User login
Outpatient care represents the largest share of mental health treatment expenditures, and it continues to get larger, while components such as retail drug prescriptions and inpatient care have declined, according to the National Center of Health Statistics.
In 2014, outpatient care took a $65.5-billion slice (about 35%) out of the $186-billion mental health care spending pie, compared with the $51.1 billion (27%) spent on retail drug prescriptions, which was the next-largest portion. Inpatient care was third with $30.3 billion in spending (16% of the total), followed by residential care at $23.2 billion (12%), and insurance administration at $15.9 billion (9%), the NCHS reported in “Health, United States, 2016.”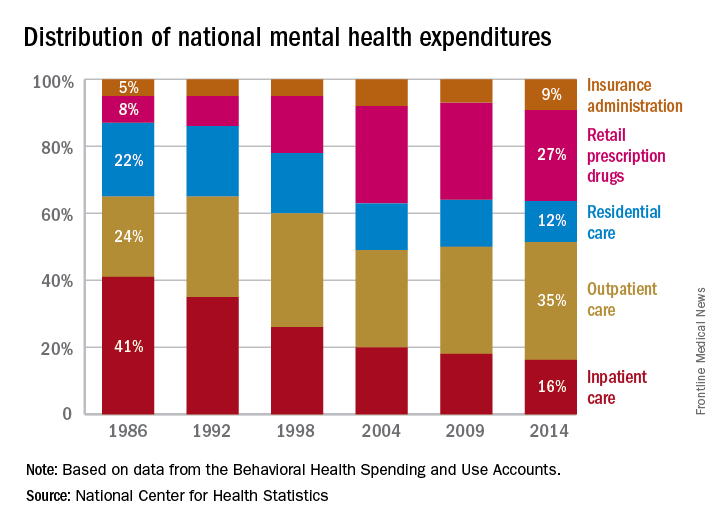
Outpatient care represents the largest share of mental health treatment expenditures, and it continues to get larger, while components such as retail drug prescriptions and inpatient care have declined, according to the National Center of Health Statistics.
In 2014, outpatient care took a $65.5-billion slice (about 35%) out of the $186-billion mental health care spending pie, compared with the $51.1 billion (27%) spent on retail drug prescriptions, which was the next-largest portion. Inpatient care was third with $30.3 billion in spending (16% of the total), followed by residential care at $23.2 billion (12%), and insurance administration at $15.9 billion (9%), the NCHS reported in “Health, United States, 2016.”
Outpatient care represents the largest share of mental health treatment expenditures, and it continues to get larger, while components such as retail drug prescriptions and inpatient care have declined, according to the National Center of Health Statistics.
In 2014, outpatient care took a $65.5-billion slice (about 35%) out of the $186-billion mental health care spending pie, compared with the $51.1 billion (27%) spent on retail drug prescriptions, which was the next-largest portion. Inpatient care was third with $30.3 billion in spending (16% of the total), followed by residential care at $23.2 billion (12%), and insurance administration at $15.9 billion (9%), the NCHS reported in “Health, United States, 2016.”