User login
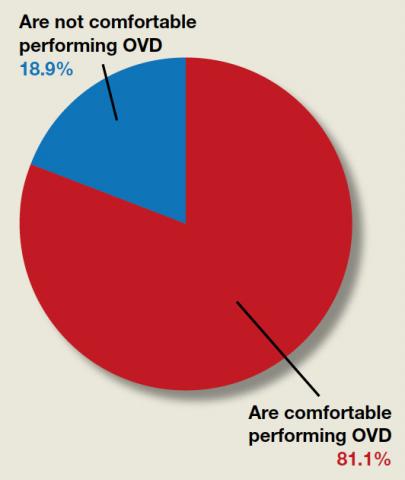
“[Operative vaginal delivery] was used in only 3% of all US births in 2013, a shift from approximately 30% in 1987,” reported Hayley M. Miller, MD, and Danielle M. Panelli, MD, in the June issue of OBG Management. In their article, “How are maternal and neonatal outcomes impacted by the contemporary practice of operative vaginal delivery [OVD],” the authors mentioned that level of experience by the operator can bias reported complication rates of OVD. Although they examined evidence that found the absolute risk of neonatal trauma to be low following OVD, perineal lacerations “appeared to remain a major driver of maternal morbidity….” Given the current infrequency of OVD, they urged that training be prioritized so OVD can be offered as a safe alternative to cesarean delivery. OBG Management followed up with a poll for readers to ask, “Are you comfortable performing OVD as an alternative to cesarean?”
A total of 302 readers cast their vote:
81.1% (245 readers) said yes
18.9% (57 readers) said no
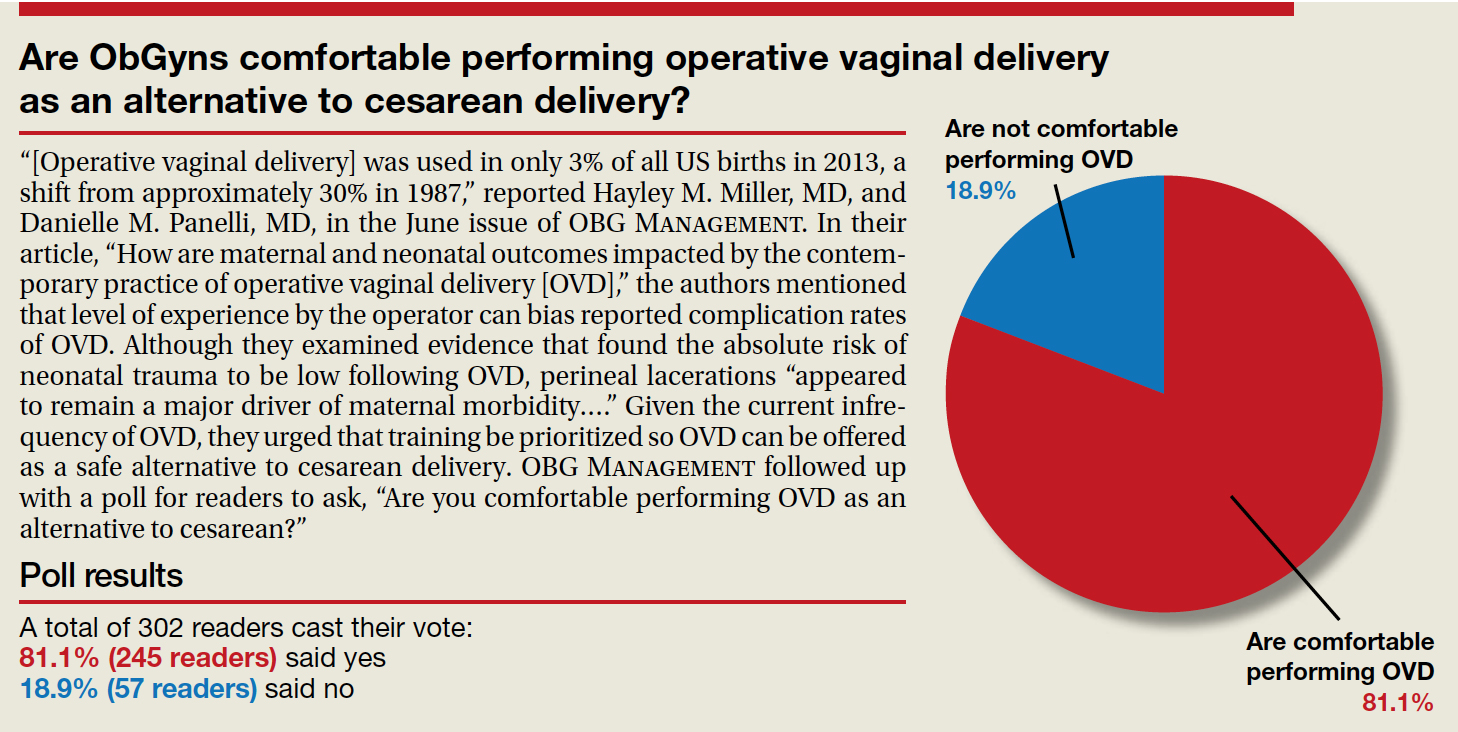
“[Operative vaginal delivery] was used in only 3% of all US births in 2013, a shift from approximately 30% in 1987,” reported Hayley M. Miller, MD, and Danielle M. Panelli, MD, in the June issue of OBG Management. In their article, “How are maternal and neonatal outcomes impacted by the contemporary practice of operative vaginal delivery [OVD],” the authors mentioned that level of experience by the operator can bias reported complication rates of OVD. Although they examined evidence that found the absolute risk of neonatal trauma to be low following OVD, perineal lacerations “appeared to remain a major driver of maternal morbidity….” Given the current infrequency of OVD, they urged that training be prioritized so OVD can be offered as a safe alternative to cesarean delivery. OBG Management followed up with a poll for readers to ask, “Are you comfortable performing OVD as an alternative to cesarean?”
A total of 302 readers cast their vote:
81.1% (245 readers) said yes
18.9% (57 readers) said no

“[Operative vaginal delivery] was used in only 3% of all US births in 2013, a shift from approximately 30% in 1987,” reported Hayley M. Miller, MD, and Danielle M. Panelli, MD, in the June issue of OBG Management. In their article, “How are maternal and neonatal outcomes impacted by the contemporary practice of operative vaginal delivery [OVD],” the authors mentioned that level of experience by the operator can bias reported complication rates of OVD. Although they examined evidence that found the absolute risk of neonatal trauma to be low following OVD, perineal lacerations “appeared to remain a major driver of maternal morbidity….” Given the current infrequency of OVD, they urged that training be prioritized so OVD can be offered as a safe alternative to cesarean delivery. OBG Management followed up with a poll for readers to ask, “Are you comfortable performing OVD as an alternative to cesarean?”
A total of 302 readers cast their vote:
81.1% (245 readers) said yes
18.9% (57 readers) said no