User login
Hospitalist scheduling: A search for balance
Survey says ...
Scheduling. Has there ever been such a simple word that is so complex? A simple Internet search of hospitalist scheduling returns thousands of possible discussions, leaving readers to conclude that the possibilities are endless and the challenges great. The answer certainly is not a one-size-fits-all approach.
Hospitalist scheduling is one of the key sections in the 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) report; the 2018 report delves deeper into hospitalist scheduling than ever before.
For those of you who have been regular users of prior SoHM reports, you should be pleasantly surprised to find new comparative values: There are nearly 50% more pages dedicated just to scheduling!
For those readers who have never subscribed to the SoHM Report, this is your chance to study how other groups approach hospitalist schedules.
Why is hospitalist scheduling such a hot topic? For one, flexible and sustainable scheduling is an important contributor to job satisfaction. It is important for hospitalists to have a high degree of input into managing and effecting change for personal work-life balance.
As John Nelson, MD, MHM, a cofounder of the Society of Hospital Medicine, wrote recently in The Hospitalist, “an optimal schedule alone isn’t the key to preventing it [burnout], but maybe a good schedule can reduce your risk you’ll suffer from it.”
Secondly, ensuring that the hospitalist team is right sized – that is, scheduling hospitalists in the right place at the right time – is an art. Using resources, such as the 2018 SoHM report, to identify quantifiable comparisons enables hospitalist groups to continuously ensure the hospitalist schedule meets the clinical demands while optimizing the hospitalist group’s schedule.
Unfilled positions
The 2018 SoHM report features a new section on unfilled positions that may provide insight and better understanding about how your group compares to others, as it relates to properly evaluating your recruitment pipeline.
For hospital medicine groups (HMGs) serving adults only, two out of three groups have unfilled positions, and about half of pediatric-only hospitalist groups have unfilled positions. Andrew White, MD, SFHM, associate professor of medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, provided us with a deep-dive discussion of this topic in a recent article in The Hospitalist.
If your group has historically had more unfilled positions than the respondents, it might mean your group should consider different strategies to close the gap. It may also lead to conversations about how to rethink the schedule to better meet the demands of clinical care with limited resources.
So, with all these unfilled positions, how are hospitalist groups filling the gap? Not all groups are using locum tenens to fill those unfilled positions. About a third of hospitalist groups reported leaving those gaps uncovered.
The most commonly reported tactic to fill in the gaps was voluntary extra shifts by existing hospitalists (physicians and/or nurse practioners/physician assistants). This approach is used by 70% of hospitalist groups. The second most-used tactic was “moonlighters” or PRN physicians (57.4%). Thirdly, was use of locum tenens physicians.
With these baselines, we will be able to better track and trend the industry going forward.
Scheduling methodologies
For pediatric practices, the fixed rotating block scheduling has decreased over the two survey periods (16.7% versus 6.7%).
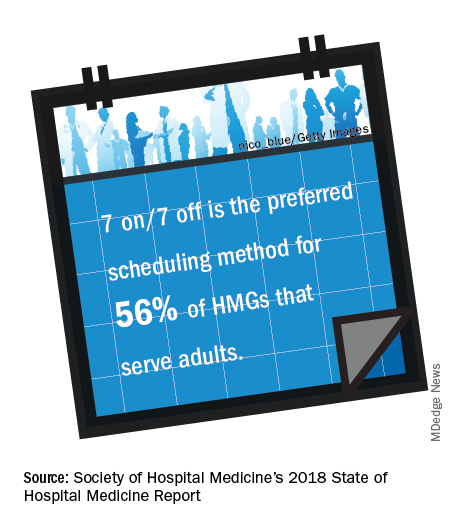
Even though the 7-on/7-off schedule remains quite popular among adult-only HMGs, many seasoned hospitalists wonder whether this is sustainable through all seasons of life. Some hospitalists have said a 7-on/7-off schedule is like turning on and off your personal life and that it takes a day or 2 to recover from 7 consecutive 12-hour days.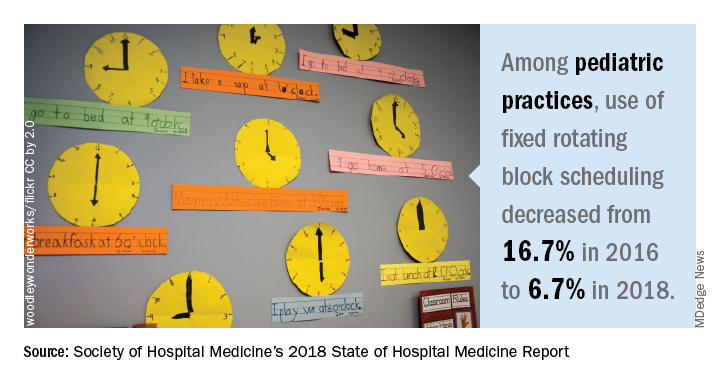
On the other hand, a fixed schedule is the easiest to explain, and many new hospitalists are requesting a fixed schedule. Even so, a fixed schedule may not allow for enough flexibility to adapt the schedule to the demands of patient care.
Nonetheless, a fixed schedule remains a very popular scheduling pattern. Does this scheduling model lead to burnout? Does this scheduling model increase or decrease elasticity? The debate of flexible versus fixed schedules continues!
Results by shift type
Very simply, the length of individual shifts has not changed much in prior years. For adult-only practices, most all day and night shifts are 12 hours in length. For pediatric-only HMGs, most day shifts are about 10 hours, and most night shifts are about 13 hours.
Most evening or swing shifts for adult-only practices are about 10 hours, which is a slight decrease from 2016. Pediatric-only practices’ evening shifts are about 8 hours in length.
A new question this year is about daytime admitters. For adult hospitalist groups, over half of groups have daytime admitters. For pediatric groups, nearly three out of four groups have daytime dedicated admitters. Also, the larger the group size, the more likely it is to have a dedicated daytime admitter.
Nocturnists remain in demand! Over 80% of adult hospitalist groups have on-site hospitalists at night. About a quarter of pediatric-only practices have nocturnists.
Scheduled workload distribution
One way of scheduling patient assignments is the phenomenon of unit-based assignments, or geographic rounding. As this has become more prevalent, the SHM Practice Analysis Committee recommended adding a question about unit-based assignments to the 2018 SoHM report.
The adoption of unit-based assignments is higher in academic groups (54.3%), as well as among hospitalists employed at a “hospital, health system or integrated delivery system” (47.4%), than in other group practice models.
Just as with the presence of daytime admitters, the larger the group the more likely it has some form of unit-based assignments. Further study would be needed to determine whether there is a link between the presence of daytime admitters and successful unit-based assignments for daytime rounders.
What’s the verdict?
Hospitalist scheduling will continue to evolve. It’s a never-ending balance of what’s best for patients and what’s best for hospitalists (and likely many other key stakeholders).
Scheduling is personal. Scheduling is an art form. The biggest question in this topic area is: Has anyone figured out the ‘secret sauce’ to hospitalist scheduling? Go online to SHM’s HMX to start the discussion!
Ms. Trask is national vice president of the Hospital Medicine Service Line at Catholic Health Initiatives in Englewood, Colo. She is also a member of The Hospitalist’s editorial advisory board.
Survey says ...
Survey says ...
Scheduling. Has there ever been such a simple word that is so complex? A simple Internet search of hospitalist scheduling returns thousands of possible discussions, leaving readers to conclude that the possibilities are endless and the challenges great. The answer certainly is not a one-size-fits-all approach.
Hospitalist scheduling is one of the key sections in the 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) report; the 2018 report delves deeper into hospitalist scheduling than ever before.
For those of you who have been regular users of prior SoHM reports, you should be pleasantly surprised to find new comparative values: There are nearly 50% more pages dedicated just to scheduling!
For those readers who have never subscribed to the SoHM Report, this is your chance to study how other groups approach hospitalist schedules.
Why is hospitalist scheduling such a hot topic? For one, flexible and sustainable scheduling is an important contributor to job satisfaction. It is important for hospitalists to have a high degree of input into managing and effecting change for personal work-life balance.
As John Nelson, MD, MHM, a cofounder of the Society of Hospital Medicine, wrote recently in The Hospitalist, “an optimal schedule alone isn’t the key to preventing it [burnout], but maybe a good schedule can reduce your risk you’ll suffer from it.”
Secondly, ensuring that the hospitalist team is right sized – that is, scheduling hospitalists in the right place at the right time – is an art. Using resources, such as the 2018 SoHM report, to identify quantifiable comparisons enables hospitalist groups to continuously ensure the hospitalist schedule meets the clinical demands while optimizing the hospitalist group’s schedule.
Unfilled positions
The 2018 SoHM report features a new section on unfilled positions that may provide insight and better understanding about how your group compares to others, as it relates to properly evaluating your recruitment pipeline.
For hospital medicine groups (HMGs) serving adults only, two out of three groups have unfilled positions, and about half of pediatric-only hospitalist groups have unfilled positions. Andrew White, MD, SFHM, associate professor of medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, provided us with a deep-dive discussion of this topic in a recent article in The Hospitalist.
If your group has historically had more unfilled positions than the respondents, it might mean your group should consider different strategies to close the gap. It may also lead to conversations about how to rethink the schedule to better meet the demands of clinical care with limited resources.
So, with all these unfilled positions, how are hospitalist groups filling the gap? Not all groups are using locum tenens to fill those unfilled positions. About a third of hospitalist groups reported leaving those gaps uncovered.
The most commonly reported tactic to fill in the gaps was voluntary extra shifts by existing hospitalists (physicians and/or nurse practioners/physician assistants). This approach is used by 70% of hospitalist groups. The second most-used tactic was “moonlighters” or PRN physicians (57.4%). Thirdly, was use of locum tenens physicians.
With these baselines, we will be able to better track and trend the industry going forward.
Scheduling methodologies

For pediatric practices, the fixed rotating block scheduling has decreased over the two survey periods (16.7% versus 6.7%).
Even though the 7-on/7-off schedule remains quite popular among adult-only HMGs, many seasoned hospitalists wonder whether this is sustainable through all seasons of life. Some hospitalists have said a 7-on/7-off schedule is like turning on and off your personal life and that it takes a day or 2 to recover from 7 consecutive 12-hour days.
On the other hand, a fixed schedule is the easiest to explain, and many new hospitalists are requesting a fixed schedule. Even so, a fixed schedule may not allow for enough flexibility to adapt the schedule to the demands of patient care.
Nonetheless, a fixed schedule remains a very popular scheduling pattern. Does this scheduling model lead to burnout? Does this scheduling model increase or decrease elasticity? The debate of flexible versus fixed schedules continues!
Results by shift type
Very simply, the length of individual shifts has not changed much in prior years. For adult-only practices, most all day and night shifts are 12 hours in length. For pediatric-only HMGs, most day shifts are about 10 hours, and most night shifts are about 13 hours.
Most evening or swing shifts for adult-only practices are about 10 hours, which is a slight decrease from 2016. Pediatric-only practices’ evening shifts are about 8 hours in length.
A new question this year is about daytime admitters. For adult hospitalist groups, over half of groups have daytime admitters. For pediatric groups, nearly three out of four groups have daytime dedicated admitters. Also, the larger the group size, the more likely it is to have a dedicated daytime admitter.
Nocturnists remain in demand! Over 80% of adult hospitalist groups have on-site hospitalists at night. About a quarter of pediatric-only practices have nocturnists.
Scheduled workload distribution
One way of scheduling patient assignments is the phenomenon of unit-based assignments, or geographic rounding. As this has become more prevalent, the SHM Practice Analysis Committee recommended adding a question about unit-based assignments to the 2018 SoHM report.
The adoption of unit-based assignments is higher in academic groups (54.3%), as well as among hospitalists employed at a “hospital, health system or integrated delivery system” (47.4%), than in other group practice models.
Just as with the presence of daytime admitters, the larger the group the more likely it has some form of unit-based assignments. Further study would be needed to determine whether there is a link between the presence of daytime admitters and successful unit-based assignments for daytime rounders.
What’s the verdict?
Hospitalist scheduling will continue to evolve. It’s a never-ending balance of what’s best for patients and what’s best for hospitalists (and likely many other key stakeholders).
Scheduling is personal. Scheduling is an art form. The biggest question in this topic area is: Has anyone figured out the ‘secret sauce’ to hospitalist scheduling? Go online to SHM’s HMX to start the discussion!
Ms. Trask is national vice president of the Hospital Medicine Service Line at Catholic Health Initiatives in Englewood, Colo. She is also a member of The Hospitalist’s editorial advisory board.
Scheduling. Has there ever been such a simple word that is so complex? A simple Internet search of hospitalist scheduling returns thousands of possible discussions, leaving readers to conclude that the possibilities are endless and the challenges great. The answer certainly is not a one-size-fits-all approach.
Hospitalist scheduling is one of the key sections in the 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) report; the 2018 report delves deeper into hospitalist scheduling than ever before.
For those of you who have been regular users of prior SoHM reports, you should be pleasantly surprised to find new comparative values: There are nearly 50% more pages dedicated just to scheduling!
For those readers who have never subscribed to the SoHM Report, this is your chance to study how other groups approach hospitalist schedules.
Why is hospitalist scheduling such a hot topic? For one, flexible and sustainable scheduling is an important contributor to job satisfaction. It is important for hospitalists to have a high degree of input into managing and effecting change for personal work-life balance.
As John Nelson, MD, MHM, a cofounder of the Society of Hospital Medicine, wrote recently in The Hospitalist, “an optimal schedule alone isn’t the key to preventing it [burnout], but maybe a good schedule can reduce your risk you’ll suffer from it.”
Secondly, ensuring that the hospitalist team is right sized – that is, scheduling hospitalists in the right place at the right time – is an art. Using resources, such as the 2018 SoHM report, to identify quantifiable comparisons enables hospitalist groups to continuously ensure the hospitalist schedule meets the clinical demands while optimizing the hospitalist group’s schedule.
Unfilled positions
The 2018 SoHM report features a new section on unfilled positions that may provide insight and better understanding about how your group compares to others, as it relates to properly evaluating your recruitment pipeline.
For hospital medicine groups (HMGs) serving adults only, two out of three groups have unfilled positions, and about half of pediatric-only hospitalist groups have unfilled positions. Andrew White, MD, SFHM, associate professor of medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, provided us with a deep-dive discussion of this topic in a recent article in The Hospitalist.
If your group has historically had more unfilled positions than the respondents, it might mean your group should consider different strategies to close the gap. It may also lead to conversations about how to rethink the schedule to better meet the demands of clinical care with limited resources.
So, with all these unfilled positions, how are hospitalist groups filling the gap? Not all groups are using locum tenens to fill those unfilled positions. About a third of hospitalist groups reported leaving those gaps uncovered.
The most commonly reported tactic to fill in the gaps was voluntary extra shifts by existing hospitalists (physicians and/or nurse practioners/physician assistants). This approach is used by 70% of hospitalist groups. The second most-used tactic was “moonlighters” or PRN physicians (57.4%). Thirdly, was use of locum tenens physicians.
With these baselines, we will be able to better track and trend the industry going forward.
Scheduling methodologies

For pediatric practices, the fixed rotating block scheduling has decreased over the two survey periods (16.7% versus 6.7%).
Even though the 7-on/7-off schedule remains quite popular among adult-only HMGs, many seasoned hospitalists wonder whether this is sustainable through all seasons of life. Some hospitalists have said a 7-on/7-off schedule is like turning on and off your personal life and that it takes a day or 2 to recover from 7 consecutive 12-hour days.
On the other hand, a fixed schedule is the easiest to explain, and many new hospitalists are requesting a fixed schedule. Even so, a fixed schedule may not allow for enough flexibility to adapt the schedule to the demands of patient care.
Nonetheless, a fixed schedule remains a very popular scheduling pattern. Does this scheduling model lead to burnout? Does this scheduling model increase or decrease elasticity? The debate of flexible versus fixed schedules continues!
Results by shift type
Very simply, the length of individual shifts has not changed much in prior years. For adult-only practices, most all day and night shifts are 12 hours in length. For pediatric-only HMGs, most day shifts are about 10 hours, and most night shifts are about 13 hours.
Most evening or swing shifts for adult-only practices are about 10 hours, which is a slight decrease from 2016. Pediatric-only practices’ evening shifts are about 8 hours in length.
A new question this year is about daytime admitters. For adult hospitalist groups, over half of groups have daytime admitters. For pediatric groups, nearly three out of four groups have daytime dedicated admitters. Also, the larger the group size, the more likely it is to have a dedicated daytime admitter.
Nocturnists remain in demand! Over 80% of adult hospitalist groups have on-site hospitalists at night. About a quarter of pediatric-only practices have nocturnists.
Scheduled workload distribution
One way of scheduling patient assignments is the phenomenon of unit-based assignments, or geographic rounding. As this has become more prevalent, the SHM Practice Analysis Committee recommended adding a question about unit-based assignments to the 2018 SoHM report.
The adoption of unit-based assignments is higher in academic groups (54.3%), as well as among hospitalists employed at a “hospital, health system or integrated delivery system” (47.4%), than in other group practice models.
Just as with the presence of daytime admitters, the larger the group the more likely it has some form of unit-based assignments. Further study would be needed to determine whether there is a link between the presence of daytime admitters and successful unit-based assignments for daytime rounders.
What’s the verdict?
Hospitalist scheduling will continue to evolve. It’s a never-ending balance of what’s best for patients and what’s best for hospitalists (and likely many other key stakeholders).
Scheduling is personal. Scheduling is an art form. The biggest question in this topic area is: Has anyone figured out the ‘secret sauce’ to hospitalist scheduling? Go online to SHM’s HMX to start the discussion!
Ms. Trask is national vice president of the Hospital Medicine Service Line at Catholic Health Initiatives in Englewood, Colo. She is also a member of The Hospitalist’s editorial advisory board.
Hospitalists on the Hill
Advocating for HM in DC
Another Hill Day is coming – the all-day advocacy event on Capitol Hill is scheduled in conjunction with the Society of Hospital Medicine’s Annual Conference whenever it is held in Washington, DC. In 2019, Hill Day will take place on March 27, the final day of HM19.
This will be the fourth Hill Day, and the last for some time, said Ron Greeno, MD, FCCP, MHM, senior advisor for government affairs at SHM and the society’s immediate past president. For at least the next 5 years, SHM’s annual conferences won’t be held in Washington, so there will not be any opportunities to plan a Hill Day during that time. “Members may want to take advantage of this opportunity,” Dr. Greeno said. “The people who do this never forget it.”
How Hill Day works
Sign up for Hill Day and you’ll spend a day visiting legislators and their health care staffers to educate them on what hospital medicine is, what a hospitalist does, and some of the pressing issues that affect the profession, said Joshua Lenchus, DO, RPh, FACP, SFHM, chair of the SHM Public Policy Committee. “We try to leverage participants’ work and home addresses to pair them up with legislators from that area. Some hospitalists have personal or professional relationships with some of the legislators, and even if they’re not in their area, we’ll try to leverage that. And for people who have expertise in a particular topic, we try to arrange an audience with a member of Congress who may be promoting or sponsoring a bill related to that.”
Hill Day volunteers will attend an orientation to learn more about what the day will look like and what they’ll be talking about in their meetings. “We’ll only have time to cover one or two issues, and we’re in the process now of choosing the issues we want to address. We orient participants on those subjects so everybody is kind of saying the same thing,” Dr. Greeno said. “People shouldn’t be afraid of not being conversant with the issues because we do sufficient orientation that everybody gets comfortable enough to do a good job.”
Registration for Hill Day is happening online now. HM19 attendees can register at https://s1.goeshow.com/shm/annual/2019/registration_form.cfm.
“We beg people: If you sign up, show up, because we have many more people trying to participate than we can accommodate,” Dr. Greeno said. “If you change your mind, that’s fine because we have a waiting list, but please let us know because somebody else wants to take your place.”
The purpose of Hill Day
Educating legislators and their health care staff is the goal of the day, and it’s an important job. “Hospital medicine is still a relatively new field,” Dr. Lenchus said. “There are a fair number of legislators who still don’t know what a hospitalist is or what hospital medicine is. Part of our visits is always to educate them about what we do and what our impact is on the health care landscape of the country.” He added that educating Hill staff about the most pressing issues is another primary goal.
“Finally, and this is what separates us from other organizations that do legislative advocacy, we try to leave them with the idea that we’re here to help,” Dr. Lenchus said. “If there’s an issue or a particular bill that we’re asking them to sponsor or cosponsor, that’s one part of a visit. But by and large, we are trying to leave them with the sense that SHM is a resource when it comes to health care–related issues. We want to be there for legislators so that they can understand our position accurately from the outset.”
In short, Hill Day offers a rare opportunity to have direct access to the people who are voting on new legislation affecting hospitalists and affecting the implementation of existing legislation. “This is where the rubber meets the road,” Dr. Lenchus said. Each time a Hill Day is held, he noted, attendance increases. “That’s a true testament to the level of involvement and the interest that hospitalists have across the country. If you’re at all interested, you should absolutely sign up. This will be an amazing experience.”
The lasting impact
Though it’s just one day, Hill Day’s effects are significant.
“Before I started doing this work, I often thought, ‘What impact could someone have going into a legislator’s office?’ ” Dr. Greeno said. “But the answer is ‘A lot.’ The members and staff really do listen – especially if an advocate is highly educated and represent what legislators consider an important constituency, like health care providers. Health care is a hot topic, and it’s probably going to be one of the hot topics in the next election. Hospitalists have good ideas, and as a result these meetings are extremely influential; we wouldn’t do it otherwise. It is fun, but we’re not doing it for fun. We’re doing it because we know we can make a difference.”
In fact, in terms of impact on Capitol Hill, SHM punches above its weight, he added.
“We’re a relatively new society; we’re not huge. There are lots of societies that are much bigger than us and have many more resources, but people on the Hill have told us they like talking with us because they know we’re not looking at things the same way,” Dr. Greeno revealed. “We’re trying to help, and the issues that we’re addressing are not necessarily self-serving. We’re not saying, ‘You need to do this because it will make more money for our doctors.’ Instead, we’re saying, ‘You need to do this because the way it’s being done now is hurting patients. It’s hurting the health care system, and we have ideas about how to make that better.’ ”
SHM’s impressive track record has earned the society a positive reputation that will underlie the Hill Day meetings. “When we first set up the policy shop at SHM, we wanted to be seen as providers who cared about the American health care system and our patients,” Dr. Greeno said. “We have established that reputation, and that has led members on Capitol Hill to recognize us as being well intentioned and knowledgeable. So we have an outsize influence in Congress for our age and our size. When 200 hospitalists go to Capitol Hill, it’s an important thing.”
For more information about Hill Day, including details about participation, visit shmannualconference.org/hill-day/.
Advocating for HM in DC
Advocating for HM in DC
Another Hill Day is coming – the all-day advocacy event on Capitol Hill is scheduled in conjunction with the Society of Hospital Medicine’s Annual Conference whenever it is held in Washington, DC. In 2019, Hill Day will take place on March 27, the final day of HM19.
This will be the fourth Hill Day, and the last for some time, said Ron Greeno, MD, FCCP, MHM, senior advisor for government affairs at SHM and the society’s immediate past president. For at least the next 5 years, SHM’s annual conferences won’t be held in Washington, so there will not be any opportunities to plan a Hill Day during that time. “Members may want to take advantage of this opportunity,” Dr. Greeno said. “The people who do this never forget it.”
How Hill Day works
Sign up for Hill Day and you’ll spend a day visiting legislators and their health care staffers to educate them on what hospital medicine is, what a hospitalist does, and some of the pressing issues that affect the profession, said Joshua Lenchus, DO, RPh, FACP, SFHM, chair of the SHM Public Policy Committee. “We try to leverage participants’ work and home addresses to pair them up with legislators from that area. Some hospitalists have personal or professional relationships with some of the legislators, and even if they’re not in their area, we’ll try to leverage that. And for people who have expertise in a particular topic, we try to arrange an audience with a member of Congress who may be promoting or sponsoring a bill related to that.”
Hill Day volunteers will attend an orientation to learn more about what the day will look like and what they’ll be talking about in their meetings. “We’ll only have time to cover one or two issues, and we’re in the process now of choosing the issues we want to address. We orient participants on those subjects so everybody is kind of saying the same thing,” Dr. Greeno said. “People shouldn’t be afraid of not being conversant with the issues because we do sufficient orientation that everybody gets comfortable enough to do a good job.”
Registration for Hill Day is happening online now. HM19 attendees can register at https://s1.goeshow.com/shm/annual/2019/registration_form.cfm.
“We beg people: If you sign up, show up, because we have many more people trying to participate than we can accommodate,” Dr. Greeno said. “If you change your mind, that’s fine because we have a waiting list, but please let us know because somebody else wants to take your place.”
The purpose of Hill Day
Educating legislators and their health care staff is the goal of the day, and it’s an important job. “Hospital medicine is still a relatively new field,” Dr. Lenchus said. “There are a fair number of legislators who still don’t know what a hospitalist is or what hospital medicine is. Part of our visits is always to educate them about what we do and what our impact is on the health care landscape of the country.” He added that educating Hill staff about the most pressing issues is another primary goal.
“Finally, and this is what separates us from other organizations that do legislative advocacy, we try to leave them with the idea that we’re here to help,” Dr. Lenchus said. “If there’s an issue or a particular bill that we’re asking them to sponsor or cosponsor, that’s one part of a visit. But by and large, we are trying to leave them with the sense that SHM is a resource when it comes to health care–related issues. We want to be there for legislators so that they can understand our position accurately from the outset.”
In short, Hill Day offers a rare opportunity to have direct access to the people who are voting on new legislation affecting hospitalists and affecting the implementation of existing legislation. “This is where the rubber meets the road,” Dr. Lenchus said. Each time a Hill Day is held, he noted, attendance increases. “That’s a true testament to the level of involvement and the interest that hospitalists have across the country. If you’re at all interested, you should absolutely sign up. This will be an amazing experience.”
The lasting impact
Though it’s just one day, Hill Day’s effects are significant.
“Before I started doing this work, I often thought, ‘What impact could someone have going into a legislator’s office?’ ” Dr. Greeno said. “But the answer is ‘A lot.’ The members and staff really do listen – especially if an advocate is highly educated and represent what legislators consider an important constituency, like health care providers. Health care is a hot topic, and it’s probably going to be one of the hot topics in the next election. Hospitalists have good ideas, and as a result these meetings are extremely influential; we wouldn’t do it otherwise. It is fun, but we’re not doing it for fun. We’re doing it because we know we can make a difference.”
In fact, in terms of impact on Capitol Hill, SHM punches above its weight, he added.
“We’re a relatively new society; we’re not huge. There are lots of societies that are much bigger than us and have many more resources, but people on the Hill have told us they like talking with us because they know we’re not looking at things the same way,” Dr. Greeno revealed. “We’re trying to help, and the issues that we’re addressing are not necessarily self-serving. We’re not saying, ‘You need to do this because it will make more money for our doctors.’ Instead, we’re saying, ‘You need to do this because the way it’s being done now is hurting patients. It’s hurting the health care system, and we have ideas about how to make that better.’ ”
SHM’s impressive track record has earned the society a positive reputation that will underlie the Hill Day meetings. “When we first set up the policy shop at SHM, we wanted to be seen as providers who cared about the American health care system and our patients,” Dr. Greeno said. “We have established that reputation, and that has led members on Capitol Hill to recognize us as being well intentioned and knowledgeable. So we have an outsize influence in Congress for our age and our size. When 200 hospitalists go to Capitol Hill, it’s an important thing.”
For more information about Hill Day, including details about participation, visit shmannualconference.org/hill-day/.
Another Hill Day is coming – the all-day advocacy event on Capitol Hill is scheduled in conjunction with the Society of Hospital Medicine’s Annual Conference whenever it is held in Washington, DC. In 2019, Hill Day will take place on March 27, the final day of HM19.
This will be the fourth Hill Day, and the last for some time, said Ron Greeno, MD, FCCP, MHM, senior advisor for government affairs at SHM and the society’s immediate past president. For at least the next 5 years, SHM’s annual conferences won’t be held in Washington, so there will not be any opportunities to plan a Hill Day during that time. “Members may want to take advantage of this opportunity,” Dr. Greeno said. “The people who do this never forget it.”
How Hill Day works
Sign up for Hill Day and you’ll spend a day visiting legislators and their health care staffers to educate them on what hospital medicine is, what a hospitalist does, and some of the pressing issues that affect the profession, said Joshua Lenchus, DO, RPh, FACP, SFHM, chair of the SHM Public Policy Committee. “We try to leverage participants’ work and home addresses to pair them up with legislators from that area. Some hospitalists have personal or professional relationships with some of the legislators, and even if they’re not in their area, we’ll try to leverage that. And for people who have expertise in a particular topic, we try to arrange an audience with a member of Congress who may be promoting or sponsoring a bill related to that.”
Hill Day volunteers will attend an orientation to learn more about what the day will look like and what they’ll be talking about in their meetings. “We’ll only have time to cover one or two issues, and we’re in the process now of choosing the issues we want to address. We orient participants on those subjects so everybody is kind of saying the same thing,” Dr. Greeno said. “People shouldn’t be afraid of not being conversant with the issues because we do sufficient orientation that everybody gets comfortable enough to do a good job.”
Registration for Hill Day is happening online now. HM19 attendees can register at https://s1.goeshow.com/shm/annual/2019/registration_form.cfm.
“We beg people: If you sign up, show up, because we have many more people trying to participate than we can accommodate,” Dr. Greeno said. “If you change your mind, that’s fine because we have a waiting list, but please let us know because somebody else wants to take your place.”
The purpose of Hill Day
Educating legislators and their health care staff is the goal of the day, and it’s an important job. “Hospital medicine is still a relatively new field,” Dr. Lenchus said. “There are a fair number of legislators who still don’t know what a hospitalist is or what hospital medicine is. Part of our visits is always to educate them about what we do and what our impact is on the health care landscape of the country.” He added that educating Hill staff about the most pressing issues is another primary goal.
“Finally, and this is what separates us from other organizations that do legislative advocacy, we try to leave them with the idea that we’re here to help,” Dr. Lenchus said. “If there’s an issue or a particular bill that we’re asking them to sponsor or cosponsor, that’s one part of a visit. But by and large, we are trying to leave them with the sense that SHM is a resource when it comes to health care–related issues. We want to be there for legislators so that they can understand our position accurately from the outset.”
In short, Hill Day offers a rare opportunity to have direct access to the people who are voting on new legislation affecting hospitalists and affecting the implementation of existing legislation. “This is where the rubber meets the road,” Dr. Lenchus said. Each time a Hill Day is held, he noted, attendance increases. “That’s a true testament to the level of involvement and the interest that hospitalists have across the country. If you’re at all interested, you should absolutely sign up. This will be an amazing experience.”
The lasting impact
Though it’s just one day, Hill Day’s effects are significant.
“Before I started doing this work, I often thought, ‘What impact could someone have going into a legislator’s office?’ ” Dr. Greeno said. “But the answer is ‘A lot.’ The members and staff really do listen – especially if an advocate is highly educated and represent what legislators consider an important constituency, like health care providers. Health care is a hot topic, and it’s probably going to be one of the hot topics in the next election. Hospitalists have good ideas, and as a result these meetings are extremely influential; we wouldn’t do it otherwise. It is fun, but we’re not doing it for fun. We’re doing it because we know we can make a difference.”
In fact, in terms of impact on Capitol Hill, SHM punches above its weight, he added.
“We’re a relatively new society; we’re not huge. There are lots of societies that are much bigger than us and have many more resources, but people on the Hill have told us they like talking with us because they know we’re not looking at things the same way,” Dr. Greeno revealed. “We’re trying to help, and the issues that we’re addressing are not necessarily self-serving. We’re not saying, ‘You need to do this because it will make more money for our doctors.’ Instead, we’re saying, ‘You need to do this because the way it’s being done now is hurting patients. It’s hurting the health care system, and we have ideas about how to make that better.’ ”
SHM’s impressive track record has earned the society a positive reputation that will underlie the Hill Day meetings. “When we first set up the policy shop at SHM, we wanted to be seen as providers who cared about the American health care system and our patients,” Dr. Greeno said. “We have established that reputation, and that has led members on Capitol Hill to recognize us as being well intentioned and knowledgeable. So we have an outsize influence in Congress for our age and our size. When 200 hospitalists go to Capitol Hill, it’s an important thing.”
For more information about Hill Day, including details about participation, visit shmannualconference.org/hill-day/.
The ever-evolving scope of hospitalists’ clinical services
More care ‘beyond the walls’ of the hospital
The 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) Report provides indispensable data about the scope of clinical services routinely provided by adult and pediatric hospitalists. This year’s SoHM report reveals that a growing number of Hospital Medicine Groups (HMGs) serving adults are involved in roles beyond the inpatient medical wards, including various surgical comanagement programs, outpatient care, and post-acute care services.
The survey also compares services provided by academic and nonacademic HMGs, which remain markedly different in some areas. As the landscape of health care continues to evolve, hospitalists transform their scope of services to meet the needs of the institutions and communities they serve.
In the previous three SoHM reports, it was well established that more than 87% of adult hospital medicine groups play some role in comanaging surgical patients. In this year’s SoHM report, that role was further stratified to capture the various subspecialties represented, and to identify whether the hospitalists generally served as admitting/attending physician or consultant.
Hospitalists’ roles in comanagement are most prominent for care of orthopedic and general surgery patients, but more than 50% of surveyed HMGs reported being involved in comanagement in some capacity with neurosurgery, obstetrics, and cardiovascular surgery. Additionally, almost 95% of surveyed adult HMGs reported that they provided comanagement services for at least one other surgical specialty that was not listed in the survey.
The report also displays comanagement services provided to various medical subspecialties, including neurology, GI/liver, oncology, and more. Of the medical subspecialties represented, adult HMGs comanaged GI/liver (98.2%) and oncology (97.7%) services more often than others.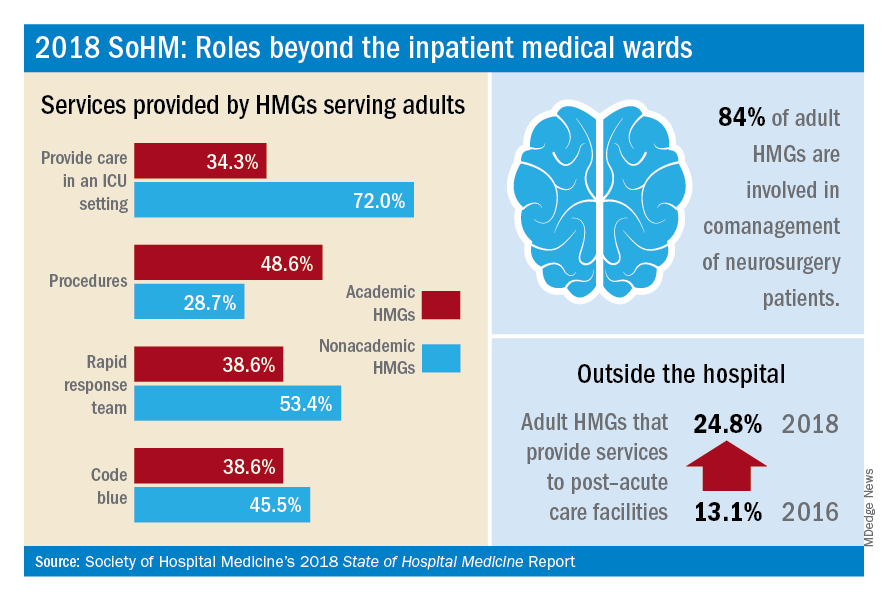
Interestingly, more HMGs are providing care for patients beyond the walls of the hospital. In the 2018 SoHM report, over 17% of surveyed HMG respondents reported providing care in an outpatient setting, representing an increase of 6.5 percentage points over 2016. Most strikingly, from 2016 to 2018, there was a 12 percentage point increase in adult HMGs reporting services provided to post-acute care facilities (from 13.1% to 24.8%).
These trends were most notable in the Midwest region where nearly 28% of HMGs provide patient care in an outpatient setting and up to 34% in post-acute care facilities. In part, this trend may result from the increased emphasis on improving transitions of care, by providing prehospital preoperative services, postdischarge follow-up encounters, or offering posthospitalization extensivist care.
Within the hospital itself, there remain striking differences in certain services provided by academic and nonacademic HMGs serving adults. Nonacademic HMGs are far more likely to cover patients in an ICU than their academic counterparts (72.0% vs. 34.3%). In contrast, academic hospitalist groups were significantly more inclined to perform procedures. However, the report also showed that there was an overall downtrend of percentage of HMGs that cover patients in an ICU or perform procedures.
As the scope of hospitalist services continues to change over time, should there be concern for scope creep? It depends on how one might view the change. As health care becomes ever more complex, high-functioning HMGs are needed to navigate it, both within and beyond the hospital. Some might consider scope evolution to be a reflection of hospitalists being recognized for their ability to provide high-quality, efficient, and comprehensive care. Hospital medicine groups will likely continue to evolve to meet the needs of an ever-changing health care environment.
Dr. Kurian is chief of the academic division of hospital medicine at Northwell Health in New York. She is a member of the SHM Practice Analysis Committee.
More care ‘beyond the walls’ of the hospital
More care ‘beyond the walls’ of the hospital
The 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) Report provides indispensable data about the scope of clinical services routinely provided by adult and pediatric hospitalists. This year’s SoHM report reveals that a growing number of Hospital Medicine Groups (HMGs) serving adults are involved in roles beyond the inpatient medical wards, including various surgical comanagement programs, outpatient care, and post-acute care services.
The survey also compares services provided by academic and nonacademic HMGs, which remain markedly different in some areas. As the landscape of health care continues to evolve, hospitalists transform their scope of services to meet the needs of the institutions and communities they serve.
In the previous three SoHM reports, it was well established that more than 87% of adult hospital medicine groups play some role in comanaging surgical patients. In this year’s SoHM report, that role was further stratified to capture the various subspecialties represented, and to identify whether the hospitalists generally served as admitting/attending physician or consultant.
Hospitalists’ roles in comanagement are most prominent for care of orthopedic and general surgery patients, but more than 50% of surveyed HMGs reported being involved in comanagement in some capacity with neurosurgery, obstetrics, and cardiovascular surgery. Additionally, almost 95% of surveyed adult HMGs reported that they provided comanagement services for at least one other surgical specialty that was not listed in the survey.
The report also displays comanagement services provided to various medical subspecialties, including neurology, GI/liver, oncology, and more. Of the medical subspecialties represented, adult HMGs comanaged GI/liver (98.2%) and oncology (97.7%) services more often than others.
Interestingly, more HMGs are providing care for patients beyond the walls of the hospital. In the 2018 SoHM report, over 17% of surveyed HMG respondents reported providing care in an outpatient setting, representing an increase of 6.5 percentage points over 2016. Most strikingly, from 2016 to 2018, there was a 12 percentage point increase in adult HMGs reporting services provided to post-acute care facilities (from 13.1% to 24.8%).
These trends were most notable in the Midwest region where nearly 28% of HMGs provide patient care in an outpatient setting and up to 34% in post-acute care facilities. In part, this trend may result from the increased emphasis on improving transitions of care, by providing prehospital preoperative services, postdischarge follow-up encounters, or offering posthospitalization extensivist care.
Within the hospital itself, there remain striking differences in certain services provided by academic and nonacademic HMGs serving adults. Nonacademic HMGs are far more likely to cover patients in an ICU than their academic counterparts (72.0% vs. 34.3%). In contrast, academic hospitalist groups were significantly more inclined to perform procedures. However, the report also showed that there was an overall downtrend of percentage of HMGs that cover patients in an ICU or perform procedures.
As the scope of hospitalist services continues to change over time, should there be concern for scope creep? It depends on how one might view the change. As health care becomes ever more complex, high-functioning HMGs are needed to navigate it, both within and beyond the hospital. Some might consider scope evolution to be a reflection of hospitalists being recognized for their ability to provide high-quality, efficient, and comprehensive care. Hospital medicine groups will likely continue to evolve to meet the needs of an ever-changing health care environment.
Dr. Kurian is chief of the academic division of hospital medicine at Northwell Health in New York. She is a member of the SHM Practice Analysis Committee.
The 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) Report provides indispensable data about the scope of clinical services routinely provided by adult and pediatric hospitalists. This year’s SoHM report reveals that a growing number of Hospital Medicine Groups (HMGs) serving adults are involved in roles beyond the inpatient medical wards, including various surgical comanagement programs, outpatient care, and post-acute care services.
The survey also compares services provided by academic and nonacademic HMGs, which remain markedly different in some areas. As the landscape of health care continues to evolve, hospitalists transform their scope of services to meet the needs of the institutions and communities they serve.
In the previous three SoHM reports, it was well established that more than 87% of adult hospital medicine groups play some role in comanaging surgical patients. In this year’s SoHM report, that role was further stratified to capture the various subspecialties represented, and to identify whether the hospitalists generally served as admitting/attending physician or consultant.
Hospitalists’ roles in comanagement are most prominent for care of orthopedic and general surgery patients, but more than 50% of surveyed HMGs reported being involved in comanagement in some capacity with neurosurgery, obstetrics, and cardiovascular surgery. Additionally, almost 95% of surveyed adult HMGs reported that they provided comanagement services for at least one other surgical specialty that was not listed in the survey.
The report also displays comanagement services provided to various medical subspecialties, including neurology, GI/liver, oncology, and more. Of the medical subspecialties represented, adult HMGs comanaged GI/liver (98.2%) and oncology (97.7%) services more often than others.
Interestingly, more HMGs are providing care for patients beyond the walls of the hospital. In the 2018 SoHM report, over 17% of surveyed HMG respondents reported providing care in an outpatient setting, representing an increase of 6.5 percentage points over 2016. Most strikingly, from 2016 to 2018, there was a 12 percentage point increase in adult HMGs reporting services provided to post-acute care facilities (from 13.1% to 24.8%).
These trends were most notable in the Midwest region where nearly 28% of HMGs provide patient care in an outpatient setting and up to 34% in post-acute care facilities. In part, this trend may result from the increased emphasis on improving transitions of care, by providing prehospital preoperative services, postdischarge follow-up encounters, or offering posthospitalization extensivist care.
Within the hospital itself, there remain striking differences in certain services provided by academic and nonacademic HMGs serving adults. Nonacademic HMGs are far more likely to cover patients in an ICU than their academic counterparts (72.0% vs. 34.3%). In contrast, academic hospitalist groups were significantly more inclined to perform procedures. However, the report also showed that there was an overall downtrend of percentage of HMGs that cover patients in an ICU or perform procedures.
As the scope of hospitalist services continues to change over time, should there be concern for scope creep? It depends on how one might view the change. As health care becomes ever more complex, high-functioning HMGs are needed to navigate it, both within and beyond the hospital. Some might consider scope evolution to be a reflection of hospitalists being recognized for their ability to provide high-quality, efficient, and comprehensive care. Hospital medicine groups will likely continue to evolve to meet the needs of an ever-changing health care environment.
Dr. Kurian is chief of the academic division of hospital medicine at Northwell Health in New York. She is a member of the SHM Practice Analysis Committee.
A novel approach to MIPS quality reporting for facility-based providers
A cornerstone of hospital medicine is the delivery of high-quality inpatient care by improving the performance of the systems and facilities in which hospitalists work. By extension, hospitalists are often held accountable, in varying ways, for improving the performance of facility metrics, such as those in the Hospital Value-Based Purchasing (HVBP), Inpatient Quality Reporting, and Hospital Readmissions Reduction programs.
Despite the work hospitalists were already doing to improve both efficiency and quality within their institutions, the 2010 Affordable Care Act introduced penalties for clinicians who did not submit qualifying provider-level data via the Physician Quality Reporting System program. Initially only an incentive program, PQRS was ultimately incorporated into the Physician Value-Based Payment (VBP) Modifier to make performance-based payment adjustments to Medicare physician payment. At this point, many hospitalists were not only accountable for helping to improve the metrics of their facilities, but also required to report individually or within their groups on provider-level measures, many of which were irrelevant to hospital medicine practice.
With this dual burden becoming evident, the Society of Hospital Medicine approached the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services with a possible solution. Could hospitalists elect to use their facilities’ metrics as a stand-in for the provider level metrics? Not only would this reduce the burden of reporting irrelevant metrics, but it would also help alleviate some of the disadvantages hospitalists face within Physician VBP.
The CMS was initially very supportive of the concept, but informed the SHM such alignment was not possible under existing law. In brief, the law required Physician VBP to remain completely within the Physician Fee Schedule and its related metrics; facility level metrics from a different payment system could not be used.
Undeterred, the SHM sought opportunities to change the law. As Congress was developing the Medicare Access and Chip Reauthorization Act (MACRA), the SHM worked closely with lawmakers to include language that would permit measures in “other payment systems” to be used for physician performance assessment. This language was retained in the final version of MACRA that was signed into law on April 16, 2015.
The SHM continued its advocacy, working closely with the CMS and its new authority to shape an option to align Medicare’s facility metrics and scores with provider reporting. Today that idea is a reality. Beginning this year, the CMS will have a new Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) reporting option available for hospitalists: facility-based measurement.
Facility-based measurement enables clinicians to receive a score for the Quality and Cost categories of the MIPS, without the need to collect and report on measures separately. Eligible providers would receive the MIPS score in those categories associated with the same percentile as their hospital’s score in HVBP. No more administrative work necessary to collect, clean and report on data for quality measures in the MIPS. If you are eligible, the CMS will automatically calculate a Quality and Cost score and combine this with your score from Improvement Activities and Promoting Interoperability (if you are not exempt) to give you a final MIPS score. If you decide to report on quality measures through the traditional MIPS pathway as well, the CMS will give you the higher of the scores.
There are certainly trade-offs associated with the facility-based measurement option. You do not have the burden of reporting measures on your own, but you do not get to pick what measures and what facility’s score you receive. Facility-level measures may be more difficult to improve performance, particularly as an individual, but the automatic application of facility-based measurement to eligible clinicians and groups serves as a backstop for MIPS reporting.
Aligning facility and clinician performance should encourage collaboration and innovation to meet these shared goals. As such, facility-based measurement represents a massive philosophical and practical shift in CMS measure reporting. As we enter these uncharted waters together, we hope to continue learning from your experiences and perspectives and working to refine facility-based measurement in the future.
For more information about facility-based reporting and the MIPS in general, visit www.macraforhm.org.
Mr. Lapps is government relations senior manager and Mr. Boswell is government relations director at the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Who is eligible for facility-based measurement?
- Individual providers who bill more than 75% of their Medicare Part B professional services in Place of Service 21 (Emergency Department), 22 (Hospital Outpatient), and 23 (Inpatient Hospital), billing at least one service in POS 21 or 23, and work in a hospital with an HVBP score.
- Groups who have at least 75% of their individual clinicians who meet the eligibility criteria.
- Nearly all hospitalists should qualify for facility-based measurement as individuals, while group eligibility depends on the demographics of their staff.
A cornerstone of hospital medicine is the delivery of high-quality inpatient care by improving the performance of the systems and facilities in which hospitalists work. By extension, hospitalists are often held accountable, in varying ways, for improving the performance of facility metrics, such as those in the Hospital Value-Based Purchasing (HVBP), Inpatient Quality Reporting, and Hospital Readmissions Reduction programs.
Despite the work hospitalists were already doing to improve both efficiency and quality within their institutions, the 2010 Affordable Care Act introduced penalties for clinicians who did not submit qualifying provider-level data via the Physician Quality Reporting System program. Initially only an incentive program, PQRS was ultimately incorporated into the Physician Value-Based Payment (VBP) Modifier to make performance-based payment adjustments to Medicare physician payment. At this point, many hospitalists were not only accountable for helping to improve the metrics of their facilities, but also required to report individually or within their groups on provider-level measures, many of which were irrelevant to hospital medicine practice.
With this dual burden becoming evident, the Society of Hospital Medicine approached the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services with a possible solution. Could hospitalists elect to use their facilities’ metrics as a stand-in for the provider level metrics? Not only would this reduce the burden of reporting irrelevant metrics, but it would also help alleviate some of the disadvantages hospitalists face within Physician VBP.
The CMS was initially very supportive of the concept, but informed the SHM such alignment was not possible under existing law. In brief, the law required Physician VBP to remain completely within the Physician Fee Schedule and its related metrics; facility level metrics from a different payment system could not be used.
Undeterred, the SHM sought opportunities to change the law. As Congress was developing the Medicare Access and Chip Reauthorization Act (MACRA), the SHM worked closely with lawmakers to include language that would permit measures in “other payment systems” to be used for physician performance assessment. This language was retained in the final version of MACRA that was signed into law on April 16, 2015.
The SHM continued its advocacy, working closely with the CMS and its new authority to shape an option to align Medicare’s facility metrics and scores with provider reporting. Today that idea is a reality. Beginning this year, the CMS will have a new Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) reporting option available for hospitalists: facility-based measurement.
Facility-based measurement enables clinicians to receive a score for the Quality and Cost categories of the MIPS, without the need to collect and report on measures separately. Eligible providers would receive the MIPS score in those categories associated with the same percentile as their hospital’s score in HVBP. No more administrative work necessary to collect, clean and report on data for quality measures in the MIPS. If you are eligible, the CMS will automatically calculate a Quality and Cost score and combine this with your score from Improvement Activities and Promoting Interoperability (if you are not exempt) to give you a final MIPS score. If you decide to report on quality measures through the traditional MIPS pathway as well, the CMS will give you the higher of the scores.
There are certainly trade-offs associated with the facility-based measurement option. You do not have the burden of reporting measures on your own, but you do not get to pick what measures and what facility’s score you receive. Facility-level measures may be more difficult to improve performance, particularly as an individual, but the automatic application of facility-based measurement to eligible clinicians and groups serves as a backstop for MIPS reporting.
Aligning facility and clinician performance should encourage collaboration and innovation to meet these shared goals. As such, facility-based measurement represents a massive philosophical and practical shift in CMS measure reporting. As we enter these uncharted waters together, we hope to continue learning from your experiences and perspectives and working to refine facility-based measurement in the future.
For more information about facility-based reporting and the MIPS in general, visit www.macraforhm.org.
Mr. Lapps is government relations senior manager and Mr. Boswell is government relations director at the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Who is eligible for facility-based measurement?
- Individual providers who bill more than 75% of their Medicare Part B professional services in Place of Service 21 (Emergency Department), 22 (Hospital Outpatient), and 23 (Inpatient Hospital), billing at least one service in POS 21 or 23, and work in a hospital with an HVBP score.
- Groups who have at least 75% of their individual clinicians who meet the eligibility criteria.
- Nearly all hospitalists should qualify for facility-based measurement as individuals, while group eligibility depends on the demographics of their staff.
A cornerstone of hospital medicine is the delivery of high-quality inpatient care by improving the performance of the systems and facilities in which hospitalists work. By extension, hospitalists are often held accountable, in varying ways, for improving the performance of facility metrics, such as those in the Hospital Value-Based Purchasing (HVBP), Inpatient Quality Reporting, and Hospital Readmissions Reduction programs.
Despite the work hospitalists were already doing to improve both efficiency and quality within their institutions, the 2010 Affordable Care Act introduced penalties for clinicians who did not submit qualifying provider-level data via the Physician Quality Reporting System program. Initially only an incentive program, PQRS was ultimately incorporated into the Physician Value-Based Payment (VBP) Modifier to make performance-based payment adjustments to Medicare physician payment. At this point, many hospitalists were not only accountable for helping to improve the metrics of their facilities, but also required to report individually or within their groups on provider-level measures, many of which were irrelevant to hospital medicine practice.
With this dual burden becoming evident, the Society of Hospital Medicine approached the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services with a possible solution. Could hospitalists elect to use their facilities’ metrics as a stand-in for the provider level metrics? Not only would this reduce the burden of reporting irrelevant metrics, but it would also help alleviate some of the disadvantages hospitalists face within Physician VBP.
The CMS was initially very supportive of the concept, but informed the SHM such alignment was not possible under existing law. In brief, the law required Physician VBP to remain completely within the Physician Fee Schedule and its related metrics; facility level metrics from a different payment system could not be used.
Undeterred, the SHM sought opportunities to change the law. As Congress was developing the Medicare Access and Chip Reauthorization Act (MACRA), the SHM worked closely with lawmakers to include language that would permit measures in “other payment systems” to be used for physician performance assessment. This language was retained in the final version of MACRA that was signed into law on April 16, 2015.
The SHM continued its advocacy, working closely with the CMS and its new authority to shape an option to align Medicare’s facility metrics and scores with provider reporting. Today that idea is a reality. Beginning this year, the CMS will have a new Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) reporting option available for hospitalists: facility-based measurement.
Facility-based measurement enables clinicians to receive a score for the Quality and Cost categories of the MIPS, without the need to collect and report on measures separately. Eligible providers would receive the MIPS score in those categories associated with the same percentile as their hospital’s score in HVBP. No more administrative work necessary to collect, clean and report on data for quality measures in the MIPS. If you are eligible, the CMS will automatically calculate a Quality and Cost score and combine this with your score from Improvement Activities and Promoting Interoperability (if you are not exempt) to give you a final MIPS score. If you decide to report on quality measures through the traditional MIPS pathway as well, the CMS will give you the higher of the scores.
There are certainly trade-offs associated with the facility-based measurement option. You do not have the burden of reporting measures on your own, but you do not get to pick what measures and what facility’s score you receive. Facility-level measures may be more difficult to improve performance, particularly as an individual, but the automatic application of facility-based measurement to eligible clinicians and groups serves as a backstop for MIPS reporting.
Aligning facility and clinician performance should encourage collaboration and innovation to meet these shared goals. As such, facility-based measurement represents a massive philosophical and practical shift in CMS measure reporting. As we enter these uncharted waters together, we hope to continue learning from your experiences and perspectives and working to refine facility-based measurement in the future.
For more information about facility-based reporting and the MIPS in general, visit www.macraforhm.org.
Mr. Lapps is government relations senior manager and Mr. Boswell is government relations director at the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Who is eligible for facility-based measurement?
- Individual providers who bill more than 75% of their Medicare Part B professional services in Place of Service 21 (Emergency Department), 22 (Hospital Outpatient), and 23 (Inpatient Hospital), billing at least one service in POS 21 or 23, and work in a hospital with an HVBP score.
- Groups who have at least 75% of their individual clinicians who meet the eligibility criteria.
- Nearly all hospitalists should qualify for facility-based measurement as individuals, while group eligibility depends on the demographics of their staff.
Shaping the future of hospital medicine
Dr. Therese Franco leads SHM’s Pacific Northwest chapter
Therese Franco, MD, SFHM, a hospitalist at the Virginia Mason Medical Center in Seattle, is the current president of SHM’s Pacific Northwest chapter.
The Hospitalist recently sat down with her to learn about her background and discuss some of the initiatives that the Pacific Northwest chapter has been working on.
Can you tell us about your education and training on the way to becoming a hospitalist?
My undergraduate degree is in engineering from Michigan State University. I then went to the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor and did one degree at the School of Public Health in environmental and industrial health, and another degree in the College of Engineering in industrial and operations engineering. In my work with the safety department at an automotive company, I found I was spending a lot of time looking at data, and not talking to people. I got into a conversation with one of the occupational medicine physicians there, and he said, “You ought to try this.” I spoke with a good friend, who was a medical student, and she agreed.
So then I went to medical school thinking that I would practice occupational medicine. I went to medical school at Wayne State University in Detroit and did a couple of rotations in occupational medicine. I wasn’t sure that was the right fit, so I then went off to residency in internal medicine at the University of Connecticut and really enjoyed my wards experience. I liked the pace, I liked the variety, and just really liked all of hospital medicine. So that’s what I decided to do.
What are your areas of research interest?
This year I’m doing a research fellowship through the Center for Healthcare Improvement Science, at Virginia Mason. Through SHM’s mentored implementation program, I have done a lot of work on diabetes and glycemic control but never really published much of it. I think it is so important to share what you learn, so I’m working on publishing some of our results from the diabetes work.
Another area of interest is advanced-practice providers in hospital medicine, which I think is very important, given all the issues that health care is facing. I think that medicine has gotten more complex and that we’re going to have to look at working in a collaborative, inter-professional, multidisciplinary way. I think that advanced practice can really improve the care of hospitalized patients, if we practice appropriate skill-task alignment, develop a culture of mutual respect, and find the best ways to deploy our advanced-practice providers and our physicians.
That can be challenging. Some people, I think, are worried about losing their jobs, and some people feel like they want to “own” all of the patient, because it’s such a part of the culture of medicine. So it’s a really complicated issue, and I think that doctors are going to have to get used to delegating tasks that they used to perform.
So a collaborative practice requires both a professional and a cultural shift?
I think so. I was our inaugural program director for an advanced-practice fellowship in hospital medicine, and in that role, I attended conferences and learning events for program development. I think that many institutions are facing some of the same challenges. For the most part, I’m optimistic about things. I think we’re on the right track, and help is on the way – we just have to figure out how to use it.
Has your institution made any changes along these lines?
We’re primarily using the fellowship as a tool to recruit and retain some of the brightest and best. We’ve got three fellows that matriculated from our program and are currently working in the section of hospital medicine. Everyone’s been really flexible and open to the idea that the job description is emerging. I think my colleagues are very appreciative of our advanced-practice providers. We’ve got two nurse practitioners and one physician assistant who is also a PhD-trained pharmacist. They’ve been great additions to our team.
What are some of the other issues that the Pacific Northwest chapter members are concerned about?
One of our most successful meetings was around telemedicine. There’s a lot of interest in that, and it’s very financially and technically complex. Some hospitals in the area are really doing novel things. One of the most interesting things is an addiction medicine teleconsult.
That’s out of Swedish Medical Center, Seattle. Of course there’s telestroke, which I think is picking up in popularity. We had speakers from Virginia Mason who presented on telestroke. Some institutions are even doing admissions this way. The University of Washington is doing some good antimicrobial stewardship work. They present cases and they teleconference and have an infectious disease consultant. It’s not a program directed at revenue generation, but is focused instead on sharing and spreading expertise.
Our chapter also hosted a presentation on burnout that was pretty well attended. And then, unfortunately, we did lose a hospitalist to suicide over the summer. That was the inspiration for offering the screening of the movie, “Do No Harm: Exposing the Hippocratic Hoax.”
What was the program that you put together around the screening?
We had the filmmaker come for the screening, and we organized a panel discussion with a wellness officer from a local clinic and a psychiatrist who used to be on the board of the Physician Health Program. John Nelson, MD, MHM, one of SHM’s cofounders and a local hospitalist here, also participated as a panelist.
Overall, the event was well received. There were some things that I didn’t really expect. I’m not sure that the film resonated with too many people in the room. It is very much directed at the educational process – med students and residents – and at times the dialogue is a little inflammatory.
I learned a few important things from the film. I did not realize that the tragedy of physician suicide is not unique to the United States – it’s an international issue. And we sometimes use the term “pimping” to talk about questioning interns or residents on rounds. Apparently, that stands for “put in my place,” which is very condescending and unacceptable. I will not use the term again.
I think future conversations need to come from thoughtful, rational, respectful leaders who are willing to work with regulatory agencies, hospitals, and administrators. If we want to move forward, physicians, administrators, and the public need to come together in the best interest of the patient and of public health. And I don’t know who leads that conversation.
Will your chapter have another event around that subject?
We will do what our membership wants and needs. We meet quarterly, and once a year we hold a people’s choice meeting and I solicit topics. If members want to keep the conversation moving, I’m going to do what I can to support them.
What are some other issues that stand out as important to your chapter?
One key topic is the financial side of hospitalist practice, and dealing with issues that seem to create inefficiencies – regulatory issues, documentation issues, things that are important because we want to tell the story of what we’re doing. We certainly want to be reimbursed for the value-added work that we’re doing, but a lot of value-added work creates inefficiencies of practice, and I hear a lot of dissatisfaction around documentation, coding, billing, and other issues related to reimbursement. While people are concerned about these problems, nobody wants to talk about them. They just want somebody to fix it. So I’m not sure what to do with that, because I think if I had a meeting about coding and billing, I would have three attendees.
But our annual poster meeting is always well attended. We always do it at the end of the year, to kick off the holiday season. It’s a nice opportunity to connect socially with colleagues because you mix and you mingle and look at the posters. We had some really great posters, and our top three prize winners were medical students, which is inspirational. They make you feel good about the future.
Our chapter is trying to diversify geographically and clinically. We were fortunate to receive a development funds grant to use technology to do streaming meetings. Our hope is that we can host streaming meetings and eventually transition hosting to rotate around the state. Once there’s large enough attendance, the different delegates can develop their own leadership teams and, eventually, their own chapter. We’re hoping to grow the organization that way.
What else is on the horizon for hospitalists in the Pacific Northwest?
I’d like to see more frequent meetings and a greater variety of meetings. I think there’s interest in adding some kind of service element to the chapter. Maybe we can do a blood pressure screening at a sporting event.
I think we’ll also be focusing on students and residents and trying to create support for them. We held a student event around financial planning, and that was very well attended. I think we would like to do something around mentorship. Of course it’s hard to find mentors, because everybody is so busy.
Our chapter really needs to leverage our technology if we want to have the reach that I’m talking about. I’m looking forward to piloting the streaming meeting concept, and I hope to do some live polling of our meeting attendees to get them engaged. I hope we continue to grow and keep the dialogue going about what matters in hospital medicine, and do our part to shape the future in the way we want it.
Dr. Therese Franco leads SHM’s Pacific Northwest chapter
Dr. Therese Franco leads SHM’s Pacific Northwest chapter
Therese Franco, MD, SFHM, a hospitalist at the Virginia Mason Medical Center in Seattle, is the current president of SHM’s Pacific Northwest chapter.
The Hospitalist recently sat down with her to learn about her background and discuss some of the initiatives that the Pacific Northwest chapter has been working on.
Can you tell us about your education and training on the way to becoming a hospitalist?
My undergraduate degree is in engineering from Michigan State University. I then went to the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor and did one degree at the School of Public Health in environmental and industrial health, and another degree in the College of Engineering in industrial and operations engineering. In my work with the safety department at an automotive company, I found I was spending a lot of time looking at data, and not talking to people. I got into a conversation with one of the occupational medicine physicians there, and he said, “You ought to try this.” I spoke with a good friend, who was a medical student, and she agreed.
So then I went to medical school thinking that I would practice occupational medicine. I went to medical school at Wayne State University in Detroit and did a couple of rotations in occupational medicine. I wasn’t sure that was the right fit, so I then went off to residency in internal medicine at the University of Connecticut and really enjoyed my wards experience. I liked the pace, I liked the variety, and just really liked all of hospital medicine. So that’s what I decided to do.
What are your areas of research interest?
This year I’m doing a research fellowship through the Center for Healthcare Improvement Science, at Virginia Mason. Through SHM’s mentored implementation program, I have done a lot of work on diabetes and glycemic control but never really published much of it. I think it is so important to share what you learn, so I’m working on publishing some of our results from the diabetes work.
Another area of interest is advanced-practice providers in hospital medicine, which I think is very important, given all the issues that health care is facing. I think that medicine has gotten more complex and that we’re going to have to look at working in a collaborative, inter-professional, multidisciplinary way. I think that advanced practice can really improve the care of hospitalized patients, if we practice appropriate skill-task alignment, develop a culture of mutual respect, and find the best ways to deploy our advanced-practice providers and our physicians.
That can be challenging. Some people, I think, are worried about losing their jobs, and some people feel like they want to “own” all of the patient, because it’s such a part of the culture of medicine. So it’s a really complicated issue, and I think that doctors are going to have to get used to delegating tasks that they used to perform.
So a collaborative practice requires both a professional and a cultural shift?
I think so. I was our inaugural program director for an advanced-practice fellowship in hospital medicine, and in that role, I attended conferences and learning events for program development. I think that many institutions are facing some of the same challenges. For the most part, I’m optimistic about things. I think we’re on the right track, and help is on the way – we just have to figure out how to use it.
Has your institution made any changes along these lines?
We’re primarily using the fellowship as a tool to recruit and retain some of the brightest and best. We’ve got three fellows that matriculated from our program and are currently working in the section of hospital medicine. Everyone’s been really flexible and open to the idea that the job description is emerging. I think my colleagues are very appreciative of our advanced-practice providers. We’ve got two nurse practitioners and one physician assistant who is also a PhD-trained pharmacist. They’ve been great additions to our team.
What are some of the other issues that the Pacific Northwest chapter members are concerned about?
One of our most successful meetings was around telemedicine. There’s a lot of interest in that, and it’s very financially and technically complex. Some hospitals in the area are really doing novel things. One of the most interesting things is an addiction medicine teleconsult.
That’s out of Swedish Medical Center, Seattle. Of course there’s telestroke, which I think is picking up in popularity. We had speakers from Virginia Mason who presented on telestroke. Some institutions are even doing admissions this way. The University of Washington is doing some good antimicrobial stewardship work. They present cases and they teleconference and have an infectious disease consultant. It’s not a program directed at revenue generation, but is focused instead on sharing and spreading expertise.
Our chapter also hosted a presentation on burnout that was pretty well attended. And then, unfortunately, we did lose a hospitalist to suicide over the summer. That was the inspiration for offering the screening of the movie, “Do No Harm: Exposing the Hippocratic Hoax.”
What was the program that you put together around the screening?
We had the filmmaker come for the screening, and we organized a panel discussion with a wellness officer from a local clinic and a psychiatrist who used to be on the board of the Physician Health Program. John Nelson, MD, MHM, one of SHM’s cofounders and a local hospitalist here, also participated as a panelist.
Overall, the event was well received. There were some things that I didn’t really expect. I’m not sure that the film resonated with too many people in the room. It is very much directed at the educational process – med students and residents – and at times the dialogue is a little inflammatory.
I learned a few important things from the film. I did not realize that the tragedy of physician suicide is not unique to the United States – it’s an international issue. And we sometimes use the term “pimping” to talk about questioning interns or residents on rounds. Apparently, that stands for “put in my place,” which is very condescending and unacceptable. I will not use the term again.
I think future conversations need to come from thoughtful, rational, respectful leaders who are willing to work with regulatory agencies, hospitals, and administrators. If we want to move forward, physicians, administrators, and the public need to come together in the best interest of the patient and of public health. And I don’t know who leads that conversation.
Will your chapter have another event around that subject?
We will do what our membership wants and needs. We meet quarterly, and once a year we hold a people’s choice meeting and I solicit topics. If members want to keep the conversation moving, I’m going to do what I can to support them.
What are some other issues that stand out as important to your chapter?
One key topic is the financial side of hospitalist practice, and dealing with issues that seem to create inefficiencies – regulatory issues, documentation issues, things that are important because we want to tell the story of what we’re doing. We certainly want to be reimbursed for the value-added work that we’re doing, but a lot of value-added work creates inefficiencies of practice, and I hear a lot of dissatisfaction around documentation, coding, billing, and other issues related to reimbursement. While people are concerned about these problems, nobody wants to talk about them. They just want somebody to fix it. So I’m not sure what to do with that, because I think if I had a meeting about coding and billing, I would have three attendees.
But our annual poster meeting is always well attended. We always do it at the end of the year, to kick off the holiday season. It’s a nice opportunity to connect socially with colleagues because you mix and you mingle and look at the posters. We had some really great posters, and our top three prize winners were medical students, which is inspirational. They make you feel good about the future.
Our chapter is trying to diversify geographically and clinically. We were fortunate to receive a development funds grant to use technology to do streaming meetings. Our hope is that we can host streaming meetings and eventually transition hosting to rotate around the state. Once there’s large enough attendance, the different delegates can develop their own leadership teams and, eventually, their own chapter. We’re hoping to grow the organization that way.
What else is on the horizon for hospitalists in the Pacific Northwest?
I’d like to see more frequent meetings and a greater variety of meetings. I think there’s interest in adding some kind of service element to the chapter. Maybe we can do a blood pressure screening at a sporting event.
I think we’ll also be focusing on students and residents and trying to create support for them. We held a student event around financial planning, and that was very well attended. I think we would like to do something around mentorship. Of course it’s hard to find mentors, because everybody is so busy.
Our chapter really needs to leverage our technology if we want to have the reach that I’m talking about. I’m looking forward to piloting the streaming meeting concept, and I hope to do some live polling of our meeting attendees to get them engaged. I hope we continue to grow and keep the dialogue going about what matters in hospital medicine, and do our part to shape the future in the way we want it.
Therese Franco, MD, SFHM, a hospitalist at the Virginia Mason Medical Center in Seattle, is the current president of SHM’s Pacific Northwest chapter.
The Hospitalist recently sat down with her to learn about her background and discuss some of the initiatives that the Pacific Northwest chapter has been working on.
Can you tell us about your education and training on the way to becoming a hospitalist?
My undergraduate degree is in engineering from Michigan State University. I then went to the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor and did one degree at the School of Public Health in environmental and industrial health, and another degree in the College of Engineering in industrial and operations engineering. In my work with the safety department at an automotive company, I found I was spending a lot of time looking at data, and not talking to people. I got into a conversation with one of the occupational medicine physicians there, and he said, “You ought to try this.” I spoke with a good friend, who was a medical student, and she agreed.
So then I went to medical school thinking that I would practice occupational medicine. I went to medical school at Wayne State University in Detroit and did a couple of rotations in occupational medicine. I wasn’t sure that was the right fit, so I then went off to residency in internal medicine at the University of Connecticut and really enjoyed my wards experience. I liked the pace, I liked the variety, and just really liked all of hospital medicine. So that’s what I decided to do.
What are your areas of research interest?
This year I’m doing a research fellowship through the Center for Healthcare Improvement Science, at Virginia Mason. Through SHM’s mentored implementation program, I have done a lot of work on diabetes and glycemic control but never really published much of it. I think it is so important to share what you learn, so I’m working on publishing some of our results from the diabetes work.
Another area of interest is advanced-practice providers in hospital medicine, which I think is very important, given all the issues that health care is facing. I think that medicine has gotten more complex and that we’re going to have to look at working in a collaborative, inter-professional, multidisciplinary way. I think that advanced practice can really improve the care of hospitalized patients, if we practice appropriate skill-task alignment, develop a culture of mutual respect, and find the best ways to deploy our advanced-practice providers and our physicians.
That can be challenging. Some people, I think, are worried about losing their jobs, and some people feel like they want to “own” all of the patient, because it’s such a part of the culture of medicine. So it’s a really complicated issue, and I think that doctors are going to have to get used to delegating tasks that they used to perform.
So a collaborative practice requires both a professional and a cultural shift?
I think so. I was our inaugural program director for an advanced-practice fellowship in hospital medicine, and in that role, I attended conferences and learning events for program development. I think that many institutions are facing some of the same challenges. For the most part, I’m optimistic about things. I think we’re on the right track, and help is on the way – we just have to figure out how to use it.
Has your institution made any changes along these lines?
We’re primarily using the fellowship as a tool to recruit and retain some of the brightest and best. We’ve got three fellows that matriculated from our program and are currently working in the section of hospital medicine. Everyone’s been really flexible and open to the idea that the job description is emerging. I think my colleagues are very appreciative of our advanced-practice providers. We’ve got two nurse practitioners and one physician assistant who is also a PhD-trained pharmacist. They’ve been great additions to our team.
What are some of the other issues that the Pacific Northwest chapter members are concerned about?
One of our most successful meetings was around telemedicine. There’s a lot of interest in that, and it’s very financially and technically complex. Some hospitals in the area are really doing novel things. One of the most interesting things is an addiction medicine teleconsult.
That’s out of Swedish Medical Center, Seattle. Of course there’s telestroke, which I think is picking up in popularity. We had speakers from Virginia Mason who presented on telestroke. Some institutions are even doing admissions this way. The University of Washington is doing some good antimicrobial stewardship work. They present cases and they teleconference and have an infectious disease consultant. It’s not a program directed at revenue generation, but is focused instead on sharing and spreading expertise.
Our chapter also hosted a presentation on burnout that was pretty well attended. And then, unfortunately, we did lose a hospitalist to suicide over the summer. That was the inspiration for offering the screening of the movie, “Do No Harm: Exposing the Hippocratic Hoax.”
What was the program that you put together around the screening?
We had the filmmaker come for the screening, and we organized a panel discussion with a wellness officer from a local clinic and a psychiatrist who used to be on the board of the Physician Health Program. John Nelson, MD, MHM, one of SHM’s cofounders and a local hospitalist here, also participated as a panelist.
Overall, the event was well received. There were some things that I didn’t really expect. I’m not sure that the film resonated with too many people in the room. It is very much directed at the educational process – med students and residents – and at times the dialogue is a little inflammatory.
I learned a few important things from the film. I did not realize that the tragedy of physician suicide is not unique to the United States – it’s an international issue. And we sometimes use the term “pimping” to talk about questioning interns or residents on rounds. Apparently, that stands for “put in my place,” which is very condescending and unacceptable. I will not use the term again.
I think future conversations need to come from thoughtful, rational, respectful leaders who are willing to work with regulatory agencies, hospitals, and administrators. If we want to move forward, physicians, administrators, and the public need to come together in the best interest of the patient and of public health. And I don’t know who leads that conversation.
Will your chapter have another event around that subject?
We will do what our membership wants and needs. We meet quarterly, and once a year we hold a people’s choice meeting and I solicit topics. If members want to keep the conversation moving, I’m going to do what I can to support them.
What are some other issues that stand out as important to your chapter?
One key topic is the financial side of hospitalist practice, and dealing with issues that seem to create inefficiencies – regulatory issues, documentation issues, things that are important because we want to tell the story of what we’re doing. We certainly want to be reimbursed for the value-added work that we’re doing, but a lot of value-added work creates inefficiencies of practice, and I hear a lot of dissatisfaction around documentation, coding, billing, and other issues related to reimbursement. While people are concerned about these problems, nobody wants to talk about them. They just want somebody to fix it. So I’m not sure what to do with that, because I think if I had a meeting about coding and billing, I would have three attendees.
But our annual poster meeting is always well attended. We always do it at the end of the year, to kick off the holiday season. It’s a nice opportunity to connect socially with colleagues because you mix and you mingle and look at the posters. We had some really great posters, and our top three prize winners were medical students, which is inspirational. They make you feel good about the future.
Our chapter is trying to diversify geographically and clinically. We were fortunate to receive a development funds grant to use technology to do streaming meetings. Our hope is that we can host streaming meetings and eventually transition hosting to rotate around the state. Once there’s large enough attendance, the different delegates can develop their own leadership teams and, eventually, their own chapter. We’re hoping to grow the organization that way.
What else is on the horizon for hospitalists in the Pacific Northwest?
I’d like to see more frequent meetings and a greater variety of meetings. I think there’s interest in adding some kind of service element to the chapter. Maybe we can do a blood pressure screening at a sporting event.
I think we’ll also be focusing on students and residents and trying to create support for them. We held a student event around financial planning, and that was very well attended. I think we would like to do something around mentorship. Of course it’s hard to find mentors, because everybody is so busy.
Our chapter really needs to leverage our technology if we want to have the reach that I’m talking about. I’m looking forward to piloting the streaming meeting concept, and I hope to do some live polling of our meeting attendees to get them engaged. I hope we continue to grow and keep the dialogue going about what matters in hospital medicine, and do our part to shape the future in the way we want it.
The amazing work we get to do
Serving people, connecting, and improving care
Stories are told of the first meeting, 20 years ago, where a hat was passed to collect donations to develop a fledgling organization of inpatient physicians. Today, 90% of hospitals with 200+ beds operate with a hospitalist model. Today, we are the Society of Hospital Medicine.
In the early 1900s, health care in many ways was simple. It was a doctor with a shingle hung. It was house calls. Remedies were limited. In the 1940s, companies developed insurance benefits to lure workers during World War II; this third party, the payer, added complexity. Meanwhile, treatment options began to diversify. Then, in the 1960s, Medicare was passed, and the government came into the mix, further increasing this complexity. Diagnostic and treatment options continued to diversify, seemingly exponentially. Some would say it took 30 years for our country to recognize that it had created the most advanced and expensive, as well as one of the least quality-controlled, health systems in the world. Thus, as hospital medicine was conceived in the 1990s, our national health system was awakening to the need – the creative niche – that hospitalists would fill.
When I began my career, I was unaware that I was a hospitalist. The title didn’t exist. Yes, I was working solely in the hospital. I was developing programs to improve care delivery. I was rounding, teaching, collaborating, connecting – everything that we now call hospital medicine. That first job has evolved into my career, one that I find both honorable and enjoyable.
As health care changes with the passing years, being a hospitalist continues to be about serving people, connecting, and improving care. Being a hospitalist is being innovative, willing, and even daring. Dare to try, dare to fail, dare to redesign and try again. Hospital medicine is thinking outside of the box while knowing how to color between the lines. In the coming decades, health care will continue to evolve, and hospital medicine will too. We now encompass surgical comanagement and perioperative care, palliative care, postacute care, and transitions of care services. In corners, hospital medicine is already experimenting with telecare, virtual health, and hospital at home. Our hospital medicine workforce is innovative, diverse, tech savvy and poised for leading.
We are ready and willing to face the pressures affecting health care in the United States today: the recognition of an overwhelming expense to society, the relative underperformance with regard to quality, the increasing complexity of illness and treatment options, the worsening health of the average American citizen, the aging population, the role of medical error in patient harm, the increasing engagement of people in their own care, and the desire to make care better. What our country is facing is actually a phenomenal opportunity, no matter what side of the political aisle you live on. Being in hospital medicine today is being at the center front of this evolutionary stage.
Since joining the SHM board of directors, I continue to find examples of the stellar work of our staff and our members across the country. Having the privilege as a board member to join several Chapter meetings, I have witnessed firsthand the camaraderie, the compassion, the team that makes our Society work. From Houston to San Francisco and from St. Louis to Seattle, I have been honored to work with SHM members that create and nurture local and regional networks with the support of SHM’s Chapters program – a program that now houses more than 50 chapters and has launched regional districts to further support networking and growth. SHM’s chapter venues allow our larger hospital medicine team – yes, the national one – to connect and collaborate.
Take the Pacific Northwest Chapter. In its early years hospitalists from various and competing health systems would convene at a restaurant and just talk. They spoke of how to staff, how to pay, and how to negotiate with hospital leadership. As I have joined chapter meetings in recent years, meetings continue to be the place to share ideas – how to develop new programs; what is the most recent approach to glycemic control, sepsis care, or antibiotic stewardship; how best to approach diagnosis without “anchoring”; and even how to care for each other in the time of loss of a colleague to suicide. It is here in our community that we share experiences, knowledge, new ideas – and this sharing makes us all stronger.
Our hospital medicine community also comes together through areas of shared interest. There are 18 Special Interest Groups (SIGs), focused on specific topic areas. I have been privileged as a board member to work with our Perioperative/Comanagement SIG as it launched in 2017 and has grown rapidly. Currently, the community hosts a “case of the month” hospital medicine discussion as well as a regular journal club webinar that allows participants to review recent literature and interact directly with the authors. As this SIG has grown, shared resources and ideas have allowed for diffusion of knowledge, providing our nation with infrastructure for improving perioperative care. It is networks like this that support our national hospital medicine team to build strength through sharing.
It is our society, our people, that have taken us from the passing of a hat to developing our national community and network. This March, we get to celebrate our field in a new way – Thursday, March 7, 2019, marks the inaugural National Hospitalist Day. Then, March 24-27, our annual conference, Hospital Medicine 2019, will bring thousands of our national team to National Harbor, Maryland. Join your colleagues. Find your niche and your community. Be a part of the change you want to see. While you are there, come introduce yourself to me and let me thank you for the amazing work you are doing.
We are all a part of this movement transforming patient care both on a local and national level. As we move to the future, our innovative, diverse, and connected network of hospital medicine will continue to create and guide health care advances in our country.
Dr. Thompson is professor and chief of the section of hospital medicine at University of Nebraska Medical Center, and medical director of clinical care transitions at Nebraska Medicine, Omaha.
Serving people, connecting, and improving care
Serving people, connecting, and improving care
Stories are told of the first meeting, 20 years ago, where a hat was passed to collect donations to develop a fledgling organization of inpatient physicians. Today, 90% of hospitals with 200+ beds operate with a hospitalist model. Today, we are the Society of Hospital Medicine.
In the early 1900s, health care in many ways was simple. It was a doctor with a shingle hung. It was house calls. Remedies were limited. In the 1940s, companies developed insurance benefits to lure workers during World War II; this third party, the payer, added complexity. Meanwhile, treatment options began to diversify. Then, in the 1960s, Medicare was passed, and the government came into the mix, further increasing this complexity. Diagnostic and treatment options continued to diversify, seemingly exponentially. Some would say it took 30 years for our country to recognize that it had created the most advanced and expensive, as well as one of the least quality-controlled, health systems in the world. Thus, as hospital medicine was conceived in the 1990s, our national health system was awakening to the need – the creative niche – that hospitalists would fill.
When I began my career, I was unaware that I was a hospitalist. The title didn’t exist. Yes, I was working solely in the hospital. I was developing programs to improve care delivery. I was rounding, teaching, collaborating, connecting – everything that we now call hospital medicine. That first job has evolved into my career, one that I find both honorable and enjoyable.
As health care changes with the passing years, being a hospitalist continues to be about serving people, connecting, and improving care. Being a hospitalist is being innovative, willing, and even daring. Dare to try, dare to fail, dare to redesign and try again. Hospital medicine is thinking outside of the box while knowing how to color between the lines. In the coming decades, health care will continue to evolve, and hospital medicine will too. We now encompass surgical comanagement and perioperative care, palliative care, postacute care, and transitions of care services. In corners, hospital medicine is already experimenting with telecare, virtual health, and hospital at home. Our hospital medicine workforce is innovative, diverse, tech savvy and poised for leading.
We are ready and willing to face the pressures affecting health care in the United States today: the recognition of an overwhelming expense to society, the relative underperformance with regard to quality, the increasing complexity of illness and treatment options, the worsening health of the average American citizen, the aging population, the role of medical error in patient harm, the increasing engagement of people in their own care, and the desire to make care better. What our country is facing is actually a phenomenal opportunity, no matter what side of the political aisle you live on. Being in hospital medicine today is being at the center front of this evolutionary stage.
Since joining the SHM board of directors, I continue to find examples of the stellar work of our staff and our members across the country. Having the privilege as a board member to join several Chapter meetings, I have witnessed firsthand the camaraderie, the compassion, the team that makes our Society work. From Houston to San Francisco and from St. Louis to Seattle, I have been honored to work with SHM members that create and nurture local and regional networks with the support of SHM’s Chapters program – a program that now houses more than 50 chapters and has launched regional districts to further support networking and growth. SHM’s chapter venues allow our larger hospital medicine team – yes, the national one – to connect and collaborate.
Take the Pacific Northwest Chapter. In its early years hospitalists from various and competing health systems would convene at a restaurant and just talk. They spoke of how to staff, how to pay, and how to negotiate with hospital leadership. As I have joined chapter meetings in recent years, meetings continue to be the place to share ideas – how to develop new programs; what is the most recent approach to glycemic control, sepsis care, or antibiotic stewardship; how best to approach diagnosis without “anchoring”; and even how to care for each other in the time of loss of a colleague to suicide. It is here in our community that we share experiences, knowledge, new ideas – and this sharing makes us all stronger.
Our hospital medicine community also comes together through areas of shared interest. There are 18 Special Interest Groups (SIGs), focused on specific topic areas. I have been privileged as a board member to work with our Perioperative/Comanagement SIG as it launched in 2017 and has grown rapidly. Currently, the community hosts a “case of the month” hospital medicine discussion as well as a regular journal club webinar that allows participants to review recent literature and interact directly with the authors. As this SIG has grown, shared resources and ideas have allowed for diffusion of knowledge, providing our nation with infrastructure for improving perioperative care. It is networks like this that support our national hospital medicine team to build strength through sharing.
It is our society, our people, that have taken us from the passing of a hat to developing our national community and network. This March, we get to celebrate our field in a new way – Thursday, March 7, 2019, marks the inaugural National Hospitalist Day. Then, March 24-27, our annual conference, Hospital Medicine 2019, will bring thousands of our national team to National Harbor, Maryland. Join your colleagues. Find your niche and your community. Be a part of the change you want to see. While you are there, come introduce yourself to me and let me thank you for the amazing work you are doing.
We are all a part of this movement transforming patient care both on a local and national level. As we move to the future, our innovative, diverse, and connected network of hospital medicine will continue to create and guide health care advances in our country.
Dr. Thompson is professor and chief of the section of hospital medicine at University of Nebraska Medical Center, and medical director of clinical care transitions at Nebraska Medicine, Omaha.
Stories are told of the first meeting, 20 years ago, where a hat was passed to collect donations to develop a fledgling organization of inpatient physicians. Today, 90% of hospitals with 200+ beds operate with a hospitalist model. Today, we are the Society of Hospital Medicine.
In the early 1900s, health care in many ways was simple. It was a doctor with a shingle hung. It was house calls. Remedies were limited. In the 1940s, companies developed insurance benefits to lure workers during World War II; this third party, the payer, added complexity. Meanwhile, treatment options began to diversify. Then, in the 1960s, Medicare was passed, and the government came into the mix, further increasing this complexity. Diagnostic and treatment options continued to diversify, seemingly exponentially. Some would say it took 30 years for our country to recognize that it had created the most advanced and expensive, as well as one of the least quality-controlled, health systems in the world. Thus, as hospital medicine was conceived in the 1990s, our national health system was awakening to the need – the creative niche – that hospitalists would fill.
When I began my career, I was unaware that I was a hospitalist. The title didn’t exist. Yes, I was working solely in the hospital. I was developing programs to improve care delivery. I was rounding, teaching, collaborating, connecting – everything that we now call hospital medicine. That first job has evolved into my career, one that I find both honorable and enjoyable.
As health care changes with the passing years, being a hospitalist continues to be about serving people, connecting, and improving care. Being a hospitalist is being innovative, willing, and even daring. Dare to try, dare to fail, dare to redesign and try again. Hospital medicine is thinking outside of the box while knowing how to color between the lines. In the coming decades, health care will continue to evolve, and hospital medicine will too. We now encompass surgical comanagement and perioperative care, palliative care, postacute care, and transitions of care services. In corners, hospital medicine is already experimenting with telecare, virtual health, and hospital at home. Our hospital medicine workforce is innovative, diverse, tech savvy and poised for leading.
We are ready and willing to face the pressures affecting health care in the United States today: the recognition of an overwhelming expense to society, the relative underperformance with regard to quality, the increasing complexity of illness and treatment options, the worsening health of the average American citizen, the aging population, the role of medical error in patient harm, the increasing engagement of people in their own care, and the desire to make care better. What our country is facing is actually a phenomenal opportunity, no matter what side of the political aisle you live on. Being in hospital medicine today is being at the center front of this evolutionary stage.
Since joining the SHM board of directors, I continue to find examples of the stellar work of our staff and our members across the country. Having the privilege as a board member to join several Chapter meetings, I have witnessed firsthand the camaraderie, the compassion, the team that makes our Society work. From Houston to San Francisco and from St. Louis to Seattle, I have been honored to work with SHM members that create and nurture local and regional networks with the support of SHM’s Chapters program – a program that now houses more than 50 chapters and has launched regional districts to further support networking and growth. SHM’s chapter venues allow our larger hospital medicine team – yes, the national one – to connect and collaborate.
Take the Pacific Northwest Chapter. In its early years hospitalists from various and competing health systems would convene at a restaurant and just talk. They spoke of how to staff, how to pay, and how to negotiate with hospital leadership. As I have joined chapter meetings in recent years, meetings continue to be the place to share ideas – how to develop new programs; what is the most recent approach to glycemic control, sepsis care, or antibiotic stewardship; how best to approach diagnosis without “anchoring”; and even how to care for each other in the time of loss of a colleague to suicide. It is here in our community that we share experiences, knowledge, new ideas – and this sharing makes us all stronger.
Our hospital medicine community also comes together through areas of shared interest. There are 18 Special Interest Groups (SIGs), focused on specific topic areas. I have been privileged as a board member to work with our Perioperative/Comanagement SIG as it launched in 2017 and has grown rapidly. Currently, the community hosts a “case of the month” hospital medicine discussion as well as a regular journal club webinar that allows participants to review recent literature and interact directly with the authors. As this SIG has grown, shared resources and ideas have allowed for diffusion of knowledge, providing our nation with infrastructure for improving perioperative care. It is networks like this that support our national hospital medicine team to build strength through sharing.
It is our society, our people, that have taken us from the passing of a hat to developing our national community and network. This March, we get to celebrate our field in a new way – Thursday, March 7, 2019, marks the inaugural National Hospitalist Day. Then, March 24-27, our annual conference, Hospital Medicine 2019, will bring thousands of our national team to National Harbor, Maryland. Join your colleagues. Find your niche and your community. Be a part of the change you want to see. While you are there, come introduce yourself to me and let me thank you for the amazing work you are doing.
We are all a part of this movement transforming patient care both on a local and national level. As we move to the future, our innovative, diverse, and connected network of hospital medicine will continue to create and guide health care advances in our country.
Dr. Thompson is professor and chief of the section of hospital medicine at University of Nebraska Medical Center, and medical director of clinical care transitions at Nebraska Medicine, Omaha.
An unplanned career
A focus on health system transformation
I have to admit that I am not sure I am a legacy in hospital medicine, and the term legacy throws me off a bit. I came to medical school after working at McKinsey & Co. consulting, and I chose pediatrics because of my love of working with children and families, as well as a vague notion that I wanted to work on “system” issues, and therefore, more generalist-type training seemed applicable.
I met Chris Landrigan, MD, MPH, and Vinny Chiang, MD, and learned what a hospitalist was, as an intern in 2002. We had a research elective and I was able to publish a couple of papers in Pediatrics on pediatric hospital medicine with Chris and Raj Srivastava, MD, MPH. In 2004, I went to my first Society of Hospital Medicine meeting and met Larry Wellikson, MD, MHM, and others. From there, I went to the Robert Wood Johnson Clinical Scholars Program, with Ron Keren, MD, MPH, and others, and along with faculty from the Cincinnati Children’s in hospital medicine.
In 2007, I applied for a White House Fellowship and told my wife that I didn’t think there was a chance that I would get it, so we should keep building our new home in Cincinnati. We were both surprised when I was selected. I served Michael Leavitt, the then-Secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services, as his White House fellow during the Bush administration, and then served as his chief medical officer. Exposure to health policy and leadership at that level was career shaping. Cincinnati Children’s was searching for a leader for the conversion of pediatric hospital medicine into a full division in 2009. So I returned to Cincinnati to take on leading pediatric hospital medicine, and a role leading quality measurement and improvement efforts for the entire health system. I loved the work and thought I would remain in that role, and our family would be in Cincinnati for a long time. Best laid plans …
In early 2011, Don Berwick, MD, who was then the administrator of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services called and asked whether I “would come talk with him in D.C.” That talk quickly became a series of interviews, and he offered me the opportunity to be chief medical officer of CMS. He said “this platform is like no other to drive change.” He was right. I have been fortunate to have a few step-change opportunities in my life, and that was one.
On my first day at CMS, I looked around the table of senior executives reporting to me and realized they had more than 200 years of CMS experience. I was a bit scared. Together, we led the implementation of Hospital Value-Based Purchasing, the Compare websites, and numerous quality measurement and improvement programs. Partnership for Patients works on patient safety and was associated with preventing more than 3 million infections and adverse events, over 125,000 lives saved, and more than $26 billion in savings.
In early 2013, I was asked to lead the CMS Innovation Center (CMMI). The goal was to launch new payment and service delivery models to improve quality and lower costs. We launched Accountable Care Organizations, Bundled Payment programs, primary care medical homes, state-based innovation, and so much more. Medicare went from zero dollars in alternative payment models, where providers are accountable for quality and total cost of care, to more than 30% of Medicare payments, representing over $200 billion through agreements with more than 200,000 providers in these alternative payment models. It was the biggest shift in U.S. history in how CMS paid for care. Later, I became principal deputy administrator and acting administrator of CMS, leading an agency that spends over $1 trillion per year, or more than $2.5 billion per day and insures over 130 million Americans. We also improved from being bottom quintile in employee engagement and satisfaction across the federal government to No. 2.
I had assumed that, after working at CMS, I would return to a hospital/health system leadership role. But then, a recruiter called about the CEO role at Blue Cross Blue Shield of North Carolina. It is one of the largest not-for-profit health plans in the country and insures most of the people in North Carolina, many for most of their lives. I met a 75-year-old woman the other day that we have insured every day of her life. I am almost a year into the role and it is a mission-driven organization that drives positive change. I love it so far.
We are going to partner with providers, so that more than half of our payments will be in advanced alternative payment models. No payer in the United States has done that yet. This allows us to innovate and decrease friction in the system (e.g., turn off prior authorization) and be jointly accountable with providers for quality and total cost of care. We insure people through the ACA [Affordable Care Act], commercial, and Medicare markets, and are competing to serve Medicaid as well. We have invested more than $50 million to address social determinants of health across the state. We are making major investments in primary care, and mental and behavioral health. Our goal is to be a Model Blue – or a Model of Health Transformation for our state and nation – and achieve better health outcomes, lower costs, and best-in-class experience for all people we serve. I have learned that no physician leads a health plan of this size, and apparently, no practicing physician has ever led a health plan of this size.
What are some lessons learned over my career? I have had five criteria for all my career decisions: 1) family; 2) impact – better care and outcomes, lower costs, and exceptional experience for populations of patients; 3) people – mentors and colleagues; 4) learning; and 5) joy in work. If someone gives you a chance to lead people in your career as a physician, jump at the chance. We do a relatively poor job of providing this type of opportunity to those early in their careers in medicine, and learning how to manage people and money allows you to progress as a leader and manager.
Don’t listen to the people who say “you must do X before Y” or “you must take this path.” They are usually wrong. Take chances. I applied for many roles for which I was a long shot, and I didn’t always succeed. That’s life and learning. Hospital medicine is a great career. I worked in the hospital on a recent weekend and was able to help families through everything from palliative care decisions and new diagnoses, to recovering from illness. It is an honor to serve and help families in their time of need. Hospitalists have been – and should continue to be – primary drivers of the shift in our health system to value-based care.
As I look back on my career (and I hope I am only halfway done), I could not have predicted more than 90% of it. I was blessed with many opportunities, mentors, and teachers along the way. I try to pass this on by mentoring and teaching others. How did my career happen? I am not sure, but it has been a fun ride! And hopefully I have helped improve the health system some, along the way.
Dr. Conway is president and CEO of Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolina. He is a hospitalist and former deputy administrator for innovation and quality at the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
A focus on health system transformation
A focus on health system transformation
I have to admit that I am not sure I am a legacy in hospital medicine, and the term legacy throws me off a bit. I came to medical school after working at McKinsey & Co. consulting, and I chose pediatrics because of my love of working with children and families, as well as a vague notion that I wanted to work on “system” issues, and therefore, more generalist-type training seemed applicable.
I met Chris Landrigan, MD, MPH, and Vinny Chiang, MD, and learned what a hospitalist was, as an intern in 2002. We had a research elective and I was able to publish a couple of papers in Pediatrics on pediatric hospital medicine with Chris and Raj Srivastava, MD, MPH. In 2004, I went to my first Society of Hospital Medicine meeting and met Larry Wellikson, MD, MHM, and others. From there, I went to the Robert Wood Johnson Clinical Scholars Program, with Ron Keren, MD, MPH, and others, and along with faculty from the Cincinnati Children’s in hospital medicine.
In 2007, I applied for a White House Fellowship and told my wife that I didn’t think there was a chance that I would get it, so we should keep building our new home in Cincinnati. We were both surprised when I was selected. I served Michael Leavitt, the then-Secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services, as his White House fellow during the Bush administration, and then served as his chief medical officer. Exposure to health policy and leadership at that level was career shaping. Cincinnati Children’s was searching for a leader for the conversion of pediatric hospital medicine into a full division in 2009. So I returned to Cincinnati to take on leading pediatric hospital medicine, and a role leading quality measurement and improvement efforts for the entire health system. I loved the work and thought I would remain in that role, and our family would be in Cincinnati for a long time. Best laid plans …
In early 2011, Don Berwick, MD, who was then the administrator of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services called and asked whether I “would come talk with him in D.C.” That talk quickly became a series of interviews, and he offered me the opportunity to be chief medical officer of CMS. He said “this platform is like no other to drive change.” He was right. I have been fortunate to have a few step-change opportunities in my life, and that was one.
On my first day at CMS, I looked around the table of senior executives reporting to me and realized they had more than 200 years of CMS experience. I was a bit scared. Together, we led the implementation of Hospital Value-Based Purchasing, the Compare websites, and numerous quality measurement and improvement programs. Partnership for Patients works on patient safety and was associated with preventing more than 3 million infections and adverse events, over 125,000 lives saved, and more than $26 billion in savings.
In early 2013, I was asked to lead the CMS Innovation Center (CMMI). The goal was to launch new payment and service delivery models to improve quality and lower costs. We launched Accountable Care Organizations, Bundled Payment programs, primary care medical homes, state-based innovation, and so much more. Medicare went from zero dollars in alternative payment models, where providers are accountable for quality and total cost of care, to more than 30% of Medicare payments, representing over $200 billion through agreements with more than 200,000 providers in these alternative payment models. It was the biggest shift in U.S. history in how CMS paid for care. Later, I became principal deputy administrator and acting administrator of CMS, leading an agency that spends over $1 trillion per year, or more than $2.5 billion per day and insures over 130 million Americans. We also improved from being bottom quintile in employee engagement and satisfaction across the federal government to No. 2.
I had assumed that, after working at CMS, I would return to a hospital/health system leadership role. But then, a recruiter called about the CEO role at Blue Cross Blue Shield of North Carolina. It is one of the largest not-for-profit health plans in the country and insures most of the people in North Carolina, many for most of their lives. I met a 75-year-old woman the other day that we have insured every day of her life. I am almost a year into the role and it is a mission-driven organization that drives positive change. I love it so far.
We are going to partner with providers, so that more than half of our payments will be in advanced alternative payment models. No payer in the United States has done that yet. This allows us to innovate and decrease friction in the system (e.g., turn off prior authorization) and be jointly accountable with providers for quality and total cost of care. We insure people through the ACA [Affordable Care Act], commercial, and Medicare markets, and are competing to serve Medicaid as well. We have invested more than $50 million to address social determinants of health across the state. We are making major investments in primary care, and mental and behavioral health. Our goal is to be a Model Blue – or a Model of Health Transformation for our state and nation – and achieve better health outcomes, lower costs, and best-in-class experience for all people we serve. I have learned that no physician leads a health plan of this size, and apparently, no practicing physician has ever led a health plan of this size.
What are some lessons learned over my career? I have had five criteria for all my career decisions: 1) family; 2) impact – better care and outcomes, lower costs, and exceptional experience for populations of patients; 3) people – mentors and colleagues; 4) learning; and 5) joy in work. If someone gives you a chance to lead people in your career as a physician, jump at the chance. We do a relatively poor job of providing this type of opportunity to those early in their careers in medicine, and learning how to manage people and money allows you to progress as a leader and manager.
Don’t listen to the people who say “you must do X before Y” or “you must take this path.” They are usually wrong. Take chances. I applied for many roles for which I was a long shot, and I didn’t always succeed. That’s life and learning. Hospital medicine is a great career. I worked in the hospital on a recent weekend and was able to help families through everything from palliative care decisions and new diagnoses, to recovering from illness. It is an honor to serve and help families in their time of need. Hospitalists have been – and should continue to be – primary drivers of the shift in our health system to value-based care.
As I look back on my career (and I hope I am only halfway done), I could not have predicted more than 90% of it. I was blessed with many opportunities, mentors, and teachers along the way. I try to pass this on by mentoring and teaching others. How did my career happen? I am not sure, but it has been a fun ride! And hopefully I have helped improve the health system some, along the way.
Dr. Conway is president and CEO of Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolina. He is a hospitalist and former deputy administrator for innovation and quality at the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
I have to admit that I am not sure I am a legacy in hospital medicine, and the term legacy throws me off a bit. I came to medical school after working at McKinsey & Co. consulting, and I chose pediatrics because of my love of working with children and families, as well as a vague notion that I wanted to work on “system” issues, and therefore, more generalist-type training seemed applicable.
I met Chris Landrigan, MD, MPH, and Vinny Chiang, MD, and learned what a hospitalist was, as an intern in 2002. We had a research elective and I was able to publish a couple of papers in Pediatrics on pediatric hospital medicine with Chris and Raj Srivastava, MD, MPH. In 2004, I went to my first Society of Hospital Medicine meeting and met Larry Wellikson, MD, MHM, and others. From there, I went to the Robert Wood Johnson Clinical Scholars Program, with Ron Keren, MD, MPH, and others, and along with faculty from the Cincinnati Children’s in hospital medicine.
In 2007, I applied for a White House Fellowship and told my wife that I didn’t think there was a chance that I would get it, so we should keep building our new home in Cincinnati. We were both surprised when I was selected. I served Michael Leavitt, the then-Secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services, as his White House fellow during the Bush administration, and then served as his chief medical officer. Exposure to health policy and leadership at that level was career shaping. Cincinnati Children’s was searching for a leader for the conversion of pediatric hospital medicine into a full division in 2009. So I returned to Cincinnati to take on leading pediatric hospital medicine, and a role leading quality measurement and improvement efforts for the entire health system. I loved the work and thought I would remain in that role, and our family would be in Cincinnati for a long time. Best laid plans …
In early 2011, Don Berwick, MD, who was then the administrator of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services called and asked whether I “would come talk with him in D.C.” That talk quickly became a series of interviews, and he offered me the opportunity to be chief medical officer of CMS. He said “this platform is like no other to drive change.” He was right. I have been fortunate to have a few step-change opportunities in my life, and that was one.
On my first day at CMS, I looked around the table of senior executives reporting to me and realized they had more than 200 years of CMS experience. I was a bit scared. Together, we led the implementation of Hospital Value-Based Purchasing, the Compare websites, and numerous quality measurement and improvement programs. Partnership for Patients works on patient safety and was associated with preventing more than 3 million infections and adverse events, over 125,000 lives saved, and more than $26 billion in savings.
In early 2013, I was asked to lead the CMS Innovation Center (CMMI). The goal was to launch new payment and service delivery models to improve quality and lower costs. We launched Accountable Care Organizations, Bundled Payment programs, primary care medical homes, state-based innovation, and so much more. Medicare went from zero dollars in alternative payment models, where providers are accountable for quality and total cost of care, to more than 30% of Medicare payments, representing over $200 billion through agreements with more than 200,000 providers in these alternative payment models. It was the biggest shift in U.S. history in how CMS paid for care. Later, I became principal deputy administrator and acting administrator of CMS, leading an agency that spends over $1 trillion per year, or more than $2.5 billion per day and insures over 130 million Americans. We also improved from being bottom quintile in employee engagement and satisfaction across the federal government to No. 2.
I had assumed that, after working at CMS, I would return to a hospital/health system leadership role. But then, a recruiter called about the CEO role at Blue Cross Blue Shield of North Carolina. It is one of the largest not-for-profit health plans in the country and insures most of the people in North Carolina, many for most of their lives. I met a 75-year-old woman the other day that we have insured every day of her life. I am almost a year into the role and it is a mission-driven organization that drives positive change. I love it so far.
We are going to partner with providers, so that more than half of our payments will be in advanced alternative payment models. No payer in the United States has done that yet. This allows us to innovate and decrease friction in the system (e.g., turn off prior authorization) and be jointly accountable with providers for quality and total cost of care. We insure people through the ACA [Affordable Care Act], commercial, and Medicare markets, and are competing to serve Medicaid as well. We have invested more than $50 million to address social determinants of health across the state. We are making major investments in primary care, and mental and behavioral health. Our goal is to be a Model Blue – or a Model of Health Transformation for our state and nation – and achieve better health outcomes, lower costs, and best-in-class experience for all people we serve. I have learned that no physician leads a health plan of this size, and apparently, no practicing physician has ever led a health plan of this size.
What are some lessons learned over my career? I have had five criteria for all my career decisions: 1) family; 2) impact – better care and outcomes, lower costs, and exceptional experience for populations of patients; 3) people – mentors and colleagues; 4) learning; and 5) joy in work. If someone gives you a chance to lead people in your career as a physician, jump at the chance. We do a relatively poor job of providing this type of opportunity to those early in their careers in medicine, and learning how to manage people and money allows you to progress as a leader and manager.
Don’t listen to the people who say “you must do X before Y” or “you must take this path.” They are usually wrong. Take chances. I applied for many roles for which I was a long shot, and I didn’t always succeed. That’s life and learning. Hospital medicine is a great career. I worked in the hospital on a recent weekend and was able to help families through everything from palliative care decisions and new diagnoses, to recovering from illness. It is an honor to serve and help families in their time of need. Hospitalists have been – and should continue to be – primary drivers of the shift in our health system to value-based care.
As I look back on my career (and I hope I am only halfway done), I could not have predicted more than 90% of it. I was blessed with many opportunities, mentors, and teachers along the way. I try to pass this on by mentoring and teaching others. How did my career happen? I am not sure, but it has been a fun ride! And hopefully I have helped improve the health system some, along the way.
Dr. Conway is president and CEO of Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolina. He is a hospitalist and former deputy administrator for innovation and quality at the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
Hospitalist PA and health system leader: Emilie Thornhill Davis
Building a collaborative practice
Emilie Thornhill Davis, PA-C, is the assistant vice president for advanced practice providers at Ochsner Health System in New Orleans. She is the former chair of SHM’s Nurse Practitioner and Physician Assistant (NP/PA) Committee, and has spoken multiple times at the SHM Annual Conference.
In honor of the inaugural National Hospitalist Day, to be held on Thursday, March 7, 2019, The Hospitalist spoke with Ms. Davis about the unique contributions of NP and PA hospitalists to the specialty of hospital medicine.
Where did you get your education?
I got my undergraduate degree from Mercer University and then went on to get my prerequisites for PA school, and worked clinically for a year prior to starting graduate school in Savannah, Georgia, at South University.
Was your intention always to be a PA?
During my sophomore year of college, Mercer was starting a PA program. Having been taken care of by PAs for most of my life, I realized that this was a profession I was very interested in. I shadowed a lot of PAs and found that they had extremely high levels of satisfaction. I saw the versatility to do so many types of medicine as a PA.
How did you become interested in hospital medicine?
When I was in PA school, we had small groups that were led by a PA who practiced clinically. The PA who was my small group leader was a hospitalist and was a fantastic role model. I did a clinical rotation with her team, and then went on to do my elective with her team in hospital medicine. When I graduated, I got my first job with the hospital medicine group that I had done those clinical rotations with in Savannah. And then in 2013, after about a year and a half, life brought me to New Orleans and I started working at Ochsner in the department of hospital medicine. I was one of the first two PAs that this group had employed.
What is your current role and title at Ochsner?
From 2013 to 2018, I worked in the department of hospital medicine, and for the last 2 years I functioned as the system lead for advanced practice providers in the department of hospital medicine. In September of 2018, I accepted the role of assistant vice president of advanced practice providers for Ochsner Health System.
What are your areas of interest or research?
I’ve had the opportunity to speak at the annual Society of Hospital Medicine Conference for 3 years in a row on innovative models of care, and nurse practitioner and PA utilization in hospital medicine. I was the chair for the NP/PA committee, and during that time we developed a toolkit aimed at providing a resource to hospital medicine groups around nurse practitioner and PA integration to practice in full utilization.
What has your experience taught you about how NPs and PAs can best fit into hospital medicine groups?
Nurse practitioners and PAs are perfectly set up to integrate into practice in hospital medicine. Training for PAs specifically is based on the medicine model, where you have a year of didactic and a year of clinical work in all the major disciplines of medicine. And so in a clinical year as a PA, I would rotate through primary care, internal medicine, general surgery, ob.gyn., psychiatry, emergency medicine, pediatrics. When I come out of school, I’m generalist trained, and depending on where your emphasis was during clinical rotations, that could include a lot of inpatient experience.
I transitioned very smoothly into my first role in hospital medicine as a PA, because I had gained that experience while I was a student on clinical rotations. PAs and nurse practitioners are – when they’re utilized appropriately and at the top of their experience and training – able to provide services to patients that can improve quality outcomes, enhance throughput, decrease length of stay, and improve all the different areas that we focus on as hospitalists.
What roles can a PA occupy in relation to physicians and nurse practitioners in hospital medicine?
When you’re looking at a PA versus a nurse practitioner in hospital medicine, you’ll notice that there are differences in the way that PAs and nurse practitioners are trained. All PAs are trained on a medical model and have a very similar kind of generalist background, whereas a nurse practitioner is typically schooled with nursing training that includes bedside experience that you can’t always guarantee with PAs. But once we enter into practice, our scope and the way that we take care of patients over time becomes very similar. So a PA and a nurse practitioner for the most part can function in very similar capacities in hospital medicine.
The only thing that creates a difference for PAs and NPs are federal and state rules and regulations, as well as hospital policies that might create “scope of practice” barriers. For instance, when I first moved to Louisiana, PAs were not able to prescribe Schedule II medications. That created a barrier whenever I was discharging patients who needed prescriptions for Schedule II. That has since changed in the state of Louisiana; now both PAs and NPs have full prescriptive authority in the state.
I would compare the work of PAs and NPs to that of physicians like this: Once you have NPs or PAs who are trained and have experience in the specialty that they are working in, they are able to provide services that would otherwise be provided by physicians.
How does a hospitalist PA work differently from a PA in other care settings?
The scope of practice for a PA is defined by the physician they’re working with. So my day-to-day work as a PA in hospital medicine looked very similar to a physician’s day-to-day work in hospital medicine. In cardiology, for example, the same would likely hold true, but with tasks unique to that specialty.
How does SHM support hospitalist PAs?
SHM is the home where you have physicians, nurse practitioners, and PAs all represented by one society, which I think is really important whenever we’re talking about a membership organization that reflects what things truly look like in practice. When I am a member of SHM, and the physician I work with is a member of SHM, we are getting the same journals and are both familiar with the changes that occur nationally in our specialty; this really helps us to align ourselves clinically, and to understand what’s going on across the country.
What kind of resources do hospitalist PAs need to succeed, either from SHM or from their own institutions?
I think the first thing we have to do is make sure that we’re getting the nomenclature right, that we’re referring to nurse practitioners and physician assistants by their appropriate names and recognizing their role in hospital medicine. Every year that I spoke at the SHM Annual Conference, I had many hospital medicine leaders come up to me and say they needed help with incorporating NPs and PAs, not only clinically, but also making sure they were represented within their hospital system. That’s why we developed the toolkit, which provides resources for integrating NPs and PAs into practice.
There is an investment early on when you bring PAs into your group to train them. We often use the SHM core competencies when we are referring to a training guide for PAs or NPs as a way to categorize the different materials that they would need to know to practice efficiently, but I do think those could be expanded upon.
What’s on the horizon for NPs and PAs in hospital medicine?
One national trend I see is an increase in the number of NPs and PAs entering hospital medicine. The other big trend is the formal development of postgraduate fellowships for PAs in hospital medicine. As the complexity of our health systems continues to grow, the feeling is that to get a nurse practitioner and PA the training they need, there are benefits to having a protected postgrad year to learn.
One unique thing about nurse practitioners and PAs is their versatility and their ability to move among the various medical specialties. As a PA or a nurse practitioner, if I’m working in hospital medicine and I have a really strong foundation, there’s nothing to say that I couldn’t then accept a job in CV surgery or cardiology and bring those skills with me from hospital medicine.
But this is kind of a double-edged sword, because it also means that you may have a PA or NP leave your HM group after 1-2 years. That kind of turnover is a difficult thing to address, because it means dealing with issues such as workplace culture and compensation. But that shows why training and engagement is important early on in that first year – to make sure that NPs and PAs feel fully supported to meet the demands that hospital medicine requires. All of those things really factor into whether an NP or PA will choose to continue in the field.
Building a collaborative practice
Building a collaborative practice
Emilie Thornhill Davis, PA-C, is the assistant vice president for advanced practice providers at Ochsner Health System in New Orleans. She is the former chair of SHM’s Nurse Practitioner and Physician Assistant (NP/PA) Committee, and has spoken multiple times at the SHM Annual Conference.
In honor of the inaugural National Hospitalist Day, to be held on Thursday, March 7, 2019, The Hospitalist spoke with Ms. Davis about the unique contributions of NP and PA hospitalists to the specialty of hospital medicine.
Where did you get your education?
I got my undergraduate degree from Mercer University and then went on to get my prerequisites for PA school, and worked clinically for a year prior to starting graduate school in Savannah, Georgia, at South University.
Was your intention always to be a PA?
During my sophomore year of college, Mercer was starting a PA program. Having been taken care of by PAs for most of my life, I realized that this was a profession I was very interested in. I shadowed a lot of PAs and found that they had extremely high levels of satisfaction. I saw the versatility to do so many types of medicine as a PA.
How did you become interested in hospital medicine?
When I was in PA school, we had small groups that were led by a PA who practiced clinically. The PA who was my small group leader was a hospitalist and was a fantastic role model. I did a clinical rotation with her team, and then went on to do my elective with her team in hospital medicine. When I graduated, I got my first job with the hospital medicine group that I had done those clinical rotations with in Savannah. And then in 2013, after about a year and a half, life brought me to New Orleans and I started working at Ochsner in the department of hospital medicine. I was one of the first two PAs that this group had employed.
What is your current role and title at Ochsner?
From 2013 to 2018, I worked in the department of hospital medicine, and for the last 2 years I functioned as the system lead for advanced practice providers in the department of hospital medicine. In September of 2018, I accepted the role of assistant vice president of advanced practice providers for Ochsner Health System.
What are your areas of interest or research?
I’ve had the opportunity to speak at the annual Society of Hospital Medicine Conference for 3 years in a row on innovative models of care, and nurse practitioner and PA utilization in hospital medicine. I was the chair for the NP/PA committee, and during that time we developed a toolkit aimed at providing a resource to hospital medicine groups around nurse practitioner and PA integration to practice in full utilization.
What has your experience taught you about how NPs and PAs can best fit into hospital medicine groups?
Nurse practitioners and PAs are perfectly set up to integrate into practice in hospital medicine. Training for PAs specifically is based on the medicine model, where you have a year of didactic and a year of clinical work in all the major disciplines of medicine. And so in a clinical year as a PA, I would rotate through primary care, internal medicine, general surgery, ob.gyn., psychiatry, emergency medicine, pediatrics. When I come out of school, I’m generalist trained, and depending on where your emphasis was during clinical rotations, that could include a lot of inpatient experience.
I transitioned very smoothly into my first role in hospital medicine as a PA, because I had gained that experience while I was a student on clinical rotations. PAs and nurse practitioners are – when they’re utilized appropriately and at the top of their experience and training – able to provide services to patients that can improve quality outcomes, enhance throughput, decrease length of stay, and improve all the different areas that we focus on as hospitalists.
What roles can a PA occupy in relation to physicians and nurse practitioners in hospital medicine?
When you’re looking at a PA versus a nurse practitioner in hospital medicine, you’ll notice that there are differences in the way that PAs and nurse practitioners are trained. All PAs are trained on a medical model and have a very similar kind of generalist background, whereas a nurse practitioner is typically schooled with nursing training that includes bedside experience that you can’t always guarantee with PAs. But once we enter into practice, our scope and the way that we take care of patients over time becomes very similar. So a PA and a nurse practitioner for the most part can function in very similar capacities in hospital medicine.
The only thing that creates a difference for PAs and NPs are federal and state rules and regulations, as well as hospital policies that might create “scope of practice” barriers. For instance, when I first moved to Louisiana, PAs were not able to prescribe Schedule II medications. That created a barrier whenever I was discharging patients who needed prescriptions for Schedule II. That has since changed in the state of Louisiana; now both PAs and NPs have full prescriptive authority in the state.
I would compare the work of PAs and NPs to that of physicians like this: Once you have NPs or PAs who are trained and have experience in the specialty that they are working in, they are able to provide services that would otherwise be provided by physicians.
How does a hospitalist PA work differently from a PA in other care settings?
The scope of practice for a PA is defined by the physician they’re working with. So my day-to-day work as a PA in hospital medicine looked very similar to a physician’s day-to-day work in hospital medicine. In cardiology, for example, the same would likely hold true, but with tasks unique to that specialty.
How does SHM support hospitalist PAs?
SHM is the home where you have physicians, nurse practitioners, and PAs all represented by one society, which I think is really important whenever we’re talking about a membership organization that reflects what things truly look like in practice. When I am a member of SHM, and the physician I work with is a member of SHM, we are getting the same journals and are both familiar with the changes that occur nationally in our specialty; this really helps us to align ourselves clinically, and to understand what’s going on across the country.
What kind of resources do hospitalist PAs need to succeed, either from SHM or from their own institutions?
I think the first thing we have to do is make sure that we’re getting the nomenclature right, that we’re referring to nurse practitioners and physician assistants by their appropriate names and recognizing their role in hospital medicine. Every year that I spoke at the SHM Annual Conference, I had many hospital medicine leaders come up to me and say they needed help with incorporating NPs and PAs, not only clinically, but also making sure they were represented within their hospital system. That’s why we developed the toolkit, which provides resources for integrating NPs and PAs into practice.
There is an investment early on when you bring PAs into your group to train them. We often use the SHM core competencies when we are referring to a training guide for PAs or NPs as a way to categorize the different materials that they would need to know to practice efficiently, but I do think those could be expanded upon.
What’s on the horizon for NPs and PAs in hospital medicine?
One national trend I see is an increase in the number of NPs and PAs entering hospital medicine. The other big trend is the formal development of postgraduate fellowships for PAs in hospital medicine. As the complexity of our health systems continues to grow, the feeling is that to get a nurse practitioner and PA the training they need, there are benefits to having a protected postgrad year to learn.
One unique thing about nurse practitioners and PAs is their versatility and their ability to move among the various medical specialties. As a PA or a nurse practitioner, if I’m working in hospital medicine and I have a really strong foundation, there’s nothing to say that I couldn’t then accept a job in CV surgery or cardiology and bring those skills with me from hospital medicine.
But this is kind of a double-edged sword, because it also means that you may have a PA or NP leave your HM group after 1-2 years. That kind of turnover is a difficult thing to address, because it means dealing with issues such as workplace culture and compensation. But that shows why training and engagement is important early on in that first year – to make sure that NPs and PAs feel fully supported to meet the demands that hospital medicine requires. All of those things really factor into whether an NP or PA will choose to continue in the field.
Emilie Thornhill Davis, PA-C, is the assistant vice president for advanced practice providers at Ochsner Health System in New Orleans. She is the former chair of SHM’s Nurse Practitioner and Physician Assistant (NP/PA) Committee, and has spoken multiple times at the SHM Annual Conference.
In honor of the inaugural National Hospitalist Day, to be held on Thursday, March 7, 2019, The Hospitalist spoke with Ms. Davis about the unique contributions of NP and PA hospitalists to the specialty of hospital medicine.
Where did you get your education?
I got my undergraduate degree from Mercer University and then went on to get my prerequisites for PA school, and worked clinically for a year prior to starting graduate school in Savannah, Georgia, at South University.
Was your intention always to be a PA?
During my sophomore year of college, Mercer was starting a PA program. Having been taken care of by PAs for most of my life, I realized that this was a profession I was very interested in. I shadowed a lot of PAs and found that they had extremely high levels of satisfaction. I saw the versatility to do so many types of medicine as a PA.
How did you become interested in hospital medicine?
When I was in PA school, we had small groups that were led by a PA who practiced clinically. The PA who was my small group leader was a hospitalist and was a fantastic role model. I did a clinical rotation with her team, and then went on to do my elective with her team in hospital medicine. When I graduated, I got my first job with the hospital medicine group that I had done those clinical rotations with in Savannah. And then in 2013, after about a year and a half, life brought me to New Orleans and I started working at Ochsner in the department of hospital medicine. I was one of the first two PAs that this group had employed.
What is your current role and title at Ochsner?
From 2013 to 2018, I worked in the department of hospital medicine, and for the last 2 years I functioned as the system lead for advanced practice providers in the department of hospital medicine. In September of 2018, I accepted the role of assistant vice president of advanced practice providers for Ochsner Health System.
What are your areas of interest or research?
I’ve had the opportunity to speak at the annual Society of Hospital Medicine Conference for 3 years in a row on innovative models of care, and nurse practitioner and PA utilization in hospital medicine. I was the chair for the NP/PA committee, and during that time we developed a toolkit aimed at providing a resource to hospital medicine groups around nurse practitioner and PA integration to practice in full utilization.
What has your experience taught you about how NPs and PAs can best fit into hospital medicine groups?
Nurse practitioners and PAs are perfectly set up to integrate into practice in hospital medicine. Training for PAs specifically is based on the medicine model, where you have a year of didactic and a year of clinical work in all the major disciplines of medicine. And so in a clinical year as a PA, I would rotate through primary care, internal medicine, general surgery, ob.gyn., psychiatry, emergency medicine, pediatrics. When I come out of school, I’m generalist trained, and depending on where your emphasis was during clinical rotations, that could include a lot of inpatient experience.
I transitioned very smoothly into my first role in hospital medicine as a PA, because I had gained that experience while I was a student on clinical rotations. PAs and nurse practitioners are – when they’re utilized appropriately and at the top of their experience and training – able to provide services to patients that can improve quality outcomes, enhance throughput, decrease length of stay, and improve all the different areas that we focus on as hospitalists.
What roles can a PA occupy in relation to physicians and nurse practitioners in hospital medicine?
When you’re looking at a PA versus a nurse practitioner in hospital medicine, you’ll notice that there are differences in the way that PAs and nurse practitioners are trained. All PAs are trained on a medical model and have a very similar kind of generalist background, whereas a nurse practitioner is typically schooled with nursing training that includes bedside experience that you can’t always guarantee with PAs. But once we enter into practice, our scope and the way that we take care of patients over time becomes very similar. So a PA and a nurse practitioner for the most part can function in very similar capacities in hospital medicine.
The only thing that creates a difference for PAs and NPs are federal and state rules and regulations, as well as hospital policies that might create “scope of practice” barriers. For instance, when I first moved to Louisiana, PAs were not able to prescribe Schedule II medications. That created a barrier whenever I was discharging patients who needed prescriptions for Schedule II. That has since changed in the state of Louisiana; now both PAs and NPs have full prescriptive authority in the state.
I would compare the work of PAs and NPs to that of physicians like this: Once you have NPs or PAs who are trained and have experience in the specialty that they are working in, they are able to provide services that would otherwise be provided by physicians.
How does a hospitalist PA work differently from a PA in other care settings?
The scope of practice for a PA is defined by the physician they’re working with. So my day-to-day work as a PA in hospital medicine looked very similar to a physician’s day-to-day work in hospital medicine. In cardiology, for example, the same would likely hold true, but with tasks unique to that specialty.
How does SHM support hospitalist PAs?
SHM is the home where you have physicians, nurse practitioners, and PAs all represented by one society, which I think is really important whenever we’re talking about a membership organization that reflects what things truly look like in practice. When I am a member of SHM, and the physician I work with is a member of SHM, we are getting the same journals and are both familiar with the changes that occur nationally in our specialty; this really helps us to align ourselves clinically, and to understand what’s going on across the country.
What kind of resources do hospitalist PAs need to succeed, either from SHM or from their own institutions?
I think the first thing we have to do is make sure that we’re getting the nomenclature right, that we’re referring to nurse practitioners and physician assistants by their appropriate names and recognizing their role in hospital medicine. Every year that I spoke at the SHM Annual Conference, I had many hospital medicine leaders come up to me and say they needed help with incorporating NPs and PAs, not only clinically, but also making sure they were represented within their hospital system. That’s why we developed the toolkit, which provides resources for integrating NPs and PAs into practice.
There is an investment early on when you bring PAs into your group to train them. We often use the SHM core competencies when we are referring to a training guide for PAs or NPs as a way to categorize the different materials that they would need to know to practice efficiently, but I do think those could be expanded upon.
What’s on the horizon for NPs and PAs in hospital medicine?
One national trend I see is an increase in the number of NPs and PAs entering hospital medicine. The other big trend is the formal development of postgraduate fellowships for PAs in hospital medicine. As the complexity of our health systems continues to grow, the feeling is that to get a nurse practitioner and PA the training they need, there are benefits to having a protected postgrad year to learn.
One unique thing about nurse practitioners and PAs is their versatility and their ability to move among the various medical specialties. As a PA or a nurse practitioner, if I’m working in hospital medicine and I have a really strong foundation, there’s nothing to say that I couldn’t then accept a job in CV surgery or cardiology and bring those skills with me from hospital medicine.
But this is kind of a double-edged sword, because it also means that you may have a PA or NP leave your HM group after 1-2 years. That kind of turnover is a difficult thing to address, because it means dealing with issues such as workplace culture and compensation. But that shows why training and engagement is important early on in that first year – to make sure that NPs and PAs feel fully supported to meet the demands that hospital medicine requires. All of those things really factor into whether an NP or PA will choose to continue in the field.
Pediatric hospitalist and researcher: Dr. Samir Shah
Stoking collaboration between adult and pediatric clinicians
Samir S. Shah, MD, MSCE, director of the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, believes that pediatric and adult hospitalists have much to learn from each other. And he aims to promote that mutual education in his new role as editor in chief of the Journal of Hospital Medicine.
Dr. Shah is the first pediatric hospitalist to hold this position for JHM, the official journal of the Society of Hospital Medicine. He says his new position, which became effective Jan. 1, is primed for fostering interaction between pediatric and adult hospitalists. “Pediatric hospital medicine is such a vibrant community of its own. There are many opportunities for partnership and collaboration between adult and pediatric hospitalists,” he said.
The field of pediatric hospital medicine has started down the path toward becoming recognized as a board-certified subspecialty.1 “That will place a greater emphasis on our role in fellowship training, which is important to ensure that pediatric hospitalists have a clearly defined skill set,” Dr. Shah said. “So much of what we learn in medical school is oriented to the medical care of adults. If you go into pediatrics, you’ve already had a fair amount of grounding in the healthy physiology and common diseases of adults. Pediatric hospital medicine fellowships offer an opportunity to refine clinical skill sets, as well as develop new skills in domains such as research and leadership.”
An emphasis on diversity
Although he has praised the innovative work of his predecessors, Mark Williams, MD, MHM, and Andrew Auerbach, MD, MPH, MHM, in shepherding the journal to its current strong position, Dr. Shah brings ideas for new features and directions.
“We as a field really benefit from a diversity of skill sets and perspectives. I’m excited to create processes to ensure equity and diversity in everything we do, starting with adding more women and more pediatric hospitalists to the journal’s leadership team, as well as purposefully developing a diverse leadership pipeline for the journal and for the field,” he said.
“We are intentionally reaching out to pediatricians to emphasize the extent to which JHM is invested in their field. For example, we have increased by seven the number of pediatricians as part of the JHM leadership team.” But pediatric hospitalists have always seen JHM as a home for their work, and Dr. Shah himself has published a couple dozen research papers in the journal. “It has always felt to me like a welcoming place,” he said.
“The great thing for me is that I’m not doing this alone. We have a marvelous crew of senior deputy editors, deputy editors, associate editors, and advisors. The opportunity I have is to leverage the phenomenal expertise and enthusiasm of this exceptional team.”
The journal under Dr. Auerbach’s lead created an editorial fellowship program offering opportunities for 1-year mentored exposure to the publication of academic scholarship and to different aspects of how a medical journal works. “We’re excited to continue investing in this program and included an editorial about it and an application form in the January 2019 issue of the Journal,” Dr. Shah said. He encourages editorial fellowship applications from physicians who historically have been underrepresented in academic medicine leadership.
“We’re also creating a column on leadership and professional development so that leaders in different fields can share their perspective and wisdom with our readers. We’ll be presenting a new, shorter review format; distilling clinical practice guidelines; and working on redesigning the journal’s web presence. We believe that our readers interact with the journal differently than they did five years ago, and increasingly are leveraging social media,” he said.
“I’m eager to broaden the scope of the journal. In the past, we focused on quality, value in health care and transitions of care in and out of the hospital, which are important topics. But I’m also excited about the adoption of new technologies, how to evaluate them and incorporate them into medical practice – things like Apple Watch for measuring heart rhythm,” Dr. Shah.
He wants to explore other technology-related topics like alarm fatigue and the use of monitors. Another big subject is the management of health of populations under new, emerging, risk-based payment models, with their pressures on health systems to take greater responsibility for risk. JHM is a medical journal and an official society journal, Dr. Shah said. “But our readership and submitters are not limited to hospitalists. As editor in chief, I’m here to make sure the journal is relevant to our members and to our other constituencies.”
Dr. Shah joined JHM’s editorial leadership team in 2009, then he became its deputy editor in 2012 and its senior deputy editor in 2015. A founding associate editor of the Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, he has also served on the editorial board of JAMA Pediatrics. He is editor or coeditor of 12 books in the fields of pediatrics and infectious diseases, including coauthoring “The Philadelphia Guide: Inpatient Pediatrics for McGraw-Hill Education” while still a fellow in academic general pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and, more recently, “Pediatric Infectious Diseases: Essentials for Practice,” a textbook for the pediatric generalist.
Broad scope of activities
Dr. Shah started practicing pediatric hospital medicine in 2001 during his fellowship training. He joined the faculty at CHOP and the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia, in 2005. In 2011 he arrived at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, a facility with more than 600 beds that’s affiliated with the University of Cincinnati, where he is professor in the department of pediatrics and holds the James M. Ewell Endowed Chair, to lead a newly created division of hospital medicine. That division now includes more than 55 physician faculty members, 10 nurse practitioners, and nine 3-year fellows.
Collectively the staff represent a broad scope of clinical and research activities along with consulting and surgical comanagement roles and a unique service staffed by med/peds hospitalists for adult patients who have been followed at the hospital since they were children. “Years ago, those patients would not have survived beyond childhood, but with medical advances, they have. Although they continue to benefit from pediatric expertise, these adults also require internal medicine expertise for their adult health needs,” he explained. Examples include patients with neurologic impairments, dependence on medical technology, or congenital heart defects.
Dr. Shah’s own schedule is 28% clinical. He also serves as the hospital’s chief metrics officer, and his research interests include serious infectious diseases, such as pneumonia and meningitis. He is studying the comparative effectiveness of different antibiotic treatments for community-acquired pneumonia and how to improve outcomes for hospital-acquired pneumonia.
Dr. Shah has tried to be deliberate in leading efforts to grow researchers within the field, both nationally and locally. He serves as the chair of the National Childhood Pneumonia Guidelines Committee of the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and he also is vice chair of the Pediatric Research in Inpatient Settings (PRIS) Network, which facilitates multicenter cost-effectiveness studies among its 120 hospital members. For example, a series of studies funded by the Patient- Centered Outcomes Research Institute has demonstrated the comparable effectiveness of oral and intravenous antibiotics for osteomyelitis and complicated pneumonia.
Sustainable positions
When he was asked whether he felt pediatric hospitalists face particular challenges in trying to take their place in the burgeoning field of hospital medicine, Dr. Shah said he and his colleagues don’t really think of it in those terms. “Hospital medicine is such a dynamic field. For example, pediatric hospital medicine has charted its own course by pursuing subspecialty certification and fellowship training. Yet support from the field broadly has been quite strong, and SHM has embraced pediatricians, who serve on its board of directors and on numerous committees.”
SHM’s commitment to supporting pediatric hospital medicine practice and research includes its cosponsorship, with the Academic Pediatric Association and the American Academy of Pediatrics, an annual pediatric hospital medicine educational and research conference, which will next be held July 25-28, 2019, in Seattle. “In my recent meetings with society leaders I have seen exceptional enthusiasm for increasing the presence of pediatric hospitalists in the society’s work. Many pediatric hospitalists already attend SHM’s annual meeting and submit their research, but we all recognize that a strong pediatric presence is important for the society.”
Dr. Shah credits Cincinnati Children’s Hospital for supporting a sustainable work schedule for its hospitalists and for a team-oriented culture that emphasizes both professional and personal development and encourages a diversity of skill sets and perspectives, skills development, and additional training. “Individuals are recognized for their achievements within and beyond the confines of the hospital. The mentorship structure we set up here is incredible. Each faculty member has a primary mentor, a peer mentor, and access to a career development committee. Additionally, there is broad participation in clinical operations, educational scholarship, research, and quality improvement.”
Dr. Shah’s professional interests in academics, research, and infectious diseases trace back in part to a thesis project he did on neonatal infections while in medical school at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. “I was working with basic sciences in a hematology lab under the direction of the neonatologist Dr. Patrick Gallagher, whose research focused on pediatric blood cell membrane disorders.” Dr. Gallagher, who directs the Yale Center for Blood Disorders, had a keen interest in infections in infants, Dr. Shah recalled.
“He would share with me interesting cases from his practice. What particularly captured my attention was realizing how the research I could do might have a direct impact on patients and families.” Thus inspired to do an additional year of medical school training at Yale before graduating in 1998, Dr. Shah used that year to focus on research, including a placement at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to investigate infectious disease outbreaks, which offered real-world mysteries to solve.
“When I was a resident, pediatric hospital medicine had not yet been recognized as a specialty. But during my fellowships, most of my work was focused on the inpatient side of medicine,” he said. That made hospital medicine a natural career path.
Dr. Shah describes himself as a devoted soccer fan with season tickets for himself, his wife, and their three children to the Major League Soccer team FC Cincinnati. He’s also a movie buff and a former avid bicyclist who’s now trying to get back into cycling. He encourages readers of The Hospitalist to contact him with input on any aspect of the Journal of Hospital Medicine. Email him at [email protected] and follow him on Twitter: @samirshahmd.
Reference
1. Barrett DJ et al. Pediatric hospital medicine: A proposed new subspecialty. Pediatrics. 2017 March;139(3):e20161823.
Stoking collaboration between adult and pediatric clinicians
Stoking collaboration between adult and pediatric clinicians
Samir S. Shah, MD, MSCE, director of the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, believes that pediatric and adult hospitalists have much to learn from each other. And he aims to promote that mutual education in his new role as editor in chief of the Journal of Hospital Medicine.
Dr. Shah is the first pediatric hospitalist to hold this position for JHM, the official journal of the Society of Hospital Medicine. He says his new position, which became effective Jan. 1, is primed for fostering interaction between pediatric and adult hospitalists. “Pediatric hospital medicine is such a vibrant community of its own. There are many opportunities for partnership and collaboration between adult and pediatric hospitalists,” he said.
The field of pediatric hospital medicine has started down the path toward becoming recognized as a board-certified subspecialty.1 “That will place a greater emphasis on our role in fellowship training, which is important to ensure that pediatric hospitalists have a clearly defined skill set,” Dr. Shah said. “So much of what we learn in medical school is oriented to the medical care of adults. If you go into pediatrics, you’ve already had a fair amount of grounding in the healthy physiology and common diseases of adults. Pediatric hospital medicine fellowships offer an opportunity to refine clinical skill sets, as well as develop new skills in domains such as research and leadership.”
An emphasis on diversity
Although he has praised the innovative work of his predecessors, Mark Williams, MD, MHM, and Andrew Auerbach, MD, MPH, MHM, in shepherding the journal to its current strong position, Dr. Shah brings ideas for new features and directions.
“We as a field really benefit from a diversity of skill sets and perspectives. I’m excited to create processes to ensure equity and diversity in everything we do, starting with adding more women and more pediatric hospitalists to the journal’s leadership team, as well as purposefully developing a diverse leadership pipeline for the journal and for the field,” he said.
“We are intentionally reaching out to pediatricians to emphasize the extent to which JHM is invested in their field. For example, we have increased by seven the number of pediatricians as part of the JHM leadership team.” But pediatric hospitalists have always seen JHM as a home for their work, and Dr. Shah himself has published a couple dozen research papers in the journal. “It has always felt to me like a welcoming place,” he said.
“The great thing for me is that I’m not doing this alone. We have a marvelous crew of senior deputy editors, deputy editors, associate editors, and advisors. The opportunity I have is to leverage the phenomenal expertise and enthusiasm of this exceptional team.”
The journal under Dr. Auerbach’s lead created an editorial fellowship program offering opportunities for 1-year mentored exposure to the publication of academic scholarship and to different aspects of how a medical journal works. “We’re excited to continue investing in this program and included an editorial about it and an application form in the January 2019 issue of the Journal,” Dr. Shah said. He encourages editorial fellowship applications from physicians who historically have been underrepresented in academic medicine leadership.
“We’re also creating a column on leadership and professional development so that leaders in different fields can share their perspective and wisdom with our readers. We’ll be presenting a new, shorter review format; distilling clinical practice guidelines; and working on redesigning the journal’s web presence. We believe that our readers interact with the journal differently than they did five years ago, and increasingly are leveraging social media,” he said.
“I’m eager to broaden the scope of the journal. In the past, we focused on quality, value in health care and transitions of care in and out of the hospital, which are important topics. But I’m also excited about the adoption of new technologies, how to evaluate them and incorporate them into medical practice – things like Apple Watch for measuring heart rhythm,” Dr. Shah.
He wants to explore other technology-related topics like alarm fatigue and the use of monitors. Another big subject is the management of health of populations under new, emerging, risk-based payment models, with their pressures on health systems to take greater responsibility for risk. JHM is a medical journal and an official society journal, Dr. Shah said. “But our readership and submitters are not limited to hospitalists. As editor in chief, I’m here to make sure the journal is relevant to our members and to our other constituencies.”
Dr. Shah joined JHM’s editorial leadership team in 2009, then he became its deputy editor in 2012 and its senior deputy editor in 2015. A founding associate editor of the Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, he has also served on the editorial board of JAMA Pediatrics. He is editor or coeditor of 12 books in the fields of pediatrics and infectious diseases, including coauthoring “The Philadelphia Guide: Inpatient Pediatrics for McGraw-Hill Education” while still a fellow in academic general pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and, more recently, “Pediatric Infectious Diseases: Essentials for Practice,” a textbook for the pediatric generalist.
Broad scope of activities
Dr. Shah started practicing pediatric hospital medicine in 2001 during his fellowship training. He joined the faculty at CHOP and the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia, in 2005. In 2011 he arrived at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, a facility with more than 600 beds that’s affiliated with the University of Cincinnati, where he is professor in the department of pediatrics and holds the James M. Ewell Endowed Chair, to lead a newly created division of hospital medicine. That division now includes more than 55 physician faculty members, 10 nurse practitioners, and nine 3-year fellows.
Collectively the staff represent a broad scope of clinical and research activities along with consulting and surgical comanagement roles and a unique service staffed by med/peds hospitalists for adult patients who have been followed at the hospital since they were children. “Years ago, those patients would not have survived beyond childhood, but with medical advances, they have. Although they continue to benefit from pediatric expertise, these adults also require internal medicine expertise for their adult health needs,” he explained. Examples include patients with neurologic impairments, dependence on medical technology, or congenital heart defects.
Dr. Shah’s own schedule is 28% clinical. He also serves as the hospital’s chief metrics officer, and his research interests include serious infectious diseases, such as pneumonia and meningitis. He is studying the comparative effectiveness of different antibiotic treatments for community-acquired pneumonia and how to improve outcomes for hospital-acquired pneumonia.
Dr. Shah has tried to be deliberate in leading efforts to grow researchers within the field, both nationally and locally. He serves as the chair of the National Childhood Pneumonia Guidelines Committee of the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and he also is vice chair of the Pediatric Research in Inpatient Settings (PRIS) Network, which facilitates multicenter cost-effectiveness studies among its 120 hospital members. For example, a series of studies funded by the Patient- Centered Outcomes Research Institute has demonstrated the comparable effectiveness of oral and intravenous antibiotics for osteomyelitis and complicated pneumonia.
Sustainable positions
When he was asked whether he felt pediatric hospitalists face particular challenges in trying to take their place in the burgeoning field of hospital medicine, Dr. Shah said he and his colleagues don’t really think of it in those terms. “Hospital medicine is such a dynamic field. For example, pediatric hospital medicine has charted its own course by pursuing subspecialty certification and fellowship training. Yet support from the field broadly has been quite strong, and SHM has embraced pediatricians, who serve on its board of directors and on numerous committees.”
SHM’s commitment to supporting pediatric hospital medicine practice and research includes its cosponsorship, with the Academic Pediatric Association and the American Academy of Pediatrics, an annual pediatric hospital medicine educational and research conference, which will next be held July 25-28, 2019, in Seattle. “In my recent meetings with society leaders I have seen exceptional enthusiasm for increasing the presence of pediatric hospitalists in the society’s work. Many pediatric hospitalists already attend SHM’s annual meeting and submit their research, but we all recognize that a strong pediatric presence is important for the society.”
Dr. Shah credits Cincinnati Children’s Hospital for supporting a sustainable work schedule for its hospitalists and for a team-oriented culture that emphasizes both professional and personal development and encourages a diversity of skill sets and perspectives, skills development, and additional training. “Individuals are recognized for their achievements within and beyond the confines of the hospital. The mentorship structure we set up here is incredible. Each faculty member has a primary mentor, a peer mentor, and access to a career development committee. Additionally, there is broad participation in clinical operations, educational scholarship, research, and quality improvement.”
Dr. Shah’s professional interests in academics, research, and infectious diseases trace back in part to a thesis project he did on neonatal infections while in medical school at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. “I was working with basic sciences in a hematology lab under the direction of the neonatologist Dr. Patrick Gallagher, whose research focused on pediatric blood cell membrane disorders.” Dr. Gallagher, who directs the Yale Center for Blood Disorders, had a keen interest in infections in infants, Dr. Shah recalled.
“He would share with me interesting cases from his practice. What particularly captured my attention was realizing how the research I could do might have a direct impact on patients and families.” Thus inspired to do an additional year of medical school training at Yale before graduating in 1998, Dr. Shah used that year to focus on research, including a placement at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to investigate infectious disease outbreaks, which offered real-world mysteries to solve.
“When I was a resident, pediatric hospital medicine had not yet been recognized as a specialty. But during my fellowships, most of my work was focused on the inpatient side of medicine,” he said. That made hospital medicine a natural career path.
Dr. Shah describes himself as a devoted soccer fan with season tickets for himself, his wife, and their three children to the Major League Soccer team FC Cincinnati. He’s also a movie buff and a former avid bicyclist who’s now trying to get back into cycling. He encourages readers of The Hospitalist to contact him with input on any aspect of the Journal of Hospital Medicine. Email him at [email protected] and follow him on Twitter: @samirshahmd.
Reference
1. Barrett DJ et al. Pediatric hospital medicine: A proposed new subspecialty. Pediatrics. 2017 March;139(3):e20161823.
Samir S. Shah, MD, MSCE, director of the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, believes that pediatric and adult hospitalists have much to learn from each other. And he aims to promote that mutual education in his new role as editor in chief of the Journal of Hospital Medicine.
Dr. Shah is the first pediatric hospitalist to hold this position for JHM, the official journal of the Society of Hospital Medicine. He says his new position, which became effective Jan. 1, is primed for fostering interaction between pediatric and adult hospitalists. “Pediatric hospital medicine is such a vibrant community of its own. There are many opportunities for partnership and collaboration between adult and pediatric hospitalists,” he said.
The field of pediatric hospital medicine has started down the path toward becoming recognized as a board-certified subspecialty.1 “That will place a greater emphasis on our role in fellowship training, which is important to ensure that pediatric hospitalists have a clearly defined skill set,” Dr. Shah said. “So much of what we learn in medical school is oriented to the medical care of adults. If you go into pediatrics, you’ve already had a fair amount of grounding in the healthy physiology and common diseases of adults. Pediatric hospital medicine fellowships offer an opportunity to refine clinical skill sets, as well as develop new skills in domains such as research and leadership.”
An emphasis on diversity
Although he has praised the innovative work of his predecessors, Mark Williams, MD, MHM, and Andrew Auerbach, MD, MPH, MHM, in shepherding the journal to its current strong position, Dr. Shah brings ideas for new features and directions.
“We as a field really benefit from a diversity of skill sets and perspectives. I’m excited to create processes to ensure equity and diversity in everything we do, starting with adding more women and more pediatric hospitalists to the journal’s leadership team, as well as purposefully developing a diverse leadership pipeline for the journal and for the field,” he said.
“We are intentionally reaching out to pediatricians to emphasize the extent to which JHM is invested in their field. For example, we have increased by seven the number of pediatricians as part of the JHM leadership team.” But pediatric hospitalists have always seen JHM as a home for their work, and Dr. Shah himself has published a couple dozen research papers in the journal. “It has always felt to me like a welcoming place,” he said.
“The great thing for me is that I’m not doing this alone. We have a marvelous crew of senior deputy editors, deputy editors, associate editors, and advisors. The opportunity I have is to leverage the phenomenal expertise and enthusiasm of this exceptional team.”
The journal under Dr. Auerbach’s lead created an editorial fellowship program offering opportunities for 1-year mentored exposure to the publication of academic scholarship and to different aspects of how a medical journal works. “We’re excited to continue investing in this program and included an editorial about it and an application form in the January 2019 issue of the Journal,” Dr. Shah said. He encourages editorial fellowship applications from physicians who historically have been underrepresented in academic medicine leadership.
“We’re also creating a column on leadership and professional development so that leaders in different fields can share their perspective and wisdom with our readers. We’ll be presenting a new, shorter review format; distilling clinical practice guidelines; and working on redesigning the journal’s web presence. We believe that our readers interact with the journal differently than they did five years ago, and increasingly are leveraging social media,” he said.
“I’m eager to broaden the scope of the journal. In the past, we focused on quality, value in health care and transitions of care in and out of the hospital, which are important topics. But I’m also excited about the adoption of new technologies, how to evaluate them and incorporate them into medical practice – things like Apple Watch for measuring heart rhythm,” Dr. Shah.
He wants to explore other technology-related topics like alarm fatigue and the use of monitors. Another big subject is the management of health of populations under new, emerging, risk-based payment models, with their pressures on health systems to take greater responsibility for risk. JHM is a medical journal and an official society journal, Dr. Shah said. “But our readership and submitters are not limited to hospitalists. As editor in chief, I’m here to make sure the journal is relevant to our members and to our other constituencies.”
Dr. Shah joined JHM’s editorial leadership team in 2009, then he became its deputy editor in 2012 and its senior deputy editor in 2015. A founding associate editor of the Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, he has also served on the editorial board of JAMA Pediatrics. He is editor or coeditor of 12 books in the fields of pediatrics and infectious diseases, including coauthoring “The Philadelphia Guide: Inpatient Pediatrics for McGraw-Hill Education” while still a fellow in academic general pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and, more recently, “Pediatric Infectious Diseases: Essentials for Practice,” a textbook for the pediatric generalist.
Broad scope of activities
Dr. Shah started practicing pediatric hospital medicine in 2001 during his fellowship training. He joined the faculty at CHOP and the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia, in 2005. In 2011 he arrived at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, a facility with more than 600 beds that’s affiliated with the University of Cincinnati, where he is professor in the department of pediatrics and holds the James M. Ewell Endowed Chair, to lead a newly created division of hospital medicine. That division now includes more than 55 physician faculty members, 10 nurse practitioners, and nine 3-year fellows.
Collectively the staff represent a broad scope of clinical and research activities along with consulting and surgical comanagement roles and a unique service staffed by med/peds hospitalists for adult patients who have been followed at the hospital since they were children. “Years ago, those patients would not have survived beyond childhood, but with medical advances, they have. Although they continue to benefit from pediatric expertise, these adults also require internal medicine expertise for their adult health needs,” he explained. Examples include patients with neurologic impairments, dependence on medical technology, or congenital heart defects.
Dr. Shah’s own schedule is 28% clinical. He also serves as the hospital’s chief metrics officer, and his research interests include serious infectious diseases, such as pneumonia and meningitis. He is studying the comparative effectiveness of different antibiotic treatments for community-acquired pneumonia and how to improve outcomes for hospital-acquired pneumonia.
Dr. Shah has tried to be deliberate in leading efforts to grow researchers within the field, both nationally and locally. He serves as the chair of the National Childhood Pneumonia Guidelines Committee of the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and he also is vice chair of the Pediatric Research in Inpatient Settings (PRIS) Network, which facilitates multicenter cost-effectiveness studies among its 120 hospital members. For example, a series of studies funded by the Patient- Centered Outcomes Research Institute has demonstrated the comparable effectiveness of oral and intravenous antibiotics for osteomyelitis and complicated pneumonia.
Sustainable positions
When he was asked whether he felt pediatric hospitalists face particular challenges in trying to take their place in the burgeoning field of hospital medicine, Dr. Shah said he and his colleagues don’t really think of it in those terms. “Hospital medicine is such a dynamic field. For example, pediatric hospital medicine has charted its own course by pursuing subspecialty certification and fellowship training. Yet support from the field broadly has been quite strong, and SHM has embraced pediatricians, who serve on its board of directors and on numerous committees.”
SHM’s commitment to supporting pediatric hospital medicine practice and research includes its cosponsorship, with the Academic Pediatric Association and the American Academy of Pediatrics, an annual pediatric hospital medicine educational and research conference, which will next be held July 25-28, 2019, in Seattle. “In my recent meetings with society leaders I have seen exceptional enthusiasm for increasing the presence of pediatric hospitalists in the society’s work. Many pediatric hospitalists already attend SHM’s annual meeting and submit their research, but we all recognize that a strong pediatric presence is important for the society.”
Dr. Shah credits Cincinnati Children’s Hospital for supporting a sustainable work schedule for its hospitalists and for a team-oriented culture that emphasizes both professional and personal development and encourages a diversity of skill sets and perspectives, skills development, and additional training. “Individuals are recognized for their achievements within and beyond the confines of the hospital. The mentorship structure we set up here is incredible. Each faculty member has a primary mentor, a peer mentor, and access to a career development committee. Additionally, there is broad participation in clinical operations, educational scholarship, research, and quality improvement.”
Dr. Shah’s professional interests in academics, research, and infectious diseases trace back in part to a thesis project he did on neonatal infections while in medical school at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. “I was working with basic sciences in a hematology lab under the direction of the neonatologist Dr. Patrick Gallagher, whose research focused on pediatric blood cell membrane disorders.” Dr. Gallagher, who directs the Yale Center for Blood Disorders, had a keen interest in infections in infants, Dr. Shah recalled.
“He would share with me interesting cases from his practice. What particularly captured my attention was realizing how the research I could do might have a direct impact on patients and families.” Thus inspired to do an additional year of medical school training at Yale before graduating in 1998, Dr. Shah used that year to focus on research, including a placement at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to investigate infectious disease outbreaks, which offered real-world mysteries to solve.
“When I was a resident, pediatric hospital medicine had not yet been recognized as a specialty. But during my fellowships, most of my work was focused on the inpatient side of medicine,” he said. That made hospital medicine a natural career path.
Dr. Shah describes himself as a devoted soccer fan with season tickets for himself, his wife, and their three children to the Major League Soccer team FC Cincinnati. He’s also a movie buff and a former avid bicyclist who’s now trying to get back into cycling. He encourages readers of The Hospitalist to contact him with input on any aspect of the Journal of Hospital Medicine. Email him at [email protected] and follow him on Twitter: @samirshahmd.
Reference
1. Barrett DJ et al. Pediatric hospital medicine: A proposed new subspecialty. Pediatrics. 2017 March;139(3):e20161823.
Looking into the future and making history
Emergence of population health management
For the first time ever, on March 7, 2019, tens of thousands of hospitalists across the United States and around the world will celebrate their day, National Hospitalist Day.
On this day, we will honor the hard work and dedication of hospitalists in the care of millions of hospitalized patients. With more than 62,000 hospitalists across the United States, hospital medicine has been the fastest growing medical specialty and among the largest of all specialties in medicine. Hospitalists now lead clinical care in over 75% of U.S. hospitals, caring for patients in their communities. We educate the future providers of health care by serving as teachers and mentors. We push the boundaries of science in hospital care through innovative research that defines the evidence-based practices for our field. Hospitalists, proudly celebrate all that we have accomplished together on March 7, and moving forward, every first Thursday in March annually.
The Society for Hospital Medicine’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day will include spotlights on hospitalists, a social medical campaign, downloadable customizable posters, and much more. Stay tuned for details!
Attend the only meeting designed just for you
Be among the thousands of hospitalists who will celebrate hospital medicine in person at Hospital Medicine 2019 (HM19), March 24-27 in National Harbor, Md.
While at HM19, check out more than 20 educational tracks, including clinical updates, diagnostic reasoning, and health policy. New this year are two mini tracks: “Between the Guidelines” and “Clinical Mastery”. Between the Guidelines explores how we can address some of the most challenging cases we encounter in hospital medicine, where clear guidelines don’t exist. Clinical Mastery is designed to enhance our bedside diagnostic skills, from ECGs to ultrasounds.
Get ready to vote in HM19’s “The Great Debate” – pairing two talented clinicians who will debate opposing sides of challenging clinical decisions that we encounter on the front lines of health care delivery. Attendees have the opportunity to hear the two sides and then vote on who they believe has the right approach. There are six precourses planned for HM19, with a new offering in Palliative Care and Pain Management. This year, the annual conference also features additional sessions for our NP/PA attendees. They include specific workshops as well as a track that includes 4 didactic sessions. Lastly, HM19 will offer CME, MOC, AOS, AAFP, and Pharmacology credits to address the needs of our attendees.
Looking into the future
While hospitalists are a vital part of U.S. health care, our delivery systems are in transition with greater focus on value-based care. To ensure hospital medicine continues to thrive in today’s dynamic scene, SHM’s Board of Directors held a strategic meeting in October 2018 to focus on the role of hospitalists and hospital medicine in population health management.
There are many hospitalists across the nation who are currently involved in population health management. These range from medical directors to vice presidents of accountable care organizations, population health management, or value-based care. Hospitalists are seeking communities focused on population health management to share best practices and learn from each other. To address this, SHM’s Advocacy and Public Policy HMX community has served as a meeting point to discuss issues related to value-based care. To join the discussion, visit the community by logging in at hospitalmedicine.org/hmx. Furthermore, at HM19, hospitalists will have the opportunity to meet face to face regarding these issues in the Advocacy Special Interest Forum.
Key points: Population health management
- Source of truth
SHM has served as the source of reliable and trusted information about hospital medicine. We will continue to develop content and resources specific to population health management on our website so hospitalists can easily access this information. To increase our awareness about population health management, presenters at HM19 will integrate a slide about the implications of population health management on their clinical topic. These slides will illustrate the clinical and nonclinical services that are necessary to enhance the patient’s quality of care and life. In addition to best practice care, these slides will highlight topics like the role of style modification and prevention, risk stratification, chronic disease management, and care coordination throughout the continuum of care.
- Advocating for us
In addition to providing a home for hospitalists to collaborate regarding population health management, SHM will advance this agenda from a regulatory perspective. The Public Policy and Performance Measurement & Reporting Committees are actively evaluating and leading the transition from value to volume. SHM is also working with potential key partners and organizations in the areas of primary care, skilled nursing facilities, and accountable care organizations that will help improve the effectiveness of delivering population health management.
- Creating expertise
SHM will lead best practice development for tools and skills that are necessary for hospitalists to lead population health management. Telemedicine is an increasingly critical tool as we help manage our patients in other facilities, inpatient or skilled nursing facilities, as well as at home. SHM has developed a white paper about telemedicine in hospital medicine that highlights modalities, offerings, implementation of programs, and work flows necessary for success. You can find it under “Resources” at hospitalmedicine.org/telemedicine.
SHM will continue to actively develop tools that appropriately address the challenges we’re facing. From National Hospitalist Day to population health management, this is an exciting time in hospital medicine – I hope to see you at HM19 to celebrate our specialty and our bright future.
Dr. Afsar is president of the Society of Hospital Medicine, and chief ambulatory officer and chief medical officer for accountable care organizations at UC Irvine Health.
Emergence of population health management
Emergence of population health management
For the first time ever, on March 7, 2019, tens of thousands of hospitalists across the United States and around the world will celebrate their day, National Hospitalist Day.
On this day, we will honor the hard work and dedication of hospitalists in the care of millions of hospitalized patients. With more than 62,000 hospitalists across the United States, hospital medicine has been the fastest growing medical specialty and among the largest of all specialties in medicine. Hospitalists now lead clinical care in over 75% of U.S. hospitals, caring for patients in their communities. We educate the future providers of health care by serving as teachers and mentors. We push the boundaries of science in hospital care through innovative research that defines the evidence-based practices for our field. Hospitalists, proudly celebrate all that we have accomplished together on March 7, and moving forward, every first Thursday in March annually.
The Society for Hospital Medicine’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day will include spotlights on hospitalists, a social medical campaign, downloadable customizable posters, and much more. Stay tuned for details!
Attend the only meeting designed just for you
Be among the thousands of hospitalists who will celebrate hospital medicine in person at Hospital Medicine 2019 (HM19), March 24-27 in National Harbor, Md.
While at HM19, check out more than 20 educational tracks, including clinical updates, diagnostic reasoning, and health policy. New this year are two mini tracks: “Between the Guidelines” and “Clinical Mastery”. Between the Guidelines explores how we can address some of the most challenging cases we encounter in hospital medicine, where clear guidelines don’t exist. Clinical Mastery is designed to enhance our bedside diagnostic skills, from ECGs to ultrasounds.
Get ready to vote in HM19’s “The Great Debate” – pairing two talented clinicians who will debate opposing sides of challenging clinical decisions that we encounter on the front lines of health care delivery. Attendees have the opportunity to hear the two sides and then vote on who they believe has the right approach. There are six precourses planned for HM19, with a new offering in Palliative Care and Pain Management. This year, the annual conference also features additional sessions for our NP/PA attendees. They include specific workshops as well as a track that includes 4 didactic sessions. Lastly, HM19 will offer CME, MOC, AOS, AAFP, and Pharmacology credits to address the needs of our attendees.
Looking into the future
While hospitalists are a vital part of U.S. health care, our delivery systems are in transition with greater focus on value-based care. To ensure hospital medicine continues to thrive in today’s dynamic scene, SHM’s Board of Directors held a strategic meeting in October 2018 to focus on the role of hospitalists and hospital medicine in population health management.
There are many hospitalists across the nation who are currently involved in population health management. These range from medical directors to vice presidents of accountable care organizations, population health management, or value-based care. Hospitalists are seeking communities focused on population health management to share best practices and learn from each other. To address this, SHM’s Advocacy and Public Policy HMX community has served as a meeting point to discuss issues related to value-based care. To join the discussion, visit the community by logging in at hospitalmedicine.org/hmx. Furthermore, at HM19, hospitalists will have the opportunity to meet face to face regarding these issues in the Advocacy Special Interest Forum.
Key points: Population health management
- Source of truth
SHM has served as the source of reliable and trusted information about hospital medicine. We will continue to develop content and resources specific to population health management on our website so hospitalists can easily access this information. To increase our awareness about population health management, presenters at HM19 will integrate a slide about the implications of population health management on their clinical topic. These slides will illustrate the clinical and nonclinical services that are necessary to enhance the patient’s quality of care and life. In addition to best practice care, these slides will highlight topics like the role of style modification and prevention, risk stratification, chronic disease management, and care coordination throughout the continuum of care.
- Advocating for us
In addition to providing a home for hospitalists to collaborate regarding population health management, SHM will advance this agenda from a regulatory perspective. The Public Policy and Performance Measurement & Reporting Committees are actively evaluating and leading the transition from value to volume. SHM is also working with potential key partners and organizations in the areas of primary care, skilled nursing facilities, and accountable care organizations that will help improve the effectiveness of delivering population health management.
- Creating expertise
SHM will lead best practice development for tools and skills that are necessary for hospitalists to lead population health management. Telemedicine is an increasingly critical tool as we help manage our patients in other facilities, inpatient or skilled nursing facilities, as well as at home. SHM has developed a white paper about telemedicine in hospital medicine that highlights modalities, offerings, implementation of programs, and work flows necessary for success. You can find it under “Resources” at hospitalmedicine.org/telemedicine.
SHM will continue to actively develop tools that appropriately address the challenges we’re facing. From National Hospitalist Day to population health management, this is an exciting time in hospital medicine – I hope to see you at HM19 to celebrate our specialty and our bright future.
Dr. Afsar is president of the Society of Hospital Medicine, and chief ambulatory officer and chief medical officer for accountable care organizations at UC Irvine Health.
For the first time ever, on March 7, 2019, tens of thousands of hospitalists across the United States and around the world will celebrate their day, National Hospitalist Day.
On this day, we will honor the hard work and dedication of hospitalists in the care of millions of hospitalized patients. With more than 62,000 hospitalists across the United States, hospital medicine has been the fastest growing medical specialty and among the largest of all specialties in medicine. Hospitalists now lead clinical care in over 75% of U.S. hospitals, caring for patients in their communities. We educate the future providers of health care by serving as teachers and mentors. We push the boundaries of science in hospital care through innovative research that defines the evidence-based practices for our field. Hospitalists, proudly celebrate all that we have accomplished together on March 7, and moving forward, every first Thursday in March annually.
The Society for Hospital Medicine’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day will include spotlights on hospitalists, a social medical campaign, downloadable customizable posters, and much more. Stay tuned for details!
Attend the only meeting designed just for you
Be among the thousands of hospitalists who will celebrate hospital medicine in person at Hospital Medicine 2019 (HM19), March 24-27 in National Harbor, Md.
While at HM19, check out more than 20 educational tracks, including clinical updates, diagnostic reasoning, and health policy. New this year are two mini tracks: “Between the Guidelines” and “Clinical Mastery”. Between the Guidelines explores how we can address some of the most challenging cases we encounter in hospital medicine, where clear guidelines don’t exist. Clinical Mastery is designed to enhance our bedside diagnostic skills, from ECGs to ultrasounds.
Get ready to vote in HM19’s “The Great Debate” – pairing two talented clinicians who will debate opposing sides of challenging clinical decisions that we encounter on the front lines of health care delivery. Attendees have the opportunity to hear the two sides and then vote on who they believe has the right approach. There are six precourses planned for HM19, with a new offering in Palliative Care and Pain Management. This year, the annual conference also features additional sessions for our NP/PA attendees. They include specific workshops as well as a track that includes 4 didactic sessions. Lastly, HM19 will offer CME, MOC, AOS, AAFP, and Pharmacology credits to address the needs of our attendees.
Looking into the future
While hospitalists are a vital part of U.S. health care, our delivery systems are in transition with greater focus on value-based care. To ensure hospital medicine continues to thrive in today’s dynamic scene, SHM’s Board of Directors held a strategic meeting in October 2018 to focus on the role of hospitalists and hospital medicine in population health management.
There are many hospitalists across the nation who are currently involved in population health management. These range from medical directors to vice presidents of accountable care organizations, population health management, or value-based care. Hospitalists are seeking communities focused on population health management to share best practices and learn from each other. To address this, SHM’s Advocacy and Public Policy HMX community has served as a meeting point to discuss issues related to value-based care. To join the discussion, visit the community by logging in at hospitalmedicine.org/hmx. Furthermore, at HM19, hospitalists will have the opportunity to meet face to face regarding these issues in the Advocacy Special Interest Forum.
Key points: Population health management
- Source of truth
SHM has served as the source of reliable and trusted information about hospital medicine. We will continue to develop content and resources specific to population health management on our website so hospitalists can easily access this information. To increase our awareness about population health management, presenters at HM19 will integrate a slide about the implications of population health management on their clinical topic. These slides will illustrate the clinical and nonclinical services that are necessary to enhance the patient’s quality of care and life. In addition to best practice care, these slides will highlight topics like the role of style modification and prevention, risk stratification, chronic disease management, and care coordination throughout the continuum of care.
- Advocating for us
In addition to providing a home for hospitalists to collaborate regarding population health management, SHM will advance this agenda from a regulatory perspective. The Public Policy and Performance Measurement & Reporting Committees are actively evaluating and leading the transition from value to volume. SHM is also working with potential key partners and organizations in the areas of primary care, skilled nursing facilities, and accountable care organizations that will help improve the effectiveness of delivering population health management.
- Creating expertise
SHM will lead best practice development for tools and skills that are necessary for hospitalists to lead population health management. Telemedicine is an increasingly critical tool as we help manage our patients in other facilities, inpatient or skilled nursing facilities, as well as at home. SHM has developed a white paper about telemedicine in hospital medicine that highlights modalities, offerings, implementation of programs, and work flows necessary for success. You can find it under “Resources” at hospitalmedicine.org/telemedicine.
SHM will continue to actively develop tools that appropriately address the challenges we’re facing. From National Hospitalist Day to population health management, this is an exciting time in hospital medicine – I hope to see you at HM19 to celebrate our specialty and our bright future.
Dr. Afsar is president of the Society of Hospital Medicine, and chief ambulatory officer and chief medical officer for accountable care organizations at UC Irvine Health.





















