User login
Is it possible to get more exercise and still gain weight? In America it is.
The steady increase in obesity prevalence among adults in the United States has been exceeded over the last decade by the percentage of adults who are getting the recommended amount of exercise, according to the National Center for Health Statistics.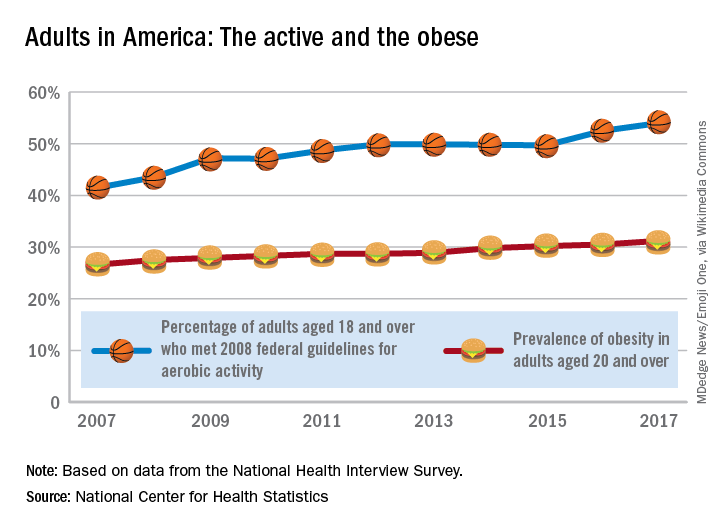
The 2008 guideline, “Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans” recommends that “adults perform at least 150 minutes a week of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity, 75 minutes a week of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate- and vigorous-intensity aerobic activity, performed in episodes of at least 10 minutes and preferably should be spread throughout the week,” the NCHS noted.
Is it possible to get more exercise and still gain weight? In America it is.
The steady increase in obesity prevalence among adults in the United States has been exceeded over the last decade by the percentage of adults who are getting the recommended amount of exercise, according to the National Center for Health Statistics.
The 2008 guideline, “Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans” recommends that “adults perform at least 150 minutes a week of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity, 75 minutes a week of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate- and vigorous-intensity aerobic activity, performed in episodes of at least 10 minutes and preferably should be spread throughout the week,” the NCHS noted.
Is it possible to get more exercise and still gain weight? In America it is.
The steady increase in obesity prevalence among adults in the United States has been exceeded over the last decade by the percentage of adults who are getting the recommended amount of exercise, according to the National Center for Health Statistics.
The 2008 guideline, “Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans” recommends that “adults perform at least 150 minutes a week of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity, 75 minutes a week of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate- and vigorous-intensity aerobic activity, performed in episodes of at least 10 minutes and preferably should be spread throughout the week,” the NCHS noted.