User login
The global incidence of multiple myeloma rose by 126% from 1990 to 2016, with the largest regional increases occurring in East Asia and tropical Latin America, according to data from the Global Burden of Disease 2016 study.
East Asia (China, North Korea, and Taiwan) saw incident cases of multiple myeloma jump by 262% – up to 1.0 per 100,000 population – from 1990 to 2016, which was the largest increase among any of the 21 global regions; tropical Latin America’s 256% rise took its age-standardized incidence rate to 1.8 per 100,000. Worldwide, incidence of multiple myeloma was 2.1 cases per 100,000 in 2016, Andrew J. Cowan, MD, and his associates reported in JAMA Oncology.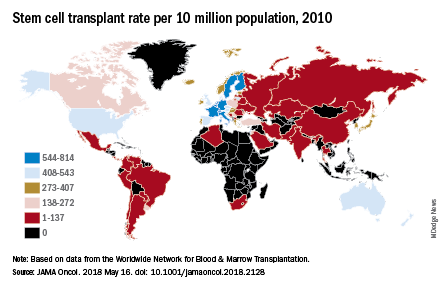
They also looked at treatment availability, with data on stem cell transplants for 2010 coming from the Worldwide Network for Blood & Marrow Transplantation (Lancet Haematol. 2015 Mar;2[3]:e91-100). The countries with the highest rates for all indications that year were Israel (814 per 10 million population), Italy (671), Germany (665), Sweden (625), and the Netherlands (614).
“Some regions of the world lack access to stem cell transplantation entirely, particularly sub-Saharan Africa (with the exception of South Africa),” wrote Dr. Cowan of the University of Washington, Seattle, and his associates.
The approval status of lenalidomide (Revlimid) and bortezomib (Velcade) in 2016 was used as a surrogate for availability of drug treatment: Lenalidomide had been approved in 73 countries out of 195 countries and territories and bortezomib in 103 countries. “On a global level, there are marked discrepancies in the availability of effective therapies. In addition to ensuring universal access to health care … it is imperative to at least ensure access to highly effective medications,” they wrote.
Dr. Cowan reported that he has received research funding from Janssen and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Cowan AJ et al. JAMA Oncol. 2018 May 16. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2128.
The global incidence of multiple myeloma rose by 126% from 1990 to 2016, with the largest regional increases occurring in East Asia and tropical Latin America, according to data from the Global Burden of Disease 2016 study.
East Asia (China, North Korea, and Taiwan) saw incident cases of multiple myeloma jump by 262% – up to 1.0 per 100,000 population – from 1990 to 2016, which was the largest increase among any of the 21 global regions; tropical Latin America’s 256% rise took its age-standardized incidence rate to 1.8 per 100,000. Worldwide, incidence of multiple myeloma was 2.1 cases per 100,000 in 2016, Andrew J. Cowan, MD, and his associates reported in JAMA Oncology.
They also looked at treatment availability, with data on stem cell transplants for 2010 coming from the Worldwide Network for Blood & Marrow Transplantation (Lancet Haematol. 2015 Mar;2[3]:e91-100). The countries with the highest rates for all indications that year were Israel (814 per 10 million population), Italy (671), Germany (665), Sweden (625), and the Netherlands (614).
“Some regions of the world lack access to stem cell transplantation entirely, particularly sub-Saharan Africa (with the exception of South Africa),” wrote Dr. Cowan of the University of Washington, Seattle, and his associates.
The approval status of lenalidomide (Revlimid) and bortezomib (Velcade) in 2016 was used as a surrogate for availability of drug treatment: Lenalidomide had been approved in 73 countries out of 195 countries and territories and bortezomib in 103 countries. “On a global level, there are marked discrepancies in the availability of effective therapies. In addition to ensuring universal access to health care … it is imperative to at least ensure access to highly effective medications,” they wrote.
Dr. Cowan reported that he has received research funding from Janssen and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Cowan AJ et al. JAMA Oncol. 2018 May 16. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2128.
The global incidence of multiple myeloma rose by 126% from 1990 to 2016, with the largest regional increases occurring in East Asia and tropical Latin America, according to data from the Global Burden of Disease 2016 study.
East Asia (China, North Korea, and Taiwan) saw incident cases of multiple myeloma jump by 262% – up to 1.0 per 100,000 population – from 1990 to 2016, which was the largest increase among any of the 21 global regions; tropical Latin America’s 256% rise took its age-standardized incidence rate to 1.8 per 100,000. Worldwide, incidence of multiple myeloma was 2.1 cases per 100,000 in 2016, Andrew J. Cowan, MD, and his associates reported in JAMA Oncology.
They also looked at treatment availability, with data on stem cell transplants for 2010 coming from the Worldwide Network for Blood & Marrow Transplantation (Lancet Haematol. 2015 Mar;2[3]:e91-100). The countries with the highest rates for all indications that year were Israel (814 per 10 million population), Italy (671), Germany (665), Sweden (625), and the Netherlands (614).
“Some regions of the world lack access to stem cell transplantation entirely, particularly sub-Saharan Africa (with the exception of South Africa),” wrote Dr. Cowan of the University of Washington, Seattle, and his associates.
The approval status of lenalidomide (Revlimid) and bortezomib (Velcade) in 2016 was used as a surrogate for availability of drug treatment: Lenalidomide had been approved in 73 countries out of 195 countries and territories and bortezomib in 103 countries. “On a global level, there are marked discrepancies in the availability of effective therapies. In addition to ensuring universal access to health care … it is imperative to at least ensure access to highly effective medications,” they wrote.
Dr. Cowan reported that he has received research funding from Janssen and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Cowan AJ et al. JAMA Oncol. 2018 May 16. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2128.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY