User login
AVAHO
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]


Improving Colorectal Cancer Screening via Mailed Fecal Immunochemical Testing in a Veterans Affairs Health System
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
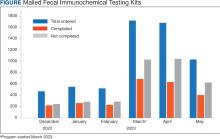
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
Adding Protein EpiScores May Better Predict CRC Survival
Adding Protein EpiScores May Better Predict CRC Survival
DNA methylation-derived biomarkers called Protein EpiScores may improve the accuracy of disease-free and overall survival prediction in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC), compared with traditional clinical risk factors alone, suggest results of a prospective study.
Although Protein EpiScores require further validation before they are ready for clinical use, the present data offer insights into the underlying processes shaping CRC outcomes, lead author Alicia R. Richards, PhD, of Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, Florida, and colleagues wrote in Clinical Epigenetics.
“The immediate value of our findings is highlighting biological pathways like immune suppression and coagulation as drivers of poor outcomes,” senior author Jacob K. Kresovich, PhD, of Moffitt Cancer Center, told Medscape Medical News.
What Are Protein EpiScores?
Previous studies have evaluated epigenetic clocks, which are derived from DNA methylation profiles, as markers for CRC risk. However, these clocks cannot pinpoint specific biological drivers of cancer progression, the investigators wrote.
Protein EpiScores may fill this gap; they were developed based on previous work suggesting that DNA methylation profiles may improve disease prediction based on circulating proteins (eg, C-reactive protein) and physiologic traits (eg, smoking status) beyond directly measuring those same variables.
“Protein EpiScores may therefore represent a complementary class of biomarker to direct measurements,” the investigators wrote.
Although Protein EpiScores have helped uncover biological processes driving various conditions such as cardiovascular disease and cancer, this is the first study to evaluate them specifically in the context of cancer survival.
How Did This Study Evaluate Protein EpiScores in Patients With CRC?
The present study involved 136 patients with newly diagnosed CRC from the prospective ColoCare Study.
For each patient, the investigators recorded 107 Protein EpiScores from pretreatment whole blood samples. Disease-free and overall survival were monitored over a median follow-up of 7.3 years and as long as 13.8 years. During follow-up, 26% of patients experienced disease recurrence, and 35% died.
With these data, the investigators compared the predictive power of the Protein EpiScores vs traditional clinical risk factors for disease-free and overall survival. “We used the standard factors doctors routinely collect before treatment starts to assess prognosis, including tumor stage, age at cancer diagnosis, sex, body mass index, race, and tumor location,” Kresovich said. “These are well-established predictors readily available from medical records.”
What Were the Key Findings?
Adding specific Protein EpiScores to the standard clinical risk factors significantly improved prognostic accuracy for survival.
After adjusting for confounding variables, the HCII, VEGFA, CCL17, and LGALS3BP Protein EpiScores were each independently associated with worse disease-free survival, with hazard ratios ranging from 1.62 to 1.71. Adding these scores to the clinical model improved the concordance index (C-index) from 0.64 to 0.70.
The LGALS3BP Protein EpiScore was also independently linked to overall survival, with a hazard ratio of 1.80. Adding this score to the model raised the C-index from 0.70 to 0.75.
Finally, the HCII, LGALS3BP, MMP12, and VEGFA Protein EpiScores were tied to both disease-free and overall survival with hazard ratios above 1.50.
Are These Findings Practice-Changing?
“The improvements [in prognostic accuracy] are modest but potentially meaningful and comparable to gains from other established biomarkers,” Kresovich said. “The 6-point improvement for recurrence (C-index 0.64 to 0.70) resulted in 34% of patients being reclassified into more accurate risk categories.”
In theory, this could have a meaningful clinical impact.
“In cancer care, even incremental gains matter if they prevent undertreating high-risk patients or overtreating low-risk ones,” Kresovich said.
Despite this potential, he was clear that more work is needed.
“If our findings are validated in other epidemiologic settings, these Protein EpiScores could eventually complement existing risk tools, but we’re realistically several years from clinical implementation,” Kresovich said. “We see these current findings more as a research tool that requires validation in larger cohorts before clinical use.”
How Might These Findings Shape Future Research?
Although more studies are needed before clinical rollout, the present findings point to key biological pathways, such as those involving immune suppression and coagulation, which may be driving worse outcomes in patients with CRC.
“This information can guide basic scientists and mechanistic studies to identify potential therapeutic targets,” Kresovich said.
Beyond evaluating Protein EpiScores in larger patient populations, future studies may also need to recruit a more diverse patient population, given the present cohort was 93% White.
Although the investigators noted that “the racial homogeneity reduced potential confounding by ancestry,” they also explained that “Protein EpiScores were developed in European populations, and their translation to individuals with different ancestries has not been closely examined.”
The study was supported by the Miles for Moffitt Team Science Mechanism. The investigators reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DNA methylation-derived biomarkers called Protein EpiScores may improve the accuracy of disease-free and overall survival prediction in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC), compared with traditional clinical risk factors alone, suggest results of a prospective study.
Although Protein EpiScores require further validation before they are ready for clinical use, the present data offer insights into the underlying processes shaping CRC outcomes, lead author Alicia R. Richards, PhD, of Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, Florida, and colleagues wrote in Clinical Epigenetics.
“The immediate value of our findings is highlighting biological pathways like immune suppression and coagulation as drivers of poor outcomes,” senior author Jacob K. Kresovich, PhD, of Moffitt Cancer Center, told Medscape Medical News.
What Are Protein EpiScores?
Previous studies have evaluated epigenetic clocks, which are derived from DNA methylation profiles, as markers for CRC risk. However, these clocks cannot pinpoint specific biological drivers of cancer progression, the investigators wrote.
Protein EpiScores may fill this gap; they were developed based on previous work suggesting that DNA methylation profiles may improve disease prediction based on circulating proteins (eg, C-reactive protein) and physiologic traits (eg, smoking status) beyond directly measuring those same variables.
“Protein EpiScores may therefore represent a complementary class of biomarker to direct measurements,” the investigators wrote.
Although Protein EpiScores have helped uncover biological processes driving various conditions such as cardiovascular disease and cancer, this is the first study to evaluate them specifically in the context of cancer survival.
How Did This Study Evaluate Protein EpiScores in Patients With CRC?
The present study involved 136 patients with newly diagnosed CRC from the prospective ColoCare Study.
For each patient, the investigators recorded 107 Protein EpiScores from pretreatment whole blood samples. Disease-free and overall survival were monitored over a median follow-up of 7.3 years and as long as 13.8 years. During follow-up, 26% of patients experienced disease recurrence, and 35% died.
With these data, the investigators compared the predictive power of the Protein EpiScores vs traditional clinical risk factors for disease-free and overall survival. “We used the standard factors doctors routinely collect before treatment starts to assess prognosis, including tumor stage, age at cancer diagnosis, sex, body mass index, race, and tumor location,” Kresovich said. “These are well-established predictors readily available from medical records.”
What Were the Key Findings?
Adding specific Protein EpiScores to the standard clinical risk factors significantly improved prognostic accuracy for survival.
After adjusting for confounding variables, the HCII, VEGFA, CCL17, and LGALS3BP Protein EpiScores were each independently associated with worse disease-free survival, with hazard ratios ranging from 1.62 to 1.71. Adding these scores to the clinical model improved the concordance index (C-index) from 0.64 to 0.70.
The LGALS3BP Protein EpiScore was also independently linked to overall survival, with a hazard ratio of 1.80. Adding this score to the model raised the C-index from 0.70 to 0.75.
Finally, the HCII, LGALS3BP, MMP12, and VEGFA Protein EpiScores were tied to both disease-free and overall survival with hazard ratios above 1.50.
Are These Findings Practice-Changing?
“The improvements [in prognostic accuracy] are modest but potentially meaningful and comparable to gains from other established biomarkers,” Kresovich said. “The 6-point improvement for recurrence (C-index 0.64 to 0.70) resulted in 34% of patients being reclassified into more accurate risk categories.”
In theory, this could have a meaningful clinical impact.
“In cancer care, even incremental gains matter if they prevent undertreating high-risk patients or overtreating low-risk ones,” Kresovich said.
Despite this potential, he was clear that more work is needed.
“If our findings are validated in other epidemiologic settings, these Protein EpiScores could eventually complement existing risk tools, but we’re realistically several years from clinical implementation,” Kresovich said. “We see these current findings more as a research tool that requires validation in larger cohorts before clinical use.”
How Might These Findings Shape Future Research?
Although more studies are needed before clinical rollout, the present findings point to key biological pathways, such as those involving immune suppression and coagulation, which may be driving worse outcomes in patients with CRC.
“This information can guide basic scientists and mechanistic studies to identify potential therapeutic targets,” Kresovich said.
Beyond evaluating Protein EpiScores in larger patient populations, future studies may also need to recruit a more diverse patient population, given the present cohort was 93% White.
Although the investigators noted that “the racial homogeneity reduced potential confounding by ancestry,” they also explained that “Protein EpiScores were developed in European populations, and their translation to individuals with different ancestries has not been closely examined.”
The study was supported by the Miles for Moffitt Team Science Mechanism. The investigators reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DNA methylation-derived biomarkers called Protein EpiScores may improve the accuracy of disease-free and overall survival prediction in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC), compared with traditional clinical risk factors alone, suggest results of a prospective study.
Although Protein EpiScores require further validation before they are ready for clinical use, the present data offer insights into the underlying processes shaping CRC outcomes, lead author Alicia R. Richards, PhD, of Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, Florida, and colleagues wrote in Clinical Epigenetics.
“The immediate value of our findings is highlighting biological pathways like immune suppression and coagulation as drivers of poor outcomes,” senior author Jacob K. Kresovich, PhD, of Moffitt Cancer Center, told Medscape Medical News.
What Are Protein EpiScores?
Previous studies have evaluated epigenetic clocks, which are derived from DNA methylation profiles, as markers for CRC risk. However, these clocks cannot pinpoint specific biological drivers of cancer progression, the investigators wrote.
Protein EpiScores may fill this gap; they were developed based on previous work suggesting that DNA methylation profiles may improve disease prediction based on circulating proteins (eg, C-reactive protein) and physiologic traits (eg, smoking status) beyond directly measuring those same variables.
“Protein EpiScores may therefore represent a complementary class of biomarker to direct measurements,” the investigators wrote.
Although Protein EpiScores have helped uncover biological processes driving various conditions such as cardiovascular disease and cancer, this is the first study to evaluate them specifically in the context of cancer survival.
How Did This Study Evaluate Protein EpiScores in Patients With CRC?
The present study involved 136 patients with newly diagnosed CRC from the prospective ColoCare Study.
For each patient, the investigators recorded 107 Protein EpiScores from pretreatment whole blood samples. Disease-free and overall survival were monitored over a median follow-up of 7.3 years and as long as 13.8 years. During follow-up, 26% of patients experienced disease recurrence, and 35% died.
With these data, the investigators compared the predictive power of the Protein EpiScores vs traditional clinical risk factors for disease-free and overall survival. “We used the standard factors doctors routinely collect before treatment starts to assess prognosis, including tumor stage, age at cancer diagnosis, sex, body mass index, race, and tumor location,” Kresovich said. “These are well-established predictors readily available from medical records.”
What Were the Key Findings?
Adding specific Protein EpiScores to the standard clinical risk factors significantly improved prognostic accuracy for survival.
After adjusting for confounding variables, the HCII, VEGFA, CCL17, and LGALS3BP Protein EpiScores were each independently associated with worse disease-free survival, with hazard ratios ranging from 1.62 to 1.71. Adding these scores to the clinical model improved the concordance index (C-index) from 0.64 to 0.70.
The LGALS3BP Protein EpiScore was also independently linked to overall survival, with a hazard ratio of 1.80. Adding this score to the model raised the C-index from 0.70 to 0.75.
Finally, the HCII, LGALS3BP, MMP12, and VEGFA Protein EpiScores were tied to both disease-free and overall survival with hazard ratios above 1.50.
Are These Findings Practice-Changing?
“The improvements [in prognostic accuracy] are modest but potentially meaningful and comparable to gains from other established biomarkers,” Kresovich said. “The 6-point improvement for recurrence (C-index 0.64 to 0.70) resulted in 34% of patients being reclassified into more accurate risk categories.”
In theory, this could have a meaningful clinical impact.
“In cancer care, even incremental gains matter if they prevent undertreating high-risk patients or overtreating low-risk ones,” Kresovich said.
Despite this potential, he was clear that more work is needed.
“If our findings are validated in other epidemiologic settings, these Protein EpiScores could eventually complement existing risk tools, but we’re realistically several years from clinical implementation,” Kresovich said. “We see these current findings more as a research tool that requires validation in larger cohorts before clinical use.”
How Might These Findings Shape Future Research?
Although more studies are needed before clinical rollout, the present findings point to key biological pathways, such as those involving immune suppression and coagulation, which may be driving worse outcomes in patients with CRC.
“This information can guide basic scientists and mechanistic studies to identify potential therapeutic targets,” Kresovich said.
Beyond evaluating Protein EpiScores in larger patient populations, future studies may also need to recruit a more diverse patient population, given the present cohort was 93% White.
Although the investigators noted that “the racial homogeneity reduced potential confounding by ancestry,” they also explained that “Protein EpiScores were developed in European populations, and their translation to individuals with different ancestries has not been closely examined.”
The study was supported by the Miles for Moffitt Team Science Mechanism. The investigators reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adding Protein EpiScores May Better Predict CRC Survival
Adding Protein EpiScores May Better Predict CRC Survival
Mailed Tests Boost Colorectal Screening in Veterans
TOPLINE: Mailed fecal immunochemical test (FIT) kits with reminder phone calls promote colorectal cancer (CRC) screening among veterans without recent primary care visits. Among 782 veterans in a randomized controlled trial (RCT), mailed FITs resulted in a 26.1% screening completion rate within 6 months, compared with 5.8% for usual care and 7.7% for mailed invitations with reminders. Improving screening in this population may help CRC morbidity and mortality among veterans.
METHODOLOGY
Researchers conducted a 3-arm pragmatic RCT at the US Department of Verterans Affairs (VA) Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center (CMC-VAMC), enrolling veterans aged 50 to 75 years without a primary care visit within 18 months.
Participants were randomized 1:1:1 to usual care (n = 260), mailed clinic-based screening invitation with reminder calls (n = 261), or mailed home FIT outreach plus prenotification letter and reminder phone calls (n = 261).
Outcome measures included documented completion of CRC screening within 6 months after randomization in the electronic health record (EHR); a secondary outcome was FIT return within 6 months among those mailed FIT.
Eligibility and exclusions were based on chart review and EHR criteria (eg, excluding symptoms, family history, inflammatory bowel disease, prior resection, or being current by having undergone a colonoscopy within 10 years, sigmoidoscopy or barium enema within 5 years, or fecal occult blood testing within 1 year).
TAKEAWAY
CRC screening completion within 6 months is 26.1% with mailed FIT vs 5.8% with usual care (RD, 20.3%; 95% CI, 14.3%-26.3%; RR, 4.5; 95% CI, 2.7-7.7; P < .001).
CRC screening completion within 6 months is 26.1% with mailed FIT vs 7.7% with mailed invitation plus reminders (RD, 18.4%; 95% CI, 12.2%-24.6%; RR, 3.4; 95% CI, 2.1-5.4; P < .001).
Screening completion does not differ between mailed invitation plus reminders (7.7%) and usual care (5.8%), and the comparison is not statistically supported (RR, 1.3; P = .39).
No statistically significant differences in screening completion are reported by age or race/ethnicity, and investigators also report no significant differences in FIT return by age or race/ethnicity in the secondary analysis.
IN PRACTICE
“This research represents the first pragmatic RCT of mailed FIT outreach screening among veterans who have not recently (18 months) used primary care services offered by the VA. In this work, there were large relative, and absolute differences in CRC screening participation rate between veterans offered home FIT screening and those who received usual care (RR = 4.52, RD = 20.2%) or a mailed invitation plus reminders (RR = 3.40, RD = 18.4%)," wrote the authors.
SOURCE
The study was led by Matthew A. Goldshore, MD, PhD, MPH, of the CMC-VAMC . It was published online in Am J Prev Med.
LIMITATIONS
The study was not able identify differences in screening completion or FIT return by patient demographic characteristics such as age and race. The sample was randomized from predominantly male veterans cared for at a single VA medical center, limiting generalizability and reducing external validity. Follow-up and subsequent evaluation of FIT-positive participants is needed for the success of a mailed FIT intervention; of the 3 FIT-positive participants who should have received follow-up evaluation, only 1 underwent colonoscopy, highlighting the challenge of FIT to colonoscopy among participants who do not use care regularly at the CMC-VAMC.
DISCLOSURES
This trial received funding from an VA Health Services Research and Development Service award, with E. Carter Paulson, MD, MSCE, and Chyke A. Doubeni, MD, MPH, serving as principal investigators. Chyke A. Doubeni received support from grant number RO1CA 213645, and Shivan J. Mehta received support from grant number K08CA 234326, both from the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported no financial disclosures.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
TOPLINE: Mailed fecal immunochemical test (FIT) kits with reminder phone calls promote colorectal cancer (CRC) screening among veterans without recent primary care visits. Among 782 veterans in a randomized controlled trial (RCT), mailed FITs resulted in a 26.1% screening completion rate within 6 months, compared with 5.8% for usual care and 7.7% for mailed invitations with reminders. Improving screening in this population may help CRC morbidity and mortality among veterans.
METHODOLOGY
Researchers conducted a 3-arm pragmatic RCT at the US Department of Verterans Affairs (VA) Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center (CMC-VAMC), enrolling veterans aged 50 to 75 years without a primary care visit within 18 months.
Participants were randomized 1:1:1 to usual care (n = 260), mailed clinic-based screening invitation with reminder calls (n = 261), or mailed home FIT outreach plus prenotification letter and reminder phone calls (n = 261).
Outcome measures included documented completion of CRC screening within 6 months after randomization in the electronic health record (EHR); a secondary outcome was FIT return within 6 months among those mailed FIT.
Eligibility and exclusions were based on chart review and EHR criteria (eg, excluding symptoms, family history, inflammatory bowel disease, prior resection, or being current by having undergone a colonoscopy within 10 years, sigmoidoscopy or barium enema within 5 years, or fecal occult blood testing within 1 year).
TAKEAWAY
CRC screening completion within 6 months is 26.1% with mailed FIT vs 5.8% with usual care (RD, 20.3%; 95% CI, 14.3%-26.3%; RR, 4.5; 95% CI, 2.7-7.7; P < .001).
CRC screening completion within 6 months is 26.1% with mailed FIT vs 7.7% with mailed invitation plus reminders (RD, 18.4%; 95% CI, 12.2%-24.6%; RR, 3.4; 95% CI, 2.1-5.4; P < .001).
Screening completion does not differ between mailed invitation plus reminders (7.7%) and usual care (5.8%), and the comparison is not statistically supported (RR, 1.3; P = .39).
No statistically significant differences in screening completion are reported by age or race/ethnicity, and investigators also report no significant differences in FIT return by age or race/ethnicity in the secondary analysis.
IN PRACTICE
“This research represents the first pragmatic RCT of mailed FIT outreach screening among veterans who have not recently (18 months) used primary care services offered by the VA. In this work, there were large relative, and absolute differences in CRC screening participation rate between veterans offered home FIT screening and those who received usual care (RR = 4.52, RD = 20.2%) or a mailed invitation plus reminders (RR = 3.40, RD = 18.4%)," wrote the authors.
SOURCE
The study was led by Matthew A. Goldshore, MD, PhD, MPH, of the CMC-VAMC . It was published online in Am J Prev Med.
LIMITATIONS
The study was not able identify differences in screening completion or FIT return by patient demographic characteristics such as age and race. The sample was randomized from predominantly male veterans cared for at a single VA medical center, limiting generalizability and reducing external validity. Follow-up and subsequent evaluation of FIT-positive participants is needed for the success of a mailed FIT intervention; of the 3 FIT-positive participants who should have received follow-up evaluation, only 1 underwent colonoscopy, highlighting the challenge of FIT to colonoscopy among participants who do not use care regularly at the CMC-VAMC.
DISCLOSURES
This trial received funding from an VA Health Services Research and Development Service award, with E. Carter Paulson, MD, MSCE, and Chyke A. Doubeni, MD, MPH, serving as principal investigators. Chyke A. Doubeni received support from grant number RO1CA 213645, and Shivan J. Mehta received support from grant number K08CA 234326, both from the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported no financial disclosures.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
TOPLINE: Mailed fecal immunochemical test (FIT) kits with reminder phone calls promote colorectal cancer (CRC) screening among veterans without recent primary care visits. Among 782 veterans in a randomized controlled trial (RCT), mailed FITs resulted in a 26.1% screening completion rate within 6 months, compared with 5.8% for usual care and 7.7% for mailed invitations with reminders. Improving screening in this population may help CRC morbidity and mortality among veterans.
METHODOLOGY
Researchers conducted a 3-arm pragmatic RCT at the US Department of Verterans Affairs (VA) Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center (CMC-VAMC), enrolling veterans aged 50 to 75 years without a primary care visit within 18 months.
Participants were randomized 1:1:1 to usual care (n = 260), mailed clinic-based screening invitation with reminder calls (n = 261), or mailed home FIT outreach plus prenotification letter and reminder phone calls (n = 261).
Outcome measures included documented completion of CRC screening within 6 months after randomization in the electronic health record (EHR); a secondary outcome was FIT return within 6 months among those mailed FIT.
Eligibility and exclusions were based on chart review and EHR criteria (eg, excluding symptoms, family history, inflammatory bowel disease, prior resection, or being current by having undergone a colonoscopy within 10 years, sigmoidoscopy or barium enema within 5 years, or fecal occult blood testing within 1 year).
TAKEAWAY
CRC screening completion within 6 months is 26.1% with mailed FIT vs 5.8% with usual care (RD, 20.3%; 95% CI, 14.3%-26.3%; RR, 4.5; 95% CI, 2.7-7.7; P < .001).
CRC screening completion within 6 months is 26.1% with mailed FIT vs 7.7% with mailed invitation plus reminders (RD, 18.4%; 95% CI, 12.2%-24.6%; RR, 3.4; 95% CI, 2.1-5.4; P < .001).
Screening completion does not differ between mailed invitation plus reminders (7.7%) and usual care (5.8%), and the comparison is not statistically supported (RR, 1.3; P = .39).
No statistically significant differences in screening completion are reported by age or race/ethnicity, and investigators also report no significant differences in FIT return by age or race/ethnicity in the secondary analysis.
IN PRACTICE
“This research represents the first pragmatic RCT of mailed FIT outreach screening among veterans who have not recently (18 months) used primary care services offered by the VA. In this work, there were large relative, and absolute differences in CRC screening participation rate between veterans offered home FIT screening and those who received usual care (RR = 4.52, RD = 20.2%) or a mailed invitation plus reminders (RR = 3.40, RD = 18.4%)," wrote the authors.
SOURCE
The study was led by Matthew A. Goldshore, MD, PhD, MPH, of the CMC-VAMC . It was published online in Am J Prev Med.
LIMITATIONS
The study was not able identify differences in screening completion or FIT return by patient demographic characteristics such as age and race. The sample was randomized from predominantly male veterans cared for at a single VA medical center, limiting generalizability and reducing external validity. Follow-up and subsequent evaluation of FIT-positive participants is needed for the success of a mailed FIT intervention; of the 3 FIT-positive participants who should have received follow-up evaluation, only 1 underwent colonoscopy, highlighting the challenge of FIT to colonoscopy among participants who do not use care regularly at the CMC-VAMC.
DISCLOSURES
This trial received funding from an VA Health Services Research and Development Service award, with E. Carter Paulson, MD, MSCE, and Chyke A. Doubeni, MD, MPH, serving as principal investigators. Chyke A. Doubeni received support from grant number RO1CA 213645, and Shivan J. Mehta received support from grant number K08CA 234326, both from the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported no financial disclosures.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
US Cancer Institute Studying Ivermectin's 'Ability to Kill Cancer Cells'
US Cancer Institute Studying Ivermectin's 'Ability to Kill Cancer Cells'
The National Cancer Institute (NCI), the federal research agency charged with leading the war against the nation’s second-largest killer, is studying ivermectin as a potential cancer treatment, according to its top official.
“There are enough reports of it, enough interest in it, that we actually did — ivermectin, in particular — did engage in sort of a better preclinical study of its properties and its ability to kill cancer cells,” said Anthony Letai, a physician the Trump administration appointed as NCI director in September.
Letai did not cite new evidence that might have prompted the institute to research the effectiveness of the antiparasitic drug against cancer. The drug, largely used to treat people or animals for infections caused by parasites, is a popular dewormer for horses.
“We’ll probably have those results in a few months,” Letai said. “So we are taking it seriously.”
He spoke about ivermectin at a January 30 event, “Reclaiming Science: The People’s NIH,” with National Institutes of Health (NIH) Director Jay Bhattacharya and other senior agency officials at Washington, DC’s Willard Hotel. The MAHA Institute hosted the discussion, framed by the “Make America Healthy Again” agenda of Health and Human Services (HSS) Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. The National Cancer Institute is the largest of the NIH’s 27 branches.
During the COVID pandemic, ivermectin’s popularity surged as fringe medical groups promoted it as an effective treatment. Clinical trials have found it isn’t effective against COVID.
Ivermectin has become a symbol of resistance against the medical establishment among MAHA adherents and conservatives. Like-minded commentators and wellness and other online influencers have hyped — without evidence — ivermectin as a miracle cure for a host of diseases, including cancer. Trump officials have pointed to research on ivermectin as an example of the administration’s receptiveness to ideas the scientific establishment has rejected.
“If lots of people believe it and it’s moving public health, we as NIH have an obligation, again, to treat it seriously,” Bhattacharya said at the event. According to The Chronicle at Duke University, Bhattacharya recently said he wants the NIH to be “the research arm of MAHA.”
The decision by the world’s premier cancer research institute to study ivermectin as a cancer treatment has alarmed career scientists at the agency.
“I am shocked and appalled,” one NCI scientist said. “We are moving funds away from so much promising research in order to do a preclinical study based on nonscientific ideas. It’s absurd.”
KFF Health News granted the scientist and other NCI workers anonymity because they are not authorized to speak to the press and fear retaliation.
HHS and the National Cancer Institute did not answer KFF Health News’ questions on the amount of money the cancer institute is spending on the study, who is carrying it out, and whether there was new evidence that prompted NCI to look into ivermectin as an anticancer therapy. Emily Hilliard, an HHS spokesperson, said NIH is dedicated to “rigorous, gold-standard research,” something the administration has repeatedly professed.
A preclinical study is an early phase of research conducted in a lab to test whether a drug or treatment may be useful and to assess potential harms. These studies take place before human clinical trials.
The scientist questioned whether there is enough initial evidence to warrant NCI’s spending of taxpayer funds to investigate the drug’s potential as a cancer treatment.
The FDA has approved ivermectin for certain uses in humans and animals. Tablets are used to treat conditions caused by parasitic worms, and the FDA has approved ivermectin lotions to treat lice and rosacea. Two scientists involved in its discovery won the Nobel Prize in 2015, tied to the drug’s success in treating certain parasitic diseases.
The FDA has warned that large doses of ivermectin can be dangerous. Overdoses can cause seizures, comas, or death.
Kennedy, supporters of the MAHA movement, and some conservative commentators have promoted the idea that the government and pharmaceutical companies quashed ivermectin and other inexpensive, off-patent drugs because they’re not profitable for the drug industry.
“FDA’s war on public health is about to end,” Kennedy wrote in an October 2024 X post that has since gone viral. “This includes its aggressive suppression of psychedelics, peptides, stem cells, raw milk, hyperbaric therapies, chelating compounds, ivermectin, hydroxychloroquine, vitamins, clean foods, sunshine, exercise, nutraceuticals and anything else that advances human health and can’t be patented by Pharma.”
Previous laboratory research has shown that ivermectin could have anticancer effects because it promotes cell death and inhibits the growth of tumor cells. “It actually has been studied both with NIH funds and outside of NIH funds,” Letai said.
However, there is no evidence that ivermectin is safe and effective in treating cancer in humans. Preliminary data from a small clinical trial that gave ivermectin to patients with one type of metastatic breast cancer, in combination with immunotherapy, found no significant benefit from the addition of ivermectin.
Some physicians are concerned that patients will delay or forgo effective cancer treatments, or be harmed in other ways, if they believe unfounded claims that ivermectin can treat their disease.
“Many, many, many things work in a test tube. Quite a few things work in a mouse or a monkey. It still doesn’t mean it’s going to work in people,” said Jeffery Edenfield, executive medical director of oncology for the South Carolina-based Prisma Health Cancer Institute.
Edenfield said cancer patients ask him about ivermectin “regularly,” mostly because of what they see on social media. He said he persuaded a patient to stop using it, and a colleague recently had a patient who decided “to forgo highly effective standard therapy in favor of ivermectin.”
“People come to the discussion having largely already made up their mind,” Edenfield said. “We’re in this delicate time when there’s sort of a fundamental mistrust of medicine,” he added. “Some people are just not going to believe me. I just have to keep trying.”
A June letter by clinicians at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center in Ohio detailed how an adolescent patient with metastatic bone cancer started taking ivermectin “after encountering social media posts touting its benefits.” The patient — who hadn’t been given a prescription by a clinician — experienced ivermectin-related neurotoxicity and had to seek emergency care because of nausea, fatigue, and other symptoms.
“We urge the pediatric oncology community to advocate for sensible health policy that prioritizes the well-being of our patients,” the clinicians wrote. The lack of evidence about ivermectin and cancer hasn’t stopped celebrities and online influencers from promoting the notion that the drug is a cure-all. On a January 2025 episode of Joe Rogan’s podcast, actor Mel Gibson claimed that a combination of drugs that included ivermectin cured 3friends with stage IV cancer. The episode has been viewed > 12 million times.
Lawmakers in a handful of states have made the drug available over the counter. And Florida — which, under Republican Governor Ron DeSantis, has become a hotbed for anti-vaccine policies and the spread of public health misinformation — announced last fall that the state plans to fund research to study the drug as a potential cancer treatment.
The Florida Department of Health did not respond to questions about that effort.
Letai, previously a Dana-Farber Cancer Institute oncologist, started at the National Cancer Institute after months of upheaval caused by Trump administration policies.
“What you’re hearing at the NIH now is an openness to ideas — even ideas that scientists would say, ‘Oh, there’s no way it could work’ — but nevertheless applying rigorous scientific methods to those ideas,” Bhattacharya said at the January 30 event.
A second NCI scientist, who was granted anonymity due to fear of retaliation, said the notion that NIH was not open to investigating the value of off-label drugs in cancer is “ridiculous.”
“This is not a new idea they came up with,” the scientist said.
Letai didn’t elaborate on whether NCI scientists are conducting the research or if it has directed funding to an outside institution. Three-fourths of the cancer institute’s research dollars go to outside scientists.
He also aimed to temper expectations.
“At least on a population level,” Letai said, “it’s not going to be a cure-all for cancer.”
The National Cancer Institute (NCI), the federal research agency charged with leading the war against the nation’s second-largest killer, is studying ivermectin as a potential cancer treatment, according to its top official.
“There are enough reports of it, enough interest in it, that we actually did — ivermectin, in particular — did engage in sort of a better preclinical study of its properties and its ability to kill cancer cells,” said Anthony Letai, a physician the Trump administration appointed as NCI director in September.
Letai did not cite new evidence that might have prompted the institute to research the effectiveness of the antiparasitic drug against cancer. The drug, largely used to treat people or animals for infections caused by parasites, is a popular dewormer for horses.
“We’ll probably have those results in a few months,” Letai said. “So we are taking it seriously.”
He spoke about ivermectin at a January 30 event, “Reclaiming Science: The People’s NIH,” with National Institutes of Health (NIH) Director Jay Bhattacharya and other senior agency officials at Washington, DC’s Willard Hotel. The MAHA Institute hosted the discussion, framed by the “Make America Healthy Again” agenda of Health and Human Services (HSS) Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. The National Cancer Institute is the largest of the NIH’s 27 branches.
During the COVID pandemic, ivermectin’s popularity surged as fringe medical groups promoted it as an effective treatment. Clinical trials have found it isn’t effective against COVID.
Ivermectin has become a symbol of resistance against the medical establishment among MAHA adherents and conservatives. Like-minded commentators and wellness and other online influencers have hyped — without evidence — ivermectin as a miracle cure for a host of diseases, including cancer. Trump officials have pointed to research on ivermectin as an example of the administration’s receptiveness to ideas the scientific establishment has rejected.
“If lots of people believe it and it’s moving public health, we as NIH have an obligation, again, to treat it seriously,” Bhattacharya said at the event. According to The Chronicle at Duke University, Bhattacharya recently said he wants the NIH to be “the research arm of MAHA.”
The decision by the world’s premier cancer research institute to study ivermectin as a cancer treatment has alarmed career scientists at the agency.
“I am shocked and appalled,” one NCI scientist said. “We are moving funds away from so much promising research in order to do a preclinical study based on nonscientific ideas. It’s absurd.”
KFF Health News granted the scientist and other NCI workers anonymity because they are not authorized to speak to the press and fear retaliation.
HHS and the National Cancer Institute did not answer KFF Health News’ questions on the amount of money the cancer institute is spending on the study, who is carrying it out, and whether there was new evidence that prompted NCI to look into ivermectin as an anticancer therapy. Emily Hilliard, an HHS spokesperson, said NIH is dedicated to “rigorous, gold-standard research,” something the administration has repeatedly professed.
A preclinical study is an early phase of research conducted in a lab to test whether a drug or treatment may be useful and to assess potential harms. These studies take place before human clinical trials.
The scientist questioned whether there is enough initial evidence to warrant NCI’s spending of taxpayer funds to investigate the drug’s potential as a cancer treatment.
The FDA has approved ivermectin for certain uses in humans and animals. Tablets are used to treat conditions caused by parasitic worms, and the FDA has approved ivermectin lotions to treat lice and rosacea. Two scientists involved in its discovery won the Nobel Prize in 2015, tied to the drug’s success in treating certain parasitic diseases.
The FDA has warned that large doses of ivermectin can be dangerous. Overdoses can cause seizures, comas, or death.
Kennedy, supporters of the MAHA movement, and some conservative commentators have promoted the idea that the government and pharmaceutical companies quashed ivermectin and other inexpensive, off-patent drugs because they’re not profitable for the drug industry.
“FDA’s war on public health is about to end,” Kennedy wrote in an October 2024 X post that has since gone viral. “This includes its aggressive suppression of psychedelics, peptides, stem cells, raw milk, hyperbaric therapies, chelating compounds, ivermectin, hydroxychloroquine, vitamins, clean foods, sunshine, exercise, nutraceuticals and anything else that advances human health and can’t be patented by Pharma.”
Previous laboratory research has shown that ivermectin could have anticancer effects because it promotes cell death and inhibits the growth of tumor cells. “It actually has been studied both with NIH funds and outside of NIH funds,” Letai said.
However, there is no evidence that ivermectin is safe and effective in treating cancer in humans. Preliminary data from a small clinical trial that gave ivermectin to patients with one type of metastatic breast cancer, in combination with immunotherapy, found no significant benefit from the addition of ivermectin.
Some physicians are concerned that patients will delay or forgo effective cancer treatments, or be harmed in other ways, if they believe unfounded claims that ivermectin can treat their disease.
“Many, many, many things work in a test tube. Quite a few things work in a mouse or a monkey. It still doesn’t mean it’s going to work in people,” said Jeffery Edenfield, executive medical director of oncology for the South Carolina-based Prisma Health Cancer Institute.
Edenfield said cancer patients ask him about ivermectin “regularly,” mostly because of what they see on social media. He said he persuaded a patient to stop using it, and a colleague recently had a patient who decided “to forgo highly effective standard therapy in favor of ivermectin.”
“People come to the discussion having largely already made up their mind,” Edenfield said. “We’re in this delicate time when there’s sort of a fundamental mistrust of medicine,” he added. “Some people are just not going to believe me. I just have to keep trying.”
A June letter by clinicians at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center in Ohio detailed how an adolescent patient with metastatic bone cancer started taking ivermectin “after encountering social media posts touting its benefits.” The patient — who hadn’t been given a prescription by a clinician — experienced ivermectin-related neurotoxicity and had to seek emergency care because of nausea, fatigue, and other symptoms.
“We urge the pediatric oncology community to advocate for sensible health policy that prioritizes the well-being of our patients,” the clinicians wrote. The lack of evidence about ivermectin and cancer hasn’t stopped celebrities and online influencers from promoting the notion that the drug is a cure-all. On a January 2025 episode of Joe Rogan’s podcast, actor Mel Gibson claimed that a combination of drugs that included ivermectin cured 3friends with stage IV cancer. The episode has been viewed > 12 million times.
Lawmakers in a handful of states have made the drug available over the counter. And Florida — which, under Republican Governor Ron DeSantis, has become a hotbed for anti-vaccine policies and the spread of public health misinformation — announced last fall that the state plans to fund research to study the drug as a potential cancer treatment.
The Florida Department of Health did not respond to questions about that effort.
Letai, previously a Dana-Farber Cancer Institute oncologist, started at the National Cancer Institute after months of upheaval caused by Trump administration policies.
“What you’re hearing at the NIH now is an openness to ideas — even ideas that scientists would say, ‘Oh, there’s no way it could work’ — but nevertheless applying rigorous scientific methods to those ideas,” Bhattacharya said at the January 30 event.
A second NCI scientist, who was granted anonymity due to fear of retaliation, said the notion that NIH was not open to investigating the value of off-label drugs in cancer is “ridiculous.”
“This is not a new idea they came up with,” the scientist said.
Letai didn’t elaborate on whether NCI scientists are conducting the research or if it has directed funding to an outside institution. Three-fourths of the cancer institute’s research dollars go to outside scientists.
He also aimed to temper expectations.
“At least on a population level,” Letai said, “it’s not going to be a cure-all for cancer.”
The National Cancer Institute (NCI), the federal research agency charged with leading the war against the nation’s second-largest killer, is studying ivermectin as a potential cancer treatment, according to its top official.
“There are enough reports of it, enough interest in it, that we actually did — ivermectin, in particular — did engage in sort of a better preclinical study of its properties and its ability to kill cancer cells,” said Anthony Letai, a physician the Trump administration appointed as NCI director in September.
Letai did not cite new evidence that might have prompted the institute to research the effectiveness of the antiparasitic drug against cancer. The drug, largely used to treat people or animals for infections caused by parasites, is a popular dewormer for horses.
“We’ll probably have those results in a few months,” Letai said. “So we are taking it seriously.”
He spoke about ivermectin at a January 30 event, “Reclaiming Science: The People’s NIH,” with National Institutes of Health (NIH) Director Jay Bhattacharya and other senior agency officials at Washington, DC’s Willard Hotel. The MAHA Institute hosted the discussion, framed by the “Make America Healthy Again” agenda of Health and Human Services (HSS) Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. The National Cancer Institute is the largest of the NIH’s 27 branches.
During the COVID pandemic, ivermectin’s popularity surged as fringe medical groups promoted it as an effective treatment. Clinical trials have found it isn’t effective against COVID.
Ivermectin has become a symbol of resistance against the medical establishment among MAHA adherents and conservatives. Like-minded commentators and wellness and other online influencers have hyped — without evidence — ivermectin as a miracle cure for a host of diseases, including cancer. Trump officials have pointed to research on ivermectin as an example of the administration’s receptiveness to ideas the scientific establishment has rejected.
“If lots of people believe it and it’s moving public health, we as NIH have an obligation, again, to treat it seriously,” Bhattacharya said at the event. According to The Chronicle at Duke University, Bhattacharya recently said he wants the NIH to be “the research arm of MAHA.”
The decision by the world’s premier cancer research institute to study ivermectin as a cancer treatment has alarmed career scientists at the agency.
“I am shocked and appalled,” one NCI scientist said. “We are moving funds away from so much promising research in order to do a preclinical study based on nonscientific ideas. It’s absurd.”
KFF Health News granted the scientist and other NCI workers anonymity because they are not authorized to speak to the press and fear retaliation.
HHS and the National Cancer Institute did not answer KFF Health News’ questions on the amount of money the cancer institute is spending on the study, who is carrying it out, and whether there was new evidence that prompted NCI to look into ivermectin as an anticancer therapy. Emily Hilliard, an HHS spokesperson, said NIH is dedicated to “rigorous, gold-standard research,” something the administration has repeatedly professed.
A preclinical study is an early phase of research conducted in a lab to test whether a drug or treatment may be useful and to assess potential harms. These studies take place before human clinical trials.
The scientist questioned whether there is enough initial evidence to warrant NCI’s spending of taxpayer funds to investigate the drug’s potential as a cancer treatment.
The FDA has approved ivermectin for certain uses in humans and animals. Tablets are used to treat conditions caused by parasitic worms, and the FDA has approved ivermectin lotions to treat lice and rosacea. Two scientists involved in its discovery won the Nobel Prize in 2015, tied to the drug’s success in treating certain parasitic diseases.
The FDA has warned that large doses of ivermectin can be dangerous. Overdoses can cause seizures, comas, or death.
Kennedy, supporters of the MAHA movement, and some conservative commentators have promoted the idea that the government and pharmaceutical companies quashed ivermectin and other inexpensive, off-patent drugs because they’re not profitable for the drug industry.
“FDA’s war on public health is about to end,” Kennedy wrote in an October 2024 X post that has since gone viral. “This includes its aggressive suppression of psychedelics, peptides, stem cells, raw milk, hyperbaric therapies, chelating compounds, ivermectin, hydroxychloroquine, vitamins, clean foods, sunshine, exercise, nutraceuticals and anything else that advances human health and can’t be patented by Pharma.”
Previous laboratory research has shown that ivermectin could have anticancer effects because it promotes cell death and inhibits the growth of tumor cells. “It actually has been studied both with NIH funds and outside of NIH funds,” Letai said.
However, there is no evidence that ivermectin is safe and effective in treating cancer in humans. Preliminary data from a small clinical trial that gave ivermectin to patients with one type of metastatic breast cancer, in combination with immunotherapy, found no significant benefit from the addition of ivermectin.
Some physicians are concerned that patients will delay or forgo effective cancer treatments, or be harmed in other ways, if they believe unfounded claims that ivermectin can treat their disease.
“Many, many, many things work in a test tube. Quite a few things work in a mouse or a monkey. It still doesn’t mean it’s going to work in people,” said Jeffery Edenfield, executive medical director of oncology for the South Carolina-based Prisma Health Cancer Institute.
Edenfield said cancer patients ask him about ivermectin “regularly,” mostly because of what they see on social media. He said he persuaded a patient to stop using it, and a colleague recently had a patient who decided “to forgo highly effective standard therapy in favor of ivermectin.”
“People come to the discussion having largely already made up their mind,” Edenfield said. “We’re in this delicate time when there’s sort of a fundamental mistrust of medicine,” he added. “Some people are just not going to believe me. I just have to keep trying.”
A June letter by clinicians at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center in Ohio detailed how an adolescent patient with metastatic bone cancer started taking ivermectin “after encountering social media posts touting its benefits.” The patient — who hadn’t been given a prescription by a clinician — experienced ivermectin-related neurotoxicity and had to seek emergency care because of nausea, fatigue, and other symptoms.
“We urge the pediatric oncology community to advocate for sensible health policy that prioritizes the well-being of our patients,” the clinicians wrote. The lack of evidence about ivermectin and cancer hasn’t stopped celebrities and online influencers from promoting the notion that the drug is a cure-all. On a January 2025 episode of Joe Rogan’s podcast, actor Mel Gibson claimed that a combination of drugs that included ivermectin cured 3friends with stage IV cancer. The episode has been viewed > 12 million times.
Lawmakers in a handful of states have made the drug available over the counter. And Florida — which, under Republican Governor Ron DeSantis, has become a hotbed for anti-vaccine policies and the spread of public health misinformation — announced last fall that the state plans to fund research to study the drug as a potential cancer treatment.
The Florida Department of Health did not respond to questions about that effort.
Letai, previously a Dana-Farber Cancer Institute oncologist, started at the National Cancer Institute after months of upheaval caused by Trump administration policies.
“What you’re hearing at the NIH now is an openness to ideas — even ideas that scientists would say, ‘Oh, there’s no way it could work’ — but nevertheless applying rigorous scientific methods to those ideas,” Bhattacharya said at the January 30 event.
A second NCI scientist, who was granted anonymity due to fear of retaliation, said the notion that NIH was not open to investigating the value of off-label drugs in cancer is “ridiculous.”
“This is not a new idea they came up with,” the scientist said.
Letai didn’t elaborate on whether NCI scientists are conducting the research or if it has directed funding to an outside institution. Three-fourths of the cancer institute’s research dollars go to outside scientists.
He also aimed to temper expectations.
“At least on a population level,” Letai said, “it’s not going to be a cure-all for cancer.”
US Cancer Institute Studying Ivermectin's 'Ability to Kill Cancer Cells'
US Cancer Institute Studying Ivermectin's 'Ability to Kill Cancer Cells'
Risk Score Personalizes CRC Screening for Veterans
Risk Score Personalizes CRC Screening for Veterans
TOPLINE:
A recalibrated environmental risk score for colorectal cancer (CRC) shows improved predictive performance in a study of 227,504 male veterans. The veteran-tailored score could help personalize screening better than previous models.
METHODOLOGY:
- Demographic, lifestyle, and CRC data from 2011 to 2022 were abstracted from survey responses and health records of 227,504 male Million Veteran Program (MVP) participants, with complete data needed to construct the environmental risk score (e-Score).
- Researchers randomly split the male sample into 2 halves to produce training and validation samples (each n = 113,752; CRC cases n = 590) using simple random sampling with strata based on the CRC variable.
- Weighting for each environmental factor's effect size was recalculated using US Department of Veterans Affairs training data to create a recalibrated e-Score, which was compared with the original weighted e-Score in the validation sample.
- Analysis included nested multiple logistic regression models testing associations between quintiles for recalibrated and original e-Scores, with likelihood ratio tests used to compare model performance.
- Factors used to construct the e-Score included BMI, height, diabetes diagnosis, aspirin use, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use, educational attainment, physical activity level, smoking status, alcohol use, and dietary intake of fiber, calcium, folate, processed meats, red meat, fruits, vegetables, and total energy.
TAKEAWAY:
- The recalibrated e-Score showed a significant association with CRC, with higher quintiles indicating increased risk.
- In the validation sample, the recalibrated e-Score model significantly improved the base model performance (P < .001), while the original GECCO e-Score model did not show significant improvement (P = .07).
- The recalibrated e-Score model quintile 5 was associated with significantly higher odds for CRC compared with quintile 1 (odds ratio [OR], 1.79; 95% CI, 1.38-2.33; P for trend < .001).
- Black participants had higher odds for CRC compared with the White reference group across all models (base model OR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.13-1.92; GECCO e-Score model OR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.09-1.88; and recalibrated e-Score model OR, 1.38; 95% CI, 1.05-1.82).
IN PRACTICE:
"Despite the robust methods used in the work by the GECCO study upon which our study was based, an e-Score using their study’s weighting was not significantly associated with colorectal cancer among the male veteran sample. However, data from nearly a quarter million (n = 227,504) male US veteran participants of the MVP were used to recalibrate the e-Score to be veteran specific, and the recalibrated e-Score validation showed that it was significantly associated with colorectal cancer," wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by April R. Williams, US Department of Veterans Affairs Million Veteran Program Coordinating Center in Boston. It was published online in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
LIMITATIONS:
The study's limitations include potential recall and self-selection bias due to the use of self-reported data from the MVP. The generalizability of the findings may be limited to the veteran population, and the sample of Black veterans may have been insufficient for conclusive analysis. Additionally, the study did not include female participants due to insufficient data for a veteran-specific e-Score.
DISCLOSURES:
B.A. Sullivan disclosed receiving grants from the American Gastroenterological Association. D. Lieberman reported support from Geneoscopy, UDX, and ColoWrap. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
TOPLINE:
A recalibrated environmental risk score for colorectal cancer (CRC) shows improved predictive performance in a study of 227,504 male veterans. The veteran-tailored score could help personalize screening better than previous models.
METHODOLOGY:
- Demographic, lifestyle, and CRC data from 2011 to 2022 were abstracted from survey responses and health records of 227,504 male Million Veteran Program (MVP) participants, with complete data needed to construct the environmental risk score (e-Score).
- Researchers randomly split the male sample into 2 halves to produce training and validation samples (each n = 113,752; CRC cases n = 590) using simple random sampling with strata based on the CRC variable.
- Weighting for each environmental factor's effect size was recalculated using US Department of Veterans Affairs training data to create a recalibrated e-Score, which was compared with the original weighted e-Score in the validation sample.
- Analysis included nested multiple logistic regression models testing associations between quintiles for recalibrated and original e-Scores, with likelihood ratio tests used to compare model performance.
- Factors used to construct the e-Score included BMI, height, diabetes diagnosis, aspirin use, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use, educational attainment, physical activity level, smoking status, alcohol use, and dietary intake of fiber, calcium, folate, processed meats, red meat, fruits, vegetables, and total energy.
TAKEAWAY:
- The recalibrated e-Score showed a significant association with CRC, with higher quintiles indicating increased risk.
- In the validation sample, the recalibrated e-Score model significantly improved the base model performance (P < .001), while the original GECCO e-Score model did not show significant improvement (P = .07).
- The recalibrated e-Score model quintile 5 was associated with significantly higher odds for CRC compared with quintile 1 (odds ratio [OR], 1.79; 95% CI, 1.38-2.33; P for trend < .001).
- Black participants had higher odds for CRC compared with the White reference group across all models (base model OR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.13-1.92; GECCO e-Score model OR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.09-1.88; and recalibrated e-Score model OR, 1.38; 95% CI, 1.05-1.82).
IN PRACTICE:
"Despite the robust methods used in the work by the GECCO study upon which our study was based, an e-Score using their study’s weighting was not significantly associated with colorectal cancer among the male veteran sample. However, data from nearly a quarter million (n = 227,504) male US veteran participants of the MVP were used to recalibrate the e-Score to be veteran specific, and the recalibrated e-Score validation showed that it was significantly associated with colorectal cancer," wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by April R. Williams, US Department of Veterans Affairs Million Veteran Program Coordinating Center in Boston. It was published online in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
LIMITATIONS:
The study's limitations include potential recall and self-selection bias due to the use of self-reported data from the MVP. The generalizability of the findings may be limited to the veteran population, and the sample of Black veterans may have been insufficient for conclusive analysis. Additionally, the study did not include female participants due to insufficient data for a veteran-specific e-Score.
DISCLOSURES:
B.A. Sullivan disclosed receiving grants from the American Gastroenterological Association. D. Lieberman reported support from Geneoscopy, UDX, and ColoWrap. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
TOPLINE:
A recalibrated environmental risk score for colorectal cancer (CRC) shows improved predictive performance in a study of 227,504 male veterans. The veteran-tailored score could help personalize screening better than previous models.
METHODOLOGY:
- Demographic, lifestyle, and CRC data from 2011 to 2022 were abstracted from survey responses and health records of 227,504 male Million Veteran Program (MVP) participants, with complete data needed to construct the environmental risk score (e-Score).
- Researchers randomly split the male sample into 2 halves to produce training and validation samples (each n = 113,752; CRC cases n = 590) using simple random sampling with strata based on the CRC variable.
- Weighting for each environmental factor's effect size was recalculated using US Department of Veterans Affairs training data to create a recalibrated e-Score, which was compared with the original weighted e-Score in the validation sample.
- Analysis included nested multiple logistic regression models testing associations between quintiles for recalibrated and original e-Scores, with likelihood ratio tests used to compare model performance.
- Factors used to construct the e-Score included BMI, height, diabetes diagnosis, aspirin use, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use, educational attainment, physical activity level, smoking status, alcohol use, and dietary intake of fiber, calcium, folate, processed meats, red meat, fruits, vegetables, and total energy.
TAKEAWAY:
- The recalibrated e-Score showed a significant association with CRC, with higher quintiles indicating increased risk.
- In the validation sample, the recalibrated e-Score model significantly improved the base model performance (P < .001), while the original GECCO e-Score model did not show significant improvement (P = .07).
- The recalibrated e-Score model quintile 5 was associated with significantly higher odds for CRC compared with quintile 1 (odds ratio [OR], 1.79; 95% CI, 1.38-2.33; P for trend < .001).
- Black participants had higher odds for CRC compared with the White reference group across all models (base model OR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.13-1.92; GECCO e-Score model OR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.09-1.88; and recalibrated e-Score model OR, 1.38; 95% CI, 1.05-1.82).
IN PRACTICE:
"Despite the robust methods used in the work by the GECCO study upon which our study was based, an e-Score using their study’s weighting was not significantly associated with colorectal cancer among the male veteran sample. However, data from nearly a quarter million (n = 227,504) male US veteran participants of the MVP were used to recalibrate the e-Score to be veteran specific, and the recalibrated e-Score validation showed that it was significantly associated with colorectal cancer," wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by April R. Williams, US Department of Veterans Affairs Million Veteran Program Coordinating Center in Boston. It was published online in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.
LIMITATIONS:
The study's limitations include potential recall and self-selection bias due to the use of self-reported data from the MVP. The generalizability of the findings may be limited to the veteran population, and the sample of Black veterans may have been insufficient for conclusive analysis. Additionally, the study did not include female participants due to insufficient data for a veteran-specific e-Score.
DISCLOSURES:
B.A. Sullivan disclosed receiving grants from the American Gastroenterological Association. D. Lieberman reported support from Geneoscopy, UDX, and ColoWrap. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
Risk Score Personalizes CRC Screening for Veterans
Risk Score Personalizes CRC Screening for Veterans
Q&A: Why Are More Americans Under 50 Years of Age Dying of Colorectal Cancer?
Why Are More Americans Under Age 50 Dying of CRC?
First, the good news: Fewer Americans aged < 50 years are dying from cancer vs just a decade ago — reflecting progress in prevention, early detection, and treatment. There is, however, one big exception. Colorectal cancer mortality has been steadily inching up, and the disease now stands as the leading cause of cancer death in this age group, up from the fifth-leading in the early 1990s.
Those are the major findings of a recent study by the American Cancer Society (ACS), published as a research letter in JAMA.
Using SEER data, researchers found that the overall age-adjusted cancer death rate among Americans aged < 50 years dropped by 44% between 1990 and 2023 — from 25.5 to 14.2 per 100,000. And for 4 of the 5 leading causes of cancer death, there were mean annual declines from 2014 to 2023. The biggest change was in lung cancer deaths, which fell by an average of 5.7% per year. Meanwhile, leukemia and breast cancer deaths showed annual declines of 2.3% and 1.4%, respectively, despite rising incidences of both diseases among younger Americans.
The outlier is colorectal cancer, where mortality has been rising by about 1% per year since 2005. And it’s a pattern seen in both men and women.
Study coauthor Nikita Sandeep Wagle, PhD, MBBS, principal scientist, Cancer Surveillance Research at the ACS, and Arif Kamal, MD, ACS chief patient officer, discussed the research and its implications with Medscape Medical News.
Can you offer some possible reasons for the declining mortality in most of the cancers you studied?
Wagle: Mortality is going down for most of the cancers because we are getting better at finding cancers earlier and treating them more effectively. We have also seen improvements in screening, imaging, and therapy, and that means more people are being diagnosed at earlier stages and are surviving longer after diagnosis.
Regarding the rise in colorectal cancer mortality, do you think it's due to the rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer?
Kamal: Partially, but not completely, because the relationship between incidence and mortality is not always straightforward. For example, breast cancer incidence has been increasing, while mortality is going down. The rising mortality in people younger than 50 years is likely suggestive of more aggressive cancers being diagnosed — potentially secondary to environmental, dietary, or lifestyle factors. The colon is a unique organ because everything we put in our bodies passes through the colon, so food-based risk factors — for example, low fiber intake, red meat, and ultra-processed foods — are increasingly rising to the top as culprits.
Further, we know that only about 25% of people between the ages of 45 and 50 years are up to date with recommended colon cancer screenings, which can lead to later-stage diagnoses and thus higher mortality. So higher mortality speaks to the need to focus on lifestyle and diet changes and get more younger people to complete recommended cancer screenings.
Wagle: I think the “why” of your question is very important. Many researchers are trying to understand possible causes, such as diet, lifestyle, environmental factors, and genetics. But we cannot pinpoint one single cause. We need even more focus on research toward understanding the etiology of early-onset colorectal cancer.
What makes colorectal cancer different is that, unlike some other major cancers in this age group where mortality has declined despite rising incidence, roughly 3 in 4 colorectal cancers diagnosed in people younger than 50 years are [regional or distant], where the outcomes are worse.
Can you contextualize the rise in colorectal cancer mortality? What is the absolute rate among younger Americans now?
Wagle: It is around two deaths per 100,000 population in 2023 for people younger than 50 years. That number may not seem large, but the upward trend — a 1.1% annual increase from 2014 to 2023 — is concerning when you think about how overall mortality in this age group has dropped substantially over the past few decades. Colorectal cancer is moving in the opposite direction. I think the hopeful part is that it is also one of the most preventable cancers. Screening can stop cancer before it starts by removing precancerous polyps. Early-stage disease is highly treatable, and outcomes are better. That means better awareness and timely screening could make a real difference.
How can clinicians use this new information with regard to screening?
Wagle: For cancers with established screening guidelines, such as colorectal cancer, clinicians should continue to emphasize guideline-based screening and individualized risk assessment.
For colorectal cancer, screening now is recommended to start at age 45 for individuals at average risk, and earlier for [some], due to family history or other risk factors. Clinicians can use these findings to remind younger individuals that colorectal cancer is not only a disease of older adults and that screening at the recommended age can save lives.
In addition, red-flag symptoms such as persistent rectal bleeding, unexplained abdominal pain, difficulty in bowel movements, or signs of anemia should prompt appropriate evaluation in younger individuals.
Kamal: Clinicians should continue to emphasize timely completion of regular screening, starting at age 45 [for average-risk people]. Many still believe that the recommended starting age is 50 or that colonoscopy is the only way to get screened. Highlighting home-based screening options often helps patients make cancer screening logistically fit better into their busy lives.
Could you elaborate on the red-flag symptoms you mentioned, and what is an appropriate evaluation in younger individuals?
Kamal: Appropriate evaluation for any suspected bleeding — bright red or black and tarry — starts with an in-office evaluation by a primary care physician. Referral to a specialist, such as a gastroenterologist or surgeon, is done later, typically for direct visualization, such as with a colonoscopy. Rarely, imaging such as CT scans or ultrasounds is performed. Overall, because of the rising incidence of colon cancer in younger people, any concerning symptoms should be reported to a physician for an in-office evaluation as the first step.
Do these findings suggest that the starting age for average-risk people should be lowered—to age 40, for example?
Kamal: ACS screening guidelines for all cancers are part of an ongoing guideline development process by ACS scientists and volunteers. We monitor medical and scientific literature for new evidence that may support a change in current guidelines or the development of new guidelines and for information about cancer screening that should be conveyed to clinicians and target populations.
Keith Mulvihill is a freelance writer based in New York City.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
First, the good news: Fewer Americans aged < 50 years are dying from cancer vs just a decade ago — reflecting progress in prevention, early detection, and treatment. There is, however, one big exception. Colorectal cancer mortality has been steadily inching up, and the disease now stands as the leading cause of cancer death in this age group, up from the fifth-leading in the early 1990s.
Those are the major findings of a recent study by the American Cancer Society (ACS), published as a research letter in JAMA.
Using SEER data, researchers found that the overall age-adjusted cancer death rate among Americans aged < 50 years dropped by 44% between 1990 and 2023 — from 25.5 to 14.2 per 100,000. And for 4 of the 5 leading causes of cancer death, there were mean annual declines from 2014 to 2023. The biggest change was in lung cancer deaths, which fell by an average of 5.7% per year. Meanwhile, leukemia and breast cancer deaths showed annual declines of 2.3% and 1.4%, respectively, despite rising incidences of both diseases among younger Americans.
The outlier is colorectal cancer, where mortality has been rising by about 1% per year since 2005. And it’s a pattern seen in both men and women.
Study coauthor Nikita Sandeep Wagle, PhD, MBBS, principal scientist, Cancer Surveillance Research at the ACS, and Arif Kamal, MD, ACS chief patient officer, discussed the research and its implications with Medscape Medical News.
Can you offer some possible reasons for the declining mortality in most of the cancers you studied?
Wagle: Mortality is going down for most of the cancers because we are getting better at finding cancers earlier and treating them more effectively. We have also seen improvements in screening, imaging, and therapy, and that means more people are being diagnosed at earlier stages and are surviving longer after diagnosis.
Regarding the rise in colorectal cancer mortality, do you think it's due to the rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer?
Kamal: Partially, but not completely, because the relationship between incidence and mortality is not always straightforward. For example, breast cancer incidence has been increasing, while mortality is going down. The rising mortality in people younger than 50 years is likely suggestive of more aggressive cancers being diagnosed — potentially secondary to environmental, dietary, or lifestyle factors. The colon is a unique organ because everything we put in our bodies passes through the colon, so food-based risk factors — for example, low fiber intake, red meat, and ultra-processed foods — are increasingly rising to the top as culprits.
Further, we know that only about 25% of people between the ages of 45 and 50 years are up to date with recommended colon cancer screenings, which can lead to later-stage diagnoses and thus higher mortality. So higher mortality speaks to the need to focus on lifestyle and diet changes and get more younger people to complete recommended cancer screenings.
Wagle: I think the “why” of your question is very important. Many researchers are trying to understand possible causes, such as diet, lifestyle, environmental factors, and genetics. But we cannot pinpoint one single cause. We need even more focus on research toward understanding the etiology of early-onset colorectal cancer.
What makes colorectal cancer different is that, unlike some other major cancers in this age group where mortality has declined despite rising incidence, roughly 3 in 4 colorectal cancers diagnosed in people younger than 50 years are [regional or distant], where the outcomes are worse.
Can you contextualize the rise in colorectal cancer mortality? What is the absolute rate among younger Americans now?
Wagle: It is around two deaths per 100,000 population in 2023 for people younger than 50 years. That number may not seem large, but the upward trend — a 1.1% annual increase from 2014 to 2023 — is concerning when you think about how overall mortality in this age group has dropped substantially over the past few decades. Colorectal cancer is moving in the opposite direction. I think the hopeful part is that it is also one of the most preventable cancers. Screening can stop cancer before it starts by removing precancerous polyps. Early-stage disease is highly treatable, and outcomes are better. That means better awareness and timely screening could make a real difference.
How can clinicians use this new information with regard to screening?
Wagle: For cancers with established screening guidelines, such as colorectal cancer, clinicians should continue to emphasize guideline-based screening and individualized risk assessment.
For colorectal cancer, screening now is recommended to start at age 45 for individuals at average risk, and earlier for [some], due to family history or other risk factors. Clinicians can use these findings to remind younger individuals that colorectal cancer is not only a disease of older adults and that screening at the recommended age can save lives.
In addition, red-flag symptoms such as persistent rectal bleeding, unexplained abdominal pain, difficulty in bowel movements, or signs of anemia should prompt appropriate evaluation in younger individuals.
Kamal: Clinicians should continue to emphasize timely completion of regular screening, starting at age 45 [for average-risk people]. Many still believe that the recommended starting age is 50 or that colonoscopy is the only way to get screened. Highlighting home-based screening options often helps patients make cancer screening logistically fit better into their busy lives.
Could you elaborate on the red-flag symptoms you mentioned, and what is an appropriate evaluation in younger individuals?
Kamal: Appropriate evaluation for any suspected bleeding — bright red or black and tarry — starts with an in-office evaluation by a primary care physician. Referral to a specialist, such as a gastroenterologist or surgeon, is done later, typically for direct visualization, such as with a colonoscopy. Rarely, imaging such as CT scans or ultrasounds is performed. Overall, because of the rising incidence of colon cancer in younger people, any concerning symptoms should be reported to a physician for an in-office evaluation as the first step.
Do these findings suggest that the starting age for average-risk people should be lowered—to age 40, for example?
Kamal: ACS screening guidelines for all cancers are part of an ongoing guideline development process by ACS scientists and volunteers. We monitor medical and scientific literature for new evidence that may support a change in current guidelines or the development of new guidelines and for information about cancer screening that should be conveyed to clinicians and target populations.
Keith Mulvihill is a freelance writer based in New York City.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
First, the good news: Fewer Americans aged < 50 years are dying from cancer vs just a decade ago — reflecting progress in prevention, early detection, and treatment. There is, however, one big exception. Colorectal cancer mortality has been steadily inching up, and the disease now stands as the leading cause of cancer death in this age group, up from the fifth-leading in the early 1990s.
Those are the major findings of a recent study by the American Cancer Society (ACS), published as a research letter in JAMA.
Using SEER data, researchers found that the overall age-adjusted cancer death rate among Americans aged < 50 years dropped by 44% between 1990 and 2023 — from 25.5 to 14.2 per 100,000. And for 4 of the 5 leading causes of cancer death, there were mean annual declines from 2014 to 2023. The biggest change was in lung cancer deaths, which fell by an average of 5.7% per year. Meanwhile, leukemia and breast cancer deaths showed annual declines of 2.3% and 1.4%, respectively, despite rising incidences of both diseases among younger Americans.
The outlier is colorectal cancer, where mortality has been rising by about 1% per year since 2005. And it’s a pattern seen in both men and women.
Study coauthor Nikita Sandeep Wagle, PhD, MBBS, principal scientist, Cancer Surveillance Research at the ACS, and Arif Kamal, MD, ACS chief patient officer, discussed the research and its implications with Medscape Medical News.
Can you offer some possible reasons for the declining mortality in most of the cancers you studied?
Wagle: Mortality is going down for most of the cancers because we are getting better at finding cancers earlier and treating them more effectively. We have also seen improvements in screening, imaging, and therapy, and that means more people are being diagnosed at earlier stages and are surviving longer after diagnosis.
Regarding the rise in colorectal cancer mortality, do you think it's due to the rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer?
Kamal: Partially, but not completely, because the relationship between incidence and mortality is not always straightforward. For example, breast cancer incidence has been increasing, while mortality is going down. The rising mortality in people younger than 50 years is likely suggestive of more aggressive cancers being diagnosed — potentially secondary to environmental, dietary, or lifestyle factors. The colon is a unique organ because everything we put in our bodies passes through the colon, so food-based risk factors — for example, low fiber intake, red meat, and ultra-processed foods — are increasingly rising to the top as culprits.
Further, we know that only about 25% of people between the ages of 45 and 50 years are up to date with recommended colon cancer screenings, which can lead to later-stage diagnoses and thus higher mortality. So higher mortality speaks to the need to focus on lifestyle and diet changes and get more younger people to complete recommended cancer screenings.
Wagle: I think the “why” of your question is very important. Many researchers are trying to understand possible causes, such as diet, lifestyle, environmental factors, and genetics. But we cannot pinpoint one single cause. We need even more focus on research toward understanding the etiology of early-onset colorectal cancer.
What makes colorectal cancer different is that, unlike some other major cancers in this age group where mortality has declined despite rising incidence, roughly 3 in 4 colorectal cancers diagnosed in people younger than 50 years are [regional or distant], where the outcomes are worse.
Can you contextualize the rise in colorectal cancer mortality? What is the absolute rate among younger Americans now?
Wagle: It is around two deaths per 100,000 population in 2023 for people younger than 50 years. That number may not seem large, but the upward trend — a 1.1% annual increase from 2014 to 2023 — is concerning when you think about how overall mortality in this age group has dropped substantially over the past few decades. Colorectal cancer is moving in the opposite direction. I think the hopeful part is that it is also one of the most preventable cancers. Screening can stop cancer before it starts by removing precancerous polyps. Early-stage disease is highly treatable, and outcomes are better. That means better awareness and timely screening could make a real difference.
How can clinicians use this new information with regard to screening?
Wagle: For cancers with established screening guidelines, such as colorectal cancer, clinicians should continue to emphasize guideline-based screening and individualized risk assessment.
For colorectal cancer, screening now is recommended to start at age 45 for individuals at average risk, and earlier for [some], due to family history or other risk factors. Clinicians can use these findings to remind younger individuals that colorectal cancer is not only a disease of older adults and that screening at the recommended age can save lives.
In addition, red-flag symptoms such as persistent rectal bleeding, unexplained abdominal pain, difficulty in bowel movements, or signs of anemia should prompt appropriate evaluation in younger individuals.
Kamal: Clinicians should continue to emphasize timely completion of regular screening, starting at age 45 [for average-risk people]. Many still believe that the recommended starting age is 50 or that colonoscopy is the only way to get screened. Highlighting home-based screening options often helps patients make cancer screening logistically fit better into their busy lives.
Could you elaborate on the red-flag symptoms you mentioned, and what is an appropriate evaluation in younger individuals?
Kamal: Appropriate evaluation for any suspected bleeding — bright red or black and tarry — starts with an in-office evaluation by a primary care physician. Referral to a specialist, such as a gastroenterologist or surgeon, is done later, typically for direct visualization, such as with a colonoscopy. Rarely, imaging such as CT scans or ultrasounds is performed. Overall, because of the rising incidence of colon cancer in younger people, any concerning symptoms should be reported to a physician for an in-office evaluation as the first step.
Do these findings suggest that the starting age for average-risk people should be lowered—to age 40, for example?
Kamal: ACS screening guidelines for all cancers are part of an ongoing guideline development process by ACS scientists and volunteers. We monitor medical and scientific literature for new evidence that may support a change in current guidelines or the development of new guidelines and for information about cancer screening that should be conveyed to clinicians and target populations.
Keith Mulvihill is a freelance writer based in New York City.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Why Are More Americans Under Age 50 Dying of CRC?
Why Are More Americans Under Age 50 Dying of CRC?
Do Ultraprocessed Foods Impact Survival After Cancer?
Do Ultraprocessed Foods Impact Survival After Cancer?
Diets heavy in ultraprocessed foods (UPFs) are associated with earlier death in cancer survivors, a new study finds — though issues with the research design suggest that the findings should be taken with a grain of salt.
The study, published on February 4 in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, is among the latest to point to health hazards from eating too many foods full of preservatives, dyes, and other industrially made ingredients.
These so-called UPFs have been linked to an increased risk for cancer, but whether they have any relationship to long-term survival after cancer has been unclear.
In the new study, of 802 adults with a previous cancer diagnosis, those in the top third for UPF consumption had a 48% higher rate of death from any cause over 15 years than those in the bottom third. Similarly, heavier UPF consumers had a 57% higher rate of death from cancer.
Those excess risks were seen after adjustment for numerous variables, including age, physical activity, BMI, smoking status, and socioeconomic indicators.
“Clinicians should encourage a shift toward fresh, minimally processed foods, [and] away from heavily industrially processed products,” said lead author Marialaura Bonaccio, PhD, of the Research Unit of Epidemiology and Prevention at IRCCS Neuromed in Pozzilli, Italy.
Oncologists not involved in the work said the findings support what researchers have suspected.
“UPFs have been linked to increased risk of obesity, diabetes, inflammation, cardiovascular disease, and...all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality,” said Urvi A. Shah, MD, a myeloma specialist who conducts nutrition research at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. “However, there was limited data on cancer-specific mortality to date until this study.”
The findings also dovetail with recommendations on cancer prevention that emphasize diets rich in plant foods and low in processed foods, particularly those loaded with sugar, starch, and fat.
The study “may make oncologists think twice before assuring patients to ‘eat whatever you want, it doesn’t really matter’ because these investigators show that it does,” said Donald I. Abrams, MD, an integrative oncologist at the UCSF Osher Center for Integrative Health.
However, Gideon Meyerowitz-Katz, PhD, an epidemiologist at the University of Wollongong in Wollongong, Australia, was not impressed by the analysis.
He pointed to several sources of potential bias and noted that the crude results actually showed that cancer survivors with the lowest UPF consumption had a higher rate of death than the heaviest consumers.
“The story of UPFs being bad is consistent with this data, but so is the story of UPFs being fine,” said Meyerowitz-Katz, who has written about prior research on the subject.
The broad questions of whether and how UPFs might be harming human health have been gaining research interest, partly because of their ubiquity. The foods reportedly make up about 60% of the typical American diet.
There’s no universal agreement on the precise definition of “ultraprocessed,” but researchers generally use the NOVA classification system, which assigns foods into one of four groups based on the level and purpose of processing. UPFs contain ingredients not found in the standard home kitchen (such as high-fructose corn syrup) and often have artificial flavors, colors, and other additives.
Examples of UPFs include the usual “junk food,” such as candy, soda, and processed meat, but many healthy-sounding products, such as flavored yogurts and plant-based milk, also qualify.
For their study, Bonaccio and her colleagues identified 802 cancer survivors from the Moli-sani cohort study (476 women and 326 men) who completed food-frequency questionnaires an average of 8 years postdiagnosis.
Using the NOVA system, the team calculated the amount of UPF in participants’ diets as both weight and energy ratios.
Over a median follow-up of nearly 15 years, there were 281 deaths. In the lowest third of UPF consumption (4.3% mean intake by weight), there were 3.3 deaths per 100 patient-years, compared with 2.4 per 100 patient-years in the highest UPF tertile (16.7% mean intake by weight). For cancer-specific deaths, those numbers were 1.5 and 1.4, respectively.
However, after adjustment for age and total energy intake, the top UPF-intake group showed significantly higher death rates. In the final model, which adjusted for > 20 variables, the hazard ratios for the highest versus lowest UPF consumption were 1.48 (95% CI, 1.07-2.03) for all-cause mortality and 1.57 (95% CI, 1.00-2.47) for cancer mortality.
To explore potential biological mechanisms, the researchers also analyzed certain biomarkers. They found that adjustment for inflammatory markers and resting heart rate at baseline attenuated the association between UPF and all-cause deaths by nearly 40%.
The authors acknowledged some limitations of their study, including its use of self-report and potential survivor bias.
But Meyerowitz-Katz found additional weak points. For one, he said the authors “downplayed” the impact of their analysis controlling for inflammation and heart rate.
“Inflammation and heart rate are both strong markers of future cancer risk,” Meyerowitz-Katz said. “In this cohort, there would be people who were already experiencing cancer recurrence, which is important to control for at baseline.”
He also highlighted a little-known but important issue in observational research called collider bias, which can create a false association between an exposure and outcome. In this study, he said, the researchers introduced “a huge potential for collider bias” by controlling for energy intake, because both UPF consumption and cancer recurrence are causally associated with energy intake.
Bonaccio called that particular critique “a fair methodological question” but defended her work.
She pointed out that study participants were long-term survivors, which reduces the chance that their calorie intake was mainly driven by active cancer or treatment side effects.
“And,” she said, “our models include a wide set of baseline covariates that capture major determinants of both mortality and dietary intake.”
For Bonaccio, the take-home message for patients remains the same: “Emphasizing simple, home-cooked meals and traditional dietary patterns might be especially beneficial during the survivorship phase.”
The two US experts agreed that overall diet quality is key, with limits on UPFs being part of that. They also noted that the average American’s diet contains substantially more UPFs than what was seen in this Italian study.
“I spend 20 minutes of my 60-minute new patient consult in integrative oncology advising patients to eat an organic, plant-based, antioxidant-rich, anti-inflammatory, real and whole-foods diet,” Abrams said.
For her part, Shah said that cancer survivors should aim to get at least 25-30 grams of dietary fiber daily. She also suggested they avoid particular types of UPF with little to no nutritional value, such as processed meats, sugar-laden beverages, and fast food.
The study received no commercial funding. Bonaccio, Abrams, and Meyerowitz-Katz reported no financial disclosures. Shah is principle investigator on the NUTRIVENTION trial and reported receiving research funding and/or personal fees from Celgene/BMS, Janssen, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Diets heavy in ultraprocessed foods (UPFs) are associated with earlier death in cancer survivors, a new study finds — though issues with the research design suggest that the findings should be taken with a grain of salt.
The study, published on February 4 in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, is among the latest to point to health hazards from eating too many foods full of preservatives, dyes, and other industrially made ingredients.
These so-called UPFs have been linked to an increased risk for cancer, but whether they have any relationship to long-term survival after cancer has been unclear.
In the new study, of 802 adults with a previous cancer diagnosis, those in the top third for UPF consumption had a 48% higher rate of death from any cause over 15 years than those in the bottom third. Similarly, heavier UPF consumers had a 57% higher rate of death from cancer.
Those excess risks were seen after adjustment for numerous variables, including age, physical activity, BMI, smoking status, and socioeconomic indicators.
“Clinicians should encourage a shift toward fresh, minimally processed foods, [and] away from heavily industrially processed products,” said lead author Marialaura Bonaccio, PhD, of the Research Unit of Epidemiology and Prevention at IRCCS Neuromed in Pozzilli, Italy.
Oncologists not involved in the work said the findings support what researchers have suspected.
“UPFs have been linked to increased risk of obesity, diabetes, inflammation, cardiovascular disease, and...all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality,” said Urvi A. Shah, MD, a myeloma specialist who conducts nutrition research at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. “However, there was limited data on cancer-specific mortality to date until this study.”
The findings also dovetail with recommendations on cancer prevention that emphasize diets rich in plant foods and low in processed foods, particularly those loaded with sugar, starch, and fat.
The study “may make oncologists think twice before assuring patients to ‘eat whatever you want, it doesn’t really matter’ because these investigators show that it does,” said Donald I. Abrams, MD, an integrative oncologist at the UCSF Osher Center for Integrative Health.
However, Gideon Meyerowitz-Katz, PhD, an epidemiologist at the University of Wollongong in Wollongong, Australia, was not impressed by the analysis.
He pointed to several sources of potential bias and noted that the crude results actually showed that cancer survivors with the lowest UPF consumption had a higher rate of death than the heaviest consumers.
“The story of UPFs being bad is consistent with this data, but so is the story of UPFs being fine,” said Meyerowitz-Katz, who has written about prior research on the subject.
The broad questions of whether and how UPFs might be harming human health have been gaining research interest, partly because of their ubiquity. The foods reportedly make up about 60% of the typical American diet.
There’s no universal agreement on the precise definition of “ultraprocessed,” but researchers generally use the NOVA classification system, which assigns foods into one of four groups based on the level and purpose of processing. UPFs contain ingredients not found in the standard home kitchen (such as high-fructose corn syrup) and often have artificial flavors, colors, and other additives.
Examples of UPFs include the usual “junk food,” such as candy, soda, and processed meat, but many healthy-sounding products, such as flavored yogurts and plant-based milk, also qualify.
For their study, Bonaccio and her colleagues identified 802 cancer survivors from the Moli-sani cohort study (476 women and 326 men) who completed food-frequency questionnaires an average of 8 years postdiagnosis.
Using the NOVA system, the team calculated the amount of UPF in participants’ diets as both weight and energy ratios.
Over a median follow-up of nearly 15 years, there were 281 deaths. In the lowest third of UPF consumption (4.3% mean intake by weight), there were 3.3 deaths per 100 patient-years, compared with 2.4 per 100 patient-years in the highest UPF tertile (16.7% mean intake by weight). For cancer-specific deaths, those numbers were 1.5 and 1.4, respectively.
However, after adjustment for age and total energy intake, the top UPF-intake group showed significantly higher death rates. In the final model, which adjusted for > 20 variables, the hazard ratios for the highest versus lowest UPF consumption were 1.48 (95% CI, 1.07-2.03) for all-cause mortality and 1.57 (95% CI, 1.00-2.47) for cancer mortality.
To explore potential biological mechanisms, the researchers also analyzed certain biomarkers. They found that adjustment for inflammatory markers and resting heart rate at baseline attenuated the association between UPF and all-cause deaths by nearly 40%.
The authors acknowledged some limitations of their study, including its use of self-report and potential survivor bias.
But Meyerowitz-Katz found additional weak points. For one, he said the authors “downplayed” the impact of their analysis controlling for inflammation and heart rate.
“Inflammation and heart rate are both strong markers of future cancer risk,” Meyerowitz-Katz said. “In this cohort, there would be people who were already experiencing cancer recurrence, which is important to control for at baseline.”
He also highlighted a little-known but important issue in observational research called collider bias, which can create a false association between an exposure and outcome. In this study, he said, the researchers introduced “a huge potential for collider bias” by controlling for energy intake, because both UPF consumption and cancer recurrence are causally associated with energy intake.
Bonaccio called that particular critique “a fair methodological question” but defended her work.
She pointed out that study participants were long-term survivors, which reduces the chance that their calorie intake was mainly driven by active cancer or treatment side effects.
“And,” she said, “our models include a wide set of baseline covariates that capture major determinants of both mortality and dietary intake.”
For Bonaccio, the take-home message for patients remains the same: “Emphasizing simple, home-cooked meals and traditional dietary patterns might be especially beneficial during the survivorship phase.”
The two US experts agreed that overall diet quality is key, with limits on UPFs being part of that. They also noted that the average American’s diet contains substantially more UPFs than what was seen in this Italian study.
“I spend 20 minutes of my 60-minute new patient consult in integrative oncology advising patients to eat an organic, plant-based, antioxidant-rich, anti-inflammatory, real and whole-foods diet,” Abrams said.
For her part, Shah said that cancer survivors should aim to get at least 25-30 grams of dietary fiber daily. She also suggested they avoid particular types of UPF with little to no nutritional value, such as processed meats, sugar-laden beverages, and fast food.
The study received no commercial funding. Bonaccio, Abrams, and Meyerowitz-Katz reported no financial disclosures. Shah is principle investigator on the NUTRIVENTION trial and reported receiving research funding and/or personal fees from Celgene/BMS, Janssen, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Diets heavy in ultraprocessed foods (UPFs) are associated with earlier death in cancer survivors, a new study finds — though issues with the research design suggest that the findings should be taken with a grain of salt.
The study, published on February 4 in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, is among the latest to point to health hazards from eating too many foods full of preservatives, dyes, and other industrially made ingredients.
These so-called UPFs have been linked to an increased risk for cancer, but whether they have any relationship to long-term survival after cancer has been unclear.
In the new study, of 802 adults with a previous cancer diagnosis, those in the top third for UPF consumption had a 48% higher rate of death from any cause over 15 years than those in the bottom third. Similarly, heavier UPF consumers had a 57% higher rate of death from cancer.
Those excess risks were seen after adjustment for numerous variables, including age, physical activity, BMI, smoking status, and socioeconomic indicators.
“Clinicians should encourage a shift toward fresh, minimally processed foods, [and] away from heavily industrially processed products,” said lead author Marialaura Bonaccio, PhD, of the Research Unit of Epidemiology and Prevention at IRCCS Neuromed in Pozzilli, Italy.
Oncologists not involved in the work said the findings support what researchers have suspected.
“UPFs have been linked to increased risk of obesity, diabetes, inflammation, cardiovascular disease, and...all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality,” said Urvi A. Shah, MD, a myeloma specialist who conducts nutrition research at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. “However, there was limited data on cancer-specific mortality to date until this study.”
The findings also dovetail with recommendations on cancer prevention that emphasize diets rich in plant foods and low in processed foods, particularly those loaded with sugar, starch, and fat.
The study “may make oncologists think twice before assuring patients to ‘eat whatever you want, it doesn’t really matter’ because these investigators show that it does,” said Donald I. Abrams, MD, an integrative oncologist at the UCSF Osher Center for Integrative Health.
However, Gideon Meyerowitz-Katz, PhD, an epidemiologist at the University of Wollongong in Wollongong, Australia, was not impressed by the analysis.
He pointed to several sources of potential bias and noted that the crude results actually showed that cancer survivors with the lowest UPF consumption had a higher rate of death than the heaviest consumers.
“The story of UPFs being bad is consistent with this data, but so is the story of UPFs being fine,” said Meyerowitz-Katz, who has written about prior research on the subject.
The broad questions of whether and how UPFs might be harming human health have been gaining research interest, partly because of their ubiquity. The foods reportedly make up about 60% of the typical American diet.
There’s no universal agreement on the precise definition of “ultraprocessed,” but researchers generally use the NOVA classification system, which assigns foods into one of four groups based on the level and purpose of processing. UPFs contain ingredients not found in the standard home kitchen (such as high-fructose corn syrup) and often have artificial flavors, colors, and other additives.
Examples of UPFs include the usual “junk food,” such as candy, soda, and processed meat, but many healthy-sounding products, such as flavored yogurts and plant-based milk, also qualify.
For their study, Bonaccio and her colleagues identified 802 cancer survivors from the Moli-sani cohort study (476 women and 326 men) who completed food-frequency questionnaires an average of 8 years postdiagnosis.
Using the NOVA system, the team calculated the amount of UPF in participants’ diets as both weight and energy ratios.
Over a median follow-up of nearly 15 years, there were 281 deaths. In the lowest third of UPF consumption (4.3% mean intake by weight), there were 3.3 deaths per 100 patient-years, compared with 2.4 per 100 patient-years in the highest UPF tertile (16.7% mean intake by weight). For cancer-specific deaths, those numbers were 1.5 and 1.4, respectively.
However, after adjustment for age and total energy intake, the top UPF-intake group showed significantly higher death rates. In the final model, which adjusted for > 20 variables, the hazard ratios for the highest versus lowest UPF consumption were 1.48 (95% CI, 1.07-2.03) for all-cause mortality and 1.57 (95% CI, 1.00-2.47) for cancer mortality.
To explore potential biological mechanisms, the researchers also analyzed certain biomarkers. They found that adjustment for inflammatory markers and resting heart rate at baseline attenuated the association between UPF and all-cause deaths by nearly 40%.
The authors acknowledged some limitations of their study, including its use of self-report and potential survivor bias.
But Meyerowitz-Katz found additional weak points. For one, he said the authors “downplayed” the impact of their analysis controlling for inflammation and heart rate.
“Inflammation and heart rate are both strong markers of future cancer risk,” Meyerowitz-Katz said. “In this cohort, there would be people who were already experiencing cancer recurrence, which is important to control for at baseline.”
He also highlighted a little-known but important issue in observational research called collider bias, which can create a false association between an exposure and outcome. In this study, he said, the researchers introduced “a huge potential for collider bias” by controlling for energy intake, because both UPF consumption and cancer recurrence are causally associated with energy intake.
Bonaccio called that particular critique “a fair methodological question” but defended her work.
She pointed out that study participants were long-term survivors, which reduces the chance that their calorie intake was mainly driven by active cancer or treatment side effects.
“And,” she said, “our models include a wide set of baseline covariates that capture major determinants of both mortality and dietary intake.”
For Bonaccio, the take-home message for patients remains the same: “Emphasizing simple, home-cooked meals and traditional dietary patterns might be especially beneficial during the survivorship phase.”
The two US experts agreed that overall diet quality is key, with limits on UPFs being part of that. They also noted that the average American’s diet contains substantially more UPFs than what was seen in this Italian study.
“I spend 20 minutes of my 60-minute new patient consult in integrative oncology advising patients to eat an organic, plant-based, antioxidant-rich, anti-inflammatory, real and whole-foods diet,” Abrams said.
For her part, Shah said that cancer survivors should aim to get at least 25-30 grams of dietary fiber daily. She also suggested they avoid particular types of UPF with little to no nutritional value, such as processed meats, sugar-laden beverages, and fast food.
The study received no commercial funding. Bonaccio, Abrams, and Meyerowitz-Katz reported no financial disclosures. Shah is principle investigator on the NUTRIVENTION trial and reported receiving research funding and/or personal fees from Celgene/BMS, Janssen, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Do Ultraprocessed Foods Impact Survival After Cancer?
Do Ultraprocessed Foods Impact Survival After Cancer?
US Vet Study Identifies Risk Factors for Acral Melanoma
US Vet Study Identifies Risk Factors for Acral Melanoma
TOPLINE:
Exposure to Agent Orange, the defoliant used by the US Air Force during the Vietnam War, was one of the factors associated with increased odds of acral melanoma (AM), a rare melanoma subtype affecting palms, soles, and nail units.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a nested case-control study in the Veterans Affairs healthcare system, and identified 1292 veterans (median age, 70.13 years; 94.0% men; 73.4% White, 14.6% Black) with AM through the Veterans Affairs Cancer Registry and a validated natural language processing pipeline from 2000 to 2024.
- Researchers matched each case of AM to 4 individuals with nonacral cutaneous melanoma (CM) and 4 control individuals without melanoma diagnoses, based on diagnosis year and outpatient visit frequency.
- Exposures included age, sex, race, ethnicity, rurality, region, military branch, comorbidities, smoking status, alcohol use, BMI, Agent Orange exposure, prior photosensitizing medications, nevi, and keratinocyte carcinoma.
TAKEAWAY:
- Veterans exposed to Agent Orange had higher odds of AM than individuals with CM (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.31; 95% CI, 1.06-1.62) and control individuals without melanoma (AOR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.04-1.56).
- Individuals with current smoking habit had lower odds of AM than those with CM (AOR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.52-0.81) and control individuals without melanoma (AOR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.40-0.62).
- Patients with prior keratinocyte carcinoma and actinic keratosis had higher odds of AM than control individuals without melanoma but lower odds than those with CM.
- History of nevus was associated with higher odds of acral melanoma compared with individuals without melanoma (AOR, 2.11; 95% CI, 1.49-2.98).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results support the need for continued investigation of AM as a distinct entity from CM and may inform future evaluations of the associations between [Agent Orange exposure] in veteran populations, as well as those between other environmental exposures in different populations," the study authors wrote. Referring to the “continued search for a better understanding of a potential link” between Agent Orange and melanoma, as well as AM, and other possible etiologic factors for AM, this study “provides a strong impetus to further these research goals and contribute to the investigation of the legacy of the Vietnam War and honor a commitment to the veterans community,” Andrew F. Olshan, PhD, Gillings School of Global Public Health, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jonathan C. Hwang, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and was published online on February 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The case-control design limits causal inference and the findings might not be generalized outside US veterans. Exposure misclassification could be present.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Department of Defense and the Department of Veterans Affairs. Several authors reported receiving grants from CU Anschutz Medical Center, Department of Defense, CDMRP Melanoma Research Program, and Merck, Bayer, and Department of Veteran Affairs. They also reported receiving royalty from UpToDate, and being shareholder in many companies, including Apple. NVIDIA, Amazon, Gilead, AstraZeneca, BioNTech, and Moderna. Olshan declared being a member of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine Veterans and Agent Orange review committee.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Exposure to Agent Orange, the defoliant used by the US Air Force during the Vietnam War, was one of the factors associated with increased odds of acral melanoma (AM), a rare melanoma subtype affecting palms, soles, and nail units.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a nested case-control study in the Veterans Affairs healthcare system, and identified 1292 veterans (median age, 70.13 years; 94.0% men; 73.4% White, 14.6% Black) with AM through the Veterans Affairs Cancer Registry and a validated natural language processing pipeline from 2000 to 2024.
- Researchers matched each case of AM to 4 individuals with nonacral cutaneous melanoma (CM) and 4 control individuals without melanoma diagnoses, based on diagnosis year and outpatient visit frequency.
- Exposures included age, sex, race, ethnicity, rurality, region, military branch, comorbidities, smoking status, alcohol use, BMI, Agent Orange exposure, prior photosensitizing medications, nevi, and keratinocyte carcinoma.
TAKEAWAY:
- Veterans exposed to Agent Orange had higher odds of AM than individuals with CM (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.31; 95% CI, 1.06-1.62) and control individuals without melanoma (AOR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.04-1.56).
- Individuals with current smoking habit had lower odds of AM than those with CM (AOR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.52-0.81) and control individuals without melanoma (AOR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.40-0.62).
- Patients with prior keratinocyte carcinoma and actinic keratosis had higher odds of AM than control individuals without melanoma but lower odds than those with CM.
- History of nevus was associated with higher odds of acral melanoma compared with individuals without melanoma (AOR, 2.11; 95% CI, 1.49-2.98).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results support the need for continued investigation of AM as a distinct entity from CM and may inform future evaluations of the associations between [Agent Orange exposure] in veteran populations, as well as those between other environmental exposures in different populations," the study authors wrote. Referring to the “continued search for a better understanding of a potential link” between Agent Orange and melanoma, as well as AM, and other possible etiologic factors for AM, this study “provides a strong impetus to further these research goals and contribute to the investigation of the legacy of the Vietnam War and honor a commitment to the veterans community,” Andrew F. Olshan, PhD, Gillings School of Global Public Health, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jonathan C. Hwang, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and was published online on February 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The case-control design limits causal inference and the findings might not be generalized outside US veterans. Exposure misclassification could be present.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Department of Defense and the Department of Veterans Affairs. Several authors reported receiving grants from CU Anschutz Medical Center, Department of Defense, CDMRP Melanoma Research Program, and Merck, Bayer, and Department of Veteran Affairs. They also reported receiving royalty from UpToDate, and being shareholder in many companies, including Apple. NVIDIA, Amazon, Gilead, AstraZeneca, BioNTech, and Moderna. Olshan declared being a member of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine Veterans and Agent Orange review committee.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Exposure to Agent Orange, the defoliant used by the US Air Force during the Vietnam War, was one of the factors associated with increased odds of acral melanoma (AM), a rare melanoma subtype affecting palms, soles, and nail units.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a nested case-control study in the Veterans Affairs healthcare system, and identified 1292 veterans (median age, 70.13 years; 94.0% men; 73.4% White, 14.6% Black) with AM through the Veterans Affairs Cancer Registry and a validated natural language processing pipeline from 2000 to 2024.
- Researchers matched each case of AM to 4 individuals with nonacral cutaneous melanoma (CM) and 4 control individuals without melanoma diagnoses, based on diagnosis year and outpatient visit frequency.
- Exposures included age, sex, race, ethnicity, rurality, region, military branch, comorbidities, smoking status, alcohol use, BMI, Agent Orange exposure, prior photosensitizing medications, nevi, and keratinocyte carcinoma.
TAKEAWAY:
- Veterans exposed to Agent Orange had higher odds of AM than individuals with CM (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.31; 95% CI, 1.06-1.62) and control individuals without melanoma (AOR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.04-1.56).
- Individuals with current smoking habit had lower odds of AM than those with CM (AOR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.52-0.81) and control individuals without melanoma (AOR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.40-0.62).
- Patients with prior keratinocyte carcinoma and actinic keratosis had higher odds of AM than control individuals without melanoma but lower odds than those with CM.
- History of nevus was associated with higher odds of acral melanoma compared with individuals without melanoma (AOR, 2.11; 95% CI, 1.49-2.98).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results support the need for continued investigation of AM as a distinct entity from CM and may inform future evaluations of the associations between [Agent Orange exposure] in veteran populations, as well as those between other environmental exposures in different populations," the study authors wrote. Referring to the “continued search for a better understanding of a potential link” between Agent Orange and melanoma, as well as AM, and other possible etiologic factors for AM, this study “provides a strong impetus to further these research goals and contribute to the investigation of the legacy of the Vietnam War and honor a commitment to the veterans community,” Andrew F. Olshan, PhD, Gillings School of Global Public Health, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jonathan C. Hwang, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and was published online on February 4 in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The case-control design limits causal inference and the findings might not be generalized outside US veterans. Exposure misclassification could be present.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Department of Defense and the Department of Veterans Affairs. Several authors reported receiving grants from CU Anschutz Medical Center, Department of Defense, CDMRP Melanoma Research Program, and Merck, Bayer, and Department of Veteran Affairs. They also reported receiving royalty from UpToDate, and being shareholder in many companies, including Apple. NVIDIA, Amazon, Gilead, AstraZeneca, BioNTech, and Moderna. Olshan declared being a member of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine Veterans and Agent Orange review committee.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
US Vet Study Identifies Risk Factors for Acral Melanoma
US Vet Study Identifies Risk Factors for Acral Melanoma
TB, Chronic Bronchitis Tied to Lung Cancer in Never Smokers
TB, Chronic Bronchitis Tied to Lung Cancer in Never Smokers
TOPLINE:
A history of tuberculosis (TB) and a history of chronic bronchitis were associated with an increased risk for lung cancer in individuals who had never smoked, whereas asthma had a positive, nonsignificant association overall and a significant association in women.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical databases from inception to July 2025, to assess the association between asthma, TB, and/or chronic bronchitis and the risk for lung cancer among participants aged 18 years or older who had never smoked.
- They included data from 20 case-control studies involving 54,135 participants and five cohort studies involving 377,983 participants.
- The primary outcome was the risk for lung cancer among participants with a history of TB, asthma, or chronic bronchitis.
- Participants were labeled as “never smokers” if they were explicitly described in the manuscripts as having “never smoked” or reported smoking < 100 cigarettes in their lifetime.
TAKEAWAY:
- In case-control studies, TB (16 studies) and chronic bronchitis (9 studies) were significantly associated with an increased risk for lung cancer (odds ratio [OR], 1.76; P < .001 and OR, 1.36; P = .012, respectively).
- In four case-cohort studies, TB was associated with an increased but nonsignificant risk for lung cancer (hazard ratio, 1.64).
- Eleven case-control studies demonstrated a positive but nonsignificant association between asthma and the risk for lung cancer (OR, 1.34). However, a significant association emerged when analyses were limited to women (five studies; OR, 1.61; P < .01).
IN PRACTICE:
History of TB was especially associated with increased LC [lung cancer] risk, meriting particular attention for prospective CT screening studies,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Nishwant Swami, MD, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. It was published online on January 11, 2026, in Chest.
LIMITATIONS:
Most studies lacked uniform adjustment for key confounders, increasing the risk for residual confounding. The inclusion of few cohort studies in the analysis may have limited the assessment of temporality and precision. Additionally, differences in covariate adjustment, variable definitions, and language restrictions may have limited comparability and generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
No specific funding was reported for this study. One author reported serving as a consultant or advisor for various companies, including AstraZeneca, Merck, and Pfizer. Another author reported receiving funding, in part, through the Prostate Cancer Foundation Young Investigator Award and through the Cancer Center Support Grant from the National Cancer Institute.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A history of tuberculosis (TB) and a history of chronic bronchitis were associated with an increased risk for lung cancer in individuals who had never smoked, whereas asthma had a positive, nonsignificant association overall and a significant association in women.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical databases from inception to July 2025, to assess the association between asthma, TB, and/or chronic bronchitis and the risk for lung cancer among participants aged 18 years or older who had never smoked.
- They included data from 20 case-control studies involving 54,135 participants and five cohort studies involving 377,983 participants.
- The primary outcome was the risk for lung cancer among participants with a history of TB, asthma, or chronic bronchitis.
- Participants were labeled as “never smokers” if they were explicitly described in the manuscripts as having “never smoked” or reported smoking < 100 cigarettes in their lifetime.
TAKEAWAY:
- In case-control studies, TB (16 studies) and chronic bronchitis (9 studies) were significantly associated with an increased risk for lung cancer (odds ratio [OR], 1.76; P < .001 and OR, 1.36; P = .012, respectively).
- In four case-cohort studies, TB was associated with an increased but nonsignificant risk for lung cancer (hazard ratio, 1.64).
- Eleven case-control studies demonstrated a positive but nonsignificant association between asthma and the risk for lung cancer (OR, 1.34). However, a significant association emerged when analyses were limited to women (five studies; OR, 1.61; P < .01).
IN PRACTICE:
History of TB was especially associated with increased LC [lung cancer] risk, meriting particular attention for prospective CT screening studies,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Nishwant Swami, MD, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. It was published online on January 11, 2026, in Chest.
LIMITATIONS:
Most studies lacked uniform adjustment for key confounders, increasing the risk for residual confounding. The inclusion of few cohort studies in the analysis may have limited the assessment of temporality and precision. Additionally, differences in covariate adjustment, variable definitions, and language restrictions may have limited comparability and generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
No specific funding was reported for this study. One author reported serving as a consultant or advisor for various companies, including AstraZeneca, Merck, and Pfizer. Another author reported receiving funding, in part, through the Prostate Cancer Foundation Young Investigator Award and through the Cancer Center Support Grant from the National Cancer Institute.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A history of tuberculosis (TB) and a history of chronic bronchitis were associated with an increased risk for lung cancer in individuals who had never smoked, whereas asthma had a positive, nonsignificant association overall and a significant association in women.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical databases from inception to July 2025, to assess the association between asthma, TB, and/or chronic bronchitis and the risk for lung cancer among participants aged 18 years or older who had never smoked.
- They included data from 20 case-control studies involving 54,135 participants and five cohort studies involving 377,983 participants.
- The primary outcome was the risk for lung cancer among participants with a history of TB, asthma, or chronic bronchitis.
- Participants were labeled as “never smokers” if they were explicitly described in the manuscripts as having “never smoked” or reported smoking < 100 cigarettes in their lifetime.
TAKEAWAY:
- In case-control studies, TB (16 studies) and chronic bronchitis (9 studies) were significantly associated with an increased risk for lung cancer (odds ratio [OR], 1.76; P < .001 and OR, 1.36; P = .012, respectively).
- In four case-cohort studies, TB was associated with an increased but nonsignificant risk for lung cancer (hazard ratio, 1.64).
- Eleven case-control studies demonstrated a positive but nonsignificant association between asthma and the risk for lung cancer (OR, 1.34). However, a significant association emerged when analyses were limited to women (five studies; OR, 1.61; P < .01).
IN PRACTICE:
History of TB was especially associated with increased LC [lung cancer] risk, meriting particular attention for prospective CT screening studies,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Nishwant Swami, MD, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. It was published online on January 11, 2026, in Chest.
LIMITATIONS:
Most studies lacked uniform adjustment for key confounders, increasing the risk for residual confounding. The inclusion of few cohort studies in the analysis may have limited the assessment of temporality and precision. Additionally, differences in covariate adjustment, variable definitions, and language restrictions may have limited comparability and generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
No specific funding was reported for this study. One author reported serving as a consultant or advisor for various companies, including AstraZeneca, Merck, and Pfizer. Another author reported receiving funding, in part, through the Prostate Cancer Foundation Young Investigator Award and through the Cancer Center Support Grant from the National Cancer Institute.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TB, Chronic Bronchitis Tied to Lung Cancer in Never Smokers
TB, Chronic Bronchitis Tied to Lung Cancer in Never Smokers
Fecal Microbiota Transplant Safety Goal Met in Kidney Cancer
Fecal Microbiota Transplant Safety Goal Met in Kidney Cancer
TOPLINE:
Healthy donor fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in metastatic renal cell carcinoma demonstrated safety with a 50% objective response rate and no grade 4-5 toxicities. Successful engraftment of diverse, anti-inflammatory microbiota correlated with improved clinical response and reduced immune-related adverse events.
METHODOLOGY:
- Many patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who take ICI experience immune-related adverse events that may require treatment interruption. Recent studies have provided proof of concept for microbiome modulation as a therapeutic adjunct in metastatic renal cell carcinoma, with FMT showing efficacy in resolving TKI-induced toxicities. However, the safety and clinical activity of healthy donor FMT in metastatic renal cell carcinoma remained unexplored, and its mechanism of action was unclear prior to this study.
- The new phase 1 trial enrolled 20 treatment-naive patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma classified as intermediate-risk or poor-risk disease, who received encapsulated healthy donor FMT (LND101) combined with ipilimumab plus nivolumab (n = 16), pembrolizumab plus axitinib (n = 3), or pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib (n = 1).
- Participants underwent polyethylene glycol bowel preparation before receiving one full dose (36-40 capsules containing 80-100 g of stool) and two half-doses (20-25 capsules each containing 50-60 g of stool) of FMT from rigorously screened healthy donors.
- The primary endpoint was safety assessed through incidence and severity of immune-related adverse events, while secondary endpoints included objective response rate by response evaluation criteria in solid tumors version 1.1, gut microbiome changes, immune correlates, and quality of life.
- Analysis included longitudinal monitoring of stool and blood samples at five timepoints: baseline, week 1 post-FMT, week 4, week 7, and week 10, with a median follow-up of 21.9 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- The safety endpoint was met, with half (10 of 20) of patients experiencing grade 3 immune-related adverse events and no serious FMT-related toxicities or grade 4-5 immune-related adverse events. One patient (5%) reported experiencing an FMT-related grade 1 gastrointestinal event.
- Among evaluable patients (n = 18), the objective response rate was 50% (9 of 18), including two complete responses (11%; 2 of 18), while 67% (12 of 18) achieved clinical benefit defined as complete response, partial response, or stable disease for at least 6 months.
- Higher alpha diversity and greater functional engraftment of short-chain fatty acid-producing and anti-inflammatory taxa correlated with protection from severe immune-related adverse events (P = .041) and improved therapeutic response (P = .006).
- Expansion of Segatella copri above 10 counts per million at 10 weeks post-FMT predicted severe toxicity in patients receiving ipilimumab plus nivolumab, regardless of donor or recipient microbiota origin.
IN PRACTICE:
These findings demonstrate the safety and potential for functional microbiome engraftment to optimize response and minimize toxicity in ICI-treated [metastatic renal cell carcinoma]. Together, our results underscore the importance of functional donor screening and targeted modulation of the microbiome in optimizing the safety and efficacy of next-generation immune-based therapies,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Ricardo Fernandes, Behnam Jabbarizadeh, and Adnan Rajeh, London Health Sciences Centre, London, Ontario, Canada. It was published online on January 28 in Nature Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
According to the authors, the study’s primary limitation was its small sample size, which was not powered to define the ideal donor microbiome composition for enhancing immunotherapy efficacy without additional toxicities. The single-center design and highly selected patient population may limit external generalizability, requiring validation in larger, multicenter trials to refine donor selection criteria and clarify microbiome-immunity mechanisms.
DISCLOSURES:
The clinical trial was primarily funded through philanthropic donations to co-authors Saman Maleki Vareki and Fernandes through the London Health Sciences Foundation clinical trials program. Vareki and Michael Silverman, another co-author, reported having US Patent application no. 63/913,940 related to FMT donor screening. Vareki reported receiving grants from the Lotte and John Hecht Memorial Foundation, the Weston Family Foundation, and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Healthy donor fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in metastatic renal cell carcinoma demonstrated safety with a 50% objective response rate and no grade 4-5 toxicities. Successful engraftment of diverse, anti-inflammatory microbiota correlated with improved clinical response and reduced immune-related adverse events.
METHODOLOGY:
- Many patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who take ICI experience immune-related adverse events that may require treatment interruption. Recent studies have provided proof of concept for microbiome modulation as a therapeutic adjunct in metastatic renal cell carcinoma, with FMT showing efficacy in resolving TKI-induced toxicities. However, the safety and clinical activity of healthy donor FMT in metastatic renal cell carcinoma remained unexplored, and its mechanism of action was unclear prior to this study.
- The new phase 1 trial enrolled 20 treatment-naive patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma classified as intermediate-risk or poor-risk disease, who received encapsulated healthy donor FMT (LND101) combined with ipilimumab plus nivolumab (n = 16), pembrolizumab plus axitinib (n = 3), or pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib (n = 1).
- Participants underwent polyethylene glycol bowel preparation before receiving one full dose (36-40 capsules containing 80-100 g of stool) and two half-doses (20-25 capsules each containing 50-60 g of stool) of FMT from rigorously screened healthy donors.
- The primary endpoint was safety assessed through incidence and severity of immune-related adverse events, while secondary endpoints included objective response rate by response evaluation criteria in solid tumors version 1.1, gut microbiome changes, immune correlates, and quality of life.
- Analysis included longitudinal monitoring of stool and blood samples at five timepoints: baseline, week 1 post-FMT, week 4, week 7, and week 10, with a median follow-up of 21.9 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- The safety endpoint was met, with half (10 of 20) of patients experiencing grade 3 immune-related adverse events and no serious FMT-related toxicities or grade 4-5 immune-related adverse events. One patient (5%) reported experiencing an FMT-related grade 1 gastrointestinal event.
- Among evaluable patients (n = 18), the objective response rate was 50% (9 of 18), including two complete responses (11%; 2 of 18), while 67% (12 of 18) achieved clinical benefit defined as complete response, partial response, or stable disease for at least 6 months.
- Higher alpha diversity and greater functional engraftment of short-chain fatty acid-producing and anti-inflammatory taxa correlated with protection from severe immune-related adverse events (P = .041) and improved therapeutic response (P = .006).
- Expansion of Segatella copri above 10 counts per million at 10 weeks post-FMT predicted severe toxicity in patients receiving ipilimumab plus nivolumab, regardless of donor or recipient microbiota origin.
IN PRACTICE:
These findings demonstrate the safety and potential for functional microbiome engraftment to optimize response and minimize toxicity in ICI-treated [metastatic renal cell carcinoma]. Together, our results underscore the importance of functional donor screening and targeted modulation of the microbiome in optimizing the safety and efficacy of next-generation immune-based therapies,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Ricardo Fernandes, Behnam Jabbarizadeh, and Adnan Rajeh, London Health Sciences Centre, London, Ontario, Canada. It was published online on January 28 in Nature Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
According to the authors, the study’s primary limitation was its small sample size, which was not powered to define the ideal donor microbiome composition for enhancing immunotherapy efficacy without additional toxicities. The single-center design and highly selected patient population may limit external generalizability, requiring validation in larger, multicenter trials to refine donor selection criteria and clarify microbiome-immunity mechanisms.
DISCLOSURES:
The clinical trial was primarily funded through philanthropic donations to co-authors Saman Maleki Vareki and Fernandes through the London Health Sciences Foundation clinical trials program. Vareki and Michael Silverman, another co-author, reported having US Patent application no. 63/913,940 related to FMT donor screening. Vareki reported receiving grants from the Lotte and John Hecht Memorial Foundation, the Weston Family Foundation, and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Healthy donor fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in metastatic renal cell carcinoma demonstrated safety with a 50% objective response rate and no grade 4-5 toxicities. Successful engraftment of diverse, anti-inflammatory microbiota correlated with improved clinical response and reduced immune-related adverse events.
METHODOLOGY:
- Many patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who take ICI experience immune-related adverse events that may require treatment interruption. Recent studies have provided proof of concept for microbiome modulation as a therapeutic adjunct in metastatic renal cell carcinoma, with FMT showing efficacy in resolving TKI-induced toxicities. However, the safety and clinical activity of healthy donor FMT in metastatic renal cell carcinoma remained unexplored, and its mechanism of action was unclear prior to this study.
- The new phase 1 trial enrolled 20 treatment-naive patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma classified as intermediate-risk or poor-risk disease, who received encapsulated healthy donor FMT (LND101) combined with ipilimumab plus nivolumab (n = 16), pembrolizumab plus axitinib (n = 3), or pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib (n = 1).
- Participants underwent polyethylene glycol bowel preparation before receiving one full dose (36-40 capsules containing 80-100 g of stool) and two half-doses (20-25 capsules each containing 50-60 g of stool) of FMT from rigorously screened healthy donors.
- The primary endpoint was safety assessed through incidence and severity of immune-related adverse events, while secondary endpoints included objective response rate by response evaluation criteria in solid tumors version 1.1, gut microbiome changes, immune correlates, and quality of life.
- Analysis included longitudinal monitoring of stool and blood samples at five timepoints: baseline, week 1 post-FMT, week 4, week 7, and week 10, with a median follow-up of 21.9 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- The safety endpoint was met, with half (10 of 20) of patients experiencing grade 3 immune-related adverse events and no serious FMT-related toxicities or grade 4-5 immune-related adverse events. One patient (5%) reported experiencing an FMT-related grade 1 gastrointestinal event.
- Among evaluable patients (n = 18), the objective response rate was 50% (9 of 18), including two complete responses (11%; 2 of 18), while 67% (12 of 18) achieved clinical benefit defined as complete response, partial response, or stable disease for at least 6 months.
- Higher alpha diversity and greater functional engraftment of short-chain fatty acid-producing and anti-inflammatory taxa correlated with protection from severe immune-related adverse events (P = .041) and improved therapeutic response (P = .006).
- Expansion of Segatella copri above 10 counts per million at 10 weeks post-FMT predicted severe toxicity in patients receiving ipilimumab plus nivolumab, regardless of donor or recipient microbiota origin.
IN PRACTICE:
These findings demonstrate the safety and potential for functional microbiome engraftment to optimize response and minimize toxicity in ICI-treated [metastatic renal cell carcinoma]. Together, our results underscore the importance of functional donor screening and targeted modulation of the microbiome in optimizing the safety and efficacy of next-generation immune-based therapies,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Ricardo Fernandes, Behnam Jabbarizadeh, and Adnan Rajeh, London Health Sciences Centre, London, Ontario, Canada. It was published online on January 28 in Nature Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
According to the authors, the study’s primary limitation was its small sample size, which was not powered to define the ideal donor microbiome composition for enhancing immunotherapy efficacy without additional toxicities. The single-center design and highly selected patient population may limit external generalizability, requiring validation in larger, multicenter trials to refine donor selection criteria and clarify microbiome-immunity mechanisms.
DISCLOSURES:
The clinical trial was primarily funded through philanthropic donations to co-authors Saman Maleki Vareki and Fernandes through the London Health Sciences Foundation clinical trials program. Vareki and Michael Silverman, another co-author, reported having US Patent application no. 63/913,940 related to FMT donor screening. Vareki reported receiving grants from the Lotte and John Hecht Memorial Foundation, the Weston Family Foundation, and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fecal Microbiota Transplant Safety Goal Met in Kidney Cancer
Fecal Microbiota Transplant Safety Goal Met in Kidney Cancer