User login
Landscaper Can't Outrun Tree
ANSWER
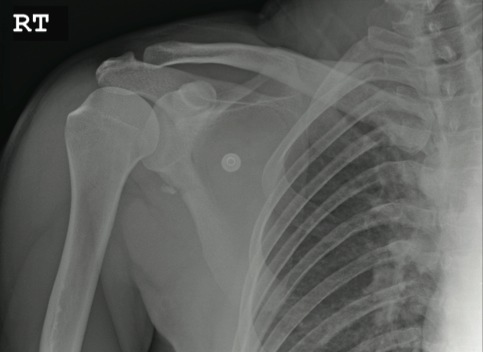
The radiograph shows an osseous fragment along the inferior aspect of the glenohumeral joint. Close examination reveals a defect within the scapula itself, most likely consistent with an acute fracture.
ANSWER
The radiograph shows an osseous fragment along the inferior aspect of the glenohumeral joint. Close examination reveals a defect within the scapula itself, most likely consistent with an acute fracture.
ANSWER
The radiograph shows an osseous fragment along the inferior aspect of the glenohumeral joint. Close examination reveals a defect within the scapula itself, most likely consistent with an acute fracture.
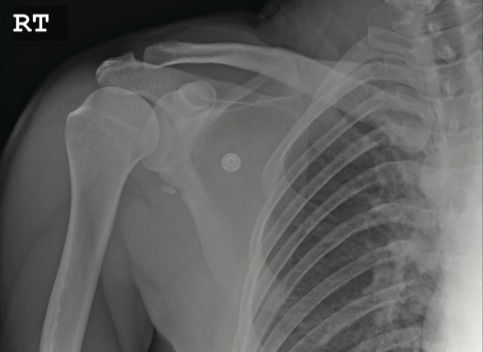
A 24-year-old man who works as a landscaper/tree-cutter presents for evaluation of right shoulder pain after a tree fell on him. He states that he attempted to run away as the tree fell, but it struck him nonetheless. He did not lose consciousness. The tree struck the right side of his body. The patient’s medical history is unremarkable. He is complaining of right-side back and shoulder pain. Initial vital signs and primary survey appear to be normal. Secondary survey shows decreased range of motion in the right shoulder, with point tenderness in the scapula. There are no obvious deformities. Distal pulses are strong, and the patient is otherwise neurovascularly intact. Radiograph of the right shoulder is shown. What is your impression?
Landscaper Can't Outrun Tree
ANSWER
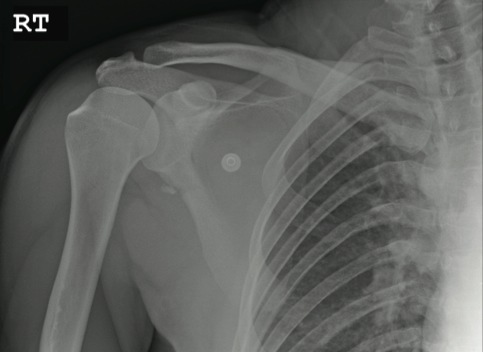
The radiograph shows an osseous fragment along the inferior aspect of the glenohumeral joint. Close examination reveals a defect within the scapula itself, most likely consistent with an acute fracture.
ANSWER
The radiograph shows an osseous fragment along the inferior aspect of the glenohumeral joint. Close examination reveals a defect within the scapula itself, most likely consistent with an acute fracture.
ANSWER
The radiograph shows an osseous fragment along the inferior aspect of the glenohumeral joint. Close examination reveals a defect within the scapula itself, most likely consistent with an acute fracture.

A 24-year-old man who works as a landscaper/tree-cutter presents for evaluation of right shoulder pain after a tree fell on him. He states that he attempted to run away as the tree fell, but it struck him nonetheless. He did not lose consciousness. The tree struck the right side of his body. The patient’s medical history is unremarkable. He is complaining of right-side back and shoulder pain. Initial vital signs and primary survey appear to be normal. Secondary survey shows decreased range of motion in the right shoulder, with point tenderness in the scapula. There are no obvious deformities. Distal pulses are strong, and the patient is otherwise neurovascularly intact. Radiograph of the right shoulder is shown. What is your impression?
Infant "Fell Out of Car Seat"
ANSWER
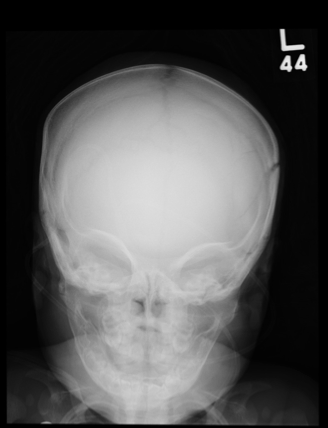
The plain film demonstrates bilateral parietal skull fractures, more evident on the left than right side. Subsequent noncontrast CT of the skull confirmed these fractures, and also showed bilateral subdural hematomas.
Such findings, both clinically and radiographically, are highly worrisome and suggestive of nonaccidental injury (ie, abuse). This unfortunate infant was placed immediately under the care of the Department of Family and Children Services and moved to the pediatric ICU for close monitoring.
ANSWER
The plain film demonstrates bilateral parietal skull fractures, more evident on the left than right side. Subsequent noncontrast CT of the skull confirmed these fractures, and also showed bilateral subdural hematomas.
Such findings, both clinically and radiographically, are highly worrisome and suggestive of nonaccidental injury (ie, abuse). This unfortunate infant was placed immediately under the care of the Department of Family and Children Services and moved to the pediatric ICU for close monitoring.
ANSWER
The plain film demonstrates bilateral parietal skull fractures, more evident on the left than right side. Subsequent noncontrast CT of the skull confirmed these fractures, and also showed bilateral subdural hematomas.
Such findings, both clinically and radiographically, are highly worrisome and suggestive of nonaccidental injury (ie, abuse). This unfortunate infant was placed immediately under the care of the Department of Family and Children Services and moved to the pediatric ICU for close monitoring.
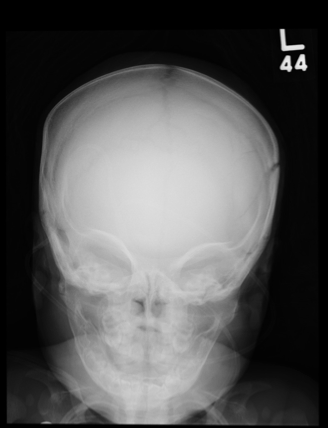
A 5-month-old girl is brought to your facility for decreased level of consciousness. According to the parents, the infant reportedly fell out of her car seat earlier this morning. Prenatal history is unremarkable; immunizations are up to date. Initial examination shows a lethargic female infant with vital signs as follows: temperature, 99.7°F; blood pressure, 91/65 mm Hg; heart rate; 180 beats/min; and initial O2 saturation, 86% on room air. Supplemental oxygen and an IV fluid bolus are given, which correct the hypoxia and tachycardia. Physical exam shows a depressed anterior fontanelle and bilateral periorbital ecchymosis, as well as multiple bruises of varying ages on the face and body. An old scar on the left side of the forehead is noted as well. While still somewhat lethargic, the infant does move all extremities to painful stimuli. A weak cry is present. Initial radiographs of the chest and skull are obtained; the one of the skull is shown. What is your impression?
Postoperative Patient Experiencing Respiratory Distress
ANSWER
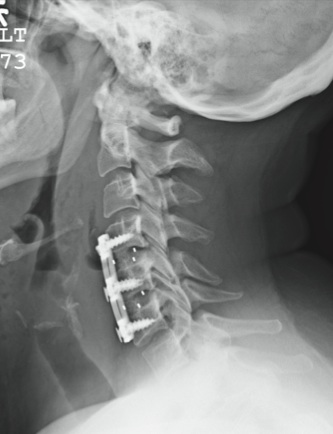
The patient is status post two-level anterior cervical diskectomy and fusion, with interbody grafts and hardware appearing intact. The radiograph demonstrates significant prevertebral soft-tissue swelling greater than 2 cm over several levels. This results in significant posterior compression of the oropharynx. Such findings are typically seen in patients who develop retropharyngeal hematomas.
This patient was urgently returned to the operating room, where she underwent successful evacuation of a hematoma that was under a moderate amount of pressure. No specific source was identified, which is not uncommon.
The patient made a full recovery.
ANSWER
The patient is status post two-level anterior cervical diskectomy and fusion, with interbody grafts and hardware appearing intact. The radiograph demonstrates significant prevertebral soft-tissue swelling greater than 2 cm over several levels. This results in significant posterior compression of the oropharynx. Such findings are typically seen in patients who develop retropharyngeal hematomas.
This patient was urgently returned to the operating room, where she underwent successful evacuation of a hematoma that was under a moderate amount of pressure. No specific source was identified, which is not uncommon.
The patient made a full recovery.
ANSWER
The patient is status post two-level anterior cervical diskectomy and fusion, with interbody grafts and hardware appearing intact. The radiograph demonstrates significant prevertebral soft-tissue swelling greater than 2 cm over several levels. This results in significant posterior compression of the oropharynx. Such findings are typically seen in patients who develop retropharyngeal hematomas.
This patient was urgently returned to the operating room, where she underwent successful evacuation of a hematoma that was under a moderate amount of pressure. No specific source was identified, which is not uncommon.
The patient made a full recovery.
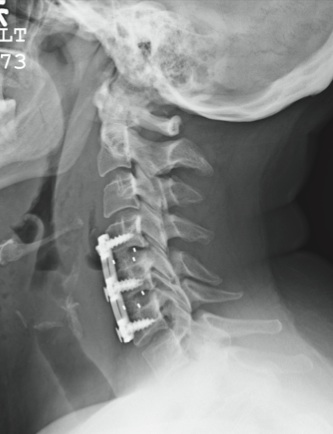
You receive a call from the nursing staff stating that a postoperative patient is experiencing respiratory distress. The patient is a 41-year-old woman who underwent a two-level anterior cervical diskectomy and fusion yesterday. There were no problems during the surgery. Earlier this morning, when the patient was examined during rounds, she was experiencing mild dysphagia, and steroids were ordered. Now, the patient says she cannot breathe well unless she is sitting upright. Her vital signs are stable, with an O2 saturation of 93%. Her incision is swollen and appears full. Stat radiograph of the cervical spine is obtained (shown). What is your impression?
Woman Thrown From Horse
ANSWER
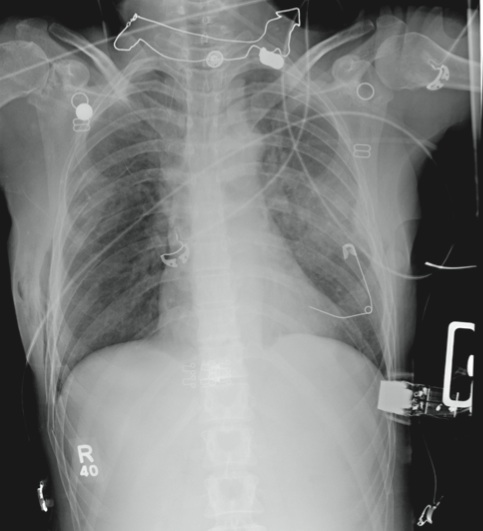
The radiograph demonstrates several findings. First, there are multiple bilateral rib fractures. Five to six ribs are broken and displaced on both sides. In addition, there are bilateral small apical pneumothoraces. Finally, there is evidence of bilateral pulmonary contusions beginning to form, more so on the left than the right side.
This patient was admitted to the ICU, where a chest tube was placed and a thoracic epidural was administered for pain control. As her contusions worsened, she was electively intubated and placed on mechanical ventilation for a few days. She subsequently underwent open reduction and internal fixation of her rib fractures. As her contusions improved, she was weaned off the ventilator and extubated, eventually making a full recovery.
ANSWER
The radiograph demonstrates several findings. First, there are multiple bilateral rib fractures. Five to six ribs are broken and displaced on both sides. In addition, there are bilateral small apical pneumothoraces. Finally, there is evidence of bilateral pulmonary contusions beginning to form, more so on the left than the right side.
This patient was admitted to the ICU, where a chest tube was placed and a thoracic epidural was administered for pain control. As her contusions worsened, she was electively intubated and placed on mechanical ventilation for a few days. She subsequently underwent open reduction and internal fixation of her rib fractures. As her contusions improved, she was weaned off the ventilator and extubated, eventually making a full recovery.
ANSWER
The radiograph demonstrates several findings. First, there are multiple bilateral rib fractures. Five to six ribs are broken and displaced on both sides. In addition, there are bilateral small apical pneumothoraces. Finally, there is evidence of bilateral pulmonary contusions beginning to form, more so on the left than the right side.
This patient was admitted to the ICU, where a chest tube was placed and a thoracic epidural was administered for pain control. As her contusions worsened, she was electively intubated and placed on mechanical ventilation for a few days. She subsequently underwent open reduction and internal fixation of her rib fractures. As her contusions improved, she was weaned off the ventilator and extubated, eventually making a full recovery.
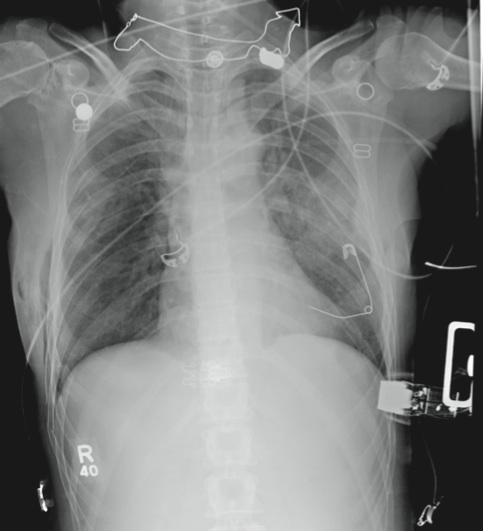
A 53-year-old woman is brought to your facility complaining of right-side chest pain. Earlier this evening, while riding her horse, she was thrown off; the horse then fell on top of her. She denies any loss of consciousness. Most of her pain occurs when she inhales. The patient’s medical history is unremarkable. Her vital signs are: blood pressure, 148/87 mm Hg; heart rate, 100 beats/min; respiratory rate, 14 breaths/min; and O2 saturation, 100% with oxygen via nasal cannula. Primary survey reveals moderate tenderness to palpation along the right side of the patient’s chest, with associated crepitus. Some decreased breath sounds are noted on the right, along with crackles. She is moving all of her extremities and otherwise appears neurologically intact. A stat portable chest radiograph is obtained in the trauma bay before the patient is transported for CT scans. What is your impression?