User login
New Therapeutic Frontiers in the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Rossi CM, Santacroce G, Lenti MV, di Sabatino A. Eosinophilic esophagitis in the era of biologics. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;18(6):271-281. doi:10.1080/17474124.2024.2374471
Dellon ES, Liacouras CA, Molina-Infante J, et al. Updated International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Proceedings of the AGREE Conference. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(4):1022-1033.e10. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2018.07.009
Geow R, Arena G, Siah C, Picardo S. A retrospective real-world study on the safety and efficacy of budesonide orodispersible tablets for the induction therapy of eosinophilic oesophagitis. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2024;17:17562848241290346. doi:10.1177/17562848241290346
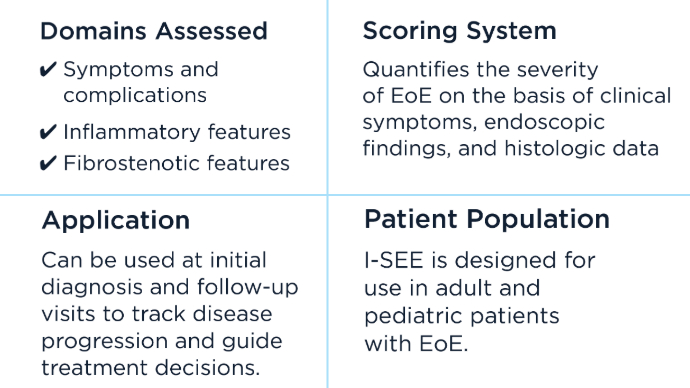
Sato H, Dellon ES, Aceves SS, et al. Clinical and molecular correlates of the Index of Severity for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024;154(2):375-386.e4. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2024.04.025
Dellon ES, Khoury P, Muir AB, et al. A Clinical Severity Index for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Development, Consensus, and Future Directions. Gastroenterology. 2022;163(1):59-76. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.03.025
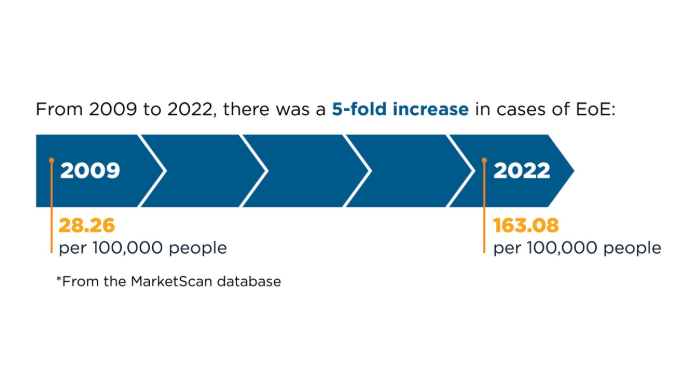
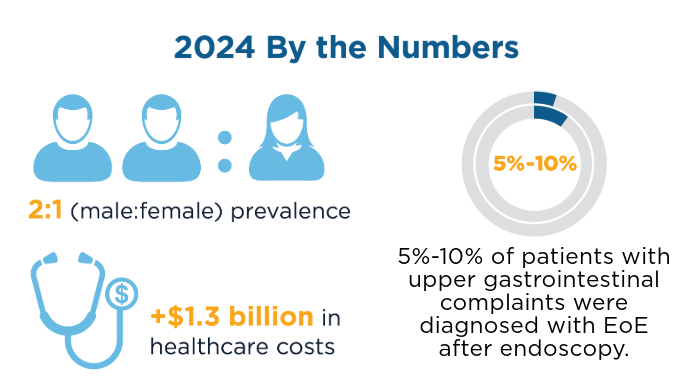
Thel HL, Anderson C, Xue AZ, Jensen ET, Dellon ES. Prevalence and Costs of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025;23(2)272-280. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2024.09.031
Yang E-J, Jung KW. Role of endoscopy in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Endosc. 2025;58(1):1-9. doi.org/10.5946/ce.2024.023
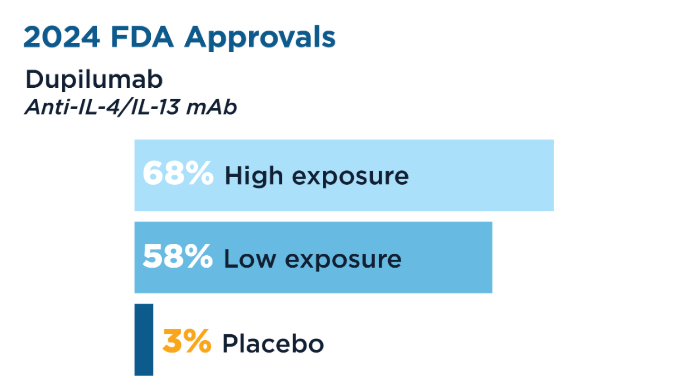
Chehade M, Dellon ES, Spergel JM, et al. Dupilumab for Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Patients 1 to 11 Years of Age. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(24):2239-2251. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2312282
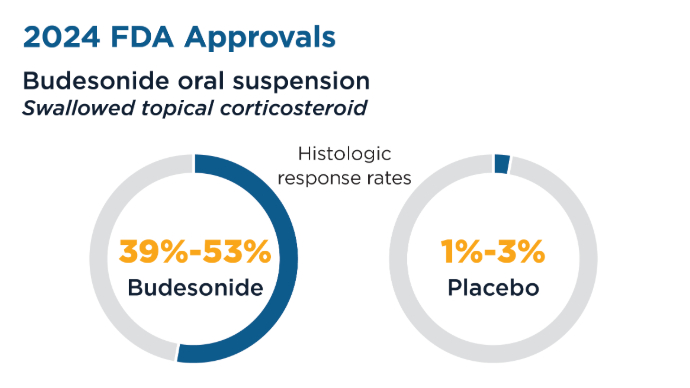
Hirano I, Collins MH, Katzka DA, et al; ORBIT1/SHP621-301 Investigators. Budesonide Oral Suspension Improves Outcomes in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Results from a Phase 3 Trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(3):525-534.e10. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.04.022
Dellon ES, Katzka DA, Collins MH, et al; MP-101-06 Investigators. Budesonide Oral Suspension Improves Symptomatic, Endoscopic, and Histologic Parameters Compared With Placebo in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(4):776-786.e5. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.11.021
Dellon ES, Charriez CM, Zhang S, et al. Cendakimab efficacy and safety in adult and adolescent patients with eosinophilic esophagitis 48-week results from the randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study (late-breaking abstract). Paper presented at: ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. October 25-30, 2024.
National Institutes of Health, National Library of Medicine, Cinicaltrials.gov website. Efficacy and Safety of Tezepelumab in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis (CROSSING). ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT05583227. Published December 2024. Accessed February 3, 2025. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05583227
National Institutes of Health, National Library of Medicine, Cinicaltrials.gov website. A Study to Investigate the Efficacy and Safety of NSI-8226 in Adults with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT06598462. Published November 2024. Accessed February 3, 2025. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06598462
National Institutes of Health, National Library of Medicine, Cinicaltrials.gov website. A Study of CDX-0519 in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EvolvE). ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT05774184. Published June 2024. Accessed February 3, 2025. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05774184
Rossi CM, Santacroce G, Lenti MV, di Sabatino A. Eosinophilic esophagitis in the era of biologics. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;18(6):271-281. doi:10.1080/17474124.2024.2374471
Dellon ES, Liacouras CA, Molina-Infante J, et al. Updated International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Proceedings of the AGREE Conference. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(4):1022-1033.e10. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2018.07.009
Geow R, Arena G, Siah C, Picardo S. A retrospective real-world study on the safety and efficacy of budesonide orodispersible tablets for the induction therapy of eosinophilic oesophagitis. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2024;17:17562848241290346. doi:10.1177/17562848241290346
Sato H, Dellon ES, Aceves SS, et al. Clinical and molecular correlates of the Index of Severity for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024;154(2):375-386.e4. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2024.04.025
Dellon ES, Khoury P, Muir AB, et al. A Clinical Severity Index for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Development, Consensus, and Future Directions. Gastroenterology. 2022;163(1):59-76. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.03.025
Thel HL, Anderson C, Xue AZ, Jensen ET, Dellon ES. Prevalence and Costs of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025;23(2)272-280. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2024.09.031
Yang E-J, Jung KW. Role of endoscopy in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Endosc. 2025;58(1):1-9. doi.org/10.5946/ce.2024.023
Chehade M, Dellon ES, Spergel JM, et al. Dupilumab for Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Patients 1 to 11 Years of Age. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(24):2239-2251. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2312282
Hirano I, Collins MH, Katzka DA, et al; ORBIT1/SHP621-301 Investigators. Budesonide Oral Suspension Improves Outcomes in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Results from a Phase 3 Trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(3):525-534.e10. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.04.022
Dellon ES, Katzka DA, Collins MH, et al; MP-101-06 Investigators. Budesonide Oral Suspension Improves Symptomatic, Endoscopic, and Histologic Parameters Compared With Placebo in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(4):776-786.e5. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.11.021
Dellon ES, Charriez CM, Zhang S, et al. Cendakimab efficacy and safety in adult and adolescent patients with eosinophilic esophagitis 48-week results from the randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study (late-breaking abstract). Paper presented at: ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. October 25-30, 2024.
National Institutes of Health, National Library of Medicine, Cinicaltrials.gov website. Efficacy and Safety of Tezepelumab in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis (CROSSING). ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT05583227. Published December 2024. Accessed February 3, 2025. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05583227
National Institutes of Health, National Library of Medicine, Cinicaltrials.gov website. A Study to Investigate the Efficacy and Safety of NSI-8226 in Adults with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT06598462. Published November 2024. Accessed February 3, 2025. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06598462
National Institutes of Health, National Library of Medicine, Cinicaltrials.gov website. A Study of CDX-0519 in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EvolvE). ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT05774184. Published June 2024. Accessed February 3, 2025. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05774184
Rossi CM, Santacroce G, Lenti MV, di Sabatino A. Eosinophilic esophagitis in the era of biologics. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;18(6):271-281. doi:10.1080/17474124.2024.2374471
Dellon ES, Liacouras CA, Molina-Infante J, et al. Updated International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Proceedings of the AGREE Conference. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(4):1022-1033.e10. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2018.07.009
Geow R, Arena G, Siah C, Picardo S. A retrospective real-world study on the safety and efficacy of budesonide orodispersible tablets for the induction therapy of eosinophilic oesophagitis. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2024;17:17562848241290346. doi:10.1177/17562848241290346
Sato H, Dellon ES, Aceves SS, et al. Clinical and molecular correlates of the Index of Severity for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024;154(2):375-386.e4. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2024.04.025
Dellon ES, Khoury P, Muir AB, et al. A Clinical Severity Index for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Development, Consensus, and Future Directions. Gastroenterology. 2022;163(1):59-76. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.03.025
Thel HL, Anderson C, Xue AZ, Jensen ET, Dellon ES. Prevalence and Costs of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025;23(2)272-280. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2024.09.031
Yang E-J, Jung KW. Role of endoscopy in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Endosc. 2025;58(1):1-9. doi.org/10.5946/ce.2024.023
Chehade M, Dellon ES, Spergel JM, et al. Dupilumab for Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Patients 1 to 11 Years of Age. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(24):2239-2251. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2312282
Hirano I, Collins MH, Katzka DA, et al; ORBIT1/SHP621-301 Investigators. Budesonide Oral Suspension Improves Outcomes in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Results from a Phase 3 Trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(3):525-534.e10. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.04.022
Dellon ES, Katzka DA, Collins MH, et al; MP-101-06 Investigators. Budesonide Oral Suspension Improves Symptomatic, Endoscopic, and Histologic Parameters Compared With Placebo in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(4):776-786.e5. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.11.021
Dellon ES, Charriez CM, Zhang S, et al. Cendakimab efficacy and safety in adult and adolescent patients with eosinophilic esophagitis 48-week results from the randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study (late-breaking abstract). Paper presented at: ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. October 25-30, 2024.
National Institutes of Health, National Library of Medicine, Cinicaltrials.gov website. Efficacy and Safety of Tezepelumab in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis (CROSSING). ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT05583227. Published December 2024. Accessed February 3, 2025. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05583227
National Institutes of Health, National Library of Medicine, Cinicaltrials.gov website. A Study to Investigate the Efficacy and Safety of NSI-8226 in Adults with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT06598462. Published November 2024. Accessed February 3, 2025. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06598462
National Institutes of Health, National Library of Medicine, Cinicaltrials.gov website. A Study of CDX-0519 in Patients With Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EvolvE). ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT05774184. Published June 2024. Accessed February 3, 2025. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05774184
New Therapeutic Frontiers in the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
New Therapeutic Frontiers in the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis