User login
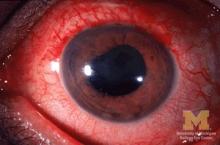
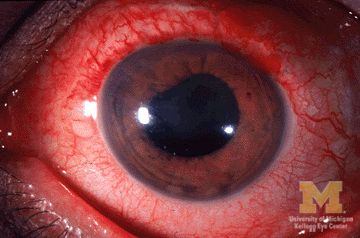
Two anti–tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibodies, adalimumab and infliximab, showed evidence of being markedly more effective than the anti-TNF–receptor inhibitor etanercept at reducing the rate of anterior uveitis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis in a retrospective Swedish cohort study.
To compare the efficacy of the three TNF inhibitors, researchers analyzed data in nationwide Swedish population-based registries for 1,365 ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients who initiated treatment during a 7-year period. Treatment began with adalimumab in 406 patients, infliximab in 605, and etanercept in 354, said Elisabeth Lie, MD, of the department of rheumatology and inflammation research at the University of Gothenburg (Sweden), and her associates.
“Compared with the rates [of anterior uveitis] pretreatment, the rates increased when initiating treatment with etanercept, but decreased when starting adalimumab or infliximab,” the investigators wrote (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Mar 2. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210931).
The biological explanation for this discrepancy is unclear. It is possible that etanercept simply isn’t as protective as the other two agents, but it also appears possible that etanercept may act paradoxically to induce anterior uveitis in some patients. However, it should be noted that “previous studies have indicated that etanercept still reduces the number of uveitis flares more effectively than placebo,” Dr. Lie and her associates noted.
Regardless of the underlying reason, these findings, taken together with those of previous studies, “support the choice of another TNF inhibitor than etanercept in patients with AS with a history of anterior uveitis,” they said.
Dr. Lie also reported the results at the 2015 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting.
This study was supported by the Swedish Research Council, Gothenburg University, the Stockholm County Council, the Swedish National Rheumatism Association, the Swedish COMBINE public-private research program, the Swedish Cancer Society, the EU-IMI BT Cure project, and the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research. Dr. Lie reported receiving personal fees from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Hospira, Pfizer, and UCB; her associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
Two anti–tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibodies, adalimumab and infliximab, showed evidence of being markedly more effective than the anti-TNF–receptor inhibitor etanercept at reducing the rate of anterior uveitis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis in a retrospective Swedish cohort study.
To compare the efficacy of the three TNF inhibitors, researchers analyzed data in nationwide Swedish population-based registries for 1,365 ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients who initiated treatment during a 7-year period. Treatment began with adalimumab in 406 patients, infliximab in 605, and etanercept in 354, said Elisabeth Lie, MD, of the department of rheumatology and inflammation research at the University of Gothenburg (Sweden), and her associates.
“Compared with the rates [of anterior uveitis] pretreatment, the rates increased when initiating treatment with etanercept, but decreased when starting adalimumab or infliximab,” the investigators wrote (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Mar 2. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210931).
The biological explanation for this discrepancy is unclear. It is possible that etanercept simply isn’t as protective as the other two agents, but it also appears possible that etanercept may act paradoxically to induce anterior uveitis in some patients. However, it should be noted that “previous studies have indicated that etanercept still reduces the number of uveitis flares more effectively than placebo,” Dr. Lie and her associates noted.
Regardless of the underlying reason, these findings, taken together with those of previous studies, “support the choice of another TNF inhibitor than etanercept in patients with AS with a history of anterior uveitis,” they said.
Dr. Lie also reported the results at the 2015 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting.
This study was supported by the Swedish Research Council, Gothenburg University, the Stockholm County Council, the Swedish National Rheumatism Association, the Swedish COMBINE public-private research program, the Swedish Cancer Society, the EU-IMI BT Cure project, and the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research. Dr. Lie reported receiving personal fees from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Hospira, Pfizer, and UCB; her associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
Two anti–tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibodies, adalimumab and infliximab, showed evidence of being markedly more effective than the anti-TNF–receptor inhibitor etanercept at reducing the rate of anterior uveitis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis in a retrospective Swedish cohort study.
To compare the efficacy of the three TNF inhibitors, researchers analyzed data in nationwide Swedish population-based registries for 1,365 ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients who initiated treatment during a 7-year period. Treatment began with adalimumab in 406 patients, infliximab in 605, and etanercept in 354, said Elisabeth Lie, MD, of the department of rheumatology and inflammation research at the University of Gothenburg (Sweden), and her associates.
“Compared with the rates [of anterior uveitis] pretreatment, the rates increased when initiating treatment with etanercept, but decreased when starting adalimumab or infliximab,” the investigators wrote (Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Mar 2. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210931).
The biological explanation for this discrepancy is unclear. It is possible that etanercept simply isn’t as protective as the other two agents, but it also appears possible that etanercept may act paradoxically to induce anterior uveitis in some patients. However, it should be noted that “previous studies have indicated that etanercept still reduces the number of uveitis flares more effectively than placebo,” Dr. Lie and her associates noted.
Regardless of the underlying reason, these findings, taken together with those of previous studies, “support the choice of another TNF inhibitor than etanercept in patients with AS with a history of anterior uveitis,” they said.
Dr. Lie also reported the results at the 2015 American College of Rheumatology annual meeting.
This study was supported by the Swedish Research Council, Gothenburg University, the Stockholm County Council, the Swedish National Rheumatism Association, the Swedish COMBINE public-private research program, the Swedish Cancer Society, the EU-IMI BT Cure project, and the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research. Dr. Lie reported receiving personal fees from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Hospira, Pfizer, and UCB; her associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Etanercept was associated with nearly a fourfold higher risk of developing uveitis than was adalimumab (HR, 3.86) and a twofold higher risk than was infliximab (HR, 1.99), but there was no difference in risk between adalimumab and infliximab.
Data source: A retrospective cohort study involving 1,365 AS patients enrolled in nationwide Swedish registries during a 7-year period.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Swedish Research Council, Gothenburg University, the Stockholm County Council, the Swedish National Rheumatism Association, the Swedish COMBINE public-private research program, the Swedish Cancer Society, the EU-IMI BT Cure project, and the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research. Dr. Lie reported receiving personal fees from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Hospira, Pfizer, and UCB; her associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.