WOMAC pain scores in the CGS-200-5 group, compared with 21.5% in patients using vehicle (P = .0001), and a 42.8% reduction for patients in the CGS-200-5 group at 90 days, compared with 22.8% in the vehicle group (P = .01). The CGS-200-1 group did not reach the primary efficacy WOMAC pain endpoint, compared with vehicle.
A post hoc analysis showed that there was a significantly greater mean reduction in WOMAC total score for patients using CGS-200-5, compared with vehicle at 31 days (P = .02), 60 days (P = .0005), and 90 days post dose (P = .005). “This durability of clinical response for single applications seems to be a promising feature of CGS-200-5,” Mr. Warneke said.
Concerning safety and tolerability, there were no serious adverse events, and one patient discontinued treatment in the CGS-200-5 group. When assessing tolerability at predose, 15-minute, 30-minute, 60-minute, and 90-minute postdose time intervals, the investigators found patients experienced mild or moderate adverse events such as erythema, edema, scaling, and pruritus, with symptoms decreasing by the fourth consecutive day of application.
Mr. Warneke acknowledged the “robust placebo response” in the trial and noted it is not unusual to see in pain studies. “It’s something that is a challenge for all of us who are in this space to overcome, but we still have significant differences here and they are statistically significant as well,” he said. “You have to be pretty good these days to beat the wonder drug placebo, it appears.”
Four authors in addition to Mr. Warneke reported being employees of Vizuri Health Sciences, the company developing CGS-200-5. One author reported being a former consultant for Vizuri. Three authors reported they were current or former employees of CT Clinical Trial & Consulting, a contract research organization employed by Vizuri to execute and manage the study, perform data analysis, and create reports.
SOURCE: Warneke T et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 2760.
ATLANTA – Use of high-concentration topical capsaicin was associated with reduced pain, a longer duration of clinical response, and was well tolerated in patients with knee osteoarthritis, compared with lower concentrations of capsaicin and placebo, according to recent research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
While the ACR has recommended topical capsaicin for the relief of hand and knee OA pain, there are issues with using low-dose capsaicin, including the need for multiple applications and burning, stinging sensations at applications sites. As repeat exposure to capsaicin results in depletion of pain neurotransmitters and a reduction in nerve fibers in a dose-dependent fashion, higher doses of topical capsaicin are a potential topical treatment for OA pain relief, but their tolerability is low, Tim Warneke, vice president of clinical operations at Vizuri Health Sciences in Columbia, Md., said in his presentation.
“[P]oor tolerability has limited the ability to maximize the analgesic effect of capsaicin,” Mr. Warneke said. “While [over-the-counter] preparations of capsaicin provide some pain relief, poor tolerability with higher doses has really left us wondering if we haven’t maximized capsaicin’s ability to provide pain relief.”
Mr. Warneke and colleagues conducted a phase 2, multicenter, double-blind, parallel-group, vehicle-controlled trial where 120 patients with knee OA were randomized in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive 5% capsaicin topical liquid (CGS-200-5), 1% capsaicin topical liquid (CGS-200-1), or vehicle (CGS-200-0) and then followed up to 90 days. “The CGS-200 vehicle was developed to mitigate the burning, stinging pain of capsaicin,” Mr. Warneke said. “It allows the 5% concentration to be well tolerated, which opens the door for increased efficacy, including durability of response.”
Inclusion criteria were radiographically confirmed knee OA using 1986 ACR classification criteria, a Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain score of 250 mm or greater, and more than 3 months of chronic knee pain. While patients were excluded for use of topical, oral, or injectable corticosteroids in the month prior to enrollment, they were allowed to continue using analgesics such as NSAIDs if they maintained their daily dose throughout the trial. Mr. Warneke noted the study population was typical of an OA population with a mostly female, mostly Caucasian cohort who had a median age of 60 years and a body mass index of 30 kg/m2. Patients had moderate to severe OA and were refractory to previous pain treatments.
The interventions consisted of a single 60-minute application of capsaicin or vehicle to both knees once per day for 4 consecutive days, and patients performed the applications in the clinic. The investigators compared change in WOMAC pain scores between the groups at 31 days, 60 days, and 90 days post dose.
The results at 31 days showed a 46.2% reduction in WOMAC pain scores from baseline for patients using CGS-200-5, compared with a 28.3% reduction in the vehicle group (P = .02). At 60 days, there was a 49.1% reduction in WOMAC pain scores in the CGS-200-5 group, compared with 21.5% in patients using vehicle (P = .0001), and a 42.8% reduction for patients in the CGS-200-5 group at 90 days, compared with 22.8% in the vehicle group (P = .01). The CGS-200-1 group did not reach the primary efficacy WOMAC pain endpoint, compared with vehicle.
A post hoc analysis showed that there was a significantly greater mean reduction in WOMAC total score for patients using CGS-200-5, compared with vehicle at 31 days (P = .02), 60 days (P = .0005), and 90 days post dose (P = .005). “This durability of clinical response for single applications seems to be a promising feature of CGS-200-5,” Mr. Warneke said.
Concerning safety and tolerability, there were no serious adverse events, and one patient discontinued treatment in the CGS-200-5 group. When assessing tolerability at predose, 15-minute, 30-minute, 60-minute, and 90-minute postdose time intervals, the investigators found patients experienced mild or moderate adverse events such as erythema, edema, scaling, and pruritus, with symptoms decreasing by the fourth consecutive day of application.
Mr. Warneke acknowledged the “robust placebo response” in the trial and noted it is not unusual to see in pain studies. “It’s something that is a challenge for all of us who are in this space to overcome, but we still have significant differences here and they are statistically significant as well,” he said. “You have to be pretty good these days to beat the wonder drug placebo, it appears.”
Four authors in addition to Mr. Warneke reported being employees of Vizuri Health Sciences, the company developing CGS-200-5. One author reported being a former consultant for Vizuri. Three authors reported they were current or former employees of CT Clinical Trial & Consulting, a contract research organization employed by Vizuri to execute and manage the study, perform data analysis, and create reports.
SOURCE: Warneke T et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 2760.
ATLANTA – Use of high-concentration topical capsaicin was associated with reduced pain, a longer duration of clinical response, and was well tolerated in patients with knee osteoarthritis, compared with lower concentrations of capsaicin and placebo, according to recent research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
While the ACR has recommended topical capsaicin for the relief of hand and knee OA pain, there are issues with using low-dose capsaicin, including the need for multiple applications and burning, stinging sensations at applications sites. As repeat exposure to capsaicin results in depletion of pain neurotransmitters and a reduction in nerve fibers in a dose-dependent fashion, higher doses of topical capsaicin are a potential topical treatment for OA pain relief, but their tolerability is low, Tim Warneke, vice president of clinical operations at Vizuri Health Sciences in Columbia, Md., said in his presentation.
“[P]oor tolerability has limited the ability to maximize the analgesic effect of capsaicin,” Mr. Warneke said. “While [over-the-counter] preparations of capsaicin provide some pain relief, poor tolerability with higher doses has really left us wondering if we haven’t maximized capsaicin’s ability to provide pain relief.”
Mr. Warneke and colleagues conducted a phase 2, multicenter, double-blind, parallel-group, vehicle-controlled trial where 120 patients with knee OA were randomized in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive 5% capsaicin topical liquid (CGS-200-5), 1% capsaicin topical liquid (CGS-200-1), or vehicle (CGS-200-0) and then followed up to 90 days. “The CGS-200 vehicle was developed to mitigate the burning, stinging pain of capsaicin,” Mr. Warneke said. “It allows the 5% concentration to be well tolerated, which opens the door for increased efficacy, including durability of response.”
Inclusion criteria were radiographically confirmed knee OA using 1986 ACR classification criteria, a Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain score of 250 mm or greater, and more than 3 months of chronic knee pain. While patients were excluded for use of topical, oral, or injectable corticosteroids in the month prior to enrollment, they were allowed to continue using analgesics such as NSAIDs if they maintained their daily dose throughout the trial. Mr. Warneke noted the study population was typical of an OA population with a mostly female, mostly Caucasian cohort who had a median age of 60 years and a body mass index of 30 kg/m2. Patients had moderate to severe OA and were refractory to previous pain treatments.
The interventions consisted of a single 60-minute application of capsaicin or vehicle to both knees once per day for 4 consecutive days, and patients performed the applications in the clinic. The investigators compared change in WOMAC pain scores between the groups at 31 days, 60 days, and 90 days post dose.
The results at 31 days showed a 46.2% reduction in WOMAC pain scores from baseline for patients using CGS-200-5, compared with a 28.3% reduction in the vehicle group (P = .02). At 60 days, there was a 49.1% reduction in WOMAC pain scores in the CGS-200-5 group, compared with 21.5% in patients using vehicle (P = .0001), and a 42.8% reduction for patients in the CGS-200-5 group at 90 days, compared with 22.8% in the vehicle group (P = .01). The CGS-200-1 group did not reach the primary efficacy WOMAC pain endpoint, compared with vehicle.
A post hoc analysis showed that there was a significantly greater mean reduction in WOMAC total score for patients using CGS-200-5, compared with vehicle at 31 days (P = .02), 60 days (P = .0005), and 90 days post dose (P = .005). “This durability of clinical response for single applications seems to be a promising feature of CGS-200-5,” Mr. Warneke said.
Concerning safety and tolerability, there were no serious adverse events, and one patient discontinued treatment in the CGS-200-5 group. When assessing tolerability at predose, 15-minute, 30-minute, 60-minute, and 90-minute postdose time intervals, the investigators found patients experienced mild or moderate adverse events such as erythema, edema, scaling, and pruritus, with symptoms decreasing by the fourth consecutive day of application.
Mr. Warneke acknowledged the “robust placebo response” in the trial and noted it is not unusual to see in pain studies. “It’s something that is a challenge for all of us who are in this space to overcome, but we still have significant differences here and they are statistically significant as well,” he said. “You have to be pretty good these days to beat the wonder drug placebo, it appears.”
Four authors in addition to Mr. Warneke reported being employees of Vizuri Health Sciences, the company developing CGS-200-5. One author reported being a former consultant for Vizuri. Three authors reported they were current or former employees of CT Clinical Trial & Consulting, a contract research organization employed by Vizuri to execute and manage the study, perform data analysis, and create reports.
SOURCE: Warneke T et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 2760.
REPORTING FROM ACR 2019
Tanezumab posts higher safety event rate than NSAIDs over 1 year in hip, knee OA
ATLANTA – as part of a recent randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 3 study.
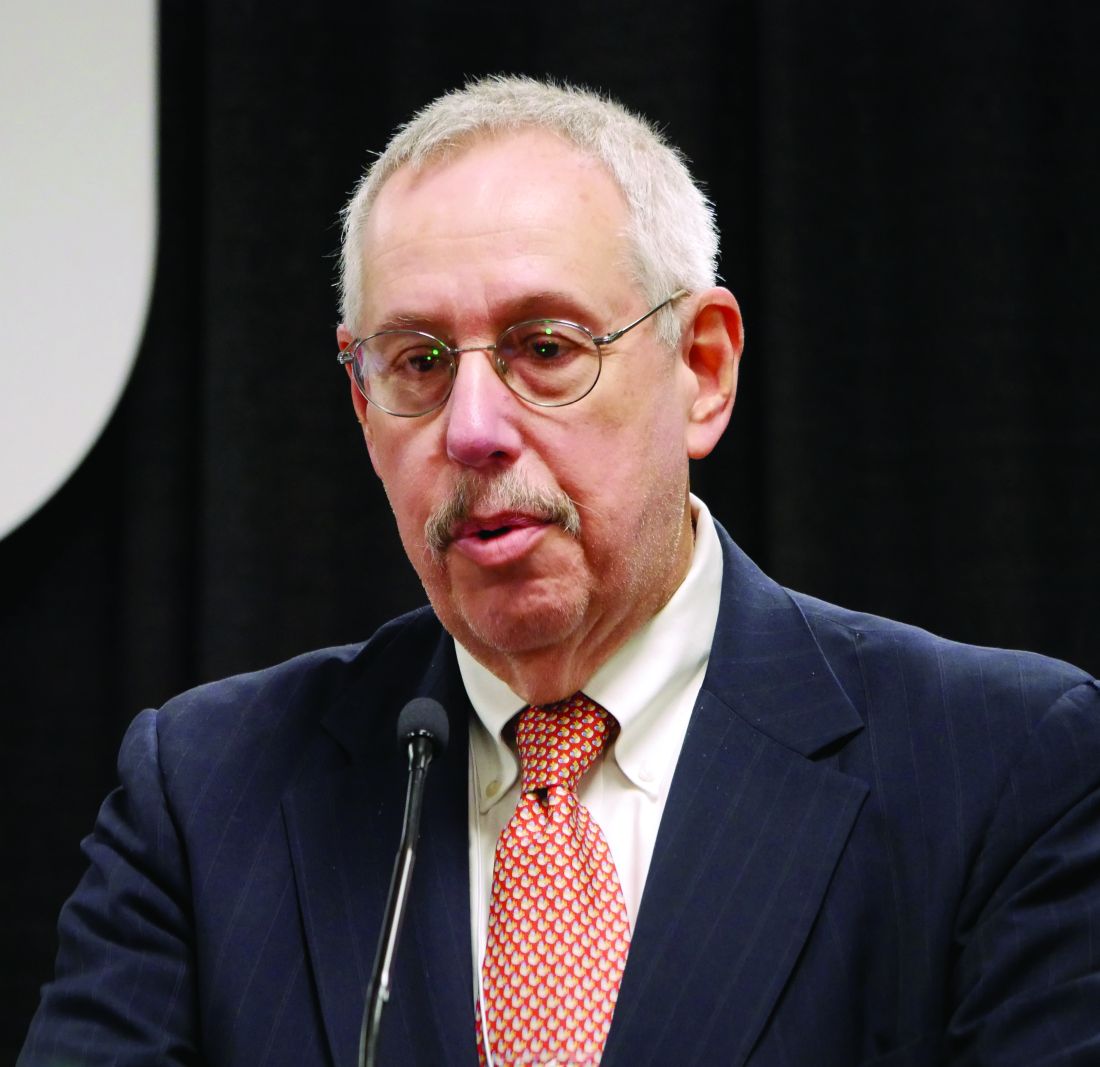
Although patients who switched from NSAIDs to 5 mg subcutaneous tanezumab every 8 weeks reported significantly improved Western Ontario and McMaster Universities (WOMAC) index pain and function scores at 16 weeks, the difference was no longer statistically significant at 56 weeks; there was an increase in the number of joint safety events in both low- and high-dose tanezumab groups when compared with patients who continued on NSAIDs, Marc C. Hochberg, MD, of the University of Maryland, Baltimore, said in his presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“Despite prior stable doses of NSAIDs, tanezumab subcutaneously administered every 8 weeks was associated with significantly more joint safety events than NSAIDs in a dose-dependent fashion,” he said.
Dr. Hochberg and colleagues conducted a phase 3 study of tanezumab in response to a Food and Drug Administration hold on the drug in 2010 in response to reports of osteonecrosis in patients taking tanezumab. “An adjudication committee was set up at that time to review all the records of individuals who participated in those studies who had been reported to have adverse joint related events, including osteonecrosis, as well as all the elected total joint replacements,” Dr. Hochberg explained. Only 4-month safety and efficacy data for tanezumab had been reported prior to these new data with at least 1 year of follow-up.
The study comprised 2,996 patients with hip or knee osteoarthritis (OA) from 446 centers in 18 countries, where patients were randomized to receive 2.5 mg of subcutaneous tanezumab (1,002 patients), tanezumab at 5 mg (998 patients) or NSAIDs (996 patients) for up to 80 weeks. Approximately two-thirds of the patients were women, and about 70% were white. About 85% of all patients had knee OA. The most common NSAIDs were celecoxib, diclofenac, and naproxen.
Less than 1% had Kellgren-Lawrence grade 0-1 at baseline, while about 30% had grade 2, 47% grade 3, and 22% grade 4. Patients had a mean 7.0 or 7.1 score on the WOMAC pain and function subscales, and a mean Patient’s Global Assessment of OA (PGA-OA) score of 7.4 or 7.5. Baseline radiographs were taken, as well as at safety follow-ups at 24 weeks, 56 weeks, and 80 weeks.
The researchers examined rapidly progressive OA (RPOA) type 1, classified as loss of 2 mm or more of joint space width within 1 year, and type 2, which was defined as abnormal bone loss or destruction, including limited or total collapse of at least one subchondral surface. Other primary joint safety endpoints examined were primary osteonecrosis, subchondral insufficiency fracture, and pathologic fracture. Each of these was reported individually in addition to the rate of total joint replacement. If an event was discovered, it was sent to an adjudication committee, Dr. Hochberg said. “You have either investigator-reported joint safety events, possible joint safety events or identified from the central raters’ assessment of imaging, or the reported total joint replacement reviewed blindly by the adjudication committee, blinded to treatment allocation, and then the adjudication results are those that are used for the analysis,” he said.
Overall, 447 patients who received tanezumab at 2.5 mg, 419 patients who received tanezumab at 5 mg, and 446 patients who continued receive NSAIDs completed treatment. There were 71 joint safety events in the tanezumab 5-mg group (7.1%) per 1,000 person-years, compared with 39 events per 1,000 person-years in the 2.5-mg group (3.9%), and 15 events per 1,000 person-years in the NSAIDs group (1.5%). The rate of joint safety events was significantly higher in both tanezumab groups, compared with the NSAIDs group (both P less than or equal to .001). Among patients with RPOA type 1, 4.9% of patients in the 5-mg group and 2.9% of patients in the 2.5-mg tanezumab group experienced joint safety events, compared with 1.1% of patients in the NSAIDs group. While RPOA type 2, primary osteonecrosis, and subchondral insufficiency fractures were uncommon in the study, Dr. Hochberg noted there was a statistically significant difference in joint safety events between the 5-mg tanezumab group and the NSAID group for patients with RPOA type 2 (1.4% vs. 0.1%; P less than or equal to .001).
The relationship between total joint replacement and tanezumab was dose-dependent: In the 5-mg group, 8.0% of patients underwent total joint replacement, while 5.3% of patients underwent total joint replacement in the 2.5-mg group, compared with 2.6% of patients in the NSAID group. “Most of the total joint replacements were due to normal progression of osteoarthritis,” Dr. Hochberg said.
When asked if he believed there is a role for tanezumab in the management of patients with OA, Dr. Hochberg said moderate to severe symptomatic hip or knee OA, including polyarticular OA, are potential areas where tanezumab and other nerve growth factor inhibitors could be beneficial.
“There is a tremendous unmet need in this population, and these are patients who have either had an inadequate response to, are intolerant of, or have contraindications to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, have not responded well to intra-articular therapy, or have multiple joint involvement,” he said. There is also a role for tanezumab in OA patients who don’t want to take weaker opioid analgesics such as tramadol, he added.
This study was funded by Pfizer and Lilly, and the companies sponsored the summarization of the study. The authors reported various ties with these and other companies.
SOURCE: Hochberg MC et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 1302 and Abstract 2756.
ATLANTA – as part of a recent randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 3 study.
Although patients who switched from NSAIDs to 5 mg subcutaneous tanezumab every 8 weeks reported significantly improved Western Ontario and McMaster Universities (WOMAC) index pain and function scores at 16 weeks, the difference was no longer statistically significant at 56 weeks; there was an increase in the number of joint safety events in both low- and high-dose tanezumab groups when compared with patients who continued on NSAIDs, Marc C. Hochberg, MD, of the University of Maryland, Baltimore, said in his presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“Despite prior stable doses of NSAIDs, tanezumab subcutaneously administered every 8 weeks was associated with significantly more joint safety events than NSAIDs in a dose-dependent fashion,” he said.
Dr. Hochberg and colleagues conducted a phase 3 study of tanezumab in response to a Food and Drug Administration hold on the drug in 2010 in response to reports of osteonecrosis in patients taking tanezumab. “An adjudication committee was set up at that time to review all the records of individuals who participated in those studies who had been reported to have adverse joint related events, including osteonecrosis, as well as all the elected total joint replacements,” Dr. Hochberg explained. Only 4-month safety and efficacy data for tanezumab had been reported prior to these new data with at least 1 year of follow-up.
The study comprised 2,996 patients with hip or knee osteoarthritis (OA) from 446 centers in 18 countries, where patients were randomized to receive 2.5 mg of subcutaneous tanezumab (1,002 patients), tanezumab at 5 mg (998 patients) or NSAIDs (996 patients) for up to 80 weeks. Approximately two-thirds of the patients were women, and about 70% were white. About 85% of all patients had knee OA. The most common NSAIDs were celecoxib, diclofenac, and naproxen.
Less than 1% had Kellgren-Lawrence grade 0-1 at baseline, while about 30% had grade 2, 47% grade 3, and 22% grade 4. Patients had a mean 7.0 or 7.1 score on the WOMAC pain and function subscales, and a mean Patient’s Global Assessment of OA (PGA-OA) score of 7.4 or 7.5. Baseline radiographs were taken, as well as at safety follow-ups at 24 weeks, 56 weeks, and 80 weeks.
The researchers examined rapidly progressive OA (RPOA) type 1, classified as loss of 2 mm or more of joint space width within 1 year, and type 2, which was defined as abnormal bone loss or destruction, including limited or total collapse of at least one subchondral surface. Other primary joint safety endpoints examined were primary osteonecrosis, subchondral insufficiency fracture, and pathologic fracture. Each of these was reported individually in addition to the rate of total joint replacement. If an event was discovered, it was sent to an adjudication committee, Dr. Hochberg said. “You have either investigator-reported joint safety events, possible joint safety events or identified from the central raters’ assessment of imaging, or the reported total joint replacement reviewed blindly by the adjudication committee, blinded to treatment allocation, and then the adjudication results are those that are used for the analysis,” he said.
Overall, 447 patients who received tanezumab at 2.5 mg, 419 patients who received tanezumab at 5 mg, and 446 patients who continued receive NSAIDs completed treatment. There were 71 joint safety events in the tanezumab 5-mg group (7.1%) per 1,000 person-years, compared with 39 events per 1,000 person-years in the 2.5-mg group (3.9%), and 15 events per 1,000 person-years in the NSAIDs group (1.5%). The rate of joint safety events was significantly higher in both tanezumab groups, compared with the NSAIDs group (both P less than or equal to .001). Among patients with RPOA type 1, 4.9% of patients in the 5-mg group and 2.9% of patients in the 2.5-mg tanezumab group experienced joint safety events, compared with 1.1% of patients in the NSAIDs group. While RPOA type 2, primary osteonecrosis, and subchondral insufficiency fractures were uncommon in the study, Dr. Hochberg noted there was a statistically significant difference in joint safety events between the 5-mg tanezumab group and the NSAID group for patients with RPOA type 2 (1.4% vs. 0.1%; P less than or equal to .001).
The relationship between total joint replacement and tanezumab was dose-dependent: In the 5-mg group, 8.0% of patients underwent total joint replacement, while 5.3% of patients underwent total joint replacement in the 2.5-mg group, compared with 2.6% of patients in the NSAID group. “Most of the total joint replacements were due to normal progression of osteoarthritis,” Dr. Hochberg said.
When asked if he believed there is a role for tanezumab in the management of patients with OA, Dr. Hochberg said moderate to severe symptomatic hip or knee OA, including polyarticular OA, are potential areas where tanezumab and other nerve growth factor inhibitors could be beneficial.
“There is a tremendous unmet need in this population, and these are patients who have either had an inadequate response to, are intolerant of, or have contraindications to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, have not responded well to intra-articular therapy, or have multiple joint involvement,” he said. There is also a role for tanezumab in OA patients who don’t want to take weaker opioid analgesics such as tramadol, he added.
This study was funded by Pfizer and Lilly, and the companies sponsored the summarization of the study. The authors reported various ties with these and other companies.
SOURCE: Hochberg MC et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 1302 and Abstract 2756.
ATLANTA – as part of a recent randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 3 study.
Although patients who switched from NSAIDs to 5 mg subcutaneous tanezumab every 8 weeks reported significantly improved Western Ontario and McMaster Universities (WOMAC) index pain and function scores at 16 weeks, the difference was no longer statistically significant at 56 weeks; there was an increase in the number of joint safety events in both low- and high-dose tanezumab groups when compared with patients who continued on NSAIDs, Marc C. Hochberg, MD, of the University of Maryland, Baltimore, said in his presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“Despite prior stable doses of NSAIDs, tanezumab subcutaneously administered every 8 weeks was associated with significantly more joint safety events than NSAIDs in a dose-dependent fashion,” he said.
Dr. Hochberg and colleagues conducted a phase 3 study of tanezumab in response to a Food and Drug Administration hold on the drug in 2010 in response to reports of osteonecrosis in patients taking tanezumab. “An adjudication committee was set up at that time to review all the records of individuals who participated in those studies who had been reported to have adverse joint related events, including osteonecrosis, as well as all the elected total joint replacements,” Dr. Hochberg explained. Only 4-month safety and efficacy data for tanezumab had been reported prior to these new data with at least 1 year of follow-up.
The study comprised 2,996 patients with hip or knee osteoarthritis (OA) from 446 centers in 18 countries, where patients were randomized to receive 2.5 mg of subcutaneous tanezumab (1,002 patients), tanezumab at 5 mg (998 patients) or NSAIDs (996 patients) for up to 80 weeks. Approximately two-thirds of the patients were women, and about 70% were white. About 85% of all patients had knee OA. The most common NSAIDs were celecoxib, diclofenac, and naproxen.
Less than 1% had Kellgren-Lawrence grade 0-1 at baseline, while about 30% had grade 2, 47% grade 3, and 22% grade 4. Patients had a mean 7.0 or 7.1 score on the WOMAC pain and function subscales, and a mean Patient’s Global Assessment of OA (PGA-OA) score of 7.4 or 7.5. Baseline radiographs were taken, as well as at safety follow-ups at 24 weeks, 56 weeks, and 80 weeks.
The researchers examined rapidly progressive OA (RPOA) type 1, classified as loss of 2 mm or more of joint space width within 1 year, and type 2, which was defined as abnormal bone loss or destruction, including limited or total collapse of at least one subchondral surface. Other primary joint safety endpoints examined were primary osteonecrosis, subchondral insufficiency fracture, and pathologic fracture. Each of these was reported individually in addition to the rate of total joint replacement. If an event was discovered, it was sent to an adjudication committee, Dr. Hochberg said. “You have either investigator-reported joint safety events, possible joint safety events or identified from the central raters’ assessment of imaging, or the reported total joint replacement reviewed blindly by the adjudication committee, blinded to treatment allocation, and then the adjudication results are those that are used for the analysis,” he said.
Overall, 447 patients who received tanezumab at 2.5 mg, 419 patients who received tanezumab at 5 mg, and 446 patients who continued receive NSAIDs completed treatment. There were 71 joint safety events in the tanezumab 5-mg group (7.1%) per 1,000 person-years, compared with 39 events per 1,000 person-years in the 2.5-mg group (3.9%), and 15 events per 1,000 person-years in the NSAIDs group (1.5%). The rate of joint safety events was significantly higher in both tanezumab groups, compared with the NSAIDs group (both P less than or equal to .001). Among patients with RPOA type 1, 4.9% of patients in the 5-mg group and 2.9% of patients in the 2.5-mg tanezumab group experienced joint safety events, compared with 1.1% of patients in the NSAIDs group. While RPOA type 2, primary osteonecrosis, and subchondral insufficiency fractures were uncommon in the study, Dr. Hochberg noted there was a statistically significant difference in joint safety events between the 5-mg tanezumab group and the NSAID group for patients with RPOA type 2 (1.4% vs. 0.1%; P less than or equal to .001).
The relationship between total joint replacement and tanezumab was dose-dependent: In the 5-mg group, 8.0% of patients underwent total joint replacement, while 5.3% of patients underwent total joint replacement in the 2.5-mg group, compared with 2.6% of patients in the NSAID group. “Most of the total joint replacements were due to normal progression of osteoarthritis,” Dr. Hochberg said.
When asked if he believed there is a role for tanezumab in the management of patients with OA, Dr. Hochberg said moderate to severe symptomatic hip or knee OA, including polyarticular OA, are potential areas where tanezumab and other nerve growth factor inhibitors could be beneficial.
“There is a tremendous unmet need in this population, and these are patients who have either had an inadequate response to, are intolerant of, or have contraindications to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, have not responded well to intra-articular therapy, or have multiple joint involvement,” he said. There is also a role for tanezumab in OA patients who don’t want to take weaker opioid analgesics such as tramadol, he added.
This study was funded by Pfizer and Lilly, and the companies sponsored the summarization of the study. The authors reported various ties with these and other companies.
SOURCE: Hochberg MC et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 1302 and Abstract 2756.
REPORTING FROM ACR 2019
OA management guidelines forgo treatment hierarchy or order but emphasize severity, patient risk factors
ATLANTA – New guidelines for management of osteoarthritis of the hand, knee, and hip from the American College of Rheumatology and the Arthritis Foundation lay out a wide range of treatment options without an algorithm or hierarchy, making strong recommendations for nondrug interventions and for tailoring plans to individual patient-level factors.
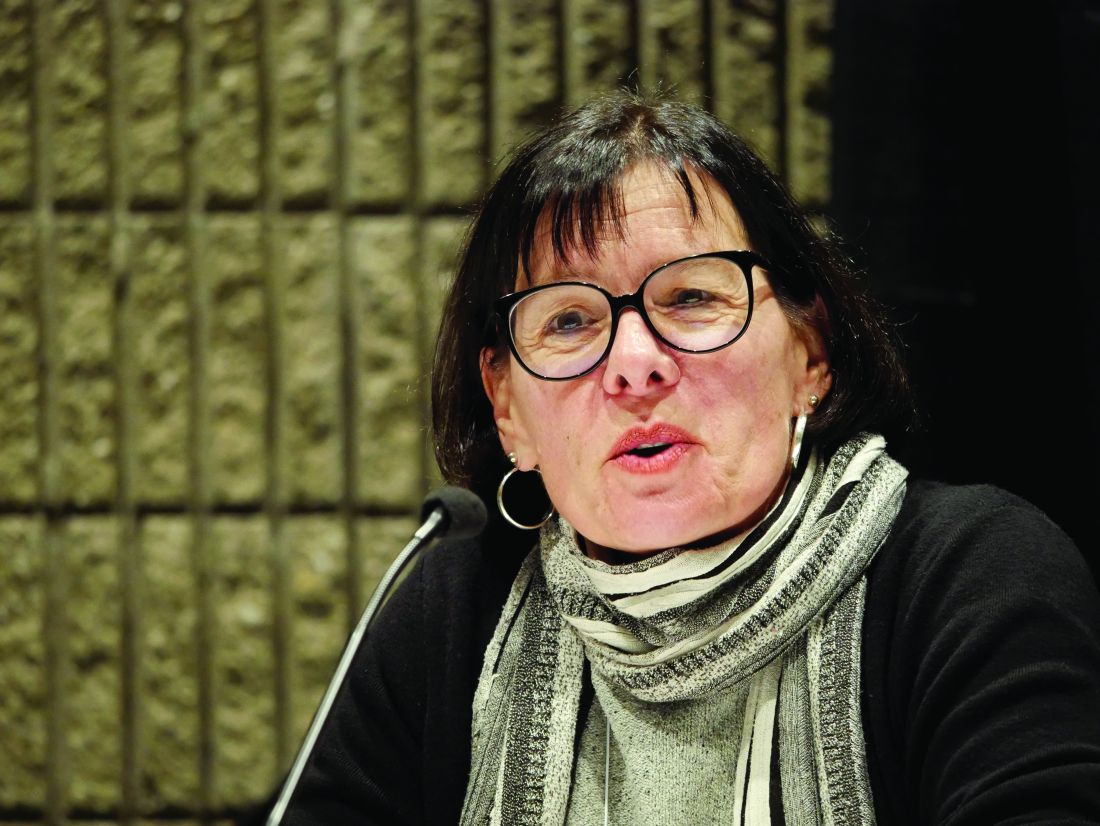
Since the ACR last released OA management guidelines in 2012, a number of recommendations have been added, changed, and removed, and the structure of the guidelines has also changed. For instance, the new OA guidelines include a broad list of management options, Sharon L. Kolasinski, MD, chair of the ACR guidelines panel and professor of clinical medicine in the division of rheumatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“The new guideline emphasizes comprehensive management of patients with OA, rather than a stepwise algorithm in a linear manner,” she said.
There is also no hierarchy to the recommendations, apart from the strength of the recommendation. “For any individual patient, a single option may be chosen at a particular time point, perhaps with or without other options, and may be reused in the future. For a given intervention, there might be a period of time over which it’s useful, and then the option might be changed,” Dr. Kolasinski noted.
Dr. Kolasinski advised making treatment decisions based on a patient’s disease severity, whether the patient uses medical devices, and in consideration of patient risk factors. “A history of injuries, surgical history, access to care, personal beliefs and preferences should all be brought to bear on decision making for osteoarthritis management,” she said.
The guidelines also advise considering a patient’s overall well-being and factors related to a patient’s perception of pain and function, such as mood disorders, altered sleep, chronic pain, impaired coping measures, and stress level. “Comprehensive management requires a broad assessment of how pain and function are affecting the patient with OA as a whole and recognizing that multiple options are available. They might be used in combination or change over time,” Dr. Kolasinski said.
The new guidelines place a strong emphasis on educational, behavioral, psychosocial, mind-body, and physical approaches. There are strong recommendations for the use of exercise, including aerobic, strengthening, neuromuscular, and aquatic exercise. Weight loss also carries a strong recommendation for patients with hip and knee OA, with a focus on group-based exercise, education, fitness and exercise goals, and a multidisciplinary approach using self-efficacy and self-management programs. The panels made a strong recommendation for tai chi to improve hip and knee OA. There are also strong recommendations for orthoses; aids and assistive devices such as canes, first carpometacarpal (CMC) orthoses, and tibiofemoral knee braces. Other interventions, such as Kinesio tape for first CMC joint and knee OA, hand orthoses, and patellofemoral knee braces, carried a conditional recommendation. Other conditional recommendations made by the panel were for acupuncture, thermal interventions, and radiofrequency ablation for patients with knee OA. Balance training for hip and knee OA, yoga for knee OA, and cognitive-behavioral therapy all were conditionally recommended by the panel.
The panel strongly recommended against the use of transcutaneous nerve stimulation for hip and knee OA, Dr. Kolasinski noted. The panel also conditionally recommended against use of modified shoes and pulsed vibration therapy in knee OA; lateral or medial wedged insoles, massage, and manual therapy with exercise in hip or knee OA; and iontophoresis in first CMC OA.
Tuhina Neogi, MD, PhD, chief of rheumatology at Boston University and member of the core team that developed the guidelines, said in her presentation the panel chose not to use the term “nonpharmacologic” in the guidelines because it may give patients a false impression that they are not receiving a treatment. “We really need to change our language and change the way in which we approach these conversations with our patients so that they don’t feel that they are not getting a treatment when we’re giving these recommendations,” she said.
Recommendations for, against pharmacologic approaches
The ACR has changed conditional recommendations for topical NSAIDs for knee and hand OA, oral NSAIDs, and intra-articular steroids for knee and hip OA into strong recommendations for the 2019 guidelines, Dr. Kolasinski said. While the 2012 guidelines conditionally recommended against topical capsaicin for knee OA, the new guidelines conditionally recommend it.
Other pharmacologic conditional recommendations included topical NSAIDs, chondroitin sulfate, and intra-articular corticosteroid injections for hand OA, acetaminophen, and duloxetine for knee OA.
With the new recommendations come changes that some rheumatologists and health care providers may find controversial. “I think that the practicing rheumatologist may be surprised that we have a recommendation against the use of hyaluronic acid in the knee as a conditional recommendation,” Dr. Kolasinski said. “The assessment of the literature at this point really reveals that there is equivalence between intra-articular hyaluronic acid injection and intra-articular saline injection, and so it was the feeling of the panel that, really, this was worth changing the recommendation from the 2012 guideline.”
The panel made strong recommendations against use of the following pharmacologic interventions:
- Bisphosphonates.
- Glucosamine sulfate.
- Combination glucosamine sulfate-chondroitin sulfate products.
- Hydroxychloroquine.
- Methotrexate.
- Intra-articular hyaluronic acid injections in hip OA.
- Chondroitin sulfate, platelet-rich plasma injections, and stem cell injections in hip and knee OA.
- Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors.
- Interleukin-1–receptor antagonists.
Additionally, the panel made a conditional recommendation against topical capsaicin on the hand, colchicine, fish oil, vitamin D, intra-articular hyaluronic acid injections in the first CMC, and intra-articular botulinum toxin and prolotherapy in hip and knee OA.
The panel did not recommend for or against use of yoga for hip and hand OA, topical lidocaine, pregabalin, gabapentin, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors apart from duloxetine, tricyclic antidepressants, and anti-nerve growth factor agents.
While the panel conditionally recommended against use of opioids, they made a conditional recommendation for use of tramadol opioids, and there was “a heated discussion about that distinction,” Dr. Neogi noted in a discussion session at the meeting. “There was a recent observational study that indicated that tramadol may have an increased risk of [all-cause] mortality, but there are lots of issues of confounding by indication in that study.”
The patient panel also raised strong concerns about the ACR and the Arthritis Foundation coming out against opioids for OA management in their guidelines. “They don’t want to damn opioids, but they’re also concerned about a specialty society coming out strongly against opioids in the concern that their physicians may limit their access to opioids if they’re in a situation where nothing else is helping them,” Dr. Neogi said.
Dr. Kolasinski noted the guidelines will be published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology in December, and will appear in print in February of next year.
Dr. Kolasinski reported no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Neogi reported relationships with EMD Serono, Merck, and Pfizer.
ATLANTA – New guidelines for management of osteoarthritis of the hand, knee, and hip from the American College of Rheumatology and the Arthritis Foundation lay out a wide range of treatment options without an algorithm or hierarchy, making strong recommendations for nondrug interventions and for tailoring plans to individual patient-level factors.
Since the ACR last released OA management guidelines in 2012, a number of recommendations have been added, changed, and removed, and the structure of the guidelines has also changed. For instance, the new OA guidelines include a broad list of management options, Sharon L. Kolasinski, MD, chair of the ACR guidelines panel and professor of clinical medicine in the division of rheumatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“The new guideline emphasizes comprehensive management of patients with OA, rather than a stepwise algorithm in a linear manner,” she said.
There is also no hierarchy to the recommendations, apart from the strength of the recommendation. “For any individual patient, a single option may be chosen at a particular time point, perhaps with or without other options, and may be reused in the future. For a given intervention, there might be a period of time over which it’s useful, and then the option might be changed,” Dr. Kolasinski noted.
Dr. Kolasinski advised making treatment decisions based on a patient’s disease severity, whether the patient uses medical devices, and in consideration of patient risk factors. “A history of injuries, surgical history, access to care, personal beliefs and preferences should all be brought to bear on decision making for osteoarthritis management,” she said.
The guidelines also advise considering a patient’s overall well-being and factors related to a patient’s perception of pain and function, such as mood disorders, altered sleep, chronic pain, impaired coping measures, and stress level. “Comprehensive management requires a broad assessment of how pain and function are affecting the patient with OA as a whole and recognizing that multiple options are available. They might be used in combination or change over time,” Dr. Kolasinski said.
The new guidelines place a strong emphasis on educational, behavioral, psychosocial, mind-body, and physical approaches. There are strong recommendations for the use of exercise, including aerobic, strengthening, neuromuscular, and aquatic exercise. Weight loss also carries a strong recommendation for patients with hip and knee OA, with a focus on group-based exercise, education, fitness and exercise goals, and a multidisciplinary approach using self-efficacy and self-management programs. The panels made a strong recommendation for tai chi to improve hip and knee OA. There are also strong recommendations for orthoses; aids and assistive devices such as canes, first carpometacarpal (CMC) orthoses, and tibiofemoral knee braces. Other interventions, such as Kinesio tape for first CMC joint and knee OA, hand orthoses, and patellofemoral knee braces, carried a conditional recommendation. Other conditional recommendations made by the panel were for acupuncture, thermal interventions, and radiofrequency ablation for patients with knee OA. Balance training for hip and knee OA, yoga for knee OA, and cognitive-behavioral therapy all were conditionally recommended by the panel.
The panel strongly recommended against the use of transcutaneous nerve stimulation for hip and knee OA, Dr. Kolasinski noted. The panel also conditionally recommended against use of modified shoes and pulsed vibration therapy in knee OA; lateral or medial wedged insoles, massage, and manual therapy with exercise in hip or knee OA; and iontophoresis in first CMC OA.
Tuhina Neogi, MD, PhD, chief of rheumatology at Boston University and member of the core team that developed the guidelines, said in her presentation the panel chose not to use the term “nonpharmacologic” in the guidelines because it may give patients a false impression that they are not receiving a treatment. “We really need to change our language and change the way in which we approach these conversations with our patients so that they don’t feel that they are not getting a treatment when we’re giving these recommendations,” she said.
Recommendations for, against pharmacologic approaches
The ACR has changed conditional recommendations for topical NSAIDs for knee and hand OA, oral NSAIDs, and intra-articular steroids for knee and hip OA into strong recommendations for the 2019 guidelines, Dr. Kolasinski said. While the 2012 guidelines conditionally recommended against topical capsaicin for knee OA, the new guidelines conditionally recommend it.
Other pharmacologic conditional recommendations included topical NSAIDs, chondroitin sulfate, and intra-articular corticosteroid injections for hand OA, acetaminophen, and duloxetine for knee OA.
With the new recommendations come changes that some rheumatologists and health care providers may find controversial. “I think that the practicing rheumatologist may be surprised that we have a recommendation against the use of hyaluronic acid in the knee as a conditional recommendation,” Dr. Kolasinski said. “The assessment of the literature at this point really reveals that there is equivalence between intra-articular hyaluronic acid injection and intra-articular saline injection, and so it was the feeling of the panel that, really, this was worth changing the recommendation from the 2012 guideline.”
The panel made strong recommendations against use of the following pharmacologic interventions:
- Bisphosphonates.
- Glucosamine sulfate.
- Combination glucosamine sulfate-chondroitin sulfate products.
- Hydroxychloroquine.
- Methotrexate.
- Intra-articular hyaluronic acid injections in hip OA.
- Chondroitin sulfate, platelet-rich plasma injections, and stem cell injections in hip and knee OA.
- Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors.
- Interleukin-1–receptor antagonists.
Additionally, the panel made a conditional recommendation against topical capsaicin on the hand, colchicine, fish oil, vitamin D, intra-articular hyaluronic acid injections in the first CMC, and intra-articular botulinum toxin and prolotherapy in hip and knee OA.
The panel did not recommend for or against use of yoga for hip and hand OA, topical lidocaine, pregabalin, gabapentin, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors apart from duloxetine, tricyclic antidepressants, and anti-nerve growth factor agents.
While the panel conditionally recommended against use of opioids, they made a conditional recommendation for use of tramadol opioids, and there was “a heated discussion about that distinction,” Dr. Neogi noted in a discussion session at the meeting. “There was a recent observational study that indicated that tramadol may have an increased risk of [all-cause] mortality, but there are lots of issues of confounding by indication in that study.”
The patient panel also raised strong concerns about the ACR and the Arthritis Foundation coming out against opioids for OA management in their guidelines. “They don’t want to damn opioids, but they’re also concerned about a specialty society coming out strongly against opioids in the concern that their physicians may limit their access to opioids if they’re in a situation where nothing else is helping them,” Dr. Neogi said.
Dr. Kolasinski noted the guidelines will be published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology in December, and will appear in print in February of next year.
Dr. Kolasinski reported no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Neogi reported relationships with EMD Serono, Merck, and Pfizer.
ATLANTA – New guidelines for management of osteoarthritis of the hand, knee, and hip from the American College of Rheumatology and the Arthritis Foundation lay out a wide range of treatment options without an algorithm or hierarchy, making strong recommendations for nondrug interventions and for tailoring plans to individual patient-level factors.
Since the ACR last released OA management guidelines in 2012, a number of recommendations have been added, changed, and removed, and the structure of the guidelines has also changed. For instance, the new OA guidelines include a broad list of management options, Sharon L. Kolasinski, MD, chair of the ACR guidelines panel and professor of clinical medicine in the division of rheumatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“The new guideline emphasizes comprehensive management of patients with OA, rather than a stepwise algorithm in a linear manner,” she said.
There is also no hierarchy to the recommendations, apart from the strength of the recommendation. “For any individual patient, a single option may be chosen at a particular time point, perhaps with or without other options, and may be reused in the future. For a given intervention, there might be a period of time over which it’s useful, and then the option might be changed,” Dr. Kolasinski noted.
Dr. Kolasinski advised making treatment decisions based on a patient’s disease severity, whether the patient uses medical devices, and in consideration of patient risk factors. “A history of injuries, surgical history, access to care, personal beliefs and preferences should all be brought to bear on decision making for osteoarthritis management,” she said.
The guidelines also advise considering a patient’s overall well-being and factors related to a patient’s perception of pain and function, such as mood disorders, altered sleep, chronic pain, impaired coping measures, and stress level. “Comprehensive management requires a broad assessment of how pain and function are affecting the patient with OA as a whole and recognizing that multiple options are available. They might be used in combination or change over time,” Dr. Kolasinski said.
The new guidelines place a strong emphasis on educational, behavioral, psychosocial, mind-body, and physical approaches. There are strong recommendations for the use of exercise, including aerobic, strengthening, neuromuscular, and aquatic exercise. Weight loss also carries a strong recommendation for patients with hip and knee OA, with a focus on group-based exercise, education, fitness and exercise goals, and a multidisciplinary approach using self-efficacy and self-management programs. The panels made a strong recommendation for tai chi to improve hip and knee OA. There are also strong recommendations for orthoses; aids and assistive devices such as canes, first carpometacarpal (CMC) orthoses, and tibiofemoral knee braces. Other interventions, such as Kinesio tape for first CMC joint and knee OA, hand orthoses, and patellofemoral knee braces, carried a conditional recommendation. Other conditional recommendations made by the panel were for acupuncture, thermal interventions, and radiofrequency ablation for patients with knee OA. Balance training for hip and knee OA, yoga for knee OA, and cognitive-behavioral therapy all were conditionally recommended by the panel.
The panel strongly recommended against the use of transcutaneous nerve stimulation for hip and knee OA, Dr. Kolasinski noted. The panel also conditionally recommended against use of modified shoes and pulsed vibration therapy in knee OA; lateral or medial wedged insoles, massage, and manual therapy with exercise in hip or knee OA; and iontophoresis in first CMC OA.
Tuhina Neogi, MD, PhD, chief of rheumatology at Boston University and member of the core team that developed the guidelines, said in her presentation the panel chose not to use the term “nonpharmacologic” in the guidelines because it may give patients a false impression that they are not receiving a treatment. “We really need to change our language and change the way in which we approach these conversations with our patients so that they don’t feel that they are not getting a treatment when we’re giving these recommendations,” she said.
Recommendations for, against pharmacologic approaches
The ACR has changed conditional recommendations for topical NSAIDs for knee and hand OA, oral NSAIDs, and intra-articular steroids for knee and hip OA into strong recommendations for the 2019 guidelines, Dr. Kolasinski said. While the 2012 guidelines conditionally recommended against topical capsaicin for knee OA, the new guidelines conditionally recommend it.
Other pharmacologic conditional recommendations included topical NSAIDs, chondroitin sulfate, and intra-articular corticosteroid injections for hand OA, acetaminophen, and duloxetine for knee OA.
With the new recommendations come changes that some rheumatologists and health care providers may find controversial. “I think that the practicing rheumatologist may be surprised that we have a recommendation against the use of hyaluronic acid in the knee as a conditional recommendation,” Dr. Kolasinski said. “The assessment of the literature at this point really reveals that there is equivalence between intra-articular hyaluronic acid injection and intra-articular saline injection, and so it was the feeling of the panel that, really, this was worth changing the recommendation from the 2012 guideline.”
The panel made strong recommendations against use of the following pharmacologic interventions:
- Bisphosphonates.
- Glucosamine sulfate.
- Combination glucosamine sulfate-chondroitin sulfate products.
- Hydroxychloroquine.
- Methotrexate.
- Intra-articular hyaluronic acid injections in hip OA.
- Chondroitin sulfate, platelet-rich plasma injections, and stem cell injections in hip and knee OA.
- Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors.
- Interleukin-1–receptor antagonists.
Additionally, the panel made a conditional recommendation against topical capsaicin on the hand, colchicine, fish oil, vitamin D, intra-articular hyaluronic acid injections in the first CMC, and intra-articular botulinum toxin and prolotherapy in hip and knee OA.
The panel did not recommend for or against use of yoga for hip and hand OA, topical lidocaine, pregabalin, gabapentin, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors apart from duloxetine, tricyclic antidepressants, and anti-nerve growth factor agents.
While the panel conditionally recommended against use of opioids, they made a conditional recommendation for use of tramadol opioids, and there was “a heated discussion about that distinction,” Dr. Neogi noted in a discussion session at the meeting. “There was a recent observational study that indicated that tramadol may have an increased risk of [all-cause] mortality, but there are lots of issues of confounding by indication in that study.”
The patient panel also raised strong concerns about the ACR and the Arthritis Foundation coming out against opioids for OA management in their guidelines. “They don’t want to damn opioids, but they’re also concerned about a specialty society coming out strongly against opioids in the concern that their physicians may limit their access to opioids if they’re in a situation where nothing else is helping them,” Dr. Neogi said.
Dr. Kolasinski noted the guidelines will be published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology in December, and will appear in print in February of next year.
Dr. Kolasinski reported no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Neogi reported relationships with EMD Serono, Merck, and Pfizer.
REPORTING FROM ACR 2019
Methotrexate may affect joint erosions but not pain in patients with erosive hand OA
ATLANTA – , according to results from the small, prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled ADEM trial.
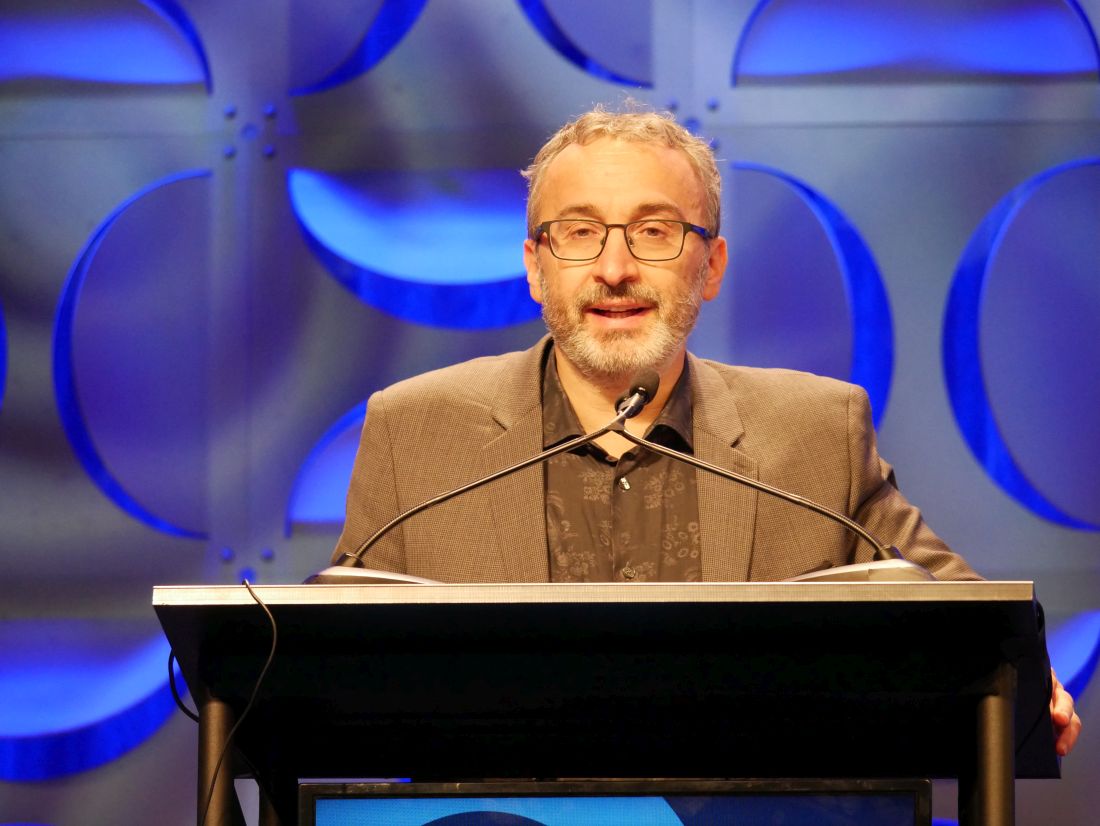
“Our study failed to show the superiority of methotrexate over placebo on pain evolution, but our results on structural evolution and the presence of inflammatory parameters as predictors of erosive evolution in nonerosive diseases may lead us to discuss the place of methotrexate in early steps of the disease evolution, and underlines the importance of the part played by the interaction between synovitis and subchondral bone in erosive progression,” Christian Roux, MD, PhD, of the department of rheumatology at Côte d’Azur University, Nice, France, said in his presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Dr. Roux and colleagues enrolled 64 patients in the ADEM trial, where patients with symptomatic erosive hand osteoarthritis (EHOA) were randomized to receive 10 mg of methotrexate (MTX) per week or placebo. At 3 months, researchers assessed patients for pain using the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) score for hand pain, and secondary outcome measures at 12 months included VAS score for hand pain, radiographic progression using Verbruggen-Veys Anatomical Phase Score and Gent University Scoring System, and MRI.
Patients were included in the study if they were between 45 and 85 years old with a VAS pain score greater than 40, had failed classic therapeutics (acetaminophen, topical NSAIDs, and symptomatic slow-acting drugs), and had at least one erosive lesion. At baseline, the MTX and placebo groups were not significantly different with regard to gender (91% vs. 97% female), mean body mass index (24.6 kg/m2 vs. 24.2 kg/m2) and mean age (67.5 years vs. 64.9 years). Radiologic data showed joint loss, erosive, and erosive plus remodeling measurements were also similar between groups at baseline.
The mean VAS score for patients in the MTX group decreased from 65.7 at baseline to 48.2 at 3 months (–17.5; P = .07), compared with a decrease from 63.9 to 55.5 (–8.4; P = .002). At 12 months, VAS scores for patients in the MTX group decreased to 47.5, compared with a decrease in the placebo group to 48.2. However, the between-group differences for VAS scores were not significant at 3 months (P = .2) and at 12 months (P = .6).
“We have different hypotheses on the failure of our study on our main outcome, which was pain,” he said. “The first is a low-dose of methotrexate, and the second may be ... a placebo effect, which is very, very important in osteoarthritis.”
Dr. Roux noted the results from the ADEM trial were similar to a recent study in which 90 patients with hand OA were randomized to receive etanercept or placebo. At 24 weeks, there was no statistically significant difference between VAS pain in the etanercept group (between group difference, −5.7; 95% confidence interval, −15.9 to 4.5; P = .27) and the placebo groups, and at 1 year (between-group difference, –8.5; 95% CI, −18.6 to 1.6; P = .10), although the results favored patients receiving anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy (Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:1757-64. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213202).
With regard to the Verbruggen-Veys score, joint degradation was not significantly higher in the placebo group (29.4%), compared with the MTX group (7.7%), but there was a significantly higher number of erosive joints progressing to a remodeling phase in the MTX group (27.2%), compared with the placebo group (15.2%) at 12 months.
Dr. Roux said two factors are likely predictors of erosive disease based on data in ADEM: the level of interleukin-6 at baseline (odds ratio, 1.04; 95% CI, 1.03-1.06; P less than .0001), and joints with synovitis at baseline (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 1.25-17.90; P = .02).
“Our study has several limitations, but we like to see our study as a pilot study,” he added, noting that a study analyzing bone turnover in patients with different doses of methotrexate and a longer disease duration is needed.
The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ferraro S et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 1759.
ATLANTA – , according to results from the small, prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled ADEM trial.
“Our study failed to show the superiority of methotrexate over placebo on pain evolution, but our results on structural evolution and the presence of inflammatory parameters as predictors of erosive evolution in nonerosive diseases may lead us to discuss the place of methotrexate in early steps of the disease evolution, and underlines the importance of the part played by the interaction between synovitis and subchondral bone in erosive progression,” Christian Roux, MD, PhD, of the department of rheumatology at Côte d’Azur University, Nice, France, said in his presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Dr. Roux and colleagues enrolled 64 patients in the ADEM trial, where patients with symptomatic erosive hand osteoarthritis (EHOA) were randomized to receive 10 mg of methotrexate (MTX) per week or placebo. At 3 months, researchers assessed patients for pain using the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) score for hand pain, and secondary outcome measures at 12 months included VAS score for hand pain, radiographic progression using Verbruggen-Veys Anatomical Phase Score and Gent University Scoring System, and MRI.
Patients were included in the study if they were between 45 and 85 years old with a VAS pain score greater than 40, had failed classic therapeutics (acetaminophen, topical NSAIDs, and symptomatic slow-acting drugs), and had at least one erosive lesion. At baseline, the MTX and placebo groups were not significantly different with regard to gender (91% vs. 97% female), mean body mass index (24.6 kg/m2 vs. 24.2 kg/m2) and mean age (67.5 years vs. 64.9 years). Radiologic data showed joint loss, erosive, and erosive plus remodeling measurements were also similar between groups at baseline.
The mean VAS score for patients in the MTX group decreased from 65.7 at baseline to 48.2 at 3 months (–17.5; P = .07), compared with a decrease from 63.9 to 55.5 (–8.4; P = .002). At 12 months, VAS scores for patients in the MTX group decreased to 47.5, compared with a decrease in the placebo group to 48.2. However, the between-group differences for VAS scores were not significant at 3 months (P = .2) and at 12 months (P = .6).
“We have different hypotheses on the failure of our study on our main outcome, which was pain,” he said. “The first is a low-dose of methotrexate, and the second may be ... a placebo effect, which is very, very important in osteoarthritis.”
Dr. Roux noted the results from the ADEM trial were similar to a recent study in which 90 patients with hand OA were randomized to receive etanercept or placebo. At 24 weeks, there was no statistically significant difference between VAS pain in the etanercept group (between group difference, −5.7; 95% confidence interval, −15.9 to 4.5; P = .27) and the placebo groups, and at 1 year (between-group difference, –8.5; 95% CI, −18.6 to 1.6; P = .10), although the results favored patients receiving anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy (Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:1757-64. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213202).
With regard to the Verbruggen-Veys score, joint degradation was not significantly higher in the placebo group (29.4%), compared with the MTX group (7.7%), but there was a significantly higher number of erosive joints progressing to a remodeling phase in the MTX group (27.2%), compared with the placebo group (15.2%) at 12 months.
Dr. Roux said two factors are likely predictors of erosive disease based on data in ADEM: the level of interleukin-6 at baseline (odds ratio, 1.04; 95% CI, 1.03-1.06; P less than .0001), and joints with synovitis at baseline (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 1.25-17.90; P = .02).
“Our study has several limitations, but we like to see our study as a pilot study,” he added, noting that a study analyzing bone turnover in patients with different doses of methotrexate and a longer disease duration is needed.
The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ferraro S et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 1759.
ATLANTA – , according to results from the small, prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled ADEM trial.
“Our study failed to show the superiority of methotrexate over placebo on pain evolution, but our results on structural evolution and the presence of inflammatory parameters as predictors of erosive evolution in nonerosive diseases may lead us to discuss the place of methotrexate in early steps of the disease evolution, and underlines the importance of the part played by the interaction between synovitis and subchondral bone in erosive progression,” Christian Roux, MD, PhD, of the department of rheumatology at Côte d’Azur University, Nice, France, said in his presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Dr. Roux and colleagues enrolled 64 patients in the ADEM trial, where patients with symptomatic erosive hand osteoarthritis (EHOA) were randomized to receive 10 mg of methotrexate (MTX) per week or placebo. At 3 months, researchers assessed patients for pain using the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) score for hand pain, and secondary outcome measures at 12 months included VAS score for hand pain, radiographic progression using Verbruggen-Veys Anatomical Phase Score and Gent University Scoring System, and MRI.
Patients were included in the study if they were between 45 and 85 years old with a VAS pain score greater than 40, had failed classic therapeutics (acetaminophen, topical NSAIDs, and symptomatic slow-acting drugs), and had at least one erosive lesion. At baseline, the MTX and placebo groups were not significantly different with regard to gender (91% vs. 97% female), mean body mass index (24.6 kg/m2 vs. 24.2 kg/m2) and mean age (67.5 years vs. 64.9 years). Radiologic data showed joint loss, erosive, and erosive plus remodeling measurements were also similar between groups at baseline.
The mean VAS score for patients in the MTX group decreased from 65.7 at baseline to 48.2 at 3 months (–17.5; P = .07), compared with a decrease from 63.9 to 55.5 (–8.4; P = .002). At 12 months, VAS scores for patients in the MTX group decreased to 47.5, compared with a decrease in the placebo group to 48.2. However, the between-group differences for VAS scores were not significant at 3 months (P = .2) and at 12 months (P = .6).
“We have different hypotheses on the failure of our study on our main outcome, which was pain,” he said. “The first is a low-dose of methotrexate, and the second may be ... a placebo effect, which is very, very important in osteoarthritis.”
Dr. Roux noted the results from the ADEM trial were similar to a recent study in which 90 patients with hand OA were randomized to receive etanercept or placebo. At 24 weeks, there was no statistically significant difference between VAS pain in the etanercept group (between group difference, −5.7; 95% confidence interval, −15.9 to 4.5; P = .27) and the placebo groups, and at 1 year (between-group difference, –8.5; 95% CI, −18.6 to 1.6; P = .10), although the results favored patients receiving anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy (Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:1757-64. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213202).
With regard to the Verbruggen-Veys score, joint degradation was not significantly higher in the placebo group (29.4%), compared with the MTX group (7.7%), but there was a significantly higher number of erosive joints progressing to a remodeling phase in the MTX group (27.2%), compared with the placebo group (15.2%) at 12 months.
Dr. Roux said two factors are likely predictors of erosive disease based on data in ADEM: the level of interleukin-6 at baseline (odds ratio, 1.04; 95% CI, 1.03-1.06; P less than .0001), and joints with synovitis at baseline (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 1.25-17.90; P = .02).
“Our study has several limitations, but we like to see our study as a pilot study,” he added, noting that a study analyzing bone turnover in patients with different doses of methotrexate and a longer disease duration is needed.
The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Ferraro S et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10), Abstract 1759.
REPORTING FROM ACR 2019
Cannabinoids, stem cells lack evidence for osteoarthritis, expert says
LAS VEGAS – Planned clinical trials may clarify whether they benefit patients, said Joel A. Block, MD, professor of rheumatology at Rush University in Chicago.
Cannabinoid therapy “is on everybody’s mind, including our patients,” Dr. Block said at the annual Perspectives in Rheumatic Diseases held by Global Academy for Medical Education. “Cannabinoid receptors are widely present in all joint tissues, and endocannabinoids are clearly present in OA joint tissue. There is good evidence that the receptors regulate pain responses and central sensitization in a variety of OA animal models.” Where cannabis is legal, many people use it for chronic noncancer pain. Side effects may include altered perception, dizziness, drowsiness, and gastrointestinal adverse events.
Cannabis in the literature
“Nonetheless, if you do a systematic review of all of the randomized clinical trials of cannabinoids in human rheumatic diseases, what you will find is there is a grand total of four,” he said. The trials included patients with rheumatoid arthritis, OA, and fibromyalgia. An analysis of aggregated data found that cannabinoids improved pain and sleep, but all of the trials had a high risk of bias, poor allocation concealment, and poor blinding, said Dr. Block (Arthritis Care Res [Hoboken]. 2016 May;68[5]:681-8.). “In OA, there is one randomized trial, and it was entirely null,” he said. “There was no positive effect on pain or on function in human OA” (Pain. 2012 Sep;153[9]:1837-46.).
ClinicalTrials.gov lists two planned randomized controlled trials of cannabinoids – one using vaporized cannabis in patients with knee OA, and one using cannabidiol for hand OA and psoriatic arthritis. “Clinical trials are still scarce as of right now, so it will take a while before we have evidence for or against,” said Dr. Block.
Stem cell injections
Intra-articular stem cell injections are widely offered in the United States and abroad, he said. “In every newspaper, wherever I go, I open it up and there are full-page ads on stem cell injections that will cure everything that you want,” he said.
A systematic review of the effect of stem cell injections on structural outcomes and pain-related behaviors in animals found that “for all outcomes, the evidence quality was either low or very low,” Dr. Block said (Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018 Apr;26[4]:445-61.). “Even in the animal models, it has been very hard to demonstrate any effect at all from just injecting stem cells into the joint.”
Systematic reviews of the evidence in humans have found that the data do not support the use of stem cell injections. The authors of one review concluded, “In the absence of high-level evidence, we do not recommend stem cell therapy” for knee OA (Br J Sports Med. 2017 Aug;51[15]:1125-33.).
For another recent review, researchers screened hundreds of articles and identified 5 trials that met their inclusion criteria. They concluded, “Current evidence does not support the use of intra-articular [mesenchymal stem cells] for improving cartilage repair in knee osteoarthritis” (Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019 Jul;139[7]:971-80.).
Many clinical trials are planned, however. “Over the next several years, I would expect that we are going to get some real data on whether these are helpful or not,” Dr. Block said.
Meanwhile, some patients spend thousands of dollars to receive stem cell injections, and clinics report average patient satisfaction rates of 82%. “How can they be getting so much relief when there is no evidence that it is helpful? In fact, whatever evidence we have says that it is no better than placebo,” said Dr. Block. “Placebo itself is very potent....People always do what they feel helps them regardless of objective data, because placebo itself is very palliative.”
Dr. Block is a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Medivir, and Zynerba Pharmaceuticals. He has received royalties from Agios, Daiichi Sankyo, and Omeros. In addition, he has received grant or research support from AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and Kolon TissueGene.
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – Planned clinical trials may clarify whether they benefit patients, said Joel A. Block, MD, professor of rheumatology at Rush University in Chicago.
Cannabinoid therapy “is on everybody’s mind, including our patients,” Dr. Block said at the annual Perspectives in Rheumatic Diseases held by Global Academy for Medical Education. “Cannabinoid receptors are widely present in all joint tissues, and endocannabinoids are clearly present in OA joint tissue. There is good evidence that the receptors regulate pain responses and central sensitization in a variety of OA animal models.” Where cannabis is legal, many people use it for chronic noncancer pain. Side effects may include altered perception, dizziness, drowsiness, and gastrointestinal adverse events.
Cannabis in the literature
“Nonetheless, if you do a systematic review of all of the randomized clinical trials of cannabinoids in human rheumatic diseases, what you will find is there is a grand total of four,” he said. The trials included patients with rheumatoid arthritis, OA, and fibromyalgia. An analysis of aggregated data found that cannabinoids improved pain and sleep, but all of the trials had a high risk of bias, poor allocation concealment, and poor blinding, said Dr. Block (Arthritis Care Res [Hoboken]. 2016 May;68[5]:681-8.). “In OA, there is one randomized trial, and it was entirely null,” he said. “There was no positive effect on pain or on function in human OA” (Pain. 2012 Sep;153[9]:1837-46.).
ClinicalTrials.gov lists two planned randomized controlled trials of cannabinoids – one using vaporized cannabis in patients with knee OA, and one using cannabidiol for hand OA and psoriatic arthritis. “Clinical trials are still scarce as of right now, so it will take a while before we have evidence for or against,” said Dr. Block.
Stem cell injections
Intra-articular stem cell injections are widely offered in the United States and abroad, he said. “In every newspaper, wherever I go, I open it up and there are full-page ads on stem cell injections that will cure everything that you want,” he said.
A systematic review of the effect of stem cell injections on structural outcomes and pain-related behaviors in animals found that “for all outcomes, the evidence quality was either low or very low,” Dr. Block said (Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018 Apr;26[4]:445-61.). “Even in the animal models, it has been very hard to demonstrate any effect at all from just injecting stem cells into the joint.”
Systematic reviews of the evidence in humans have found that the data do not support the use of stem cell injections. The authors of one review concluded, “In the absence of high-level evidence, we do not recommend stem cell therapy” for knee OA (Br J Sports Med. 2017 Aug;51[15]:1125-33.).
For another recent review, researchers screened hundreds of articles and identified 5 trials that met their inclusion criteria. They concluded, “Current evidence does not support the use of intra-articular [mesenchymal stem cells] for improving cartilage repair in knee osteoarthritis” (Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019 Jul;139[7]:971-80.).
Many clinical trials are planned, however. “Over the next several years, I would expect that we are going to get some real data on whether these are helpful or not,” Dr. Block said.
Meanwhile, some patients spend thousands of dollars to receive stem cell injections, and clinics report average patient satisfaction rates of 82%. “How can they be getting so much relief when there is no evidence that it is helpful? In fact, whatever evidence we have says that it is no better than placebo,” said Dr. Block. “Placebo itself is very potent....People always do what they feel helps them regardless of objective data, because placebo itself is very palliative.”
Dr. Block is a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Medivir, and Zynerba Pharmaceuticals. He has received royalties from Agios, Daiichi Sankyo, and Omeros. In addition, he has received grant or research support from AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and Kolon TissueGene.
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – Planned clinical trials may clarify whether they benefit patients, said Joel A. Block, MD, professor of rheumatology at Rush University in Chicago.
Cannabinoid therapy “is on everybody’s mind, including our patients,” Dr. Block said at the annual Perspectives in Rheumatic Diseases held by Global Academy for Medical Education. “Cannabinoid receptors are widely present in all joint tissues, and endocannabinoids are clearly present in OA joint tissue. There is good evidence that the receptors regulate pain responses and central sensitization in a variety of OA animal models.” Where cannabis is legal, many people use it for chronic noncancer pain. Side effects may include altered perception, dizziness, drowsiness, and gastrointestinal adverse events.
Cannabis in the literature
“Nonetheless, if you do a systematic review of all of the randomized clinical trials of cannabinoids in human rheumatic diseases, what you will find is there is a grand total of four,” he said. The trials included patients with rheumatoid arthritis, OA, and fibromyalgia. An analysis of aggregated data found that cannabinoids improved pain and sleep, but all of the trials had a high risk of bias, poor allocation concealment, and poor blinding, said Dr. Block (Arthritis Care Res [Hoboken]. 2016 May;68[5]:681-8.). “In OA, there is one randomized trial, and it was entirely null,” he said. “There was no positive effect on pain or on function in human OA” (Pain. 2012 Sep;153[9]:1837-46.).
ClinicalTrials.gov lists two planned randomized controlled trials of cannabinoids – one using vaporized cannabis in patients with knee OA, and one using cannabidiol for hand OA and psoriatic arthritis. “Clinical trials are still scarce as of right now, so it will take a while before we have evidence for or against,” said Dr. Block.
Stem cell injections
Intra-articular stem cell injections are widely offered in the United States and abroad, he said. “In every newspaper, wherever I go, I open it up and there are full-page ads on stem cell injections that will cure everything that you want,” he said.
A systematic review of the effect of stem cell injections on structural outcomes and pain-related behaviors in animals found that “for all outcomes, the evidence quality was either low or very low,” Dr. Block said (Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018 Apr;26[4]:445-61.). “Even in the animal models, it has been very hard to demonstrate any effect at all from just injecting stem cells into the joint.”
Systematic reviews of the evidence in humans have found that the data do not support the use of stem cell injections. The authors of one review concluded, “In the absence of high-level evidence, we do not recommend stem cell therapy” for knee OA (Br J Sports Med. 2017 Aug;51[15]:1125-33.).
For another recent review, researchers screened hundreds of articles and identified 5 trials that met their inclusion criteria. They concluded, “Current evidence does not support the use of intra-articular [mesenchymal stem cells] for improving cartilage repair in knee osteoarthritis” (Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019 Jul;139[7]:971-80.).
Many clinical trials are planned, however. “Over the next several years, I would expect that we are going to get some real data on whether these are helpful or not,” Dr. Block said.
Meanwhile, some patients spend thousands of dollars to receive stem cell injections, and clinics report average patient satisfaction rates of 82%. “How can they be getting so much relief when there is no evidence that it is helpful? In fact, whatever evidence we have says that it is no better than placebo,” said Dr. Block. “Placebo itself is very potent....People always do what they feel helps them regardless of objective data, because placebo itself is very palliative.”
Dr. Block is a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Medivir, and Zynerba Pharmaceuticals. He has received royalties from Agios, Daiichi Sankyo, and Omeros. In addition, he has received grant or research support from AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and Kolon TissueGene.
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM PRD 2019
Consider centralized pain in patients with rheumatic disease
Las Vegas – A fibromyalgia survey may provide important information about the degree to which patients with rheumatic disease experience centralized pain. This information may guide treatment decisions, said Daniel J. Clauw, MD, professor of anesthesiology, rheumatology, and psychiatry and director of the Chronic Pain and Fatigue Research Center at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor.
The questionnaire that Dr. Clauw uses is a patient self-report survey for the assessment of fibromyalgia based on criteria in the 2011 modification of the American College of Rheumatology preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia. In it, he asks patients to report where they experience pain throughout the body and symptoms such as fatigue, sleep problems, and memory problems. The survey predicts outcomes of surgery for osteoarthritis better than x-rays, MRI scans, or psychological factors do, he said.
Physicians should ask every patient with chronic pain, including patients with OA, rheumatoid arthritis, or lupus, to complete the survey, Dr. Clauw said at the annual Perspectives in Rheumatic Diseases held by Global Academy for Medical Education. “This score will tell you the degree to which their central nervous system is augmenting or amplifying what is going on in their body,” he said. “And the higher their score is, the more you should treat them like you would someone with fibromyalgia, even if their underlying disease might be an autoimmune disease.”
Physicians should not use a cutoff of 13 points on the fibromyalgia measure to define whether a patient has the disease, as has been done in the past, he said. The threshold is arbitrary, he said. “We should not think about fibromyalgia as ‘yes’ or ‘no.’ We should think of the degree of fibromyalgia that people have.”
A poor relationship between pain and imaging
Some patients who have severe knee OA on imaging walk without pain. Other patients have normal x-rays, but severe pain. “There is a terrible relationship between what you see on a knee x-ray or an MRI and whether someone has pain,” Dr. Clauw said. Furthermore, the poor relationship between imaging and pain is common across chronic pain conditions, he said.
This phenomenon may occur because pain manifests in different ways, similar to there being multiple ways to adjust the volume of an electric guitar, he said. How hard the strings are strummed affects the volume. But so does the amplifier setting. “In these centralized pain conditions, the problem is an amplifier problem, not a guitar problem,” he said. “The amplifier, i.e., the central nervous system, is set too high.”
Researchers have found that people who have severe OA of the knee on x-ray but do not experience pain “have a very low amplifier setting,” he said. That is, they are nontender and less sensitive to pain. Most of these patients are men. “On average, men have a much lower amplifier setting than women,” he said. “This is also why ... women have 1.5 to 2 times the rate of any type of chronic pain than men, because on average women have a higher amplifier setting. ... In OA, at any given age, men and women have the exact same percentage of radiographic OA. But if you look at the clinical condition of OA, it is always two-thirds women, one-third men.”
Opioid responsiveness
To examine whether fibromyalgia survey results correlate with outcomes after knee and hip arthroplasty, Dr. Clauw and colleagues conducted a prospective, observational cohort study that included approximately 500 people. Patients completed the questionnaire on the day of surgery.
Patients with higher levels of fibromyalgia were less responsive to opioids. “For each 1-point increase in the fibromyalgia score, people needed about one more hydrocodone tablet in the first 24-48 hours to control their pain,” he said (Anesthesiology. 2013 Dec;119[6]:1434-43). In addition, each 1-point increase in the fibromyalgia score made people about 25% less likely to have a 50% improvement in knee pain level after 6 months (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 May;67[5]:1386-94). The correlations were independent of psychological factors. In addition, the associations were linear. “There was nothing magical about a fibromyalgia score of 13,” Dr. Clauw said.
Dr. Clauw is a coauthor of a study to be presented at the 2019 American College of Rheumatology/Association of Rheumatology Professionals annual meeting that found pain centralization in patients with RA is associated with poor response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Prior studies in patients with RA have found that the degree of fibromyalgia is a better predictor of pain and disability than erythrocyte sedimentation rate or the number of swollen joints.
Diagnosed cases are the “tip of the iceberg”
Researchers at Dr. Clauw’s institution have identified dozens of patients undergoing knee surgery who met criteria for fibromyalgia but had not received the diagnosis. “This is at the University of Michigan, which is the epicenter for fibromyalgia research. If we are not seeing fibromyalgia superimposed on OA in our patients, no one is seeing it,” he said.
Patients with diagnosed fibromyalgia are “the tip of the iceberg,” he said. “There are far greater numbers of individuals whose primary diagnosis is OA, RA, lupus, ankylosing spondylitis, cancer pain, or sickle cell disease that have the same fundamental problem as fibromyalgia patients. But you do not see it because you label them as having an autoimmune disease or osteoarthritis. And that is at your peril and at their peril. Because treating that individual as if all of their pain and other symptoms are due to a problem out on the periphery will not make that person better.”
Patients with high levels of centralized pain may be less responsive to peripherally directed therapies such as surgery or injections, Dr. Clauw said. Pharmacologic options for patients with centralized pain include gabapentinoids (e.g., pregabalin and gabapentin), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (e.g., duloxetine and milnacipran), and tricyclic compounds (e.g., amitriptyline and cyclobenzaprine), he said. “Opioids are going to be quite unlikely to help these individuals,” he said. “In fact, it is likely that opioids will make this kind of pain worse.”
Dr. Clauw is a consultant for Aptinyx, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Intec Pharma, Pfizer, Samumed, Theravance, Tonix, and Zynerba Pharma. He has received grant or research support from Aptinyx and Pfizer and is an expert witness.
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Las Vegas – A fibromyalgia survey may provide important information about the degree to which patients with rheumatic disease experience centralized pain. This information may guide treatment decisions, said Daniel J. Clauw, MD, professor of anesthesiology, rheumatology, and psychiatry and director of the Chronic Pain and Fatigue Research Center at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor.
The questionnaire that Dr. Clauw uses is a patient self-report survey for the assessment of fibromyalgia based on criteria in the 2011 modification of the American College of Rheumatology preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia. In it, he asks patients to report where they experience pain throughout the body and symptoms such as fatigue, sleep problems, and memory problems. The survey predicts outcomes of surgery for osteoarthritis better than x-rays, MRI scans, or psychological factors do, he said.
Physicians should ask every patient with chronic pain, including patients with OA, rheumatoid arthritis, or lupus, to complete the survey, Dr. Clauw said at the annual Perspectives in Rheumatic Diseases held by Global Academy for Medical Education. “This score will tell you the degree to which their central nervous system is augmenting or amplifying what is going on in their body,” he said. “And the higher their score is, the more you should treat them like you would someone with fibromyalgia, even if their underlying disease might be an autoimmune disease.”
Physicians should not use a cutoff of 13 points on the fibromyalgia measure to define whether a patient has the disease, as has been done in the past, he said. The threshold is arbitrary, he said. “We should not think about fibromyalgia as ‘yes’ or ‘no.’ We should think of the degree of fibromyalgia that people have.”
A poor relationship between pain and imaging
Some patients who have severe knee OA on imaging walk without pain. Other patients have normal x-rays, but severe pain. “There is a terrible relationship between what you see on a knee x-ray or an MRI and whether someone has pain,” Dr. Clauw said. Furthermore, the poor relationship between imaging and pain is common across chronic pain conditions, he said.
This phenomenon may occur because pain manifests in different ways, similar to there being multiple ways to adjust the volume of an electric guitar, he said. How hard the strings are strummed affects the volume. But so does the amplifier setting. “In these centralized pain conditions, the problem is an amplifier problem, not a guitar problem,” he said. “The amplifier, i.e., the central nervous system, is set too high.”
Researchers have found that people who have severe OA of the knee on x-ray but do not experience pain “have a very low amplifier setting,” he said. That is, they are nontender and less sensitive to pain. Most of these patients are men. “On average, men have a much lower amplifier setting than women,” he said. “This is also why ... women have 1.5 to 2 times the rate of any type of chronic pain than men, because on average women have a higher amplifier setting. ... In OA, at any given age, men and women have the exact same percentage of radiographic OA. But if you look at the clinical condition of OA, it is always two-thirds women, one-third men.”
Opioid responsiveness
To examine whether fibromyalgia survey results correlate with outcomes after knee and hip arthroplasty, Dr. Clauw and colleagues conducted a prospective, observational cohort study that included approximately 500 people. Patients completed the questionnaire on the day of surgery.
Patients with higher levels of fibromyalgia were less responsive to opioids. “For each 1-point increase in the fibromyalgia score, people needed about one more hydrocodone tablet in the first 24-48 hours to control their pain,” he said (Anesthesiology. 2013 Dec;119[6]:1434-43). In addition, each 1-point increase in the fibromyalgia score made people about 25% less likely to have a 50% improvement in knee pain level after 6 months (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 May;67[5]:1386-94). The correlations were independent of psychological factors. In addition, the associations were linear. “There was nothing magical about a fibromyalgia score of 13,” Dr. Clauw said.
Dr. Clauw is a coauthor of a study to be presented at the 2019 American College of Rheumatology/Association of Rheumatology Professionals annual meeting that found pain centralization in patients with RA is associated with poor response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Prior studies in patients with RA have found that the degree of fibromyalgia is a better predictor of pain and disability than erythrocyte sedimentation rate or the number of swollen joints.
Diagnosed cases are the “tip of the iceberg”
Researchers at Dr. Clauw’s institution have identified dozens of patients undergoing knee surgery who met criteria for fibromyalgia but had not received the diagnosis. “This is at the University of Michigan, which is the epicenter for fibromyalgia research. If we are not seeing fibromyalgia superimposed on OA in our patients, no one is seeing it,” he said.
Patients with diagnosed fibromyalgia are “the tip of the iceberg,” he said. “There are far greater numbers of individuals whose primary diagnosis is OA, RA, lupus, ankylosing spondylitis, cancer pain, or sickle cell disease that have the same fundamental problem as fibromyalgia patients. But you do not see it because you label them as having an autoimmune disease or osteoarthritis. And that is at your peril and at their peril. Because treating that individual as if all of their pain and other symptoms are due to a problem out on the periphery will not make that person better.”
Patients with high levels of centralized pain may be less responsive to peripherally directed therapies such as surgery or injections, Dr. Clauw said. Pharmacologic options for patients with centralized pain include gabapentinoids (e.g., pregabalin and gabapentin), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (e.g., duloxetine and milnacipran), and tricyclic compounds (e.g., amitriptyline and cyclobenzaprine), he said. “Opioids are going to be quite unlikely to help these individuals,” he said. “In fact, it is likely that opioids will make this kind of pain worse.”
Dr. Clauw is a consultant for Aptinyx, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Intec Pharma, Pfizer, Samumed, Theravance, Tonix, and Zynerba Pharma. He has received grant or research support from Aptinyx and Pfizer and is an expert witness.
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Las Vegas – A fibromyalgia survey may provide important information about the degree to which patients with rheumatic disease experience centralized pain. This information may guide treatment decisions, said Daniel J. Clauw, MD, professor of anesthesiology, rheumatology, and psychiatry and director of the Chronic Pain and Fatigue Research Center at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor.
The questionnaire that Dr. Clauw uses is a patient self-report survey for the assessment of fibromyalgia based on criteria in the 2011 modification of the American College of Rheumatology preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia. In it, he asks patients to report where they experience pain throughout the body and symptoms such as fatigue, sleep problems, and memory problems. The survey predicts outcomes of surgery for osteoarthritis better than x-rays, MRI scans, or psychological factors do, he said.
Physicians should ask every patient with chronic pain, including patients with OA, rheumatoid arthritis, or lupus, to complete the survey, Dr. Clauw said at the annual Perspectives in Rheumatic Diseases held by Global Academy for Medical Education. “This score will tell you the degree to which their central nervous system is augmenting or amplifying what is going on in their body,” he said. “And the higher their score is, the more you should treat them like you would someone with fibromyalgia, even if their underlying disease might be an autoimmune disease.”
Physicians should not use a cutoff of 13 points on the fibromyalgia measure to define whether a patient has the disease, as has been done in the past, he said. The threshold is arbitrary, he said. “We should not think about fibromyalgia as ‘yes’ or ‘no.’ We should think of the degree of fibromyalgia that people have.”
A poor relationship between pain and imaging
Some patients who have severe knee OA on imaging walk without pain. Other patients have normal x-rays, but severe pain. “There is a terrible relationship between what you see on a knee x-ray or an MRI and whether someone has pain,” Dr. Clauw said. Furthermore, the poor relationship between imaging and pain is common across chronic pain conditions, he said.
This phenomenon may occur because pain manifests in different ways, similar to there being multiple ways to adjust the volume of an electric guitar, he said. How hard the strings are strummed affects the volume. But so does the amplifier setting. “In these centralized pain conditions, the problem is an amplifier problem, not a guitar problem,” he said. “The amplifier, i.e., the central nervous system, is set too high.”
Researchers have found that people who have severe OA of the knee on x-ray but do not experience pain “have a very low amplifier setting,” he said. That is, they are nontender and less sensitive to pain. Most of these patients are men. “On average, men have a much lower amplifier setting than women,” he said. “This is also why ... women have 1.5 to 2 times the rate of any type of chronic pain than men, because on average women have a higher amplifier setting. ... In OA, at any given age, men and women have the exact same percentage of radiographic OA. But if you look at the clinical condition of OA, it is always two-thirds women, one-third men.”
Opioid responsiveness
To examine whether fibromyalgia survey results correlate with outcomes after knee and hip arthroplasty, Dr. Clauw and colleagues conducted a prospective, observational cohort study that included approximately 500 people. Patients completed the questionnaire on the day of surgery.
Patients with higher levels of fibromyalgia were less responsive to opioids. “For each 1-point increase in the fibromyalgia score, people needed about one more hydrocodone tablet in the first 24-48 hours to control their pain,” he said (Anesthesiology. 2013 Dec;119[6]:1434-43). In addition, each 1-point increase in the fibromyalgia score made people about 25% less likely to have a 50% improvement in knee pain level after 6 months (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 May;67[5]:1386-94). The correlations were independent of psychological factors. In addition, the associations were linear. “There was nothing magical about a fibromyalgia score of 13,” Dr. Clauw said.
Dr. Clauw is a coauthor of a study to be presented at the 2019 American College of Rheumatology/Association of Rheumatology Professionals annual meeting that found pain centralization in patients with RA is associated with poor response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Prior studies in patients with RA have found that the degree of fibromyalgia is a better predictor of pain and disability than erythrocyte sedimentation rate or the number of swollen joints.
Diagnosed cases are the “tip of the iceberg”
Researchers at Dr. Clauw’s institution have identified dozens of patients undergoing knee surgery who met criteria for fibromyalgia but had not received the diagnosis. “This is at the University of Michigan, which is the epicenter for fibromyalgia research. If we are not seeing fibromyalgia superimposed on OA in our patients, no one is seeing it,” he said.
Patients with diagnosed fibromyalgia are “the tip of the iceberg,” he said. “There are far greater numbers of individuals whose primary diagnosis is OA, RA, lupus, ankylosing spondylitis, cancer pain, or sickle cell disease that have the same fundamental problem as fibromyalgia patients. But you do not see it because you label them as having an autoimmune disease or osteoarthritis. And that is at your peril and at their peril. Because treating that individual as if all of their pain and other symptoms are due to a problem out on the periphery will not make that person better.”
Patients with high levels of centralized pain may be less responsive to peripherally directed therapies such as surgery or injections, Dr. Clauw said. Pharmacologic options for patients with centralized pain include gabapentinoids (e.g., pregabalin and gabapentin), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (e.g., duloxetine and milnacipran), and tricyclic compounds (e.g., amitriptyline and cyclobenzaprine), he said. “Opioids are going to be quite unlikely to help these individuals,” he said. “In fact, it is likely that opioids will make this kind of pain worse.”
Dr. Clauw is a consultant for Aptinyx, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Intec Pharma, Pfizer, Samumed, Theravance, Tonix, and Zynerba Pharma. He has received grant or research support from Aptinyx and Pfizer and is an expert witness.
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM PRD 2019
Bariatric surgery has mostly positive impact in knee arthroplasty
a large study has found.
The study, led by Yicun Wang, PhD, of Nanjing (China) University was published in the Journal of Arthroplasty. “Generally speaking, bariatric surgery decreases some postoperative complications, decreases length of stay, and lowers mortality,” the study investigators wrote, [but] anemia and blood transfusion seem to be more common in patients with prior bariatric surgery.
They analyzed the effect of bariatric surgery on subsequent arthroplasty in morbidly obese patients in the United States using Nationwide Inpatient Sample 2006-2014 data on total hip arthroplasty (THA) and total knee arthroplasty (TKA). The researchers defined morbid obese patients as those with a body mass index higher than 40 kg/m2.
Among patients who underwent TKA, the researchers compared a group of 9,803 morbidly obese patients with the same number of patients who had undergone bariatric surgery. The two groups were matched by age, sex, income, primary insurance payer, and race.
There were large differences between the bariatric surgery group vs. morbidly obese group: Pulmonary embolism was much more common in the morbid obesity group (odds ratio, 0.22; 95% confidence interval, 0.05-1.03; P = .0346) while blood transfusion was more common in the bariatric surgery group (OR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.52-2.03; P less than .0001).
For TKA, the researchers used the same approach to analyze 2,540 matched pairs of patients. In the bariatric surgery vs. morbidly obese comparison, pulmonary embolism was more common in the morbidly obese group (OR, 0.34; 95% CI, 0.20-0.57; P less than .0001), as were respiratory complications (OR, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.26-0.78; P = .0032) and death (OR, 0.07; 95% CI, 0.01-0.50; P = .0005). But the bariatric surgery group had higher levels of blood transfusion (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.71-2.04; P less than .0001) and anemia (OR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.09-1.24; P less than .0001).
Going forward, the researchers write, “future studies on these patients should attempt to evaluate the impact of bariatric surgery on the long-term outcomes of arthroplasty.”
The study was supported by various funders including the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, the Project of Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Guangdong Province and others. No author disclosures are reported.
SOURCE: Wang Y et al. J Arthroplasty. 2019;S0883-5403(19)30667-9.
a large study has found.
The study, led by Yicun Wang, PhD, of Nanjing (China) University was published in the Journal of Arthroplasty. “Generally speaking, bariatric surgery decreases some postoperative complications, decreases length of stay, and lowers mortality,” the study investigators wrote, [but] anemia and blood transfusion seem to be more common in patients with prior bariatric surgery.
They analyzed the effect of bariatric surgery on subsequent arthroplasty in morbidly obese patients in the United States using Nationwide Inpatient Sample 2006-2014 data on total hip arthroplasty (THA) and total knee arthroplasty (TKA). The researchers defined morbid obese patients as those with a body mass index higher than 40 kg/m2.
Among patients who underwent TKA, the researchers compared a group of 9,803 morbidly obese patients with the same number of patients who had undergone bariatric surgery. The two groups were matched by age, sex, income, primary insurance payer, and race.
There were large differences between the bariatric surgery group vs. morbidly obese group: Pulmonary embolism was much more common in the morbid obesity group (odds ratio, 0.22; 95% confidence interval, 0.05-1.03; P = .0346) while blood transfusion was more common in the bariatric surgery group (OR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.52-2.03; P less than .0001).
For TKA, the researchers used the same approach to analyze 2,540 matched pairs of patients. In the bariatric surgery vs. morbidly obese comparison, pulmonary embolism was more common in the morbidly obese group (OR, 0.34; 95% CI, 0.20-0.57; P less than .0001), as were respiratory complications (OR, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.26-0.78; P = .0032) and death (OR, 0.07; 95% CI, 0.01-0.50; P = .0005). But the bariatric surgery group had higher levels of blood transfusion (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.71-2.04; P less than .0001) and anemia (OR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.09-1.24; P less than .0001).
Going forward, the researchers write, “future studies on these patients should attempt to evaluate the impact of bariatric surgery on the long-term outcomes of arthroplasty.”
The study was supported by various funders including the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, the Project of Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Guangdong Province and others. No author disclosures are reported.
SOURCE: Wang Y et al. J Arthroplasty. 2019;S0883-5403(19)30667-9.
a large study has found.
The study, led by Yicun Wang, PhD, of Nanjing (China) University was published in the Journal of Arthroplasty. “Generally speaking, bariatric surgery decreases some postoperative complications, decreases length of stay, and lowers mortality,” the study investigators wrote, [but] anemia and blood transfusion seem to be more common in patients with prior bariatric surgery.
They analyzed the effect of bariatric surgery on subsequent arthroplasty in morbidly obese patients in the United States using Nationwide Inpatient Sample 2006-2014 data on total hip arthroplasty (THA) and total knee arthroplasty (TKA). The researchers defined morbid obese patients as those with a body mass index higher than 40 kg/m2.
Among patients who underwent TKA, the researchers compared a group of 9,803 morbidly obese patients with the same number of patients who had undergone bariatric surgery. The two groups were matched by age, sex, income, primary insurance payer, and race.
There were large differences between the bariatric surgery group vs. morbidly obese group: Pulmonary embolism was much more common in the morbid obesity group (odds ratio, 0.22; 95% confidence interval, 0.05-1.03; P = .0346) while blood transfusion was more common in the bariatric surgery group (OR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.52-2.03; P less than .0001).
For TKA, the researchers used the same approach to analyze 2,540 matched pairs of patients. In the bariatric surgery vs. morbidly obese comparison, pulmonary embolism was more common in the morbidly obese group (OR, 0.34; 95% CI, 0.20-0.57; P less than .0001), as were respiratory complications (OR, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.26-0.78; P = .0032) and death (OR, 0.07; 95% CI, 0.01-0.50; P = .0005). But the bariatric surgery group had higher levels of blood transfusion (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.71-2.04; P less than .0001) and anemia (OR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.09-1.24; P less than .0001).
Going forward, the researchers write, “future studies on these patients should attempt to evaluate the impact of bariatric surgery on the long-term outcomes of arthroplasty.”
The study was supported by various funders including the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, the Project of Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Guangdong Province and others. No author disclosures are reported.
SOURCE: Wang Y et al. J Arthroplasty. 2019;S0883-5403(19)30667-9.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ARTHROPLASTY
Cannabidiol may interact with rheumatologic drugs
A number of medications commonly prescribed by rheumatologists may interact with cannabidiol oil, investigators at the Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, reported.
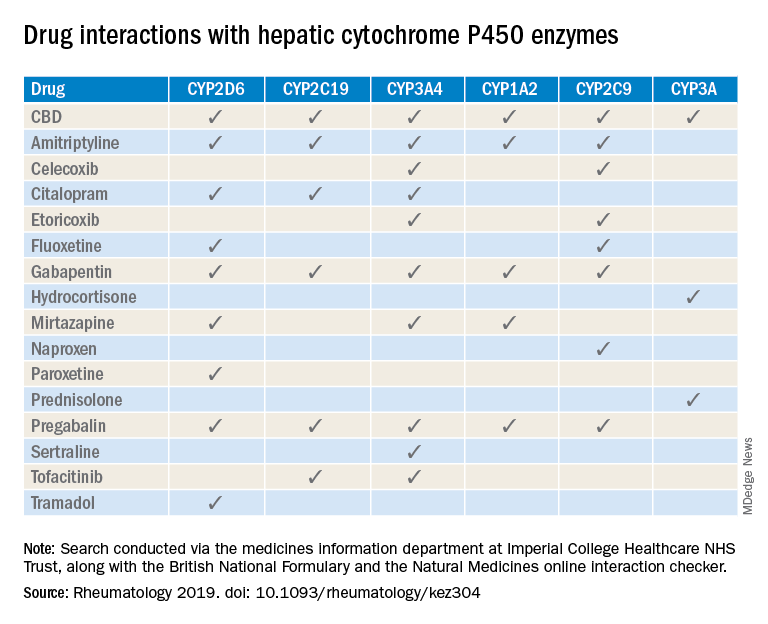
“Patients are increasingly requesting information concerning the safety of CBD oil,” Taryn Youngstein, MD, and associates said in letter to the editor in Rheumatology, but current guidelines on the use of medical cannabis do “not address the potential interactions between CBD oil and medicines frequently used in the rheumatology clinic.”
The most important potential CBD interaction, they suggested, may be with corticosteroids. Hydrocortisone and prednisolone both inhibit the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP3A, but CBD is a potent inhibitor of CYP3A, so “concomitant use may decrease glucocorticoid clearance and increase risk of systemic [corticosteroid] side effects,” the investigators wrote.
CBD also is known to inhibit the cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP3A4, and CYP1A2, which, alone or in combination, are involved in the metabolization of naproxen, tramadol, amitriptyline, and tofacitinib (Xeljanz), according to a literature search done via the college’s medicine information department that also used the British National Formulary and the Natural Medicines online interaction checker.
The Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib is included among the possible interactions, but the other Food and Drug Administration–approved JAK inhibitor, baricitinib (Olumiant), is primarily metabolized by the kidneys and should not have significant interaction with CBD, Dr. Youngstein and associates said. Most of the conventional synthetic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, including methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, adalimumab (Humira), and abatacept (Orencia), also are expected to be relatively free from CBD interactions.
This first published report on interactions between CBD oil and common rheumatology medications “highlights the importance of taking comprehensive drug histories, by asking directly about drugs considered alternative medicines and food supplements,” they said.
The investigators declared no conflicts of interest, and there was no specific funding for the study.
SOURCE: Wilson-Morkeh H et al. Rheumatology. 2019 July 29. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez304.
A number of medications commonly prescribed by rheumatologists may interact with cannabidiol oil, investigators at the Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, reported.

“Patients are increasingly requesting information concerning the safety of CBD oil,” Taryn Youngstein, MD, and associates said in letter to the editor in Rheumatology, but current guidelines on the use of medical cannabis do “not address the potential interactions between CBD oil and medicines frequently used in the rheumatology clinic.”
The most important potential CBD interaction, they suggested, may be with corticosteroids. Hydrocortisone and prednisolone both inhibit the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP3A, but CBD is a potent inhibitor of CYP3A, so “concomitant use may decrease glucocorticoid clearance and increase risk of systemic [corticosteroid] side effects,” the investigators wrote.
CBD also is known to inhibit the cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP3A4, and CYP1A2, which, alone or in combination, are involved in the metabolization of naproxen, tramadol, amitriptyline, and tofacitinib (Xeljanz), according to a literature search done via the college’s medicine information department that also used the British National Formulary and the Natural Medicines online interaction checker.
The Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib is included among the possible interactions, but the other Food and Drug Administration–approved JAK inhibitor, baricitinib (Olumiant), is primarily metabolized by the kidneys and should not have significant interaction with CBD, Dr. Youngstein and associates said. Most of the conventional synthetic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, including methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, adalimumab (Humira), and abatacept (Orencia), also are expected to be relatively free from CBD interactions.
This first published report on interactions between CBD oil and common rheumatology medications “highlights the importance of taking comprehensive drug histories, by asking directly about drugs considered alternative medicines and food supplements,” they said.
The investigators declared no conflicts of interest, and there was no specific funding for the study.
SOURCE: Wilson-Morkeh H et al. Rheumatology. 2019 July 29. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez304.
A number of medications commonly prescribed by rheumatologists may interact with cannabidiol oil, investigators at the Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, reported.

“Patients are increasingly requesting information concerning the safety of CBD oil,” Taryn Youngstein, MD, and associates said in letter to the editor in Rheumatology, but current guidelines on the use of medical cannabis do “not address the potential interactions between CBD oil and medicines frequently used in the rheumatology clinic.”
The most important potential CBD interaction, they suggested, may be with corticosteroids. Hydrocortisone and prednisolone both inhibit the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP3A, but CBD is a potent inhibitor of CYP3A, so “concomitant use may decrease glucocorticoid clearance and increase risk of systemic [corticosteroid] side effects,” the investigators wrote.
CBD also is known to inhibit the cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP3A4, and CYP1A2, which, alone or in combination, are involved in the metabolization of naproxen, tramadol, amitriptyline, and tofacitinib (Xeljanz), according to a literature search done via the college’s medicine information department that also used the British National Formulary and the Natural Medicines online interaction checker.
The Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib is included among the possible interactions, but the other Food and Drug Administration–approved JAK inhibitor, baricitinib (Olumiant), is primarily metabolized by the kidneys and should not have significant interaction with CBD, Dr. Youngstein and associates said. Most of the conventional synthetic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, including methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, adalimumab (Humira), and abatacept (Orencia), also are expected to be relatively free from CBD interactions.
This first published report on interactions between CBD oil and common rheumatology medications “highlights the importance of taking comprehensive drug histories, by asking directly about drugs considered alternative medicines and food supplements,” they said.
The investigators declared no conflicts of interest, and there was no specific funding for the study.
SOURCE: Wilson-Morkeh H et al. Rheumatology. 2019 July 29. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez304.
FROM RHEUMATOLOGY