User login
A wearable pulsed electromagnetic fields device reduced pain intensity and improved physical functioning in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis (OA) in a double-blind, randomized trial.
The commercially available device (ActiPatch, Bioelectronics Corp.) did not improve patients’ mental health, but significantly reduced patients’ intake of NSAIDs and analgesics, compared with placebo.
“Although NSAIDs remain the gold standard for the treatment of pain in OA, there is increasing need to find conservative and alternative approaches, in order to avoid the toxicity associated with the chronic use of the analgesics, mostly in the elderly population,” wrote Dr. Gian Luca Bagnato of the University of Messina (Italy) and his colleagues (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2015 Dec 24. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev426).
Pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) therapy has been shown to reduce chondrocyte apoptosis and MMP-13 expression of knee cartilage and favorably affect cartilage homeostasis in animal models, but data regarding osteoarthritis (OA) pain and function in humans are mixed.
A recent systematic review found no effect in all 14 trials analyzed, but when only high-quality randomized clinical trials were included, PEMF provided significantly better pain relief at 4 and 8 weeks and better function at 8 weeks than did placebo (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2013;52[5]:815-24).
Not only has the quality of trials varied, so has the PEMF pulse frequency and duration used in trials, “further limiting the possibility of comparing efficacy and safety,” Dr. Bagnato and associates observed.
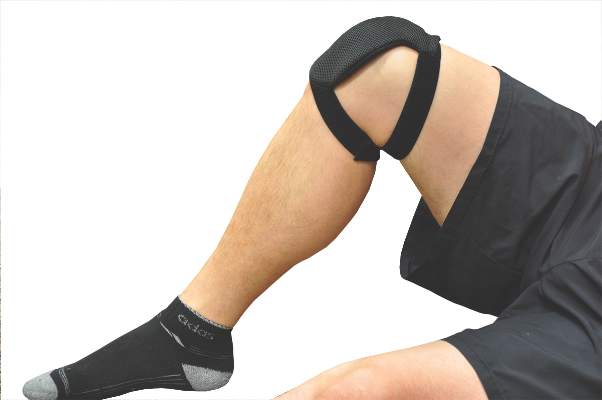
The current study evenly randomized 60 patients with radiologic evidence of knee OA and persistent pain to wear the PEMF or a placebo device for a minimum of 12 hours, mainly at night, with the device kept in place with a wrap. The active device emits a form of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation at a frequency of 27.12 MHz, a pulse rate of 1,000 Hz, and a burst width of 100 microsec.
Persistent pain was defined as a minimal mean score of 40 mm for global pain on the VAS (visual analog scale) and daily pain during the month prior to enrollment despite maximal tolerated doses of conventional medical therapy, including acetaminophen and/or an NSAID. The patients’ mean age was 67.7 years and mean OA duration 12 years.
The primary efficacy endpoint was reduction in pain intensity at 1 month on the VAS and WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index). The mean WOMAC total score at baseline was 132.9.
At 1 month, VAS pain scores were reduced 25.5% with the PEMF device and 3.6% with the placebo device. The standardized treatment effect size induced by PEMF therapy was –0.73 (95% confidence interval, –1.24 to –0.19), the investigators reported.
WOMAC pain subscale and total scores fell 23.4% and 18.4% with the PEMF device versus a 2.3% reduction for both scores with the placebo device. The standardized effect size was –0.61 for WOMAC pain (95% CI, –1.12 to –0.09) and –0.34 for WOMAC total score (95% CI, –0.85 to 0.17).
At 1 month, the mean Short Form-36 physical health score was significantly better in the PEMF group than in the placebo group (55.8 vs. 53.1; P = .024), while SF-36 mental health scores were nearly identical (43.8 vs. 43.6; P = .6).
Patients were allowed per protocol to take prescribed analgesic therapy as needed, but eight patients from the PEMF group stopped these medications, while one patient from the placebo group stopped medication and three started a new therapy for chronic pain. No adverse events were reported during the study.
“Given that our data are limited to a low number of participants and the long-term efficacy of the wearable device is unknown, the generalizability of the results needs to be confirmed in a larger clinical trial with a longer duration of treatment,” Dr. Bagnato and his coauthors concluded. “However, the use of a wearable PEMF therapy in knee OA can be considered as an alternative safe and effective therapy in knee OA, providing the possibility for home-based management of pain, compared with previous studies.”
Nonpharmacologic therapies and pharmacologic agents are helpful for a large segment of the population with knee osteoarthritis (OA). In contrast to rheumatoid arthritis for which there are now many truly effective agents, the physician and patient are frustrated with the borderline effective therapies for a proportion of those poorly responsive patients on present day therapy with knee OA. Joint replacement continues to be the most effective treatment for hip and knee OA, but many have postoperative joint pain. In addition, the population of patients with pain from knee OA is growing with the aging population and already exceeds the number that can be accommodated by our present physicians, without even considering the financial burden.

|
Dr. Roy D. Altman |
Until something is of proven benefit, researchers continue to fine-tune existing programs to maximize their benefit. One of the nonpharmacologic therapies is a wearable device that delivers pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF). Clinical trials supporting pulsed electrical stimulation for knee OA have been present for more than 20 years (J Rheumatol. 1993 Mar;20:456-60 and J Rheumatol. 1995 Sep;22:1757-61). Indeed, the devices have been commercially available for more than 10 years.
In the conclusions of a 2013 Cochrane review, “... electromagnetic field treatment may provide moderate benefit for osteoarthritis sufferers in terms of pain relief,” with more data needed for physical function and quality of life (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;Dec 14;12:CD003523). The studies tended to be small, as there were nine studies including 636 patients in the review. One of the problems in performing a systematic review is that there have been a variety of devices tested that vary in their functions. Examples of devices that have been tested in knee OA are the ActiPatch (used in the study by Dr. Bagnato and his colleagues), BioniCare, EarthPulse, MAGCELL ARTHRO, and Magnetofield devices. They vary in structure, size, frequency (Hz) per area, magnetic flux density, time intervals of each frequency (burst milliseconds), voltage, decibel level, duty cycle, contact time and intervals, wearing device for minutes/hours, etc. Blinding of when the device is on or off in studies has been complicated.
Dr. Bagnato and his associates add to the limited literature with a well-designed and well-conducted but relatively small trial. However, until there are more data, it will be difficult to use these devices on a regular basis, as they tend to be quite expensive and require a strong commitment of time and energy by the patient, who often thinks of the device as a form of alternative medicine.
Dr. Roy D. Altman is professor emeritus of medicine in the division of rheumatology and immunology at the University of California, Los Angeles. He has no relevant disclosures.
Nonpharmacologic therapies and pharmacologic agents are helpful for a large segment of the population with knee osteoarthritis (OA). In contrast to rheumatoid arthritis for which there are now many truly effective agents, the physician and patient are frustrated with the borderline effective therapies for a proportion of those poorly responsive patients on present day therapy with knee OA. Joint replacement continues to be the most effective treatment for hip and knee OA, but many have postoperative joint pain. In addition, the population of patients with pain from knee OA is growing with the aging population and already exceeds the number that can be accommodated by our present physicians, without even considering the financial burden.

|
Dr. Roy D. Altman |
Until something is of proven benefit, researchers continue to fine-tune existing programs to maximize their benefit. One of the nonpharmacologic therapies is a wearable device that delivers pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF). Clinical trials supporting pulsed electrical stimulation for knee OA have been present for more than 20 years (J Rheumatol. 1993 Mar;20:456-60 and J Rheumatol. 1995 Sep;22:1757-61). Indeed, the devices have been commercially available for more than 10 years.
In the conclusions of a 2013 Cochrane review, “... electromagnetic field treatment may provide moderate benefit for osteoarthritis sufferers in terms of pain relief,” with more data needed for physical function and quality of life (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;Dec 14;12:CD003523). The studies tended to be small, as there were nine studies including 636 patients in the review. One of the problems in performing a systematic review is that there have been a variety of devices tested that vary in their functions. Examples of devices that have been tested in knee OA are the ActiPatch (used in the study by Dr. Bagnato and his colleagues), BioniCare, EarthPulse, MAGCELL ARTHRO, and Magnetofield devices. They vary in structure, size, frequency (Hz) per area, magnetic flux density, time intervals of each frequency (burst milliseconds), voltage, decibel level, duty cycle, contact time and intervals, wearing device for minutes/hours, etc. Blinding of when the device is on or off in studies has been complicated.
Dr. Bagnato and his associates add to the limited literature with a well-designed and well-conducted but relatively small trial. However, until there are more data, it will be difficult to use these devices on a regular basis, as they tend to be quite expensive and require a strong commitment of time and energy by the patient, who often thinks of the device as a form of alternative medicine.
Dr. Roy D. Altman is professor emeritus of medicine in the division of rheumatology and immunology at the University of California, Los Angeles. He has no relevant disclosures.
Nonpharmacologic therapies and pharmacologic agents are helpful for a large segment of the population with knee osteoarthritis (OA). In contrast to rheumatoid arthritis for which there are now many truly effective agents, the physician and patient are frustrated with the borderline effective therapies for a proportion of those poorly responsive patients on present day therapy with knee OA. Joint replacement continues to be the most effective treatment for hip and knee OA, but many have postoperative joint pain. In addition, the population of patients with pain from knee OA is growing with the aging population and already exceeds the number that can be accommodated by our present physicians, without even considering the financial burden.

|
Dr. Roy D. Altman |
Until something is of proven benefit, researchers continue to fine-tune existing programs to maximize their benefit. One of the nonpharmacologic therapies is a wearable device that delivers pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF). Clinical trials supporting pulsed electrical stimulation for knee OA have been present for more than 20 years (J Rheumatol. 1993 Mar;20:456-60 and J Rheumatol. 1995 Sep;22:1757-61). Indeed, the devices have been commercially available for more than 10 years.
In the conclusions of a 2013 Cochrane review, “... electromagnetic field treatment may provide moderate benefit for osteoarthritis sufferers in terms of pain relief,” with more data needed for physical function and quality of life (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;Dec 14;12:CD003523). The studies tended to be small, as there were nine studies including 636 patients in the review. One of the problems in performing a systematic review is that there have been a variety of devices tested that vary in their functions. Examples of devices that have been tested in knee OA are the ActiPatch (used in the study by Dr. Bagnato and his colleagues), BioniCare, EarthPulse, MAGCELL ARTHRO, and Magnetofield devices. They vary in structure, size, frequency (Hz) per area, magnetic flux density, time intervals of each frequency (burst milliseconds), voltage, decibel level, duty cycle, contact time and intervals, wearing device for minutes/hours, etc. Blinding of when the device is on or off in studies has been complicated.
Dr. Bagnato and his associates add to the limited literature with a well-designed and well-conducted but relatively small trial. However, until there are more data, it will be difficult to use these devices on a regular basis, as they tend to be quite expensive and require a strong commitment of time and energy by the patient, who often thinks of the device as a form of alternative medicine.
Dr. Roy D. Altman is professor emeritus of medicine in the division of rheumatology and immunology at the University of California, Los Angeles. He has no relevant disclosures.
A wearable pulsed electromagnetic fields device reduced pain intensity and improved physical functioning in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis (OA) in a double-blind, randomized trial.
The commercially available device (ActiPatch, Bioelectronics Corp.) did not improve patients’ mental health, but significantly reduced patients’ intake of NSAIDs and analgesics, compared with placebo.
“Although NSAIDs remain the gold standard for the treatment of pain in OA, there is increasing need to find conservative and alternative approaches, in order to avoid the toxicity associated with the chronic use of the analgesics, mostly in the elderly population,” wrote Dr. Gian Luca Bagnato of the University of Messina (Italy) and his colleagues (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2015 Dec 24. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev426).
Pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) therapy has been shown to reduce chondrocyte apoptosis and MMP-13 expression of knee cartilage and favorably affect cartilage homeostasis in animal models, but data regarding osteoarthritis (OA) pain and function in humans are mixed.
A recent systematic review found no effect in all 14 trials analyzed, but when only high-quality randomized clinical trials were included, PEMF provided significantly better pain relief at 4 and 8 weeks and better function at 8 weeks than did placebo (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2013;52[5]:815-24).
Not only has the quality of trials varied, so has the PEMF pulse frequency and duration used in trials, “further limiting the possibility of comparing efficacy and safety,” Dr. Bagnato and associates observed.
The current study evenly randomized 60 patients with radiologic evidence of knee OA and persistent pain to wear the PEMF or a placebo device for a minimum of 12 hours, mainly at night, with the device kept in place with a wrap. The active device emits a form of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation at a frequency of 27.12 MHz, a pulse rate of 1,000 Hz, and a burst width of 100 microsec.
Persistent pain was defined as a minimal mean score of 40 mm for global pain on the VAS (visual analog scale) and daily pain during the month prior to enrollment despite maximal tolerated doses of conventional medical therapy, including acetaminophen and/or an NSAID. The patients’ mean age was 67.7 years and mean OA duration 12 years.
The primary efficacy endpoint was reduction in pain intensity at 1 month on the VAS and WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index). The mean WOMAC total score at baseline was 132.9.
At 1 month, VAS pain scores were reduced 25.5% with the PEMF device and 3.6% with the placebo device. The standardized treatment effect size induced by PEMF therapy was –0.73 (95% confidence interval, –1.24 to –0.19), the investigators reported.
WOMAC pain subscale and total scores fell 23.4% and 18.4% with the PEMF device versus a 2.3% reduction for both scores with the placebo device. The standardized effect size was –0.61 for WOMAC pain (95% CI, –1.12 to –0.09) and –0.34 for WOMAC total score (95% CI, –0.85 to 0.17).
At 1 month, the mean Short Form-36 physical health score was significantly better in the PEMF group than in the placebo group (55.8 vs. 53.1; P = .024), while SF-36 mental health scores were nearly identical (43.8 vs. 43.6; P = .6).
Patients were allowed per protocol to take prescribed analgesic therapy as needed, but eight patients from the PEMF group stopped these medications, while one patient from the placebo group stopped medication and three started a new therapy for chronic pain. No adverse events were reported during the study.
“Given that our data are limited to a low number of participants and the long-term efficacy of the wearable device is unknown, the generalizability of the results needs to be confirmed in a larger clinical trial with a longer duration of treatment,” Dr. Bagnato and his coauthors concluded. “However, the use of a wearable PEMF therapy in knee OA can be considered as an alternative safe and effective therapy in knee OA, providing the possibility for home-based management of pain, compared with previous studies.”
A wearable pulsed electromagnetic fields device reduced pain intensity and improved physical functioning in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis (OA) in a double-blind, randomized trial.
The commercially available device (ActiPatch, Bioelectronics Corp.) did not improve patients’ mental health, but significantly reduced patients’ intake of NSAIDs and analgesics, compared with placebo.
“Although NSAIDs remain the gold standard for the treatment of pain in OA, there is increasing need to find conservative and alternative approaches, in order to avoid the toxicity associated with the chronic use of the analgesics, mostly in the elderly population,” wrote Dr. Gian Luca Bagnato of the University of Messina (Italy) and his colleagues (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2015 Dec 24. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev426).
Pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) therapy has been shown to reduce chondrocyte apoptosis and MMP-13 expression of knee cartilage and favorably affect cartilage homeostasis in animal models, but data regarding osteoarthritis (OA) pain and function in humans are mixed.
A recent systematic review found no effect in all 14 trials analyzed, but when only high-quality randomized clinical trials were included, PEMF provided significantly better pain relief at 4 and 8 weeks and better function at 8 weeks than did placebo (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2013;52[5]:815-24).
Not only has the quality of trials varied, so has the PEMF pulse frequency and duration used in trials, “further limiting the possibility of comparing efficacy and safety,” Dr. Bagnato and associates observed.
The current study evenly randomized 60 patients with radiologic evidence of knee OA and persistent pain to wear the PEMF or a placebo device for a minimum of 12 hours, mainly at night, with the device kept in place with a wrap. The active device emits a form of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation at a frequency of 27.12 MHz, a pulse rate of 1,000 Hz, and a burst width of 100 microsec.
Persistent pain was defined as a minimal mean score of 40 mm for global pain on the VAS (visual analog scale) and daily pain during the month prior to enrollment despite maximal tolerated doses of conventional medical therapy, including acetaminophen and/or an NSAID. The patients’ mean age was 67.7 years and mean OA duration 12 years.
The primary efficacy endpoint was reduction in pain intensity at 1 month on the VAS and WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index). The mean WOMAC total score at baseline was 132.9.
At 1 month, VAS pain scores were reduced 25.5% with the PEMF device and 3.6% with the placebo device. The standardized treatment effect size induced by PEMF therapy was –0.73 (95% confidence interval, –1.24 to –0.19), the investigators reported.
WOMAC pain subscale and total scores fell 23.4% and 18.4% with the PEMF device versus a 2.3% reduction for both scores with the placebo device. The standardized effect size was –0.61 for WOMAC pain (95% CI, –1.12 to –0.09) and –0.34 for WOMAC total score (95% CI, –0.85 to 0.17).
At 1 month, the mean Short Form-36 physical health score was significantly better in the PEMF group than in the placebo group (55.8 vs. 53.1; P = .024), while SF-36 mental health scores were nearly identical (43.8 vs. 43.6; P = .6).
Patients were allowed per protocol to take prescribed analgesic therapy as needed, but eight patients from the PEMF group stopped these medications, while one patient from the placebo group stopped medication and three started a new therapy for chronic pain. No adverse events were reported during the study.
“Given that our data are limited to a low number of participants and the long-term efficacy of the wearable device is unknown, the generalizability of the results needs to be confirmed in a larger clinical trial with a longer duration of treatment,” Dr. Bagnato and his coauthors concluded. “However, the use of a wearable PEMF therapy in knee OA can be considered as an alternative safe and effective therapy in knee OA, providing the possibility for home-based management of pain, compared with previous studies.”
FROM RHEUMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Pulsed electromagnetic fields therapy is safe and effective in improving knee osteoarthritis symptoms.
Major finding: The mean treatment effect size was –0.73 in the VAS score and –0.34 in the WOMAC score.
Data source: Double-blind, randomized trial in 60 patients with knee osteoarthritis and persistent pain.
Disclosures: Bioelectronics provided the pulsed electromagnetic fields and placebo devices. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.