User login
The Integration of Extended Reality in Arthroplasty: Reviewing Technological Progress and Clinical Benefits
The Integration of Extended Reality in Arthroplasty: Reviewing Technological Progress and Clinical Benefits
The introduction of extended reality (XR) to the operating room (OR) has proved promising for enhancing surgical precision and improving patient outcomes. In the field of orthopedic surgery, precise alignment of implants is integral to maintaining functional range of motion and preventing impingement of adjacent neurovascular structures. XR systems have shown promise in arthroplasty including by improving precision and streamlining surgery by allowing surgeons to create 3D preoperative plans that are accessible intraoperatively. This article explores the current applications of XR in arthroplasty, highlights recent advancements and benefits, and describes limitations in comparison to traditional techniques.
Methods
A literature search identified studies involving the use of XR in arthroplasty and current US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved XR systems. Multiple electronic databases were used, including PubMed, Google Scholar, and IEEE Xplore. Search terms included: extended reality, augmented reality, virtual reality, arthroplasty, joint replacement, total knee arthroplasty, total shoulder arthroplasty, and total hip arthroplasty. The study design, intervention details, outcomes, and comparisons with traditional surgical techniques were thematically analyzed, with identification of common ideas associated with XR use in arthroplasty. This narrative report highlights the integration of XR in arthroplasty.
Extended Reality Fundamentals
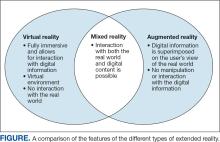
XR encompasses augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR). AR involves superimposing digitally rendered information and images onto the surgeon’s view of the real world, typically through the use of a headset and smart glasses.1 AR allows the surgeon to move and interact freely within the OR, removing the need for additional screens or devices to display patient information or imaging. VR is a fully immersive simulation using a headset that obstructs the view of the real world but allows the user to move freely within this virtual setting, often with audio or other sensory stimuli. MR combines AR and VR to create a digital model that allows for real-world interaction, with the advantage of adapting information and models in real time.2 Whereas in AR the surgeon can view the data projected from the headset, MR provides the ability to interact with and manipulate the digital content (Figure). Both AR and MR have been adapted for use in the OR, while VR has been adapted for use in surgical planning and training.
Extended Reality Use in Orthopedics
The HipNav system was introduced in 1995 to create preoperative plans that assist surgeons in accurately implanting the acetabular cup during total hip arthroplasty (THA).3 Although not commercially successful, this system spurred surgeons to experiment with XR to improve the accuracy and alignment of orthopedic implants. Systems capable of displaying the desired intraoperative implant placement have flourished, with applications in fracture reduction, arthroplasty, solid tumor resection, and hardware placement.4-7 Accurate alignment has been linked to improvements in patient outcomes.8-10 XR has great potential within the field of arthroplasty, with multiple new systems approved by the FDA and currently available in the US (Table).
Hip Arthroplasty
Orientation of the acetabular cup is a technically challenging part of THA. Accuracy in the anteversion and inclination angles of the acetabular cup is required to maintain implant stability, preserve functional range of motion (ROM), and prevent precocious wear.11,12 Despite preoperative planning, surgeons often overestimate the inclination angle and underestimate anteversion.13 Improper implantation of the acetabular cup can lead to joint instability caused by aseptic loosening, increasing the risk of dislocation and the need for revision surgery.14,15 Dislocations typically present to the emergency department, but primary care practitioners may encounter patients with pain or diminished sensation due to impingement or instability.16
The introduction of XR into the OR has provided the opportunity for real-time navigation and adjustment of the acetabular cup to maximize anteversion and inclination angles. Currently, 2 FDA-approved systems are available for THA: the Zimmer and Surgical Planning Associates HipInsight system, and the Insight Augmented Reality Visualization and Information System (ARVIS). The HipInsight system consists of a hologram projection using the Microsoft HoloLens2 device and optimizes preoperative planning, producing accuracy of anteversion and inclination angles within 3°.17 ARVIS employs existing surgical helmets and 2 mounted tracking cameras to provide navigation intraoperatively. ARVIS has also been approved for use in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.18
HipInsight has shown utility in increasing the accuracy of acetabular cup placement along with the use of biplanar radiographic scans.19 However, there are no studies validating the efficacy of ARVIS and HipInsight and assessing long-term disease-oriented or patient-oriented outcomes.
Knee Arthroplasty
In the setting of TKA, XR is most effective in ensuring accurate resection of the tibial and femoral components. Achieving the planned femoral coronal, axial, and sagittal angles allows the prosthesis to be on the femoral axis of rotation, improving functional outcomes. XR systems for TKA have been shown to increase the accuracy of distal femoral resection with a limited increase in surgery duration.20,21 For TKA in particular, patients are often less satisfied with the result than surgeons expect.22 Accurate alignment can improve patient satisfaction and reduce return-to-clinic rates for postoperative pain management, a factor that primary care practitioners should consider when recommending a patient for TKA.23
Along with ARVIS, 3 additional XR systems are FDA-approved for use in TKA. The Pixee Medical Knee+ system uses smart glasses and trackers to aid in the positioning of instruments for improved accuracy while allowing real-time navigation.24 The Medacta NextAR Knee’s single-use tracking system allows for intraoperative navigation with the use of AR glasses.25 The Polaris STELLAR Knee uses MR and avoids the need for preoperative imaging by capturing real-time anatomic data.26
The Pixee Medical Knee+ system was commercially available in Europe for several years prior to FDA approval, so more research exists on its efficacy. One study found that the Pixee Medical Knee+ system initially demonstrated an inferior clinical outcome, attributed to the learning curve associated with using the system.27 However, more recent studies have shown its utility in improving alignment, regardless of implant specifications.28,29 The Medacta NextAR Knee system has been shown to improve accuracy of tibial rotation and soft tissue balance and even increase OR efficiency.30,31 The Polaris STELLAR Knee system received FDA approval in 2023; no published research exists on its accuracy and outcomes.26
Shoulder Arthroplasty
Minimally invasive techniques are favored in total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) due to the vitality of maintaining the surrounding soft tissue to maximize preservation of motility and strength.32 However, this complicates the procedure by decreasing the ability to effectively access and visualize key structures of the shoulder. Accordingly, issues with implant positioning and alignment are more common with TSA than other joint arthroplasties, making XR particularly promising.33 Some studies report that up to 67% of patients experience glenohumeral instability, which can clinically present as weakness, decreased range of motion, and persistent shoulder pain.34,35 The use of preoperative computed tomography to improve understanding of glenoid anatomy and glenohumeral subluxation is becoming increasingly common, and it can be combined with XR to improve accuracy.36,37
Two FDA-approved systems are available. The Stryker Blueprint MR system is used for intraoperative guidance and integration for patient imaging used for preoperative planning. The Medacta NextAR Shoulder system is a parallel of the company’s TKA system. The Stryker Blueprint MR system combines the Microsoft HoloLens 2 headset to display preoperative plans with a secondary display for coordination with the rest of the surgical team.38 Similar to the Medacta NextAR Knee, the Medacta NextAR Shoulder system uses the same single-use tracking system and AR glasses for intraoperative guidance.39
Data on the long-term outcomes of using these systems are still limited, but the Stryker Blueprint MR system has not been shown to accurately predict postoperative ROM.40 Cadaveric studies have demonstrated that the Medacta NextAR Shoulder system can provide accurate inclination, retroversion, entry point, depth, and rotation values based on the preoperative planned values.41,42 However, this accuracy has yet to be confirmed in vivo, and the impact of using XR in TSA on long-term outcomes is still unknown.
Challenges and Limitations
Though XR has proven to be promising in arthroplasty, several limitations regarding widespread implementation exist. In particular, there is a steep learning curve associated with the use of XR systems, which can cause increased operative time and even initial inferior outcomes, as demonstrated with the Pixee Medical Knee+ system. The need for extensive practice and training prior to use could delay widespread adoption and may cause discrepancies in surgical outcomes. Unfamiliarity with the system and technological difficulties that may require troubleshooting can also increase operative time, particularly for surgeons new to using the XR system. Though intraoperative navigation is expected to improve accuracy of implant alignment, its added complexity may also result in longer surgeries.
In addition to the steep learning curve and increased operative time, there is a high upfront cost associated with XR systems. Exact costs of XR systems are not typically disclosed, but available estimates suggest an average sales price of about $1000 per case. Given the proprietary nature of these technologies, publicly available cost data are limited, making it challenging to fully assess the financial burden on health care institutions. Though some systems, such as ARVIS, can be integrated with existing surgical helmets, many require the purchase of AR glasses and secondary displays. This can cause further variation in the total expense for each system. In low-resource settings, this represents a significant challenge to widespread implementation. To justify this cost, additional research on long-term patient outcomes is needed to ensure the benefits of XR systems outweigh the cost.
Although early studies on XR systems in arthroplasty have shown improvements in precision and short-term outcomes, long-term data regarding effectiveness remains. Even systems such as ARVIS and HipInsight have limited long-term follow-up, making it difficult to assess whether the improved accuracy with these XR systems translates into improved patient outcomes compared with traditional arthroplasty.
CONCLUSIONS
XR technologies have shown significant potential in enhancing precision and patient outcomes. Through the integration of XR in the OR, surgeons can visualize preoperative plans and even make intraoperative changes, with the benefit of improving implant alignment.
There are some disadvantages to its use, however, including high cost and increased operative time. Despite this, the integration of XR into surgical practice can deliver more precise implant alignment and address other challenges faced with conventional techniques. As these technologies evolve and studies on long-term outcomes validate their utility, XR has the potential to transform the field of arthroplasty.
Azuma RT. A survey of augmented reality. Presence-Teleop Virt. 1997;6:355-385. doi:10.1162/pres.1997.6.4.355
Speicher M, Hall BD, Nebeling M. What is Mixed Reality? In: Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Association for Computing Machinery; 2019:1-15. doi:10.1145/3290605.3300767
Digioia AM, Jaramaz B, Nikou C, et al. Surgical navigation for total hip replacement with the use of hipnav. Oper Tech Orthop. 2000;10:3-8. doi:10.1016/S1048-6666(00)80036-1
Ogawa H, Hasegawa S, Tsukada S, et al. A pilot study of augmented reality technology applied to the acetabular cup placement during total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:1833-1837. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.01.067
Shen F, Chen B, Guo Q, et al. Augmented reality patient-specific reconstruction plate design for pelvic and acetabular fracture surgery. Int J CARS. 2013;8:169-179. doi:10.1007/s11548-012-0775-5
Cho HS, Park YK, Gupta S, et al. Augmented reality in bone tumour resection: an experimental study. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6:137-143. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.63.bjr-2016-0289.r1
Wu X, Liu R, Yu J, et al. Mixed reality technology launches in orthopedic surgery for comprehensive preoperative management of complicated cervical fractures. Surg Innov. 2018;25:421-422. doi:10.1177/1553350618761758
Dossett HG, Arthur JR, Makovicka JL, et al. A randomized controlled trial of kinematically and mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasties: long-term follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38:S209-S214. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.03.065
Kazarian GS, Haddad FS, Donaldson MJ, et al. Implant malalignment may be a risk factor for poor patient-reported outcomes measures (PROMs) following total knee arthroplasty (TKA). J Arthroplasty. 2022;37:S129-S133. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2022.02.087
Peng Y, Arauz P, An S, et al. Does component alignment affect patient reported outcomes following bicruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty? An in vivo three-dimensional analysis. J Knee Surg. 2020;33:798-803. doi:10.1055/s-0039-1688500
D’Lima DD, Urquhart AG, Buehler KO, et al. The effect of the orientation of the acetabular and femoral components on the range of motion of the hip at different head-neck ratios. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:315-321. doi:10.2106/00004623-200003000-00003
Yamaguchi M, Akisue T, Bauer TW, et al. The spatial location of impingement in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15:305-313. doi:10.1016/s0883-5403(00)90601-6
Grammatopoulos G, Alvand A, Monk AP, et al. Surgeons’ accuracy in achieving their desired acetabular component orientation. J Bone Joint Surg. 2016;98:e72. doi:10.2106/JBJS.15.01080
Kennedy JG, Rogers WB, Soffe KE, et al. Effect of acetabular component orientation on recurrent dislocation, pelvic osteolysis, polyethylene wear, and component migration. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:530-534. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(98)90052-3
Del Schutte H, Lipman AJ, Bannar SM, et al. Effects of acetabular abduction on cup wear rates in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:621-626. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(98)80003-X
Aresti N, Kassam J, Bartlett D, et al. Primary care management of postoperative shoulder, hip, and knee arthroplasty. BMJ. 2017;359:j4431. doi:10.1136/bmj.j4431
HipInsightTM System. Zimmer Biomet. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.zimmerbiomet.com/en/products-and-solutions/zb-edge/mixed-reality-portfolio/hipinsight-system.html
ARVIS. Insight Medical Systems. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.insightmedsys.com/arvis
Sun DC, Murphy WS, Amundson AJ, et al. Validation of a novel method of measuring cup orientation using biplanar simultaneous radiographic images. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38:S252-S256. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.04.011
Tsukada S, Ogawa H, Nishino M, et al. Augmented reality-assisted femoral bone resection in total knee arthroplasty. JBJS Open Access. 2021;6:e21.00001. doi:10.2106/JBJS.OA.21.00001
Castellarin G, Bori E, Barbieux E, et al. Is total knee arthroplasty surgical performance enhanced using augmented reality? A single-center study on 76 consecutive patients. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39:332-335. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.08.013
Choi YJ, Ra HJ. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2016;28:1. doi:10.5792/ksrr.2016.28.1.1
Hazratwala K, Gouk C, Wilkinson MPR, et al. Navigated functional alignment total knee arthroplasty achieves reliable, reproducible and accurate results with high patient satisfaction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31:3861-3870. doi:10.1007/s00167-023-07327-w
Knee+. Pixee Medical. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.pixee-medical.com/en/products/knee-nexsight/
KNEE | NEXTAR. Nextar. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://nextar.medacta.com/knee
POLARIS AR receives clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for STELLAR Knee. News release. PRNewswire. November 3, 2023. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/polarisar-receives-clearance-from-the-us-food-and-drug-administration-for-stellar-knee-301976747.html
van Overschelde P, Vansintjan P, Byn P, Lapierre C, van Lysebettens W. Does augmented reality improve clinical outcome in TKA? A prospective observational report. In: The 20th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery. 2022:170-174.
Sakellariou E, Alevrogiannis P, Alevrogianni F, et al. Single-center experience with Knee+TM augmented reality navigation system in primary total knee arthroplasty. World J Orthop. 2024;15:247-256. doi:10.5312/wjo.v15.i3.247
León-Muñoz VJ, Moya-Angeler J, López-López M, et al. Integration of square fiducial markers in patient-specific instrumentation and their applicability in knee surgery. J Pers Med. 2023;13:727. doi:10.3390/jpm13050727
Fucentese SF, Koch PP. A novel augmented reality-based surgical guidance system for total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141:2227-2233. doi:10.1007/s00402-021-04204-4
Sabatini L, Ascani D, Vezza D, et al. Novel surgical technique for total knee arthroplasty integrating kinematic alignment and real-time elongation of the ligaments using the NextAR system. J Pers Med. 2024;14:794. doi:10.3390/jpm14080794
Daher M, Ghanimeh J, Otayek J, et al. Augmented reality and shoulder replacement: a state-of-the-art review article. JSES Rev Rep Tech. 2023;3:274-278. doi:10.1016/j.xrrt.2023.01.008
Atmani H, Merienne F, Fofi D, et al. Computer aided surgery system for shoulder prosthesis placement. Comput Aided Surg. 2007;12:60-70. doi:10.3109/10929080701210832
Eichinger JK, Galvin JW. Management of complications after total shoulder arthroplasty. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2015;8:83-91. doi:10.1007/s12178-014-9251-x
Bonnevialle N, Melis B, Neyton L, et al. Aseptic glenoid loosening or failure in total shoulder arthroplasty: revision with glenoid reimplantation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22:745-751. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.08.009
Erickson BJ, Chalmers PN, Denard P, et al. Does commercially available shoulder arthroplasty preoperative planning software agree with surgeon measurements of version, inclination, and subluxation? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021;30:413-420. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2020.05.027
Werner BS, Hudek R, Burkhart KJ, et al. The influence of three-dimensional planning on decision-making in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26:1477-1483. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2017.01.006
Blueprint. Stryker. Updated August 2025. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.stryker.com/us/en/trauma-and-extremities/products/blueprint.html
NextAR Shoulder. Medacta. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://nextar.medacta.com/shoulder
Baumgarten KM. Accuracy of Blueprint software in predicting range of motion 1 year after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32:1088-1094. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2022.12.009
Rojas JT, Jost B, Zipeto C, et al. Glenoid component placement in reverse shoulder arthroplasty assisted with augmented reality through a head-mounted display leads to low deviation between planned and postoperative parameters. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32:e587-e596. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2023.05.002
Dey Hazra RO, Paksoy A, Imiolczyk JP, et al. Augmented reality–assisted intraoperative navigation increases precision of glenoid inclination in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2025;34(2):577-583. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2024.05.039
The introduction of extended reality (XR) to the operating room (OR) has proved promising for enhancing surgical precision and improving patient outcomes. In the field of orthopedic surgery, precise alignment of implants is integral to maintaining functional range of motion and preventing impingement of adjacent neurovascular structures. XR systems have shown promise in arthroplasty including by improving precision and streamlining surgery by allowing surgeons to create 3D preoperative plans that are accessible intraoperatively. This article explores the current applications of XR in arthroplasty, highlights recent advancements and benefits, and describes limitations in comparison to traditional techniques.
Methods
A literature search identified studies involving the use of XR in arthroplasty and current US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved XR systems. Multiple electronic databases were used, including PubMed, Google Scholar, and IEEE Xplore. Search terms included: extended reality, augmented reality, virtual reality, arthroplasty, joint replacement, total knee arthroplasty, total shoulder arthroplasty, and total hip arthroplasty. The study design, intervention details, outcomes, and comparisons with traditional surgical techniques were thematically analyzed, with identification of common ideas associated with XR use in arthroplasty. This narrative report highlights the integration of XR in arthroplasty.
Extended Reality Fundamentals
XR encompasses augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR). AR involves superimposing digitally rendered information and images onto the surgeon’s view of the real world, typically through the use of a headset and smart glasses.1 AR allows the surgeon to move and interact freely within the OR, removing the need for additional screens or devices to display patient information or imaging. VR is a fully immersive simulation using a headset that obstructs the view of the real world but allows the user to move freely within this virtual setting, often with audio or other sensory stimuli. MR combines AR and VR to create a digital model that allows for real-world interaction, with the advantage of adapting information and models in real time.2 Whereas in AR the surgeon can view the data projected from the headset, MR provides the ability to interact with and manipulate the digital content (Figure). Both AR and MR have been adapted for use in the OR, while VR has been adapted for use in surgical planning and training.
Extended Reality Use in Orthopedics
The HipNav system was introduced in 1995 to create preoperative plans that assist surgeons in accurately implanting the acetabular cup during total hip arthroplasty (THA).3 Although not commercially successful, this system spurred surgeons to experiment with XR to improve the accuracy and alignment of orthopedic implants. Systems capable of displaying the desired intraoperative implant placement have flourished, with applications in fracture reduction, arthroplasty, solid tumor resection, and hardware placement.4-7 Accurate alignment has been linked to improvements in patient outcomes.8-10 XR has great potential within the field of arthroplasty, with multiple new systems approved by the FDA and currently available in the US (Table).
Hip Arthroplasty
Orientation of the acetabular cup is a technically challenging part of THA. Accuracy in the anteversion and inclination angles of the acetabular cup is required to maintain implant stability, preserve functional range of motion (ROM), and prevent precocious wear.11,12 Despite preoperative planning, surgeons often overestimate the inclination angle and underestimate anteversion.13 Improper implantation of the acetabular cup can lead to joint instability caused by aseptic loosening, increasing the risk of dislocation and the need for revision surgery.14,15 Dislocations typically present to the emergency department, but primary care practitioners may encounter patients with pain or diminished sensation due to impingement or instability.16
The introduction of XR into the OR has provided the opportunity for real-time navigation and adjustment of the acetabular cup to maximize anteversion and inclination angles. Currently, 2 FDA-approved systems are available for THA: the Zimmer and Surgical Planning Associates HipInsight system, and the Insight Augmented Reality Visualization and Information System (ARVIS). The HipInsight system consists of a hologram projection using the Microsoft HoloLens2 device and optimizes preoperative planning, producing accuracy of anteversion and inclination angles within 3°.17 ARVIS employs existing surgical helmets and 2 mounted tracking cameras to provide navigation intraoperatively. ARVIS has also been approved for use in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.18
HipInsight has shown utility in increasing the accuracy of acetabular cup placement along with the use of biplanar radiographic scans.19 However, there are no studies validating the efficacy of ARVIS and HipInsight and assessing long-term disease-oriented or patient-oriented outcomes.
Knee Arthroplasty
In the setting of TKA, XR is most effective in ensuring accurate resection of the tibial and femoral components. Achieving the planned femoral coronal, axial, and sagittal angles allows the prosthesis to be on the femoral axis of rotation, improving functional outcomes. XR systems for TKA have been shown to increase the accuracy of distal femoral resection with a limited increase in surgery duration.20,21 For TKA in particular, patients are often less satisfied with the result than surgeons expect.22 Accurate alignment can improve patient satisfaction and reduce return-to-clinic rates for postoperative pain management, a factor that primary care practitioners should consider when recommending a patient for TKA.23
Along with ARVIS, 3 additional XR systems are FDA-approved for use in TKA. The Pixee Medical Knee+ system uses smart glasses and trackers to aid in the positioning of instruments for improved accuracy while allowing real-time navigation.24 The Medacta NextAR Knee’s single-use tracking system allows for intraoperative navigation with the use of AR glasses.25 The Polaris STELLAR Knee uses MR and avoids the need for preoperative imaging by capturing real-time anatomic data.26
The Pixee Medical Knee+ system was commercially available in Europe for several years prior to FDA approval, so more research exists on its efficacy. One study found that the Pixee Medical Knee+ system initially demonstrated an inferior clinical outcome, attributed to the learning curve associated with using the system.27 However, more recent studies have shown its utility in improving alignment, regardless of implant specifications.28,29 The Medacta NextAR Knee system has been shown to improve accuracy of tibial rotation and soft tissue balance and even increase OR efficiency.30,31 The Polaris STELLAR Knee system received FDA approval in 2023; no published research exists on its accuracy and outcomes.26
Shoulder Arthroplasty
Minimally invasive techniques are favored in total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) due to the vitality of maintaining the surrounding soft tissue to maximize preservation of motility and strength.32 However, this complicates the procedure by decreasing the ability to effectively access and visualize key structures of the shoulder. Accordingly, issues with implant positioning and alignment are more common with TSA than other joint arthroplasties, making XR particularly promising.33 Some studies report that up to 67% of patients experience glenohumeral instability, which can clinically present as weakness, decreased range of motion, and persistent shoulder pain.34,35 The use of preoperative computed tomography to improve understanding of glenoid anatomy and glenohumeral subluxation is becoming increasingly common, and it can be combined with XR to improve accuracy.36,37
Two FDA-approved systems are available. The Stryker Blueprint MR system is used for intraoperative guidance and integration for patient imaging used for preoperative planning. The Medacta NextAR Shoulder system is a parallel of the company’s TKA system. The Stryker Blueprint MR system combines the Microsoft HoloLens 2 headset to display preoperative plans with a secondary display for coordination with the rest of the surgical team.38 Similar to the Medacta NextAR Knee, the Medacta NextAR Shoulder system uses the same single-use tracking system and AR glasses for intraoperative guidance.39
Data on the long-term outcomes of using these systems are still limited, but the Stryker Blueprint MR system has not been shown to accurately predict postoperative ROM.40 Cadaveric studies have demonstrated that the Medacta NextAR Shoulder system can provide accurate inclination, retroversion, entry point, depth, and rotation values based on the preoperative planned values.41,42 However, this accuracy has yet to be confirmed in vivo, and the impact of using XR in TSA on long-term outcomes is still unknown.
Challenges and Limitations
Though XR has proven to be promising in arthroplasty, several limitations regarding widespread implementation exist. In particular, there is a steep learning curve associated with the use of XR systems, which can cause increased operative time and even initial inferior outcomes, as demonstrated with the Pixee Medical Knee+ system. The need for extensive practice and training prior to use could delay widespread adoption and may cause discrepancies in surgical outcomes. Unfamiliarity with the system and technological difficulties that may require troubleshooting can also increase operative time, particularly for surgeons new to using the XR system. Though intraoperative navigation is expected to improve accuracy of implant alignment, its added complexity may also result in longer surgeries.
In addition to the steep learning curve and increased operative time, there is a high upfront cost associated with XR systems. Exact costs of XR systems are not typically disclosed, but available estimates suggest an average sales price of about $1000 per case. Given the proprietary nature of these technologies, publicly available cost data are limited, making it challenging to fully assess the financial burden on health care institutions. Though some systems, such as ARVIS, can be integrated with existing surgical helmets, many require the purchase of AR glasses and secondary displays. This can cause further variation in the total expense for each system. In low-resource settings, this represents a significant challenge to widespread implementation. To justify this cost, additional research on long-term patient outcomes is needed to ensure the benefits of XR systems outweigh the cost.
Although early studies on XR systems in arthroplasty have shown improvements in precision and short-term outcomes, long-term data regarding effectiveness remains. Even systems such as ARVIS and HipInsight have limited long-term follow-up, making it difficult to assess whether the improved accuracy with these XR systems translates into improved patient outcomes compared with traditional arthroplasty.
CONCLUSIONS
XR technologies have shown significant potential in enhancing precision and patient outcomes. Through the integration of XR in the OR, surgeons can visualize preoperative plans and even make intraoperative changes, with the benefit of improving implant alignment.
There are some disadvantages to its use, however, including high cost and increased operative time. Despite this, the integration of XR into surgical practice can deliver more precise implant alignment and address other challenges faced with conventional techniques. As these technologies evolve and studies on long-term outcomes validate their utility, XR has the potential to transform the field of arthroplasty.
The introduction of extended reality (XR) to the operating room (OR) has proved promising for enhancing surgical precision and improving patient outcomes. In the field of orthopedic surgery, precise alignment of implants is integral to maintaining functional range of motion and preventing impingement of adjacent neurovascular structures. XR systems have shown promise in arthroplasty including by improving precision and streamlining surgery by allowing surgeons to create 3D preoperative plans that are accessible intraoperatively. This article explores the current applications of XR in arthroplasty, highlights recent advancements and benefits, and describes limitations in comparison to traditional techniques.
Methods
A literature search identified studies involving the use of XR in arthroplasty and current US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved XR systems. Multiple electronic databases were used, including PubMed, Google Scholar, and IEEE Xplore. Search terms included: extended reality, augmented reality, virtual reality, arthroplasty, joint replacement, total knee arthroplasty, total shoulder arthroplasty, and total hip arthroplasty. The study design, intervention details, outcomes, and comparisons with traditional surgical techniques were thematically analyzed, with identification of common ideas associated with XR use in arthroplasty. This narrative report highlights the integration of XR in arthroplasty.
Extended Reality Fundamentals
XR encompasses augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR). AR involves superimposing digitally rendered information and images onto the surgeon’s view of the real world, typically through the use of a headset and smart glasses.1 AR allows the surgeon to move and interact freely within the OR, removing the need for additional screens or devices to display patient information or imaging. VR is a fully immersive simulation using a headset that obstructs the view of the real world but allows the user to move freely within this virtual setting, often with audio or other sensory stimuli. MR combines AR and VR to create a digital model that allows for real-world interaction, with the advantage of adapting information and models in real time.2 Whereas in AR the surgeon can view the data projected from the headset, MR provides the ability to interact with and manipulate the digital content (Figure). Both AR and MR have been adapted for use in the OR, while VR has been adapted for use in surgical planning and training.
Extended Reality Use in Orthopedics
The HipNav system was introduced in 1995 to create preoperative plans that assist surgeons in accurately implanting the acetabular cup during total hip arthroplasty (THA).3 Although not commercially successful, this system spurred surgeons to experiment with XR to improve the accuracy and alignment of orthopedic implants. Systems capable of displaying the desired intraoperative implant placement have flourished, with applications in fracture reduction, arthroplasty, solid tumor resection, and hardware placement.4-7 Accurate alignment has been linked to improvements in patient outcomes.8-10 XR has great potential within the field of arthroplasty, with multiple new systems approved by the FDA and currently available in the US (Table).
Hip Arthroplasty
Orientation of the acetabular cup is a technically challenging part of THA. Accuracy in the anteversion and inclination angles of the acetabular cup is required to maintain implant stability, preserve functional range of motion (ROM), and prevent precocious wear.11,12 Despite preoperative planning, surgeons often overestimate the inclination angle and underestimate anteversion.13 Improper implantation of the acetabular cup can lead to joint instability caused by aseptic loosening, increasing the risk of dislocation and the need for revision surgery.14,15 Dislocations typically present to the emergency department, but primary care practitioners may encounter patients with pain or diminished sensation due to impingement or instability.16
The introduction of XR into the OR has provided the opportunity for real-time navigation and adjustment of the acetabular cup to maximize anteversion and inclination angles. Currently, 2 FDA-approved systems are available for THA: the Zimmer and Surgical Planning Associates HipInsight system, and the Insight Augmented Reality Visualization and Information System (ARVIS). The HipInsight system consists of a hologram projection using the Microsoft HoloLens2 device and optimizes preoperative planning, producing accuracy of anteversion and inclination angles within 3°.17 ARVIS employs existing surgical helmets and 2 mounted tracking cameras to provide navigation intraoperatively. ARVIS has also been approved for use in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.18
HipInsight has shown utility in increasing the accuracy of acetabular cup placement along with the use of biplanar radiographic scans.19 However, there are no studies validating the efficacy of ARVIS and HipInsight and assessing long-term disease-oriented or patient-oriented outcomes.
Knee Arthroplasty
In the setting of TKA, XR is most effective in ensuring accurate resection of the tibial and femoral components. Achieving the planned femoral coronal, axial, and sagittal angles allows the prosthesis to be on the femoral axis of rotation, improving functional outcomes. XR systems for TKA have been shown to increase the accuracy of distal femoral resection with a limited increase in surgery duration.20,21 For TKA in particular, patients are often less satisfied with the result than surgeons expect.22 Accurate alignment can improve patient satisfaction and reduce return-to-clinic rates for postoperative pain management, a factor that primary care practitioners should consider when recommending a patient for TKA.23
Along with ARVIS, 3 additional XR systems are FDA-approved for use in TKA. The Pixee Medical Knee+ system uses smart glasses and trackers to aid in the positioning of instruments for improved accuracy while allowing real-time navigation.24 The Medacta NextAR Knee’s single-use tracking system allows for intraoperative navigation with the use of AR glasses.25 The Polaris STELLAR Knee uses MR and avoids the need for preoperative imaging by capturing real-time anatomic data.26
The Pixee Medical Knee+ system was commercially available in Europe for several years prior to FDA approval, so more research exists on its efficacy. One study found that the Pixee Medical Knee+ system initially demonstrated an inferior clinical outcome, attributed to the learning curve associated with using the system.27 However, more recent studies have shown its utility in improving alignment, regardless of implant specifications.28,29 The Medacta NextAR Knee system has been shown to improve accuracy of tibial rotation and soft tissue balance and even increase OR efficiency.30,31 The Polaris STELLAR Knee system received FDA approval in 2023; no published research exists on its accuracy and outcomes.26
Shoulder Arthroplasty
Minimally invasive techniques are favored in total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) due to the vitality of maintaining the surrounding soft tissue to maximize preservation of motility and strength.32 However, this complicates the procedure by decreasing the ability to effectively access and visualize key structures of the shoulder. Accordingly, issues with implant positioning and alignment are more common with TSA than other joint arthroplasties, making XR particularly promising.33 Some studies report that up to 67% of patients experience glenohumeral instability, which can clinically present as weakness, decreased range of motion, and persistent shoulder pain.34,35 The use of preoperative computed tomography to improve understanding of glenoid anatomy and glenohumeral subluxation is becoming increasingly common, and it can be combined with XR to improve accuracy.36,37
Two FDA-approved systems are available. The Stryker Blueprint MR system is used for intraoperative guidance and integration for patient imaging used for preoperative planning. The Medacta NextAR Shoulder system is a parallel of the company’s TKA system. The Stryker Blueprint MR system combines the Microsoft HoloLens 2 headset to display preoperative plans with a secondary display for coordination with the rest of the surgical team.38 Similar to the Medacta NextAR Knee, the Medacta NextAR Shoulder system uses the same single-use tracking system and AR glasses for intraoperative guidance.39
Data on the long-term outcomes of using these systems are still limited, but the Stryker Blueprint MR system has not been shown to accurately predict postoperative ROM.40 Cadaveric studies have demonstrated that the Medacta NextAR Shoulder system can provide accurate inclination, retroversion, entry point, depth, and rotation values based on the preoperative planned values.41,42 However, this accuracy has yet to be confirmed in vivo, and the impact of using XR in TSA on long-term outcomes is still unknown.
Challenges and Limitations
Though XR has proven to be promising in arthroplasty, several limitations regarding widespread implementation exist. In particular, there is a steep learning curve associated with the use of XR systems, which can cause increased operative time and even initial inferior outcomes, as demonstrated with the Pixee Medical Knee+ system. The need for extensive practice and training prior to use could delay widespread adoption and may cause discrepancies in surgical outcomes. Unfamiliarity with the system and technological difficulties that may require troubleshooting can also increase operative time, particularly for surgeons new to using the XR system. Though intraoperative navigation is expected to improve accuracy of implant alignment, its added complexity may also result in longer surgeries.
In addition to the steep learning curve and increased operative time, there is a high upfront cost associated with XR systems. Exact costs of XR systems are not typically disclosed, but available estimates suggest an average sales price of about $1000 per case. Given the proprietary nature of these technologies, publicly available cost data are limited, making it challenging to fully assess the financial burden on health care institutions. Though some systems, such as ARVIS, can be integrated with existing surgical helmets, many require the purchase of AR glasses and secondary displays. This can cause further variation in the total expense for each system. In low-resource settings, this represents a significant challenge to widespread implementation. To justify this cost, additional research on long-term patient outcomes is needed to ensure the benefits of XR systems outweigh the cost.
Although early studies on XR systems in arthroplasty have shown improvements in precision and short-term outcomes, long-term data regarding effectiveness remains. Even systems such as ARVIS and HipInsight have limited long-term follow-up, making it difficult to assess whether the improved accuracy with these XR systems translates into improved patient outcomes compared with traditional arthroplasty.
CONCLUSIONS
XR technologies have shown significant potential in enhancing precision and patient outcomes. Through the integration of XR in the OR, surgeons can visualize preoperative plans and even make intraoperative changes, with the benefit of improving implant alignment.
There are some disadvantages to its use, however, including high cost and increased operative time. Despite this, the integration of XR into surgical practice can deliver more precise implant alignment and address other challenges faced with conventional techniques. As these technologies evolve and studies on long-term outcomes validate their utility, XR has the potential to transform the field of arthroplasty.
Azuma RT. A survey of augmented reality. Presence-Teleop Virt. 1997;6:355-385. doi:10.1162/pres.1997.6.4.355
Speicher M, Hall BD, Nebeling M. What is Mixed Reality? In: Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Association for Computing Machinery; 2019:1-15. doi:10.1145/3290605.3300767
Digioia AM, Jaramaz B, Nikou C, et al. Surgical navigation for total hip replacement with the use of hipnav. Oper Tech Orthop. 2000;10:3-8. doi:10.1016/S1048-6666(00)80036-1
Ogawa H, Hasegawa S, Tsukada S, et al. A pilot study of augmented reality technology applied to the acetabular cup placement during total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:1833-1837. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.01.067
Shen F, Chen B, Guo Q, et al. Augmented reality patient-specific reconstruction plate design for pelvic and acetabular fracture surgery. Int J CARS. 2013;8:169-179. doi:10.1007/s11548-012-0775-5
Cho HS, Park YK, Gupta S, et al. Augmented reality in bone tumour resection: an experimental study. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6:137-143. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.63.bjr-2016-0289.r1
Wu X, Liu R, Yu J, et al. Mixed reality technology launches in orthopedic surgery for comprehensive preoperative management of complicated cervical fractures. Surg Innov. 2018;25:421-422. doi:10.1177/1553350618761758
Dossett HG, Arthur JR, Makovicka JL, et al. A randomized controlled trial of kinematically and mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasties: long-term follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38:S209-S214. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.03.065
Kazarian GS, Haddad FS, Donaldson MJ, et al. Implant malalignment may be a risk factor for poor patient-reported outcomes measures (PROMs) following total knee arthroplasty (TKA). J Arthroplasty. 2022;37:S129-S133. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2022.02.087
Peng Y, Arauz P, An S, et al. Does component alignment affect patient reported outcomes following bicruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty? An in vivo three-dimensional analysis. J Knee Surg. 2020;33:798-803. doi:10.1055/s-0039-1688500
D’Lima DD, Urquhart AG, Buehler KO, et al. The effect of the orientation of the acetabular and femoral components on the range of motion of the hip at different head-neck ratios. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:315-321. doi:10.2106/00004623-200003000-00003
Yamaguchi M, Akisue T, Bauer TW, et al. The spatial location of impingement in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15:305-313. doi:10.1016/s0883-5403(00)90601-6
Grammatopoulos G, Alvand A, Monk AP, et al. Surgeons’ accuracy in achieving their desired acetabular component orientation. J Bone Joint Surg. 2016;98:e72. doi:10.2106/JBJS.15.01080
Kennedy JG, Rogers WB, Soffe KE, et al. Effect of acetabular component orientation on recurrent dislocation, pelvic osteolysis, polyethylene wear, and component migration. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:530-534. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(98)90052-3
Del Schutte H, Lipman AJ, Bannar SM, et al. Effects of acetabular abduction on cup wear rates in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:621-626. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(98)80003-X
Aresti N, Kassam J, Bartlett D, et al. Primary care management of postoperative shoulder, hip, and knee arthroplasty. BMJ. 2017;359:j4431. doi:10.1136/bmj.j4431
HipInsightTM System. Zimmer Biomet. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.zimmerbiomet.com/en/products-and-solutions/zb-edge/mixed-reality-portfolio/hipinsight-system.html
ARVIS. Insight Medical Systems. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.insightmedsys.com/arvis
Sun DC, Murphy WS, Amundson AJ, et al. Validation of a novel method of measuring cup orientation using biplanar simultaneous radiographic images. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38:S252-S256. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.04.011
Tsukada S, Ogawa H, Nishino M, et al. Augmented reality-assisted femoral bone resection in total knee arthroplasty. JBJS Open Access. 2021;6:e21.00001. doi:10.2106/JBJS.OA.21.00001
Castellarin G, Bori E, Barbieux E, et al. Is total knee arthroplasty surgical performance enhanced using augmented reality? A single-center study on 76 consecutive patients. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39:332-335. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.08.013
Choi YJ, Ra HJ. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2016;28:1. doi:10.5792/ksrr.2016.28.1.1
Hazratwala K, Gouk C, Wilkinson MPR, et al. Navigated functional alignment total knee arthroplasty achieves reliable, reproducible and accurate results with high patient satisfaction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31:3861-3870. doi:10.1007/s00167-023-07327-w
Knee+. Pixee Medical. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.pixee-medical.com/en/products/knee-nexsight/
KNEE | NEXTAR. Nextar. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://nextar.medacta.com/knee
POLARIS AR receives clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for STELLAR Knee. News release. PRNewswire. November 3, 2023. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/polarisar-receives-clearance-from-the-us-food-and-drug-administration-for-stellar-knee-301976747.html
van Overschelde P, Vansintjan P, Byn P, Lapierre C, van Lysebettens W. Does augmented reality improve clinical outcome in TKA? A prospective observational report. In: The 20th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery. 2022:170-174.
Sakellariou E, Alevrogiannis P, Alevrogianni F, et al. Single-center experience with Knee+TM augmented reality navigation system in primary total knee arthroplasty. World J Orthop. 2024;15:247-256. doi:10.5312/wjo.v15.i3.247
León-Muñoz VJ, Moya-Angeler J, López-López M, et al. Integration of square fiducial markers in patient-specific instrumentation and their applicability in knee surgery. J Pers Med. 2023;13:727. doi:10.3390/jpm13050727
Fucentese SF, Koch PP. A novel augmented reality-based surgical guidance system for total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141:2227-2233. doi:10.1007/s00402-021-04204-4
Sabatini L, Ascani D, Vezza D, et al. Novel surgical technique for total knee arthroplasty integrating kinematic alignment and real-time elongation of the ligaments using the NextAR system. J Pers Med. 2024;14:794. doi:10.3390/jpm14080794
Daher M, Ghanimeh J, Otayek J, et al. Augmented reality and shoulder replacement: a state-of-the-art review article. JSES Rev Rep Tech. 2023;3:274-278. doi:10.1016/j.xrrt.2023.01.008
Atmani H, Merienne F, Fofi D, et al. Computer aided surgery system for shoulder prosthesis placement. Comput Aided Surg. 2007;12:60-70. doi:10.3109/10929080701210832
Eichinger JK, Galvin JW. Management of complications after total shoulder arthroplasty. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2015;8:83-91. doi:10.1007/s12178-014-9251-x
Bonnevialle N, Melis B, Neyton L, et al. Aseptic glenoid loosening or failure in total shoulder arthroplasty: revision with glenoid reimplantation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22:745-751. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.08.009
Erickson BJ, Chalmers PN, Denard P, et al. Does commercially available shoulder arthroplasty preoperative planning software agree with surgeon measurements of version, inclination, and subluxation? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021;30:413-420. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2020.05.027
Werner BS, Hudek R, Burkhart KJ, et al. The influence of three-dimensional planning on decision-making in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26:1477-1483. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2017.01.006
Blueprint. Stryker. Updated August 2025. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.stryker.com/us/en/trauma-and-extremities/products/blueprint.html
NextAR Shoulder. Medacta. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://nextar.medacta.com/shoulder
Baumgarten KM. Accuracy of Blueprint software in predicting range of motion 1 year after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32:1088-1094. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2022.12.009
Rojas JT, Jost B, Zipeto C, et al. Glenoid component placement in reverse shoulder arthroplasty assisted with augmented reality through a head-mounted display leads to low deviation between planned and postoperative parameters. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32:e587-e596. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2023.05.002
Dey Hazra RO, Paksoy A, Imiolczyk JP, et al. Augmented reality–assisted intraoperative navigation increases precision of glenoid inclination in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2025;34(2):577-583. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2024.05.039
Azuma RT. A survey of augmented reality. Presence-Teleop Virt. 1997;6:355-385. doi:10.1162/pres.1997.6.4.355
Speicher M, Hall BD, Nebeling M. What is Mixed Reality? In: Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Association for Computing Machinery; 2019:1-15. doi:10.1145/3290605.3300767
Digioia AM, Jaramaz B, Nikou C, et al. Surgical navigation for total hip replacement with the use of hipnav. Oper Tech Orthop. 2000;10:3-8. doi:10.1016/S1048-6666(00)80036-1
Ogawa H, Hasegawa S, Tsukada S, et al. A pilot study of augmented reality technology applied to the acetabular cup placement during total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:1833-1837. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.01.067
Shen F, Chen B, Guo Q, et al. Augmented reality patient-specific reconstruction plate design for pelvic and acetabular fracture surgery. Int J CARS. 2013;8:169-179. doi:10.1007/s11548-012-0775-5
Cho HS, Park YK, Gupta S, et al. Augmented reality in bone tumour resection: an experimental study. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6:137-143. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.63.bjr-2016-0289.r1
Wu X, Liu R, Yu J, et al. Mixed reality technology launches in orthopedic surgery for comprehensive preoperative management of complicated cervical fractures. Surg Innov. 2018;25:421-422. doi:10.1177/1553350618761758
Dossett HG, Arthur JR, Makovicka JL, et al. A randomized controlled trial of kinematically and mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasties: long-term follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38:S209-S214. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.03.065
Kazarian GS, Haddad FS, Donaldson MJ, et al. Implant malalignment may be a risk factor for poor patient-reported outcomes measures (PROMs) following total knee arthroplasty (TKA). J Arthroplasty. 2022;37:S129-S133. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2022.02.087
Peng Y, Arauz P, An S, et al. Does component alignment affect patient reported outcomes following bicruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty? An in vivo three-dimensional analysis. J Knee Surg. 2020;33:798-803. doi:10.1055/s-0039-1688500
D’Lima DD, Urquhart AG, Buehler KO, et al. The effect of the orientation of the acetabular and femoral components on the range of motion of the hip at different head-neck ratios. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:315-321. doi:10.2106/00004623-200003000-00003
Yamaguchi M, Akisue T, Bauer TW, et al. The spatial location of impingement in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15:305-313. doi:10.1016/s0883-5403(00)90601-6
Grammatopoulos G, Alvand A, Monk AP, et al. Surgeons’ accuracy in achieving their desired acetabular component orientation. J Bone Joint Surg. 2016;98:e72. doi:10.2106/JBJS.15.01080
Kennedy JG, Rogers WB, Soffe KE, et al. Effect of acetabular component orientation on recurrent dislocation, pelvic osteolysis, polyethylene wear, and component migration. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:530-534. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(98)90052-3
Del Schutte H, Lipman AJ, Bannar SM, et al. Effects of acetabular abduction on cup wear rates in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:621-626. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(98)80003-X
Aresti N, Kassam J, Bartlett D, et al. Primary care management of postoperative shoulder, hip, and knee arthroplasty. BMJ. 2017;359:j4431. doi:10.1136/bmj.j4431
HipInsightTM System. Zimmer Biomet. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.zimmerbiomet.com/en/products-and-solutions/zb-edge/mixed-reality-portfolio/hipinsight-system.html
ARVIS. Insight Medical Systems. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.insightmedsys.com/arvis
Sun DC, Murphy WS, Amundson AJ, et al. Validation of a novel method of measuring cup orientation using biplanar simultaneous radiographic images. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38:S252-S256. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.04.011
Tsukada S, Ogawa H, Nishino M, et al. Augmented reality-assisted femoral bone resection in total knee arthroplasty. JBJS Open Access. 2021;6:e21.00001. doi:10.2106/JBJS.OA.21.00001
Castellarin G, Bori E, Barbieux E, et al. Is total knee arthroplasty surgical performance enhanced using augmented reality? A single-center study on 76 consecutive patients. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39:332-335. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.08.013
Choi YJ, Ra HJ. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2016;28:1. doi:10.5792/ksrr.2016.28.1.1
Hazratwala K, Gouk C, Wilkinson MPR, et al. Navigated functional alignment total knee arthroplasty achieves reliable, reproducible and accurate results with high patient satisfaction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31:3861-3870. doi:10.1007/s00167-023-07327-w
Knee+. Pixee Medical. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.pixee-medical.com/en/products/knee-nexsight/
KNEE | NEXTAR. Nextar. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://nextar.medacta.com/knee
POLARIS AR receives clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for STELLAR Knee. News release. PRNewswire. November 3, 2023. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/polarisar-receives-clearance-from-the-us-food-and-drug-administration-for-stellar-knee-301976747.html
van Overschelde P, Vansintjan P, Byn P, Lapierre C, van Lysebettens W. Does augmented reality improve clinical outcome in TKA? A prospective observational report. In: The 20th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery. 2022:170-174.
Sakellariou E, Alevrogiannis P, Alevrogianni F, et al. Single-center experience with Knee+TM augmented reality navigation system in primary total knee arthroplasty. World J Orthop. 2024;15:247-256. doi:10.5312/wjo.v15.i3.247
León-Muñoz VJ, Moya-Angeler J, López-López M, et al. Integration of square fiducial markers in patient-specific instrumentation and their applicability in knee surgery. J Pers Med. 2023;13:727. doi:10.3390/jpm13050727
Fucentese SF, Koch PP. A novel augmented reality-based surgical guidance system for total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141:2227-2233. doi:10.1007/s00402-021-04204-4
Sabatini L, Ascani D, Vezza D, et al. Novel surgical technique for total knee arthroplasty integrating kinematic alignment and real-time elongation of the ligaments using the NextAR system. J Pers Med. 2024;14:794. doi:10.3390/jpm14080794
Daher M, Ghanimeh J, Otayek J, et al. Augmented reality and shoulder replacement: a state-of-the-art review article. JSES Rev Rep Tech. 2023;3:274-278. doi:10.1016/j.xrrt.2023.01.008
Atmani H, Merienne F, Fofi D, et al. Computer aided surgery system for shoulder prosthesis placement. Comput Aided Surg. 2007;12:60-70. doi:10.3109/10929080701210832
Eichinger JK, Galvin JW. Management of complications after total shoulder arthroplasty. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2015;8:83-91. doi:10.1007/s12178-014-9251-x
Bonnevialle N, Melis B, Neyton L, et al. Aseptic glenoid loosening or failure in total shoulder arthroplasty: revision with glenoid reimplantation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22:745-751. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.08.009
Erickson BJ, Chalmers PN, Denard P, et al. Does commercially available shoulder arthroplasty preoperative planning software agree with surgeon measurements of version, inclination, and subluxation? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021;30:413-420. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2020.05.027
Werner BS, Hudek R, Burkhart KJ, et al. The influence of three-dimensional planning on decision-making in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26:1477-1483. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2017.01.006
Blueprint. Stryker. Updated August 2025. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.stryker.com/us/en/trauma-and-extremities/products/blueprint.html
NextAR Shoulder. Medacta. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://nextar.medacta.com/shoulder
Baumgarten KM. Accuracy of Blueprint software in predicting range of motion 1 year after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32:1088-1094. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2022.12.009
Rojas JT, Jost B, Zipeto C, et al. Glenoid component placement in reverse shoulder arthroplasty assisted with augmented reality through a head-mounted display leads to low deviation between planned and postoperative parameters. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32:e587-e596. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2023.05.002
Dey Hazra RO, Paksoy A, Imiolczyk JP, et al. Augmented reality–assisted intraoperative navigation increases precision of glenoid inclination in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2025;34(2):577-583. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2024.05.039
The Integration of Extended Reality in Arthroplasty: Reviewing Technological Progress and Clinical Benefits
The Integration of Extended Reality in Arthroplasty: Reviewing Technological Progress and Clinical Benefits
Effects of Lumbar Fusion and Dual-Mobility Liners on Dislocation Rates Following Total Hip Arthroplasty in a Veteran Population
Effects of Lumbar Fusion and Dual-Mobility Liners on Dislocation Rates Following Total Hip Arthroplasty in a Veteran Population
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) is among the most common elective orthopedic procedures performed annually in the United States, with an estimated 635,000 to 909,000 THAs expected each year by 2030.1 Consequently, complication rates and revision surgeries related to THA have been increasing, along with the financial burden on the health care system.2-4 Optimizing outcomes for patients undergoing THA and identifying risk factors for treatment failure have become areas of focus.
Over the last decade, there has been a renewed interest in the effect of previous lumbar spine fusion (LSF) surgery on THA outcomes. Studies have explored the rates of complications, postoperative mobility, and THA implant impingement.5-8 However, the outcome receiving the most attention in recent literature is the rate and effect of dislocation in patients with lumbar fusion surgery. Large Medicare database analyses have discovered an association with increased rates of dislocations in patients with lumbar fusion surgeries compared with those without.9,10 Prosthetic hip dislocation is an expensive complication of THA and is projected to have greater impact through 2035 due to a growing number of THA procedures.11 Identifying risk factors associated with hip dislocation is paramount to mitigating its effect on patients who have undergone THA.
Recent research has found increased rates of THA dislocation and revision surgery in patients with LSF, with some studies showing previous LSF as the strongest independent predictor.6-16 However, controversy surrounds this relationship, including the sequence of procedures (LSF before or after THA), the time between procedures, and involvement of the sacrum in LSF. One study found that patients had a 106% increased risk of dislocation when LSF was performed before THA compared with patients who underwent LSF 5 years after undergoing THA, while another study showed no significant difference in dislocations pre- vs post-LSF.16,17 An additional study showed no significant difference in the rate of dislocation in patients without sacral involvement in the LSF, while also showing significantly higher rates of dislocation in LSF with sacral involvement.12 The researchers also found a trend toward more dislocations in longer lumbosacral fusions. Recent studies have also examined dislocation rates with lumbar fusion in patients treated with dual-mobility liners.18-20 The consensus from these studies is that dual-mobility liners significantly decrease the rate of dislocation in primary THAs with lumbar fusion.
The present study sought to determine the rates of hip dislocations in a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) hospital setting. To the authors’ knowledge, no retrospective study focusing on THAs in the veteran population has been performed. This study benefits from controlling for various surgeon techniques and surgical preferences when compared to large Medicare database studies because the orthopedic surgeon (ABK) only performed the posterior approach for all patients during the study period.
The primary objective of this study was to determine whether the rates of hip dislocation would, in fact, be higher in patients with lumbar fusion surgery, as recent database studies suggest. Secondary objectives included determining whether patient characteristics, comorbidities, number of levels fused, or inclusion of the sacrum in the fusion construct influenced dislocation rates. Furthermore, VA Dayton Healthcare System (VADHS) began routine use of dual-mobility liners for lumbar fusion patients in 2018, allowing for examination of these patients.
Methods
The Wright State University and VADHS Institutional Review Board approved this study design. A retrospective review of all primary THAs at VADHS was performed to investigate the relationship between previous lumbar spine fusion and the incidence of THA revision. Manual chart review was performed for patients who underwent primary THA between January 2003, and December 2022. One surgeon performed all surgeries using only the posterior approach. Patients were not excluded if they had bilateral procedures and all eligible hips were included. Patients with a concomitant diagnosis of fracture of the femoral head or femoral neck at the time of surgery were excluded. Additionally, only patients with ≥ 12 months of follow-up data were included.
The primary outcome was dislocation within 12 months of THA; the primary independent variable was LSF prior to THA. Covariates included patient demographics (age, sex, body mass index [BMI]) and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) score, with additional data collected on the number of levels fused, sacral spine involvement, revision rates, and use of dual-mobility liners. Year of surgery was also included in analyses to account for any changes that may have occurred during the study period.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed in SAS 9.4. Patients were grouped into 2 cohorts, depending on whether they had received LSF prior to THA. Analyses were adjusted for repeated measures to account for the small percentage of patients with bilateral procedures.
Univariate comparisons between cohorts for covariates, as well as rates of dislocation and revision, were performed using the independent samples t test for continuous variables and the Fisher exact test for dichotomous categorical variables. Significant comorbidities, as well as age, sex, BMI, liner type, LSF cohort, and surgery year, were included in a logistic regression model to determine what effect, if any, they had on the likelihood of dislocation. Variables were removed using a backward stepwise approach, starting with the nonsignificant variable effect with the lowest χ2 value, and continuing until reaching a final model where all remaining variable effects were significant. For the variables retained in the final model, odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs were derived, with dislocation designated as the event. Individual comorbidity subcomponents of the CCI were also analyzed for their effects on dislocation using backward stepwise logistic regression. A secondary analysis among patients with LSF tested for the influence of the number of vertebral levels fused, the presence or absence of sacral involvement in the fusion, and the use of dual-mobility liners on the likelihood of hip dislocation.
Results
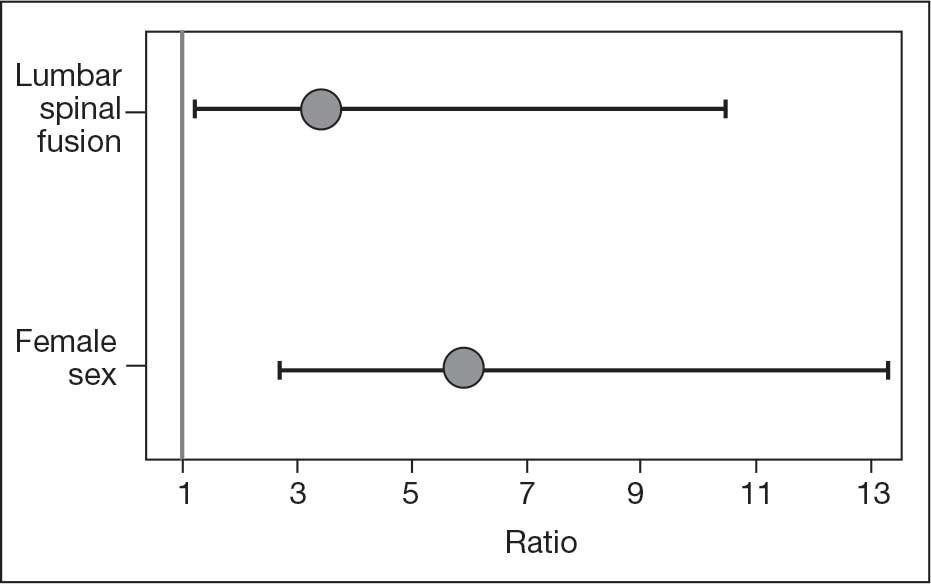
The LSF cohort included 39 patients with THA and prior LSF, 3 of whom had bilateral procedures, for a total of 42 hips. The non-LSF cohort included 813 patients with THA, 112 of whom had bilateral procedures, for a total of 925 hips. The LSF and non-LSF cohorts did not differ significantly in age, sex, BMI, CCI, or revision rates (Table). The LSF cohort included a significantly higher percentage of hips receiving dual-mobility liners than did the non-LSF cohort (23.8% vs 0.6%; P < .001) and had more than twice the rate of dislocation (4 of 42 hips [9.5%] vs 35 of 925 hips [3.8%]), although this difference was not statistically significant (P = .08).
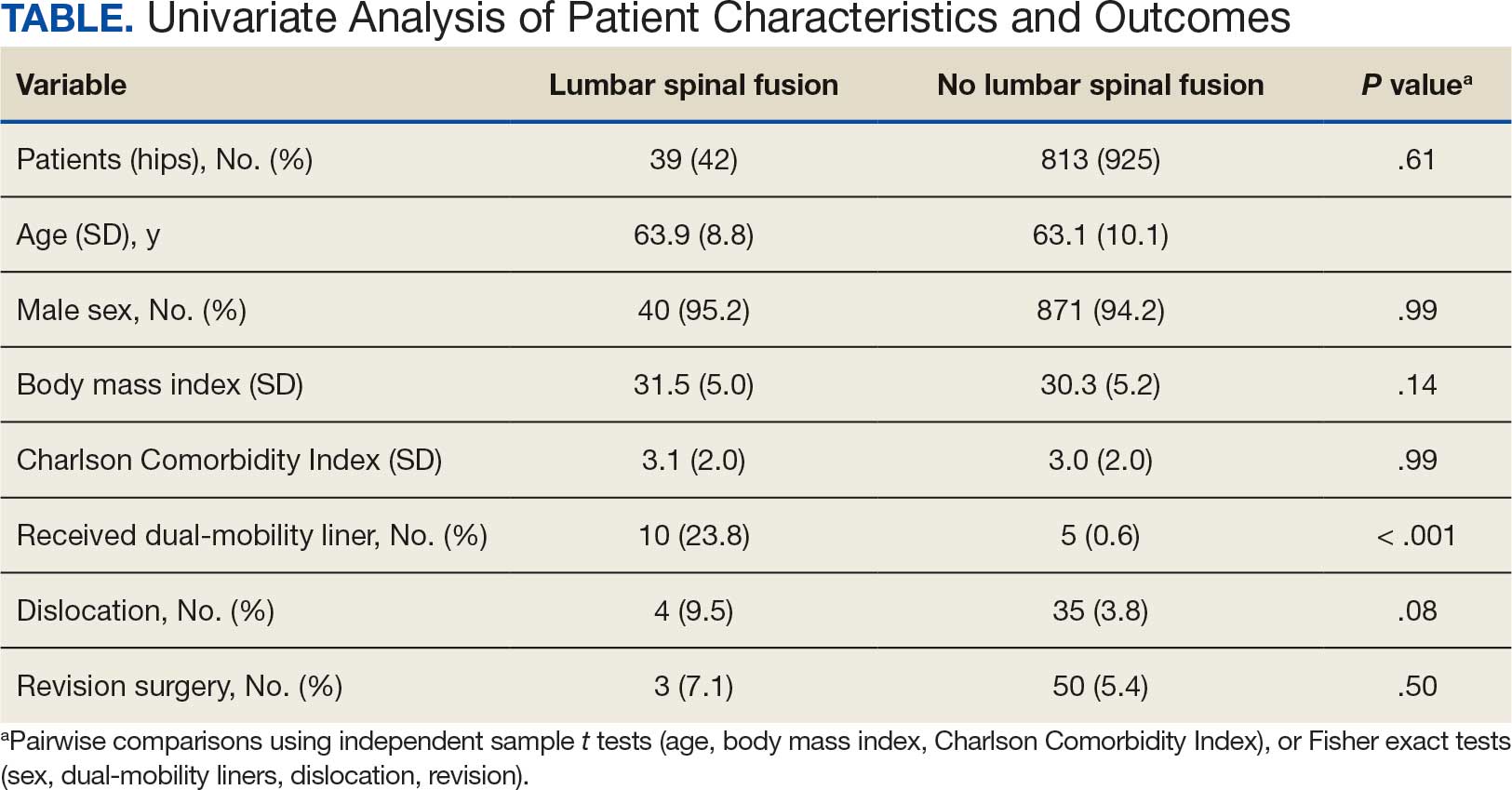
The final logistic regression model with dislocation as the outcome was statistically significant (χ2, 17.47; P < .001) and retained 2 significant predictor variables: LSF cohort (χ2, 4.63; P = .03), and sex (χ2, 18.27; P < .001). Females were more likely than males to experience dislocation (OR, 5.84; 95% CI, 2.60-13.13; P < .001) as were patients who had LSF prior to THA (OR, 3.42; 95% CI, 1.12-10.47; P = .03) (Figure). None of the CCI subcomponent comorbidities significantly affected the probability of dislocation (myocardial infarction, P = .46; congestive heart failure, P = .47; peripheral vascular disease, P = .97; stroke, P = .51; dementia, P = .99; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, P = .95; connective tissue disease, P = .25; peptic ulcer, P = .41; liver disease, P = .30; diabetes, P = .06; hemiplegia, P = .99; chronic kidney disease, P = .82; solid tumor, P = .90; leukemia, P = .99; lymphoma, P = .99; AIDS, P = .99). Within the LSF cohort, neither the number of levels fused (P = .83) nor sacral involvement (P = .42), significantly affected the probability of hip dislocation. None of the patients in either cohort who received dual-mobility liners subsequently dislocated their hips, nor did any of them require revision surgery.
Discussion
Spinopelvic biomechanics have been an area of increasing interest and research. Spinal fusion has been shown to alter the mobility of the pelvis and has been associated with decreased stability of THA implants.21 For example, in the setting of a fused spine, the lack of compensatory changes in pelvic tilt or acetabular anteversion when adjusting to a seated or standing position may predispose patients to impingement because the acetabular component is not properly positioned. Dual-mobility constructs mitigate this risk by providing an additional articulation, which increases jump distance and range of motion prior to impingement, thereby enhancing stability.
The use of dual-mobility liners in patients with LSF has also been examined.18-20 These studies demonstrate a reduced risk of postoperative THA dislocation in patients with previous LSF. The rate of postoperative complications and revisions for LSF patients with dual-mobility liners was also found to be similar to that of THAs without dual-mobility in patients without prior LSF. This study focused on a veteran population to demonstrate the efficacy of dual-mobility liners in patients with LSF. The results indicate that LSF prior to THA and female sex were predictors for prosthetic hip dislocations in the 12-month postoperative period in this patient population, which aligns with the current literature.
The dislocation rate in the LSF-THA group (9.5%) was higher than the dislocation rate in the control group (3.8%). Although not statistically significant in the univariate analysis, LSF was shown to be a significant risk factor after controlling for patient sex. Other studies have found the dislocation rate to be 3% to 7%, which is lower than the dislocation rate observed in this study.8,10,16
The reasons for this higher rate of dislocation are not entirely clear. A veteran population has poorer overall health than the general population, which may contribute to the higher than previously reported dislocation rates.22 These results can be applied to the management of veterans seeking THA.
There have been conflicting reports regarding the impact a patient’s sex has on THA outcomes in the general population.23-26 This study found that female patients had higher rates of dislocation within 1 year of THA than male patients. This difference, which could be due to differences in baseline anatomic hip morphology between the sexes; females tend to have smaller femoral head sizes and less offset compared with males.27,28 However, this finding could have been confounded by the small number of female veterans in the study cohort.
A type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) diagnosis, which is a component of CCI, trended toward increased risk of prosthetic hip dislocation. Multiple studies have also discussed the increased risk of postoperative infections and revisions following THA in patients with T2DM.29-31 One study found T2DM to be an independent risk factor for immediate in-hospital postoperative complications following hip arthroplasty.32
Another factor that may influence postoperative dislocation risk is surgical approach. The posterior approach has historically been associated with higher rates of instability when compared to anterior or lateral THA.33 Researchers have also looked at the role that surgical approach plays in patients with prior LSF. Huebschmann et al confirmed that not only is LSF a significant risk factor for dislocation following THA, but anterior and laterally based surgical approaches may mitigate this risk.34
Limitations
As a retrospective cohort study, the reliability of the data hinges on complete documentation. Documentation of all encounters for dislocations was obtained from the VA Computerized Patient Record System, which may have led to some dislocation events being missed. However, as long as there was adequate postoperative follow-up, it was assumed all events outside the VA were included. Another limitation of this study was that male patients greatly outnumbered female patients, and this fact could limit the generalizability of findings to the population as a whole.
Conclusions
This study in a veteran population found that prior LSF and female sex were significant predictors for postoperative dislocation within 1 year of THA surgery. Additionally, the use of a dual-mobility liner was found to be protective against postoperative dislocation events. These data allow clinicians to better counsel veterans on the risk factors associated with postoperative dislocation and strategies to mitigate this risk.
- Sloan M, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. Projected volume of primary total joint arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100:1455-1460. doi:10.2106/JBJS.17.01617
- Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:128-133. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00155
- Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Schmier J, et al. Future clinical and economic impact of revision total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:144-151. doi:10.2106/JBJS.G.00587
- Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Schmier J, et al. Primary and revision arthroplasty surgery caseloads in the United States from 1990 to 2004. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:195-203. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2007.11.015
- Yamato Y, Furuhashi H, Hasegawa T, et al. Simulation of implant impingement after spinal corrective fusion surgery in patients with previous total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective case series. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46:512-519. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000003836
- Mudrick CA, Melvin JS, Springer BD. Late posterior hip instability after lumbar spinopelvic fusion. Arthroplast Today. 2015;1:25-29. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2015.05.002
- Diebo BG, Beyer GA, Grieco PW, et al. Complications in patients undergoing spinal fusion after THA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476:412-417.doi:10.1007/s11999.0000000000000009 8.
- Sing DC, Barry JJ, Aguilar TU, et al. Prior lumbar spinal arthrodesis increases risk of prosthetic-related complication in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31:227-232.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2016.02.069
- King CA, Landy DC, Martell JM, et al. Time to dislocation analysis of lumbar spine fusion following total hip arthroplasty: breaking up a happy home. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:3768-3772. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.08.029
- Buckland AJ, Puvanesarajah V, Vigdorchik J, et al. Dislocation of a primary total hip arthroplasty is more common in patients with a lumbar spinal fusion. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B:585-591.doi:10.1302/0301-620X.99B5.BJJ-2016-0657.R1
- Pirruccio K, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. The burden of prosthetic hip dislocations in the United States is projected to significantly increase by 2035. Hip Int. 2021;31:714-721. doi:10.1177/1120700020923619
- Salib CG, Reina N, Perry KI, et al. Lumbar fusion involving the sacrum increases dislocation risk in primary total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B:198-206. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.101B2.BJJ-2018-0754.R1
- An VVG, Phan K, Sivakumar BS, et al. Prior lumbar spinal fusion is associated with an increased risk of dislocation and revision in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:297-300. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2017.08.040
- Klemt C, Padmanabha A, Tirumala V, et al. Lumbar spine fusion before revision total hip arthroplasty is associated with increased dislocation rates. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29:e860-e868. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-20-00824
- Gausden EB, Parhar HS, Popper JE, et al. Risk factors for early dislocation following primary elective total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:1567-1571. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2017.12.034
- Malkani AL, Himschoot KJ, Ong KL, et al. Does timing of primary total hip arthroplasty prior to or after lumbar spine fusion have an effect on dislocation and revision rates?. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:907-911. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.01.009
- Parilla FW, Shah RR, Gordon AC, et al. Does it matter: total hip arthroplasty or lumbar spinal fusion first? Preoperative sagittal spinopelvic measurements guide patient-specific surgical strategies in patients requiring both. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:2652-2662. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.05.053
- Chalmers BP, Syku M, Sculco TP, et al. Dual-mobility constructs in primary total hip arthroplasty in high-risk patients with spinal fusions: our institutional experience. Arthroplast Today. 2020;6:749-754. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2020.07.024
- Nessler JM, Malkani AL, Sachdeva S, et al. Use of dual mobility cups in patients undergoing primary total hip arthroplasty with prior lumbar spine fusion. Int Orthop. 2020;44:857-862. doi:10.1007/s00264-020-04507-y
- Nessler JM, Malkani AL, Yep PJ, et al. Dislocation rates of primary total hip arthroplasty in patients with prior lumbar spine fusion and lumbar degenerative disk disease with and without utilization of dual mobility cups: an American Joint Replacement Registry study. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2023;31:e271-e277. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-22-00767
- Phan D, Bederman SS, Schwarzkopf R. The influence of sagittal spinal deformity on anteversion of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B:1017-1023. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.97B8.35700
- Agha Z, Lofgren RP, VanRuiswyk JV, et al. Are patients at Veterans Affairs medical centers sicker? A comparative analysis of health status and medical resource use. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:3252-3257. doi:10.1001/archinte.160.21.325223.
- Basques BA, Bell JA, Fillingham YA, et al. Gender differences for hip and knee arthroplasty: complications and healthcare utilization. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:1593-1597.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.03.064
- Kim YH, Choi Y, Kim JS. Influence of patient-, design-, and surgery-related factors on rate of dislocation after primary cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:1258-1263. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2009.03.017
- Chen A, Paxton L, Zheng X, et al. Association of sex with risk of 2-year revision among patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2110687. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10687
- Inacio MCS, Ake CF, Paxton EW, et al. Sex and risk of hip implant failure: assessing total hip arthroplasty outcomes in the United States. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:435-441. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.3271
- Karlson EW, Daltroy LH, Liang MH, et al. Gender differences in patient preferences may underlie differential utilization of elective surgery. Am J Med. 1997;102:524-530. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(97)00050-8
- Kostamo T, Bourne RB, Whittaker JP, et al. No difference in gender-specific hip replacement outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:135-140. doi:10.1007/s11999-008-0466-2
- Papagelopoulos PJ, Idusuyi OB, Wallrichs SL, et al. Long term outcome and survivorship analysis of primary total knee arthroplasty in patients with diabetes mellitus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(330):124-132. doi:10.1097/00003086-199609000-00015
- Fitzgerald RH Jr, Nolan DR, Ilstrup DM, et al. Deep wound sepsis following total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59:847-855.
- Blom AW, Brown J, Taylor AH, et al. Infection after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86:688-691. doi:10.1302/0301-620x.86b5.14887
- Jain NB, Guller U, Pietrobon R, et al. Comorbidities increase complication rates in patients having arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;435:232-238. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000156479.97488.a2
- Docter S, Philpott HT, Godkin L, et al. Comparison of intra and post-operative complication rates among surgical approaches in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop. 2020;20:310-325. doi:10.1016/j.jor.2020.05.008
- Huebschmann NA, Lawrence KW, Robin JX, et al. Does surgical approach affect dislocation rate after total hip arthroplasty in patients who have prior lumbar spinal fusion? A retrospective analysis of 16,223 cases. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39:S306-S313. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2024.03.068
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) is among the most common elective orthopedic procedures performed annually in the United States, with an estimated 635,000 to 909,000 THAs expected each year by 2030.1 Consequently, complication rates and revision surgeries related to THA have been increasing, along with the financial burden on the health care system.2-4 Optimizing outcomes for patients undergoing THA and identifying risk factors for treatment failure have become areas of focus.
Over the last decade, there has been a renewed interest in the effect of previous lumbar spine fusion (LSF) surgery on THA outcomes. Studies have explored the rates of complications, postoperative mobility, and THA implant impingement.5-8 However, the outcome receiving the most attention in recent literature is the rate and effect of dislocation in patients with lumbar fusion surgery. Large Medicare database analyses have discovered an association with increased rates of dislocations in patients with lumbar fusion surgeries compared with those without.9,10 Prosthetic hip dislocation is an expensive complication of THA and is projected to have greater impact through 2035 due to a growing number of THA procedures.11 Identifying risk factors associated with hip dislocation is paramount to mitigating its effect on patients who have undergone THA.
Recent research has found increased rates of THA dislocation and revision surgery in patients with LSF, with some studies showing previous LSF as the strongest independent predictor.6-16 However, controversy surrounds this relationship, including the sequence of procedures (LSF before or after THA), the time between procedures, and involvement of the sacrum in LSF. One study found that patients had a 106% increased risk of dislocation when LSF was performed before THA compared with patients who underwent LSF 5 years after undergoing THA, while another study showed no significant difference in dislocations pre- vs post-LSF.16,17 An additional study showed no significant difference in the rate of dislocation in patients without sacral involvement in the LSF, while also showing significantly higher rates of dislocation in LSF with sacral involvement.12 The researchers also found a trend toward more dislocations in longer lumbosacral fusions. Recent studies have also examined dislocation rates with lumbar fusion in patients treated with dual-mobility liners.18-20 The consensus from these studies is that dual-mobility liners significantly decrease the rate of dislocation in primary THAs with lumbar fusion.
The present study sought to determine the rates of hip dislocations in a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) hospital setting. To the authors’ knowledge, no retrospective study focusing on THAs in the veteran population has been performed. This study benefits from controlling for various surgeon techniques and surgical preferences when compared to large Medicare database studies because the orthopedic surgeon (ABK) only performed the posterior approach for all patients during the study period.
The primary objective of this study was to determine whether the rates of hip dislocation would, in fact, be higher in patients with lumbar fusion surgery, as recent database studies suggest. Secondary objectives included determining whether patient characteristics, comorbidities, number of levels fused, or inclusion of the sacrum in the fusion construct influenced dislocation rates. Furthermore, VA Dayton Healthcare System (VADHS) began routine use of dual-mobility liners for lumbar fusion patients in 2018, allowing for examination of these patients.
Methods
The Wright State University and VADHS Institutional Review Board approved this study design. A retrospective review of all primary THAs at VADHS was performed to investigate the relationship between previous lumbar spine fusion and the incidence of THA revision. Manual chart review was performed for patients who underwent primary THA between January 2003, and December 2022. One surgeon performed all surgeries using only the posterior approach. Patients were not excluded if they had bilateral procedures and all eligible hips were included. Patients with a concomitant diagnosis of fracture of the femoral head or femoral neck at the time of surgery were excluded. Additionally, only patients with ≥ 12 months of follow-up data were included.
The primary outcome was dislocation within 12 months of THA; the primary independent variable was LSF prior to THA. Covariates included patient demographics (age, sex, body mass index [BMI]) and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) score, with additional data collected on the number of levels fused, sacral spine involvement, revision rates, and use of dual-mobility liners. Year of surgery was also included in analyses to account for any changes that may have occurred during the study period.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed in SAS 9.4. Patients were grouped into 2 cohorts, depending on whether they had received LSF prior to THA. Analyses were adjusted for repeated measures to account for the small percentage of patients with bilateral procedures.
Univariate comparisons between cohorts for covariates, as well as rates of dislocation and revision, were performed using the independent samples t test for continuous variables and the Fisher exact test for dichotomous categorical variables. Significant comorbidities, as well as age, sex, BMI, liner type, LSF cohort, and surgery year, were included in a logistic regression model to determine what effect, if any, they had on the likelihood of dislocation. Variables were removed using a backward stepwise approach, starting with the nonsignificant variable effect with the lowest χ2 value, and continuing until reaching a final model where all remaining variable effects were significant. For the variables retained in the final model, odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs were derived, with dislocation designated as the event. Individual comorbidity subcomponents of the CCI were also analyzed for their effects on dislocation using backward stepwise logistic regression. A secondary analysis among patients with LSF tested for the influence of the number of vertebral levels fused, the presence or absence of sacral involvement in the fusion, and the use of dual-mobility liners on the likelihood of hip dislocation.
Results
The LSF cohort included 39 patients with THA and prior LSF, 3 of whom had bilateral procedures, for a total of 42 hips. The non-LSF cohort included 813 patients with THA, 112 of whom had bilateral procedures, for a total of 925 hips. The LSF and non-LSF cohorts did not differ significantly in age, sex, BMI, CCI, or revision rates (Table). The LSF cohort included a significantly higher percentage of hips receiving dual-mobility liners than did the non-LSF cohort (23.8% vs 0.6%; P < .001) and had more than twice the rate of dislocation (4 of 42 hips [9.5%] vs 35 of 925 hips [3.8%]), although this difference was not statistically significant (P = .08).

The final logistic regression model with dislocation as the outcome was statistically significant (χ2, 17.47; P < .001) and retained 2 significant predictor variables: LSF cohort (χ2, 4.63; P = .03), and sex (χ2, 18.27; P < .001). Females were more likely than males to experience dislocation (OR, 5.84; 95% CI, 2.60-13.13; P < .001) as were patients who had LSF prior to THA (OR, 3.42; 95% CI, 1.12-10.47; P = .03) (Figure). None of the CCI subcomponent comorbidities significantly affected the probability of dislocation (myocardial infarction, P = .46; congestive heart failure, P = .47; peripheral vascular disease, P = .97; stroke, P = .51; dementia, P = .99; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, P = .95; connective tissue disease, P = .25; peptic ulcer, P = .41; liver disease, P = .30; diabetes, P = .06; hemiplegia, P = .99; chronic kidney disease, P = .82; solid tumor, P = .90; leukemia, P = .99; lymphoma, P = .99; AIDS, P = .99). Within the LSF cohort, neither the number of levels fused (P = .83) nor sacral involvement (P = .42), significantly affected the probability of hip dislocation. None of the patients in either cohort who received dual-mobility liners subsequently dislocated their hips, nor did any of them require revision surgery.

Discussion
Spinopelvic biomechanics have been an area of increasing interest and research. Spinal fusion has been shown to alter the mobility of the pelvis and has been associated with decreased stability of THA implants.21 For example, in the setting of a fused spine, the lack of compensatory changes in pelvic tilt or acetabular anteversion when adjusting to a seated or standing position may predispose patients to impingement because the acetabular component is not properly positioned. Dual-mobility constructs mitigate this risk by providing an additional articulation, which increases jump distance and range of motion prior to impingement, thereby enhancing stability.
The use of dual-mobility liners in patients with LSF has also been examined.18-20 These studies demonstrate a reduced risk of postoperative THA dislocation in patients with previous LSF. The rate of postoperative complications and revisions for LSF patients with dual-mobility liners was also found to be similar to that of THAs without dual-mobility in patients without prior LSF. This study focused on a veteran population to demonstrate the efficacy of dual-mobility liners in patients with LSF. The results indicate that LSF prior to THA and female sex were predictors for prosthetic hip dislocations in the 12-month postoperative period in this patient population, which aligns with the current literature.
The dislocation rate in the LSF-THA group (9.5%) was higher than the dislocation rate in the control group (3.8%). Although not statistically significant in the univariate analysis, LSF was shown to be a significant risk factor after controlling for patient sex. Other studies have found the dislocation rate to be 3% to 7%, which is lower than the dislocation rate observed in this study.8,10,16
The reasons for this higher rate of dislocation are not entirely clear. A veteran population has poorer overall health than the general population, which may contribute to the higher than previously reported dislocation rates.22 These results can be applied to the management of veterans seeking THA.
There have been conflicting reports regarding the impact a patient’s sex has on THA outcomes in the general population.23-26 This study found that female patients had higher rates of dislocation within 1 year of THA than male patients. This difference, which could be due to differences in baseline anatomic hip morphology between the sexes; females tend to have smaller femoral head sizes and less offset compared with males.27,28 However, this finding could have been confounded by the small number of female veterans in the study cohort.
A type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) diagnosis, which is a component of CCI, trended toward increased risk of prosthetic hip dislocation. Multiple studies have also discussed the increased risk of postoperative infections and revisions following THA in patients with T2DM.29-31 One study found T2DM to be an independent risk factor for immediate in-hospital postoperative complications following hip arthroplasty.32
Another factor that may influence postoperative dislocation risk is surgical approach. The posterior approach has historically been associated with higher rates of instability when compared to anterior or lateral THA.33 Researchers have also looked at the role that surgical approach plays in patients with prior LSF. Huebschmann et al confirmed that not only is LSF a significant risk factor for dislocation following THA, but anterior and laterally based surgical approaches may mitigate this risk.34
Limitations
As a retrospective cohort study, the reliability of the data hinges on complete documentation. Documentation of all encounters for dislocations was obtained from the VA Computerized Patient Record System, which may have led to some dislocation events being missed. However, as long as there was adequate postoperative follow-up, it was assumed all events outside the VA were included. Another limitation of this study was that male patients greatly outnumbered female patients, and this fact could limit the generalizability of findings to the population as a whole.
Conclusions
This study in a veteran population found that prior LSF and female sex were significant predictors for postoperative dislocation within 1 year of THA surgery. Additionally, the use of a dual-mobility liner was found to be protective against postoperative dislocation events. These data allow clinicians to better counsel veterans on the risk factors associated with postoperative dislocation and strategies to mitigate this risk.
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) is among the most common elective orthopedic procedures performed annually in the United States, with an estimated 635,000 to 909,000 THAs expected each year by 2030.1 Consequently, complication rates and revision surgeries related to THA have been increasing, along with the financial burden on the health care system.2-4 Optimizing outcomes for patients undergoing THA and identifying risk factors for treatment failure have become areas of focus.
Over the last decade, there has been a renewed interest in the effect of previous lumbar spine fusion (LSF) surgery on THA outcomes. Studies have explored the rates of complications, postoperative mobility, and THA implant impingement.5-8 However, the outcome receiving the most attention in recent literature is the rate and effect of dislocation in patients with lumbar fusion surgery. Large Medicare database analyses have discovered an association with increased rates of dislocations in patients with lumbar fusion surgeries compared with those without.9,10 Prosthetic hip dislocation is an expensive complication of THA and is projected to have greater impact through 2035 due to a growing number of THA procedures.11 Identifying risk factors associated with hip dislocation is paramount to mitigating its effect on patients who have undergone THA.
Recent research has found increased rates of THA dislocation and revision surgery in patients with LSF, with some studies showing previous LSF as the strongest independent predictor.6-16 However, controversy surrounds this relationship, including the sequence of procedures (LSF before or after THA), the time between procedures, and involvement of the sacrum in LSF. One study found that patients had a 106% increased risk of dislocation when LSF was performed before THA compared with patients who underwent LSF 5 years after undergoing THA, while another study showed no significant difference in dislocations pre- vs post-LSF.16,17 An additional study showed no significant difference in the rate of dislocation in patients without sacral involvement in the LSF, while also showing significantly higher rates of dislocation in LSF with sacral involvement.12 The researchers also found a trend toward more dislocations in longer lumbosacral fusions. Recent studies have also examined dislocation rates with lumbar fusion in patients treated with dual-mobility liners.18-20 The consensus from these studies is that dual-mobility liners significantly decrease the rate of dislocation in primary THAs with lumbar fusion.
The present study sought to determine the rates of hip dislocations in a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) hospital setting. To the authors’ knowledge, no retrospective study focusing on THAs in the veteran population has been performed. This study benefits from controlling for various surgeon techniques and surgical preferences when compared to large Medicare database studies because the orthopedic surgeon (ABK) only performed the posterior approach for all patients during the study period.
The primary objective of this study was to determine whether the rates of hip dislocation would, in fact, be higher in patients with lumbar fusion surgery, as recent database studies suggest. Secondary objectives included determining whether patient characteristics, comorbidities, number of levels fused, or inclusion of the sacrum in the fusion construct influenced dislocation rates. Furthermore, VA Dayton Healthcare System (VADHS) began routine use of dual-mobility liners for lumbar fusion patients in 2018, allowing for examination of these patients.
Methods
The Wright State University and VADHS Institutional Review Board approved this study design. A retrospective review of all primary THAs at VADHS was performed to investigate the relationship between previous lumbar spine fusion and the incidence of THA revision. Manual chart review was performed for patients who underwent primary THA between January 2003, and December 2022. One surgeon performed all surgeries using only the posterior approach. Patients were not excluded if they had bilateral procedures and all eligible hips were included. Patients with a concomitant diagnosis of fracture of the femoral head or femoral neck at the time of surgery were excluded. Additionally, only patients with ≥ 12 months of follow-up data were included.
The primary outcome was dislocation within 12 months of THA; the primary independent variable was LSF prior to THA. Covariates included patient demographics (age, sex, body mass index [BMI]) and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) score, with additional data collected on the number of levels fused, sacral spine involvement, revision rates, and use of dual-mobility liners. Year of surgery was also included in analyses to account for any changes that may have occurred during the study period.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed in SAS 9.4. Patients were grouped into 2 cohorts, depending on whether they had received LSF prior to THA. Analyses were adjusted for repeated measures to account for the small percentage of patients with bilateral procedures.
Univariate comparisons between cohorts for covariates, as well as rates of dislocation and revision, were performed using the independent samples t test for continuous variables and the Fisher exact test for dichotomous categorical variables. Significant comorbidities, as well as age, sex, BMI, liner type, LSF cohort, and surgery year, were included in a logistic regression model to determine what effect, if any, they had on the likelihood of dislocation. Variables were removed using a backward stepwise approach, starting with the nonsignificant variable effect with the lowest χ2 value, and continuing until reaching a final model where all remaining variable effects were significant. For the variables retained in the final model, odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs were derived, with dislocation designated as the event. Individual comorbidity subcomponents of the CCI were also analyzed for their effects on dislocation using backward stepwise logistic regression. A secondary analysis among patients with LSF tested for the influence of the number of vertebral levels fused, the presence or absence of sacral involvement in the fusion, and the use of dual-mobility liners on the likelihood of hip dislocation.
Results
The LSF cohort included 39 patients with THA and prior LSF, 3 of whom had bilateral procedures, for a total of 42 hips. The non-LSF cohort included 813 patients with THA, 112 of whom had bilateral procedures, for a total of 925 hips. The LSF and non-LSF cohorts did not differ significantly in age, sex, BMI, CCI, or revision rates (Table). The LSF cohort included a significantly higher percentage of hips receiving dual-mobility liners than did the non-LSF cohort (23.8% vs 0.6%; P < .001) and had more than twice the rate of dislocation (4 of 42 hips [9.5%] vs 35 of 925 hips [3.8%]), although this difference was not statistically significant (P = .08).

The final logistic regression model with dislocation as the outcome was statistically significant (χ2, 17.47; P < .001) and retained 2 significant predictor variables: LSF cohort (χ2, 4.63; P = .03), and sex (χ2, 18.27; P < .001). Females were more likely than males to experience dislocation (OR, 5.84; 95% CI, 2.60-13.13; P < .001) as were patients who had LSF prior to THA (OR, 3.42; 95% CI, 1.12-10.47; P = .03) (Figure). None of the CCI subcomponent comorbidities significantly affected the probability of dislocation (myocardial infarction, P = .46; congestive heart failure, P = .47; peripheral vascular disease, P = .97; stroke, P = .51; dementia, P = .99; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, P = .95; connective tissue disease, P = .25; peptic ulcer, P = .41; liver disease, P = .30; diabetes, P = .06; hemiplegia, P = .99; chronic kidney disease, P = .82; solid tumor, P = .90; leukemia, P = .99; lymphoma, P = .99; AIDS, P = .99). Within the LSF cohort, neither the number of levels fused (P = .83) nor sacral involvement (P = .42), significantly affected the probability of hip dislocation. None of the patients in either cohort who received dual-mobility liners subsequently dislocated their hips, nor did any of them require revision surgery.

Discussion
Spinopelvic biomechanics have been an area of increasing interest and research. Spinal fusion has been shown to alter the mobility of the pelvis and has been associated with decreased stability of THA implants.21 For example, in the setting of a fused spine, the lack of compensatory changes in pelvic tilt or acetabular anteversion when adjusting to a seated or standing position may predispose patients to impingement because the acetabular component is not properly positioned. Dual-mobility constructs mitigate this risk by providing an additional articulation, which increases jump distance and range of motion prior to impingement, thereby enhancing stability.
The use of dual-mobility liners in patients with LSF has also been examined.18-20 These studies demonstrate a reduced risk of postoperative THA dislocation in patients with previous LSF. The rate of postoperative complications and revisions for LSF patients with dual-mobility liners was also found to be similar to that of THAs without dual-mobility in patients without prior LSF. This study focused on a veteran population to demonstrate the efficacy of dual-mobility liners in patients with LSF. The results indicate that LSF prior to THA and female sex were predictors for prosthetic hip dislocations in the 12-month postoperative period in this patient population, which aligns with the current literature.
The dislocation rate in the LSF-THA group (9.5%) was higher than the dislocation rate in the control group (3.8%). Although not statistically significant in the univariate analysis, LSF was shown to be a significant risk factor after controlling for patient sex. Other studies have found the dislocation rate to be 3% to 7%, which is lower than the dislocation rate observed in this study.8,10,16
The reasons for this higher rate of dislocation are not entirely clear. A veteran population has poorer overall health than the general population, which may contribute to the higher than previously reported dislocation rates.22 These results can be applied to the management of veterans seeking THA.
There have been conflicting reports regarding the impact a patient’s sex has on THA outcomes in the general population.23-26 This study found that female patients had higher rates of dislocation within 1 year of THA than male patients. This difference, which could be due to differences in baseline anatomic hip morphology between the sexes; females tend to have smaller femoral head sizes and less offset compared with males.27,28 However, this finding could have been confounded by the small number of female veterans in the study cohort.
A type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) diagnosis, which is a component of CCI, trended toward increased risk of prosthetic hip dislocation. Multiple studies have also discussed the increased risk of postoperative infections and revisions following THA in patients with T2DM.29-31 One study found T2DM to be an independent risk factor for immediate in-hospital postoperative complications following hip arthroplasty.32
Another factor that may influence postoperative dislocation risk is surgical approach. The posterior approach has historically been associated with higher rates of instability when compared to anterior or lateral THA.33 Researchers have also looked at the role that surgical approach plays in patients with prior LSF. Huebschmann et al confirmed that not only is LSF a significant risk factor for dislocation following THA, but anterior and laterally based surgical approaches may mitigate this risk.34
Limitations
As a retrospective cohort study, the reliability of the data hinges on complete documentation. Documentation of all encounters for dislocations was obtained from the VA Computerized Patient Record System, which may have led to some dislocation events being missed. However, as long as there was adequate postoperative follow-up, it was assumed all events outside the VA were included. Another limitation of this study was that male patients greatly outnumbered female patients, and this fact could limit the generalizability of findings to the population as a whole.
Conclusions
This study in a veteran population found that prior LSF and female sex were significant predictors for postoperative dislocation within 1 year of THA surgery. Additionally, the use of a dual-mobility liner was found to be protective against postoperative dislocation events. These data allow clinicians to better counsel veterans on the risk factors associated with postoperative dislocation and strategies to mitigate this risk.
- Sloan M, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. Projected volume of primary total joint arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100:1455-1460. doi:10.2106/JBJS.17.01617
- Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:128-133. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00155
- Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Schmier J, et al. Future clinical and economic impact of revision total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:144-151. doi:10.2106/JBJS.G.00587
- Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Schmier J, et al. Primary and revision arthroplasty surgery caseloads in the United States from 1990 to 2004. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:195-203. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2007.11.015
- Yamato Y, Furuhashi H, Hasegawa T, et al. Simulation of implant impingement after spinal corrective fusion surgery in patients with previous total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective case series. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46:512-519. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000003836
- Mudrick CA, Melvin JS, Springer BD. Late posterior hip instability after lumbar spinopelvic fusion. Arthroplast Today. 2015;1:25-29. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2015.05.002
- Diebo BG, Beyer GA, Grieco PW, et al. Complications in patients undergoing spinal fusion after THA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476:412-417.doi:10.1007/s11999.0000000000000009 8.
- Sing DC, Barry JJ, Aguilar TU, et al. Prior lumbar spinal arthrodesis increases risk of prosthetic-related complication in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31:227-232.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2016.02.069
- King CA, Landy DC, Martell JM, et al. Time to dislocation analysis of lumbar spine fusion following total hip arthroplasty: breaking up a happy home. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:3768-3772. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.08.029
- Buckland AJ, Puvanesarajah V, Vigdorchik J, et al. Dislocation of a primary total hip arthroplasty is more common in patients with a lumbar spinal fusion. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B:585-591.doi:10.1302/0301-620X.99B5.BJJ-2016-0657.R1
- Pirruccio K, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. The burden of prosthetic hip dislocations in the United States is projected to significantly increase by 2035. Hip Int. 2021;31:714-721. doi:10.1177/1120700020923619
- Salib CG, Reina N, Perry KI, et al. Lumbar fusion involving the sacrum increases dislocation risk in primary total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B:198-206. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.101B2.BJJ-2018-0754.R1
- An VVG, Phan K, Sivakumar BS, et al. Prior lumbar spinal fusion is associated with an increased risk of dislocation and revision in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:297-300. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2017.08.040
- Klemt C, Padmanabha A, Tirumala V, et al. Lumbar spine fusion before revision total hip arthroplasty is associated with increased dislocation rates. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29:e860-e868. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-20-00824
- Gausden EB, Parhar HS, Popper JE, et al. Risk factors for early dislocation following primary elective total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:1567-1571. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2017.12.034
- Malkani AL, Himschoot KJ, Ong KL, et al. Does timing of primary total hip arthroplasty prior to or after lumbar spine fusion have an effect on dislocation and revision rates?. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:907-911. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.01.009
- Parilla FW, Shah RR, Gordon AC, et al. Does it matter: total hip arthroplasty or lumbar spinal fusion first? Preoperative sagittal spinopelvic measurements guide patient-specific surgical strategies in patients requiring both. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:2652-2662. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.05.053
- Chalmers BP, Syku M, Sculco TP, et al. Dual-mobility constructs in primary total hip arthroplasty in high-risk patients with spinal fusions: our institutional experience. Arthroplast Today. 2020;6:749-754. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2020.07.024
- Nessler JM, Malkani AL, Sachdeva S, et al. Use of dual mobility cups in patients undergoing primary total hip arthroplasty with prior lumbar spine fusion. Int Orthop. 2020;44:857-862. doi:10.1007/s00264-020-04507-y
- Nessler JM, Malkani AL, Yep PJ, et al. Dislocation rates of primary total hip arthroplasty in patients with prior lumbar spine fusion and lumbar degenerative disk disease with and without utilization of dual mobility cups: an American Joint Replacement Registry study. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2023;31:e271-e277. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-22-00767
- Phan D, Bederman SS, Schwarzkopf R. The influence of sagittal spinal deformity on anteversion of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B:1017-1023. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.97B8.35700
- Agha Z, Lofgren RP, VanRuiswyk JV, et al. Are patients at Veterans Affairs medical centers sicker? A comparative analysis of health status and medical resource use. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:3252-3257. doi:10.1001/archinte.160.21.325223.
- Basques BA, Bell JA, Fillingham YA, et al. Gender differences for hip and knee arthroplasty: complications and healthcare utilization. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:1593-1597.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.03.064
- Kim YH, Choi Y, Kim JS. Influence of patient-, design-, and surgery-related factors on rate of dislocation after primary cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:1258-1263. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2009.03.017
- Chen A, Paxton L, Zheng X, et al. Association of sex with risk of 2-year revision among patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2110687. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10687
- Inacio MCS, Ake CF, Paxton EW, et al. Sex and risk of hip implant failure: assessing total hip arthroplasty outcomes in the United States. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:435-441. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.3271
- Karlson EW, Daltroy LH, Liang MH, et al. Gender differences in patient preferences may underlie differential utilization of elective surgery. Am J Med. 1997;102:524-530. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(97)00050-8
- Kostamo T, Bourne RB, Whittaker JP, et al. No difference in gender-specific hip replacement outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:135-140. doi:10.1007/s11999-008-0466-2
- Papagelopoulos PJ, Idusuyi OB, Wallrichs SL, et al. Long term outcome and survivorship analysis of primary total knee arthroplasty in patients with diabetes mellitus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(330):124-132. doi:10.1097/00003086-199609000-00015
- Fitzgerald RH Jr, Nolan DR, Ilstrup DM, et al. Deep wound sepsis following total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59:847-855.
- Blom AW, Brown J, Taylor AH, et al. Infection after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86:688-691. doi:10.1302/0301-620x.86b5.14887
- Jain NB, Guller U, Pietrobon R, et al. Comorbidities increase complication rates in patients having arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;435:232-238. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000156479.97488.a2
- Docter S, Philpott HT, Godkin L, et al. Comparison of intra and post-operative complication rates among surgical approaches in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop. 2020;20:310-325. doi:10.1016/j.jor.2020.05.008
- Huebschmann NA, Lawrence KW, Robin JX, et al. Does surgical approach affect dislocation rate after total hip arthroplasty in patients who have prior lumbar spinal fusion? A retrospective analysis of 16,223 cases. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39:S306-S313. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2024.03.068
- Sloan M, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. Projected volume of primary total joint arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100:1455-1460. doi:10.2106/JBJS.17.01617
- Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:128-133. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00155
- Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Schmier J, et al. Future clinical and economic impact of revision total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:144-151. doi:10.2106/JBJS.G.00587
- Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Schmier J, et al. Primary and revision arthroplasty surgery caseloads in the United States from 1990 to 2004. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:195-203. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2007.11.015
- Yamato Y, Furuhashi H, Hasegawa T, et al. Simulation of implant impingement after spinal corrective fusion surgery in patients with previous total hip arthroplasty: a retrospective case series. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46:512-519. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000003836
- Mudrick CA, Melvin JS, Springer BD. Late posterior hip instability after lumbar spinopelvic fusion. Arthroplast Today. 2015;1:25-29. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2015.05.002
- Diebo BG, Beyer GA, Grieco PW, et al. Complications in patients undergoing spinal fusion after THA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476:412-417.doi:10.1007/s11999.0000000000000009 8.
- Sing DC, Barry JJ, Aguilar TU, et al. Prior lumbar spinal arthrodesis increases risk of prosthetic-related complication in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31:227-232.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2016.02.069
- King CA, Landy DC, Martell JM, et al. Time to dislocation analysis of lumbar spine fusion following total hip arthroplasty: breaking up a happy home. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:3768-3772. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.08.029
- Buckland AJ, Puvanesarajah V, Vigdorchik J, et al. Dislocation of a primary total hip arthroplasty is more common in patients with a lumbar spinal fusion. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B:585-591.doi:10.1302/0301-620X.99B5.BJJ-2016-0657.R1
- Pirruccio K, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. The burden of prosthetic hip dislocations in the United States is projected to significantly increase by 2035. Hip Int. 2021;31:714-721. doi:10.1177/1120700020923619
- Salib CG, Reina N, Perry KI, et al. Lumbar fusion involving the sacrum increases dislocation risk in primary total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B:198-206. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.101B2.BJJ-2018-0754.R1
- An VVG, Phan K, Sivakumar BS, et al. Prior lumbar spinal fusion is associated with an increased risk of dislocation and revision in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:297-300. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2017.08.040
- Klemt C, Padmanabha A, Tirumala V, et al. Lumbar spine fusion before revision total hip arthroplasty is associated with increased dislocation rates. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29:e860-e868. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-20-00824
- Gausden EB, Parhar HS, Popper JE, et al. Risk factors for early dislocation following primary elective total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:1567-1571. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2017.12.034
- Malkani AL, Himschoot KJ, Ong KL, et al. Does timing of primary total hip arthroplasty prior to or after lumbar spine fusion have an effect on dislocation and revision rates?. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:907-911. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.01.009
- Parilla FW, Shah RR, Gordon AC, et al. Does it matter: total hip arthroplasty or lumbar spinal fusion first? Preoperative sagittal spinopelvic measurements guide patient-specific surgical strategies in patients requiring both. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:2652-2662. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.05.053
- Chalmers BP, Syku M, Sculco TP, et al. Dual-mobility constructs in primary total hip arthroplasty in high-risk patients with spinal fusions: our institutional experience. Arthroplast Today. 2020;6:749-754. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2020.07.024
- Nessler JM, Malkani AL, Sachdeva S, et al. Use of dual mobility cups in patients undergoing primary total hip arthroplasty with prior lumbar spine fusion. Int Orthop. 2020;44:857-862. doi:10.1007/s00264-020-04507-y
- Nessler JM, Malkani AL, Yep PJ, et al. Dislocation rates of primary total hip arthroplasty in patients with prior lumbar spine fusion and lumbar degenerative disk disease with and without utilization of dual mobility cups: an American Joint Replacement Registry study. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2023;31:e271-e277. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-22-00767
- Phan D, Bederman SS, Schwarzkopf R. The influence of sagittal spinal deformity on anteversion of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B:1017-1023. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.97B8.35700
- Agha Z, Lofgren RP, VanRuiswyk JV, et al. Are patients at Veterans Affairs medical centers sicker? A comparative analysis of health status and medical resource use. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:3252-3257. doi:10.1001/archinte.160.21.325223.
- Basques BA, Bell JA, Fillingham YA, et al. Gender differences for hip and knee arthroplasty: complications and healthcare utilization. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34:1593-1597.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2019.03.064
- Kim YH, Choi Y, Kim JS. Influence of patient-, design-, and surgery-related factors on rate of dislocation after primary cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24:1258-1263. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2009.03.017
- Chen A, Paxton L, Zheng X, et al. Association of sex with risk of 2-year revision among patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2110687. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10687
- Inacio MCS, Ake CF, Paxton EW, et al. Sex and risk of hip implant failure: assessing total hip arthroplasty outcomes in the United States. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:435-441. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.3271
- Karlson EW, Daltroy LH, Liang MH, et al. Gender differences in patient preferences may underlie differential utilization of elective surgery. Am J Med. 1997;102:524-530. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(97)00050-8
- Kostamo T, Bourne RB, Whittaker JP, et al. No difference in gender-specific hip replacement outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:135-140. doi:10.1007/s11999-008-0466-2
- Papagelopoulos PJ, Idusuyi OB, Wallrichs SL, et al. Long term outcome and survivorship analysis of primary total knee arthroplasty in patients with diabetes mellitus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(330):124-132. doi:10.1097/00003086-199609000-00015
- Fitzgerald RH Jr, Nolan DR, Ilstrup DM, et al. Deep wound sepsis following total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59:847-855.
- Blom AW, Brown J, Taylor AH, et al. Infection after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86:688-691. doi:10.1302/0301-620x.86b5.14887
- Jain NB, Guller U, Pietrobon R, et al. Comorbidities increase complication rates in patients having arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;435:232-238. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000156479.97488.a2
- Docter S, Philpott HT, Godkin L, et al. Comparison of intra and post-operative complication rates among surgical approaches in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop. 2020;20:310-325. doi:10.1016/j.jor.2020.05.008
- Huebschmann NA, Lawrence KW, Robin JX, et al. Does surgical approach affect dislocation rate after total hip arthroplasty in patients who have prior lumbar spinal fusion? A retrospective analysis of 16,223 cases. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39:S306-S313. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2024.03.068
Effects of Lumbar Fusion and Dual-Mobility Liners on Dislocation Rates Following Total Hip Arthroplasty in a Veteran Population
Effects of Lumbar Fusion and Dual-Mobility Liners on Dislocation Rates Following Total Hip Arthroplasty in a Veteran Population
A Candida Glabrata-Associated Prosthetic Joint Infection: Case Report and Literature Review
A Candida Glabrata-Associated Prosthetic Joint Infection: Case Report and Literature Review
Prosthetic joint infection (PJI) occurs in about 1% to 2% of joint replacements. 1 Risk factors include immunosuppression, diabetes, chronic illnesses, and prolonged operative time.2 Bacterial infections constitute most of these infections, while fungal pathogens account for about 1%. Candida (C.) species, predominantly C. albicans, are responsible for most PJIs.1,3 In contrast, C. glabrata is a rare cause of fungal PJI, with only 18 PJI cases currently reported in the literature.4 C. glabrata PJI occurs more frequently among immunosuppressed patients and is associated with a higher treatment failure rate despite antifungal therapy.5 Treatment of fungal PJI is often complicated, involving multiple surgical debridements, prolonged antifungal therapy, and in some cases, prosthesis removal.6 However, given the rarity of C. glabrata as a PJI pathogen, no standardized treatment guidelines exist, leading to potential delays in diagnosis and tailored treatment.7,8
CASE PRESENTATION
A male Vietnam veteran aged 75 years presented to the emergency department in July 2023 with a fluid collection over his left hip surgical incision site. The patient had a complex medical history that included chronic kidney disease, well-controlled type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and osteoarthritis. His history was further complicated by nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with hepatocellular carcinoma that was treated with transarterial radioembolization and yttrium-90. The patient had undergone a left total hip arthroplasty in 1996 and subsequent open reduction and internal fixation about 9 months prior to his presentation. The patient reported the fluid had been present for about 6 weeks, while he received outpatient monitoring by the orthopedic surgery service. He sought emergency care after noting a moderate amount of purulent discharge on his clothing originating from his hip. In the week prior to admission, the patient observed progressive erythema, warmth, and tenderness over the incision site. Despite these symptoms, the patient remained ambulatory and able to walk long distances with the use of an assistive device.
Upon presentation, the patient was afebrile and normotensive. Laboratory testing revealed an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 77 mm/h (reference range, 0-20 mm/h) and a C-reactive protein of 9.8 mg/L (reference range, 0-2.5 mg/L), suggesting an underlying infectious process. A physical examination revealed a well-healed incision over the left hip with a poorly defined area of fluctuance and evidence of wound dehiscence. The left lower extremity was swollen with 2+ pitting edema, but tenderness was localized to the incision site. Magnetic resonance imaging of the left hip revealed a multiloculated fluid collection abutting the left greater trochanter with extension to the skin surface and inferior extension along the entire length of the surgical fixation hardware (Figure).
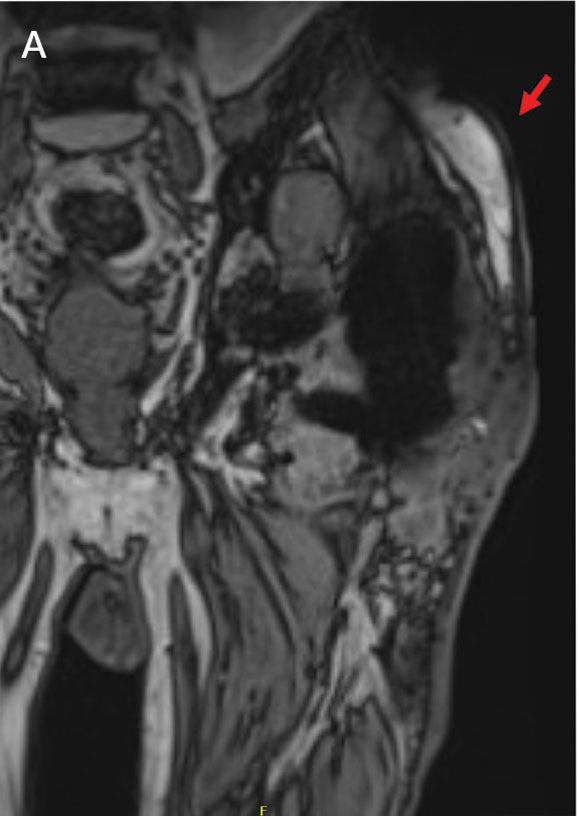
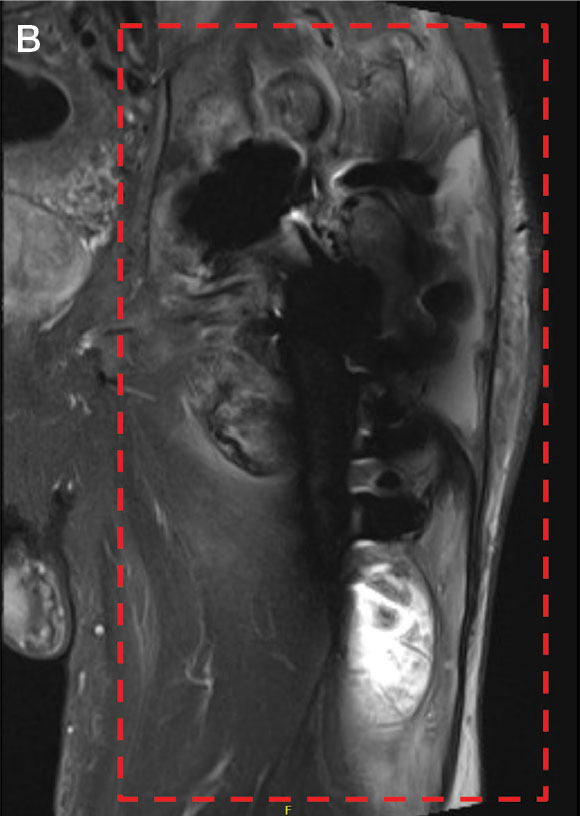
Upon admission, orthopedic surgery performed a bedside aspiration of the fluid collection. Samples were sent for analysis, including cell count and bacterial and fungal cultures. Initial blood cultures were sterile. Due to concerns for a bacterial infection, the patient was started on empiric intravenous (IV) ceftriaxone 2 g/day and IV vancomycin 1250 mg/day. Synovial fluid analysis revealed an elevated white blood cell count of 45,000/ìL, but bacterial cultures were negative. Five days after admission, the fungal culture from the left hip wound was notable for presence of C. glabrata, prompting an infectious diseases (ID) consultation. IV micafungin 100 mg/day was initiated as empiric antifungal therapy.
ID and orthopedic surgery teams determined that a combined medical and surgical approach would be best suited for infection control. They proposed 2 main approaches: complete hardware replacement with washout, which carried a higher morbidity risk but a better chance of infection resolution, or partial hardware replacement with washout, which was associated with a lower morbidity risk but a higher risk of infection persistence and recurrence. This decision was particularly challenging for the patient, who prioritized maintaining his functional status, including his ability to continue dancing for pleasure. The patient opted for a more conservative approach, electing to proceed with antifungal therapy and debridement while retaining the prosthetic joint.
After 11 days of hospitalization, the patient was discharged with a peripherally inserted central catheter for long-term antifungal infusions of micafungin 150 mg/day at home. Fungal sensitivity test results several days after discharge confirmed susceptibility to micafungin.
About 2 weeks after discharge, the patient underwent debridement and implant retention (DAIR). Wound cultures were positive for C. glabrata, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Corynebacterium tuberculostearicum. Based on susceptibilities, he completed a 2-month course of IV micafungin 150 mg daily and daptomycin 750 mg daily, followed by an oral suppressive regimen consisting of doxycycline 100 mg twice daily, amoxicillin-clavulanate 2 g twice daily, and fluconazole initially 800 mg daily adjusted to 400 mg daily. The patient continued wound management with twice-daily dressing changes.
Nine months after DAIR, the patient remained on suppressive antifungal and antibacterial therapy. He continued to experience serous drainage from the wound, which greatly affected his quality of life. After discussion with his family and the orthopedic surgery team, he agreed to proceed with a 2-staged revision arthroplasty involving prosthetic explant and antibiotic spacer placement. However, the surgery was postponed due to findings of anemia (hemoglobin, 8.9 g/dL) and thrombocytopenia (platelet count, 73 x 103/λL). At the time of this report, the patient was being monitored closely with his multidisciplinary care team for the planned orthopedic procedure.
DISCUSSION
PJI is the most common cause of primary hip arthroplasty failure; however, fungal species only make up about 1% of PJIs.3,9-11 Patients are typically immunocompromised, undergoing antineoplastic therapies for malignancy, or have other comorbid conditions such as diabetes.12,13 C. glabrata presents a unique diagnostic and therapeutic challenge as it is not only rare but also notorious for its resistance to common antifungal agents. C. glabrata is known to develop multidrug resistance through the rapid accumulation of genomic mutations.14 Its propensity towards forming protective biofilm also arms it with intrinsic resistance to agents like fluconazole.15 Furthermore, based on a review of the available reports in the literature, C. glabrata PJIs are often insidious and present with symptoms closely mimicking those of bacterial PJIs, as it did in the patient in this case.16
Synovial fluid analysis, fungal cultures, and sensitivity testing are paramount for ensuring proper diagnosis for fungal PJI. The patient in this case was empirically treated with micafungin based on recommendations from the ID team. When the sensitivities results were reviewed, the same antifungal therapy was continued. Echinocandins have a favorable toxicity profile in long-term use, as well as efficacy against biofilm-producing organisms like C. glabrata.17,18
While there are a few cases citing DAIR as a feasible surgical strategy for treating fungal PJI, more recent studies have reported greater success with a 2-staged revision arthroplasty involving some combination of debridement, placement of antibiotic-loaded bone cement spacers, and partial or total exchange of the infected prosthetic joint.4,19-23 In this case, complete hardware replacement would have offered the patient the most favorable outlook for eliminating this fungal infection. However, given the patient’s advanced age, significant underlying comorbidities, and functional status, medical management with antifungal therapy and DAIR was favored.
Based on the discussion from the 6-month follow-up visit, the patient was experiencing progressive and persistent wound drainage and frequent dressing changes, highlighting the limitations of medical management for PJI in the setting of retained prosthesis. If the patient ultimately proceeds with a more invasive surgical intervention, another important consideration will be the likelihood of fungal PJI recurrence. At present, fungal PJI recurrence rates following antifungal and surgical treatment have been reported to range between 0% to 50%, which is too imprecise to be considered clinically useful.22-24
Given the ambiguity surrounding management guidelines and limited treatment options, it is crucial to emphasize the timeline of this patient’s clinical presentation and subsequent course of treatment. Upon presentation to the ED in late July, fungal PJI was considered less likely. Initial blood cultures from presentation were negative, which is common with PJIs. It was not until 5 days later that the left hip wound culture showed moderate growth of C. glabrata. Identifying a PJI is clinically challenging due to the lack of standardized diagnostic criteria. However, timely identification and diagnosis of fungal PJI with appropriate antifungal therapy, in patients with limited curative options due to comorbidities, can significantly improve quality of life and overall outcomes.25 Routine fungal and mycobacterial cultures are not currently recommended in PJI guidelines, but this case illustrates it is imperative in immunocompromised hosts.26
This case and the current paucity of similar cases in the literature stress the importance of clinicians publishing their experience in the management of fungal PJI. We strongly recommend that clinicians approach each suspected PJI with careful consideration of the patient’s unique risk factors, comorbidities, and goals of care, when deciding on a curative vs suppressive approach to therapy.
CONCLUSIONS
This case report highlights the importance of considering fungal pathogens for PJIs, especially in high-risk patients, the value of obtaining fungal cultures, the necessity of a multidisciplinary approach, the role of antifungal susceptibility testing, and consideration for the feasibility of a surgical intervention. It underscores the challenges in diagnosis and treatment of C. glabrata-associated PJI, emphasizing the importance of clinician experience-sharing in developing evidence-based management strategies. As the understanding of fungal PJI evolves, continued research and clinical data collection remain crucial for improving patient outcomes in the management of these complex cases.
- Osmon DR, Berbari EF, Berendt AR, et al. Executive summary: diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(1):1-10. doi:10.1093/cid/cis966
- Eka A, Chen AF. Patient-related medical risk factors for periprosthetic joint infection of the hip and knee. Ann Transl Med. 2015;3(16):233. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.09.26
- Darouiche RO, Hamill RJ, Musher DM, Young EJ, Harris RL. Periprosthetic candidal infections following arthroplasty. Rev Infect Dis. 1989;11(1):89-96. doi:10.1093/clinids/11.1.89
- Koutserimpas C, Zervakis SG, Maraki S, et al. Non-albicans Candida prosthetic joint infections: a systematic review of treatment. World J Clin Cases. 2019;7(12):1430- 1443. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v7.i12.1430
- Fidel PL Jr, Vazquez JA, Sobel JD. Candida glabrata: review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and clinical disease with comparison to C. albicans. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999;12(1):80-96. doi:10.1128/CMR.12.1.80
- Aboltins C, Daffy J, Choong P, Stanley P. Current concepts in the management of prosthetic joint infection. Intern Med J. 2014;44(9):834-840. doi:10.1111/imj.12510
- Lee YR, Kim HJ, Lee EJ, Sohn JW, Kim MJ, Yoon YK. Prosthetic joint infections caused by candida species: a systematic review and a case series. Mycopathologia. 2019;184(1):23-33. doi:10.1007/s11046-018-0286-1
- Herndon CL, Rowe TM, Metcalf RW, et al. Treatment outcomes of fungal periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38(11):2436-2440.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.05.009
- Delaunay C, Hamadouche M, Girard J, Duhamel A; SoFCOT. What are the causes for failures of primary hip arthroplasties in France? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(12): 3863-3869. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-2935-5
- Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, Ong K, Vail TP, Berry DJ. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(1): 128-133. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00155
- Furnes O, Lie SA, Espehaug B, Vollset SE, Engesaeter LB, Havelin LI. Hip disease and the prognosis of total hip replacements. A review of 53,698 primary total hip replacements reported to the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register 1987-99. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83(4):579-586. doi:10.1302/0301-620x.83b4.11223
- Gonzalez MR, Bedi ADS, Karczewski D, Lozano-Calderon SA. Treatment and outcomes of fungal prosthetic joint infections: a systematic review of 225 cases. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38(11):2464-2471.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.05.003
- Gonzalez MR, Pretell-Mazzini J, Lozano-Calderon SA. Risk factors and management of prosthetic joint infections in megaprostheses-a review of the literature. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023;13(1):25. doi:10.3390/antibiotics13010025
- Biswas C, Chen SC, Halliday C, et al. Identification of genetic markers of resistance to echinocandins, azoles and 5-fluorocytosine in Candida glabrata by next-generation sequencing: a feasibility study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017;23(9):676.e7-676.e10. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2017.03.014
- Hassan Y, Chew SY, Than LTL. Candida glabrata: pathogenicity and resistance mechanisms for adaptation and survival. J Fungi (Basel). 2021;7(8):667. doi:10.3390/jof7080667
- Aboltins C, Daffy J, Choong P, Stanley P. Current concepts in the management of prosthetic joint infection. Intern Med J. 2014;44(9):834-840. doi:10.1111/imj.12510
- Pierce CG, Uppuluri P, Tristan AR, et al. A simple and reproducible 96-well plate-based method for the formation of fungal biofilms and its application to antifungal susceptibility testing. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(9):1494-1500. doi:10.1038/nport.2008.141
- Koutserimpas C, Samonis G, Velivassakis E, Iliopoulou- Kosmadaki S, Kontakis G, Kofteridis DP. Candida glabrata prosthetic joint infection, successfully treated with anidulafungin: a case report and review of the literature. Mycoses. 2018;61(4):266-269. doi:10.1111/myc.12736
- Brooks DH, Pupparo F. Successful salvage of a primary total knee arthroplasty infected with Candida parapsilosis. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13(6):707-712. doi:10.1016/s0883-5403(98)80017-x
- Merrer J, Dupont B, Nieszkowska A, De Jonghe B, Outin H. Candida albicans prosthetic arthritis treated with fluconazole alone. J Infect. 2001;42(3):208-209. doi:10.1053/jinf.2001.0819
- Koutserimpas C, Naoum S, Alpantaki K, et al. Fungal prosthetic joint infection in revised knee arthroplasty: an orthopaedic surgeon’s nightmare. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12(7):1606. doi:10.3390/diagnostics12071606
- Gao Z, Li X, Du Y, Peng Y, Wu W, Zhou Y. Success rate of fungal peri-prosthetic joint infection treated by 2-stage revision and potential risk factors of treatment failure: a retrospective study. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:5549-5557. doi:10.12659/MSM.909168
- Hwang BH, Yoon JY, Nam CH, et al. Fungal periprosthetic joint infection after primary total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(5):656-659. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.94B5.28125
- Ueng SW, Lee CY, Hu CC, Hsieh PH, Chang Y. What is the success of treatment of hip and knee candidal periprosthetic joint infection? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(9):3002-3009. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-3007-6
- Nodzo, Scott R. MD; Bauer, Thomas MD, PhD; Pottinger, et al. Conventional diagnostic challenges in periprosthetic joint infection. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23 Suppl:S18-S25. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00385
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Diagnosis and prevention of periprosthetic joint infections. March 11, 2019. Accessed February 5, 2025. https://www.aaos.org/pjicpg
Prosthetic joint infection (PJI) occurs in about 1% to 2% of joint replacements. 1 Risk factors include immunosuppression, diabetes, chronic illnesses, and prolonged operative time.2 Bacterial infections constitute most of these infections, while fungal pathogens account for about 1%. Candida (C.) species, predominantly C. albicans, are responsible for most PJIs.1,3 In contrast, C. glabrata is a rare cause of fungal PJI, with only 18 PJI cases currently reported in the literature.4 C. glabrata PJI occurs more frequently among immunosuppressed patients and is associated with a higher treatment failure rate despite antifungal therapy.5 Treatment of fungal PJI is often complicated, involving multiple surgical debridements, prolonged antifungal therapy, and in some cases, prosthesis removal.6 However, given the rarity of C. glabrata as a PJI pathogen, no standardized treatment guidelines exist, leading to potential delays in diagnosis and tailored treatment.7,8
CASE PRESENTATION
A male Vietnam veteran aged 75 years presented to the emergency department in July 2023 with a fluid collection over his left hip surgical incision site. The patient had a complex medical history that included chronic kidney disease, well-controlled type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and osteoarthritis. His history was further complicated by nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with hepatocellular carcinoma that was treated with transarterial radioembolization and yttrium-90. The patient had undergone a left total hip arthroplasty in 1996 and subsequent open reduction and internal fixation about 9 months prior to his presentation. The patient reported the fluid had been present for about 6 weeks, while he received outpatient monitoring by the orthopedic surgery service. He sought emergency care after noting a moderate amount of purulent discharge on his clothing originating from his hip. In the week prior to admission, the patient observed progressive erythema, warmth, and tenderness over the incision site. Despite these symptoms, the patient remained ambulatory and able to walk long distances with the use of an assistive device.
Upon presentation, the patient was afebrile and normotensive. Laboratory testing revealed an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 77 mm/h (reference range, 0-20 mm/h) and a C-reactive protein of 9.8 mg/L (reference range, 0-2.5 mg/L), suggesting an underlying infectious process. A physical examination revealed a well-healed incision over the left hip with a poorly defined area of fluctuance and evidence of wound dehiscence. The left lower extremity was swollen with 2+ pitting edema, but tenderness was localized to the incision site. Magnetic resonance imaging of the left hip revealed a multiloculated fluid collection abutting the left greater trochanter with extension to the skin surface and inferior extension along the entire length of the surgical fixation hardware (Figure).


Upon admission, orthopedic surgery performed a bedside aspiration of the fluid collection. Samples were sent for analysis, including cell count and bacterial and fungal cultures. Initial blood cultures were sterile. Due to concerns for a bacterial infection, the patient was started on empiric intravenous (IV) ceftriaxone 2 g/day and IV vancomycin 1250 mg/day. Synovial fluid analysis revealed an elevated white blood cell count of 45,000/ìL, but bacterial cultures were negative. Five days after admission, the fungal culture from the left hip wound was notable for presence of C. glabrata, prompting an infectious diseases (ID) consultation. IV micafungin 100 mg/day was initiated as empiric antifungal therapy.
ID and orthopedic surgery teams determined that a combined medical and surgical approach would be best suited for infection control. They proposed 2 main approaches: complete hardware replacement with washout, which carried a higher morbidity risk but a better chance of infection resolution, or partial hardware replacement with washout, which was associated with a lower morbidity risk but a higher risk of infection persistence and recurrence. This decision was particularly challenging for the patient, who prioritized maintaining his functional status, including his ability to continue dancing for pleasure. The patient opted for a more conservative approach, electing to proceed with antifungal therapy and debridement while retaining the prosthetic joint.
After 11 days of hospitalization, the patient was discharged with a peripherally inserted central catheter for long-term antifungal infusions of micafungin 150 mg/day at home. Fungal sensitivity test results several days after discharge confirmed susceptibility to micafungin.
About 2 weeks after discharge, the patient underwent debridement and implant retention (DAIR). Wound cultures were positive for C. glabrata, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Corynebacterium tuberculostearicum. Based on susceptibilities, he completed a 2-month course of IV micafungin 150 mg daily and daptomycin 750 mg daily, followed by an oral suppressive regimen consisting of doxycycline 100 mg twice daily, amoxicillin-clavulanate 2 g twice daily, and fluconazole initially 800 mg daily adjusted to 400 mg daily. The patient continued wound management with twice-daily dressing changes.
Nine months after DAIR, the patient remained on suppressive antifungal and antibacterial therapy. He continued to experience serous drainage from the wound, which greatly affected his quality of life. After discussion with his family and the orthopedic surgery team, he agreed to proceed with a 2-staged revision arthroplasty involving prosthetic explant and antibiotic spacer placement. However, the surgery was postponed due to findings of anemia (hemoglobin, 8.9 g/dL) and thrombocytopenia (platelet count, 73 x 103/λL). At the time of this report, the patient was being monitored closely with his multidisciplinary care team for the planned orthopedic procedure.
DISCUSSION
PJI is the most common cause of primary hip arthroplasty failure; however, fungal species only make up about 1% of PJIs.3,9-11 Patients are typically immunocompromised, undergoing antineoplastic therapies for malignancy, or have other comorbid conditions such as diabetes.12,13 C. glabrata presents a unique diagnostic and therapeutic challenge as it is not only rare but also notorious for its resistance to common antifungal agents. C. glabrata is known to develop multidrug resistance through the rapid accumulation of genomic mutations.14 Its propensity towards forming protective biofilm also arms it with intrinsic resistance to agents like fluconazole.15 Furthermore, based on a review of the available reports in the literature, C. glabrata PJIs are often insidious and present with symptoms closely mimicking those of bacterial PJIs, as it did in the patient in this case.16
Synovial fluid analysis, fungal cultures, and sensitivity testing are paramount for ensuring proper diagnosis for fungal PJI. The patient in this case was empirically treated with micafungin based on recommendations from the ID team. When the sensitivities results were reviewed, the same antifungal therapy was continued. Echinocandins have a favorable toxicity profile in long-term use, as well as efficacy against biofilm-producing organisms like C. glabrata.17,18
While there are a few cases citing DAIR as a feasible surgical strategy for treating fungal PJI, more recent studies have reported greater success with a 2-staged revision arthroplasty involving some combination of debridement, placement of antibiotic-loaded bone cement spacers, and partial or total exchange of the infected prosthetic joint.4,19-23 In this case, complete hardware replacement would have offered the patient the most favorable outlook for eliminating this fungal infection. However, given the patient’s advanced age, significant underlying comorbidities, and functional status, medical management with antifungal therapy and DAIR was favored.
Based on the discussion from the 6-month follow-up visit, the patient was experiencing progressive and persistent wound drainage and frequent dressing changes, highlighting the limitations of medical management for PJI in the setting of retained prosthesis. If the patient ultimately proceeds with a more invasive surgical intervention, another important consideration will be the likelihood of fungal PJI recurrence. At present, fungal PJI recurrence rates following antifungal and surgical treatment have been reported to range between 0% to 50%, which is too imprecise to be considered clinically useful.22-24
Given the ambiguity surrounding management guidelines and limited treatment options, it is crucial to emphasize the timeline of this patient’s clinical presentation and subsequent course of treatment. Upon presentation to the ED in late July, fungal PJI was considered less likely. Initial blood cultures from presentation were negative, which is common with PJIs. It was not until 5 days later that the left hip wound culture showed moderate growth of C. glabrata. Identifying a PJI is clinically challenging due to the lack of standardized diagnostic criteria. However, timely identification and diagnosis of fungal PJI with appropriate antifungal therapy, in patients with limited curative options due to comorbidities, can significantly improve quality of life and overall outcomes.25 Routine fungal and mycobacterial cultures are not currently recommended in PJI guidelines, but this case illustrates it is imperative in immunocompromised hosts.26
This case and the current paucity of similar cases in the literature stress the importance of clinicians publishing their experience in the management of fungal PJI. We strongly recommend that clinicians approach each suspected PJI with careful consideration of the patient’s unique risk factors, comorbidities, and goals of care, when deciding on a curative vs suppressive approach to therapy.
CONCLUSIONS
This case report highlights the importance of considering fungal pathogens for PJIs, especially in high-risk patients, the value of obtaining fungal cultures, the necessity of a multidisciplinary approach, the role of antifungal susceptibility testing, and consideration for the feasibility of a surgical intervention. It underscores the challenges in diagnosis and treatment of C. glabrata-associated PJI, emphasizing the importance of clinician experience-sharing in developing evidence-based management strategies. As the understanding of fungal PJI evolves, continued research and clinical data collection remain crucial for improving patient outcomes in the management of these complex cases.
Prosthetic joint infection (PJI) occurs in about 1% to 2% of joint replacements. 1 Risk factors include immunosuppression, diabetes, chronic illnesses, and prolonged operative time.2 Bacterial infections constitute most of these infections, while fungal pathogens account for about 1%. Candida (C.) species, predominantly C. albicans, are responsible for most PJIs.1,3 In contrast, C. glabrata is a rare cause of fungal PJI, with only 18 PJI cases currently reported in the literature.4 C. glabrata PJI occurs more frequently among immunosuppressed patients and is associated with a higher treatment failure rate despite antifungal therapy.5 Treatment of fungal PJI is often complicated, involving multiple surgical debridements, prolonged antifungal therapy, and in some cases, prosthesis removal.6 However, given the rarity of C. glabrata as a PJI pathogen, no standardized treatment guidelines exist, leading to potential delays in diagnosis and tailored treatment.7,8
CASE PRESENTATION
A male Vietnam veteran aged 75 years presented to the emergency department in July 2023 with a fluid collection over his left hip surgical incision site. The patient had a complex medical history that included chronic kidney disease, well-controlled type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and osteoarthritis. His history was further complicated by nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with hepatocellular carcinoma that was treated with transarterial radioembolization and yttrium-90. The patient had undergone a left total hip arthroplasty in 1996 and subsequent open reduction and internal fixation about 9 months prior to his presentation. The patient reported the fluid had been present for about 6 weeks, while he received outpatient monitoring by the orthopedic surgery service. He sought emergency care after noting a moderate amount of purulent discharge on his clothing originating from his hip. In the week prior to admission, the patient observed progressive erythema, warmth, and tenderness over the incision site. Despite these symptoms, the patient remained ambulatory and able to walk long distances with the use of an assistive device.
Upon presentation, the patient was afebrile and normotensive. Laboratory testing revealed an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 77 mm/h (reference range, 0-20 mm/h) and a C-reactive protein of 9.8 mg/L (reference range, 0-2.5 mg/L), suggesting an underlying infectious process. A physical examination revealed a well-healed incision over the left hip with a poorly defined area of fluctuance and evidence of wound dehiscence. The left lower extremity was swollen with 2+ pitting edema, but tenderness was localized to the incision site. Magnetic resonance imaging of the left hip revealed a multiloculated fluid collection abutting the left greater trochanter with extension to the skin surface and inferior extension along the entire length of the surgical fixation hardware (Figure).


Upon admission, orthopedic surgery performed a bedside aspiration of the fluid collection. Samples were sent for analysis, including cell count and bacterial and fungal cultures. Initial blood cultures were sterile. Due to concerns for a bacterial infection, the patient was started on empiric intravenous (IV) ceftriaxone 2 g/day and IV vancomycin 1250 mg/day. Synovial fluid analysis revealed an elevated white blood cell count of 45,000/ìL, but bacterial cultures were negative. Five days after admission, the fungal culture from the left hip wound was notable for presence of C. glabrata, prompting an infectious diseases (ID) consultation. IV micafungin 100 mg/day was initiated as empiric antifungal therapy.
ID and orthopedic surgery teams determined that a combined medical and surgical approach would be best suited for infection control. They proposed 2 main approaches: complete hardware replacement with washout, which carried a higher morbidity risk but a better chance of infection resolution, or partial hardware replacement with washout, which was associated with a lower morbidity risk but a higher risk of infection persistence and recurrence. This decision was particularly challenging for the patient, who prioritized maintaining his functional status, including his ability to continue dancing for pleasure. The patient opted for a more conservative approach, electing to proceed with antifungal therapy and debridement while retaining the prosthetic joint.
After 11 days of hospitalization, the patient was discharged with a peripherally inserted central catheter for long-term antifungal infusions of micafungin 150 mg/day at home. Fungal sensitivity test results several days after discharge confirmed susceptibility to micafungin.
About 2 weeks after discharge, the patient underwent debridement and implant retention (DAIR). Wound cultures were positive for C. glabrata, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Corynebacterium tuberculostearicum. Based on susceptibilities, he completed a 2-month course of IV micafungin 150 mg daily and daptomycin 750 mg daily, followed by an oral suppressive regimen consisting of doxycycline 100 mg twice daily, amoxicillin-clavulanate 2 g twice daily, and fluconazole initially 800 mg daily adjusted to 400 mg daily. The patient continued wound management with twice-daily dressing changes.
Nine months after DAIR, the patient remained on suppressive antifungal and antibacterial therapy. He continued to experience serous drainage from the wound, which greatly affected his quality of life. After discussion with his family and the orthopedic surgery team, he agreed to proceed with a 2-staged revision arthroplasty involving prosthetic explant and antibiotic spacer placement. However, the surgery was postponed due to findings of anemia (hemoglobin, 8.9 g/dL) and thrombocytopenia (platelet count, 73 x 103/λL). At the time of this report, the patient was being monitored closely with his multidisciplinary care team for the planned orthopedic procedure.
DISCUSSION
PJI is the most common cause of primary hip arthroplasty failure; however, fungal species only make up about 1% of PJIs.3,9-11 Patients are typically immunocompromised, undergoing antineoplastic therapies for malignancy, or have other comorbid conditions such as diabetes.12,13 C. glabrata presents a unique diagnostic and therapeutic challenge as it is not only rare but also notorious for its resistance to common antifungal agents. C. glabrata is known to develop multidrug resistance through the rapid accumulation of genomic mutations.14 Its propensity towards forming protective biofilm also arms it with intrinsic resistance to agents like fluconazole.15 Furthermore, based on a review of the available reports in the literature, C. glabrata PJIs are often insidious and present with symptoms closely mimicking those of bacterial PJIs, as it did in the patient in this case.16
Synovial fluid analysis, fungal cultures, and sensitivity testing are paramount for ensuring proper diagnosis for fungal PJI. The patient in this case was empirically treated with micafungin based on recommendations from the ID team. When the sensitivities results were reviewed, the same antifungal therapy was continued. Echinocandins have a favorable toxicity profile in long-term use, as well as efficacy against biofilm-producing organisms like C. glabrata.17,18
While there are a few cases citing DAIR as a feasible surgical strategy for treating fungal PJI, more recent studies have reported greater success with a 2-staged revision arthroplasty involving some combination of debridement, placement of antibiotic-loaded bone cement spacers, and partial or total exchange of the infected prosthetic joint.4,19-23 In this case, complete hardware replacement would have offered the patient the most favorable outlook for eliminating this fungal infection. However, given the patient’s advanced age, significant underlying comorbidities, and functional status, medical management with antifungal therapy and DAIR was favored.
Based on the discussion from the 6-month follow-up visit, the patient was experiencing progressive and persistent wound drainage and frequent dressing changes, highlighting the limitations of medical management for PJI in the setting of retained prosthesis. If the patient ultimately proceeds with a more invasive surgical intervention, another important consideration will be the likelihood of fungal PJI recurrence. At present, fungal PJI recurrence rates following antifungal and surgical treatment have been reported to range between 0% to 50%, which is too imprecise to be considered clinically useful.22-24
Given the ambiguity surrounding management guidelines and limited treatment options, it is crucial to emphasize the timeline of this patient’s clinical presentation and subsequent course of treatment. Upon presentation to the ED in late July, fungal PJI was considered less likely. Initial blood cultures from presentation were negative, which is common with PJIs. It was not until 5 days later that the left hip wound culture showed moderate growth of C. glabrata. Identifying a PJI is clinically challenging due to the lack of standardized diagnostic criteria. However, timely identification and diagnosis of fungal PJI with appropriate antifungal therapy, in patients with limited curative options due to comorbidities, can significantly improve quality of life and overall outcomes.25 Routine fungal and mycobacterial cultures are not currently recommended in PJI guidelines, but this case illustrates it is imperative in immunocompromised hosts.26
This case and the current paucity of similar cases in the literature stress the importance of clinicians publishing their experience in the management of fungal PJI. We strongly recommend that clinicians approach each suspected PJI with careful consideration of the patient’s unique risk factors, comorbidities, and goals of care, when deciding on a curative vs suppressive approach to therapy.
CONCLUSIONS
This case report highlights the importance of considering fungal pathogens for PJIs, especially in high-risk patients, the value of obtaining fungal cultures, the necessity of a multidisciplinary approach, the role of antifungal susceptibility testing, and consideration for the feasibility of a surgical intervention. It underscores the challenges in diagnosis and treatment of C. glabrata-associated PJI, emphasizing the importance of clinician experience-sharing in developing evidence-based management strategies. As the understanding of fungal PJI evolves, continued research and clinical data collection remain crucial for improving patient outcomes in the management of these complex cases.
- Osmon DR, Berbari EF, Berendt AR, et al. Executive summary: diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(1):1-10. doi:10.1093/cid/cis966
- Eka A, Chen AF. Patient-related medical risk factors for periprosthetic joint infection of the hip and knee. Ann Transl Med. 2015;3(16):233. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.09.26
- Darouiche RO, Hamill RJ, Musher DM, Young EJ, Harris RL. Periprosthetic candidal infections following arthroplasty. Rev Infect Dis. 1989;11(1):89-96. doi:10.1093/clinids/11.1.89
- Koutserimpas C, Zervakis SG, Maraki S, et al. Non-albicans Candida prosthetic joint infections: a systematic review of treatment. World J Clin Cases. 2019;7(12):1430- 1443. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v7.i12.1430
- Fidel PL Jr, Vazquez JA, Sobel JD. Candida glabrata: review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and clinical disease with comparison to C. albicans. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999;12(1):80-96. doi:10.1128/CMR.12.1.80
- Aboltins C, Daffy J, Choong P, Stanley P. Current concepts in the management of prosthetic joint infection. Intern Med J. 2014;44(9):834-840. doi:10.1111/imj.12510
- Lee YR, Kim HJ, Lee EJ, Sohn JW, Kim MJ, Yoon YK. Prosthetic joint infections caused by candida species: a systematic review and a case series. Mycopathologia. 2019;184(1):23-33. doi:10.1007/s11046-018-0286-1
- Herndon CL, Rowe TM, Metcalf RW, et al. Treatment outcomes of fungal periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38(11):2436-2440.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.05.009
- Delaunay C, Hamadouche M, Girard J, Duhamel A; SoFCOT. What are the causes for failures of primary hip arthroplasties in France? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(12): 3863-3869. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-2935-5
- Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, Ong K, Vail TP, Berry DJ. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(1): 128-133. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00155
- Furnes O, Lie SA, Espehaug B, Vollset SE, Engesaeter LB, Havelin LI. Hip disease and the prognosis of total hip replacements. A review of 53,698 primary total hip replacements reported to the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register 1987-99. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83(4):579-586. doi:10.1302/0301-620x.83b4.11223
- Gonzalez MR, Bedi ADS, Karczewski D, Lozano-Calderon SA. Treatment and outcomes of fungal prosthetic joint infections: a systematic review of 225 cases. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38(11):2464-2471.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.05.003
- Gonzalez MR, Pretell-Mazzini J, Lozano-Calderon SA. Risk factors and management of prosthetic joint infections in megaprostheses-a review of the literature. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023;13(1):25. doi:10.3390/antibiotics13010025
- Biswas C, Chen SC, Halliday C, et al. Identification of genetic markers of resistance to echinocandins, azoles and 5-fluorocytosine in Candida glabrata by next-generation sequencing: a feasibility study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017;23(9):676.e7-676.e10. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2017.03.014
- Hassan Y, Chew SY, Than LTL. Candida glabrata: pathogenicity and resistance mechanisms for adaptation and survival. J Fungi (Basel). 2021;7(8):667. doi:10.3390/jof7080667
- Aboltins C, Daffy J, Choong P, Stanley P. Current concepts in the management of prosthetic joint infection. Intern Med J. 2014;44(9):834-840. doi:10.1111/imj.12510
- Pierce CG, Uppuluri P, Tristan AR, et al. A simple and reproducible 96-well plate-based method for the formation of fungal biofilms and its application to antifungal susceptibility testing. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(9):1494-1500. doi:10.1038/nport.2008.141
- Koutserimpas C, Samonis G, Velivassakis E, Iliopoulou- Kosmadaki S, Kontakis G, Kofteridis DP. Candida glabrata prosthetic joint infection, successfully treated with anidulafungin: a case report and review of the literature. Mycoses. 2018;61(4):266-269. doi:10.1111/myc.12736
- Brooks DH, Pupparo F. Successful salvage of a primary total knee arthroplasty infected with Candida parapsilosis. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13(6):707-712. doi:10.1016/s0883-5403(98)80017-x
- Merrer J, Dupont B, Nieszkowska A, De Jonghe B, Outin H. Candida albicans prosthetic arthritis treated with fluconazole alone. J Infect. 2001;42(3):208-209. doi:10.1053/jinf.2001.0819
- Koutserimpas C, Naoum S, Alpantaki K, et al. Fungal prosthetic joint infection in revised knee arthroplasty: an orthopaedic surgeon’s nightmare. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12(7):1606. doi:10.3390/diagnostics12071606
- Gao Z, Li X, Du Y, Peng Y, Wu W, Zhou Y. Success rate of fungal peri-prosthetic joint infection treated by 2-stage revision and potential risk factors of treatment failure: a retrospective study. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:5549-5557. doi:10.12659/MSM.909168
- Hwang BH, Yoon JY, Nam CH, et al. Fungal periprosthetic joint infection after primary total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(5):656-659. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.94B5.28125
- Ueng SW, Lee CY, Hu CC, Hsieh PH, Chang Y. What is the success of treatment of hip and knee candidal periprosthetic joint infection? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(9):3002-3009. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-3007-6
- Nodzo, Scott R. MD; Bauer, Thomas MD, PhD; Pottinger, et al. Conventional diagnostic challenges in periprosthetic joint infection. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23 Suppl:S18-S25. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00385
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Diagnosis and prevention of periprosthetic joint infections. March 11, 2019. Accessed February 5, 2025. https://www.aaos.org/pjicpg
- Osmon DR, Berbari EF, Berendt AR, et al. Executive summary: diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(1):1-10. doi:10.1093/cid/cis966
- Eka A, Chen AF. Patient-related medical risk factors for periprosthetic joint infection of the hip and knee. Ann Transl Med. 2015;3(16):233. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.09.26
- Darouiche RO, Hamill RJ, Musher DM, Young EJ, Harris RL. Periprosthetic candidal infections following arthroplasty. Rev Infect Dis. 1989;11(1):89-96. doi:10.1093/clinids/11.1.89
- Koutserimpas C, Zervakis SG, Maraki S, et al. Non-albicans Candida prosthetic joint infections: a systematic review of treatment. World J Clin Cases. 2019;7(12):1430- 1443. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v7.i12.1430
- Fidel PL Jr, Vazquez JA, Sobel JD. Candida glabrata: review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and clinical disease with comparison to C. albicans. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1999;12(1):80-96. doi:10.1128/CMR.12.1.80
- Aboltins C, Daffy J, Choong P, Stanley P. Current concepts in the management of prosthetic joint infection. Intern Med J. 2014;44(9):834-840. doi:10.1111/imj.12510
- Lee YR, Kim HJ, Lee EJ, Sohn JW, Kim MJ, Yoon YK. Prosthetic joint infections caused by candida species: a systematic review and a case series. Mycopathologia. 2019;184(1):23-33. doi:10.1007/s11046-018-0286-1
- Herndon CL, Rowe TM, Metcalf RW, et al. Treatment outcomes of fungal periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38(11):2436-2440.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.05.009
- Delaunay C, Hamadouche M, Girard J, Duhamel A; SoFCOT. What are the causes for failures of primary hip arthroplasties in France? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(12): 3863-3869. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-2935-5
- Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, Ong K, Vail TP, Berry DJ. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(1): 128-133. doi:10.2106/JBJS.H.00155
- Furnes O, Lie SA, Espehaug B, Vollset SE, Engesaeter LB, Havelin LI. Hip disease and the prognosis of total hip replacements. A review of 53,698 primary total hip replacements reported to the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register 1987-99. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83(4):579-586. doi:10.1302/0301-620x.83b4.11223
- Gonzalez MR, Bedi ADS, Karczewski D, Lozano-Calderon SA. Treatment and outcomes of fungal prosthetic joint infections: a systematic review of 225 cases. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38(11):2464-2471.e1. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.05.003
- Gonzalez MR, Pretell-Mazzini J, Lozano-Calderon SA. Risk factors and management of prosthetic joint infections in megaprostheses-a review of the literature. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023;13(1):25. doi:10.3390/antibiotics13010025
- Biswas C, Chen SC, Halliday C, et al. Identification of genetic markers of resistance to echinocandins, azoles and 5-fluorocytosine in Candida glabrata by next-generation sequencing: a feasibility study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017;23(9):676.e7-676.e10. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2017.03.014
- Hassan Y, Chew SY, Than LTL. Candida glabrata: pathogenicity and resistance mechanisms for adaptation and survival. J Fungi (Basel). 2021;7(8):667. doi:10.3390/jof7080667
- Aboltins C, Daffy J, Choong P, Stanley P. Current concepts in the management of prosthetic joint infection. Intern Med J. 2014;44(9):834-840. doi:10.1111/imj.12510
- Pierce CG, Uppuluri P, Tristan AR, et al. A simple and reproducible 96-well plate-based method for the formation of fungal biofilms and its application to antifungal susceptibility testing. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(9):1494-1500. doi:10.1038/nport.2008.141
- Koutserimpas C, Samonis G, Velivassakis E, Iliopoulou- Kosmadaki S, Kontakis G, Kofteridis DP. Candida glabrata prosthetic joint infection, successfully treated with anidulafungin: a case report and review of the literature. Mycoses. 2018;61(4):266-269. doi:10.1111/myc.12736
- Brooks DH, Pupparo F. Successful salvage of a primary total knee arthroplasty infected with Candida parapsilosis. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13(6):707-712. doi:10.1016/s0883-5403(98)80017-x
- Merrer J, Dupont B, Nieszkowska A, De Jonghe B, Outin H. Candida albicans prosthetic arthritis treated with fluconazole alone. J Infect. 2001;42(3):208-209. doi:10.1053/jinf.2001.0819
- Koutserimpas C, Naoum S, Alpantaki K, et al. Fungal prosthetic joint infection in revised knee arthroplasty: an orthopaedic surgeon’s nightmare. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12(7):1606. doi:10.3390/diagnostics12071606
- Gao Z, Li X, Du Y, Peng Y, Wu W, Zhou Y. Success rate of fungal peri-prosthetic joint infection treated by 2-stage revision and potential risk factors of treatment failure: a retrospective study. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:5549-5557. doi:10.12659/MSM.909168
- Hwang BH, Yoon JY, Nam CH, et al. Fungal periprosthetic joint infection after primary total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(5):656-659. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.94B5.28125
- Ueng SW, Lee CY, Hu CC, Hsieh PH, Chang Y. What is the success of treatment of hip and knee candidal periprosthetic joint infection? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(9):3002-3009. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-3007-6
- Nodzo, Scott R. MD; Bauer, Thomas MD, PhD; Pottinger, et al. Conventional diagnostic challenges in periprosthetic joint infection. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23 Suppl:S18-S25. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00385
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Diagnosis and prevention of periprosthetic joint infections. March 11, 2019. Accessed February 5, 2025. https://www.aaos.org/pjicpg
A Candida Glabrata-Associated Prosthetic Joint Infection: Case Report and Literature Review
A Candida Glabrata-Associated Prosthetic Joint Infection: Case Report and Literature Review
Sports Injuries of the Hip in Primary Care
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, how are you feeling about sports injuries?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m feeling great, Matt.
Watto: You had a sports injury of the hip. Maybe that’s an overshare, Paul, but we talked about it on a podcast with Dr Carlin Senter (part 1 and part 2).
Williams: I think I’ve shared more than my hip injury, for sure.
Watto: Whenever a patient presented with hip pain, I used to pray it was trochanteric bursitis, which now I know is not really the right thing to think about. Intra-articular hip pain presents as anterior hip pain, usually in the crease of the hip. Depending on the patient’s age and history, the differential for that type of pain includes iliopsoas tendonitis, FAI syndrome, a labral tear, a bone stress injury of the femoral neck, or osteoarthritis.
So, what exactly is FAI and how might we diagnose it?
Williams: FAI is what the cool kids call femoral acetabular impingement, and it’s exactly what it sounds like.
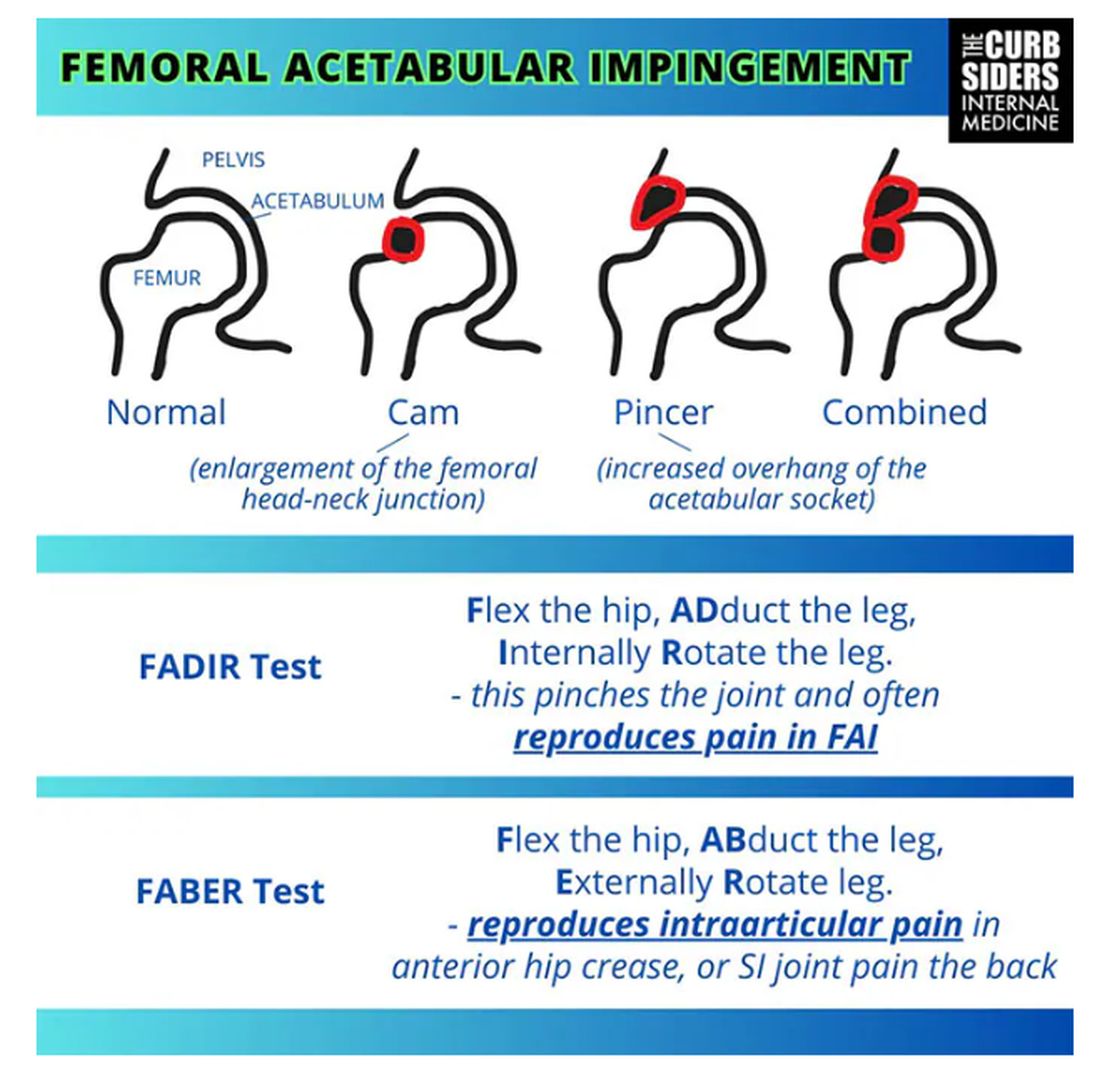
Something is pinching or impinging upon the joint itself and preventing full range of motion. This is a ball-and-socket joint, so it should have tremendous range of motion, able to move in all planes. If it’s impinged, then pain will occur with certain movements. There’s a cam type, which is characterized by enlargement of the femoral head neck junction, or a pincer type, which has more to do with overhang of the acetabulum, and it can also be mixed. In any case, impingement upon the patient’s full range of motion results in pain.
You evaluate this with a couple of tests — the FABER and the FADIR.
The FABER is flexion, abduction, and external rotation, and the FADIR is flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. If you elicit anterior pain with either of those tests, it’s probably one of the intra-articular pathologies, although it is hard to know for sure which one it is because these tests are fairly sensitive but not very specific.
Watto: You can get x-rays to help with the diagnosis. You would order two views of the hip: an AP of the pelvis, which is just a straight-on shot to look for arthritis or fracture. Is there a healthy joint line there? The second is the Dunn view, in which the hip is flexed 90 degrees and abducted about 20 degrees. You are looking for fracture or impingement. You can diagnose FAI based on that view, and you might be able to diagnose a hip stress injury or osteoarthritis.
Unfortunately, you’re not going to see a labral tear, but Dr Senter said that both FAI and labral tears are treated the same way, with physical therapy. Patients with FAI who aren’t getting better might end up going for surgery, so at some point I would refer them to orthopedic surgery. But I feel much more comfortable now diagnosing these conditions with these tests.
Let’s talk a little bit about trochanteric pain syndrome. I used to think it was all bursitis. Why is that not correct?
Williams: It’s nice of you to feign ignorance for the purpose of education. It used to be thought of as bursitis, but these days we know it is probably more likely a tendinopathy.
Trochanteric pain syndrome was formerly known as trochanteric bursitis, but the bursa is not typically involved. Trochanteric pain syndrome is a tendinopathy of the surrounding structures: the gluteus medius, the iliotibial band, and the tensor fascia latae. The way these structures relate looks a bit like the face of a clock, as you can see on the infographic. In general, you manage this condition the same way you do with bursitis — physical therapy. You can also give corticosteroid injections. Physical therapy is probably more durable in terms of pain relief and functionality, but in the short term, corticosteroids might provide some degree of analgesia as well.
Watto: The last thing we wanted to mention is bone stress injury, which can occur in high-mileage runners (20 miles or more per week). Patients with bone stress injury need to rest, usually non‒weight bearing, for a period of time.

Treatment of a bone stress fracture depends on which side it’s on (top or bottom). If it’s on the top of the femoral neck (the tension side), it has to be fixed. If it’s on the compression side (the bottom side of the femoral neck), it might be able to be managed conservatively, but many patients are going to need surgery. This is a big deal. But it’s a spectrum; in some cases the bone is merely irritated and unhappy, without a break in the cortex. Those patients might not need surgery.
In patients with a fracture of the femoral neck — especially younger, healthier patients — you should think about getting a bone density test and screening for relative energy deficiency in sport. This used to be called the female athlete triad, which includes disrupted menstrual cycles, being underweight, and fracture. We should be screening patients, asking them in a nonjudgmental way about their relationship with food, to make sure they are getting an appropriate number of calories.
They are actually in an energy deficit. They’re not eating enough to maintain a healthy body with so much activity.
Williams: If you’re interested in this topic, you should refer to the full podcast with Dr Senter which is chock-full of helpful information.
Dr Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, how are you feeling about sports injuries?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m feeling great, Matt.
Watto: You had a sports injury of the hip. Maybe that’s an overshare, Paul, but we talked about it on a podcast with Dr Carlin Senter (part 1 and part 2).
Williams: I think I’ve shared more than my hip injury, for sure.
Watto: Whenever a patient presented with hip pain, I used to pray it was trochanteric bursitis, which now I know is not really the right thing to think about. Intra-articular hip pain presents as anterior hip pain, usually in the crease of the hip. Depending on the patient’s age and history, the differential for that type of pain includes iliopsoas tendonitis, FAI syndrome, a labral tear, a bone stress injury of the femoral neck, or osteoarthritis.
So, what exactly is FAI and how might we diagnose it?
Williams: FAI is what the cool kids call femoral acetabular impingement, and it’s exactly what it sounds like.

Something is pinching or impinging upon the joint itself and preventing full range of motion. This is a ball-and-socket joint, so it should have tremendous range of motion, able to move in all planes. If it’s impinged, then pain will occur with certain movements. There’s a cam type, which is characterized by enlargement of the femoral head neck junction, or a pincer type, which has more to do with overhang of the acetabulum, and it can also be mixed. In any case, impingement upon the patient’s full range of motion results in pain.
You evaluate this with a couple of tests — the FABER and the FADIR.
The FABER is flexion, abduction, and external rotation, and the FADIR is flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. If you elicit anterior pain with either of those tests, it’s probably one of the intra-articular pathologies, although it is hard to know for sure which one it is because these tests are fairly sensitive but not very specific.
Watto: You can get x-rays to help with the diagnosis. You would order two views of the hip: an AP of the pelvis, which is just a straight-on shot to look for arthritis or fracture. Is there a healthy joint line there? The second is the Dunn view, in which the hip is flexed 90 degrees and abducted about 20 degrees. You are looking for fracture or impingement. You can diagnose FAI based on that view, and you might be able to diagnose a hip stress injury or osteoarthritis.
Unfortunately, you’re not going to see a labral tear, but Dr Senter said that both FAI and labral tears are treated the same way, with physical therapy. Patients with FAI who aren’t getting better might end up going for surgery, so at some point I would refer them to orthopedic surgery. But I feel much more comfortable now diagnosing these conditions with these tests.
Let’s talk a little bit about trochanteric pain syndrome. I used to think it was all bursitis. Why is that not correct?
Williams: It’s nice of you to feign ignorance for the purpose of education. It used to be thought of as bursitis, but these days we know it is probably more likely a tendinopathy.

Trochanteric pain syndrome was formerly known as trochanteric bursitis, but the bursa is not typically involved. Trochanteric pain syndrome is a tendinopathy of the surrounding structures: the gluteus medius, the iliotibial band, and the tensor fascia latae. The way these structures relate looks a bit like the face of a clock, as you can see on the infographic. In general, you manage this condition the same way you do with bursitis — physical therapy. You can also give corticosteroid injections. Physical therapy is probably more durable in terms of pain relief and functionality, but in the short term, corticosteroids might provide some degree of analgesia as well.
Watto: The last thing we wanted to mention is bone stress injury, which can occur in high-mileage runners (20 miles or more per week). Patients with bone stress injury need to rest, usually non‒weight bearing, for a period of time.

Treatment of a bone stress fracture depends on which side it’s on (top or bottom). If it’s on the top of the femoral neck (the tension side), it has to be fixed. If it’s on the compression side (the bottom side of the femoral neck), it might be able to be managed conservatively, but many patients are going to need surgery. This is a big deal. But it’s a spectrum; in some cases the bone is merely irritated and unhappy, without a break in the cortex. Those patients might not need surgery.
In patients with a fracture of the femoral neck — especially younger, healthier patients — you should think about getting a bone density test and screening for relative energy deficiency in sport. This used to be called the female athlete triad, which includes disrupted menstrual cycles, being underweight, and fracture. We should be screening patients, asking them in a nonjudgmental way about their relationship with food, to make sure they are getting an appropriate number of calories.
They are actually in an energy deficit. They’re not eating enough to maintain a healthy body with so much activity.
Williams: If you’re interested in this topic, you should refer to the full podcast with Dr Senter which is chock-full of helpful information.
Dr Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, how are you feeling about sports injuries?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m feeling great, Matt.
Watto: You had a sports injury of the hip. Maybe that’s an overshare, Paul, but we talked about it on a podcast with Dr Carlin Senter (part 1 and part 2).
Williams: I think I’ve shared more than my hip injury, for sure.
Watto: Whenever a patient presented with hip pain, I used to pray it was trochanteric bursitis, which now I know is not really the right thing to think about. Intra-articular hip pain presents as anterior hip pain, usually in the crease of the hip. Depending on the patient’s age and history, the differential for that type of pain includes iliopsoas tendonitis, FAI syndrome, a labral tear, a bone stress injury of the femoral neck, or osteoarthritis.
So, what exactly is FAI and how might we diagnose it?
Williams: FAI is what the cool kids call femoral acetabular impingement, and it’s exactly what it sounds like.

Something is pinching or impinging upon the joint itself and preventing full range of motion. This is a ball-and-socket joint, so it should have tremendous range of motion, able to move in all planes. If it’s impinged, then pain will occur with certain movements. There’s a cam type, which is characterized by enlargement of the femoral head neck junction, or a pincer type, which has more to do with overhang of the acetabulum, and it can also be mixed. In any case, impingement upon the patient’s full range of motion results in pain.
You evaluate this with a couple of tests — the FABER and the FADIR.
The FABER is flexion, abduction, and external rotation, and the FADIR is flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. If you elicit anterior pain with either of those tests, it’s probably one of the intra-articular pathologies, although it is hard to know for sure which one it is because these tests are fairly sensitive but not very specific.
Watto: You can get x-rays to help with the diagnosis. You would order two views of the hip: an AP of the pelvis, which is just a straight-on shot to look for arthritis or fracture. Is there a healthy joint line there? The second is the Dunn view, in which the hip is flexed 90 degrees and abducted about 20 degrees. You are looking for fracture or impingement. You can diagnose FAI based on that view, and you might be able to diagnose a hip stress injury or osteoarthritis.
Unfortunately, you’re not going to see a labral tear, but Dr Senter said that both FAI and labral tears are treated the same way, with physical therapy. Patients with FAI who aren’t getting better might end up going for surgery, so at some point I would refer them to orthopedic surgery. But I feel much more comfortable now diagnosing these conditions with these tests.
Let’s talk a little bit about trochanteric pain syndrome. I used to think it was all bursitis. Why is that not correct?
Williams: It’s nice of you to feign ignorance for the purpose of education. It used to be thought of as bursitis, but these days we know it is probably more likely a tendinopathy.

Trochanteric pain syndrome was formerly known as trochanteric bursitis, but the bursa is not typically involved. Trochanteric pain syndrome is a tendinopathy of the surrounding structures: the gluteus medius, the iliotibial band, and the tensor fascia latae. The way these structures relate looks a bit like the face of a clock, as you can see on the infographic. In general, you manage this condition the same way you do with bursitis — physical therapy. You can also give corticosteroid injections. Physical therapy is probably more durable in terms of pain relief and functionality, but in the short term, corticosteroids might provide some degree of analgesia as well.
Watto: The last thing we wanted to mention is bone stress injury, which can occur in high-mileage runners (20 miles or more per week). Patients with bone stress injury need to rest, usually non‒weight bearing, for a period of time.

Treatment of a bone stress fracture depends on which side it’s on (top or bottom). If it’s on the top of the femoral neck (the tension side), it has to be fixed. If it’s on the compression side (the bottom side of the femoral neck), it might be able to be managed conservatively, but many patients are going to need surgery. This is a big deal. But it’s a spectrum; in some cases the bone is merely irritated and unhappy, without a break in the cortex. Those patients might not need surgery.
In patients with a fracture of the femoral neck — especially younger, healthier patients — you should think about getting a bone density test and screening for relative energy deficiency in sport. This used to be called the female athlete triad, which includes disrupted menstrual cycles, being underweight, and fracture. We should be screening patients, asking them in a nonjudgmental way about their relationship with food, to make sure they are getting an appropriate number of calories.
They are actually in an energy deficit. They’re not eating enough to maintain a healthy body with so much activity.
Williams: If you’re interested in this topic, you should refer to the full podcast with Dr Senter which is chock-full of helpful information.
Dr Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Using GLP-1s to Meet BMI Goal for Orthopedic Surgery
The woman, in severe pain from hip and knee osteoarthritis, was confined to a wheelchair and had been told that would likely be for life. To qualify for hip replacement surgery, she needed to lose 100 pounds, a seemingly impossible goal. But she wanted to try.
“We tried a couple of medicines — oral medicines off-label — topiramate, phentermine,” said Leslie Golden, MD, MPH, DABM, a family medicine physician and obesity medicine specialist in Watertown, Wisconsin, 42 miles northeast of Madison.
They weren’t enough. But then Golden turned to glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, and they delivered.
“She did lose a significant amount of weight and was able to get the hip replacement,” said Golden.
It took a couple of years. However, seeing her walk into her office, rather than wheel in, “is still one of the joys of my practice,” Golden said. “She’s so grateful. She felt everyone else had written her off.”
As she told Golden: “If I fell and broke my leg today, they would take me to surgery without concern.”
Because her hip replacement was viewed as a nonemergency procedure, the accepted threshold for elective safe surgery was a body mass index (BMI) < 40. That BMI cutoff can vary from provider to provider and medical facility to medical facility but is often required for other surgeries as well, including kidney and lung transplants, gender-affirming surgery, bariatric surgery, hernia surgery, and in vitro fertilization procedures.
She worked with Rajit Chakravarty, MD, an adult reconstructive surgeon who practices in Watertown and nearby Madison, to oversee the weight loss.
High BMIs & Surgery Issues
High BMIs have long been linked with postsurgery complications, poor wound healing, and other issues, although some research now is questioning some of those associations. Even so, surgeons have long stressed weight loss for their patients with obesity before orthopedic and other procedures.
These days, surgeons are more likely to need to have that talk. In the last decade, the age-adjusted prevalence of severe obesity — a BMI of ≥ 40 — has increased from 7.7% to 9.7% of US adults. The number of joint replacements is also rising — more than 700,000 total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and more than 450,000 total hip arthroplasty (THA), according to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. As the population ages, those numbers are expected to increase.
Making the GLP-1 Choice
GLP-1s aren’t the only choice, of course. But they’re often more effective, as Golden found, than other medications. And when his patients with obesity are offered bariatric surgery or GLP-1s, “people definitely want to avoid the bariatric surgery,” Chakravarty said.
With the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of semaglutide (Wegovy) in June 2021 for chronic weight management and then tirzepatide (Zepbound) in November 2023, interest has boomed, he said, among his surgery candidates with a high BMI.
The FDA approved Wegovy based on clinical trials, including one in which participants lost an average of 12.4% of initial body weight compared with those on placebo. It approved Zepbound based on clinical trials, including one in which those on Zepbound lost an average of 18% of their body weight, compared with those on placebo.
The wheelchair-bound woman, now 65, began with a BMI of 63, Golden said. She negotiated a cutoff of 45 with the surgeon and got the go-ahead. Currently, her BMI is 36 as she stayed on the medications.
Beyond the benefit of GLP-1s helping patients meet the BMI cutoff, some research finds fewer postoperative infections and readmissions with their use. This study found the medications did lower both, and another found reduced readmissions and complications.
Growing Partnerships, Increasing Success
Helping patients lose weight isn’t just about lowering the BMI, Chakravarty pointed out. The aim is to improve nutritional health — to teach patients how to eat healthfully for their needs, in turn improving other health barometers. Referring them to an obesity medicine physician helps to meet those goals.
When Daniel Wiznia, MD, a Yale Medicine orthopedic surgeon and codirector of the Avascular Necrosis Program, has a patient who must delay a TKA or THA until they meet a BMI cutoff, he refers that patient to the Yale Medicine Center for Weight Management, New Haven, Connecticut, to learn about weight loss, including the options of anti-obesity medications or bariatric surgery.
Taking the GLP-1s can be a game changer, according to Wiznia and John Morton, MD, MPH, FACS, FASMBS, Yale’s medical director of Bariatric Surgery and professor and vice chair of surgery, who is a physician-director of the center. The program includes other options, such as bariatric surgery, and emphasizes diet and other lifestyle measures. GLP-1s give about a 15% weight loss, Morton said, compared with bariatric surgery providing up to 30%.
Sarah Stombaugh, MD, a family medicine and obesity medicine physician in Charlottesville, Virginia, often gets referrals from two orthopedic surgeons in her community. One recent patient in her early 60s had a BMI of 43.2, too high to qualify for the TKA she needed. On GLP-1s, the initial goal was to decrease a weight of 244 to 225, bringing the BMI to 39.9. The woman did that, then kept losing before her surgery was scheduled, getting to a weight of 210 or a BMI of 37 and staying there for 3 months before the surgery.
She had the TKA, and 5 months out, she is doing well, Stombaugh said. “We do medical weight loss primarily with the GLP-1s because they’re simply the best, the most effective,” Stombaugh said. She does occasionally use oral medications such as naltrexone/bupropion (Contrave).
Stombaugh sees the collaborating trend as still evolving. When she attends obesity medicine conferences, not all her colleagues report they are partnering with surgeons. But she predicts the practice will increase, saying the popularization of what she terms the more effective GLP-1 medications Wegovy and Zepbound is driving it. Partnering with the surgeon requires a conversation at the beginning, when the referral is made, about goals. After that, she sees her patient monthly and sends progress notes to the surgeon.
Golden collaborates with three orthopedic groups in her area, primarily for knee and hip surgeries, but has also helped patients meet the BMI cutoff before spine-related surgeries. She is helping a lung transplant patient now. She has seen several patients who must meet BMI requirements before starting in vitro fertilization, due to the need for conscious sedation for egg retrieval. She has had a few patients who had to meet a BMI cutoff for nonemergency hernia repair.
Insurance Issues
Insurance remains an issue for the pricey medications. “Only about a third of patients are routinely covered with insurance,” Morton said.
However, it’s improving, he said. Golden also finds about a third of private payers cover the medication but tries to use manufacturers’ coupons to help defray the costs (from about $1000 or $1400 to about $500 a month). She has sometimes gotten enough samples to get patients to their BMI goal
Morton consulted for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Olympus, Teleflex, and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The woman, in severe pain from hip and knee osteoarthritis, was confined to a wheelchair and had been told that would likely be for life. To qualify for hip replacement surgery, she needed to lose 100 pounds, a seemingly impossible goal. But she wanted to try.
“We tried a couple of medicines — oral medicines off-label — topiramate, phentermine,” said Leslie Golden, MD, MPH, DABM, a family medicine physician and obesity medicine specialist in Watertown, Wisconsin, 42 miles northeast of Madison.
They weren’t enough. But then Golden turned to glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, and they delivered.
“She did lose a significant amount of weight and was able to get the hip replacement,” said Golden.
It took a couple of years. However, seeing her walk into her office, rather than wheel in, “is still one of the joys of my practice,” Golden said. “She’s so grateful. She felt everyone else had written her off.”
As she told Golden: “If I fell and broke my leg today, they would take me to surgery without concern.”
Because her hip replacement was viewed as a nonemergency procedure, the accepted threshold for elective safe surgery was a body mass index (BMI) < 40. That BMI cutoff can vary from provider to provider and medical facility to medical facility but is often required for other surgeries as well, including kidney and lung transplants, gender-affirming surgery, bariatric surgery, hernia surgery, and in vitro fertilization procedures.
She worked with Rajit Chakravarty, MD, an adult reconstructive surgeon who practices in Watertown and nearby Madison, to oversee the weight loss.
High BMIs & Surgery Issues
High BMIs have long been linked with postsurgery complications, poor wound healing, and other issues, although some research now is questioning some of those associations. Even so, surgeons have long stressed weight loss for their patients with obesity before orthopedic and other procedures.
These days, surgeons are more likely to need to have that talk. In the last decade, the age-adjusted prevalence of severe obesity — a BMI of ≥ 40 — has increased from 7.7% to 9.7% of US adults. The number of joint replacements is also rising — more than 700,000 total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and more than 450,000 total hip arthroplasty (THA), according to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. As the population ages, those numbers are expected to increase.
Making the GLP-1 Choice
GLP-1s aren’t the only choice, of course. But they’re often more effective, as Golden found, than other medications. And when his patients with obesity are offered bariatric surgery or GLP-1s, “people definitely want to avoid the bariatric surgery,” Chakravarty said.
With the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of semaglutide (Wegovy) in June 2021 for chronic weight management and then tirzepatide (Zepbound) in November 2023, interest has boomed, he said, among his surgery candidates with a high BMI.
The FDA approved Wegovy based on clinical trials, including one in which participants lost an average of 12.4% of initial body weight compared with those on placebo. It approved Zepbound based on clinical trials, including one in which those on Zepbound lost an average of 18% of their body weight, compared with those on placebo.
The wheelchair-bound woman, now 65, began with a BMI of 63, Golden said. She negotiated a cutoff of 45 with the surgeon and got the go-ahead. Currently, her BMI is 36 as she stayed on the medications.
Beyond the benefit of GLP-1s helping patients meet the BMI cutoff, some research finds fewer postoperative infections and readmissions with their use. This study found the medications did lower both, and another found reduced readmissions and complications.
Growing Partnerships, Increasing Success
Helping patients lose weight isn’t just about lowering the BMI, Chakravarty pointed out. The aim is to improve nutritional health — to teach patients how to eat healthfully for their needs, in turn improving other health barometers. Referring them to an obesity medicine physician helps to meet those goals.
When Daniel Wiznia, MD, a Yale Medicine orthopedic surgeon and codirector of the Avascular Necrosis Program, has a patient who must delay a TKA or THA until they meet a BMI cutoff, he refers that patient to the Yale Medicine Center for Weight Management, New Haven, Connecticut, to learn about weight loss, including the options of anti-obesity medications or bariatric surgery.
Taking the GLP-1s can be a game changer, according to Wiznia and John Morton, MD, MPH, FACS, FASMBS, Yale’s medical director of Bariatric Surgery and professor and vice chair of surgery, who is a physician-director of the center. The program includes other options, such as bariatric surgery, and emphasizes diet and other lifestyle measures. GLP-1s give about a 15% weight loss, Morton said, compared with bariatric surgery providing up to 30%.
Sarah Stombaugh, MD, a family medicine and obesity medicine physician in Charlottesville, Virginia, often gets referrals from two orthopedic surgeons in her community. One recent patient in her early 60s had a BMI of 43.2, too high to qualify for the TKA she needed. On GLP-1s, the initial goal was to decrease a weight of 244 to 225, bringing the BMI to 39.9. The woman did that, then kept losing before her surgery was scheduled, getting to a weight of 210 or a BMI of 37 and staying there for 3 months before the surgery.
She had the TKA, and 5 months out, she is doing well, Stombaugh said. “We do medical weight loss primarily with the GLP-1s because they’re simply the best, the most effective,” Stombaugh said. She does occasionally use oral medications such as naltrexone/bupropion (Contrave).
Stombaugh sees the collaborating trend as still evolving. When she attends obesity medicine conferences, not all her colleagues report they are partnering with surgeons. But she predicts the practice will increase, saying the popularization of what she terms the more effective GLP-1 medications Wegovy and Zepbound is driving it. Partnering with the surgeon requires a conversation at the beginning, when the referral is made, about goals. After that, she sees her patient monthly and sends progress notes to the surgeon.
Golden collaborates with three orthopedic groups in her area, primarily for knee and hip surgeries, but has also helped patients meet the BMI cutoff before spine-related surgeries. She is helping a lung transplant patient now. She has seen several patients who must meet BMI requirements before starting in vitro fertilization, due to the need for conscious sedation for egg retrieval. She has had a few patients who had to meet a BMI cutoff for nonemergency hernia repair.
Insurance Issues
Insurance remains an issue for the pricey medications. “Only about a third of patients are routinely covered with insurance,” Morton said.
However, it’s improving, he said. Golden also finds about a third of private payers cover the medication but tries to use manufacturers’ coupons to help defray the costs (from about $1000 or $1400 to about $500 a month). She has sometimes gotten enough samples to get patients to their BMI goal
Morton consulted for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Olympus, Teleflex, and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The woman, in severe pain from hip and knee osteoarthritis, was confined to a wheelchair and had been told that would likely be for life. To qualify for hip replacement surgery, she needed to lose 100 pounds, a seemingly impossible goal. But she wanted to try.
“We tried a couple of medicines — oral medicines off-label — topiramate, phentermine,” said Leslie Golden, MD, MPH, DABM, a family medicine physician and obesity medicine specialist in Watertown, Wisconsin, 42 miles northeast of Madison.
They weren’t enough. But then Golden turned to glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, and they delivered.
“She did lose a significant amount of weight and was able to get the hip replacement,” said Golden.
It took a couple of years. However, seeing her walk into her office, rather than wheel in, “is still one of the joys of my practice,” Golden said. “She’s so grateful. She felt everyone else had written her off.”
As she told Golden: “If I fell and broke my leg today, they would take me to surgery without concern.”
Because her hip replacement was viewed as a nonemergency procedure, the accepted threshold for elective safe surgery was a body mass index (BMI) < 40. That BMI cutoff can vary from provider to provider and medical facility to medical facility but is often required for other surgeries as well, including kidney and lung transplants, gender-affirming surgery, bariatric surgery, hernia surgery, and in vitro fertilization procedures.
She worked with Rajit Chakravarty, MD, an adult reconstructive surgeon who practices in Watertown and nearby Madison, to oversee the weight loss.
High BMIs & Surgery Issues
High BMIs have long been linked with postsurgery complications, poor wound healing, and other issues, although some research now is questioning some of those associations. Even so, surgeons have long stressed weight loss for their patients with obesity before orthopedic and other procedures.
These days, surgeons are more likely to need to have that talk. In the last decade, the age-adjusted prevalence of severe obesity — a BMI of ≥ 40 — has increased from 7.7% to 9.7% of US adults. The number of joint replacements is also rising — more than 700,000 total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and more than 450,000 total hip arthroplasty (THA), according to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. As the population ages, those numbers are expected to increase.
Making the GLP-1 Choice
GLP-1s aren’t the only choice, of course. But they’re often more effective, as Golden found, than other medications. And when his patients with obesity are offered bariatric surgery or GLP-1s, “people definitely want to avoid the bariatric surgery,” Chakravarty said.
With the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of semaglutide (Wegovy) in June 2021 for chronic weight management and then tirzepatide (Zepbound) in November 2023, interest has boomed, he said, among his surgery candidates with a high BMI.
The FDA approved Wegovy based on clinical trials, including one in which participants lost an average of 12.4% of initial body weight compared with those on placebo. It approved Zepbound based on clinical trials, including one in which those on Zepbound lost an average of 18% of their body weight, compared with those on placebo.
The wheelchair-bound woman, now 65, began with a BMI of 63, Golden said. She negotiated a cutoff of 45 with the surgeon and got the go-ahead. Currently, her BMI is 36 as she stayed on the medications.
Beyond the benefit of GLP-1s helping patients meet the BMI cutoff, some research finds fewer postoperative infections and readmissions with their use. This study found the medications did lower both, and another found reduced readmissions and complications.
Growing Partnerships, Increasing Success
Helping patients lose weight isn’t just about lowering the BMI, Chakravarty pointed out. The aim is to improve nutritional health — to teach patients how to eat healthfully for their needs, in turn improving other health barometers. Referring them to an obesity medicine physician helps to meet those goals.
When Daniel Wiznia, MD, a Yale Medicine orthopedic surgeon and codirector of the Avascular Necrosis Program, has a patient who must delay a TKA or THA until they meet a BMI cutoff, he refers that patient to the Yale Medicine Center for Weight Management, New Haven, Connecticut, to learn about weight loss, including the options of anti-obesity medications or bariatric surgery.
Taking the GLP-1s can be a game changer, according to Wiznia and John Morton, MD, MPH, FACS, FASMBS, Yale’s medical director of Bariatric Surgery and professor and vice chair of surgery, who is a physician-director of the center. The program includes other options, such as bariatric surgery, and emphasizes diet and other lifestyle measures. GLP-1s give about a 15% weight loss, Morton said, compared with bariatric surgery providing up to 30%.
Sarah Stombaugh, MD, a family medicine and obesity medicine physician in Charlottesville, Virginia, often gets referrals from two orthopedic surgeons in her community. One recent patient in her early 60s had a BMI of 43.2, too high to qualify for the TKA she needed. On GLP-1s, the initial goal was to decrease a weight of 244 to 225, bringing the BMI to 39.9. The woman did that, then kept losing before her surgery was scheduled, getting to a weight of 210 or a BMI of 37 and staying there for 3 months before the surgery.
She had the TKA, and 5 months out, she is doing well, Stombaugh said. “We do medical weight loss primarily with the GLP-1s because they’re simply the best, the most effective,” Stombaugh said. She does occasionally use oral medications such as naltrexone/bupropion (Contrave).
Stombaugh sees the collaborating trend as still evolving. When she attends obesity medicine conferences, not all her colleagues report they are partnering with surgeons. But she predicts the practice will increase, saying the popularization of what she terms the more effective GLP-1 medications Wegovy and Zepbound is driving it. Partnering with the surgeon requires a conversation at the beginning, when the referral is made, about goals. After that, she sees her patient monthly and sends progress notes to the surgeon.
Golden collaborates with three orthopedic groups in her area, primarily for knee and hip surgeries, but has also helped patients meet the BMI cutoff before spine-related surgeries. She is helping a lung transplant patient now. She has seen several patients who must meet BMI requirements before starting in vitro fertilization, due to the need for conscious sedation for egg retrieval. She has had a few patients who had to meet a BMI cutoff for nonemergency hernia repair.
Insurance Issues
Insurance remains an issue for the pricey medications. “Only about a third of patients are routinely covered with insurance,” Morton said.
However, it’s improving, he said. Golden also finds about a third of private payers cover the medication but tries to use manufacturers’ coupons to help defray the costs (from about $1000 or $1400 to about $500 a month). She has sometimes gotten enough samples to get patients to their BMI goal
Morton consulted for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Olympus, Teleflex, and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VA Awards Grants to Support Adaptive Sports
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is awarding $15.9 million in grants to fund adaptive sports, recreational activities, and equine therapy for > 15,000 veterans and service members living with disabilities.
Marine Corps veteran Jataya Taylor — who competed in wheelchair fencing at the 2024 Paralympics — experienced mental health symptoms until she began participating in adaptive sports through an organization supported by the VA Adaptive Sports Grant Program.
“Getting involved in adaptive sports was a saving grace for me,” Taylor said. “Participating in these programs got me on the bike to start with, then got me climbing, and eventually it became an important part of my mental health to participate. I found my people. I found my new network of friends.”
Adaptive sports, which are customized to fit the needs of veterans with disabilities, include paralympic sports, archery, cycling, skiing, hunting, rock climbing, and sky diving. Mike Gooler, another Marine Corps veteran, praised the Adaptive Sports Center’s facilities in Crested Butte, Colorado, calling it “nothing short of amazing.”
“[S]ki therapy has been instrumental in helping me navigate through my experiences and injuries,” Gooler said. “Skiing provides me with sense of freedom and empowerment … and having my family by my side, witnessing my progress and sharing the joy of skiing, was truly special.”
The grant program is facilitated and managed by the National Veterans Sports Programs and Special Events Office and will provide grants to 91 national, regional, and community-based programs for fiscal year 2024 across all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Guam, and Puerto Rico.
“These grants give veterans life-changing opportunities,” Secretary of VA Denis McDonough said. “We know adaptive sports and recreational activities can be transformational for veterans living with disabilities, improving their overall physical and mental health, and also giving them important community with fellow heroes who served.”
Information about the awardees and details of the program are available at www.va.gov/adaptivesports and on Facebook at Sports4Vets.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is awarding $15.9 million in grants to fund adaptive sports, recreational activities, and equine therapy for > 15,000 veterans and service members living with disabilities.
Marine Corps veteran Jataya Taylor — who competed in wheelchair fencing at the 2024 Paralympics — experienced mental health symptoms until she began participating in adaptive sports through an organization supported by the VA Adaptive Sports Grant Program.
“Getting involved in adaptive sports was a saving grace for me,” Taylor said. “Participating in these programs got me on the bike to start with, then got me climbing, and eventually it became an important part of my mental health to participate. I found my people. I found my new network of friends.”
Adaptive sports, which are customized to fit the needs of veterans with disabilities, include paralympic sports, archery, cycling, skiing, hunting, rock climbing, and sky diving. Mike Gooler, another Marine Corps veteran, praised the Adaptive Sports Center’s facilities in Crested Butte, Colorado, calling it “nothing short of amazing.”
“[S]ki therapy has been instrumental in helping me navigate through my experiences and injuries,” Gooler said. “Skiing provides me with sense of freedom and empowerment … and having my family by my side, witnessing my progress and sharing the joy of skiing, was truly special.”
The grant program is facilitated and managed by the National Veterans Sports Programs and Special Events Office and will provide grants to 91 national, regional, and community-based programs for fiscal year 2024 across all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Guam, and Puerto Rico.
“These grants give veterans life-changing opportunities,” Secretary of VA Denis McDonough said. “We know adaptive sports and recreational activities can be transformational for veterans living with disabilities, improving their overall physical and mental health, and also giving them important community with fellow heroes who served.”
Information about the awardees and details of the program are available at www.va.gov/adaptivesports and on Facebook at Sports4Vets.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is awarding $15.9 million in grants to fund adaptive sports, recreational activities, and equine therapy for > 15,000 veterans and service members living with disabilities.
Marine Corps veteran Jataya Taylor — who competed in wheelchair fencing at the 2024 Paralympics — experienced mental health symptoms until she began participating in adaptive sports through an organization supported by the VA Adaptive Sports Grant Program.
“Getting involved in adaptive sports was a saving grace for me,” Taylor said. “Participating in these programs got me on the bike to start with, then got me climbing, and eventually it became an important part of my mental health to participate. I found my people. I found my new network of friends.”
Adaptive sports, which are customized to fit the needs of veterans with disabilities, include paralympic sports, archery, cycling, skiing, hunting, rock climbing, and sky diving. Mike Gooler, another Marine Corps veteran, praised the Adaptive Sports Center’s facilities in Crested Butte, Colorado, calling it “nothing short of amazing.”
“[S]ki therapy has been instrumental in helping me navigate through my experiences and injuries,” Gooler said. “Skiing provides me with sense of freedom and empowerment … and having my family by my side, witnessing my progress and sharing the joy of skiing, was truly special.”
The grant program is facilitated and managed by the National Veterans Sports Programs and Special Events Office and will provide grants to 91 national, regional, and community-based programs for fiscal year 2024 across all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Guam, and Puerto Rico.
“These grants give veterans life-changing opportunities,” Secretary of VA Denis McDonough said. “We know adaptive sports and recreational activities can be transformational for veterans living with disabilities, improving their overall physical and mental health, and also giving them important community with fellow heroes who served.”
Information about the awardees and details of the program are available at www.va.gov/adaptivesports and on Facebook at Sports4Vets.
Total Hip Replacement Superior to Exercise Therapy for Improving Hip Osteoarthritis Pain and Function
For people with severe symptomatic hip osteoarthritis, total hip replacement (THR) alleviates hip pain and improves function much more effectively than a resistance training program supervised by a physiotherapist, according to the results of a randomized controlled clinical trial.
In the PROHIP study, the mean increases in Oxford Hip Scores from baseline to 6 months were 15.9 points for THR and 4.5 points for resistance training. The 11.4-point difference in scores was both statistically and clinically significant, the study’s investigators reported in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“Our results are clear: Surgery is superior to exercise in patients who have hip osteoarthritis and indication for surgery, and now we have finally proven that with the highest level of evidence,” corresponding author Thomas Frydendal, PT, PhD, MSc, told this news organization.
Frydendal, who was involved in the study while working on his PhD at University Hospital of Southern Denmark – Lillebaelt Hospital, Vejle, Denmark, the primary center for the trial, is now a postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, and Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Aarhus University Hospital.
“We believe that our findings are pretty robust,” Frydendal added. “I think if someone in the world conducts a trial similar to ours, they will find fairly close or consistent findings, no matter what type of exercise they choose.”
The PROHIP Study
THR is routinely recommended for the management of severe hip osteoarthritis, but since there are no clinical trial data on the effectiveness of this procedure as compared with first-line treatment such as resistance training, the PROHIP study was conceived.
The trial was conducted at four Danish orthopedic centers and designed as a superiority study, the hypothesis being that THR would be better at alleviating self-reported hip pain and improving hip function than resistance training.
Of a possible 1474 individuals with a clinical suspicion of hip osteoarthritis, 791 were deemed eligible for inclusion in the trial. Inclusion criteria were being aged 50 years or older and having an indication for THR based on the presence of hip pain and clinical and radiographic findings.
However, the majority (86%) declined to enter the study, with almost half (43%) deciding to have a THR and enroll in a parallel observational cohort. This meant that only 110 (14%) individuals agreed to participate and underwent randomization, which does limit the study’s generalizability, the PROHIP investigators acknowledged.
Design and Study Population
The change in Oxford Hip Score from baseline to 6 months was selected as the primary outcome measure based on the findings of a prior qualitative study. This 12-item, patient-reported outcome measure gives a score ranging from 0 to 48, with higher scores indicating less hip pain and better hip function. The estimated minimal clinically important difference is a change of 5 points.
After a baseline assessment, 53 of 109 individuals were randomly assigned to undergo THR and 56 to participate in the resistance training program. Overall, the mean age of participants was 67.6 years, and half were women. The average duration of hip pain was a median of 1.7 years.
The median time to receipt of the allocated treatment was 2.8 months in the THR group and 0.5 months in the resistance training group.
Those allocated to the THR group also underwent a “fast track” program that involved patient education, pain management, and early mobilization.
The resistance training group received 12 weeks of exercise supervised by a physiotherapist and then offered 12 weeks of additional exercise conducted on their own. The physiotherapist-supervised exercise sessions were held twice weekly and lasted for 1 hour. These started with a 10-minute warm-up on a stationary bike, followed by a standard set of resistance-based exercises that included a leg press, hip extension, hip flexion, and hip abduction.
‘Reassuring’ Results
In a comment, consultant orthopedic surgeon Antony Palmer, MA, BMBCh, DPhil, said: “It’s reassuring that patients with advanced symptomatic osteoarthritis do well with hip replacements.”
THR does of course come with the potential risk for complications, but “the rate of these is what you’d expect for that procedure,” Palmer said, who works for the Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, and is a senior clinical research fellow at Oxford University in England.
In the THR arm, there was one case of prosthetic joint infection, one hip dislocation, two revision surgeries, one instance of foot drop, and one case of gastroesophageal reflux. Meanwhile, in the resistance training group, there was one hip dislocation, one pelvic fracture, one case of atrial fibrillation, and one urinary tract and renal infection.
Overall, any serious adverse event was reported in six (12%) of 48 patients in the THR arm vs five (9%) of 55 participants in the resistance training group, of which only one, occurring in the resistance training group, resulted in discontinuation of the program.
Resistance Training Role
A notable finding was that, at 6 months, five (9%) people assigned to the THR arm had not undergone surgery, and 12 (21%) people in the resistance training group had undergone a THR.
This could suggest two things, Palmer suggested in the interview. The first is that there could be a small proportion of people assigned to THR who may not need the operation and do well with exercise therapy. And, conversely, there may be those who would do well having the surgery without first going through the intermediate stage of physical therapy.
It’s a suggestion that “maybe we’ve got to refine that a bit better and identify the patients that really do benefit from physiotherapy and who might not need hip replacement as a result,” Palmer said.
Or in other words, “should all patients undergo a program of physiotherapy before considering surgery?” he added.
Authors’ View
The PROHIP investigators conclude: “These results support current recommendations for the management of hip osteoarthritis and may be used to inform and guide shared decision making in clinical practice.”
Moreover, the results “do not oppose the use of resistance training as initial treatment,” says the authors.
Frydendal highlighted in his interview that nearly three out of four of the patients reported not to have undertaken any type of supervised exercise before entry into the study, which is a first-line, guideline-recommended option.
“If a patient tells me, ‘I haven’t done any exercise previously,’ I’d recommend starting with completing a 6- to 12-week exercise program that is tailored to your individual needs and evaluate your symptoms afterward,” he said.
“But we should refer the patient if our first-line treatment does not offer any improvements in the patient’s symptoms, as surgery with total hip replacement is clearly a really good treatment option,” Frydendal said.
The study was funded by the Danish Rheumatism Association, among other independent bodies. Frydendal and Palmer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For people with severe symptomatic hip osteoarthritis, total hip replacement (THR) alleviates hip pain and improves function much more effectively than a resistance training program supervised by a physiotherapist, according to the results of a randomized controlled clinical trial.
In the PROHIP study, the mean increases in Oxford Hip Scores from baseline to 6 months were 15.9 points for THR and 4.5 points for resistance training. The 11.4-point difference in scores was both statistically and clinically significant, the study’s investigators reported in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“Our results are clear: Surgery is superior to exercise in patients who have hip osteoarthritis and indication for surgery, and now we have finally proven that with the highest level of evidence,” corresponding author Thomas Frydendal, PT, PhD, MSc, told this news organization.
Frydendal, who was involved in the study while working on his PhD at University Hospital of Southern Denmark – Lillebaelt Hospital, Vejle, Denmark, the primary center for the trial, is now a postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, and Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Aarhus University Hospital.
“We believe that our findings are pretty robust,” Frydendal added. “I think if someone in the world conducts a trial similar to ours, they will find fairly close or consistent findings, no matter what type of exercise they choose.”
The PROHIP Study
THR is routinely recommended for the management of severe hip osteoarthritis, but since there are no clinical trial data on the effectiveness of this procedure as compared with first-line treatment such as resistance training, the PROHIP study was conceived.
The trial was conducted at four Danish orthopedic centers and designed as a superiority study, the hypothesis being that THR would be better at alleviating self-reported hip pain and improving hip function than resistance training.
Of a possible 1474 individuals with a clinical suspicion of hip osteoarthritis, 791 were deemed eligible for inclusion in the trial. Inclusion criteria were being aged 50 years or older and having an indication for THR based on the presence of hip pain and clinical and radiographic findings.
However, the majority (86%) declined to enter the study, with almost half (43%) deciding to have a THR and enroll in a parallel observational cohort. This meant that only 110 (14%) individuals agreed to participate and underwent randomization, which does limit the study’s generalizability, the PROHIP investigators acknowledged.
Design and Study Population
The change in Oxford Hip Score from baseline to 6 months was selected as the primary outcome measure based on the findings of a prior qualitative study. This 12-item, patient-reported outcome measure gives a score ranging from 0 to 48, with higher scores indicating less hip pain and better hip function. The estimated minimal clinically important difference is a change of 5 points.
After a baseline assessment, 53 of 109 individuals were randomly assigned to undergo THR and 56 to participate in the resistance training program. Overall, the mean age of participants was 67.6 years, and half were women. The average duration of hip pain was a median of 1.7 years.
The median time to receipt of the allocated treatment was 2.8 months in the THR group and 0.5 months in the resistance training group.
Those allocated to the THR group also underwent a “fast track” program that involved patient education, pain management, and early mobilization.
The resistance training group received 12 weeks of exercise supervised by a physiotherapist and then offered 12 weeks of additional exercise conducted on their own. The physiotherapist-supervised exercise sessions were held twice weekly and lasted for 1 hour. These started with a 10-minute warm-up on a stationary bike, followed by a standard set of resistance-based exercises that included a leg press, hip extension, hip flexion, and hip abduction.
‘Reassuring’ Results
In a comment, consultant orthopedic surgeon Antony Palmer, MA, BMBCh, DPhil, said: “It’s reassuring that patients with advanced symptomatic osteoarthritis do well with hip replacements.”
THR does of course come with the potential risk for complications, but “the rate of these is what you’d expect for that procedure,” Palmer said, who works for the Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, and is a senior clinical research fellow at Oxford University in England.
In the THR arm, there was one case of prosthetic joint infection, one hip dislocation, two revision surgeries, one instance of foot drop, and one case of gastroesophageal reflux. Meanwhile, in the resistance training group, there was one hip dislocation, one pelvic fracture, one case of atrial fibrillation, and one urinary tract and renal infection.
Overall, any serious adverse event was reported in six (12%) of 48 patients in the THR arm vs five (9%) of 55 participants in the resistance training group, of which only one, occurring in the resistance training group, resulted in discontinuation of the program.
Resistance Training Role
A notable finding was that, at 6 months, five (9%) people assigned to the THR arm had not undergone surgery, and 12 (21%) people in the resistance training group had undergone a THR.
This could suggest two things, Palmer suggested in the interview. The first is that there could be a small proportion of people assigned to THR who may not need the operation and do well with exercise therapy. And, conversely, there may be those who would do well having the surgery without first going through the intermediate stage of physical therapy.
It’s a suggestion that “maybe we’ve got to refine that a bit better and identify the patients that really do benefit from physiotherapy and who might not need hip replacement as a result,” Palmer said.
Or in other words, “should all patients undergo a program of physiotherapy before considering surgery?” he added.
Authors’ View
The PROHIP investigators conclude: “These results support current recommendations for the management of hip osteoarthritis and may be used to inform and guide shared decision making in clinical practice.”
Moreover, the results “do not oppose the use of resistance training as initial treatment,” says the authors.
Frydendal highlighted in his interview that nearly three out of four of the patients reported not to have undertaken any type of supervised exercise before entry into the study, which is a first-line, guideline-recommended option.
“If a patient tells me, ‘I haven’t done any exercise previously,’ I’d recommend starting with completing a 6- to 12-week exercise program that is tailored to your individual needs and evaluate your symptoms afterward,” he said.
“But we should refer the patient if our first-line treatment does not offer any improvements in the patient’s symptoms, as surgery with total hip replacement is clearly a really good treatment option,” Frydendal said.
The study was funded by the Danish Rheumatism Association, among other independent bodies. Frydendal and Palmer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For people with severe symptomatic hip osteoarthritis, total hip replacement (THR) alleviates hip pain and improves function much more effectively than a resistance training program supervised by a physiotherapist, according to the results of a randomized controlled clinical trial.
In the PROHIP study, the mean increases in Oxford Hip Scores from baseline to 6 months were 15.9 points for THR and 4.5 points for resistance training. The 11.4-point difference in scores was both statistically and clinically significant, the study’s investigators reported in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“Our results are clear: Surgery is superior to exercise in patients who have hip osteoarthritis and indication for surgery, and now we have finally proven that with the highest level of evidence,” corresponding author Thomas Frydendal, PT, PhD, MSc, told this news organization.
Frydendal, who was involved in the study while working on his PhD at University Hospital of Southern Denmark – Lillebaelt Hospital, Vejle, Denmark, the primary center for the trial, is now a postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, and Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Aarhus University Hospital.
“We believe that our findings are pretty robust,” Frydendal added. “I think if someone in the world conducts a trial similar to ours, they will find fairly close or consistent findings, no matter what type of exercise they choose.”
The PROHIP Study
THR is routinely recommended for the management of severe hip osteoarthritis, but since there are no clinical trial data on the effectiveness of this procedure as compared with first-line treatment such as resistance training, the PROHIP study was conceived.
The trial was conducted at four Danish orthopedic centers and designed as a superiority study, the hypothesis being that THR would be better at alleviating self-reported hip pain and improving hip function than resistance training.
Of a possible 1474 individuals with a clinical suspicion of hip osteoarthritis, 791 were deemed eligible for inclusion in the trial. Inclusion criteria were being aged 50 years or older and having an indication for THR based on the presence of hip pain and clinical and radiographic findings.
However, the majority (86%) declined to enter the study, with almost half (43%) deciding to have a THR and enroll in a parallel observational cohort. This meant that only 110 (14%) individuals agreed to participate and underwent randomization, which does limit the study’s generalizability, the PROHIP investigators acknowledged.
Design and Study Population
The change in Oxford Hip Score from baseline to 6 months was selected as the primary outcome measure based on the findings of a prior qualitative study. This 12-item, patient-reported outcome measure gives a score ranging from 0 to 48, with higher scores indicating less hip pain and better hip function. The estimated minimal clinically important difference is a change of 5 points.
After a baseline assessment, 53 of 109 individuals were randomly assigned to undergo THR and 56 to participate in the resistance training program. Overall, the mean age of participants was 67.6 years, and half were women. The average duration of hip pain was a median of 1.7 years.
The median time to receipt of the allocated treatment was 2.8 months in the THR group and 0.5 months in the resistance training group.
Those allocated to the THR group also underwent a “fast track” program that involved patient education, pain management, and early mobilization.
The resistance training group received 12 weeks of exercise supervised by a physiotherapist and then offered 12 weeks of additional exercise conducted on their own. The physiotherapist-supervised exercise sessions were held twice weekly and lasted for 1 hour. These started with a 10-minute warm-up on a stationary bike, followed by a standard set of resistance-based exercises that included a leg press, hip extension, hip flexion, and hip abduction.
‘Reassuring’ Results
In a comment, consultant orthopedic surgeon Antony Palmer, MA, BMBCh, DPhil, said: “It’s reassuring that patients with advanced symptomatic osteoarthritis do well with hip replacements.”
THR does of course come with the potential risk for complications, but “the rate of these is what you’d expect for that procedure,” Palmer said, who works for the Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, and is a senior clinical research fellow at Oxford University in England.
In the THR arm, there was one case of prosthetic joint infection, one hip dislocation, two revision surgeries, one instance of foot drop, and one case of gastroesophageal reflux. Meanwhile, in the resistance training group, there was one hip dislocation, one pelvic fracture, one case of atrial fibrillation, and one urinary tract and renal infection.
Overall, any serious adverse event was reported in six (12%) of 48 patients in the THR arm vs five (9%) of 55 participants in the resistance training group, of which only one, occurring in the resistance training group, resulted in discontinuation of the program.
Resistance Training Role
A notable finding was that, at 6 months, five (9%) people assigned to the THR arm had not undergone surgery, and 12 (21%) people in the resistance training group had undergone a THR.
This could suggest two things, Palmer suggested in the interview. The first is that there could be a small proportion of people assigned to THR who may not need the operation and do well with exercise therapy. And, conversely, there may be those who would do well having the surgery without first going through the intermediate stage of physical therapy.
It’s a suggestion that “maybe we’ve got to refine that a bit better and identify the patients that really do benefit from physiotherapy and who might not need hip replacement as a result,” Palmer said.
Or in other words, “should all patients undergo a program of physiotherapy before considering surgery?” he added.
Authors’ View
The PROHIP investigators conclude: “These results support current recommendations for the management of hip osteoarthritis and may be used to inform and guide shared decision making in clinical practice.”
Moreover, the results “do not oppose the use of resistance training as initial treatment,” says the authors.
Frydendal highlighted in his interview that nearly three out of four of the patients reported not to have undertaken any type of supervised exercise before entry into the study, which is a first-line, guideline-recommended option.
“If a patient tells me, ‘I haven’t done any exercise previously,’ I’d recommend starting with completing a 6- to 12-week exercise program that is tailored to your individual needs and evaluate your symptoms afterward,” he said.
“But we should refer the patient if our first-line treatment does not offer any improvements in the patient’s symptoms, as surgery with total hip replacement is clearly a really good treatment option,” Frydendal said.
The study was funded by the Danish Rheumatism Association, among other independent bodies. Frydendal and Palmer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Disc Degeneration in Chronic Low Back Pain: Can Stem Cells Help?
TOPLINE:
Allogeneic bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stromal cells (BM-MSCs) are safe but do not show efficacy in treating intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) in patients with chronic low back pain.
METHODOLOGY:
- The RESPINE trial assessed the efficacy and safety of a single intradiscal injection of allogeneic BM-MSCs in the treatment of chronic low back pain caused by single-level IDD.
- Overall, 114 patients (mean age, 40.9 years; 35% women) with IDD-associated chronic low back pain that was persistent for 3 months or more despite conventional medical therapy and without previous surgery, were recruited across four European countries from April 2018 to April 2021 and randomly assigned to receive either intradiscal injections of allogeneic BM-MSCs (n = 58) or sham injections (n = 56).
- The first co-primary endpoint was the rate of response to BM-MSC injections at 12 months after treatment, defined as improvement of at least 20% or 20 mm in the Visual Analog Scale for pain or improvement of at least 20% in the Oswestry Disability Index for functional status.
- The secondary co-primary endpoint was structural efficacy, based on disc fluid content measured by quantitative T2 MRI between baseline and month 12.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 12 months post-intervention, 74% of patients in the BM-MSC group were classified as responders compared with 68.8% in the placebo group. However, the difference between the groups was not statistically significant.
- The probability of being a responder was higher in the BM-MSC group than in the sham group; however, the findings did not reach statistical significance.
- The average change in disc fluid content, indicative of disc regeneration, from baseline to 12 months was 37.9% in the BM-MSC group and 41.7% in the placebo group, with no significant difference between the groups.
- The incidence of adverse events and serious adverse events was not significantly different between the treatment groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“BM-MSC represents a promising opportunity for the biological treatment of IDD, but only high-quality randomized controlled trials, comparing it to standard care, can determine whether it is a truly effective alternative to spine fusion or disc replacement,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yves-Marie Pers, MD, PhD, Clinical Immunology and Osteoarticular Diseases Therapeutic Unit, CHRU Lapeyronie, Montpellier, France. It was published online on October 11, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
MRI results were collected from only 55 patients across both trial arms, which may have affected the statistical power of the findings. Although patients were monitored for up to 24 months, the long-term efficacy and safety of BM-MSC therapy for IDD may not have been fully captured. Selection bias could not be excluded because of the difficulty in accurately identifying patients with chronic low back pain caused by single-level IDD.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Allogeneic bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stromal cells (BM-MSCs) are safe but do not show efficacy in treating intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) in patients with chronic low back pain.
METHODOLOGY:
- The RESPINE trial assessed the efficacy and safety of a single intradiscal injection of allogeneic BM-MSCs in the treatment of chronic low back pain caused by single-level IDD.
- Overall, 114 patients (mean age, 40.9 years; 35% women) with IDD-associated chronic low back pain that was persistent for 3 months or more despite conventional medical therapy and without previous surgery, were recruited across four European countries from April 2018 to April 2021 and randomly assigned to receive either intradiscal injections of allogeneic BM-MSCs (n = 58) or sham injections (n = 56).
- The first co-primary endpoint was the rate of response to BM-MSC injections at 12 months after treatment, defined as improvement of at least 20% or 20 mm in the Visual Analog Scale for pain or improvement of at least 20% in the Oswestry Disability Index for functional status.
- The secondary co-primary endpoint was structural efficacy, based on disc fluid content measured by quantitative T2 MRI between baseline and month 12.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 12 months post-intervention, 74% of patients in the BM-MSC group were classified as responders compared with 68.8% in the placebo group. However, the difference between the groups was not statistically significant.
- The probability of being a responder was higher in the BM-MSC group than in the sham group; however, the findings did not reach statistical significance.
- The average change in disc fluid content, indicative of disc regeneration, from baseline to 12 months was 37.9% in the BM-MSC group and 41.7% in the placebo group, with no significant difference between the groups.
- The incidence of adverse events and serious adverse events was not significantly different between the treatment groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“BM-MSC represents a promising opportunity for the biological treatment of IDD, but only high-quality randomized controlled trials, comparing it to standard care, can determine whether it is a truly effective alternative to spine fusion or disc replacement,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yves-Marie Pers, MD, PhD, Clinical Immunology and Osteoarticular Diseases Therapeutic Unit, CHRU Lapeyronie, Montpellier, France. It was published online on October 11, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
MRI results were collected from only 55 patients across both trial arms, which may have affected the statistical power of the findings. Although patients were monitored for up to 24 months, the long-term efficacy and safety of BM-MSC therapy for IDD may not have been fully captured. Selection bias could not be excluded because of the difficulty in accurately identifying patients with chronic low back pain caused by single-level IDD.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Allogeneic bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stromal cells (BM-MSCs) are safe but do not show efficacy in treating intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) in patients with chronic low back pain.
METHODOLOGY:
- The RESPINE trial assessed the efficacy and safety of a single intradiscal injection of allogeneic BM-MSCs in the treatment of chronic low back pain caused by single-level IDD.
- Overall, 114 patients (mean age, 40.9 years; 35% women) with IDD-associated chronic low back pain that was persistent for 3 months or more despite conventional medical therapy and without previous surgery, were recruited across four European countries from April 2018 to April 2021 and randomly assigned to receive either intradiscal injections of allogeneic BM-MSCs (n = 58) or sham injections (n = 56).
- The first co-primary endpoint was the rate of response to BM-MSC injections at 12 months after treatment, defined as improvement of at least 20% or 20 mm in the Visual Analog Scale for pain or improvement of at least 20% in the Oswestry Disability Index for functional status.
- The secondary co-primary endpoint was structural efficacy, based on disc fluid content measured by quantitative T2 MRI between baseline and month 12.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 12 months post-intervention, 74% of patients in the BM-MSC group were classified as responders compared with 68.8% in the placebo group. However, the difference between the groups was not statistically significant.
- The probability of being a responder was higher in the BM-MSC group than in the sham group; however, the findings did not reach statistical significance.
- The average change in disc fluid content, indicative of disc regeneration, from baseline to 12 months was 37.9% in the BM-MSC group and 41.7% in the placebo group, with no significant difference between the groups.
- The incidence of adverse events and serious adverse events was not significantly different between the treatment groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“BM-MSC represents a promising opportunity for the biological treatment of IDD, but only high-quality randomized controlled trials, comparing it to standard care, can determine whether it is a truly effective alternative to spine fusion or disc replacement,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yves-Marie Pers, MD, PhD, Clinical Immunology and Osteoarticular Diseases Therapeutic Unit, CHRU Lapeyronie, Montpellier, France. It was published online on October 11, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
MRI results were collected from only 55 patients across both trial arms, which may have affected the statistical power of the findings. Although patients were monitored for up to 24 months, the long-term efficacy and safety of BM-MSC therapy for IDD may not have been fully captured. Selection bias could not be excluded because of the difficulty in accurately identifying patients with chronic low back pain caused by single-level IDD.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Arthroscopy Doesn’t Delay Total Knee Replacement in Knee Osteoarthritis
TOPLINE:
Adding arthroscopic surgery to nonoperative management neither delays nor accelerates the timing of total knee arthroplasty (TKA) in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA).
METHODOLOGY:
- Some case series show that arthroscopic surgery for knee OA may delay more invasive procedures, such as TKA or osteotomy, while longitudinal cohort studies often contradict this. Current OA guidelines are yet to address this issue.
- This secondary analysis of a randomized trial compared the long-term incidence of TKA in 178 patients (mean age, 59 years; 64.3% women) with knee OA who were referred for potential arthroscopic surgery at a tertiary care center in Canada.
- The patients received nonoperative care with or without additional arthroscopic surgery.
- Patients in the arthroscopic surgery group had specific knee procedures (resection of degenerative knee tissues) along with nonoperative management (physical therapy plus medications as required), while the control group received nonoperative management alone.
- The primary outcome was TKA on the knee being studied, and the secondary outcome was TKA or osteotomy on either knee.
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 13.8 years, 37.6% of patients underwent TKA, with comparable proportions of patients in the arthroscopic surgery and control groups undergoing TKA (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.85; 95% CI, 0.52-1.40).
- The rates of TKA or osteotomy on either knee were similar in both groups (aHR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.59-1.41).
- A time-stratified analysis done for 0-5 years, 5-10 years, and beyond 10 years of follow-up also showed a consistent interpretation.
- When patients with crossover to arthroscopic surgery during the follow-up were included, the results remained similar for both the primary (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.53-1.44) and secondary (HR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.69-1.68) outcomes.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study findings do not support the use of arthroscopic surgery for OA of the knee.” “Arthroscopic surgery does not provide additional benefit to nonoperative management for improving pain, stiffness, and function and is likely not cost-effective at 2 years of follow-up,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Trevor B. Birmingham, PhD, Fowler Kennedy Sport Medicine Clinic, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada. It was published online in JAMA Network Open
LIMITATIONS:
The study was designed to assess differences in 2-year patient-reported outcomes rather than long-term TKA incidence. Factors influencing decisions to undergo TKA or osteotomy were not considered. Moreover, the effects observed in this study should be evaluated considering the estimated confidence intervals.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-Term Care. Some authors declared consulting, performing contracted services, or receiving grant funding, royalties, and nonfinancial support from various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adding arthroscopic surgery to nonoperative management neither delays nor accelerates the timing of total knee arthroplasty (TKA) in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA).
METHODOLOGY:
- Some case series show that arthroscopic surgery for knee OA may delay more invasive procedures, such as TKA or osteotomy, while longitudinal cohort studies often contradict this. Current OA guidelines are yet to address this issue.
- This secondary analysis of a randomized trial compared the long-term incidence of TKA in 178 patients (mean age, 59 years; 64.3% women) with knee OA who were referred for potential arthroscopic surgery at a tertiary care center in Canada.
- The patients received nonoperative care with or without additional arthroscopic surgery.
- Patients in the arthroscopic surgery group had specific knee procedures (resection of degenerative knee tissues) along with nonoperative management (physical therapy plus medications as required), while the control group received nonoperative management alone.
- The primary outcome was TKA on the knee being studied, and the secondary outcome was TKA or osteotomy on either knee.
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 13.8 years, 37.6% of patients underwent TKA, with comparable proportions of patients in the arthroscopic surgery and control groups undergoing TKA (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.85; 95% CI, 0.52-1.40).
- The rates of TKA or osteotomy on either knee were similar in both groups (aHR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.59-1.41).
- A time-stratified analysis done for 0-5 years, 5-10 years, and beyond 10 years of follow-up also showed a consistent interpretation.
- When patients with crossover to arthroscopic surgery during the follow-up were included, the results remained similar for both the primary (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.53-1.44) and secondary (HR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.69-1.68) outcomes.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study findings do not support the use of arthroscopic surgery for OA of the knee.” “Arthroscopic surgery does not provide additional benefit to nonoperative management for improving pain, stiffness, and function and is likely not cost-effective at 2 years of follow-up,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Trevor B. Birmingham, PhD, Fowler Kennedy Sport Medicine Clinic, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada. It was published online in JAMA Network Open
LIMITATIONS:
The study was designed to assess differences in 2-year patient-reported outcomes rather than long-term TKA incidence. Factors influencing decisions to undergo TKA or osteotomy were not considered. Moreover, the effects observed in this study should be evaluated considering the estimated confidence intervals.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-Term Care. Some authors declared consulting, performing contracted services, or receiving grant funding, royalties, and nonfinancial support from various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adding arthroscopic surgery to nonoperative management neither delays nor accelerates the timing of total knee arthroplasty (TKA) in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA).
METHODOLOGY:
- Some case series show that arthroscopic surgery for knee OA may delay more invasive procedures, such as TKA or osteotomy, while longitudinal cohort studies often contradict this. Current OA guidelines are yet to address this issue.
- This secondary analysis of a randomized trial compared the long-term incidence of TKA in 178 patients (mean age, 59 years; 64.3% women) with knee OA who were referred for potential arthroscopic surgery at a tertiary care center in Canada.
- The patients received nonoperative care with or without additional arthroscopic surgery.
- Patients in the arthroscopic surgery group had specific knee procedures (resection of degenerative knee tissues) along with nonoperative management (physical therapy plus medications as required), while the control group received nonoperative management alone.
- The primary outcome was TKA on the knee being studied, and the secondary outcome was TKA or osteotomy on either knee.
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 13.8 years, 37.6% of patients underwent TKA, with comparable proportions of patients in the arthroscopic surgery and control groups undergoing TKA (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.85; 95% CI, 0.52-1.40).
- The rates of TKA or osteotomy on either knee were similar in both groups (aHR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.59-1.41).
- A time-stratified analysis done for 0-5 years, 5-10 years, and beyond 10 years of follow-up also showed a consistent interpretation.
- When patients with crossover to arthroscopic surgery during the follow-up were included, the results remained similar for both the primary (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.53-1.44) and secondary (HR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.69-1.68) outcomes.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study findings do not support the use of arthroscopic surgery for OA of the knee.” “Arthroscopic surgery does not provide additional benefit to nonoperative management for improving pain, stiffness, and function and is likely not cost-effective at 2 years of follow-up,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Trevor B. Birmingham, PhD, Fowler Kennedy Sport Medicine Clinic, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada. It was published online in JAMA Network Open
LIMITATIONS:
The study was designed to assess differences in 2-year patient-reported outcomes rather than long-term TKA incidence. Factors influencing decisions to undergo TKA or osteotomy were not considered. Moreover, the effects observed in this study should be evaluated considering the estimated confidence intervals.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-Term Care. Some authors declared consulting, performing contracted services, or receiving grant funding, royalties, and nonfinancial support from various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
What Does Natural Healing of ACL Ruptures Mean for Long-Term Outcomes?
VIENNA — Nearly one third of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries appear to heal without surgery, according to an analysis of three-dimensional MRI data taken from the NACOX study, presented as a late-breaking poster at the OARSI 2024 World Congress.
At 2 years after injury, three-dimensional MRI showed that 13 of 43 (30%) knees had evidence of normal, continuous ACL fibers. Moreover, a further 14 (33%) knees had a continuous ACL fiber structure following rehabilitation alone. ACL fibers were partly (16%) or completely (21%) ruptured in the remainder of cases.
“If you think of the ACL like a rope, when there is continuity, it means those fibers have rejoined,” study coauthor Stephanie Filbay, PhD, an associate professor at the University of Melbourne in Australia, told this news organization.
“Within that, there’s a few variations of healing that we’re seeing. Some look like they’ve never been injured, while some have rejoined but appear thinner or longer than a normal ACL,” Dr. Filbay said.
She added: “What all this research is showing is that it’s happening at a much higher rate than we thought possible. And in some of the studies, it looks like ACL healing is associated with very favorable outcomes.”
At OARSI 2024, Dr. Filbay presented additional data from her and others’ research on the relationships between ACL healing and long-term functional outcomes and osteoarthritis (OA) incidence in comparisons between patients’ treatment pathways: Early ACL surgery, rehabilitation followed by delayed surgery, or rehabilitation only.
Healing Without Surgery
The idea that the ACL can heal without surgery is relatively recent and perhaps still not widely accepted as a concept, as Dr. Filbay explained during a plenary lecture at the congress.
Dr. Filbay explained that the ideal management of ACL injury depends on the severity of knee injury and whether someone’s knee is stable after trying nonsurgical management. Results of the ACL SNNAP trial, for example, have suggested that surgical reconstruction is superior to a rehabilitation strategy for managing non-acute ACL injuries where there are persistent symptoms of instability.
However, there have been two trials — COMPARE performed in the Netherlands and KANON performed in Sweden — that found that early surgery was no better than a strategy of initial rehabilitation with the option of having a delayed ACL surgery if needed.
What Happens Long Term?
Posttraumatic OA is a well-known long-term consequence of ACL injury. According to a recent meta-analysis, there is a sevenfold increased risk for OA comparing people who have and have not had an ACL injury.
ACL injury also results in OA occurring at an earlier age than in people with OA who have not had an ACL injury. This has been shown to progress at a faster rate and be associated with a longer period of disability, Dr. Filbay said at the congress, sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
But does the ACL really heal? Dr. Filbay thinks that it does and has been involved in several studies that have used MRI to look at how the ACL may do so.
In a recently published paper, Dr. Filbay and colleagues reported the findings from a secondary analysis of the KANON trial and found that nearly one in three (30%) of the participants who had been randomized to optional delayed surgery had MRI evidence of healing at 2 years. But when they excluded people who had delayed surgery, 53% of people managed by rehabilitation alone had evidence of healing.
The evaluation also found that those who had a healed vs non-healed ligament had better results using the Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS), and that there were better outcomes at 2 years among those with ACL healing vs those who had early or delayed ACL surgery.
ACL Continuity and Long-Term Outcomes
At OARSI 2024, Dr. Filbay and colleagues reported an even longer-term secondary analysis of the KANON trial on the relationship between ACL healing at 5 years and outcomes at 11 years. The results were first reported in NEJM Evidence.
Dr. Filbay reported that participants with ACL continuity on MRI at 5 years actually had worse patient-reported outcomes 11 years later than those who were managed with early or delayed ACL reconstruction.
“This does not align with previous findings suggesting better 2-year outcomes compared to the surgically managed groups,” Dr. Filbay said.
However, people with ACL continuity following rehabilitation did seem to show numerically similar or fewer signs of radiographic OA at 11 years vs the surgical groups.
Radiographic OA of the tibiofemoral joint (TFJ) or patellofemoral joint (PFJ) at 11 years was observed in a respective 14% and 21% of people with ACL continuity at 5 years (n = 14) and in 22% and 11% of people with ACL discontinuity at 5 years in the rehabilitation alone group.
By comparison, radiographic OA of the TFJ or PFJ at 11 years was seen in a respective 23% and 35% of people who had rehabilitation with delayed surgery (n = 26) and in 18% and 41% of those who had early surgery (n = 49).
These are descriptive results, Dr. Filbay said, because the numbers were too small to do a statistical analysis. Further, larger, longitudinal studies will be needed.
Posttraumatic OA After ACL Surgery
Elsewhere at OARSI 2024, Matthew Harkey, PhD, and colleagues from Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan, reported data showing that nearly two thirds of people who undergo surgical reconstruction have symptoms at 6 months that could be indicative of early knee OA.
Knee symptoms indicative of OA declined to 53% at 12 months and 45% at 24 months.
“It’s a bit complex — we can’t outright say arthritis is developing, but there’s a large group of patients whose symptoms linger long after surgery,” Dr. Harkey said in a press release.
“Often, clinicians assume that these postoperative symptoms will naturally improve as patients reengage with their usual activities. However, what we’re seeing suggests these symptoms persist and likely require a targeted approach to manage or improve them,” Dr. Harkey said.
The analysis used data on 3752 individuals aged 14-40 years who were enrolled in the New Zealand ACL Registry and who completed the KOOS at 6, 12, and 24 months after having ACL reconstruction.
Dr. Harkey and team reported that one in three people had persistent early OA symptoms at 2 years, while 23% had no early OA symptoms at any timepoint.
The studies were independently supported. Dr. Filbay and Dr. Harkey had no relevant financial relationships to report.
Dr. Filbay and colleagues have developed a treatment decision aid for individuals who have sustained an ACL injury. This provides information on the different treatment options available and how they compare.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — Nearly one third of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries appear to heal without surgery, according to an analysis of three-dimensional MRI data taken from the NACOX study, presented as a late-breaking poster at the OARSI 2024 World Congress.
At 2 years after injury, three-dimensional MRI showed that 13 of 43 (30%) knees had evidence of normal, continuous ACL fibers. Moreover, a further 14 (33%) knees had a continuous ACL fiber structure following rehabilitation alone. ACL fibers were partly (16%) or completely (21%) ruptured in the remainder of cases.
“If you think of the ACL like a rope, when there is continuity, it means those fibers have rejoined,” study coauthor Stephanie Filbay, PhD, an associate professor at the University of Melbourne in Australia, told this news organization.
“Within that, there’s a few variations of healing that we’re seeing. Some look like they’ve never been injured, while some have rejoined but appear thinner or longer than a normal ACL,” Dr. Filbay said.
She added: “What all this research is showing is that it’s happening at a much higher rate than we thought possible. And in some of the studies, it looks like ACL healing is associated with very favorable outcomes.”
At OARSI 2024, Dr. Filbay presented additional data from her and others’ research on the relationships between ACL healing and long-term functional outcomes and osteoarthritis (OA) incidence in comparisons between patients’ treatment pathways: Early ACL surgery, rehabilitation followed by delayed surgery, or rehabilitation only.
Healing Without Surgery
The idea that the ACL can heal without surgery is relatively recent and perhaps still not widely accepted as a concept, as Dr. Filbay explained during a plenary lecture at the congress.
Dr. Filbay explained that the ideal management of ACL injury depends on the severity of knee injury and whether someone’s knee is stable after trying nonsurgical management. Results of the ACL SNNAP trial, for example, have suggested that surgical reconstruction is superior to a rehabilitation strategy for managing non-acute ACL injuries where there are persistent symptoms of instability.
However, there have been two trials — COMPARE performed in the Netherlands and KANON performed in Sweden — that found that early surgery was no better than a strategy of initial rehabilitation with the option of having a delayed ACL surgery if needed.
What Happens Long Term?
Posttraumatic OA is a well-known long-term consequence of ACL injury. According to a recent meta-analysis, there is a sevenfold increased risk for OA comparing people who have and have not had an ACL injury.
ACL injury also results in OA occurring at an earlier age than in people with OA who have not had an ACL injury. This has been shown to progress at a faster rate and be associated with a longer period of disability, Dr. Filbay said at the congress, sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
But does the ACL really heal? Dr. Filbay thinks that it does and has been involved in several studies that have used MRI to look at how the ACL may do so.
In a recently published paper, Dr. Filbay and colleagues reported the findings from a secondary analysis of the KANON trial and found that nearly one in three (30%) of the participants who had been randomized to optional delayed surgery had MRI evidence of healing at 2 years. But when they excluded people who had delayed surgery, 53% of people managed by rehabilitation alone had evidence of healing.
The evaluation also found that those who had a healed vs non-healed ligament had better results using the Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS), and that there were better outcomes at 2 years among those with ACL healing vs those who had early or delayed ACL surgery.
ACL Continuity and Long-Term Outcomes
At OARSI 2024, Dr. Filbay and colleagues reported an even longer-term secondary analysis of the KANON trial on the relationship between ACL healing at 5 years and outcomes at 11 years. The results were first reported in NEJM Evidence.
Dr. Filbay reported that participants with ACL continuity on MRI at 5 years actually had worse patient-reported outcomes 11 years later than those who were managed with early or delayed ACL reconstruction.
“This does not align with previous findings suggesting better 2-year outcomes compared to the surgically managed groups,” Dr. Filbay said.
However, people with ACL continuity following rehabilitation did seem to show numerically similar or fewer signs of radiographic OA at 11 years vs the surgical groups.
Radiographic OA of the tibiofemoral joint (TFJ) or patellofemoral joint (PFJ) at 11 years was observed in a respective 14% and 21% of people with ACL continuity at 5 years (n = 14) and in 22% and 11% of people with ACL discontinuity at 5 years in the rehabilitation alone group.
By comparison, radiographic OA of the TFJ or PFJ at 11 years was seen in a respective 23% and 35% of people who had rehabilitation with delayed surgery (n = 26) and in 18% and 41% of those who had early surgery (n = 49).
These are descriptive results, Dr. Filbay said, because the numbers were too small to do a statistical analysis. Further, larger, longitudinal studies will be needed.
Posttraumatic OA After ACL Surgery
Elsewhere at OARSI 2024, Matthew Harkey, PhD, and colleagues from Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan, reported data showing that nearly two thirds of people who undergo surgical reconstruction have symptoms at 6 months that could be indicative of early knee OA.
Knee symptoms indicative of OA declined to 53% at 12 months and 45% at 24 months.
“It’s a bit complex — we can’t outright say arthritis is developing, but there’s a large group of patients whose symptoms linger long after surgery,” Dr. Harkey said in a press release.
“Often, clinicians assume that these postoperative symptoms will naturally improve as patients reengage with their usual activities. However, what we’re seeing suggests these symptoms persist and likely require a targeted approach to manage or improve them,” Dr. Harkey said.
The analysis used data on 3752 individuals aged 14-40 years who were enrolled in the New Zealand ACL Registry and who completed the KOOS at 6, 12, and 24 months after having ACL reconstruction.
Dr. Harkey and team reported that one in three people had persistent early OA symptoms at 2 years, while 23% had no early OA symptoms at any timepoint.
The studies were independently supported. Dr. Filbay and Dr. Harkey had no relevant financial relationships to report.
Dr. Filbay and colleagues have developed a treatment decision aid for individuals who have sustained an ACL injury. This provides information on the different treatment options available and how they compare.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — Nearly one third of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries appear to heal without surgery, according to an analysis of three-dimensional MRI data taken from the NACOX study, presented as a late-breaking poster at the OARSI 2024 World Congress.
At 2 years after injury, three-dimensional MRI showed that 13 of 43 (30%) knees had evidence of normal, continuous ACL fibers. Moreover, a further 14 (33%) knees had a continuous ACL fiber structure following rehabilitation alone. ACL fibers were partly (16%) or completely (21%) ruptured in the remainder of cases.
“If you think of the ACL like a rope, when there is continuity, it means those fibers have rejoined,” study coauthor Stephanie Filbay, PhD, an associate professor at the University of Melbourne in Australia, told this news organization.
“Within that, there’s a few variations of healing that we’re seeing. Some look like they’ve never been injured, while some have rejoined but appear thinner or longer than a normal ACL,” Dr. Filbay said.
She added: “What all this research is showing is that it’s happening at a much higher rate than we thought possible. And in some of the studies, it looks like ACL healing is associated with very favorable outcomes.”
At OARSI 2024, Dr. Filbay presented additional data from her and others’ research on the relationships between ACL healing and long-term functional outcomes and osteoarthritis (OA) incidence in comparisons between patients’ treatment pathways: Early ACL surgery, rehabilitation followed by delayed surgery, or rehabilitation only.
Healing Without Surgery
The idea that the ACL can heal without surgery is relatively recent and perhaps still not widely accepted as a concept, as Dr. Filbay explained during a plenary lecture at the congress.
Dr. Filbay explained that the ideal management of ACL injury depends on the severity of knee injury and whether someone’s knee is stable after trying nonsurgical management. Results of the ACL SNNAP trial, for example, have suggested that surgical reconstruction is superior to a rehabilitation strategy for managing non-acute ACL injuries where there are persistent symptoms of instability.
However, there have been two trials — COMPARE performed in the Netherlands and KANON performed in Sweden — that found that early surgery was no better than a strategy of initial rehabilitation with the option of having a delayed ACL surgery if needed.
What Happens Long Term?
Posttraumatic OA is a well-known long-term consequence of ACL injury. According to a recent meta-analysis, there is a sevenfold increased risk for OA comparing people who have and have not had an ACL injury.
ACL injury also results in OA occurring at an earlier age than in people with OA who have not had an ACL injury. This has been shown to progress at a faster rate and be associated with a longer period of disability, Dr. Filbay said at the congress, sponsored by the Osteoarthritis Research Society International.
But does the ACL really heal? Dr. Filbay thinks that it does and has been involved in several studies that have used MRI to look at how the ACL may do so.
In a recently published paper, Dr. Filbay and colleagues reported the findings from a secondary analysis of the KANON trial and found that nearly one in three (30%) of the participants who had been randomized to optional delayed surgery had MRI evidence of healing at 2 years. But when they excluded people who had delayed surgery, 53% of people managed by rehabilitation alone had evidence of healing.
The evaluation also found that those who had a healed vs non-healed ligament had better results using the Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS), and that there were better outcomes at 2 years among those with ACL healing vs those who had early or delayed ACL surgery.
ACL Continuity and Long-Term Outcomes
At OARSI 2024, Dr. Filbay and colleagues reported an even longer-term secondary analysis of the KANON trial on the relationship between ACL healing at 5 years and outcomes at 11 years. The results were first reported in NEJM Evidence.
Dr. Filbay reported that participants with ACL continuity on MRI at 5 years actually had worse patient-reported outcomes 11 years later than those who were managed with early or delayed ACL reconstruction.
“This does not align with previous findings suggesting better 2-year outcomes compared to the surgically managed groups,” Dr. Filbay said.
However, people with ACL continuity following rehabilitation did seem to show numerically similar or fewer signs of radiographic OA at 11 years vs the surgical groups.
Radiographic OA of the tibiofemoral joint (TFJ) or patellofemoral joint (PFJ) at 11 years was observed in a respective 14% and 21% of people with ACL continuity at 5 years (n = 14) and in 22% and 11% of people with ACL discontinuity at 5 years in the rehabilitation alone group.
By comparison, radiographic OA of the TFJ or PFJ at 11 years was seen in a respective 23% and 35% of people who had rehabilitation with delayed surgery (n = 26) and in 18% and 41% of those who had early surgery (n = 49).
These are descriptive results, Dr. Filbay said, because the numbers were too small to do a statistical analysis. Further, larger, longitudinal studies will be needed.
Posttraumatic OA After ACL Surgery
Elsewhere at OARSI 2024, Matthew Harkey, PhD, and colleagues from Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan, reported data showing that nearly two thirds of people who undergo surgical reconstruction have symptoms at 6 months that could be indicative of early knee OA.
Knee symptoms indicative of OA declined to 53% at 12 months and 45% at 24 months.
“It’s a bit complex — we can’t outright say arthritis is developing, but there’s a large group of patients whose symptoms linger long after surgery,” Dr. Harkey said in a press release.
“Often, clinicians assume that these postoperative symptoms will naturally improve as patients reengage with their usual activities. However, what we’re seeing suggests these symptoms persist and likely require a targeted approach to manage or improve them,” Dr. Harkey said.
The analysis used data on 3752 individuals aged 14-40 years who were enrolled in the New Zealand ACL Registry and who completed the KOOS at 6, 12, and 24 months after having ACL reconstruction.
Dr. Harkey and team reported that one in three people had persistent early OA symptoms at 2 years, while 23% had no early OA symptoms at any timepoint.
The studies were independently supported. Dr. Filbay and Dr. Harkey had no relevant financial relationships to report.
Dr. Filbay and colleagues have developed a treatment decision aid for individuals who have sustained an ACL injury. This provides information on the different treatment options available and how they compare.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM OARSI 2024