User login
Evaluating the Impact and Educational Value of YouTube Videos on Nail Biopsy Procedures
To the Editor:
Nail biopsy is an important surgical procedure for diagnosis of nail pathology. YouTube has become a potential instrument for physicians and patients to learn about medical procedures.1,2 However, the sources, content, and quality of the information available have not been fully studied or characterized. Our objective was to analyze the efficiency of information and quality of YouTube videos on nail biopsies. We hypothesized that the quality of patient education and physician training videos would be unrepresentative on YouTube.
The term nail biopsy was searched on January 29, 2019, and filtered by relevance and rating using the default YouTube algorithm. Data were collected from the top 40 hits for the search term and filter coupling. All videos were viewed and sorted for nail biopsy procedures, and then those videos were categorized as being produced by a physician or other health care provider. The US medical board status of each physician videographer was determined using the American Board of Medical Specialties database.3 DISCERN criteria for assessing consumer health care information4 were used to interpret the videos by researchers (S.I. and S.R.L.) in this study.
From the queried search term collection, only 10 videos (1,023,423 combined views) were analyzed in this study (eTable). Although the other resulting videos were tagged as nail biopsy, they were excluded due to irrelevant content (eg, patient blogs, PowerPoints, nail avulsions). The mean age of the videos was 4 years (range, 4 days to 11 years), with a mean video length of 3.30 minutes (range, 49 seconds to 9.03 minutes). Four of 10 videos were performed for longitudinal melanonychia, and 5 of 10 videos were performed for melanonychia, clinically consistent with subungual hematoma. Dermatologists, plastic surgeons, and podiatrists produced the majority of the nail biopsy videos. The overall mean DISCERN rating was 1.60/5.00 (range, 1–3), meaning that the quality of content on nail biopsies was poor. This low DISCERN score signifies poor consumer health information. Video 2 (published in 2015) received a DISCERN score of 2 and received almost 1 million views, which is likely because the specific channel has a well-established subscriber pool (4.9 million subscribers). The highest DISCERN score of 3, demonstrating a tangential shave biopsy, was given to video 4 (published in 2010) and only received about 17,400 views (56 subscribers). Additionally, many videos lacked important information about the procedure. For instance, only 3 of 10 videos demonstrated the anesthetic technique and only 5 videos showed repair methods.
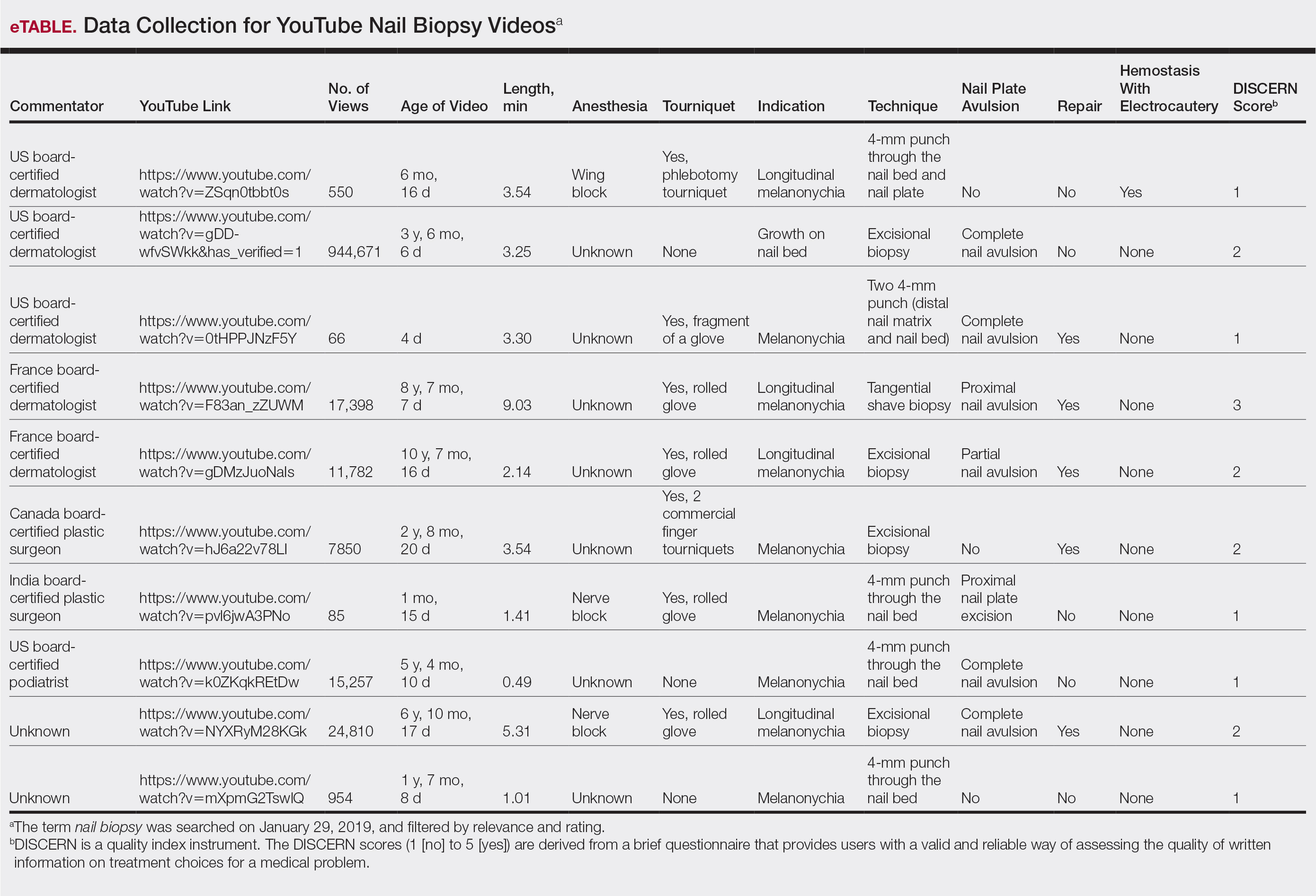
YouTube is an electronic learning source for general information; however, the content and quality of information on nail biopsy is not updated, reliable, or abundant. Patients undergoing nail biopsies are unlikely to find reliable and comprehensible information on YouTube; thus, there is a strong need for patient education in this area. In addition, physicians who did not learn to perform a nail biopsy during training are unlikely to learn this procedure from YouTube. Therefore, there is an unmet need for an outlet that will provide updated reliable content on nail biopsies geared toward both patients and physicians.
- Kwok TM, Singla AA, Phang K, et al. YouTube as a source of patient information for varicose vein treatment options. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2017;5:238-243.
- Ward B, Ward M, Nicheporuck A, et al. Assessment of YouTube as an informative resource on facial plastic surgery procedures. JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery. 2019;21:75-76.
- American Board of Medical Specialties. Certification Matters. https://www.certificationmatters.org. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- The DISCERN Instrument. DISCERN Online. http://www.discern.org.uk/discern_instrument.php. Published October 1999. Accessed February 7, 2020.
To the Editor:
Nail biopsy is an important surgical procedure for diagnosis of nail pathology. YouTube has become a potential instrument for physicians and patients to learn about medical procedures.1,2 However, the sources, content, and quality of the information available have not been fully studied or characterized. Our objective was to analyze the efficiency of information and quality of YouTube videos on nail biopsies. We hypothesized that the quality of patient education and physician training videos would be unrepresentative on YouTube.
The term nail biopsy was searched on January 29, 2019, and filtered by relevance and rating using the default YouTube algorithm. Data were collected from the top 40 hits for the search term and filter coupling. All videos were viewed and sorted for nail biopsy procedures, and then those videos were categorized as being produced by a physician or other health care provider. The US medical board status of each physician videographer was determined using the American Board of Medical Specialties database.3 DISCERN criteria for assessing consumer health care information4 were used to interpret the videos by researchers (S.I. and S.R.L.) in this study.
From the queried search term collection, only 10 videos (1,023,423 combined views) were analyzed in this study (eTable). Although the other resulting videos were tagged as nail biopsy, they were excluded due to irrelevant content (eg, patient blogs, PowerPoints, nail avulsions). The mean age of the videos was 4 years (range, 4 days to 11 years), with a mean video length of 3.30 minutes (range, 49 seconds to 9.03 minutes). Four of 10 videos were performed for longitudinal melanonychia, and 5 of 10 videos were performed for melanonychia, clinically consistent with subungual hematoma. Dermatologists, plastic surgeons, and podiatrists produced the majority of the nail biopsy videos. The overall mean DISCERN rating was 1.60/5.00 (range, 1–3), meaning that the quality of content on nail biopsies was poor. This low DISCERN score signifies poor consumer health information. Video 2 (published in 2015) received a DISCERN score of 2 and received almost 1 million views, which is likely because the specific channel has a well-established subscriber pool (4.9 million subscribers). The highest DISCERN score of 3, demonstrating a tangential shave biopsy, was given to video 4 (published in 2010) and only received about 17,400 views (56 subscribers). Additionally, many videos lacked important information about the procedure. For instance, only 3 of 10 videos demonstrated the anesthetic technique and only 5 videos showed repair methods.

YouTube is an electronic learning source for general information; however, the content and quality of information on nail biopsy is not updated, reliable, or abundant. Patients undergoing nail biopsies are unlikely to find reliable and comprehensible information on YouTube; thus, there is a strong need for patient education in this area. In addition, physicians who did not learn to perform a nail biopsy during training are unlikely to learn this procedure from YouTube. Therefore, there is an unmet need for an outlet that will provide updated reliable content on nail biopsies geared toward both patients and physicians.
To the Editor:
Nail biopsy is an important surgical procedure for diagnosis of nail pathology. YouTube has become a potential instrument for physicians and patients to learn about medical procedures.1,2 However, the sources, content, and quality of the information available have not been fully studied or characterized. Our objective was to analyze the efficiency of information and quality of YouTube videos on nail biopsies. We hypothesized that the quality of patient education and physician training videos would be unrepresentative on YouTube.
The term nail biopsy was searched on January 29, 2019, and filtered by relevance and rating using the default YouTube algorithm. Data were collected from the top 40 hits for the search term and filter coupling. All videos were viewed and sorted for nail biopsy procedures, and then those videos were categorized as being produced by a physician or other health care provider. The US medical board status of each physician videographer was determined using the American Board of Medical Specialties database.3 DISCERN criteria for assessing consumer health care information4 were used to interpret the videos by researchers (S.I. and S.R.L.) in this study.
From the queried search term collection, only 10 videos (1,023,423 combined views) were analyzed in this study (eTable). Although the other resulting videos were tagged as nail biopsy, they were excluded due to irrelevant content (eg, patient blogs, PowerPoints, nail avulsions). The mean age of the videos was 4 years (range, 4 days to 11 years), with a mean video length of 3.30 minutes (range, 49 seconds to 9.03 minutes). Four of 10 videos were performed for longitudinal melanonychia, and 5 of 10 videos were performed for melanonychia, clinically consistent with subungual hematoma. Dermatologists, plastic surgeons, and podiatrists produced the majority of the nail biopsy videos. The overall mean DISCERN rating was 1.60/5.00 (range, 1–3), meaning that the quality of content on nail biopsies was poor. This low DISCERN score signifies poor consumer health information. Video 2 (published in 2015) received a DISCERN score of 2 and received almost 1 million views, which is likely because the specific channel has a well-established subscriber pool (4.9 million subscribers). The highest DISCERN score of 3, demonstrating a tangential shave biopsy, was given to video 4 (published in 2010) and only received about 17,400 views (56 subscribers). Additionally, many videos lacked important information about the procedure. For instance, only 3 of 10 videos demonstrated the anesthetic technique and only 5 videos showed repair methods.

YouTube is an electronic learning source for general information; however, the content and quality of information on nail biopsy is not updated, reliable, or abundant. Patients undergoing nail biopsies are unlikely to find reliable and comprehensible information on YouTube; thus, there is a strong need for patient education in this area. In addition, physicians who did not learn to perform a nail biopsy during training are unlikely to learn this procedure from YouTube. Therefore, there is an unmet need for an outlet that will provide updated reliable content on nail biopsies geared toward both patients and physicians.
- Kwok TM, Singla AA, Phang K, et al. YouTube as a source of patient information for varicose vein treatment options. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2017;5:238-243.
- Ward B, Ward M, Nicheporuck A, et al. Assessment of YouTube as an informative resource on facial plastic surgery procedures. JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery. 2019;21:75-76.
- American Board of Medical Specialties. Certification Matters. https://www.certificationmatters.org. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- The DISCERN Instrument. DISCERN Online. http://www.discern.org.uk/discern_instrument.php. Published October 1999. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- Kwok TM, Singla AA, Phang K, et al. YouTube as a source of patient information for varicose vein treatment options. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2017;5:238-243.
- Ward B, Ward M, Nicheporuck A, et al. Assessment of YouTube as an informative resource on facial plastic surgery procedures. JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery. 2019;21:75-76.
- American Board of Medical Specialties. Certification Matters. https://www.certificationmatters.org. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- The DISCERN Instrument. DISCERN Online. http://www.discern.org.uk/discern_instrument.php. Published October 1999. Accessed February 7, 2020.
Practice Points
- A nail biopsy is sometimes necessary for histopathologic confirmation of a clinical diagnosis.
- YouTube has become a potential educational platform for physicians and patients to learn about nail biopsy procedures.
- Physicians and patients interested in learning more about nail biopsies are unlikely to find reliable and comprehensible information on YouTube; therefore, there is a need for updated reliable video content on nail biopsies geared toward both physicians and patients.
Concurrent Beau Lines, Onychomadesis, and Retronychia Following Scurvy
Beau lines are palpable transverse depressions on the dorsal aspect of the nail plate that result from a temporary slowing of nail plate production by the proximal nail matrix. Onychomadesis is a separation of the proximal nail plate from the distal nail plate leading to shedding of the nail. It occurs due to a complete growth arrest in the nail matrix and is thought to be on a continuum with Beau lines. The etiologies of these 2 conditions overlap and include trauma, inflammatory diseases, systemic illnesses, hereditary conditions, and infections.1-5 In almost all cases of both conditions, normal nail plate production ensues upon identification and removal of the inciting agent or recuperation from the causal illness.3,4,6 Beau lines will move distally as the nail grows out and can be clipped. In onychomadesis, the affected nails will be shed with time. Resolution of these nail defects can be estimated from average nail growth rates (1 mm/mo for fingernails and 2–3 mm/mo for toenails).7
Retronychia is defined as a proximal ingrowing of the nail plate into the ventral surface of the proximal nail fold.4,6 It is thought to occur via vertical progression of the nail plate into the proximal nail fold, repetitive nail matrix trauma, or shearing forces, resulting in inflammation that leads to nail plate stacking.8,9 Although conservative treatment using topical corticosteroids may be attempted, proximal nail plate avulsion typically is required for treatment.10
Braswell et al1 suggested a unifying hypothesis for a common pathophysiologic basis for these 3 conditions; that is, nail matrix injury results in slowing and/or cessation of nail plate production, followed by recommencement of nail plate production by the nail matrix after removal of the insult. We report a case of a patient presenting with concurrent Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia following scurvy, thus supporting the hypothesis that these 3 nail conditions lie on a continuum.
Case Report
A 41-year-old woman with a history of thyroiditis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, endometriosis, osteoarthritis, gastric ulcer, pancreatitis, fatty liver, and polycystic ovarian syndrome presented with lines on the toenails and no growth of the right second toenail of several months’ duration. She denied any pain or prior trauma to the nails, participation in sports activities, or wearing tight or high-heeled shoes. She had presented 6 months prior for evaluation of perifollicular erythema on the posterior thighs, legs, and abdomen, as well as gingival bleeding.11 At that time, one of the authors (S.R.L.) found that she was vitamin C deficient, and a diagnosis of scurvy was made. The rash and gingival bleeding resolved with vitamin C supplementation.11
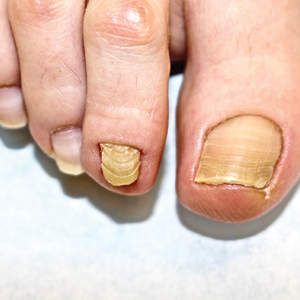
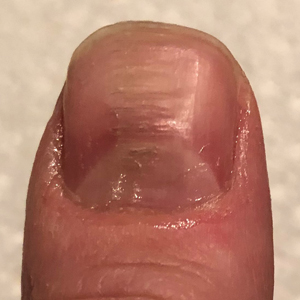
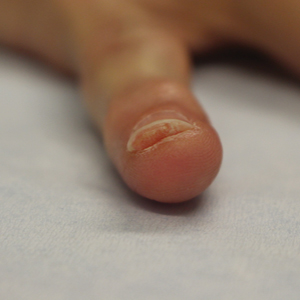
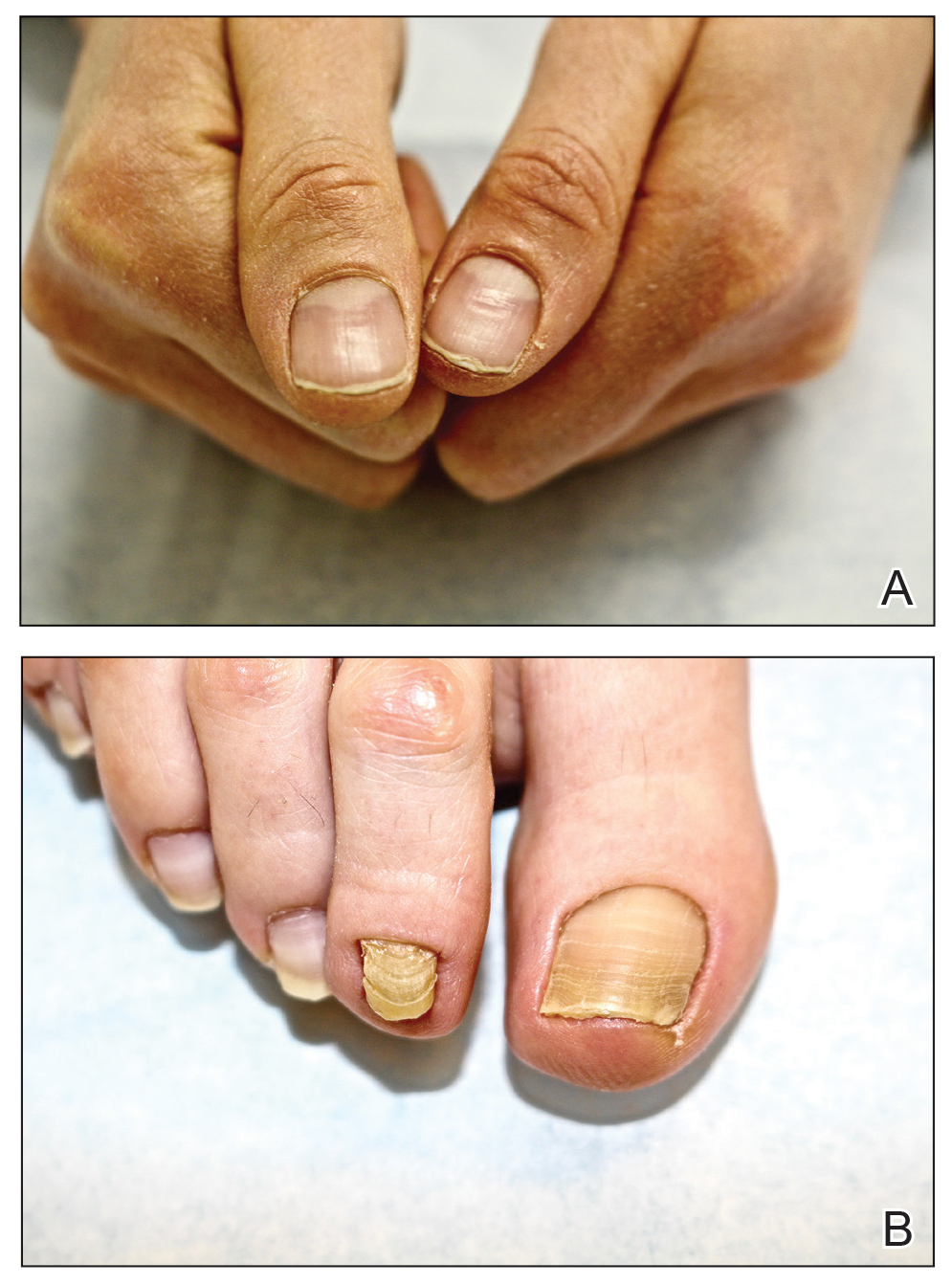
At the current presentation, physical examination revealed transverse grooves involving several fingernails but most evident on the left thumbnail (Figure, A). The grooves did not span the entire breadth of the nail, which was consistent with Beau lines. Several toenails had parallel transverse grooves spanning the entire width of the nail plate such that the proximal nail plate was discontinuous with the distal nail plate, which was consistent with onychomadesis (Figure, B). The right second toenail was yellow and thickened with layered nail plates, indicative of retronychia (Figure, B). Histopathology of a nail plate clipping from the right second toenail was negative for fungal hyphae, and a radiograph was negative for bony changes or exostosis.
Comment
The nail matrix is responsible for nail plate production, and the newly formed nail plate then moves outward over the nail bed. It is hypothesized that the pathophysiologic basis for Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia lies on a continuum such that all 3 conditions are caused by an insult to the nail matrix that results in slowing and/or halting of nail plate growth. Beau lines result from slowing or disruption in cell growth from the nail matrix, whereas onychomadesis is associated with a complete halt in nail plate production.1,3 In retronychia, the new nail growing from the matrix pushes the old one upward, interrupting the longitudinal growth of the nail and leading to nail plate stacking.10
Our patient presented with concurrent Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia. Although Beau lines and onychomadesis have been reported together in some instances,12-14 retronychia is not commonly reported with either of these conditions. The exact incidence of each condition has not been studied, but Beau lines are relatively common, onychomadesis is less common, and retronychia is seen infrequently; therefore, the concurrent presentation of these 3 conditions in the same patient is exceedingly rare. Thus, it was most likely that one etiology accounted for all 3 nail findings.
Because the patient had been diagnosed with scurvy 6 months prior to presentation, we hypothesized that the associated vitamin C deficiency caused a systemic insult to the nail matrix, which resulted in cessation of nail growth. The mechanism of nail matrix arrest in the setting of systemic disease is thought to be due to inhibition of cellular proliferation or a change in the quality of the newly manufactured nail plate, which becomes thinner and more dystrophic.15 Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) deficiency causes scurvy, which is characterized by cutaneous signs such as perifollicular hemorrhage and purpura, corkscrew hairs, bruising, gingivitis, arthralgia, and impaired wound healing.16 These clinical manifestations are due to impaired collagen synthesis and disordered connective tissue. Ascorbic acid also is involved in fatty acid transport, neurotransmitter synthesis, prostaglandin metabolism, and nitric oxide synthesis.17 Ascorbic acid has not been studied for its role in nail plate synthesis18; however, given the role that ascorbic acid plays in a myriad of biologic processes, the deficiency associated with scurvy likely had a considerable systemic effect in our patient that halted nail plate synthesis and resulted in the concurrent presentation of Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia.
- Braswell MA, Daniel CR III, Brodell RT. Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia: a unifying hypothesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:849-855.
- Lipner SR. Onychomadesis following a fish pedicure. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1091-1092.
- Bettoli V, Zauli S, Toni G, et al. Onychomadesis following hand, foot, and mouth disease: a case report from Italy and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:728-730.
- Lawry M, Daniel CR III. Nails in systemic disease. In: Scher RK, Daniel CR III, eds. Nails: Diagnosis, Therapy, Surgery. 3rd ed. Oxford, England: Elsevier Saunders; 2005:147-176.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Evaluation of nail lines: color and shape hold clues. Cleve Clin J Med. 2016;83:385.
- Rich P. Nail signs and symptoms. In: Scher RK, Daniel CR III, eds. Nails: Diagnosis, Therapy, Surgery. 3rd ed. Oxford, England: Elsevier Saunders; 2005:1-6.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Nail growth evaluation and factors affecting nail growth. In: Humbert P, Fanian F, Maibach H, et al, eds. Agache’s Measuring the Skin. Cham, Switzerland: Springer; 2017:1-15.
- de Berker DA, Richert B, Duhard E, et al. Retronychia: proximal ingrowing of the nail plate. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:978-983.
- Wortsman X, Wortsman J, Guerrero R, et al. Anatomical changes in retronychia and onychomadesis detected using ultrasound. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1615-1620.
- Piraccini BM, Richert B, de Berker DA, et al. Retronychia in children, adolescents, and young adults: a case series. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:388-390.
- Lipner S. A classic case of scurvy. Lancet. 2018;392:431.
- Jacobsen L, Zimmerman S, Lohr J. Nail findings in hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015;34:449-450.
- Damevska K, Gocev G, Pollozhani N, et al. Onychomadesis following cutaneous vasculitis. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2017;25:77-79.
- Clementz GC, Mancini AJ. Nail matrix arrest following hand‐foot‐mouth disease: a report of five children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2000;17:7-11.
- Weismann K. J.H.S Beau and his descriptions of transverse depressions on nails. Br J Dermatol. 1977;97:571-572.
- Abdullah M, Jamil RT, Attia FN. Vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499877/. Updated October 21, 2019. Accessed February 24, 2020.
- Pazirandeh S, Burns DL. Overview of water-soluble vitamins. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-water-soluble-vitamins. Updated January 29, 2020. Accessed February 24, 2020.
- Scheinfeld N, Dahdah MJ, Scher RK. Vitamins and minerals: their role in nail health and disease. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:782-787.
Beau lines are palpable transverse depressions on the dorsal aspect of the nail plate that result from a temporary slowing of nail plate production by the proximal nail matrix. Onychomadesis is a separation of the proximal nail plate from the distal nail plate leading to shedding of the nail. It occurs due to a complete growth arrest in the nail matrix and is thought to be on a continuum with Beau lines. The etiologies of these 2 conditions overlap and include trauma, inflammatory diseases, systemic illnesses, hereditary conditions, and infections.1-5 In almost all cases of both conditions, normal nail plate production ensues upon identification and removal of the inciting agent or recuperation from the causal illness.3,4,6 Beau lines will move distally as the nail grows out and can be clipped. In onychomadesis, the affected nails will be shed with time. Resolution of these nail defects can be estimated from average nail growth rates (1 mm/mo for fingernails and 2–3 mm/mo for toenails).7
Retronychia is defined as a proximal ingrowing of the nail plate into the ventral surface of the proximal nail fold.4,6 It is thought to occur via vertical progression of the nail plate into the proximal nail fold, repetitive nail matrix trauma, or shearing forces, resulting in inflammation that leads to nail plate stacking.8,9 Although conservative treatment using topical corticosteroids may be attempted, proximal nail plate avulsion typically is required for treatment.10
Braswell et al1 suggested a unifying hypothesis for a common pathophysiologic basis for these 3 conditions; that is, nail matrix injury results in slowing and/or cessation of nail plate production, followed by recommencement of nail plate production by the nail matrix after removal of the insult. We report a case of a patient presenting with concurrent Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia following scurvy, thus supporting the hypothesis that these 3 nail conditions lie on a continuum.
Case Report
A 41-year-old woman with a history of thyroiditis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, endometriosis, osteoarthritis, gastric ulcer, pancreatitis, fatty liver, and polycystic ovarian syndrome presented with lines on the toenails and no growth of the right second toenail of several months’ duration. She denied any pain or prior trauma to the nails, participation in sports activities, or wearing tight or high-heeled shoes. She had presented 6 months prior for evaluation of perifollicular erythema on the posterior thighs, legs, and abdomen, as well as gingival bleeding.11 At that time, one of the authors (S.R.L.) found that she was vitamin C deficient, and a diagnosis of scurvy was made. The rash and gingival bleeding resolved with vitamin C supplementation.11
At the current presentation, physical examination revealed transverse grooves involving several fingernails but most evident on the left thumbnail (Figure, A). The grooves did not span the entire breadth of the nail, which was consistent with Beau lines. Several toenails had parallel transverse grooves spanning the entire width of the nail plate such that the proximal nail plate was discontinuous with the distal nail plate, which was consistent with onychomadesis (Figure, B). The right second toenail was yellow and thickened with layered nail plates, indicative of retronychia (Figure, B). Histopathology of a nail plate clipping from the right second toenail was negative for fungal hyphae, and a radiograph was negative for bony changes or exostosis.

Comment
The nail matrix is responsible for nail plate production, and the newly formed nail plate then moves outward over the nail bed. It is hypothesized that the pathophysiologic basis for Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia lies on a continuum such that all 3 conditions are caused by an insult to the nail matrix that results in slowing and/or halting of nail plate growth. Beau lines result from slowing or disruption in cell growth from the nail matrix, whereas onychomadesis is associated with a complete halt in nail plate production.1,3 In retronychia, the new nail growing from the matrix pushes the old one upward, interrupting the longitudinal growth of the nail and leading to nail plate stacking.10
Our patient presented with concurrent Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia. Although Beau lines and onychomadesis have been reported together in some instances,12-14 retronychia is not commonly reported with either of these conditions. The exact incidence of each condition has not been studied, but Beau lines are relatively common, onychomadesis is less common, and retronychia is seen infrequently; therefore, the concurrent presentation of these 3 conditions in the same patient is exceedingly rare. Thus, it was most likely that one etiology accounted for all 3 nail findings.
Because the patient had been diagnosed with scurvy 6 months prior to presentation, we hypothesized that the associated vitamin C deficiency caused a systemic insult to the nail matrix, which resulted in cessation of nail growth. The mechanism of nail matrix arrest in the setting of systemic disease is thought to be due to inhibition of cellular proliferation or a change in the quality of the newly manufactured nail plate, which becomes thinner and more dystrophic.15 Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) deficiency causes scurvy, which is characterized by cutaneous signs such as perifollicular hemorrhage and purpura, corkscrew hairs, bruising, gingivitis, arthralgia, and impaired wound healing.16 These clinical manifestations are due to impaired collagen synthesis and disordered connective tissue. Ascorbic acid also is involved in fatty acid transport, neurotransmitter synthesis, prostaglandin metabolism, and nitric oxide synthesis.17 Ascorbic acid has not been studied for its role in nail plate synthesis18; however, given the role that ascorbic acid plays in a myriad of biologic processes, the deficiency associated with scurvy likely had a considerable systemic effect in our patient that halted nail plate synthesis and resulted in the concurrent presentation of Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia.
Beau lines are palpable transverse depressions on the dorsal aspect of the nail plate that result from a temporary slowing of nail plate production by the proximal nail matrix. Onychomadesis is a separation of the proximal nail plate from the distal nail plate leading to shedding of the nail. It occurs due to a complete growth arrest in the nail matrix and is thought to be on a continuum with Beau lines. The etiologies of these 2 conditions overlap and include trauma, inflammatory diseases, systemic illnesses, hereditary conditions, and infections.1-5 In almost all cases of both conditions, normal nail plate production ensues upon identification and removal of the inciting agent or recuperation from the causal illness.3,4,6 Beau lines will move distally as the nail grows out and can be clipped. In onychomadesis, the affected nails will be shed with time. Resolution of these nail defects can be estimated from average nail growth rates (1 mm/mo for fingernails and 2–3 mm/mo for toenails).7
Retronychia is defined as a proximal ingrowing of the nail plate into the ventral surface of the proximal nail fold.4,6 It is thought to occur via vertical progression of the nail plate into the proximal nail fold, repetitive nail matrix trauma, or shearing forces, resulting in inflammation that leads to nail plate stacking.8,9 Although conservative treatment using topical corticosteroids may be attempted, proximal nail plate avulsion typically is required for treatment.10
Braswell et al1 suggested a unifying hypothesis for a common pathophysiologic basis for these 3 conditions; that is, nail matrix injury results in slowing and/or cessation of nail plate production, followed by recommencement of nail plate production by the nail matrix after removal of the insult. We report a case of a patient presenting with concurrent Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia following scurvy, thus supporting the hypothesis that these 3 nail conditions lie on a continuum.
Case Report
A 41-year-old woman with a history of thyroiditis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, endometriosis, osteoarthritis, gastric ulcer, pancreatitis, fatty liver, and polycystic ovarian syndrome presented with lines on the toenails and no growth of the right second toenail of several months’ duration. She denied any pain or prior trauma to the nails, participation in sports activities, or wearing tight or high-heeled shoes. She had presented 6 months prior for evaluation of perifollicular erythema on the posterior thighs, legs, and abdomen, as well as gingival bleeding.11 At that time, one of the authors (S.R.L.) found that she was vitamin C deficient, and a diagnosis of scurvy was made. The rash and gingival bleeding resolved with vitamin C supplementation.11
At the current presentation, physical examination revealed transverse grooves involving several fingernails but most evident on the left thumbnail (Figure, A). The grooves did not span the entire breadth of the nail, which was consistent with Beau lines. Several toenails had parallel transverse grooves spanning the entire width of the nail plate such that the proximal nail plate was discontinuous with the distal nail plate, which was consistent with onychomadesis (Figure, B). The right second toenail was yellow and thickened with layered nail plates, indicative of retronychia (Figure, B). Histopathology of a nail plate clipping from the right second toenail was negative for fungal hyphae, and a radiograph was negative for bony changes or exostosis.

Comment
The nail matrix is responsible for nail plate production, and the newly formed nail plate then moves outward over the nail bed. It is hypothesized that the pathophysiologic basis for Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia lies on a continuum such that all 3 conditions are caused by an insult to the nail matrix that results in slowing and/or halting of nail plate growth. Beau lines result from slowing or disruption in cell growth from the nail matrix, whereas onychomadesis is associated with a complete halt in nail plate production.1,3 In retronychia, the new nail growing from the matrix pushes the old one upward, interrupting the longitudinal growth of the nail and leading to nail plate stacking.10
Our patient presented with concurrent Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia. Although Beau lines and onychomadesis have been reported together in some instances,12-14 retronychia is not commonly reported with either of these conditions. The exact incidence of each condition has not been studied, but Beau lines are relatively common, onychomadesis is less common, and retronychia is seen infrequently; therefore, the concurrent presentation of these 3 conditions in the same patient is exceedingly rare. Thus, it was most likely that one etiology accounted for all 3 nail findings.
Because the patient had been diagnosed with scurvy 6 months prior to presentation, we hypothesized that the associated vitamin C deficiency caused a systemic insult to the nail matrix, which resulted in cessation of nail growth. The mechanism of nail matrix arrest in the setting of systemic disease is thought to be due to inhibition of cellular proliferation or a change in the quality of the newly manufactured nail plate, which becomes thinner and more dystrophic.15 Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) deficiency causes scurvy, which is characterized by cutaneous signs such as perifollicular hemorrhage and purpura, corkscrew hairs, bruising, gingivitis, arthralgia, and impaired wound healing.16 These clinical manifestations are due to impaired collagen synthesis and disordered connective tissue. Ascorbic acid also is involved in fatty acid transport, neurotransmitter synthesis, prostaglandin metabolism, and nitric oxide synthesis.17 Ascorbic acid has not been studied for its role in nail plate synthesis18; however, given the role that ascorbic acid plays in a myriad of biologic processes, the deficiency associated with scurvy likely had a considerable systemic effect in our patient that halted nail plate synthesis and resulted in the concurrent presentation of Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia.
- Braswell MA, Daniel CR III, Brodell RT. Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia: a unifying hypothesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:849-855.
- Lipner SR. Onychomadesis following a fish pedicure. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1091-1092.
- Bettoli V, Zauli S, Toni G, et al. Onychomadesis following hand, foot, and mouth disease: a case report from Italy and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:728-730.
- Lawry M, Daniel CR III. Nails in systemic disease. In: Scher RK, Daniel CR III, eds. Nails: Diagnosis, Therapy, Surgery. 3rd ed. Oxford, England: Elsevier Saunders; 2005:147-176.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Evaluation of nail lines: color and shape hold clues. Cleve Clin J Med. 2016;83:385.
- Rich P. Nail signs and symptoms. In: Scher RK, Daniel CR III, eds. Nails: Diagnosis, Therapy, Surgery. 3rd ed. Oxford, England: Elsevier Saunders; 2005:1-6.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Nail growth evaluation and factors affecting nail growth. In: Humbert P, Fanian F, Maibach H, et al, eds. Agache’s Measuring the Skin. Cham, Switzerland: Springer; 2017:1-15.
- de Berker DA, Richert B, Duhard E, et al. Retronychia: proximal ingrowing of the nail plate. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:978-983.
- Wortsman X, Wortsman J, Guerrero R, et al. Anatomical changes in retronychia and onychomadesis detected using ultrasound. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1615-1620.
- Piraccini BM, Richert B, de Berker DA, et al. Retronychia in children, adolescents, and young adults: a case series. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:388-390.
- Lipner S. A classic case of scurvy. Lancet. 2018;392:431.
- Jacobsen L, Zimmerman S, Lohr J. Nail findings in hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015;34:449-450.
- Damevska K, Gocev G, Pollozhani N, et al. Onychomadesis following cutaneous vasculitis. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2017;25:77-79.
- Clementz GC, Mancini AJ. Nail matrix arrest following hand‐foot‐mouth disease: a report of five children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2000;17:7-11.
- Weismann K. J.H.S Beau and his descriptions of transverse depressions on nails. Br J Dermatol. 1977;97:571-572.
- Abdullah M, Jamil RT, Attia FN. Vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499877/. Updated October 21, 2019. Accessed February 24, 2020.
- Pazirandeh S, Burns DL. Overview of water-soluble vitamins. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-water-soluble-vitamins. Updated January 29, 2020. Accessed February 24, 2020.
- Scheinfeld N, Dahdah MJ, Scher RK. Vitamins and minerals: their role in nail health and disease. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:782-787.
- Braswell MA, Daniel CR III, Brodell RT. Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia: a unifying hypothesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:849-855.
- Lipner SR. Onychomadesis following a fish pedicure. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1091-1092.
- Bettoli V, Zauli S, Toni G, et al. Onychomadesis following hand, foot, and mouth disease: a case report from Italy and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:728-730.
- Lawry M, Daniel CR III. Nails in systemic disease. In: Scher RK, Daniel CR III, eds. Nails: Diagnosis, Therapy, Surgery. 3rd ed. Oxford, England: Elsevier Saunders; 2005:147-176.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Evaluation of nail lines: color and shape hold clues. Cleve Clin J Med. 2016;83:385.
- Rich P. Nail signs and symptoms. In: Scher RK, Daniel CR III, eds. Nails: Diagnosis, Therapy, Surgery. 3rd ed. Oxford, England: Elsevier Saunders; 2005:1-6.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Nail growth evaluation and factors affecting nail growth. In: Humbert P, Fanian F, Maibach H, et al, eds. Agache’s Measuring the Skin. Cham, Switzerland: Springer; 2017:1-15.
- de Berker DA, Richert B, Duhard E, et al. Retronychia: proximal ingrowing of the nail plate. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:978-983.
- Wortsman X, Wortsman J, Guerrero R, et al. Anatomical changes in retronychia and onychomadesis detected using ultrasound. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:1615-1620.
- Piraccini BM, Richert B, de Berker DA, et al. Retronychia in children, adolescents, and young adults: a case series. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:388-390.
- Lipner S. A classic case of scurvy. Lancet. 2018;392:431.
- Jacobsen L, Zimmerman S, Lohr J. Nail findings in hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015;34:449-450.
- Damevska K, Gocev G, Pollozhani N, et al. Onychomadesis following cutaneous vasculitis. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2017;25:77-79.
- Clementz GC, Mancini AJ. Nail matrix arrest following hand‐foot‐mouth disease: a report of five children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2000;17:7-11.
- Weismann K. J.H.S Beau and his descriptions of transverse depressions on nails. Br J Dermatol. 1977;97:571-572.
- Abdullah M, Jamil RT, Attia FN. Vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499877/. Updated October 21, 2019. Accessed February 24, 2020.
- Pazirandeh S, Burns DL. Overview of water-soluble vitamins. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-water-soluble-vitamins. Updated January 29, 2020. Accessed February 24, 2020.
- Scheinfeld N, Dahdah MJ, Scher RK. Vitamins and minerals: their role in nail health and disease. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:782-787.
Practice Points
- Beau lines, onychomadesis, and retronychia are nail conditions with distinct clinical findings.
- Beau lines and onychomadesis may be seen concurrently following trauma, inflammatory diseases, systemic illnesses, hereditary conditions, and infections.
- Retronychia shares a common pathophysiology with Beau lines and onychomadesis, and all reflect slowing or cessation of nail plate production.
Transillumination for Improved Diagnosis of Digital Myxoid Cysts
Practice Gap
Myxoid cysts are among the most common space-occupying lesions involving the nail unit. Their etiology has not been fully elucidated, but these cysts likely form due to leakage of synovial fluid following trauma or chronic wear and tear. They are highly associated with osteoarthritis and typically are found in close proximity to the distal interphalangeal joints.1 Myxoid cysts often extend into the eponychium, where mechanical stress on the nail matrix may lead to nail dystrophy, most commonly resulting in a longitudinal groove in the nail plate (Figure, A). The presence of multiple myxoid cysts is not uncommon. Differentiation of this lesion from other nodules of the digits, including epidermoid cysts, acquired digital fibrokeratomas, and giant cell tendon sheath tumors often is challenging without a biopsy.

Technique
The normal nail unit transmits light to some extent, and masses may be identified by how easily they transmit light relative to the adjacent skin. Solid tumors of the nail unit, such as acquired digital fibrokeratomas and giant cell tendon sheath tumors, will not transmit light, while myxoid cysts transmit light easily. A dermatoscope can be used to project light from the dorsal digit through the nail unit. The area occupied by the myxoid cyst will appear bright compared to the surrounding skin (Figure, B). Drainage of the lesion using an 18-gauge needle yielded a clear jellylike fluid that was consistent with a myxoid cyst. This technique aids in localizing and characterizing the myxoid cyst for treatment or drainage. Physician assessment of transillumination has been shown to demonstrate clinical accuracy and high intraobserver reliability in differentiating between cystic and solid tumors.2
Practice Implications
Transillumination is a valuable technique that may aid dermatologists in both the diagnosis and subsequent treatment of myxoid cysts. Location is important to consider when choosing a treatment option. Although lower recurrence rates are achieved with nail surgery, permanent nail dystrophy is likely when cysts are in close proximity to the nail matrix.3 When multiple cysts are present, only the largest may be apparent. Transillumination can guide the physician in achieving more accurate and thorough drainage of the cyst contents, negating the need for more costly imaging modalities. Dermatologists may utilize transillumination as a rapid and economical diagnostic method for space-occupying lesions involving the nail unit.
- Dermatol Surg. 2008;34:364-369.
- Erne HC, Gardner TR, Strauch RJ. Transillumination of hand tumors: a cadaver study to evaluate accuracy and intraobserver reliability. Hand (N Y). 2011;6:390-393.
- Fritz GR, Stern PJ, Dickey M. Complications following mucous cyst excision. J Hand Surg Br. 1997;22:222-225.
Practice Gap
Myxoid cysts are among the most common space-occupying lesions involving the nail unit. Their etiology has not been fully elucidated, but these cysts likely form due to leakage of synovial fluid following trauma or chronic wear and tear. They are highly associated with osteoarthritis and typically are found in close proximity to the distal interphalangeal joints.1 Myxoid cysts often extend into the eponychium, where mechanical stress on the nail matrix may lead to nail dystrophy, most commonly resulting in a longitudinal groove in the nail plate (Figure, A). The presence of multiple myxoid cysts is not uncommon. Differentiation of this lesion from other nodules of the digits, including epidermoid cysts, acquired digital fibrokeratomas, and giant cell tendon sheath tumors often is challenging without a biopsy.

Technique
The normal nail unit transmits light to some extent, and masses may be identified by how easily they transmit light relative to the adjacent skin. Solid tumors of the nail unit, such as acquired digital fibrokeratomas and giant cell tendon sheath tumors, will not transmit light, while myxoid cysts transmit light easily. A dermatoscope can be used to project light from the dorsal digit through the nail unit. The area occupied by the myxoid cyst will appear bright compared to the surrounding skin (Figure, B). Drainage of the lesion using an 18-gauge needle yielded a clear jellylike fluid that was consistent with a myxoid cyst. This technique aids in localizing and characterizing the myxoid cyst for treatment or drainage. Physician assessment of transillumination has been shown to demonstrate clinical accuracy and high intraobserver reliability in differentiating between cystic and solid tumors.2
Practice Implications
Transillumination is a valuable technique that may aid dermatologists in both the diagnosis and subsequent treatment of myxoid cysts. Location is important to consider when choosing a treatment option. Although lower recurrence rates are achieved with nail surgery, permanent nail dystrophy is likely when cysts are in close proximity to the nail matrix.3 When multiple cysts are present, only the largest may be apparent. Transillumination can guide the physician in achieving more accurate and thorough drainage of the cyst contents, negating the need for more costly imaging modalities. Dermatologists may utilize transillumination as a rapid and economical diagnostic method for space-occupying lesions involving the nail unit.
Practice Gap
Myxoid cysts are among the most common space-occupying lesions involving the nail unit. Their etiology has not been fully elucidated, but these cysts likely form due to leakage of synovial fluid following trauma or chronic wear and tear. They are highly associated with osteoarthritis and typically are found in close proximity to the distal interphalangeal joints.1 Myxoid cysts often extend into the eponychium, where mechanical stress on the nail matrix may lead to nail dystrophy, most commonly resulting in a longitudinal groove in the nail plate (Figure, A). The presence of multiple myxoid cysts is not uncommon. Differentiation of this lesion from other nodules of the digits, including epidermoid cysts, acquired digital fibrokeratomas, and giant cell tendon sheath tumors often is challenging without a biopsy.

Technique
The normal nail unit transmits light to some extent, and masses may be identified by how easily they transmit light relative to the adjacent skin. Solid tumors of the nail unit, such as acquired digital fibrokeratomas and giant cell tendon sheath tumors, will not transmit light, while myxoid cysts transmit light easily. A dermatoscope can be used to project light from the dorsal digit through the nail unit. The area occupied by the myxoid cyst will appear bright compared to the surrounding skin (Figure, B). Drainage of the lesion using an 18-gauge needle yielded a clear jellylike fluid that was consistent with a myxoid cyst. This technique aids in localizing and characterizing the myxoid cyst for treatment or drainage. Physician assessment of transillumination has been shown to demonstrate clinical accuracy and high intraobserver reliability in differentiating between cystic and solid tumors.2
Practice Implications
Transillumination is a valuable technique that may aid dermatologists in both the diagnosis and subsequent treatment of myxoid cysts. Location is important to consider when choosing a treatment option. Although lower recurrence rates are achieved with nail surgery, permanent nail dystrophy is likely when cysts are in close proximity to the nail matrix.3 When multiple cysts are present, only the largest may be apparent. Transillumination can guide the physician in achieving more accurate and thorough drainage of the cyst contents, negating the need for more costly imaging modalities. Dermatologists may utilize transillumination as a rapid and economical diagnostic method for space-occupying lesions involving the nail unit.
- Dermatol Surg. 2008;34:364-369.
- Erne HC, Gardner TR, Strauch RJ. Transillumination of hand tumors: a cadaver study to evaluate accuracy and intraobserver reliability. Hand (N Y). 2011;6:390-393.
- Fritz GR, Stern PJ, Dickey M. Complications following mucous cyst excision. J Hand Surg Br. 1997;22:222-225.
- Dermatol Surg. 2008;34:364-369.
- Erne HC, Gardner TR, Strauch RJ. Transillumination of hand tumors: a cadaver study to evaluate accuracy and intraobserver reliability. Hand (N Y). 2011;6:390-393.
- Fritz GR, Stern PJ, Dickey M. Complications following mucous cyst excision. J Hand Surg Br. 1997;22:222-225.
Comment on “Intraoperative Electrosurgical Smoke During Outpatient Surgery: A Survey of Dermatologic Surgeon and Staff Preferences”
To the Editor:
We read with great interest the recent Cutis article by Golda et al,1 “Intraoperative Electrosurgical Smoke During Outpatient Surgery: A Survey of Dermatologic Surgeon and Staff Preferences.” We applaud the growing interest in the topic of dermatologist safety, as there are currently no established guidelines for precautions while performing surgical procedures. In 2018 we conducted a comprehensive review2 to characterize the specific risks, hazard reduction strategies available, and current use of surgical smoke safety techniques during surgery among dermatologists, and ultimately recommend guidance based on the current available evidence. To conduct this review, we collected data from 45 manuscripts in the dermatology, surgery, infectious disease, obstetrics, and cancer biology literature. Herein, we summarize key findings.2
Dermatologic surgeons, residents, staff, and patients are exposed to many infectious, inhalational, chemical, and mutagenic hazards when performing procedures that liberate smoke and plume. These risks are commonplace; however, they are particularly notable during ablative laser and laser hair removal procedures, which produce a heavy plume (averaging >100,000 particles/cm3). Brief periods of heavy plume exposure also are commonplace during electrosurgery.
Infectious particles in surgical plume have been extensively studied, and viral transmission has been demonstrated in animal studies. Human papillomavirus transmission appears to be the most prevalent risk. Surgical smoke has been shown to cause acute and chronic inhalational injury in rat and sheep studies.3-6
Additionally, chemicals with carcinogenic potential are present in surgical smoke and have been described.7,8 Chemicals in the greatest quantity include hydrocarbons, nitriles, fatty acids, and phenols. Although there have been no human studies on smoke carcinogenesis to date, surgical smoke has been shown to have carcinogenic properties in vitro.
Given these risks—both evidence based and theoretical—we believe that diligent hazard reduction strategies should be employed whenever possible. Surgical masks and high-efficiency particulate air respirators, such as N95 respirator masks, have been well studied and do provide smoke protection. High-efficiency particulate air masks can be worn when possible, especially during procedures that produce heavy plume, though surgical masks are capable of filtering most of the noxious chemicals in surgical smoke. It should be noted that proper fit with minimal air leak is the most important aspect of overall performance.
Smoke evacuators provide another level of protection. The physician should consider the evacuator’s filtration efficiency, capture velocity, and suction strength when evaluating overall performance. Furthermore, the smoke collection tip should be within 2 in of the surgical field to maximize efficacy. Maintenance for smoke evacuation systems should include regular (as defined by manufacturer instructions) flushing of the smoke evacuator lines.
Despite the risks of surgical smoke and the available options of minimizing these risks, the hazards of surgical smoke and the importance of protection are likely underemphasized. Many dermatologic surgeons do not use surgical masks or smoke evacuators in routine practice, according to several survey studies.9-11
It is important for the dermatologic community to consider effective ways of spreading awareness. We propose that surgical smoke safety be taught early in residency training. Additionally, smoke safety can be implemented into certification examinations. Access to masks and smoke evacuation devices are an important part of dermatology training. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education funds should be appropriated to provide for such resources.
Finally, and perhaps most importantly, continued awareness should be established in the dermatology community via standardized guidelines and periodic updates in the dermatology literature and lectures at local and national conferences. Not until these strategies are implemented will surgical smoke protection be viewed as a necessary and important component of routine practice when performing dermatologic surgical procedures.
- Golda N, Merrill B, Neill B. Intraoperative electrosurgical smoke during outpatient surgery: a survey of dermatologic surgeon and staff preferences. Cutis. 2019;104:120-124.
- Georgesen C, Lipner SR. Surgical smoke: risk assessment and mitigation strategies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:746-755.
- Wenig BL, Stenson KM, Wenig BM, et al. Effects of plume produced by the Nd:YAG laser and electrocautery on the respiratory system. Lasers Surg Med. 1993;13:242-245.
- Baggish MS, Elbakry M. The effects of laser smoke on the lungs of rats. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987;156:1260-1265.
- Baggish MS, Baltoyannis P, Sze E. Protection of the rat lung from the harmful effects of laser smoke. Lasers Surg Med. 1988;8:248-253.
- Freitag L, Chapman GA, Sielczak M, et al. Laser smoke effect on the bronchial system. Lasers Surg Med. 1987;7:283-288.
- Barrett WL, Garber SM. Surgical smoke: a review of the literature. Is this just a lot of hot air? Surg Endosc. 2003;17:979-987.
- Hensman C, Baty D, Willis RG, et al. Chemical composition of smoke produced by high-frequency electrosurgery in a closed gaseous environment. Surg Endosc. 1998;12:1017-1019.
- Edwards BE, Reiman RE. Results of a survey on current surgical smoke control practices. AORN J. 2008;87:739-749.
- Oganesyan G, Eimpunth S, Kim SS, et al. Surgical smoke in dermatologic surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:1373-1377.
- Chapman LW, Korta DZ, Lee PK, et al. Awareness of surgical smoke risks and assessment of safety practices during electrosurgery among US dermatology residents. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:467-468.
To the Editor:
We read with great interest the recent Cutis article by Golda et al,1 “Intraoperative Electrosurgical Smoke During Outpatient Surgery: A Survey of Dermatologic Surgeon and Staff Preferences.” We applaud the growing interest in the topic of dermatologist safety, as there are currently no established guidelines for precautions while performing surgical procedures. In 2018 we conducted a comprehensive review2 to characterize the specific risks, hazard reduction strategies available, and current use of surgical smoke safety techniques during surgery among dermatologists, and ultimately recommend guidance based on the current available evidence. To conduct this review, we collected data from 45 manuscripts in the dermatology, surgery, infectious disease, obstetrics, and cancer biology literature. Herein, we summarize key findings.2
Dermatologic surgeons, residents, staff, and patients are exposed to many infectious, inhalational, chemical, and mutagenic hazards when performing procedures that liberate smoke and plume. These risks are commonplace; however, they are particularly notable during ablative laser and laser hair removal procedures, which produce a heavy plume (averaging >100,000 particles/cm3). Brief periods of heavy plume exposure also are commonplace during electrosurgery.
Infectious particles in surgical plume have been extensively studied, and viral transmission has been demonstrated in animal studies. Human papillomavirus transmission appears to be the most prevalent risk. Surgical smoke has been shown to cause acute and chronic inhalational injury in rat and sheep studies.3-6
Additionally, chemicals with carcinogenic potential are present in surgical smoke and have been described.7,8 Chemicals in the greatest quantity include hydrocarbons, nitriles, fatty acids, and phenols. Although there have been no human studies on smoke carcinogenesis to date, surgical smoke has been shown to have carcinogenic properties in vitro.
Given these risks—both evidence based and theoretical—we believe that diligent hazard reduction strategies should be employed whenever possible. Surgical masks and high-efficiency particulate air respirators, such as N95 respirator masks, have been well studied and do provide smoke protection. High-efficiency particulate air masks can be worn when possible, especially during procedures that produce heavy plume, though surgical masks are capable of filtering most of the noxious chemicals in surgical smoke. It should be noted that proper fit with minimal air leak is the most important aspect of overall performance.
Smoke evacuators provide another level of protection. The physician should consider the evacuator’s filtration efficiency, capture velocity, and suction strength when evaluating overall performance. Furthermore, the smoke collection tip should be within 2 in of the surgical field to maximize efficacy. Maintenance for smoke evacuation systems should include regular (as defined by manufacturer instructions) flushing of the smoke evacuator lines.
Despite the risks of surgical smoke and the available options of minimizing these risks, the hazards of surgical smoke and the importance of protection are likely underemphasized. Many dermatologic surgeons do not use surgical masks or smoke evacuators in routine practice, according to several survey studies.9-11
It is important for the dermatologic community to consider effective ways of spreading awareness. We propose that surgical smoke safety be taught early in residency training. Additionally, smoke safety can be implemented into certification examinations. Access to masks and smoke evacuation devices are an important part of dermatology training. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education funds should be appropriated to provide for such resources.
Finally, and perhaps most importantly, continued awareness should be established in the dermatology community via standardized guidelines and periodic updates in the dermatology literature and lectures at local and national conferences. Not until these strategies are implemented will surgical smoke protection be viewed as a necessary and important component of routine practice when performing dermatologic surgical procedures.
To the Editor:
We read with great interest the recent Cutis article by Golda et al,1 “Intraoperative Electrosurgical Smoke During Outpatient Surgery: A Survey of Dermatologic Surgeon and Staff Preferences.” We applaud the growing interest in the topic of dermatologist safety, as there are currently no established guidelines for precautions while performing surgical procedures. In 2018 we conducted a comprehensive review2 to characterize the specific risks, hazard reduction strategies available, and current use of surgical smoke safety techniques during surgery among dermatologists, and ultimately recommend guidance based on the current available evidence. To conduct this review, we collected data from 45 manuscripts in the dermatology, surgery, infectious disease, obstetrics, and cancer biology literature. Herein, we summarize key findings.2
Dermatologic surgeons, residents, staff, and patients are exposed to many infectious, inhalational, chemical, and mutagenic hazards when performing procedures that liberate smoke and plume. These risks are commonplace; however, they are particularly notable during ablative laser and laser hair removal procedures, which produce a heavy plume (averaging >100,000 particles/cm3). Brief periods of heavy plume exposure also are commonplace during electrosurgery.
Infectious particles in surgical plume have been extensively studied, and viral transmission has been demonstrated in animal studies. Human papillomavirus transmission appears to be the most prevalent risk. Surgical smoke has been shown to cause acute and chronic inhalational injury in rat and sheep studies.3-6
Additionally, chemicals with carcinogenic potential are present in surgical smoke and have been described.7,8 Chemicals in the greatest quantity include hydrocarbons, nitriles, fatty acids, and phenols. Although there have been no human studies on smoke carcinogenesis to date, surgical smoke has been shown to have carcinogenic properties in vitro.
Given these risks—both evidence based and theoretical—we believe that diligent hazard reduction strategies should be employed whenever possible. Surgical masks and high-efficiency particulate air respirators, such as N95 respirator masks, have been well studied and do provide smoke protection. High-efficiency particulate air masks can be worn when possible, especially during procedures that produce heavy plume, though surgical masks are capable of filtering most of the noxious chemicals in surgical smoke. It should be noted that proper fit with minimal air leak is the most important aspect of overall performance.
Smoke evacuators provide another level of protection. The physician should consider the evacuator’s filtration efficiency, capture velocity, and suction strength when evaluating overall performance. Furthermore, the smoke collection tip should be within 2 in of the surgical field to maximize efficacy. Maintenance for smoke evacuation systems should include regular (as defined by manufacturer instructions) flushing of the smoke evacuator lines.
Despite the risks of surgical smoke and the available options of minimizing these risks, the hazards of surgical smoke and the importance of protection are likely underemphasized. Many dermatologic surgeons do not use surgical masks or smoke evacuators in routine practice, according to several survey studies.9-11
It is important for the dermatologic community to consider effective ways of spreading awareness. We propose that surgical smoke safety be taught early in residency training. Additionally, smoke safety can be implemented into certification examinations. Access to masks and smoke evacuation devices are an important part of dermatology training. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education funds should be appropriated to provide for such resources.
Finally, and perhaps most importantly, continued awareness should be established in the dermatology community via standardized guidelines and periodic updates in the dermatology literature and lectures at local and national conferences. Not until these strategies are implemented will surgical smoke protection be viewed as a necessary and important component of routine practice when performing dermatologic surgical procedures.
- Golda N, Merrill B, Neill B. Intraoperative electrosurgical smoke during outpatient surgery: a survey of dermatologic surgeon and staff preferences. Cutis. 2019;104:120-124.
- Georgesen C, Lipner SR. Surgical smoke: risk assessment and mitigation strategies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:746-755.
- Wenig BL, Stenson KM, Wenig BM, et al. Effects of plume produced by the Nd:YAG laser and electrocautery on the respiratory system. Lasers Surg Med. 1993;13:242-245.
- Baggish MS, Elbakry M. The effects of laser smoke on the lungs of rats. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987;156:1260-1265.
- Baggish MS, Baltoyannis P, Sze E. Protection of the rat lung from the harmful effects of laser smoke. Lasers Surg Med. 1988;8:248-253.
- Freitag L, Chapman GA, Sielczak M, et al. Laser smoke effect on the bronchial system. Lasers Surg Med. 1987;7:283-288.
- Barrett WL, Garber SM. Surgical smoke: a review of the literature. Is this just a lot of hot air? Surg Endosc. 2003;17:979-987.
- Hensman C, Baty D, Willis RG, et al. Chemical composition of smoke produced by high-frequency electrosurgery in a closed gaseous environment. Surg Endosc. 1998;12:1017-1019.
- Edwards BE, Reiman RE. Results of a survey on current surgical smoke control practices. AORN J. 2008;87:739-749.
- Oganesyan G, Eimpunth S, Kim SS, et al. Surgical smoke in dermatologic surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:1373-1377.
- Chapman LW, Korta DZ, Lee PK, et al. Awareness of surgical smoke risks and assessment of safety practices during electrosurgery among US dermatology residents. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:467-468.
- Golda N, Merrill B, Neill B. Intraoperative electrosurgical smoke during outpatient surgery: a survey of dermatologic surgeon and staff preferences. Cutis. 2019;104:120-124.
- Georgesen C, Lipner SR. Surgical smoke: risk assessment and mitigation strategies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:746-755.
- Wenig BL, Stenson KM, Wenig BM, et al. Effects of plume produced by the Nd:YAG laser and electrocautery on the respiratory system. Lasers Surg Med. 1993;13:242-245.
- Baggish MS, Elbakry M. The effects of laser smoke on the lungs of rats. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987;156:1260-1265.
- Baggish MS, Baltoyannis P, Sze E. Protection of the rat lung from the harmful effects of laser smoke. Lasers Surg Med. 1988;8:248-253.
- Freitag L, Chapman GA, Sielczak M, et al. Laser smoke effect on the bronchial system. Lasers Surg Med. 1987;7:283-288.
- Barrett WL, Garber SM. Surgical smoke: a review of the literature. Is this just a lot of hot air? Surg Endosc. 2003;17:979-987.
- Hensman C, Baty D, Willis RG, et al. Chemical composition of smoke produced by high-frequency electrosurgery in a closed gaseous environment. Surg Endosc. 1998;12:1017-1019.
- Edwards BE, Reiman RE. Results of a survey on current surgical smoke control practices. AORN J. 2008;87:739-749.
- Oganesyan G, Eimpunth S, Kim SS, et al. Surgical smoke in dermatologic surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:1373-1377.
- Chapman LW, Korta DZ, Lee PK, et al. Awareness of surgical smoke risks and assessment of safety practices during electrosurgery among US dermatology residents. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:467-468.
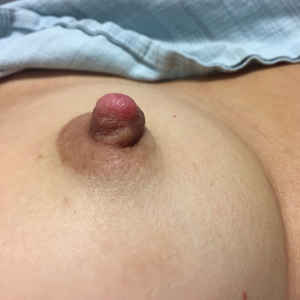
Enlarging Nodule on the Nipple
The Diagnosis: Nipple Adenoma (Florid Papillomatosis of the Nipple)
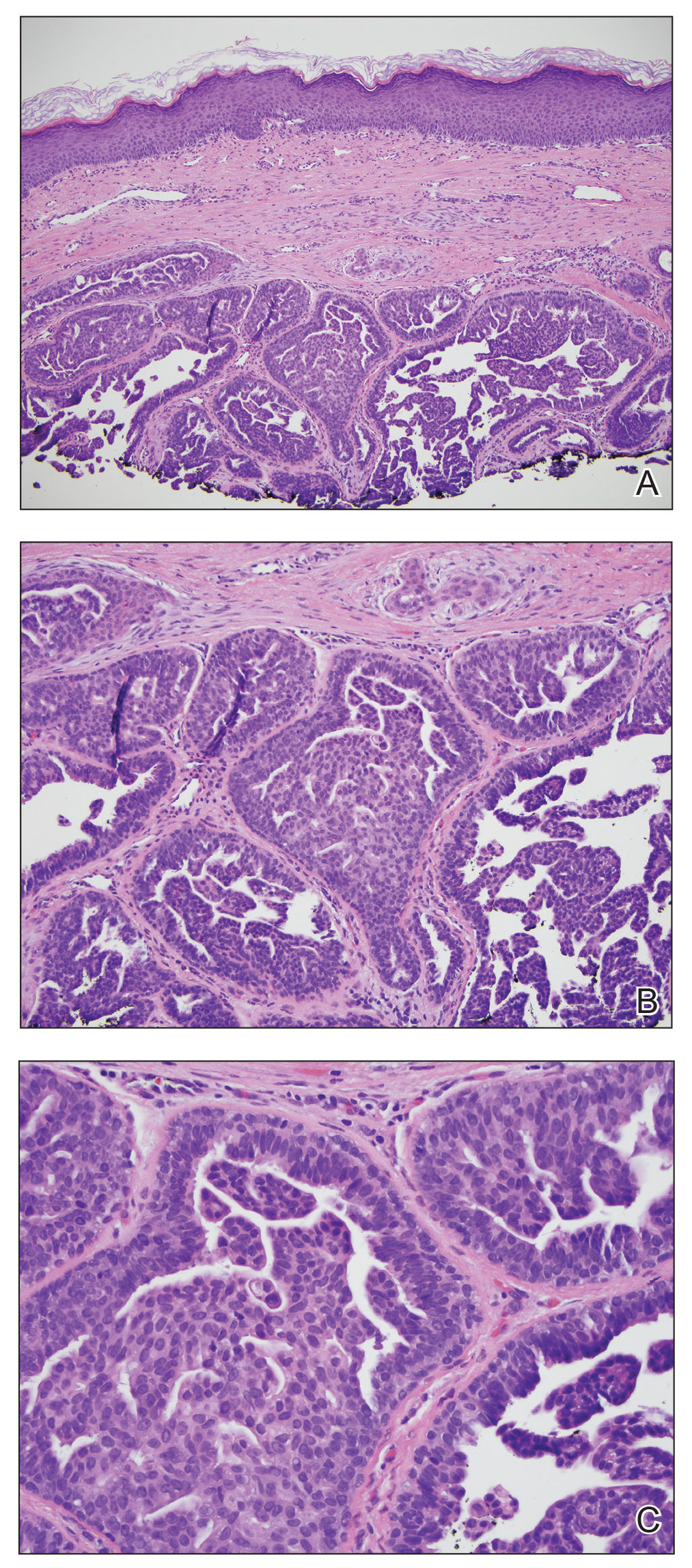
Biopsy of the nodule showed florid papillary hyperplasia of the ductal epithelium within the dermis that was sharply demarcated from the background stroma (Figure, A and B). Neither cytological nor architectural atypia were evident. There was no notable necrosis (Figure C). There was a background of fibrosis whereby the glandular ductal structures assumed a somewhat irregular growth pattern within the dermis with attendant hemorrhage. The patient underwent complete excision of the lesion. No evidence of carcinoma was seen on the final pathology, and the final margins were negative.
First described in 1923 and fully characterized in 1955, nipple adenoma (also known as florid papillomatosis of the nipple) is a benign proliferative neoplasm that originates in the lactiferous ducts of the nipple.1,2 It most commonly affects women aged 40 to 50 years (range, 0-89 years); less than 5% of cases are reported in men.3,4 It predominantly is unilateral, with only rare cases of bilateral papillomatosis reported. Patients often present with serous or serosanguineous discharge and an itching or burning sensation. Symptoms may worsen with the menstrual cycle.4 On physical examination, it presents as an ill-defined red nodule on the nipple with crusting, erosion, or erythema of the nipple surface. Although imaging generally is not used to confirm the diagnosis, mammography should be performed prior to biopsy to rule out underlying breast pathology. Dermoscopy may show linear cherry red structures or red serpiginous and annular structures.5,6 The differential diagnosis of nipple adenoma includes Paget disease of the breast, adenomyoepithelioma, subareolar subsclerosing duct hyperplasia, syringomatous adenoma, adenosis tumor, low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma, low-grade ductal carcinoma in situ, tubular carcinoma, and sweat gland tumors.3
Microscopic features of nipple adenoma have been categorized into 4 subtypes: sclerosing papillomatosis, papillomatosis, adenosis, and a mixed pattern.3,7 The tumors may have keratin cysts and focal necrosis but no atypia, and the myoepithelial cell layer is retained. Nipple adenomas show a glandular proliferation in the dermis that is relatively well circumscribed with glands that vary in appearance between a simple adenosislike pattern of growth to a papillary hyperplasia and/or usual ductal hyperplasia growth pattern. A pseudoinfiltrative pattern can occur when the glandular epithelium is entrapped within stromal fibrosis; however, the myoepithelial layer is retained. Occasionally, the glandular epithelium can grow in continuity with the surface squamous epithelium of the nipple, clinically simulating Paget disease of the breast.8 Immunohistochemical stains, specifically p63, p40, calponin 1, h-caldesmon, cytokeratin 5/6, CD10, and α; smooth muscle actin, highlight the myoepithelial cells, while cytokeratin 7 identifies the ductal epithelium, supporting the diagnosis.6 In addition to biopsy and microscopic tissue examination, touch preparation cytology, curettage cytology, and fine needle aspiration techniques have been used to perform cytologic examination of the lesions, aiding in identification of the benign or malignant nature of the neoplasm.6 Nipple adenoma also is referred to as florid papillomatosis of the nipple, papillary adenoma, erosive adenomatosis, and subareolar duct papillomatosis.7
Although nipple adenoma is a benign tumor, up to 16.5% of affected patients had an ipsilateral or contralateral mammary carcinoma.9 The majority arose coincidentally but separately in the same breast, and carcinoma arose directly from the nipple adenoma in 8 cases; 3 cases were carcinomas that arose in men.10 A definitive association or causal relationship between nipple adenoma and subsequent development of breast cancer has not been identified, and the incidence of nipple adenoma in patients with a positive family history of breast cancer has not been examined. Therefore, although various treatments including cryosurgery, nipple splitting enucleation, and Mohs micrographic surgery have been proposed, complete excision remains the gold standard of therapy. Regular breast examinations and digital mammography are necessary to screen for local recurrences.
- Miller E, Lewis D. The significance of serohemorrhagic or hemorrhagic discharge from the nipple. JAMA. 1923;81:1651-1657.
- Jones DB. Florid papillomatosis of the nipple ducts. Cancer. 1955;8:315-319.
- Rosen PP. Rosen's Breast Pathology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009:120-128.
- Brownstein MH, Phelps RG, Maqnin PH. Papillary adenoma of the nipple: analysis of fifteen new cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;12:707-715.
- Takashima S, Fujita Y, Miyauchi T, et al. Dermoscopic observation in adenoma of the nipple. J Dermatol. 2015;42:341-342.
- Spohn G, Trotter S, Tozbikian G, et al. Nipple adenoma in a female patient presenting with persistent erythema of the right nipple skin: case report, review of the literature, clinical implications, and relevancy to health care providers who evaluate and treat patients with dermatologic conditions of the breast skin. BMC Dermatol. 2016;16:4.
- Shin SJ. Nipple adenoma (florid papillomatosis of the nipple). In: Dabbs DJ, ed. Breast Pathology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:286-292.
- Schnitt SJ, Collins LC. Biopsy Interpretation of the Breast. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2013.
- Salemis NS. Florid papillomatosis of the nipple: a rare presentation and review of the literature. Breast Dis. 2015;35:153-156.
- Di Bonito M, Cantile M, Collina F, et al. Adenoma of the nipple: a clinicopathological report of 13 cases. Oncol Lett. 2014;7:1839-1842.
The Diagnosis: Nipple Adenoma (Florid Papillomatosis of the Nipple)
Biopsy of the nodule showed florid papillary hyperplasia of the ductal epithelium within the dermis that was sharply demarcated from the background stroma (Figure, A and B). Neither cytological nor architectural atypia were evident. There was no notable necrosis (Figure C). There was a background of fibrosis whereby the glandular ductal structures assumed a somewhat irregular growth pattern within the dermis with attendant hemorrhage. The patient underwent complete excision of the lesion. No evidence of carcinoma was seen on the final pathology, and the final margins were negative.

First described in 1923 and fully characterized in 1955, nipple adenoma (also known as florid papillomatosis of the nipple) is a benign proliferative neoplasm that originates in the lactiferous ducts of the nipple.1,2 It most commonly affects women aged 40 to 50 years (range, 0-89 years); less than 5% of cases are reported in men.3,4 It predominantly is unilateral, with only rare cases of bilateral papillomatosis reported. Patients often present with serous or serosanguineous discharge and an itching or burning sensation. Symptoms may worsen with the menstrual cycle.4 On physical examination, it presents as an ill-defined red nodule on the nipple with crusting, erosion, or erythema of the nipple surface. Although imaging generally is not used to confirm the diagnosis, mammography should be performed prior to biopsy to rule out underlying breast pathology. Dermoscopy may show linear cherry red structures or red serpiginous and annular structures.5,6 The differential diagnosis of nipple adenoma includes Paget disease of the breast, adenomyoepithelioma, subareolar subsclerosing duct hyperplasia, syringomatous adenoma, adenosis tumor, low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma, low-grade ductal carcinoma in situ, tubular carcinoma, and sweat gland tumors.3
Microscopic features of nipple adenoma have been categorized into 4 subtypes: sclerosing papillomatosis, papillomatosis, adenosis, and a mixed pattern.3,7 The tumors may have keratin cysts and focal necrosis but no atypia, and the myoepithelial cell layer is retained. Nipple adenomas show a glandular proliferation in the dermis that is relatively well circumscribed with glands that vary in appearance between a simple adenosislike pattern of growth to a papillary hyperplasia and/or usual ductal hyperplasia growth pattern. A pseudoinfiltrative pattern can occur when the glandular epithelium is entrapped within stromal fibrosis; however, the myoepithelial layer is retained. Occasionally, the glandular epithelium can grow in continuity with the surface squamous epithelium of the nipple, clinically simulating Paget disease of the breast.8 Immunohistochemical stains, specifically p63, p40, calponin 1, h-caldesmon, cytokeratin 5/6, CD10, and α; smooth muscle actin, highlight the myoepithelial cells, while cytokeratin 7 identifies the ductal epithelium, supporting the diagnosis.6 In addition to biopsy and microscopic tissue examination, touch preparation cytology, curettage cytology, and fine needle aspiration techniques have been used to perform cytologic examination of the lesions, aiding in identification of the benign or malignant nature of the neoplasm.6 Nipple adenoma also is referred to as florid papillomatosis of the nipple, papillary adenoma, erosive adenomatosis, and subareolar duct papillomatosis.7
Although nipple adenoma is a benign tumor, up to 16.5% of affected patients had an ipsilateral or contralateral mammary carcinoma.9 The majority arose coincidentally but separately in the same breast, and carcinoma arose directly from the nipple adenoma in 8 cases; 3 cases were carcinomas that arose in men.10 A definitive association or causal relationship between nipple adenoma and subsequent development of breast cancer has not been identified, and the incidence of nipple adenoma in patients with a positive family history of breast cancer has not been examined. Therefore, although various treatments including cryosurgery, nipple splitting enucleation, and Mohs micrographic surgery have been proposed, complete excision remains the gold standard of therapy. Regular breast examinations and digital mammography are necessary to screen for local recurrences.
The Diagnosis: Nipple Adenoma (Florid Papillomatosis of the Nipple)
Biopsy of the nodule showed florid papillary hyperplasia of the ductal epithelium within the dermis that was sharply demarcated from the background stroma (Figure, A and B). Neither cytological nor architectural atypia were evident. There was no notable necrosis (Figure C). There was a background of fibrosis whereby the glandular ductal structures assumed a somewhat irregular growth pattern within the dermis with attendant hemorrhage. The patient underwent complete excision of the lesion. No evidence of carcinoma was seen on the final pathology, and the final margins were negative.

First described in 1923 and fully characterized in 1955, nipple adenoma (also known as florid papillomatosis of the nipple) is a benign proliferative neoplasm that originates in the lactiferous ducts of the nipple.1,2 It most commonly affects women aged 40 to 50 years (range, 0-89 years); less than 5% of cases are reported in men.3,4 It predominantly is unilateral, with only rare cases of bilateral papillomatosis reported. Patients often present with serous or serosanguineous discharge and an itching or burning sensation. Symptoms may worsen with the menstrual cycle.4 On physical examination, it presents as an ill-defined red nodule on the nipple with crusting, erosion, or erythema of the nipple surface. Although imaging generally is not used to confirm the diagnosis, mammography should be performed prior to biopsy to rule out underlying breast pathology. Dermoscopy may show linear cherry red structures or red serpiginous and annular structures.5,6 The differential diagnosis of nipple adenoma includes Paget disease of the breast, adenomyoepithelioma, subareolar subsclerosing duct hyperplasia, syringomatous adenoma, adenosis tumor, low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma, low-grade ductal carcinoma in situ, tubular carcinoma, and sweat gland tumors.3
Microscopic features of nipple adenoma have been categorized into 4 subtypes: sclerosing papillomatosis, papillomatosis, adenosis, and a mixed pattern.3,7 The tumors may have keratin cysts and focal necrosis but no atypia, and the myoepithelial cell layer is retained. Nipple adenomas show a glandular proliferation in the dermis that is relatively well circumscribed with glands that vary in appearance between a simple adenosislike pattern of growth to a papillary hyperplasia and/or usual ductal hyperplasia growth pattern. A pseudoinfiltrative pattern can occur when the glandular epithelium is entrapped within stromal fibrosis; however, the myoepithelial layer is retained. Occasionally, the glandular epithelium can grow in continuity with the surface squamous epithelium of the nipple, clinically simulating Paget disease of the breast.8 Immunohistochemical stains, specifically p63, p40, calponin 1, h-caldesmon, cytokeratin 5/6, CD10, and α; smooth muscle actin, highlight the myoepithelial cells, while cytokeratin 7 identifies the ductal epithelium, supporting the diagnosis.6 In addition to biopsy and microscopic tissue examination, touch preparation cytology, curettage cytology, and fine needle aspiration techniques have been used to perform cytologic examination of the lesions, aiding in identification of the benign or malignant nature of the neoplasm.6 Nipple adenoma also is referred to as florid papillomatosis of the nipple, papillary adenoma, erosive adenomatosis, and subareolar duct papillomatosis.7
Although nipple adenoma is a benign tumor, up to 16.5% of affected patients had an ipsilateral or contralateral mammary carcinoma.9 The majority arose coincidentally but separately in the same breast, and carcinoma arose directly from the nipple adenoma in 8 cases; 3 cases were carcinomas that arose in men.10 A definitive association or causal relationship between nipple adenoma and subsequent development of breast cancer has not been identified, and the incidence of nipple adenoma in patients with a positive family history of breast cancer has not been examined. Therefore, although various treatments including cryosurgery, nipple splitting enucleation, and Mohs micrographic surgery have been proposed, complete excision remains the gold standard of therapy. Regular breast examinations and digital mammography are necessary to screen for local recurrences.
- Miller E, Lewis D. The significance of serohemorrhagic or hemorrhagic discharge from the nipple. JAMA. 1923;81:1651-1657.
- Jones DB. Florid papillomatosis of the nipple ducts. Cancer. 1955;8:315-319.
- Rosen PP. Rosen's Breast Pathology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009:120-128.
- Brownstein MH, Phelps RG, Maqnin PH. Papillary adenoma of the nipple: analysis of fifteen new cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;12:707-715.
- Takashima S, Fujita Y, Miyauchi T, et al. Dermoscopic observation in adenoma of the nipple. J Dermatol. 2015;42:341-342.
- Spohn G, Trotter S, Tozbikian G, et al. Nipple adenoma in a female patient presenting with persistent erythema of the right nipple skin: case report, review of the literature, clinical implications, and relevancy to health care providers who evaluate and treat patients with dermatologic conditions of the breast skin. BMC Dermatol. 2016;16:4.
- Shin SJ. Nipple adenoma (florid papillomatosis of the nipple). In: Dabbs DJ, ed. Breast Pathology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:286-292.
- Schnitt SJ, Collins LC. Biopsy Interpretation of the Breast. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2013.
- Salemis NS. Florid papillomatosis of the nipple: a rare presentation and review of the literature. Breast Dis. 2015;35:153-156.
- Di Bonito M, Cantile M, Collina F, et al. Adenoma of the nipple: a clinicopathological report of 13 cases. Oncol Lett. 2014;7:1839-1842.
- Miller E, Lewis D. The significance of serohemorrhagic or hemorrhagic discharge from the nipple. JAMA. 1923;81:1651-1657.
- Jones DB. Florid papillomatosis of the nipple ducts. Cancer. 1955;8:315-319.
- Rosen PP. Rosen's Breast Pathology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009:120-128.
- Brownstein MH, Phelps RG, Maqnin PH. Papillary adenoma of the nipple: analysis of fifteen new cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;12:707-715.
- Takashima S, Fujita Y, Miyauchi T, et al. Dermoscopic observation in adenoma of the nipple. J Dermatol. 2015;42:341-342.
- Spohn G, Trotter S, Tozbikian G, et al. Nipple adenoma in a female patient presenting with persistent erythema of the right nipple skin: case report, review of the literature, clinical implications, and relevancy to health care providers who evaluate and treat patients with dermatologic conditions of the breast skin. BMC Dermatol. 2016;16:4.
- Shin SJ. Nipple adenoma (florid papillomatosis of the nipple). In: Dabbs DJ, ed. Breast Pathology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012:286-292.
- Schnitt SJ, Collins LC. Biopsy Interpretation of the Breast. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2013.
- Salemis NS. Florid papillomatosis of the nipple: a rare presentation and review of the literature. Breast Dis. 2015;35:153-156.
- Di Bonito M, Cantile M, Collina F, et al. Adenoma of the nipple: a clinicopathological report of 13 cases. Oncol Lett. 2014;7:1839-1842.
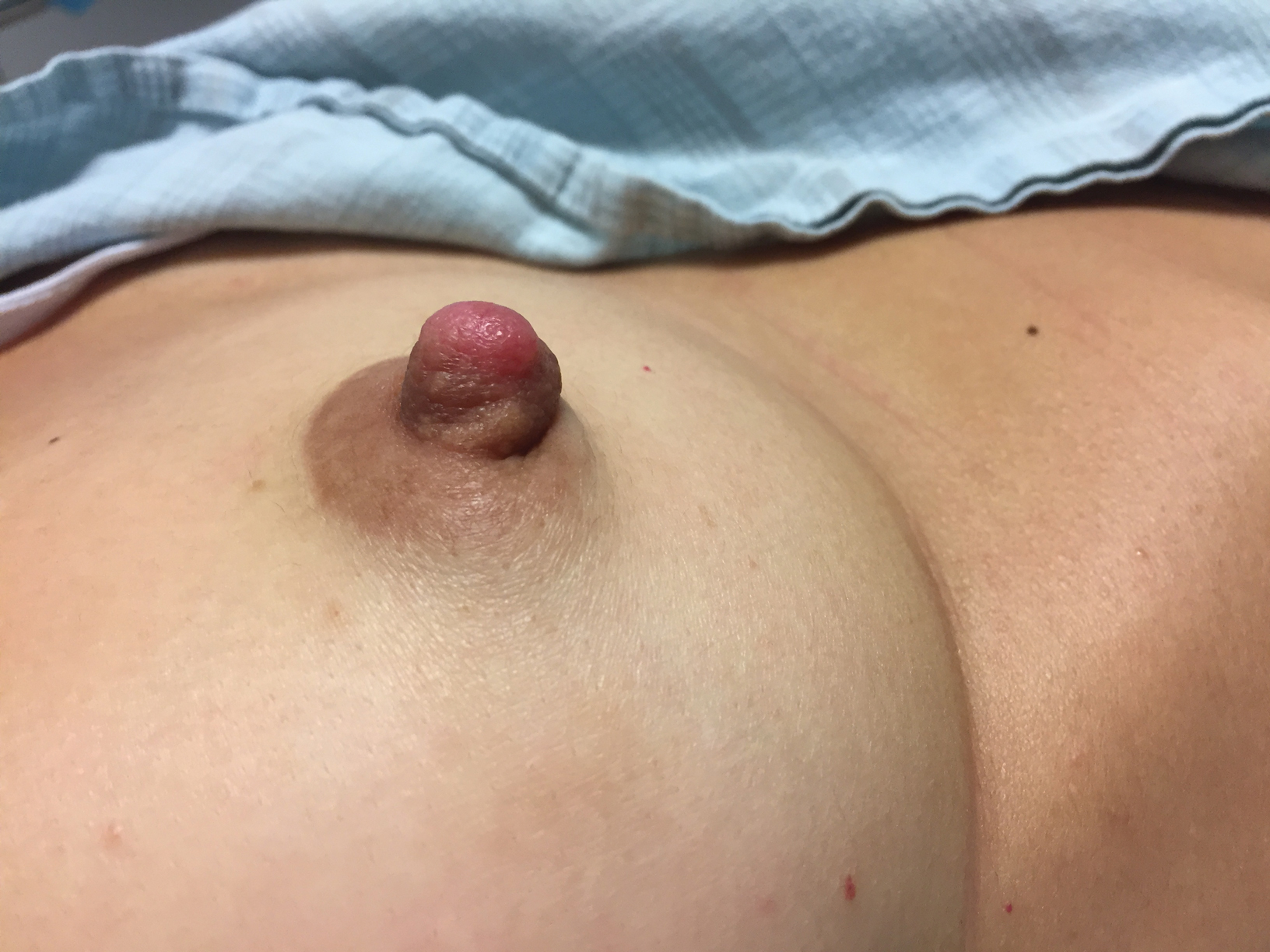
A healthy 48-year-old woman presented with a growth on the right nipple that had been slowly enlarging over the last few months. She initially noticed mild swelling in the area that persisted and formed a soft lump. She described mild pain with intermittent drainage but no bleeding. Her medical history was unremarkable, including a negative personal and family history of breast and skin cancer. She was taking no medications prior to development of the mass. She had no recent history of pregnancy or breastfeeding. A mammogram and breast ultrasound were not concerning for carcinoma. Physical examination showed a soft, exophytic, mildly tender, pink nodule on the right nipple that measured 12.2×7 mm; no drainage, bleeding, or ulceration was present. The surrounding skin of the areola and breast demonstrated no clinical changes. The contralateral breast, areola, and nipple were unaffected. The patient had no appreciable axillary or cervical lymphadenopathy. A deep shave biopsy of the nodule was performed and sent for histopathologic examination.
Clinical Pearl: Benzethonium Chloride for Habit-Tic Nail Deformity
Practice Gap
Habit-tic nail deformity results from repetitive manipulation of the cuticle and/or proximal nail fold. It most commonly affects one or both thumbnails and presents with a characteristic longitudinal midline furrow with parallel transverse ridges in the nail plate. Complications may include permanent onychodystrophy, frictional melanonychia, and infections. Treatment is challenging, as diagnosis first requires patient insight to the cause of symptoms. Therapeutic options include nonpharmacologic techniques (eg, occlusion of the nails to prevent trauma, cyanoacrylate adhesives, cognitive behavioral therapy) and pharmacologic techniques (eg, N-acetyl cysteine, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, antipsychotics), with limited supporting data and potential adverse effects.1
The Technique
Benzethonium chloride solution 0.2% is an antiseptic that creates a polymeric layer that binds to the skin. It normally is used to treat small skin erosions and prevent blisters. In patients with habit-tic nail deformity, we recommend once-daily application of benzethonium chloride to the proximal nail fold, thereby artificially recreating the cuticle and forming a sustainable barrier from trauma (Figure, A). Patients should be reminded not to manipulate the cuticle and/or nail fold during treatment. In one 36-year-old man with habit tic nail deformity, we saw clear nail growth after 4 months of treatment (Figure, B).

Practice Implications
Successful treatment of habit-tic nail deformity requires patients to have some insight into their behavior. The benzethonium chloride serves as a reminder for patients to stop picking as an unfamiliar artificial barrier and reminds them to substitute the picking behavior for another more positive behavior. Therefore, benzethonium chloride may be offered to patients as a novel therapy to both protect the cuticle and alter behavior in patients with habit-tic nail deformity, as it can be difficult to treat with few available therapies.
Allergic contact dermatitis to benzethonium chloride is a potential side effect and patients should be cautioned prior to treatment; however, it is extremely rare with 6 cases reported to date based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms allergic contact dermatitis and benzethonium chloride,2 and much rarer than contact allergy to cyanoacrylates.
- Halteh P, Scher RK, Lipner SR. Onychotillomania: diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:763-770.
- Hirata Y, Yanagi T, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Ulcerative contact dermatitis caused by benzethonium chloride. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;76:188-190.
Practice Gap
Habit-tic nail deformity results from repetitive manipulation of the cuticle and/or proximal nail fold. It most commonly affects one or both thumbnails and presents with a characteristic longitudinal midline furrow with parallel transverse ridges in the nail plate. Complications may include permanent onychodystrophy, frictional melanonychia, and infections. Treatment is challenging, as diagnosis first requires patient insight to the cause of symptoms. Therapeutic options include nonpharmacologic techniques (eg, occlusion of the nails to prevent trauma, cyanoacrylate adhesives, cognitive behavioral therapy) and pharmacologic techniques (eg, N-acetyl cysteine, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, antipsychotics), with limited supporting data and potential adverse effects.1
The Technique
Benzethonium chloride solution 0.2% is an antiseptic that creates a polymeric layer that binds to the skin. It normally is used to treat small skin erosions and prevent blisters. In patients with habit-tic nail deformity, we recommend once-daily application of benzethonium chloride to the proximal nail fold, thereby artificially recreating the cuticle and forming a sustainable barrier from trauma (Figure, A). Patients should be reminded not to manipulate the cuticle and/or nail fold during treatment. In one 36-year-old man with habit tic nail deformity, we saw clear nail growth after 4 months of treatment (Figure, B).

Practice Implications
Successful treatment of habit-tic nail deformity requires patients to have some insight into their behavior. The benzethonium chloride serves as a reminder for patients to stop picking as an unfamiliar artificial barrier and reminds them to substitute the picking behavior for another more positive behavior. Therefore, benzethonium chloride may be offered to patients as a novel therapy to both protect the cuticle and alter behavior in patients with habit-tic nail deformity, as it can be difficult to treat with few available therapies.
Allergic contact dermatitis to benzethonium chloride is a potential side effect and patients should be cautioned prior to treatment; however, it is extremely rare with 6 cases reported to date based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms allergic contact dermatitis and benzethonium chloride,2 and much rarer than contact allergy to cyanoacrylates.
Practice Gap
Habit-tic nail deformity results from repetitive manipulation of the cuticle and/or proximal nail fold. It most commonly affects one or both thumbnails and presents with a characteristic longitudinal midline furrow with parallel transverse ridges in the nail plate. Complications may include permanent onychodystrophy, frictional melanonychia, and infections. Treatment is challenging, as diagnosis first requires patient insight to the cause of symptoms. Therapeutic options include nonpharmacologic techniques (eg, occlusion of the nails to prevent trauma, cyanoacrylate adhesives, cognitive behavioral therapy) and pharmacologic techniques (eg, N-acetyl cysteine, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, antipsychotics), with limited supporting data and potential adverse effects.1
The Technique
Benzethonium chloride solution 0.2% is an antiseptic that creates a polymeric layer that binds to the skin. It normally is used to treat small skin erosions and prevent blisters. In patients with habit-tic nail deformity, we recommend once-daily application of benzethonium chloride to the proximal nail fold, thereby artificially recreating the cuticle and forming a sustainable barrier from trauma (Figure, A). Patients should be reminded not to manipulate the cuticle and/or nail fold during treatment. In one 36-year-old man with habit tic nail deformity, we saw clear nail growth after 4 months of treatment (Figure, B).

Practice Implications
Successful treatment of habit-tic nail deformity requires patients to have some insight into their behavior. The benzethonium chloride serves as a reminder for patients to stop picking as an unfamiliar artificial barrier and reminds them to substitute the picking behavior for another more positive behavior. Therefore, benzethonium chloride may be offered to patients as a novel therapy to both protect the cuticle and alter behavior in patients with habit-tic nail deformity, as it can be difficult to treat with few available therapies.
Allergic contact dermatitis to benzethonium chloride is a potential side effect and patients should be cautioned prior to treatment; however, it is extremely rare with 6 cases reported to date based on a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms allergic contact dermatitis and benzethonium chloride,2 and much rarer than contact allergy to cyanoacrylates.
- Halteh P, Scher RK, Lipner SR. Onychotillomania: diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:763-770.
- Hirata Y, Yanagi T, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Ulcerative contact dermatitis caused by benzethonium chloride. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;76:188-190.
- Halteh P, Scher RK, Lipner SR. Onychotillomania: diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18:763-770.
- Hirata Y, Yanagi T, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Ulcerative contact dermatitis caused by benzethonium chloride. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;76:188-190.
Acquired Digital Fibrokeratoma Presenting as a Painless Nodule on the Right Fifth Fingernail
Case Report
A 53-year-old woman presented for an initial visit to the dermatology clinic for a growth under the right fifth fingernail of 1 year’s duration. She had no history of trauma to the digit or pain or bleeding. She self-treated with over-the-counter wart remover for several months without improvement. She reported no other skin concerns. She had a medical history of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and basal cell carcinoma of the nose; she was taking methotrexate and adalimumab for the RA. She had a family history of melanoma in her father.
On physical examination, a firm nontender nodule was noted on the distal nail bed of the right fifth fingernail with onycholysis; the nail plate was otherwise intact (Figure 1). All other nails were normal. A plain radiograph of the involved digit showed no bony abnormality. Excisional biopsy of the nodule was performed and analyzed by histopathology (Figure 2). The biopsy specimen showed a benign epidermis that was acanthotic and surmounted by hyperkeratotic scale. The dermis was fibrotic with collagen bundles assuming a vertical orientation to the long axis of the epidermis, typical of a fibrokeratoma. There were no atypical features in the dermal component or epidermis (Figure 2). These findings were consistent with the diagnosis of acquired digital fibrokeratoma (ADF). The patient tolerated excisional biopsy well and had no evidence of recurrence 4 months following excision.
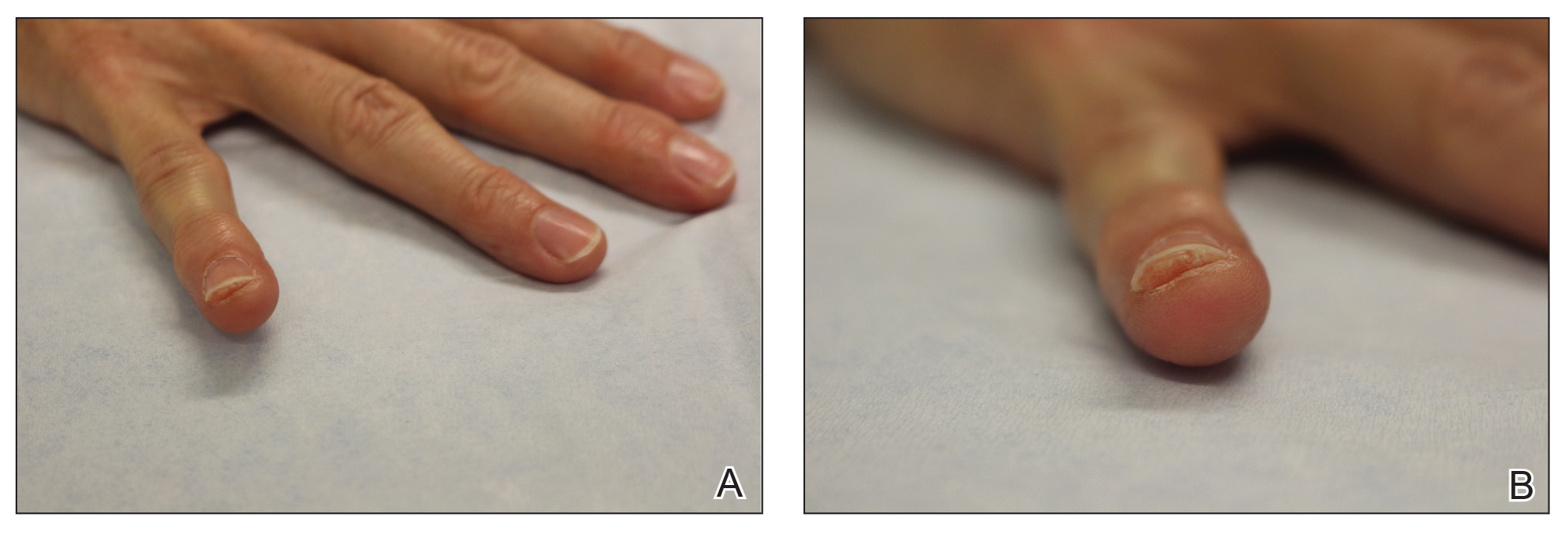
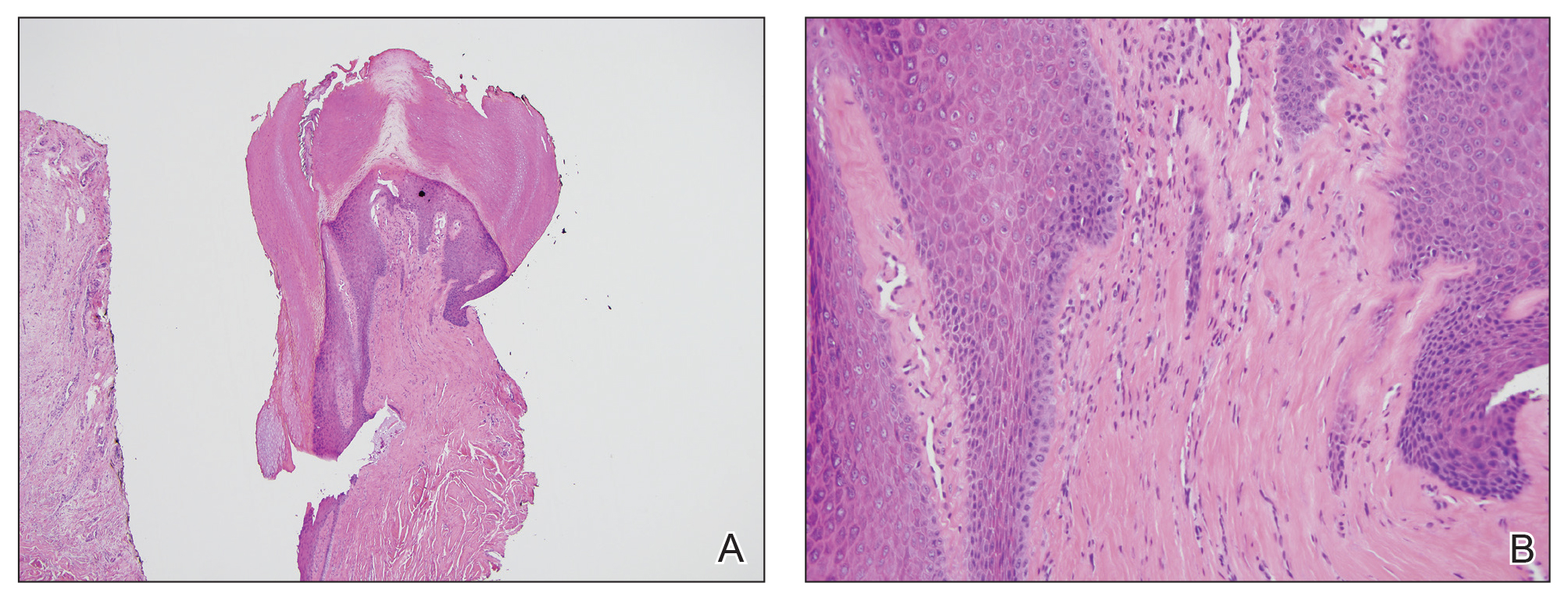
Comment
History and Clinical Presentation
First described by Bart et al1 in 1968, ADF is a rare benign fibrous tumor localized to the nail bed or periungual area.1 Typically, it presents as a solitary flesh-colored papule measuring 3 to 5 mm in diameter. It can be keratotic with a surrounding collarette of elevated skin. Acquired digital fibrokeratoma usually is localized to the digits of the hands or feet; when presenting subungually, it is more commonly found arising from the proximal matrix or nail bed of the great toe. Observed nail changes include longitudinal grooves, trachyonychia, subungual hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis.2 The affected nail can be painful, depending on the size and location of the tumor.
Acquired digital fibrokeratoma is more commonly found in middle-aged men; however, it has been reported among patients of various ages and in both sexes.1,3 In a study of 20 cases, the average duration before presenting for medical advice was 28 months.2 Acquired digital fibrokeratoma arises sporadically; some patients report prior local trauma. Lesions typically do not self-resolve.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ADF is made using a combination of clinical and histopathological findings. Dermoscopy is helpful and may show homogenous white or milky white structures, likely representing hyperkeratosis, proliferation of capillaries, and an increase in collagen bundles with a surrounding collarette of scale.4,5 Histopathology shows acanthosis and hyperkeratosis of the epidermis. Collagen bundles assume a characteristic vertical orientation to the long axis of the epidermis.
Two other histomorphologic subtypes, less common than the type I variant, are the type II variant, in which the number of fibroblasts is increased and the number of elastic fibers is decreased, and the type III variant, in which the stroma are edematous and cell poor. There is an even greater reduction in elastic tissue content in the type III variant than in the type I variant. There is evidence that type II ADFs exhibit more hyperkeratosis clinically than the other 2 subtypes, but from a practical perspective, this subclassification is not conducted in routine practice because it does not have clinical significance.5
Differential Diagnosis
The clinical differential diagnosis of ADF is broad and includes squamous cell carcinoma, onychomatricoma, onychopapilloma, verruca vulgaris, supernumerary digit, neurofibroma, cellular digital fibroma, and Koenen tumor (periungual fibroma). Almost all of these entities are easily differentiated from ADF on biopsy. A fibrokeratoma does not exhibit the atypia seen in squamous cell carcinoma. The multiple fibroepithelial projections and nail plate perforations characteristic of onychomatricoma are not observed in ADF. Onychopapilloma shows acanthosis and papillomatosis, similar to ADF; however, onychopapilloma lacks the characteristic vertical orientation of collagen in ADF. Verruca vulgaris classically shows koilocytosis, dilated blood vessels in papillae, and hypergranulosis. A supernumerary digit clinically lacks a collarette of scale and often presents in a bilateral fashion on the lateral fifth digits in children; histopathologically, a supernumerary digit is distinct from an ADF in that nerve bundles are abundant in the dermis, defining a form of amputation neuroma. Neurofibroma exhibits a spindle cell proliferation that assumes a patternless disposition in the dermis, accompanied by mucin, mast cells, and delicate collagen. The defining cell populace has a typical serpiginous nuclear outline that is characteristic of a Schwann cell. Cellular digital fibroma can present similar to ADF; it is considered by some to be a mucin-poor variant of superficial acral fibromyxoma. Its morphology is distinct: a proliferation of bland-appearing spindled cells exhibiting a storiform or fascicular growth pattern and CD34 positivity.
The differential diagnosis to consider when ADF is suspected is a Koenen tumor, which resembles a fibrokeratoma clinically and also is localized to the digits. Koenen tumors can be differentiated from fibrokeratoma by its association with tuberous sclerosis; a multiple, rather than solitary, presentation; a distinctive clove-shaped gross appearance; and an appearance on histopathology of stellate-shaped fibroblasts with occasional giant cells. Despite these important differences, Koenen tumor does exhibit a striking morphologic similarity to ADF, given that the vertical orientation of collagen bundles in Koenen tumor is virtually identical to ADF.6
Management
There are no known associations between ADF and medication use, including methotrexate and adalimumab, which our patient was taking; additionally, no association with RA or other systemic disorder has been reported.2 The preferred treatment of ADF is complete excision to the basal attachment of the tumor; recurrence is uncommon. Alternative therapies include destructive methods, such as cryotherapy, CO2 laser ablation, and electrodesiccation.2
- Bart RS, Andrade R, Kopf AW, et al. Acquired digital fibrokeratomas. Arch Dermatol. 1968;2:120-129.
- Hwang S, Kim M, Cho BK, et al. Clinical characteristics of acquired ungual fibrokeratoma. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2017;83:337-343.
- Yu D, Morgan RF. Acquired digital fibrokeratoma: a case report. Ann Plast Surg. 2015;74:304-305.
- Ehara Y, Yoshida Y, Ishizu S, et al. Acquired subungual fibrokeratoma. J Dermatol. 2017;44:e140-e141.
- Rubegni P, Poggiali S, Lamberti A, et al. Dermoscopy of acquired digital fibrokeratoma. Australas J Dermatol. 2012:53:47-48.
- Kint A, Baran R, De Keyser H. Acquired (digital) fibrokeratoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;12:816-821.
Case Report
A 53-year-old woman presented for an initial visit to the dermatology clinic for a growth under the right fifth fingernail of 1 year’s duration. She had no history of trauma to the digit or pain or bleeding. She self-treated with over-the-counter wart remover for several months without improvement. She reported no other skin concerns. She had a medical history of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and basal cell carcinoma of the nose; she was taking methotrexate and adalimumab for the RA. She had a family history of melanoma in her father.
On physical examination, a firm nontender nodule was noted on the distal nail bed of the right fifth fingernail with onycholysis; the nail plate was otherwise intact (Figure 1). All other nails were normal. A plain radiograph of the involved digit showed no bony abnormality. Excisional biopsy of the nodule was performed and analyzed by histopathology (Figure 2). The biopsy specimen showed a benign epidermis that was acanthotic and surmounted by hyperkeratotic scale. The dermis was fibrotic with collagen bundles assuming a vertical orientation to the long axis of the epidermis, typical of a fibrokeratoma. There were no atypical features in the dermal component or epidermis (Figure 2). These findings were consistent with the diagnosis of acquired digital fibrokeratoma (ADF). The patient tolerated excisional biopsy well and had no evidence of recurrence 4 months following excision.


Comment
History and Clinical Presentation
First described by Bart et al1 in 1968, ADF is a rare benign fibrous tumor localized to the nail bed or periungual area.1 Typically, it presents as a solitary flesh-colored papule measuring 3 to 5 mm in diameter. It can be keratotic with a surrounding collarette of elevated skin. Acquired digital fibrokeratoma usually is localized to the digits of the hands or feet; when presenting subungually, it is more commonly found arising from the proximal matrix or nail bed of the great toe. Observed nail changes include longitudinal grooves, trachyonychia, subungual hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis.2 The affected nail can be painful, depending on the size and location of the tumor.
Acquired digital fibrokeratoma is more commonly found in middle-aged men; however, it has been reported among patients of various ages and in both sexes.1,3 In a study of 20 cases, the average duration before presenting for medical advice was 28 months.2 Acquired digital fibrokeratoma arises sporadically; some patients report prior local trauma. Lesions typically do not self-resolve.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ADF is made using a combination of clinical and histopathological findings. Dermoscopy is helpful and may show homogenous white or milky white structures, likely representing hyperkeratosis, proliferation of capillaries, and an increase in collagen bundles with a surrounding collarette of scale.4,5 Histopathology shows acanthosis and hyperkeratosis of the epidermis. Collagen bundles assume a characteristic vertical orientation to the long axis of the epidermis.
Two other histomorphologic subtypes, less common than the type I variant, are the type II variant, in which the number of fibroblasts is increased and the number of elastic fibers is decreased, and the type III variant, in which the stroma are edematous and cell poor. There is an even greater reduction in elastic tissue content in the type III variant than in the type I variant. There is evidence that type II ADFs exhibit more hyperkeratosis clinically than the other 2 subtypes, but from a practical perspective, this subclassification is not conducted in routine practice because it does not have clinical significance.5
Differential Diagnosis
The clinical differential diagnosis of ADF is broad and includes squamous cell carcinoma, onychomatricoma, onychopapilloma, verruca vulgaris, supernumerary digit, neurofibroma, cellular digital fibroma, and Koenen tumor (periungual fibroma). Almost all of these entities are easily differentiated from ADF on biopsy. A fibrokeratoma does not exhibit the atypia seen in squamous cell carcinoma. The multiple fibroepithelial projections and nail plate perforations characteristic of onychomatricoma are not observed in ADF. Onychopapilloma shows acanthosis and papillomatosis, similar to ADF; however, onychopapilloma lacks the characteristic vertical orientation of collagen in ADF. Verruca vulgaris classically shows koilocytosis, dilated blood vessels in papillae, and hypergranulosis. A supernumerary digit clinically lacks a collarette of scale and often presents in a bilateral fashion on the lateral fifth digits in children; histopathologically, a supernumerary digit is distinct from an ADF in that nerve bundles are abundant in the dermis, defining a form of amputation neuroma. Neurofibroma exhibits a spindle cell proliferation that assumes a patternless disposition in the dermis, accompanied by mucin, mast cells, and delicate collagen. The defining cell populace has a typical serpiginous nuclear outline that is characteristic of a Schwann cell. Cellular digital fibroma can present similar to ADF; it is considered by some to be a mucin-poor variant of superficial acral fibromyxoma. Its morphology is distinct: a proliferation of bland-appearing spindled cells exhibiting a storiform or fascicular growth pattern and CD34 positivity.
The differential diagnosis to consider when ADF is suspected is a Koenen tumor, which resembles a fibrokeratoma clinically and also is localized to the digits. Koenen tumors can be differentiated from fibrokeratoma by its association with tuberous sclerosis; a multiple, rather than solitary, presentation; a distinctive clove-shaped gross appearance; and an appearance on histopathology of stellate-shaped fibroblasts with occasional giant cells. Despite these important differences, Koenen tumor does exhibit a striking morphologic similarity to ADF, given that the vertical orientation of collagen bundles in Koenen tumor is virtually identical to ADF.6
Management
There are no known associations between ADF and medication use, including methotrexate and adalimumab, which our patient was taking; additionally, no association with RA or other systemic disorder has been reported.2 The preferred treatment of ADF is complete excision to the basal attachment of the tumor; recurrence is uncommon. Alternative therapies include destructive methods, such as cryotherapy, CO2 laser ablation, and electrodesiccation.2
Case Report
A 53-year-old woman presented for an initial visit to the dermatology clinic for a growth under the right fifth fingernail of 1 year’s duration. She had no history of trauma to the digit or pain or bleeding. She self-treated with over-the-counter wart remover for several months without improvement. She reported no other skin concerns. She had a medical history of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and basal cell carcinoma of the nose; she was taking methotrexate and adalimumab for the RA. She had a family history of melanoma in her father.
On physical examination, a firm nontender nodule was noted on the distal nail bed of the right fifth fingernail with onycholysis; the nail plate was otherwise intact (Figure 1). All other nails were normal. A plain radiograph of the involved digit showed no bony abnormality. Excisional biopsy of the nodule was performed and analyzed by histopathology (Figure 2). The biopsy specimen showed a benign epidermis that was acanthotic and surmounted by hyperkeratotic scale. The dermis was fibrotic with collagen bundles assuming a vertical orientation to the long axis of the epidermis, typical of a fibrokeratoma. There were no atypical features in the dermal component or epidermis (Figure 2). These findings were consistent with the diagnosis of acquired digital fibrokeratoma (ADF). The patient tolerated excisional biopsy well and had no evidence of recurrence 4 months following excision.


Comment
History and Clinical Presentation
First described by Bart et al1 in 1968, ADF is a rare benign fibrous tumor localized to the nail bed or periungual area.1 Typically, it presents as a solitary flesh-colored papule measuring 3 to 5 mm in diameter. It can be keratotic with a surrounding collarette of elevated skin. Acquired digital fibrokeratoma usually is localized to the digits of the hands or feet; when presenting subungually, it is more commonly found arising from the proximal matrix or nail bed of the great toe. Observed nail changes include longitudinal grooves, trachyonychia, subungual hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis.2 The affected nail can be painful, depending on the size and location of the tumor.
Acquired digital fibrokeratoma is more commonly found in middle-aged men; however, it has been reported among patients of various ages and in both sexes.1,3 In a study of 20 cases, the average duration before presenting for medical advice was 28 months.2 Acquired digital fibrokeratoma arises sporadically; some patients report prior local trauma. Lesions typically do not self-resolve.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ADF is made using a combination of clinical and histopathological findings. Dermoscopy is helpful and may show homogenous white or milky white structures, likely representing hyperkeratosis, proliferation of capillaries, and an increase in collagen bundles with a surrounding collarette of scale.4,5 Histopathology shows acanthosis and hyperkeratosis of the epidermis. Collagen bundles assume a characteristic vertical orientation to the long axis of the epidermis.
Two other histomorphologic subtypes, less common than the type I variant, are the type II variant, in which the number of fibroblasts is increased and the number of elastic fibers is decreased, and the type III variant, in which the stroma are edematous and cell poor. There is an even greater reduction in elastic tissue content in the type III variant than in the type I variant. There is evidence that type II ADFs exhibit more hyperkeratosis clinically than the other 2 subtypes, but from a practical perspective, this subclassification is not conducted in routine practice because it does not have clinical significance.5
Differential Diagnosis
The clinical differential diagnosis of ADF is broad and includes squamous cell carcinoma, onychomatricoma, onychopapilloma, verruca vulgaris, supernumerary digit, neurofibroma, cellular digital fibroma, and Koenen tumor (periungual fibroma). Almost all of these entities are easily differentiated from ADF on biopsy. A fibrokeratoma does not exhibit the atypia seen in squamous cell carcinoma. The multiple fibroepithelial projections and nail plate perforations characteristic of onychomatricoma are not observed in ADF. Onychopapilloma shows acanthosis and papillomatosis, similar to ADF; however, onychopapilloma lacks the characteristic vertical orientation of collagen in ADF. Verruca vulgaris classically shows koilocytosis, dilated blood vessels in papillae, and hypergranulosis. A supernumerary digit clinically lacks a collarette of scale and often presents in a bilateral fashion on the lateral fifth digits in children; histopathologically, a supernumerary digit is distinct from an ADF in that nerve bundles are abundant in the dermis, defining a form of amputation neuroma. Neurofibroma exhibits a spindle cell proliferation that assumes a patternless disposition in the dermis, accompanied by mucin, mast cells, and delicate collagen. The defining cell populace has a typical serpiginous nuclear outline that is characteristic of a Schwann cell. Cellular digital fibroma can present similar to ADF; it is considered by some to be a mucin-poor variant of superficial acral fibromyxoma. Its morphology is distinct: a proliferation of bland-appearing spindled cells exhibiting a storiform or fascicular growth pattern and CD34 positivity.
The differential diagnosis to consider when ADF is suspected is a Koenen tumor, which resembles a fibrokeratoma clinically and also is localized to the digits. Koenen tumors can be differentiated from fibrokeratoma by its association with tuberous sclerosis; a multiple, rather than solitary, presentation; a distinctive clove-shaped gross appearance; and an appearance on histopathology of stellate-shaped fibroblasts with occasional giant cells. Despite these important differences, Koenen tumor does exhibit a striking morphologic similarity to ADF, given that the vertical orientation of collagen bundles in Koenen tumor is virtually identical to ADF.6
Management
There are no known associations between ADF and medication use, including methotrexate and adalimumab, which our patient was taking; additionally, no association with RA or other systemic disorder has been reported.2 The preferred treatment of ADF is complete excision to the basal attachment of the tumor; recurrence is uncommon. Alternative therapies include destructive methods, such as cryotherapy, CO2 laser ablation, and electrodesiccation.2
- Bart RS, Andrade R, Kopf AW, et al. Acquired digital fibrokeratomas. Arch Dermatol. 1968;2:120-129.
- Hwang S, Kim M, Cho BK, et al. Clinical characteristics of acquired ungual fibrokeratoma. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2017;83:337-343.
- Yu D, Morgan RF. Acquired digital fibrokeratoma: a case report. Ann Plast Surg. 2015;74:304-305.
- Ehara Y, Yoshida Y, Ishizu S, et al. Acquired subungual fibrokeratoma. J Dermatol. 2017;44:e140-e141.
- Rubegni P, Poggiali S, Lamberti A, et al. Dermoscopy of acquired digital fibrokeratoma. Australas J Dermatol. 2012:53:47-48.
- Kint A, Baran R, De Keyser H. Acquired (digital) fibrokeratoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;12:816-821.
- Bart RS, Andrade R, Kopf AW, et al. Acquired digital fibrokeratomas. Arch Dermatol. 1968;2:120-129.
- Hwang S, Kim M, Cho BK, et al. Clinical characteristics of acquired ungual fibrokeratoma. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2017;83:337-343.
- Yu D, Morgan RF. Acquired digital fibrokeratoma: a case report. Ann Plast Surg. 2015;74:304-305.
- Ehara Y, Yoshida Y, Ishizu S, et al. Acquired subungual fibrokeratoma. J Dermatol. 2017;44:e140-e141.
- Rubegni P, Poggiali S, Lamberti A, et al. Dermoscopy of acquired digital fibrokeratoma. Australas J Dermatol. 2012:53:47-48.
- Kint A, Baran R, De Keyser H. Acquired (digital) fibrokeratoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;12:816-821.
Practice Points
- Acquired digital fibrokeratoma is a benign tumor of the nail bed and periungual area.
- Histopathology shows epidermal acanthosis and hyperkeratosis, and collagen bundles are arranged in a vertical orientation to the long axis of the epidermis.
- Acquired digital fibrokeratoma should be considered in the differential diagnosis of flesh-colored papules on the nail unit associated with longitudinal grooves, trachyonychia, subungual hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis.
Analysis of Nail-Related Content in the Basic Dermatology Curriculum
Patients frequently present to dermatologists with nail disorders as their chief concern. Alternatively, nail conditions may be encountered by the examining physician as an incidental finding that may be a clue to underlying systemic disease. Competence in the diagnosis and treatment of nail diseases can drastically improve patient quality of life and can be lifesaving,1 but many dermatologists find management of nail diseases challenging.2 Bridging this educational gap begins with dermatology resident and medical student education. In a collaboration with dermatology educators, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) prepared a free online core curriculum for medical students that covers the essential concepts of dermatology. We sought to determine the integration of nail education in the AAD Basic Dermatology Curriculum.
Methods
A cross-sectional study of the AAD Basic Dermatology Curriculum was conducted to determine nail disease content. The curriculum modules were downloaded in June 2018,
Results
Of 342 patients discussed in cases and quizzes, nails were mentioned for 19 patients (89 times total)(Table 1). Additionally, there were 2 mentions each of nail clippings and nail tumors, 0 mentions of nail biopsies, and 1 mention each of fungal cultures and microscopy on nail scrapings (Table 1). Of the 40 modules, nails were mentioned in 12 modules (Table 2) and 6 introductions to the modules (Table 1). There were no mentions of the terms nails, subungual, or onychomycosis in the learning objectives.3
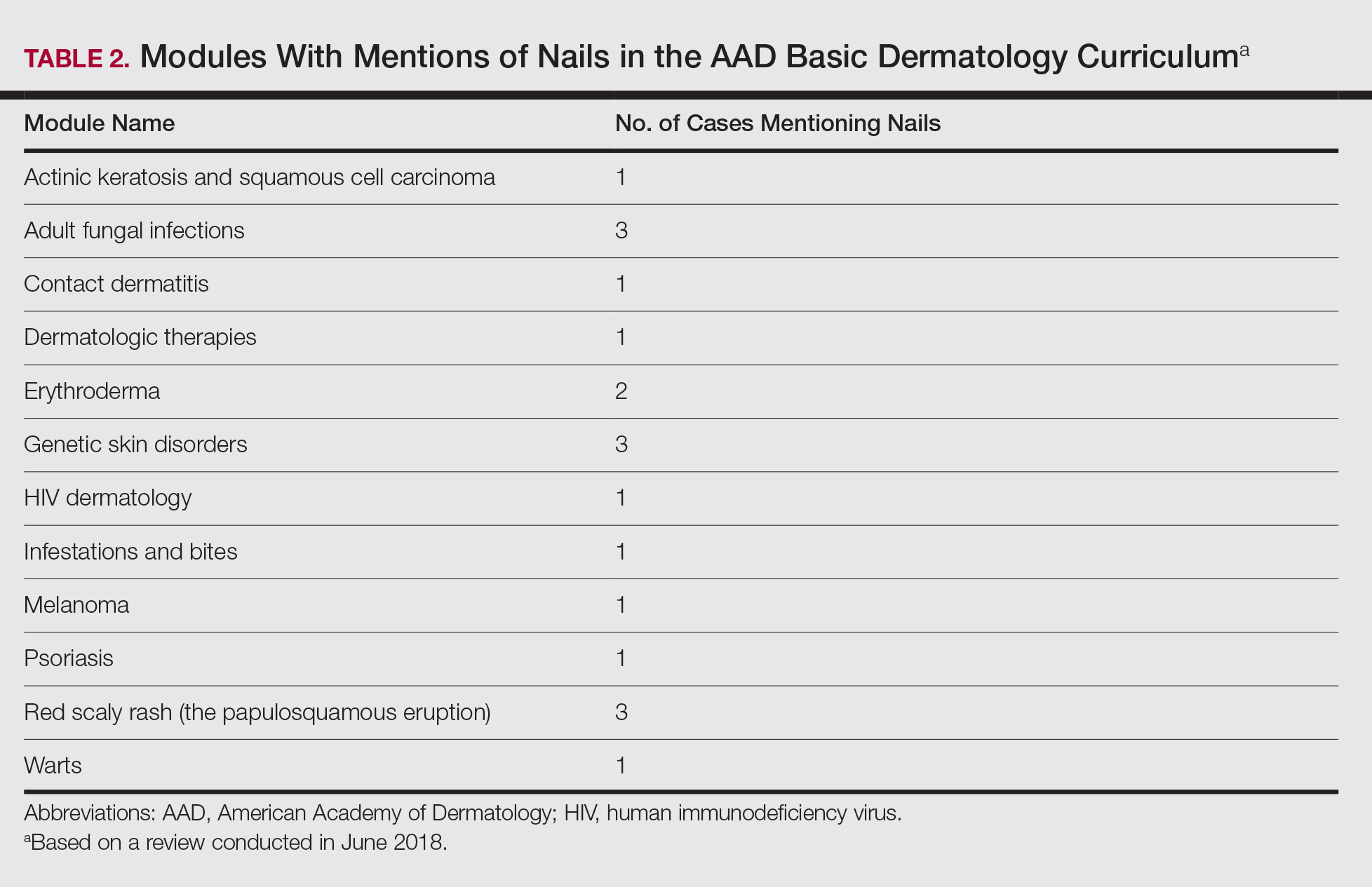
Comment
Our study demonstrates a paucity of content relevant to nails in the AAD Basic Dermatology Curriculum. Medical students are missing an important opportunity to learn about diagnosis and management of nail conditions and may incorrectly conclude that nail expertise is not essential to becoming a competent board-certified dermatologist.
Particularly concerning is the exclusion of nail examinations in the skin exam module addressing full-body skin examinations (0 mentions in 31 slides). This curriculum may negatively influence medical students and may then follow at the resident level, with a study reporting that 50.3% (69/137) of residents examine nails only when the patient brings it to their attention.4
Most concerning was the inadequate coverage of nail unit melanoma in the melanoma module (1 mention in 53 slides). Furthermore, the ABCDE—asymmetry, border, color, diameter, and evolving—mnemonic for cutaneous melanoma was covered in 6 slides in this module, and the ABCDEF—family history added—mnemonic for nail unit melanoma was completely excluded. Not surprisingly, resident knowledge of melanonychia diagnosis is deficient, with a prior study demonstrating that 62% (88/142) of residents were not confident diagnosing and managing patients with melanonychia, and only 88% (125/142) of residents were aware of the nail melanoma mnemonic.4
Similarly, nail biopsy for melanonychia diagnosis was excluded from the curriculum, whereas skin biopsy was thoroughly discussed in the context of a cutaneous melanoma diagnosis. This deficient teaching may track to the dermatology resident curriculum, as a survey of third-year dermatology residents (N=240) showed that 58% performed 10 or fewer nail procedures, and one-third of residents felt incompetent in nail surgery.5
We acknowledge that the AAD Basic Dermatology Curriculum is simply an introduction to dermatology. However, given that dermatologists are among the major specialists who care for nail patients, we advocate for more content on nail diseases in this curriculum. Nails can easily be incorporated into existing modules, and a new module specifically dedicated to nail disease should be added. Moreover, we envision that our findings will positively reflect on competence in treating nail disease for dermatology residents.
- Lipner SR. Ulcerated nodule of the fingernail. JAMA. 2018;319:713-714.
- Hare AQ, Rich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273.
- American Academy of Dermatology. Basic Dermatology Curriculum. https://www.aad.org/education/basic-derm-curriculum. Accessed March 25, 2019.
- Halteh P, Scher R, Artis A, et al. A survey-based study of management of longitudinal melanonychia amongst attending and resident dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:994-996.
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483, 483.e1-5.
Patients frequently present to dermatologists with nail disorders as their chief concern. Alternatively, nail conditions may be encountered by the examining physician as an incidental finding that may be a clue to underlying systemic disease. Competence in the diagnosis and treatment of nail diseases can drastically improve patient quality of life and can be lifesaving,1 but many dermatologists find management of nail diseases challenging.2 Bridging this educational gap begins with dermatology resident and medical student education. In a collaboration with dermatology educators, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) prepared a free online core curriculum for medical students that covers the essential concepts of dermatology. We sought to determine the integration of nail education in the AAD Basic Dermatology Curriculum.
Methods
A cross-sectional study of the AAD Basic Dermatology Curriculum was conducted to determine nail disease content. The curriculum modules were downloaded in June 2018,
Results
Of 342 patients discussed in cases and quizzes, nails were mentioned for 19 patients (89 times total)(Table 1). Additionally, there were 2 mentions each of nail clippings and nail tumors, 0 mentions of nail biopsies, and 1 mention each of fungal cultures and microscopy on nail scrapings (Table 1). Of the 40 modules, nails were mentioned in 12 modules (Table 2) and 6 introductions to the modules (Table 1). There were no mentions of the terms nails, subungual, or onychomycosis in the learning objectives.3


Comment
Our study demonstrates a paucity of content relevant to nails in the AAD Basic Dermatology Curriculum. Medical students are missing an important opportunity to learn about diagnosis and management of nail conditions and may incorrectly conclude that nail expertise is not essential to becoming a competent board-certified dermatologist.
Particularly concerning is the exclusion of nail examinations in the skin exam module addressing full-body skin examinations (0 mentions in 31 slides). This curriculum may negatively influence medical students and may then follow at the resident level, with a study reporting that 50.3% (69/137) of residents examine nails only when the patient brings it to their attention.4
Most concerning was the inadequate coverage of nail unit melanoma in the melanoma module (1 mention in 53 slides). Furthermore, the ABCDE—asymmetry, border, color, diameter, and evolving—mnemonic for cutaneous melanoma was covered in 6 slides in this module, and the ABCDEF—family history added—mnemonic for nail unit melanoma was completely excluded. Not surprisingly, resident knowledge of melanonychia diagnosis is deficient, with a prior study demonstrating that 62% (88/142) of residents were not confident diagnosing and managing patients with melanonychia, and only 88% (125/142) of residents were aware of the nail melanoma mnemonic.4
Similarly, nail biopsy for melanonychia diagnosis was excluded from the curriculum, whereas skin biopsy was thoroughly discussed in the context of a cutaneous melanoma diagnosis. This deficient teaching may track to the dermatology resident curriculum, as a survey of third-year dermatology residents (N=240) showed that 58% performed 10 or fewer nail procedures, and one-third of residents felt incompetent in nail surgery.5
We acknowledge that the AAD Basic Dermatology Curriculum is simply an introduction to dermatology. However, given that dermatologists are among the major specialists who care for nail patients, we advocate for more content on nail diseases in this curriculum. Nails can easily be incorporated into existing modules, and a new module specifically dedicated to nail disease should be added. Moreover, we envision that our findings will positively reflect on competence in treating nail disease for dermatology residents.
Patients frequently present to dermatologists with nail disorders as their chief concern. Alternatively, nail conditions may be encountered by the examining physician as an incidental finding that may be a clue to underlying systemic disease. Competence in the diagnosis and treatment of nail diseases can drastically improve patient quality of life and can be lifesaving,1 but many dermatologists find management of nail diseases challenging.2 Bridging this educational gap begins with dermatology resident and medical student education. In a collaboration with dermatology educators, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) prepared a free online core curriculum for medical students that covers the essential concepts of dermatology. We sought to determine the integration of nail education in the AAD Basic Dermatology Curriculum.
Methods
A cross-sectional study of the AAD Basic Dermatology Curriculum was conducted to determine nail disease content. The curriculum modules were downloaded in June 2018,
Results
Of 342 patients discussed in cases and quizzes, nails were mentioned for 19 patients (89 times total)(Table 1). Additionally, there were 2 mentions each of nail clippings and nail tumors, 0 mentions of nail biopsies, and 1 mention each of fungal cultures and microscopy on nail scrapings (Table 1). Of the 40 modules, nails were mentioned in 12 modules (Table 2) and 6 introductions to the modules (Table 1). There were no mentions of the terms nails, subungual, or onychomycosis in the learning objectives.3


Comment
Our study demonstrates a paucity of content relevant to nails in the AAD Basic Dermatology Curriculum. Medical students are missing an important opportunity to learn about diagnosis and management of nail conditions and may incorrectly conclude that nail expertise is not essential to becoming a competent board-certified dermatologist.
Particularly concerning is the exclusion of nail examinations in the skin exam module addressing full-body skin examinations (0 mentions in 31 slides). This curriculum may negatively influence medical students and may then follow at the resident level, with a study reporting that 50.3% (69/137) of residents examine nails only when the patient brings it to their attention.4
Most concerning was the inadequate coverage of nail unit melanoma in the melanoma module (1 mention in 53 slides). Furthermore, the ABCDE—asymmetry, border, color, diameter, and evolving—mnemonic for cutaneous melanoma was covered in 6 slides in this module, and the ABCDEF—family history added—mnemonic for nail unit melanoma was completely excluded. Not surprisingly, resident knowledge of melanonychia diagnosis is deficient, with a prior study demonstrating that 62% (88/142) of residents were not confident diagnosing and managing patients with melanonychia, and only 88% (125/142) of residents were aware of the nail melanoma mnemonic.4
Similarly, nail biopsy for melanonychia diagnosis was excluded from the curriculum, whereas skin biopsy was thoroughly discussed in the context of a cutaneous melanoma diagnosis. This deficient teaching may track to the dermatology resident curriculum, as a survey of third-year dermatology residents (N=240) showed that 58% performed 10 or fewer nail procedures, and one-third of residents felt incompetent in nail surgery.5
We acknowledge that the AAD Basic Dermatology Curriculum is simply an introduction to dermatology. However, given that dermatologists are among the major specialists who care for nail patients, we advocate for more content on nail diseases in this curriculum. Nails can easily be incorporated into existing modules, and a new module specifically dedicated to nail disease should be added. Moreover, we envision that our findings will positively reflect on competence in treating nail disease for dermatology residents.
- Lipner SR. Ulcerated nodule of the fingernail. JAMA. 2018;319:713-714.
- Hare AQ, Rich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273.
- American Academy of Dermatology. Basic Dermatology Curriculum. https://www.aad.org/education/basic-derm-curriculum. Accessed March 25, 2019.
- Halteh P, Scher R, Artis A, et al. A survey-based study of management of longitudinal melanonychia amongst attending and resident dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:994-996.
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483, 483.e1-5.
- Lipner SR. Ulcerated nodule of the fingernail. JAMA. 2018;319:713-714.
- Hare AQ, Rich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273.
- American Academy of Dermatology. Basic Dermatology Curriculum. https://www.aad.org/education/basic-derm-curriculum. Accessed March 25, 2019.
- Halteh P, Scher R, Artis A, et al. A survey-based study of management of longitudinal melanonychia amongst attending and resident dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:994-996.
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483, 483.e1-5.
Practice Points
- Competence in the diagnosis and treatment of nail diseases can drastically improve patient quality of life and can be lifesaving.
- Education on diagnosis and management of nail conditions is deficient in the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) Basic Dermatology Curriculum.
- Increased efforts are needed to incorporate relevant nail education materials into the AAD Basic Dermatology Curriculum.
Clinical Pearl: Kinesiology Tape for Onychocryptosis
Practice Gap
Onychocryptosis, or ingrown toenail, is a highly prevalent nail condition characterized by penetration of the periungual skin by the nail plate (Figure, A). Patients may report pain either while at rest or walking, which may be debilitating in severe cases and may adversely affect daily living. Treatment may be approached using conservative or surgical therapies. Conservative methods are noninvasive and appropriate for mild cases but require excellent compliance. Although nail trimming is the simplest method, it may necessitate cutting soft tissue, particularly when the nail is anchored deep within the periungual skin. Another conservative method is taping, which aims to separate the nail fold from the offending nail edge by using an adhesive. In common practice, the adhesive often detaches within a few hours, which is further exacerbated by moisture from sweating or bathing.1 Therefore, for effective treatment of onychocryptosis, the tape typically must be reapplied multiple times per day, limiting compliance.
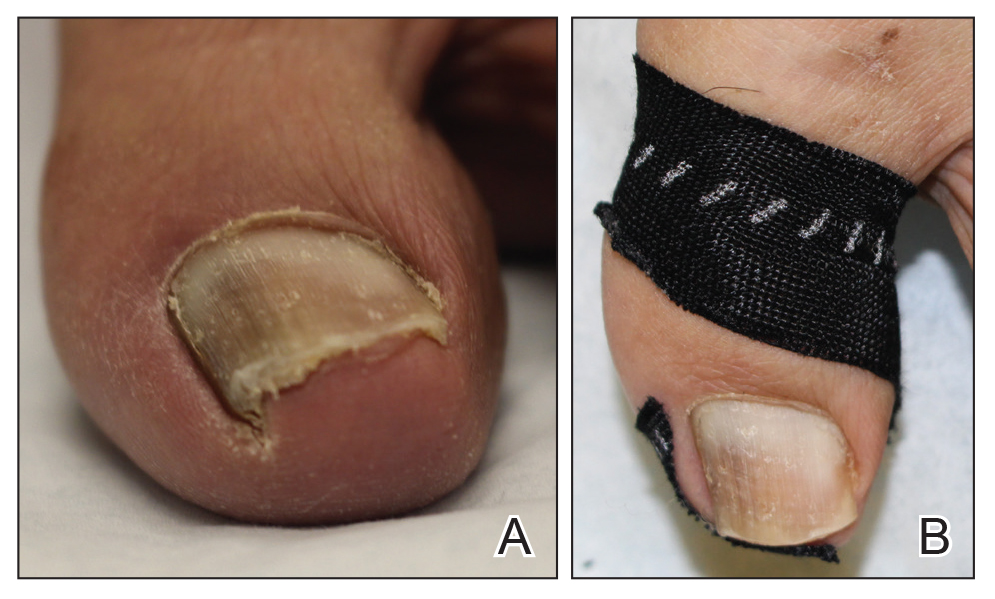
Tools
We propose using kinesiology tape to treat onychocryptosis. Kinesiology tape is a highly elastic adhesive that was originally employed by athletes to relieve pain while supporting muscles, tendons, and ligaments during strenuous activity. We hypothesized that its stronger adherent properties and greater elasticity would be advantageous for treatment of onychocryptosis compared to standard tape.
The Technique
A strip of tape is cut to approximately 10 to 15 mm×5 cm and is applied once daily to the lateral nail fold, pulling it away from the nail plate in oblique and proximal directions and then wrapping it around the plantar surface dorsally (Figure, B). Kinesiology tape properties allow for less frequent application and greater tension to be applied to the nail fold while reducing the risk for
Practice Implications
Kinesiology tape adheres more firmly than other tapes and requires less frequent applications. Use of kinesiology tape for onychocryptosis therapy often is effective and may negate the need for more invasive procedures and improve quality of life during and after treatment.
1. Haneke E. Controversies in the treatment of ingrown nails [published online May 20, 2012]. Dermatol Res Pract. 2012;2012:783924.
Practice Gap
Onychocryptosis, or ingrown toenail, is a highly prevalent nail condition characterized by penetration of the periungual skin by the nail plate (Figure, A). Patients may report pain either while at rest or walking, which may be debilitating in severe cases and may adversely affect daily living. Treatment may be approached using conservative or surgical therapies. Conservative methods are noninvasive and appropriate for mild cases but require excellent compliance. Although nail trimming is the simplest method, it may necessitate cutting soft tissue, particularly when the nail is anchored deep within the periungual skin. Another conservative method is taping, which aims to separate the nail fold from the offending nail edge by using an adhesive. In common practice, the adhesive often detaches within a few hours, which is further exacerbated by moisture from sweating or bathing.1 Therefore, for effective treatment of onychocryptosis, the tape typically must be reapplied multiple times per day, limiting compliance.

Tools
We propose using kinesiology tape to treat onychocryptosis. Kinesiology tape is a highly elastic adhesive that was originally employed by athletes to relieve pain while supporting muscles, tendons, and ligaments during strenuous activity. We hypothesized that its stronger adherent properties and greater elasticity would be advantageous for treatment of onychocryptosis compared to standard tape.
The Technique
A strip of tape is cut to approximately 10 to 15 mm×5 cm and is applied once daily to the lateral nail fold, pulling it away from the nail plate in oblique and proximal directions and then wrapping it around the plantar surface dorsally (Figure, B). Kinesiology tape properties allow for less frequent application and greater tension to be applied to the nail fold while reducing the risk for
Practice Implications
Kinesiology tape adheres more firmly than other tapes and requires less frequent applications. Use of kinesiology tape for onychocryptosis therapy often is effective and may negate the need for more invasive procedures and improve quality of life during and after treatment.
Practice Gap
Onychocryptosis, or ingrown toenail, is a highly prevalent nail condition characterized by penetration of the periungual skin by the nail plate (Figure, A). Patients may report pain either while at rest or walking, which may be debilitating in severe cases and may adversely affect daily living. Treatment may be approached using conservative or surgical therapies. Conservative methods are noninvasive and appropriate for mild cases but require excellent compliance. Although nail trimming is the simplest method, it may necessitate cutting soft tissue, particularly when the nail is anchored deep within the periungual skin. Another conservative method is taping, which aims to separate the nail fold from the offending nail edge by using an adhesive. In common practice, the adhesive often detaches within a few hours, which is further exacerbated by moisture from sweating or bathing.1 Therefore, for effective treatment of onychocryptosis, the tape typically must be reapplied multiple times per day, limiting compliance.

Tools
We propose using kinesiology tape to treat onychocryptosis. Kinesiology tape is a highly elastic adhesive that was originally employed by athletes to relieve pain while supporting muscles, tendons, and ligaments during strenuous activity. We hypothesized that its stronger adherent properties and greater elasticity would be advantageous for treatment of onychocryptosis compared to standard tape.
The Technique
A strip of tape is cut to approximately 10 to 15 mm×5 cm and is applied once daily to the lateral nail fold, pulling it away from the nail plate in oblique and proximal directions and then wrapping it around the plantar surface dorsally (Figure, B). Kinesiology tape properties allow for less frequent application and greater tension to be applied to the nail fold while reducing the risk for
Practice Implications
Kinesiology tape adheres more firmly than other tapes and requires less frequent applications. Use of kinesiology tape for onychocryptosis therapy often is effective and may negate the need for more invasive procedures and improve quality of life during and after treatment.
1. Haneke E. Controversies in the treatment of ingrown nails [published online May 20, 2012]. Dermatol Res Pract. 2012;2012:783924.
1. Haneke E. Controversies in the treatment of ingrown nails [published online May 20, 2012]. Dermatol Res Pract. 2012;2012:783924.
Optimizing Topical Therapy for Onychomycosis: The Importance of Patient Education
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nail unit due to dermatophytes, yeasts, and nondermatophyte molds (NDMs). It accounts for approximately 50% of all nail disorders seen in clinical practice and is estimated to affect 10% to 12% of the US population.1,2 Oral medications approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) include terbinafine and itraconazole, which have demonstrated good efficacy in treating onychomycosis but are associated with potential drug-drug interactions and systemic side effects.3,4 Although liver failure associated with these drugs is rare,5 many patients are anxious about systemic adverse events and therefore prefer to use topical therapies for onychomycosis.
Many patients desire topical therapy but not every patient is an appropriate candidate. Patients who will likely respond well to topical therapy include those with superficial onychomycosis, distal lateral subungual onychomycosis that involves less than 50% of the nail plate surface area (without matrix involvement and a nail plate thickness less than 2 mm), and only up to 3 or 4 nails affected.6 In patients who have contraindications to oral therapy, topical therapy may be the only treatment option. To maximize efficacy of FDA-approved topical agents for onychomycosis therapy, patient education is of utmost importance. Failure to properly counsel the patient on proper medication application may result in decreased antifungal efficacy; poor patient compliance due to lack of improvement; and progression of disease, leading to increased onychodystrophy and pain.
Before initiating therapy, patients should be counseled that treatment with topical drugs is long, requiring daily application of the medication for 6 months for fingernails and 12 months for toenails, based on average nail growth rates (2–3 mm per month for fingernails; 1 mm per month for toenails).7 Patients also are advised to avoid nail polish application during the course of therapy, as clinical trials were performed without nail polish and the true efficacy with nail polish is unknown.8-10 Because patients who have had onychomycosis for shorter durations generally have better cure rates than those who have disease for longer durations, it is prudent to initiate topical therapy as early as possible.11,12 Treating the feet with an antifungal while treating the nails for onychomycosis further enhances efficacy.13,14 There are 3 FDA-approved topical therapies for onychomycosis: ciclopirox nail lacquer 8%, efinaconazole solution 10%, and tavaborole solution 5%.15-17
Ciclopirox is a hydroxypyridone with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against dermatophytes, NDMs, yeasts, and bacteria. Its mechanism of action is to chelate polyvalent cations, such as Fe3+, and inhibit fungal metal-dependent enzymes responsible for the degradation of toxic metabolites.15 Ciclopirox nail lacquer 8% was FDA approved for the treatment of onychomycosis in 1999, making it the first topical approved for this purpose. Its indication is for immunocompetent patients with mild to moderate onychomycosis (Trichophyton rubrum) without lunula involvement, with mycologic cure rates of 29% to 36% and complete cure rates of 5.5% to 8.5% (toenails).15 It is the only FDA-approved topical treatment for both fingernails and toenails. Using a brush applicator, it is applied daily to the nail plate and its undersurface, hyponychium, and 5 mm of the surrounding skin. It is important to counsel the patient to remove the lacquer from the nail plate weekly because failure to do so will result in accumulation of numerous layers of medication, such that the active drug cannot reach the site of infection (Figures 1 and 2). The nail plate also should be trimmed and filed weekly by the patient, with monthly clipping/debridement by a physician recommended.6,15
Efinaconazole is a triazole with antifungal activity against dermatophytes, NDMs, and Candida species. Its mechanism of action is inhibition of lanosterol 14α-demethylase, an enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of ergosterol, which is a component of the fungal cell membrane. Efinaconazole solution 10% was FDA approved in June 2014 for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis due to T rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes, with package insert mycologic cure rates of 53.4% to 55.2% and complete cure rates of 15.2% to 17.8%.9,16 It is applied with a brush applicator to the nail plate, as well as its undersurface, nail folds, and hyponychium. Two drops are recommended for the great toenail and one drop for all other toenails, and no removal of the solution or debridement is required.6,16
Tavaborole is a benzoxaborole with antifungal activity against dermatophytes, NDMs, and yeasts. Its mechanism of action is inhibition of fungal aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetase, thus impeding protein synthesis.18 Tavaborole solution 5% was FDA approved in July 2014 for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis due to T rubrum and T mentagrophytes, with mycologic cure rates of 31.1% and 35.9% and complete cure rates of 6.5% and 9.1%, respectively.11,17 It is applied with a glass pointed-tip dropper to the nail plate, such that the entire nail is covered as well as under the nail tip. No removal of the solution or debridement is required.17
Topical therapies for onychomycosis require long treatment durations, thus excellent compliance and adherence to the treatment protocol are vital to maximize efficacy. Dermatologists who prescribe ciclopirox nail lacquer 8% should counsel patients to remove the lacquer with alcohol weekly, such that the antifungal penetrates the nail plate to reach the site of infection. Monthly debridement also must be clarified before initiating therapy. With all topical therapy for onychomycosis, it is important to treat early, treat concurrently for tinea pedis, and avoid use of nail polish so that patients have the best possible cure rates.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Onychomycosis: diagnosis and therapy. In: Razzaghi-Abyaneh M, Shams-Ghahfarokhi M, Rai M, eds. Medical Mycology: Current Trends and Future Prospects. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2015:28.
- Scher RK, Rich P, Pariser D, et al. The epidemiology, etiology, and pathophysiology of onychomycosis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2013;32(2 suppl 1):S2-S4.
- Lamisil [package insert]. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; 1997.
- Sporanox [package insert]. Titusville, NJ: Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2001.
- National Institutes of Health. Terbinafine. LiverTox website. https://livertox.nlm.nih.gov/Terbinafine.htm. Accessed November 7, 2018.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Onychomycosis: topical therapy and devices. In: Rubin AI, Jellinek NJ, Daniel CR III, et al, eds. Scher and Daniel’s Nails: Diagnosis, Surgery, Therapy. 4th ed. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2018:173-184.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Nail growth evaluation and factors affecting nail growth. In: Humbert P, Fanian F, Maibach HI, et al, eds. Agache’s Measuring the Skin. 2nd ed. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2017:867-881.
- Gupta AK, Elewski BE, Sugarman JL, et al. The efficacy and safety of efinaconazole 10% solution for treatment of mild to moderate onychomycosis: a pooled analysis of two phase 3 randomized trials. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:815-820.
- Elewski BE, Rich P, Pollak R, et al. Efinaconazole 10% solution in the treatment of toenail onychomycosis: two phase III multicenter, randomized, double-blind studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:600-608.
- Elewski BE, Aly R, Baldwin SL, et al. Efficacy and safety of tavaborole topical solution, 5%, a novel boron-based antifungal agent, for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis: results from 2 randomized phase-III studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:62-69.
- Rich P. Efinaconazole topical solution, 10%: the benefits of treating onychomycosis early. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:58-62.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Efinaconazole 10% topical solution for the topical treatment of onychomycosis of the toenail. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2015;8:719-731.
- Del Rosso JQ. Onychomycosis of toenails and post-hoc analyses with efinaconazole 10% solution once-daily treatment: impact of disease severity and other concomitant associated factors on selection of therapy and therapeutic outcomes. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9:42.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Management of onychomycosis and co-existing tinea pedis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:492-494.
- Penlac [package insert]. Berwyn, PA: Dermik Laboratories; 2004.
- Jublia [package insert]. Bridgewater, NJ: Valeant Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2014.
- Kerydin [package insert]. Palo Alto, CA: Anacor Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2014.
- Rock FL, Mao W, Yaremchuk A, et al. An antifungal agent inhibits an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase by trapping tRNA in the editing site. Science. 2007;316:1759-1761.
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nail unit due to dermatophytes, yeasts, and nondermatophyte molds (NDMs). It accounts for approximately 50% of all nail disorders seen in clinical practice and is estimated to affect 10% to 12% of the US population.1,2 Oral medications approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) include terbinafine and itraconazole, which have demonstrated good efficacy in treating onychomycosis but are associated with potential drug-drug interactions and systemic side effects.3,4 Although liver failure associated with these drugs is rare,5 many patients are anxious about systemic adverse events and therefore prefer to use topical therapies for onychomycosis.
Many patients desire topical therapy but not every patient is an appropriate candidate. Patients who will likely respond well to topical therapy include those with superficial onychomycosis, distal lateral subungual onychomycosis that involves less than 50% of the nail plate surface area (without matrix involvement and a nail plate thickness less than 2 mm), and only up to 3 or 4 nails affected.6 In patients who have contraindications to oral therapy, topical therapy may be the only treatment option. To maximize efficacy of FDA-approved topical agents for onychomycosis therapy, patient education is of utmost importance. Failure to properly counsel the patient on proper medication application may result in decreased antifungal efficacy; poor patient compliance due to lack of improvement; and progression of disease, leading to increased onychodystrophy and pain.
Before initiating therapy, patients should be counseled that treatment with topical drugs is long, requiring daily application of the medication for 6 months for fingernails and 12 months for toenails, based on average nail growth rates (2–3 mm per month for fingernails; 1 mm per month for toenails).7 Patients also are advised to avoid nail polish application during the course of therapy, as clinical trials were performed without nail polish and the true efficacy with nail polish is unknown.8-10 Because patients who have had onychomycosis for shorter durations generally have better cure rates than those who have disease for longer durations, it is prudent to initiate topical therapy as early as possible.11,12 Treating the feet with an antifungal while treating the nails for onychomycosis further enhances efficacy.13,14 There are 3 FDA-approved topical therapies for onychomycosis: ciclopirox nail lacquer 8%, efinaconazole solution 10%, and tavaborole solution 5%.15-17
Ciclopirox is a hydroxypyridone with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against dermatophytes, NDMs, yeasts, and bacteria. Its mechanism of action is to chelate polyvalent cations, such as Fe3+, and inhibit fungal metal-dependent enzymes responsible for the degradation of toxic metabolites.15 Ciclopirox nail lacquer 8% was FDA approved for the treatment of onychomycosis in 1999, making it the first topical approved for this purpose. Its indication is for immunocompetent patients with mild to moderate onychomycosis (Trichophyton rubrum) without lunula involvement, with mycologic cure rates of 29% to 36% and complete cure rates of 5.5% to 8.5% (toenails).15 It is the only FDA-approved topical treatment for both fingernails and toenails. Using a brush applicator, it is applied daily to the nail plate and its undersurface, hyponychium, and 5 mm of the surrounding skin. It is important to counsel the patient to remove the lacquer from the nail plate weekly because failure to do so will result in accumulation of numerous layers of medication, such that the active drug cannot reach the site of infection (Figures 1 and 2). The nail plate also should be trimmed and filed weekly by the patient, with monthly clipping/debridement by a physician recommended.6,15


Efinaconazole is a triazole with antifungal activity against dermatophytes, NDMs, and Candida species. Its mechanism of action is inhibition of lanosterol 14α-demethylase, an enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of ergosterol, which is a component of the fungal cell membrane. Efinaconazole solution 10% was FDA approved in June 2014 for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis due to T rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes, with package insert mycologic cure rates of 53.4% to 55.2% and complete cure rates of 15.2% to 17.8%.9,16 It is applied with a brush applicator to the nail plate, as well as its undersurface, nail folds, and hyponychium. Two drops are recommended for the great toenail and one drop for all other toenails, and no removal of the solution or debridement is required.6,16
Tavaborole is a benzoxaborole with antifungal activity against dermatophytes, NDMs, and yeasts. Its mechanism of action is inhibition of fungal aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetase, thus impeding protein synthesis.18 Tavaborole solution 5% was FDA approved in July 2014 for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis due to T rubrum and T mentagrophytes, with mycologic cure rates of 31.1% and 35.9% and complete cure rates of 6.5% and 9.1%, respectively.11,17 It is applied with a glass pointed-tip dropper to the nail plate, such that the entire nail is covered as well as under the nail tip. No removal of the solution or debridement is required.17
Topical therapies for onychomycosis require long treatment durations, thus excellent compliance and adherence to the treatment protocol are vital to maximize efficacy. Dermatologists who prescribe ciclopirox nail lacquer 8% should counsel patients to remove the lacquer with alcohol weekly, such that the antifungal penetrates the nail plate to reach the site of infection. Monthly debridement also must be clarified before initiating therapy. With all topical therapy for onychomycosis, it is important to treat early, treat concurrently for tinea pedis, and avoid use of nail polish so that patients have the best possible cure rates.
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nail unit due to dermatophytes, yeasts, and nondermatophyte molds (NDMs). It accounts for approximately 50% of all nail disorders seen in clinical practice and is estimated to affect 10% to 12% of the US population.1,2 Oral medications approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) include terbinafine and itraconazole, which have demonstrated good efficacy in treating onychomycosis but are associated with potential drug-drug interactions and systemic side effects.3,4 Although liver failure associated with these drugs is rare,5 many patients are anxious about systemic adverse events and therefore prefer to use topical therapies for onychomycosis.
Many patients desire topical therapy but not every patient is an appropriate candidate. Patients who will likely respond well to topical therapy include those with superficial onychomycosis, distal lateral subungual onychomycosis that involves less than 50% of the nail plate surface area (without matrix involvement and a nail plate thickness less than 2 mm), and only up to 3 or 4 nails affected.6 In patients who have contraindications to oral therapy, topical therapy may be the only treatment option. To maximize efficacy of FDA-approved topical agents for onychomycosis therapy, patient education is of utmost importance. Failure to properly counsel the patient on proper medication application may result in decreased antifungal efficacy; poor patient compliance due to lack of improvement; and progression of disease, leading to increased onychodystrophy and pain.
Before initiating therapy, patients should be counseled that treatment with topical drugs is long, requiring daily application of the medication for 6 months for fingernails and 12 months for toenails, based on average nail growth rates (2–3 mm per month for fingernails; 1 mm per month for toenails).7 Patients also are advised to avoid nail polish application during the course of therapy, as clinical trials were performed without nail polish and the true efficacy with nail polish is unknown.8-10 Because patients who have had onychomycosis for shorter durations generally have better cure rates than those who have disease for longer durations, it is prudent to initiate topical therapy as early as possible.11,12 Treating the feet with an antifungal while treating the nails for onychomycosis further enhances efficacy.13,14 There are 3 FDA-approved topical therapies for onychomycosis: ciclopirox nail lacquer 8%, efinaconazole solution 10%, and tavaborole solution 5%.15-17
Ciclopirox is a hydroxypyridone with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against dermatophytes, NDMs, yeasts, and bacteria. Its mechanism of action is to chelate polyvalent cations, such as Fe3+, and inhibit fungal metal-dependent enzymes responsible for the degradation of toxic metabolites.15 Ciclopirox nail lacquer 8% was FDA approved for the treatment of onychomycosis in 1999, making it the first topical approved for this purpose. Its indication is for immunocompetent patients with mild to moderate onychomycosis (Trichophyton rubrum) without lunula involvement, with mycologic cure rates of 29% to 36% and complete cure rates of 5.5% to 8.5% (toenails).15 It is the only FDA-approved topical treatment for both fingernails and toenails. Using a brush applicator, it is applied daily to the nail plate and its undersurface, hyponychium, and 5 mm of the surrounding skin. It is important to counsel the patient to remove the lacquer from the nail plate weekly because failure to do so will result in accumulation of numerous layers of medication, such that the active drug cannot reach the site of infection (Figures 1 and 2). The nail plate also should be trimmed and filed weekly by the patient, with monthly clipping/debridement by a physician recommended.6,15


Efinaconazole is a triazole with antifungal activity against dermatophytes, NDMs, and Candida species. Its mechanism of action is inhibition of lanosterol 14α-demethylase, an enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of ergosterol, which is a component of the fungal cell membrane. Efinaconazole solution 10% was FDA approved in June 2014 for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis due to T rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes, with package insert mycologic cure rates of 53.4% to 55.2% and complete cure rates of 15.2% to 17.8%.9,16 It is applied with a brush applicator to the nail plate, as well as its undersurface, nail folds, and hyponychium. Two drops are recommended for the great toenail and one drop for all other toenails, and no removal of the solution or debridement is required.6,16
Tavaborole is a benzoxaborole with antifungal activity against dermatophytes, NDMs, and yeasts. Its mechanism of action is inhibition of fungal aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetase, thus impeding protein synthesis.18 Tavaborole solution 5% was FDA approved in July 2014 for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis due to T rubrum and T mentagrophytes, with mycologic cure rates of 31.1% and 35.9% and complete cure rates of 6.5% and 9.1%, respectively.11,17 It is applied with a glass pointed-tip dropper to the nail plate, such that the entire nail is covered as well as under the nail tip. No removal of the solution or debridement is required.17
Topical therapies for onychomycosis require long treatment durations, thus excellent compliance and adherence to the treatment protocol are vital to maximize efficacy. Dermatologists who prescribe ciclopirox nail lacquer 8% should counsel patients to remove the lacquer with alcohol weekly, such that the antifungal penetrates the nail plate to reach the site of infection. Monthly debridement also must be clarified before initiating therapy. With all topical therapy for onychomycosis, it is important to treat early, treat concurrently for tinea pedis, and avoid use of nail polish so that patients have the best possible cure rates.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Onychomycosis: diagnosis and therapy. In: Razzaghi-Abyaneh M, Shams-Ghahfarokhi M, Rai M, eds. Medical Mycology: Current Trends and Future Prospects. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2015:28.
- Scher RK, Rich P, Pariser D, et al. The epidemiology, etiology, and pathophysiology of onychomycosis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2013;32(2 suppl 1):S2-S4.
- Lamisil [package insert]. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; 1997.
- Sporanox [package insert]. Titusville, NJ: Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2001.
- National Institutes of Health. Terbinafine. LiverTox website. https://livertox.nlm.nih.gov/Terbinafine.htm. Accessed November 7, 2018.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Onychomycosis: topical therapy and devices. In: Rubin AI, Jellinek NJ, Daniel CR III, et al, eds. Scher and Daniel’s Nails: Diagnosis, Surgery, Therapy. 4th ed. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2018:173-184.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Nail growth evaluation and factors affecting nail growth. In: Humbert P, Fanian F, Maibach HI, et al, eds. Agache’s Measuring the Skin. 2nd ed. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2017:867-881.
- Gupta AK, Elewski BE, Sugarman JL, et al. The efficacy and safety of efinaconazole 10% solution for treatment of mild to moderate onychomycosis: a pooled analysis of two phase 3 randomized trials. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:815-820.
- Elewski BE, Rich P, Pollak R, et al. Efinaconazole 10% solution in the treatment of toenail onychomycosis: two phase III multicenter, randomized, double-blind studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:600-608.
- Elewski BE, Aly R, Baldwin SL, et al. Efficacy and safety of tavaborole topical solution, 5%, a novel boron-based antifungal agent, for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis: results from 2 randomized phase-III studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:62-69.
- Rich P. Efinaconazole topical solution, 10%: the benefits of treating onychomycosis early. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:58-62.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Efinaconazole 10% topical solution for the topical treatment of onychomycosis of the toenail. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2015;8:719-731.
- Del Rosso JQ. Onychomycosis of toenails and post-hoc analyses with efinaconazole 10% solution once-daily treatment: impact of disease severity and other concomitant associated factors on selection of therapy and therapeutic outcomes. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9:42.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Management of onychomycosis and co-existing tinea pedis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:492-494.
- Penlac [package insert]. Berwyn, PA: Dermik Laboratories; 2004.
- Jublia [package insert]. Bridgewater, NJ: Valeant Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2014.
- Kerydin [package insert]. Palo Alto, CA: Anacor Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2014.
- Rock FL, Mao W, Yaremchuk A, et al. An antifungal agent inhibits an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase by trapping tRNA in the editing site. Science. 2007;316:1759-1761.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Onychomycosis: diagnosis and therapy. In: Razzaghi-Abyaneh M, Shams-Ghahfarokhi M, Rai M, eds. Medical Mycology: Current Trends and Future Prospects. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2015:28.
- Scher RK, Rich P, Pariser D, et al. The epidemiology, etiology, and pathophysiology of onychomycosis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2013;32(2 suppl 1):S2-S4.
- Lamisil [package insert]. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; 1997.
- Sporanox [package insert]. Titusville, NJ: Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2001.
- National Institutes of Health. Terbinafine. LiverTox website. https://livertox.nlm.nih.gov/Terbinafine.htm. Accessed November 7, 2018.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Onychomycosis: topical therapy and devices. In: Rubin AI, Jellinek NJ, Daniel CR III, et al, eds. Scher and Daniel’s Nails: Diagnosis, Surgery, Therapy. 4th ed. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2018:173-184.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Nail growth evaluation and factors affecting nail growth. In: Humbert P, Fanian F, Maibach HI, et al, eds. Agache’s Measuring the Skin. 2nd ed. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2017:867-881.
- Gupta AK, Elewski BE, Sugarman JL, et al. The efficacy and safety of efinaconazole 10% solution for treatment of mild to moderate onychomycosis: a pooled analysis of two phase 3 randomized trials. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:815-820.
- Elewski BE, Rich P, Pollak R, et al. Efinaconazole 10% solution in the treatment of toenail onychomycosis: two phase III multicenter, randomized, double-blind studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:600-608.
- Elewski BE, Aly R, Baldwin SL, et al. Efficacy and safety of tavaborole topical solution, 5%, a novel boron-based antifungal agent, for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis: results from 2 randomized phase-III studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:62-69.
- Rich P. Efinaconazole topical solution, 10%: the benefits of treating onychomycosis early. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:58-62.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Efinaconazole 10% topical solution for the topical treatment of onychomycosis of the toenail. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2015;8:719-731.
- Del Rosso JQ. Onychomycosis of toenails and post-hoc analyses with efinaconazole 10% solution once-daily treatment: impact of disease severity and other concomitant associated factors on selection of therapy and therapeutic outcomes. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9:42.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Management of onychomycosis and co-existing tinea pedis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14:492-494.
- Penlac [package insert]. Berwyn, PA: Dermik Laboratories; 2004.
- Jublia [package insert]. Bridgewater, NJ: Valeant Pharmaceuticals, LLC; 2014.
- Kerydin [package insert]. Palo Alto, CA: Anacor Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2014.
- Rock FL, Mao W, Yaremchuk A, et al. An antifungal agent inhibits an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase by trapping tRNA in the editing site. Science. 2007;316:1759-1761.