User login
Postmenopausal women with early breast cancer can go chemo-free
New results from the phase 3 RxPONDER trial add to mounting evidence that most postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer derive no added benefits from chemotherapy and can be effectively treated with endocrine therapy alone.
The study, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, conversely shows that premenopausal women do benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy, theorized by many to largely be the result of chemotherapy-induced ovarian function suppression.
The RxPONDER trial results are in line with those from the practice-changing TAILORx trial and underscore that “postmenopausal women with 1 to 3 positive nodes and [a recurrence score] of 0 to 25 can likely safely forgo adjuvant chemotherapy without compromising invasive disease-free survival,” first author Kevin Kalinsky, MD, of the Winship Cancer Institute at Emory University, Atlanta, told this news organization. “This will save tens of thousands of women the time, expense, and potentially harmful side effects that can be associated with chemotherapy infusions.”
However, the authors note, “premenopausal women with 1-3 positive lymph nodes had a significant benefit from chemotherapy.”
The study, conducted by the Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) Cancer Research Network, involved 5,018 women with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer with one to three positive axillary lymph nodes – a breast cancer profile that represents approximately 20% of cases in the U.S.
All women had recurrence scores on the 100-point 21-gene breast cancer assay (Oncotype Dx) under 25, which is considered the lowest risk of recurrence. Patients were randomized to treatment with endocrine therapy only (n = 2,507) or chemotherapy followed by endocrine therapy (n = 2,511).
After a median follow-up of 5.3 years, women treated with adjunctive chemotherapy plus endocrine therapy exhibited no significant improvements in invasive disease-free survival compared to those who received endocrine therapy alone.
A prespecified analysis stratifying women by menopausal status underscored those results among postmenopausal women. In this cohort, researchers reported invasive disease-free survival was 91.9% in the endocrine-only group and 91.3% in the chemotherapy group (HR, 1.02; P = .89), indicating no benefit of the adjunctive chemotherapy.
However, among premenopausal women, the invasive disease-free survival rate was significantly higher with the addition of chemotherapy – 89.0% with endocrine-only therapy and 93.9% with both therapies (HR, 0.60; P = .002). Increases in distant relapse-free survival observed in the dual-therapy group similarly favored adding chemotherapy (HR, 0.58; P = .009).
Even when the authors further stratified the women into recurrence scores of 0 to 13 or 14 to 25, the results remained consistent. Postmenopausal women in each of the recurrence score groups continued to show no difference in invasive disease recurrence, new primary cancer, or death from chemotherapy (HR, 1.01 for each score group). Conversely, premenopausal women showed significant improvements in those outcomes when chemotherapy was added to endocrine therapy.
To what degree were the effects observed in premenopausal women the result of chemotherapy-induced ovarian suppression?
“I think it’s fair to say it’s the most interesting question right now in early-stage breast cancer for ER-positive tumors,” Harold Burstein, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said during a debate at the recent San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
According to Sibylle Loibl, MD, PhD, when it comes to the use of chemotherapy, “age matters.”
“I strongly believe the biology of tumors is different in younger women with HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer,” Dr. Loibl, an associate professor at the University of Frankfurt, said during the debate. “It’s a different disease and the effects of chemotherapy are different.”
In young women, chemotherapy has “a direct cytotoxic effect, which cannot be neglected, and an endocrine effect on ovarian function suppression,” Dr. Loibl added. “I think both are needed in young premenopausal patients.”
According to the RxPONDER authors, “whether a chemotherapy benefit in premenopausal women is due to both direct cytocidal effects and treatment-induced menopause remains unclear,” but they noted that “it is possible that the contribution of these mechanisms may vary according to age.”
Further complicating matters, Dr. Loibl added, is that age appears to be poorly represented in genetic diagnostic tools.
“I think the gene expression profiles we are currently using as standard diagnostic tools do not capture the right biology for our premenopausal patients,” she said. “We have to keep in mind that these tests were designed and validated in postmenopausal patients and were only retrospectively used in premenopausal patients.”
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute and others. Dr. Loibl has received honoraria from Prime and Chugai and numerous institutional research grants.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New results from the phase 3 RxPONDER trial add to mounting evidence that most postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer derive no added benefits from chemotherapy and can be effectively treated with endocrine therapy alone.
The study, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, conversely shows that premenopausal women do benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy, theorized by many to largely be the result of chemotherapy-induced ovarian function suppression.
The RxPONDER trial results are in line with those from the practice-changing TAILORx trial and underscore that “postmenopausal women with 1 to 3 positive nodes and [a recurrence score] of 0 to 25 can likely safely forgo adjuvant chemotherapy without compromising invasive disease-free survival,” first author Kevin Kalinsky, MD, of the Winship Cancer Institute at Emory University, Atlanta, told this news organization. “This will save tens of thousands of women the time, expense, and potentially harmful side effects that can be associated with chemotherapy infusions.”
However, the authors note, “premenopausal women with 1-3 positive lymph nodes had a significant benefit from chemotherapy.”
The study, conducted by the Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) Cancer Research Network, involved 5,018 women with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer with one to three positive axillary lymph nodes – a breast cancer profile that represents approximately 20% of cases in the U.S.
All women had recurrence scores on the 100-point 21-gene breast cancer assay (Oncotype Dx) under 25, which is considered the lowest risk of recurrence. Patients were randomized to treatment with endocrine therapy only (n = 2,507) or chemotherapy followed by endocrine therapy (n = 2,511).
After a median follow-up of 5.3 years, women treated with adjunctive chemotherapy plus endocrine therapy exhibited no significant improvements in invasive disease-free survival compared to those who received endocrine therapy alone.
A prespecified analysis stratifying women by menopausal status underscored those results among postmenopausal women. In this cohort, researchers reported invasive disease-free survival was 91.9% in the endocrine-only group and 91.3% in the chemotherapy group (HR, 1.02; P = .89), indicating no benefit of the adjunctive chemotherapy.
However, among premenopausal women, the invasive disease-free survival rate was significantly higher with the addition of chemotherapy – 89.0% with endocrine-only therapy and 93.9% with both therapies (HR, 0.60; P = .002). Increases in distant relapse-free survival observed in the dual-therapy group similarly favored adding chemotherapy (HR, 0.58; P = .009).
Even when the authors further stratified the women into recurrence scores of 0 to 13 or 14 to 25, the results remained consistent. Postmenopausal women in each of the recurrence score groups continued to show no difference in invasive disease recurrence, new primary cancer, or death from chemotherapy (HR, 1.01 for each score group). Conversely, premenopausal women showed significant improvements in those outcomes when chemotherapy was added to endocrine therapy.
To what degree were the effects observed in premenopausal women the result of chemotherapy-induced ovarian suppression?
“I think it’s fair to say it’s the most interesting question right now in early-stage breast cancer for ER-positive tumors,” Harold Burstein, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said during a debate at the recent San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
According to Sibylle Loibl, MD, PhD, when it comes to the use of chemotherapy, “age matters.”
“I strongly believe the biology of tumors is different in younger women with HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer,” Dr. Loibl, an associate professor at the University of Frankfurt, said during the debate. “It’s a different disease and the effects of chemotherapy are different.”
In young women, chemotherapy has “a direct cytotoxic effect, which cannot be neglected, and an endocrine effect on ovarian function suppression,” Dr. Loibl added. “I think both are needed in young premenopausal patients.”
According to the RxPONDER authors, “whether a chemotherapy benefit in premenopausal women is due to both direct cytocidal effects and treatment-induced menopause remains unclear,” but they noted that “it is possible that the contribution of these mechanisms may vary according to age.”
Further complicating matters, Dr. Loibl added, is that age appears to be poorly represented in genetic diagnostic tools.
“I think the gene expression profiles we are currently using as standard diagnostic tools do not capture the right biology for our premenopausal patients,” she said. “We have to keep in mind that these tests were designed and validated in postmenopausal patients and were only retrospectively used in premenopausal patients.”
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute and others. Dr. Loibl has received honoraria from Prime and Chugai and numerous institutional research grants.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New results from the phase 3 RxPONDER trial add to mounting evidence that most postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer derive no added benefits from chemotherapy and can be effectively treated with endocrine therapy alone.
The study, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, conversely shows that premenopausal women do benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy, theorized by many to largely be the result of chemotherapy-induced ovarian function suppression.
The RxPONDER trial results are in line with those from the practice-changing TAILORx trial and underscore that “postmenopausal women with 1 to 3 positive nodes and [a recurrence score] of 0 to 25 can likely safely forgo adjuvant chemotherapy without compromising invasive disease-free survival,” first author Kevin Kalinsky, MD, of the Winship Cancer Institute at Emory University, Atlanta, told this news organization. “This will save tens of thousands of women the time, expense, and potentially harmful side effects that can be associated with chemotherapy infusions.”
However, the authors note, “premenopausal women with 1-3 positive lymph nodes had a significant benefit from chemotherapy.”
The study, conducted by the Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) Cancer Research Network, involved 5,018 women with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer with one to three positive axillary lymph nodes – a breast cancer profile that represents approximately 20% of cases in the U.S.
All women had recurrence scores on the 100-point 21-gene breast cancer assay (Oncotype Dx) under 25, which is considered the lowest risk of recurrence. Patients were randomized to treatment with endocrine therapy only (n = 2,507) or chemotherapy followed by endocrine therapy (n = 2,511).
After a median follow-up of 5.3 years, women treated with adjunctive chemotherapy plus endocrine therapy exhibited no significant improvements in invasive disease-free survival compared to those who received endocrine therapy alone.
A prespecified analysis stratifying women by menopausal status underscored those results among postmenopausal women. In this cohort, researchers reported invasive disease-free survival was 91.9% in the endocrine-only group and 91.3% in the chemotherapy group (HR, 1.02; P = .89), indicating no benefit of the adjunctive chemotherapy.
However, among premenopausal women, the invasive disease-free survival rate was significantly higher with the addition of chemotherapy – 89.0% with endocrine-only therapy and 93.9% with both therapies (HR, 0.60; P = .002). Increases in distant relapse-free survival observed in the dual-therapy group similarly favored adding chemotherapy (HR, 0.58; P = .009).
Even when the authors further stratified the women into recurrence scores of 0 to 13 or 14 to 25, the results remained consistent. Postmenopausal women in each of the recurrence score groups continued to show no difference in invasive disease recurrence, new primary cancer, or death from chemotherapy (HR, 1.01 for each score group). Conversely, premenopausal women showed significant improvements in those outcomes when chemotherapy was added to endocrine therapy.
To what degree were the effects observed in premenopausal women the result of chemotherapy-induced ovarian suppression?
“I think it’s fair to say it’s the most interesting question right now in early-stage breast cancer for ER-positive tumors,” Harold Burstein, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said during a debate at the recent San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
According to Sibylle Loibl, MD, PhD, when it comes to the use of chemotherapy, “age matters.”
“I strongly believe the biology of tumors is different in younger women with HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer,” Dr. Loibl, an associate professor at the University of Frankfurt, said during the debate. “It’s a different disease and the effects of chemotherapy are different.”
In young women, chemotherapy has “a direct cytotoxic effect, which cannot be neglected, and an endocrine effect on ovarian function suppression,” Dr. Loibl added. “I think both are needed in young premenopausal patients.”
According to the RxPONDER authors, “whether a chemotherapy benefit in premenopausal women is due to both direct cytocidal effects and treatment-induced menopause remains unclear,” but they noted that “it is possible that the contribution of these mechanisms may vary according to age.”
Further complicating matters, Dr. Loibl added, is that age appears to be poorly represented in genetic diagnostic tools.
“I think the gene expression profiles we are currently using as standard diagnostic tools do not capture the right biology for our premenopausal patients,” she said. “We have to keep in mind that these tests were designed and validated in postmenopausal patients and were only retrospectively used in premenopausal patients.”
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute and others. Dr. Loibl has received honoraria from Prime and Chugai and numerous institutional research grants.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular effects of breast cancer treatment vary based on weight, menopausal status
For example, certain chemotherapy drugs may confer higher risk in breast cancer survivors of normal weight, whereas they may lower stroke risk in those who are obese, according to Heather Greenlee, ND, PhD, a public health researcher and naturopathic physician with the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle.
In postmenopausal women with breast cancer, aromatase inhibitors may increase cardiovascular risk, while tamoxifen appears to reduce the risk of incident dyslipidemia, she said.
The findings are from separate analyses of data from studies presented during a poster discussion session at the symposium.
Breast cancer treatment and cardiovascular effects: The role of weight
In one analysis, Dr. Greenlee and colleagues examined outcomes in 13,582 breast cancer survivors with a median age of 60 years and median follow-up of 7 years to assess whether cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk associated with specific breast cancer therapies varies by body mass index (BMI) category at diagnosis.
Many routinely used breast cancer therapies are cardiotoxic, and being overweight or obese are known risk factors for CVD, but few studies have assessed whether BMI modifies the effect of these treatment on cardiovascular risk, Dr. Greenlee explained.
After adjusting for baseline demographic and health-related factors, and other breast cancer treatment, they found that:
- Ischemic heart disease risk was higher among normal-weight women who received anthracyclines, compared with those who did not (hazard ratio, 4.2). No other risk associations were observed for other breast cancer therapies and BMI groups.
- Heart failure/cardiomyopathy risk was higher among women with normal weight who received anthracyclines, cyclophosphamides, or left-sided radiation, compared with those who did not (HRs, 5.24, 3.27, and 2.05, respectively), and among overweight women who received anthracyclines, compared with those who did not (HR, 2.18). No risk associations were observed for women who received trastuzumab, taxanes, endocrine therapy, or radiation on any side, and no risk associations were observed for women who were obese.
- Stroke risk was higher in normal-weight women who received taxanes, cyclophosphamides, or left-sided radiation versus those who did not (HRs, 2.14, 2.35, and 1.31, respectively), and stroke risk was lower in obese women who received anthracyclines, taxanes, or cyclophosphamide, compared with those who did not (HRs, 0.32, 0.41, and 0.29, respectively). No risk associations were observed for trastuzumab, endocrine therapy, or radiation on any side, and no risk associations were observed for women who were overweight.
The lack of associations noted between treatments and heart failure risk among obese patients could be caused by the “obesity paradox” observed in prior obese populations, the investigators noted, adding that additional analyses are planned to “examine whether different dosage and duration of breast cancer therapy exposures across the BMI groups contributed to these risk associations.”
Breast cancer treatment and cardiometabolic effects: The role of menopausal status
In a separate analysis, Dr. Greenlee and colleagues looked at the association between endocrine therapies and cardiometabolic risk based on menopausal status.
Endocrine therapy is associated with CVD in breast cancer survivors and may be associated with developing cardiometabolic risk factors like diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, they noted, explaining that tamoxifen has mixed estrogenic and antiestrogenic activity, while aromatase inhibitors deplete endogenous estrogen.
Since most studies have compared tamoxifen with aromatase inhibitor use, it has been a challenge challenging to discern the effects of each, Dr. Greenlee said.
She and her colleagues reviewed records for 14,942 breast cancer survivors who were diagnosed between 2005 and 2013. The patients had a mean age of 61 years at baseline, and 24.9% were premenopausal at the time of diagnosis. Of the premenopausal women, 27.3% used tamoxifen, 19.2% used aromatase inhibitors, and 53.5% did not use endocrine therapy, and of the postmenopausal women, 6.6% used tamoxifen, 47.7% used aromatase inhibitors, and 45.7% did not use endocrine therapy.
After adjusting for baseline demographics and health factors, the investigators found that:
- The use of tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors was not associated with a risk of developing diabetes, dyslipidemia, or hypertension in premenopausal women, or with a risk of developing diabetes or hypertension in postmenopausal women.
- The risk of dyslipidemia was higher in postmenopausal aromatase inhibitor users, and lower in postmenopausal tamoxifen users, compared with postmenopausal non-users of endocrine therapy (HRs, 1.15 and 0.75, respectively).
The lack of associations between endocrine therapy and CVD risk in premenopausal women may be from low power, Dr. Greenlee said, noting that analyses in larger sample sizes are needed.
She and her colleagues plan to conduct further analyses looking at treatment dosage and duration, and comparing steroidal versus nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitors.
Future studies should examine the implications of these associations on long-term CVD and how best to manage lipid profiles in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors who have a history of endocrine therapy treatment, they concluded.
This research was funded by grants from the National Cancer Institute.
For example, certain chemotherapy drugs may confer higher risk in breast cancer survivors of normal weight, whereas they may lower stroke risk in those who are obese, according to Heather Greenlee, ND, PhD, a public health researcher and naturopathic physician with the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle.
In postmenopausal women with breast cancer, aromatase inhibitors may increase cardiovascular risk, while tamoxifen appears to reduce the risk of incident dyslipidemia, she said.
The findings are from separate analyses of data from studies presented during a poster discussion session at the symposium.
Breast cancer treatment and cardiovascular effects: The role of weight
In one analysis, Dr. Greenlee and colleagues examined outcomes in 13,582 breast cancer survivors with a median age of 60 years and median follow-up of 7 years to assess whether cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk associated with specific breast cancer therapies varies by body mass index (BMI) category at diagnosis.
Many routinely used breast cancer therapies are cardiotoxic, and being overweight or obese are known risk factors for CVD, but few studies have assessed whether BMI modifies the effect of these treatment on cardiovascular risk, Dr. Greenlee explained.
After adjusting for baseline demographic and health-related factors, and other breast cancer treatment, they found that:
- Ischemic heart disease risk was higher among normal-weight women who received anthracyclines, compared with those who did not (hazard ratio, 4.2). No other risk associations were observed for other breast cancer therapies and BMI groups.
- Heart failure/cardiomyopathy risk was higher among women with normal weight who received anthracyclines, cyclophosphamides, or left-sided radiation, compared with those who did not (HRs, 5.24, 3.27, and 2.05, respectively), and among overweight women who received anthracyclines, compared with those who did not (HR, 2.18). No risk associations were observed for women who received trastuzumab, taxanes, endocrine therapy, or radiation on any side, and no risk associations were observed for women who were obese.
- Stroke risk was higher in normal-weight women who received taxanes, cyclophosphamides, or left-sided radiation versus those who did not (HRs, 2.14, 2.35, and 1.31, respectively), and stroke risk was lower in obese women who received anthracyclines, taxanes, or cyclophosphamide, compared with those who did not (HRs, 0.32, 0.41, and 0.29, respectively). No risk associations were observed for trastuzumab, endocrine therapy, or radiation on any side, and no risk associations were observed for women who were overweight.
The lack of associations noted between treatments and heart failure risk among obese patients could be caused by the “obesity paradox” observed in prior obese populations, the investigators noted, adding that additional analyses are planned to “examine whether different dosage and duration of breast cancer therapy exposures across the BMI groups contributed to these risk associations.”
Breast cancer treatment and cardiometabolic effects: The role of menopausal status
In a separate analysis, Dr. Greenlee and colleagues looked at the association between endocrine therapies and cardiometabolic risk based on menopausal status.
Endocrine therapy is associated with CVD in breast cancer survivors and may be associated with developing cardiometabolic risk factors like diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, they noted, explaining that tamoxifen has mixed estrogenic and antiestrogenic activity, while aromatase inhibitors deplete endogenous estrogen.
Since most studies have compared tamoxifen with aromatase inhibitor use, it has been a challenge challenging to discern the effects of each, Dr. Greenlee said.
She and her colleagues reviewed records for 14,942 breast cancer survivors who were diagnosed between 2005 and 2013. The patients had a mean age of 61 years at baseline, and 24.9% were premenopausal at the time of diagnosis. Of the premenopausal women, 27.3% used tamoxifen, 19.2% used aromatase inhibitors, and 53.5% did not use endocrine therapy, and of the postmenopausal women, 6.6% used tamoxifen, 47.7% used aromatase inhibitors, and 45.7% did not use endocrine therapy.
After adjusting for baseline demographics and health factors, the investigators found that:
- The use of tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors was not associated with a risk of developing diabetes, dyslipidemia, or hypertension in premenopausal women, or with a risk of developing diabetes or hypertension in postmenopausal women.
- The risk of dyslipidemia was higher in postmenopausal aromatase inhibitor users, and lower in postmenopausal tamoxifen users, compared with postmenopausal non-users of endocrine therapy (HRs, 1.15 and 0.75, respectively).
The lack of associations between endocrine therapy and CVD risk in premenopausal women may be from low power, Dr. Greenlee said, noting that analyses in larger sample sizes are needed.
She and her colleagues plan to conduct further analyses looking at treatment dosage and duration, and comparing steroidal versus nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitors.
Future studies should examine the implications of these associations on long-term CVD and how best to manage lipid profiles in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors who have a history of endocrine therapy treatment, they concluded.
This research was funded by grants from the National Cancer Institute.
For example, certain chemotherapy drugs may confer higher risk in breast cancer survivors of normal weight, whereas they may lower stroke risk in those who are obese, according to Heather Greenlee, ND, PhD, a public health researcher and naturopathic physician with the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle.
In postmenopausal women with breast cancer, aromatase inhibitors may increase cardiovascular risk, while tamoxifen appears to reduce the risk of incident dyslipidemia, she said.
The findings are from separate analyses of data from studies presented during a poster discussion session at the symposium.
Breast cancer treatment and cardiovascular effects: The role of weight
In one analysis, Dr. Greenlee and colleagues examined outcomes in 13,582 breast cancer survivors with a median age of 60 years and median follow-up of 7 years to assess whether cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk associated with specific breast cancer therapies varies by body mass index (BMI) category at diagnosis.
Many routinely used breast cancer therapies are cardiotoxic, and being overweight or obese are known risk factors for CVD, but few studies have assessed whether BMI modifies the effect of these treatment on cardiovascular risk, Dr. Greenlee explained.
After adjusting for baseline demographic and health-related factors, and other breast cancer treatment, they found that:
- Ischemic heart disease risk was higher among normal-weight women who received anthracyclines, compared with those who did not (hazard ratio, 4.2). No other risk associations were observed for other breast cancer therapies and BMI groups.
- Heart failure/cardiomyopathy risk was higher among women with normal weight who received anthracyclines, cyclophosphamides, or left-sided radiation, compared with those who did not (HRs, 5.24, 3.27, and 2.05, respectively), and among overweight women who received anthracyclines, compared with those who did not (HR, 2.18). No risk associations were observed for women who received trastuzumab, taxanes, endocrine therapy, or radiation on any side, and no risk associations were observed for women who were obese.
- Stroke risk was higher in normal-weight women who received taxanes, cyclophosphamides, or left-sided radiation versus those who did not (HRs, 2.14, 2.35, and 1.31, respectively), and stroke risk was lower in obese women who received anthracyclines, taxanes, or cyclophosphamide, compared with those who did not (HRs, 0.32, 0.41, and 0.29, respectively). No risk associations were observed for trastuzumab, endocrine therapy, or radiation on any side, and no risk associations were observed for women who were overweight.
The lack of associations noted between treatments and heart failure risk among obese patients could be caused by the “obesity paradox” observed in prior obese populations, the investigators noted, adding that additional analyses are planned to “examine whether different dosage and duration of breast cancer therapy exposures across the BMI groups contributed to these risk associations.”
Breast cancer treatment and cardiometabolic effects: The role of menopausal status
In a separate analysis, Dr. Greenlee and colleagues looked at the association between endocrine therapies and cardiometabolic risk based on menopausal status.
Endocrine therapy is associated with CVD in breast cancer survivors and may be associated with developing cardiometabolic risk factors like diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, they noted, explaining that tamoxifen has mixed estrogenic and antiestrogenic activity, while aromatase inhibitors deplete endogenous estrogen.
Since most studies have compared tamoxifen with aromatase inhibitor use, it has been a challenge challenging to discern the effects of each, Dr. Greenlee said.
She and her colleagues reviewed records for 14,942 breast cancer survivors who were diagnosed between 2005 and 2013. The patients had a mean age of 61 years at baseline, and 24.9% were premenopausal at the time of diagnosis. Of the premenopausal women, 27.3% used tamoxifen, 19.2% used aromatase inhibitors, and 53.5% did not use endocrine therapy, and of the postmenopausal women, 6.6% used tamoxifen, 47.7% used aromatase inhibitors, and 45.7% did not use endocrine therapy.
After adjusting for baseline demographics and health factors, the investigators found that:
- The use of tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors was not associated with a risk of developing diabetes, dyslipidemia, or hypertension in premenopausal women, or with a risk of developing diabetes or hypertension in postmenopausal women.
- The risk of dyslipidemia was higher in postmenopausal aromatase inhibitor users, and lower in postmenopausal tamoxifen users, compared with postmenopausal non-users of endocrine therapy (HRs, 1.15 and 0.75, respectively).
The lack of associations between endocrine therapy and CVD risk in premenopausal women may be from low power, Dr. Greenlee said, noting that analyses in larger sample sizes are needed.
She and her colleagues plan to conduct further analyses looking at treatment dosage and duration, and comparing steroidal versus nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitors.
Future studies should examine the implications of these associations on long-term CVD and how best to manage lipid profiles in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors who have a history of endocrine therapy treatment, they concluded.
This research was funded by grants from the National Cancer Institute.
FROM SABCS 2021
Average-risk women with dense breasts—What breast screening is appropriate?
Text copyright DenseBreast-info.org.
Answer
A. For women with extremely dense breasts who are not otherwise at increased risk for breast cancer, screening magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is preferred, plus her mammogram or tomosynthesis. If MRI is not an option, consider ultrasonography or contrast-enhanced mammography.
The same screening considerations apply to women with heterogeneously dense breasts; however, there is limited capacity for MRI or even ultrasound screening at many facilities. Research supports MRI in dense breasts, and abbreviated, lower-cost protocols have been validated that address some of the barriers to MRI.1 Although not yet widely available, abbreviated MRI will likely have a greater role in screening women with dense breasts who are not high risk. It is important to note that preauthorization from insurance may be required for screening MRI, and in most US states, deductibles and copays apply.
The exam
Contrast-enhanced MRI requires IV injection of gadolinium-based contrast to look at the anatomy and blood flow patterns of the breast tissue. The patient lies face down with the breasts placed in two rectangular openings, or “coils.” The exam takes place inside the tunnel of the scanner, with the head facing out.After initial images are obtained, the contrast agent is injected into a vein in the arm, and additional images are taken, which will show areas of enhancement. The exam takes about 20 to 40 minutes. An “abbreviated” MRI can be performed for screening in some centers, which uses fewer sequences and takes about 10 minutes.
Benefits
At least 40% of cancers are missed on mammography in women with dense breasts.2 MRI is the most widely studied technique using a contrast agent, and it produces the highest additional cancer detection of all the supplemental technologies to date, yielding, in the first year, 10-16 additional cancers per 1,000 women screened after mammography/tomosynthesis (reviewed in Berg et al.3). The cancer-detection benefit is seen across all breast density categories, even among average-risk women.4 There is no ionizing radiation, and it has been shown to reduce the rate of interval cancers (those detected due to symptoms after a negative screening mammogram), as well as the rate of late-stage disease. Axillary lymph nodes can be examined at the same screening exam.
While tomosynthesis improves cancer detection in women with fatty breasts, scattered fibroglandular breast tissue, and heterogeneously dense breasts, it does not significantly improve cancer detection in women with extremely dense breasts.5,6 Current American Cancer Society and National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend annual screening MRI for women at high risk for breast cancer (regardless of breast density); however, increasingly, research supports the effectiveness of MRI in women with dense breasts who are otherwise considered average risk. A large randomized controlled trial in the Netherlands compared outcomes in women with extremely dense breasts invited to have screening MRI after negative mammography to those assigned to continue receiving screening mammography only. The incremental cancer detection rate was 16.5 per 1,000 (79/4,783) women screened with MRI in the first round7 and 6 per 1,000 women screened in the second round 2 years later.8 The interval cancer rate was 0.8 per 1,000 (4/4,783) women screened with MRI, compared with 4.9 per 1,000 (16/3,278) women who declined MRI and received mammography only.7
Screening ultrasound will show up to 3 additional cancers per 1,000 women screened after mammography/tomosynthesis (reviewed in Vourtsis and Berg9 and Berg and Vourtsis10), far lower than the added cancer-detection rate of MRI. Consider screening ultrasound for women who cannot tolerate or access screening MRI.11 Contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) uses iodinated contrast (as in computed tomography). CEM is not widely available but appears to show cancer-detection similar to MRI. For further discussion, see Berg et al’s 2021 review.3
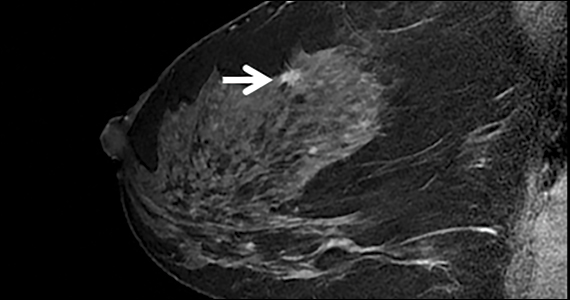
The FIGURE shows an example of an invasive cancer depicted on contrast-enhanced MRI in a 53-year-old woman with dense breasts and a family history of breast cancer that was not visible on tomosynthesis, even in retrospect, due to masking by dense tissue.

Considerations
Breast MRI increases callbacks even after mammography and ultrasound; however, such false alarms are reduced in subsequent screening rounds. MRI cannot be performed in women who have certain metal implants— some pacemakers or spinal fixation rods—and is not recommended for pregnant women. Claustrophobia may be an issue for some women. MRI is expensive and requires IV contrast. Gadolinium is known to accumulate in the brain, although the long-term effects of this are unknown and no harm has been shown.●
For more information, visit medically sourced DenseBreast-info.org. Comprehensive resources include a free CME opportunity, Dense Breasts and Supplemental Screening.
- Comstock CE, Gatsonis C, Newstead GM, et al. Comparison of abbreviated breast MRI vs digital breast tomosynthesis for breast cancer detection among women with dense breasts undergoing screening. JAMA. 2020;323:746-756. doi: 10.1001 /jama.2020.0572
- Kerlikowske K, Zhu W, Tosteson AN, et al. Identifying women with dense breasts at high risk for interval cancer: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:673-681. doi: 10.7326/M14-1465.
- Berg WA, Rafferty EA, Friedewald SM, Hruska CB, Rahbar H. Screening Algorithms in Dense Breasts: AJR Expert Panel Narrative Review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216:275-294. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.24436.
- Kuhl CK, Strobel K, Bieling H, et al. Supplemental breast MR imaging screening of women with average risk of breast cancer. Radiology. 2017;283:361-370. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016161444.
- Rafferty EA, Durand MA, Conant EF, et al. Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis and digital mammography in dense and nondense breasts. JAMA. 2016;315:1784-1786. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.1708.
- Osteras BH, Martinsen ACT, Gullien R, et al. Digital mammography versus breast tomosynthesis: impact of breast density on diagnostic performance in population-based screening. Radiology. 2019;293:60-68. doi: 10.1148 /radiol.2019190425.
- Bakker MF, de Lange SV, Pijnappel RM, et al. Supplemental MRI screening for women with extremely dense breast tissue. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:2091-2102. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1903986.
- Veenhuizen SGA, de Lange SV, Bakker MF, et al. Supplemental breast MRI for women with extremely dense breasts: results of the second screening round of the DENSE trial. Radiology. 2021;299:278-286. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021203633.
- Vourtsis A, Berg WA. Breast density implications and supplemental screening. Eur Radiol. 2019;29:1762-1777. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5668-8.
- Berg WA, Vourtsis A. Screening ultrasound using handheld or automated technique in women with dense breasts. J Breast Imaging. 2019;1:283-296.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis (Version 1.2021). https://www.nccn. org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast-screening.pdf. Accessed November 18, 2021.
Text copyright DenseBreast-info.org.
Answer
A. For women with extremely dense breasts who are not otherwise at increased risk for breast cancer, screening magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is preferred, plus her mammogram or tomosynthesis. If MRI is not an option, consider ultrasonography or contrast-enhanced mammography.
The same screening considerations apply to women with heterogeneously dense breasts; however, there is limited capacity for MRI or even ultrasound screening at many facilities. Research supports MRI in dense breasts, and abbreviated, lower-cost protocols have been validated that address some of the barriers to MRI.1 Although not yet widely available, abbreviated MRI will likely have a greater role in screening women with dense breasts who are not high risk. It is important to note that preauthorization from insurance may be required for screening MRI, and in most US states, deductibles and copays apply.
The exam
Contrast-enhanced MRI requires IV injection of gadolinium-based contrast to look at the anatomy and blood flow patterns of the breast tissue. The patient lies face down with the breasts placed in two rectangular openings, or “coils.” The exam takes place inside the tunnel of the scanner, with the head facing out.After initial images are obtained, the contrast agent is injected into a vein in the arm, and additional images are taken, which will show areas of enhancement. The exam takes about 20 to 40 minutes. An “abbreviated” MRI can be performed for screening in some centers, which uses fewer sequences and takes about 10 minutes.
Benefits
At least 40% of cancers are missed on mammography in women with dense breasts.2 MRI is the most widely studied technique using a contrast agent, and it produces the highest additional cancer detection of all the supplemental technologies to date, yielding, in the first year, 10-16 additional cancers per 1,000 women screened after mammography/tomosynthesis (reviewed in Berg et al.3). The cancer-detection benefit is seen across all breast density categories, even among average-risk women.4 There is no ionizing radiation, and it has been shown to reduce the rate of interval cancers (those detected due to symptoms after a negative screening mammogram), as well as the rate of late-stage disease. Axillary lymph nodes can be examined at the same screening exam.
While tomosynthesis improves cancer detection in women with fatty breasts, scattered fibroglandular breast tissue, and heterogeneously dense breasts, it does not significantly improve cancer detection in women with extremely dense breasts.5,6 Current American Cancer Society and National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend annual screening MRI for women at high risk for breast cancer (regardless of breast density); however, increasingly, research supports the effectiveness of MRI in women with dense breasts who are otherwise considered average risk. A large randomized controlled trial in the Netherlands compared outcomes in women with extremely dense breasts invited to have screening MRI after negative mammography to those assigned to continue receiving screening mammography only. The incremental cancer detection rate was 16.5 per 1,000 (79/4,783) women screened with MRI in the first round7 and 6 per 1,000 women screened in the second round 2 years later.8 The interval cancer rate was 0.8 per 1,000 (4/4,783) women screened with MRI, compared with 4.9 per 1,000 (16/3,278) women who declined MRI and received mammography only.7
Screening ultrasound will show up to 3 additional cancers per 1,000 women screened after mammography/tomosynthesis (reviewed in Vourtsis and Berg9 and Berg and Vourtsis10), far lower than the added cancer-detection rate of MRI. Consider screening ultrasound for women who cannot tolerate or access screening MRI.11 Contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) uses iodinated contrast (as in computed tomography). CEM is not widely available but appears to show cancer-detection similar to MRI. For further discussion, see Berg et al’s 2021 review.3
The FIGURE shows an example of an invasive cancer depicted on contrast-enhanced MRI in a 53-year-old woman with dense breasts and a family history of breast cancer that was not visible on tomosynthesis, even in retrospect, due to masking by dense tissue.

Considerations
Breast MRI increases callbacks even after mammography and ultrasound; however, such false alarms are reduced in subsequent screening rounds. MRI cannot be performed in women who have certain metal implants— some pacemakers or spinal fixation rods—and is not recommended for pregnant women. Claustrophobia may be an issue for some women. MRI is expensive and requires IV contrast. Gadolinium is known to accumulate in the brain, although the long-term effects of this are unknown and no harm has been shown.●
For more information, visit medically sourced DenseBreast-info.org. Comprehensive resources include a free CME opportunity, Dense Breasts and Supplemental Screening.
Text copyright DenseBreast-info.org.
Answer
A. For women with extremely dense breasts who are not otherwise at increased risk for breast cancer, screening magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is preferred, plus her mammogram or tomosynthesis. If MRI is not an option, consider ultrasonography or contrast-enhanced mammography.
The same screening considerations apply to women with heterogeneously dense breasts; however, there is limited capacity for MRI or even ultrasound screening at many facilities. Research supports MRI in dense breasts, and abbreviated, lower-cost protocols have been validated that address some of the barriers to MRI.1 Although not yet widely available, abbreviated MRI will likely have a greater role in screening women with dense breasts who are not high risk. It is important to note that preauthorization from insurance may be required for screening MRI, and in most US states, deductibles and copays apply.
The exam
Contrast-enhanced MRI requires IV injection of gadolinium-based contrast to look at the anatomy and blood flow patterns of the breast tissue. The patient lies face down with the breasts placed in two rectangular openings, or “coils.” The exam takes place inside the tunnel of the scanner, with the head facing out.After initial images are obtained, the contrast agent is injected into a vein in the arm, and additional images are taken, which will show areas of enhancement. The exam takes about 20 to 40 minutes. An “abbreviated” MRI can be performed for screening in some centers, which uses fewer sequences and takes about 10 minutes.
Benefits
At least 40% of cancers are missed on mammography in women with dense breasts.2 MRI is the most widely studied technique using a contrast agent, and it produces the highest additional cancer detection of all the supplemental technologies to date, yielding, in the first year, 10-16 additional cancers per 1,000 women screened after mammography/tomosynthesis (reviewed in Berg et al.3). The cancer-detection benefit is seen across all breast density categories, even among average-risk women.4 There is no ionizing radiation, and it has been shown to reduce the rate of interval cancers (those detected due to symptoms after a negative screening mammogram), as well as the rate of late-stage disease. Axillary lymph nodes can be examined at the same screening exam.
While tomosynthesis improves cancer detection in women with fatty breasts, scattered fibroglandular breast tissue, and heterogeneously dense breasts, it does not significantly improve cancer detection in women with extremely dense breasts.5,6 Current American Cancer Society and National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines recommend annual screening MRI for women at high risk for breast cancer (regardless of breast density); however, increasingly, research supports the effectiveness of MRI in women with dense breasts who are otherwise considered average risk. A large randomized controlled trial in the Netherlands compared outcomes in women with extremely dense breasts invited to have screening MRI after negative mammography to those assigned to continue receiving screening mammography only. The incremental cancer detection rate was 16.5 per 1,000 (79/4,783) women screened with MRI in the first round7 and 6 per 1,000 women screened in the second round 2 years later.8 The interval cancer rate was 0.8 per 1,000 (4/4,783) women screened with MRI, compared with 4.9 per 1,000 (16/3,278) women who declined MRI and received mammography only.7
Screening ultrasound will show up to 3 additional cancers per 1,000 women screened after mammography/tomosynthesis (reviewed in Vourtsis and Berg9 and Berg and Vourtsis10), far lower than the added cancer-detection rate of MRI. Consider screening ultrasound for women who cannot tolerate or access screening MRI.11 Contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) uses iodinated contrast (as in computed tomography). CEM is not widely available but appears to show cancer-detection similar to MRI. For further discussion, see Berg et al’s 2021 review.3
The FIGURE shows an example of an invasive cancer depicted on contrast-enhanced MRI in a 53-year-old woman with dense breasts and a family history of breast cancer that was not visible on tomosynthesis, even in retrospect, due to masking by dense tissue.

Considerations
Breast MRI increases callbacks even after mammography and ultrasound; however, such false alarms are reduced in subsequent screening rounds. MRI cannot be performed in women who have certain metal implants— some pacemakers or spinal fixation rods—and is not recommended for pregnant women. Claustrophobia may be an issue for some women. MRI is expensive and requires IV contrast. Gadolinium is known to accumulate in the brain, although the long-term effects of this are unknown and no harm has been shown.●
For more information, visit medically sourced DenseBreast-info.org. Comprehensive resources include a free CME opportunity, Dense Breasts and Supplemental Screening.
- Comstock CE, Gatsonis C, Newstead GM, et al. Comparison of abbreviated breast MRI vs digital breast tomosynthesis for breast cancer detection among women with dense breasts undergoing screening. JAMA. 2020;323:746-756. doi: 10.1001 /jama.2020.0572
- Kerlikowske K, Zhu W, Tosteson AN, et al. Identifying women with dense breasts at high risk for interval cancer: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:673-681. doi: 10.7326/M14-1465.
- Berg WA, Rafferty EA, Friedewald SM, Hruska CB, Rahbar H. Screening Algorithms in Dense Breasts: AJR Expert Panel Narrative Review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216:275-294. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.24436.
- Kuhl CK, Strobel K, Bieling H, et al. Supplemental breast MR imaging screening of women with average risk of breast cancer. Radiology. 2017;283:361-370. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016161444.
- Rafferty EA, Durand MA, Conant EF, et al. Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis and digital mammography in dense and nondense breasts. JAMA. 2016;315:1784-1786. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.1708.
- Osteras BH, Martinsen ACT, Gullien R, et al. Digital mammography versus breast tomosynthesis: impact of breast density on diagnostic performance in population-based screening. Radiology. 2019;293:60-68. doi: 10.1148 /radiol.2019190425.
- Bakker MF, de Lange SV, Pijnappel RM, et al. Supplemental MRI screening for women with extremely dense breast tissue. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:2091-2102. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1903986.
- Veenhuizen SGA, de Lange SV, Bakker MF, et al. Supplemental breast MRI for women with extremely dense breasts: results of the second screening round of the DENSE trial. Radiology. 2021;299:278-286. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021203633.
- Vourtsis A, Berg WA. Breast density implications and supplemental screening. Eur Radiol. 2019;29:1762-1777. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5668-8.
- Berg WA, Vourtsis A. Screening ultrasound using handheld or automated technique in women with dense breasts. J Breast Imaging. 2019;1:283-296.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis (Version 1.2021). https://www.nccn. org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast-screening.pdf. Accessed November 18, 2021.
- Comstock CE, Gatsonis C, Newstead GM, et al. Comparison of abbreviated breast MRI vs digital breast tomosynthesis for breast cancer detection among women with dense breasts undergoing screening. JAMA. 2020;323:746-756. doi: 10.1001 /jama.2020.0572
- Kerlikowske K, Zhu W, Tosteson AN, et al. Identifying women with dense breasts at high risk for interval cancer: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:673-681. doi: 10.7326/M14-1465.
- Berg WA, Rafferty EA, Friedewald SM, Hruska CB, Rahbar H. Screening Algorithms in Dense Breasts: AJR Expert Panel Narrative Review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216:275-294. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.24436.
- Kuhl CK, Strobel K, Bieling H, et al. Supplemental breast MR imaging screening of women with average risk of breast cancer. Radiology. 2017;283:361-370. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016161444.
- Rafferty EA, Durand MA, Conant EF, et al. Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis and digital mammography in dense and nondense breasts. JAMA. 2016;315:1784-1786. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.1708.
- Osteras BH, Martinsen ACT, Gullien R, et al. Digital mammography versus breast tomosynthesis: impact of breast density on diagnostic performance in population-based screening. Radiology. 2019;293:60-68. doi: 10.1148 /radiol.2019190425.
- Bakker MF, de Lange SV, Pijnappel RM, et al. Supplemental MRI screening for women with extremely dense breast tissue. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:2091-2102. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1903986.
- Veenhuizen SGA, de Lange SV, Bakker MF, et al. Supplemental breast MRI for women with extremely dense breasts: results of the second screening round of the DENSE trial. Radiology. 2021;299:278-286. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021203633.
- Vourtsis A, Berg WA. Breast density implications and supplemental screening. Eur Radiol. 2019;29:1762-1777. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5668-8.
- Berg WA, Vourtsis A. Screening ultrasound using handheld or automated technique in women with dense breasts. J Breast Imaging. 2019;1:283-296.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis (Version 1.2021). https://www.nccn. org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast-screening.pdf. Accessed November 18, 2021.
Quiz developed in collaboration with 
Cancer risk tied to some manufactured foods
SAN ANTONIO –
The findings were reported in three poster presentations (P1-09-01, P1-09-02 and P3-12-35) at the 2021 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium from the ongoing French NutriNet-Santé web-based study of 171,000 people that was launched in France in 2009 to investigate nutrition and health relationships. The authors of the analyses note that while evidence of deleterious health effects has been established for the dietary focus of their studies, and cancer risks have been suspected, strong evidence of a cancer association has been lacking.
Nitrates and nitrites are used in processed meats to increase shelf life and to avoid bacterial growth, said Eloi Chazelas, PhD, Nutritional Epidemiology Research Team (EREN) at Sorbonne Paris Nord University. Dr. Chazelas looked at consumption of nitrites and nitrates through repeated 24 hour dietary records, linked to a comprehensive food composition database. The study’s main outcome measure was adjusted associations between nitrite and nitrate exposures and the risk of cancer (overall and by main cancer sites).
During follow-up, 966 breast and 400 prostate cancers were diagnosed among 3,311 first incident cancer cases. Breast cancer risk was elevated (HR = 1.24 [1.03-1.48], P = 0.02) among higher consumers of nitrates from food additives, especially with potassium nitrate consumption (HR = 1.25 [1.04-1.50], P = 0.01). Elevated prostate cancer risk was associated with nitrites (HR = 1.58 [1.14-2.18], P = 0.008), specifically for sodium nitrite (HR = 1.62 [1.17-2.25], P = 0.004). Nitrates and nitrites from natural sources were not associated significantly with higher cancer risk, Dr. Chazelas said.
He and his team found that food additive nitrates were positively associated with breast cancer risk, and food additive nitrites were positively associated with prostate cancer risk. “While these results need confirmation in other large-scale prospective studies, they provide new insights in a context of lively debate around the ban of nitrite additives in the food industry,” said Dr. Chazelas, who is a doctoral candidate at Sorbonne Paris Nord University.
In “Breast and prostate cancer risk associated with nitrites and nitrates from food additives (P1-09-01),” the study included 102,046 adults from the French NutriNet-Santé prospective cohort (2009-2021). It examined associations between artificial sweetener intakes (total from all dietary sources, the most frequently consumed ones [aspartame e951, acesulfame-K e950 and sucralose e955]) and cancer risk (overall and by sites: breast, prostate and obesity-related cancers).
Overall cancer risk in people who consumed higher amounts of total sweeteners (i.e. above the median exposure in consumers) was elevated (n = 2,527 cases, hazard ratio = 1.12, 95 percent confidence interval = 1.00-1.25, P-trend=0.005), especially for aspartame (HR = 1.20 [1.05-1.38] P = 0.001) and acesulfame-K (HR = 1.18 [1.04-1.34] P = 0.003). Elevated breast cancer risks (among 723 cases) were observed for total sweeteners (HR = 1.25 [1.02-1.53] P = 0.01), for aspartame (HR = 1.33 [1.05-1.69] P = 0.007), and for acesulfame-K (HR = 1.39 [1.11-1.74] P = 0.003). Also, obesity-related cancers (1,509 cases) were increased for total sweeteners (HR = 1.16 [1.00-1.33] P = 0.02), for aspartame (HR = 1.22 [1.02-1.45] P = 0.01) and for acesulfame-K (HR = 1.23 [1.04-1.45] P = 0.01).
Artificial sweeteners are found in more than 10,000 foods and beverages, said Charlotte Debras, a doctoral candidate in nutritional epidemiology at Sorbonne Paris Nord University. “These findings provide important and novel insights for the ongoing re-evaluation of food additive sweeteners by the European Food Safety Authority and other health agencies globally,” she said.
Trans fatty acid intakes and cancer risk
Investigating associations between trans fatty acid intake (total ruminant [rTFAs], industrial [iTFAs], and corresponding specific isomers and cancer risk), the analysis of Gaëlle Wendeu-Foyet, PhD, Sorbonne Paris Nord University, found a total of 3,374 incident cancer cases (982 breast, 405 prostate) in an overall population of 104,909. Dietary intake of total TFAs was associated with higher prostate cancer risk (hazard ration for quartile 4 versus 1: 1.27, 1.11-1.77 P-trend = 0.005). Also, rTFAs were associated with increased overall cancer risk (1.16, 1.02-1.32 P-trend = 0.07), in particular the conjugated linoleic acid isomers (CLA) (1.19, 1.04-1.36 P-trend = 0.04). These associations were specifically observed for breast cancer (rTFAs: 1.35, 1.06-1.72 P-trend = 0.01; CLA: 1.29, 1.00-1.66 P-trend = 0.048), in particular before menopause (rTFAs: 1.68, 1.06-2.67 P-trend = 0.02; CLA: 2.013, 1.25-3.23 P-trend = 0.003). Several iTFAs were associated with overall (1.18, 1.06-1.31 P-trend = 0.02 for transdocosenoic acid), breast (isomer 18:2t: 1.30, 1.06-1.58 P-trend = 0.01; hexadecenoic acid: 1.28, 1.05-1.56 P-trend = 0.02) and prostate (transdocosenoic acid: 1.52, 1.09-2.12 P-trend = 0.07) cancer risks.
“These results support the WHO’s goal of achieving elimination from food supplies of industrially produced TFAs,” Dr. Foyet said. “The consumption of food products containing partially hydrogenated oils should be avoided.”
Nutrition, along with avoiding tobacco intake, is one of the main modifiable risk factors for chronic diseases. “There is a lot at stake in terms of prevention. This requires a combination of actions at the individual level to the public level by informing the public through food labeling,” Ms. Debras said.
It also requires influencing the context in which citizens evolve by encouraging manufacturers to improve their products (pricing policies, commitment charters for product reformulation, etc.), and limiting advertising and marketing for products of poor nutritional quality (especially among children),” she said.
SAN ANTONIO –
The findings were reported in three poster presentations (P1-09-01, P1-09-02 and P3-12-35) at the 2021 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium from the ongoing French NutriNet-Santé web-based study of 171,000 people that was launched in France in 2009 to investigate nutrition and health relationships. The authors of the analyses note that while evidence of deleterious health effects has been established for the dietary focus of their studies, and cancer risks have been suspected, strong evidence of a cancer association has been lacking.
Nitrates and nitrites are used in processed meats to increase shelf life and to avoid bacterial growth, said Eloi Chazelas, PhD, Nutritional Epidemiology Research Team (EREN) at Sorbonne Paris Nord University. Dr. Chazelas looked at consumption of nitrites and nitrates through repeated 24 hour dietary records, linked to a comprehensive food composition database. The study’s main outcome measure was adjusted associations between nitrite and nitrate exposures and the risk of cancer (overall and by main cancer sites).
During follow-up, 966 breast and 400 prostate cancers were diagnosed among 3,311 first incident cancer cases. Breast cancer risk was elevated (HR = 1.24 [1.03-1.48], P = 0.02) among higher consumers of nitrates from food additives, especially with potassium nitrate consumption (HR = 1.25 [1.04-1.50], P = 0.01). Elevated prostate cancer risk was associated with nitrites (HR = 1.58 [1.14-2.18], P = 0.008), specifically for sodium nitrite (HR = 1.62 [1.17-2.25], P = 0.004). Nitrates and nitrites from natural sources were not associated significantly with higher cancer risk, Dr. Chazelas said.
He and his team found that food additive nitrates were positively associated with breast cancer risk, and food additive nitrites were positively associated with prostate cancer risk. “While these results need confirmation in other large-scale prospective studies, they provide new insights in a context of lively debate around the ban of nitrite additives in the food industry,” said Dr. Chazelas, who is a doctoral candidate at Sorbonne Paris Nord University.
In “Breast and prostate cancer risk associated with nitrites and nitrates from food additives (P1-09-01),” the study included 102,046 adults from the French NutriNet-Santé prospective cohort (2009-2021). It examined associations between artificial sweetener intakes (total from all dietary sources, the most frequently consumed ones [aspartame e951, acesulfame-K e950 and sucralose e955]) and cancer risk (overall and by sites: breast, prostate and obesity-related cancers).
Overall cancer risk in people who consumed higher amounts of total sweeteners (i.e. above the median exposure in consumers) was elevated (n = 2,527 cases, hazard ratio = 1.12, 95 percent confidence interval = 1.00-1.25, P-trend=0.005), especially for aspartame (HR = 1.20 [1.05-1.38] P = 0.001) and acesulfame-K (HR = 1.18 [1.04-1.34] P = 0.003). Elevated breast cancer risks (among 723 cases) were observed for total sweeteners (HR = 1.25 [1.02-1.53] P = 0.01), for aspartame (HR = 1.33 [1.05-1.69] P = 0.007), and for acesulfame-K (HR = 1.39 [1.11-1.74] P = 0.003). Also, obesity-related cancers (1,509 cases) were increased for total sweeteners (HR = 1.16 [1.00-1.33] P = 0.02), for aspartame (HR = 1.22 [1.02-1.45] P = 0.01) and for acesulfame-K (HR = 1.23 [1.04-1.45] P = 0.01).
Artificial sweeteners are found in more than 10,000 foods and beverages, said Charlotte Debras, a doctoral candidate in nutritional epidemiology at Sorbonne Paris Nord University. “These findings provide important and novel insights for the ongoing re-evaluation of food additive sweeteners by the European Food Safety Authority and other health agencies globally,” she said.
Trans fatty acid intakes and cancer risk
Investigating associations between trans fatty acid intake (total ruminant [rTFAs], industrial [iTFAs], and corresponding specific isomers and cancer risk), the analysis of Gaëlle Wendeu-Foyet, PhD, Sorbonne Paris Nord University, found a total of 3,374 incident cancer cases (982 breast, 405 prostate) in an overall population of 104,909. Dietary intake of total TFAs was associated with higher prostate cancer risk (hazard ration for quartile 4 versus 1: 1.27, 1.11-1.77 P-trend = 0.005). Also, rTFAs were associated with increased overall cancer risk (1.16, 1.02-1.32 P-trend = 0.07), in particular the conjugated linoleic acid isomers (CLA) (1.19, 1.04-1.36 P-trend = 0.04). These associations were specifically observed for breast cancer (rTFAs: 1.35, 1.06-1.72 P-trend = 0.01; CLA: 1.29, 1.00-1.66 P-trend = 0.048), in particular before menopause (rTFAs: 1.68, 1.06-2.67 P-trend = 0.02; CLA: 2.013, 1.25-3.23 P-trend = 0.003). Several iTFAs were associated with overall (1.18, 1.06-1.31 P-trend = 0.02 for transdocosenoic acid), breast (isomer 18:2t: 1.30, 1.06-1.58 P-trend = 0.01; hexadecenoic acid: 1.28, 1.05-1.56 P-trend = 0.02) and prostate (transdocosenoic acid: 1.52, 1.09-2.12 P-trend = 0.07) cancer risks.
“These results support the WHO’s goal of achieving elimination from food supplies of industrially produced TFAs,” Dr. Foyet said. “The consumption of food products containing partially hydrogenated oils should be avoided.”
Nutrition, along with avoiding tobacco intake, is one of the main modifiable risk factors for chronic diseases. “There is a lot at stake in terms of prevention. This requires a combination of actions at the individual level to the public level by informing the public through food labeling,” Ms. Debras said.
It also requires influencing the context in which citizens evolve by encouraging manufacturers to improve their products (pricing policies, commitment charters for product reformulation, etc.), and limiting advertising and marketing for products of poor nutritional quality (especially among children),” she said.
SAN ANTONIO –
The findings were reported in three poster presentations (P1-09-01, P1-09-02 and P3-12-35) at the 2021 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium from the ongoing French NutriNet-Santé web-based study of 171,000 people that was launched in France in 2009 to investigate nutrition and health relationships. The authors of the analyses note that while evidence of deleterious health effects has been established for the dietary focus of their studies, and cancer risks have been suspected, strong evidence of a cancer association has been lacking.
Nitrates and nitrites are used in processed meats to increase shelf life and to avoid bacterial growth, said Eloi Chazelas, PhD, Nutritional Epidemiology Research Team (EREN) at Sorbonne Paris Nord University. Dr. Chazelas looked at consumption of nitrites and nitrates through repeated 24 hour dietary records, linked to a comprehensive food composition database. The study’s main outcome measure was adjusted associations between nitrite and nitrate exposures and the risk of cancer (overall and by main cancer sites).
During follow-up, 966 breast and 400 prostate cancers were diagnosed among 3,311 first incident cancer cases. Breast cancer risk was elevated (HR = 1.24 [1.03-1.48], P = 0.02) among higher consumers of nitrates from food additives, especially with potassium nitrate consumption (HR = 1.25 [1.04-1.50], P = 0.01). Elevated prostate cancer risk was associated with nitrites (HR = 1.58 [1.14-2.18], P = 0.008), specifically for sodium nitrite (HR = 1.62 [1.17-2.25], P = 0.004). Nitrates and nitrites from natural sources were not associated significantly with higher cancer risk, Dr. Chazelas said.
He and his team found that food additive nitrates were positively associated with breast cancer risk, and food additive nitrites were positively associated with prostate cancer risk. “While these results need confirmation in other large-scale prospective studies, they provide new insights in a context of lively debate around the ban of nitrite additives in the food industry,” said Dr. Chazelas, who is a doctoral candidate at Sorbonne Paris Nord University.
In “Breast and prostate cancer risk associated with nitrites and nitrates from food additives (P1-09-01),” the study included 102,046 adults from the French NutriNet-Santé prospective cohort (2009-2021). It examined associations between artificial sweetener intakes (total from all dietary sources, the most frequently consumed ones [aspartame e951, acesulfame-K e950 and sucralose e955]) and cancer risk (overall and by sites: breast, prostate and obesity-related cancers).
Overall cancer risk in people who consumed higher amounts of total sweeteners (i.e. above the median exposure in consumers) was elevated (n = 2,527 cases, hazard ratio = 1.12, 95 percent confidence interval = 1.00-1.25, P-trend=0.005), especially for aspartame (HR = 1.20 [1.05-1.38] P = 0.001) and acesulfame-K (HR = 1.18 [1.04-1.34] P = 0.003). Elevated breast cancer risks (among 723 cases) were observed for total sweeteners (HR = 1.25 [1.02-1.53] P = 0.01), for aspartame (HR = 1.33 [1.05-1.69] P = 0.007), and for acesulfame-K (HR = 1.39 [1.11-1.74] P = 0.003). Also, obesity-related cancers (1,509 cases) were increased for total sweeteners (HR = 1.16 [1.00-1.33] P = 0.02), for aspartame (HR = 1.22 [1.02-1.45] P = 0.01) and for acesulfame-K (HR = 1.23 [1.04-1.45] P = 0.01).
Artificial sweeteners are found in more than 10,000 foods and beverages, said Charlotte Debras, a doctoral candidate in nutritional epidemiology at Sorbonne Paris Nord University. “These findings provide important and novel insights for the ongoing re-evaluation of food additive sweeteners by the European Food Safety Authority and other health agencies globally,” she said.
Trans fatty acid intakes and cancer risk
Investigating associations between trans fatty acid intake (total ruminant [rTFAs], industrial [iTFAs], and corresponding specific isomers and cancer risk), the analysis of Gaëlle Wendeu-Foyet, PhD, Sorbonne Paris Nord University, found a total of 3,374 incident cancer cases (982 breast, 405 prostate) in an overall population of 104,909. Dietary intake of total TFAs was associated with higher prostate cancer risk (hazard ration for quartile 4 versus 1: 1.27, 1.11-1.77 P-trend = 0.005). Also, rTFAs were associated with increased overall cancer risk (1.16, 1.02-1.32 P-trend = 0.07), in particular the conjugated linoleic acid isomers (CLA) (1.19, 1.04-1.36 P-trend = 0.04). These associations were specifically observed for breast cancer (rTFAs: 1.35, 1.06-1.72 P-trend = 0.01; CLA: 1.29, 1.00-1.66 P-trend = 0.048), in particular before menopause (rTFAs: 1.68, 1.06-2.67 P-trend = 0.02; CLA: 2.013, 1.25-3.23 P-trend = 0.003). Several iTFAs were associated with overall (1.18, 1.06-1.31 P-trend = 0.02 for transdocosenoic acid), breast (isomer 18:2t: 1.30, 1.06-1.58 P-trend = 0.01; hexadecenoic acid: 1.28, 1.05-1.56 P-trend = 0.02) and prostate (transdocosenoic acid: 1.52, 1.09-2.12 P-trend = 0.07) cancer risks.
“These results support the WHO’s goal of achieving elimination from food supplies of industrially produced TFAs,” Dr. Foyet said. “The consumption of food products containing partially hydrogenated oils should be avoided.”
Nutrition, along with avoiding tobacco intake, is one of the main modifiable risk factors for chronic diseases. “There is a lot at stake in terms of prevention. This requires a combination of actions at the individual level to the public level by informing the public through food labeling,” Ms. Debras said.
It also requires influencing the context in which citizens evolve by encouraging manufacturers to improve their products (pricing policies, commitment charters for product reformulation, etc.), and limiting advertising and marketing for products of poor nutritional quality (especially among children),” she said.
FROM SABCS 2021
Breast cancer-related musculoskeletal pain alleviated with acupuncture
SAN ANTONIO –
Both techniques led to clinically meaningful and persistent reduction of pain, but electroacupuncture was more effective in reducing pain severity, according to study author Wanqing Iris Zhi, MD, PhD, of the Breast Medicine Service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Among breast cancer survivors, Dr. Zhi said, chronic musculoskeletal pain is common and debilitating. In earlier results of the PEACE (Personalized Electroacupuncture versus Auricular Acupuncture Comparative Effectiveness) trial, both electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture improved pain control better than usual care in cancer survivors. The comparative effectiveness between electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture among breast cancer survivors, specifically for chronic musculoskeletal pain, remains unknown.
To evaluate potential differences between electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture, Dr. Zhi et al. examined data from PEACE, a three-arm, parallel, single center randomized trial investigating electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture for chronic musculoskeletal pain, compared with usual care. Among 360 cancer survivors in PEACE, mean age in 165 cancer survivors with a primary diagnosis of breast cancer was 60.3 years (35.8 percent non-White) with a mean of 5.4 years since their cancer diagnoses. Patients in both the electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture groups received 10 weekly treatments. Change in mean Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) pain severity from baseline to week 12 was the primary endpoint, with BPI change to week 24 as a secondary endpoint. Usual care patients, after week 12, could receive 10 electroacupuncture treatments.
The most common locations of chronic musculoskeletal pain, Dr. Zhi observed, were lower back (24 percent), knee/leg (24 percent) and shoulder/elbow (14 percent). About 70 percent of patients were taking pain medication. Both electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture were associated with clinically meaningful and persistent pain reductions among the evaluated breast cancer survivors. The change in BPI severity from baseline to week 12 was –0.29 (confidence interval, –0.08, 0.28) in the UC group. In the electroacupuncture group it was –2.65 (CI, –3.06, –2.25; P ≤0.001 from baseline) and –2.37 versus usual care (CI, –3.05, –1.68; P ≤0.001 versus UC). For the auricular acupuncture group, the change from baseline was –1.75 (CI, –2.15, –1.35; P ≤0.001 from baseline) and –1.46 versus usual care (CI, –2.14, –0.78; P ≤0.001 versus UC). The difference in BPI pain severity reduction from baseline between electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture of –0.90 (CI, –1.45, –0.36) was statistically significant (P ≤0.001). Electroacupuncture also reduced pain severity significantly more than auricular acupuncture at week 24 (CI, –0.82, [–1.38, –0.27], P = 0.004).
Dr. Zhi concluded that among breast cancer survivors, although both electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture were associated with clinically meaningful and persistent pain reduction, electroacupuncture was more effective at reducing pain severity.
She pointed out also that neither surgery type (mastectomy versus lumpectomy; P = 0.83) nor aromatase inhibitor versus tamoxifen versus neither (P = 0.59) was associated with BPI/severity response among electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture patients.
“Both electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture are significantly better than usual care, so it suggests that both acupuncture methods can be utilized for treating chronic muscle skeletal pain in breast cancer survivors, but electroacupuncture is preferred,” Dr. Zhi said.
“Auricular acupuncture can be more painful,” said PEACE principal investigator Jun Mao, MD, who is chair of integrative medicine at Memorial Sloan Kettering. “Ten percent of women could not tolerate the ear pain or discomfort. Electroacupuncture is generally well tolerated. People are more relaxed after treatment. If both are available, start with electroacupuncture,” he said.
SAN ANTONIO –
Both techniques led to clinically meaningful and persistent reduction of pain, but electroacupuncture was more effective in reducing pain severity, according to study author Wanqing Iris Zhi, MD, PhD, of the Breast Medicine Service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Among breast cancer survivors, Dr. Zhi said, chronic musculoskeletal pain is common and debilitating. In earlier results of the PEACE (Personalized Electroacupuncture versus Auricular Acupuncture Comparative Effectiveness) trial, both electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture improved pain control better than usual care in cancer survivors. The comparative effectiveness between electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture among breast cancer survivors, specifically for chronic musculoskeletal pain, remains unknown.
To evaluate potential differences between electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture, Dr. Zhi et al. examined data from PEACE, a three-arm, parallel, single center randomized trial investigating electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture for chronic musculoskeletal pain, compared with usual care. Among 360 cancer survivors in PEACE, mean age in 165 cancer survivors with a primary diagnosis of breast cancer was 60.3 years (35.8 percent non-White) with a mean of 5.4 years since their cancer diagnoses. Patients in both the electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture groups received 10 weekly treatments. Change in mean Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) pain severity from baseline to week 12 was the primary endpoint, with BPI change to week 24 as a secondary endpoint. Usual care patients, after week 12, could receive 10 electroacupuncture treatments.
The most common locations of chronic musculoskeletal pain, Dr. Zhi observed, were lower back (24 percent), knee/leg (24 percent) and shoulder/elbow (14 percent). About 70 percent of patients were taking pain medication. Both electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture were associated with clinically meaningful and persistent pain reductions among the evaluated breast cancer survivors. The change in BPI severity from baseline to week 12 was –0.29 (confidence interval, –0.08, 0.28) in the UC group. In the electroacupuncture group it was –2.65 (CI, –3.06, –2.25; P ≤0.001 from baseline) and –2.37 versus usual care (CI, –3.05, –1.68; P ≤0.001 versus UC). For the auricular acupuncture group, the change from baseline was –1.75 (CI, –2.15, –1.35; P ≤0.001 from baseline) and –1.46 versus usual care (CI, –2.14, –0.78; P ≤0.001 versus UC). The difference in BPI pain severity reduction from baseline between electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture of –0.90 (CI, –1.45, –0.36) was statistically significant (P ≤0.001). Electroacupuncture also reduced pain severity significantly more than auricular acupuncture at week 24 (CI, –0.82, [–1.38, –0.27], P = 0.004).
Dr. Zhi concluded that among breast cancer survivors, although both electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture were associated with clinically meaningful and persistent pain reduction, electroacupuncture was more effective at reducing pain severity.
She pointed out also that neither surgery type (mastectomy versus lumpectomy; P = 0.83) nor aromatase inhibitor versus tamoxifen versus neither (P = 0.59) was associated with BPI/severity response among electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture patients.
“Both electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture are significantly better than usual care, so it suggests that both acupuncture methods can be utilized for treating chronic muscle skeletal pain in breast cancer survivors, but electroacupuncture is preferred,” Dr. Zhi said.
“Auricular acupuncture can be more painful,” said PEACE principal investigator Jun Mao, MD, who is chair of integrative medicine at Memorial Sloan Kettering. “Ten percent of women could not tolerate the ear pain or discomfort. Electroacupuncture is generally well tolerated. People are more relaxed after treatment. If both are available, start with electroacupuncture,” he said.
SAN ANTONIO –
Both techniques led to clinically meaningful and persistent reduction of pain, but electroacupuncture was more effective in reducing pain severity, according to study author Wanqing Iris Zhi, MD, PhD, of the Breast Medicine Service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Among breast cancer survivors, Dr. Zhi said, chronic musculoskeletal pain is common and debilitating. In earlier results of the PEACE (Personalized Electroacupuncture versus Auricular Acupuncture Comparative Effectiveness) trial, both electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture improved pain control better than usual care in cancer survivors. The comparative effectiveness between electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture among breast cancer survivors, specifically for chronic musculoskeletal pain, remains unknown.
To evaluate potential differences between electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture, Dr. Zhi et al. examined data from PEACE, a three-arm, parallel, single center randomized trial investigating electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture for chronic musculoskeletal pain, compared with usual care. Among 360 cancer survivors in PEACE, mean age in 165 cancer survivors with a primary diagnosis of breast cancer was 60.3 years (35.8 percent non-White) with a mean of 5.4 years since their cancer diagnoses. Patients in both the electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture groups received 10 weekly treatments. Change in mean Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) pain severity from baseline to week 12 was the primary endpoint, with BPI change to week 24 as a secondary endpoint. Usual care patients, after week 12, could receive 10 electroacupuncture treatments.
The most common locations of chronic musculoskeletal pain, Dr. Zhi observed, were lower back (24 percent), knee/leg (24 percent) and shoulder/elbow (14 percent). About 70 percent of patients were taking pain medication. Both electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture were associated with clinically meaningful and persistent pain reductions among the evaluated breast cancer survivors. The change in BPI severity from baseline to week 12 was –0.29 (confidence interval, –0.08, 0.28) in the UC group. In the electroacupuncture group it was –2.65 (CI, –3.06, –2.25; P ≤0.001 from baseline) and –2.37 versus usual care (CI, –3.05, –1.68; P ≤0.001 versus UC). For the auricular acupuncture group, the change from baseline was –1.75 (CI, –2.15, –1.35; P ≤0.001 from baseline) and –1.46 versus usual care (CI, –2.14, –0.78; P ≤0.001 versus UC). The difference in BPI pain severity reduction from baseline between electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture of –0.90 (CI, –1.45, –0.36) was statistically significant (P ≤0.001). Electroacupuncture also reduced pain severity significantly more than auricular acupuncture at week 24 (CI, –0.82, [–1.38, –0.27], P = 0.004).
Dr. Zhi concluded that among breast cancer survivors, although both electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture were associated with clinically meaningful and persistent pain reduction, electroacupuncture was more effective at reducing pain severity.
She pointed out also that neither surgery type (mastectomy versus lumpectomy; P = 0.83) nor aromatase inhibitor versus tamoxifen versus neither (P = 0.59) was associated with BPI/severity response among electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture patients.
“Both electroacupuncture and auricular acupuncture are significantly better than usual care, so it suggests that both acupuncture methods can be utilized for treating chronic muscle skeletal pain in breast cancer survivors, but electroacupuncture is preferred,” Dr. Zhi said.
“Auricular acupuncture can be more painful,” said PEACE principal investigator Jun Mao, MD, who is chair of integrative medicine at Memorial Sloan Kettering. “Ten percent of women could not tolerate the ear pain or discomfort. Electroacupuncture is generally well tolerated. People are more relaxed after treatment. If both are available, start with electroacupuncture,” he said.
FROM SABCS 2021
More evidence ties some antipsychotics to increased breast cancer risk
New research provides more evidence that antipsychotics that raise prolactin levels are tied to a significantly increased risk for breast cancer.
The relative risk for breast cancer was 62% higher in women who took category 1 antipsychotic medications associated with high prolactin levels. These include haloperidol (Haldol), paliperidone (Invega), and risperidone (Risperdal). Additionally, the risk was 54% higher in those taking category 2 antipsychotics that have mid-range effects on prolactin. These include iloperidone (Fanapt), lurasidone (Latuda), and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
In contrast, category 3 antipsychotics which have a lesser effect on prolactin levels were not associated with any increase in breast cancer risk. These drugs include aripiprazole (Abilify), asenapine (Saphris), brexpiprazole (Rexulti), cariprazine (Vraylar), clozapine (multiple brands), quetiapine (Seroquel), and ziprasidone (Geodon).
While the “absolute” breast cancer risk for these drugs is unclear, “we can make the case that high circulating prolactin levels are associated with breast cancer risk. This follows what is already known about prolactin from prior studies, notably the nurses’ health studies,” Tahir Rahman, MD, associate professor of psychiatry, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, told this news organization.
“We don’t want to alarm patients taking antipsychotic drugs for life-threatening mental health problems, but we also think it is time for doctors to track prolactin levels and vigilantly monitor their patients who are being treated with antipsychotics,” Dr. Rahman added in a news release.
The study was published online Dec. 3 in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology.
Test prolactin levels
Using administrative claims data, the researchers evaluated breast cancer risk in women aged 18-64 exposed to antipsychotic medications compared with anticonvulsants and/or lithium.
They identified 914 cases of invasive breast cancer among 540,737 women.
Roughly 52% of the study population filled at least one prescription for a category 3 antipsychotic agent, whereas 15% filled at least one prescription for a category 1 agent; 49% of women filled at least one prescription for an anticonvulsant medication during the study period.
Exposure to all antipsychotics was independently associated with a 35% increased risk for breast cancer (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.14-1.61), the study team found.
Compared with anticonvulsants or lithium, the risk for breast cancer was significantly increased for high prolactin (category 1) antipsychotics (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.30-2.03) and for mid-prolactin (category 2) drugs (aHR 1.54; 95% CI, 1.19-1.99), with no increased risk for category 3 antipsychotics.
“Our research is obviously of interest for preventing breast cancer in antipsychotic-treated patients. Checking a blood prolactin level is cheap and easy [and a high level is] fairly simple to mitigate,” said Dr. Rahman.
A matter of debate
Reached for comment, Christoph Correll, MD, professor of psychiatry and molecular medicine, Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, New York, said, “The potential elevation of breast cancer risk depending on the dose and time of treatment with antipsychotic medications with varying degrees of prolactin-raising properties has been a topic of research and matter of debate.”
This new study “adds another data point indicating that antipsychotics that are associated on average with a higher prolactin-raising effect than other antipsychotics may increase the risk of breast cancer in women to some degree,” said Dr. Correll, who was not involved with the study.
However, he cautioned that “naturalistic data are always vulnerable to residual confounding, for example, unmeasured effects that could also at least partially explain the results, and the follow-up time of only 4 years (maximum 6 years) in this study was relatively short.
“Nevertheless, given availability of many different antipsychotics with varying degrees of prolactin-raising potential, in women requiring antipsychotic treatment, less prolactin-raising antipsychotics may be preferable,” Dr. Correll said.
“In women receiving prolactin-raising antipsychotics for medium- and longer-term maintenance therapy, prolactin levels should be monitored,” he added.
When an elevated prolactin level is detected, this should be addressed “either via dose reduction, a switch to an alternative antipsychotic that does not raise prolactin levels significantly, or the addition of a partial or full D2 agonist when the prolactin-raising antipsychotic should be continued based on individualized risk assessment,” Dr. Correll advised.
This work was supported by an award from the Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center; the National Cancer Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health; the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research; and the Center for Brain Research in Mood Disorders. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Correll has received royalties from UpToDate and is a stock option holder of LB Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research provides more evidence that antipsychotics that raise prolactin levels are tied to a significantly increased risk for breast cancer.
The relative risk for breast cancer was 62% higher in women who took category 1 antipsychotic medications associated with high prolactin levels. These include haloperidol (Haldol), paliperidone (Invega), and risperidone (Risperdal). Additionally, the risk was 54% higher in those taking category 2 antipsychotics that have mid-range effects on prolactin. These include iloperidone (Fanapt), lurasidone (Latuda), and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
In contrast, category 3 antipsychotics which have a lesser effect on prolactin levels were not associated with any increase in breast cancer risk. These drugs include aripiprazole (Abilify), asenapine (Saphris), brexpiprazole (Rexulti), cariprazine (Vraylar), clozapine (multiple brands), quetiapine (Seroquel), and ziprasidone (Geodon).
While the “absolute” breast cancer risk for these drugs is unclear, “we can make the case that high circulating prolactin levels are associated with breast cancer risk. This follows what is already known about prolactin from prior studies, notably the nurses’ health studies,” Tahir Rahman, MD, associate professor of psychiatry, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, told this news organization.
“We don’t want to alarm patients taking antipsychotic drugs for life-threatening mental health problems, but we also think it is time for doctors to track prolactin levels and vigilantly monitor their patients who are being treated with antipsychotics,” Dr. Rahman added in a news release.
The study was published online Dec. 3 in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology.
Test prolactin levels
Using administrative claims data, the researchers evaluated breast cancer risk in women aged 18-64 exposed to antipsychotic medications compared with anticonvulsants and/or lithium.
They identified 914 cases of invasive breast cancer among 540,737 women.
Roughly 52% of the study population filled at least one prescription for a category 3 antipsychotic agent, whereas 15% filled at least one prescription for a category 1 agent; 49% of women filled at least one prescription for an anticonvulsant medication during the study period.
Exposure to all antipsychotics was independently associated with a 35% increased risk for breast cancer (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.14-1.61), the study team found.
Compared with anticonvulsants or lithium, the risk for breast cancer was significantly increased for high prolactin (category 1) antipsychotics (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.30-2.03) and for mid-prolactin (category 2) drugs (aHR 1.54; 95% CI, 1.19-1.99), with no increased risk for category 3 antipsychotics.
“Our research is obviously of interest for preventing breast cancer in antipsychotic-treated patients. Checking a blood prolactin level is cheap and easy [and a high level is] fairly simple to mitigate,” said Dr. Rahman.
A matter of debate
Reached for comment, Christoph Correll, MD, professor of psychiatry and molecular medicine, Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, New York, said, “The potential elevation of breast cancer risk depending on the dose and time of treatment with antipsychotic medications with varying degrees of prolactin-raising properties has been a topic of research and matter of debate.”
This new study “adds another data point indicating that antipsychotics that are associated on average with a higher prolactin-raising effect than other antipsychotics may increase the risk of breast cancer in women to some degree,” said Dr. Correll, who was not involved with the study.
However, he cautioned that “naturalistic data are always vulnerable to residual confounding, for example, unmeasured effects that could also at least partially explain the results, and the follow-up time of only 4 years (maximum 6 years) in this study was relatively short.
“Nevertheless, given availability of many different antipsychotics with varying degrees of prolactin-raising potential, in women requiring antipsychotic treatment, less prolactin-raising antipsychotics may be preferable,” Dr. Correll said.
“In women receiving prolactin-raising antipsychotics for medium- and longer-term maintenance therapy, prolactin levels should be monitored,” he added.
When an elevated prolactin level is detected, this should be addressed “either via dose reduction, a switch to an alternative antipsychotic that does not raise prolactin levels significantly, or the addition of a partial or full D2 agonist when the prolactin-raising antipsychotic should be continued based on individualized risk assessment,” Dr. Correll advised.
This work was supported by an award from the Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center; the National Cancer Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health; the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research; and the Center for Brain Research in Mood Disorders. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Correll has received royalties from UpToDate and is a stock option holder of LB Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research provides more evidence that antipsychotics that raise prolactin levels are tied to a significantly increased risk for breast cancer.
The relative risk for breast cancer was 62% higher in women who took category 1 antipsychotic medications associated with high prolactin levels. These include haloperidol (Haldol), paliperidone (Invega), and risperidone (Risperdal). Additionally, the risk was 54% higher in those taking category 2 antipsychotics that have mid-range effects on prolactin. These include iloperidone (Fanapt), lurasidone (Latuda), and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
In contrast, category 3 antipsychotics which have a lesser effect on prolactin levels were not associated with any increase in breast cancer risk. These drugs include aripiprazole (Abilify), asenapine (Saphris), brexpiprazole (Rexulti), cariprazine (Vraylar), clozapine (multiple brands), quetiapine (Seroquel), and ziprasidone (Geodon).
While the “absolute” breast cancer risk for these drugs is unclear, “we can make the case that high circulating prolactin levels are associated with breast cancer risk. This follows what is already known about prolactin from prior studies, notably the nurses’ health studies,” Tahir Rahman, MD, associate professor of psychiatry, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, told this news organization.
“We don’t want to alarm patients taking antipsychotic drugs for life-threatening mental health problems, but we also think it is time for doctors to track prolactin levels and vigilantly monitor their patients who are being treated with antipsychotics,” Dr. Rahman added in a news release.
The study was published online Dec. 3 in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology.
Test prolactin levels
Using administrative claims data, the researchers evaluated breast cancer risk in women aged 18-64 exposed to antipsychotic medications compared with anticonvulsants and/or lithium.
They identified 914 cases of invasive breast cancer among 540,737 women.
Roughly 52% of the study population filled at least one prescription for a category 3 antipsychotic agent, whereas 15% filled at least one prescription for a category 1 agent; 49% of women filled at least one prescription for an anticonvulsant medication during the study period.
Exposure to all antipsychotics was independently associated with a 35% increased risk for breast cancer (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.14-1.61), the study team found.
Compared with anticonvulsants or lithium, the risk for breast cancer was significantly increased for high prolactin (category 1) antipsychotics (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.30-2.03) and for mid-prolactin (category 2) drugs (aHR 1.54; 95% CI, 1.19-1.99), with no increased risk for category 3 antipsychotics.
“Our research is obviously of interest for preventing breast cancer in antipsychotic-treated patients. Checking a blood prolactin level is cheap and easy [and a high level is] fairly simple to mitigate,” said Dr. Rahman.
A matter of debate
Reached for comment, Christoph Correll, MD, professor of psychiatry and molecular medicine, Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, New York, said, “The potential elevation of breast cancer risk depending on the dose and time of treatment with antipsychotic medications with varying degrees of prolactin-raising properties has been a topic of research and matter of debate.”
This new study “adds another data point indicating that antipsychotics that are associated on average with a higher prolactin-raising effect than other antipsychotics may increase the risk of breast cancer in women to some degree,” said Dr. Correll, who was not involved with the study.
However, he cautioned that “naturalistic data are always vulnerable to residual confounding, for example, unmeasured effects that could also at least partially explain the results, and the follow-up time of only 4 years (maximum 6 years) in this study was relatively short.
“Nevertheless, given availability of many different antipsychotics with varying degrees of prolactin-raising potential, in women requiring antipsychotic treatment, less prolactin-raising antipsychotics may be preferable,” Dr. Correll said.
“In women receiving prolactin-raising antipsychotics for medium- and longer-term maintenance therapy, prolactin levels should be monitored,” he added.
When an elevated prolactin level is detected, this should be addressed “either via dose reduction, a switch to an alternative antipsychotic that does not raise prolactin levels significantly, or the addition of a partial or full D2 agonist when the prolactin-raising antipsychotic should be continued based on individualized risk assessment,” Dr. Correll advised.
This work was supported by an award from the Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center; the National Cancer Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health; the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research; and the Center for Brain Research in Mood Disorders. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Correll has received royalties from UpToDate and is a stock option holder of LB Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY
Sacituzumab govitecan effective in Black mTNBC patients
, shows a prespecified analysis of ASCENT.
A heterogenous disease with few treatment options and poor outcomes, mTNBC has an incidence rate twice as high in Black as in White women.
Black women with mTNBC may also experience worse outcomes than other groups, with a greater risk of mortality related to disparities in access to health care and in income, delays in treatment, a higher prevalence of comorbidities, and differences in tumor biology.
Previously presented data from the phase 3 ASCENT trial showed that SG nearly doubled overall survival versus single-agent chemotherapy in pretreated women with mTNBC, with the benefit observed across patient subgroups.
Based on these findings, the Food and Drug Administration approved SG for patients with mTNBC who have received at least two prior chemotherapies, at least one of which is to have been given in the metastatic setting.
Now, an analysis of the ASCENT data in just over 60 Black women with mTNBC showed that they can expect to see their progression-free survival (PFS) improve by 56% and their overall survival increase by a nonsignificant 36% when given SG as opposed to single-agent chemotherapy.
The research (abstract P5-16-07) was presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium on Dec. 10.
The team says that Black women with mTNBC “derived a similar clinical benefit” from SG versus chemotherapy to other women in the study, and had a “manageable” safety profile, which was “consistent with the full trial population.”
Consequently, SG “should be considered a treatment option for Black patients with mTNBC who have received ≥ 2 prior chemotherapies,” at least one of which having been given in the metastatic setting.
Lead researcher Lisa A. Carey, MD, told this news organiztion that it is “very important” to show that the drug works in Black patients, adding: “We know that certain drugs don’t perform so well and it’s also true that people of color are particularly affected by TNBC.”
She said there were “only 62” Black patients in ASCENT, “so if you look at the entire trial and make assumptions that the drug performs the same in all the subsets, then sometimes you’re wrong.”
Dr. Carey, the Richardson and Marilyn Jacobs Preyer Distinguished Professor in Breast Cancer Research, UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center, Chapel Hill, N.C., said there is “emerging interest” in racial disparities in cancer outcomes.
“Black patients have more trouble with access to care,” she said, noting that “in trial populations, [the outcomes] generally seem similar because the patients who go onto the trials tend to be those that can participate, but you never know until you look.”
Overall, Dr. Carey said the current results suggest that, “at least from the standpoint of the therapeutic implications of this drug – which is really a pretty remarkable drug in the overall study – it behaves very similarly in this group.”
Jennifer K. Litton, MD, vice president of clinical research at University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said: “We have known that minority patients, especially Black patients, have a higher rate of triple negative breast cancer and aggressive biologies, and have had worse breast cancer outcomes in many published series.”
She told this news organization that, “additionally, they are often underrepresented in breast cancer clinical trials.”
Dr. Litton said “the very favorable outcomes” reported in “this important subset of patients who participated in the ASCENT trial” confirm the use of SG in patients with mTNBC.
To examine the clinical outcomes of Black patients in the ASCENT study, the team conduced a prespecified analysis of participants self-reporting Black race who had been randomized to SG or single-agent chemotherapy of physician’s choice, including those with and without brain metastases.
Of the 529 patients enrolled to ASCENT, 62 (12%) were Black, of whom 28 were assigned to SG and 34 to single agent chemotherapy. The two groups were generally well balanced, although six patients in the chemotherapy arm had known brain metastases at baseline versus none of those given SG.
After a median treatment duration of 5.3 months with SG and 1.6 months for single-agent chemotherapy, there was a significant improvement in PFS with SG, at 5.4 months versus 2.2 months for chemotherapy, and a hazard ratio of 0.44 (P = .008).
There was also a nonsignificant improvement in overall survival with SG at 13.8 months versus 8.5 months for chemotherapy, and a hazard ratio of 0.64 (P = .159).
The objective response rate was 32% with SG versus 6% in patients given chemotherapy, while the median duration of response was 9.2 months in the SG arm and not evaluable for chemotherapy.
The researchers note that these efficacy findings were “consistent” with those seen in the full ASCENT study population.
In terms of safety, the most common treatment-related adverse events were neutropenia, seen in 64% of SG and 61% of chemotherapy patients, diarrhea in 64% and 13%, respectively, and fatigue, in 52% and 39%, respectively.
The most common grade ≥3 events were neutropenia, in 48% and 42% of SG and chemotherapy patients, respectively, followed by anemia, in 12% and 6%, respectively, leukopenia in 8% and 16%, respectively, and febrile neutropenia in 8% and 3%, respectively.
No treatment-related deaths occurred in either treatment arm.
Dose reduction due to treatment-emergent adverse events was recorded in 28% of patients receiving SG and 35% of those assigned to single-agent chemotherapy, and discontinuations occurred in 0% and 3%, respectively.
The study was sponsored by Gilead Sciences. Dr. Carey reports research funding from Sanofi, Novartis, Genentech/Roche, and GSK; spouse serves on the board of Falcon Therapeutics.
, shows a prespecified analysis of ASCENT.
A heterogenous disease with few treatment options and poor outcomes, mTNBC has an incidence rate twice as high in Black as in White women.
Black women with mTNBC may also experience worse outcomes than other groups, with a greater risk of mortality related to disparities in access to health care and in income, delays in treatment, a higher prevalence of comorbidities, and differences in tumor biology.
Previously presented data from the phase 3 ASCENT trial showed that SG nearly doubled overall survival versus single-agent chemotherapy in pretreated women with mTNBC, with the benefit observed across patient subgroups.
Based on these findings, the Food and Drug Administration approved SG for patients with mTNBC who have received at least two prior chemotherapies, at least one of which is to have been given in the metastatic setting.
Now, an analysis of the ASCENT data in just over 60 Black women with mTNBC showed that they can expect to see their progression-free survival (PFS) improve by 56% and their overall survival increase by a nonsignificant 36% when given SG as opposed to single-agent chemotherapy.
The research (abstract P5-16-07) was presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium on Dec. 10.
The team says that Black women with mTNBC “derived a similar clinical benefit” from SG versus chemotherapy to other women in the study, and had a “manageable” safety profile, which was “consistent with the full trial population.”
Consequently, SG “should be considered a treatment option for Black patients with mTNBC who have received ≥ 2 prior chemotherapies,” at least one of which having been given in the metastatic setting.
Lead researcher Lisa A. Carey, MD, told this news organiztion that it is “very important” to show that the drug works in Black patients, adding: “We know that certain drugs don’t perform so well and it’s also true that people of color are particularly affected by TNBC.”
She said there were “only 62” Black patients in ASCENT, “so if you look at the entire trial and make assumptions that the drug performs the same in all the subsets, then sometimes you’re wrong.”
Dr. Carey, the Richardson and Marilyn Jacobs Preyer Distinguished Professor in Breast Cancer Research, UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center, Chapel Hill, N.C., said there is “emerging interest” in racial disparities in cancer outcomes.
“Black patients have more trouble with access to care,” she said, noting that “in trial populations, [the outcomes] generally seem similar because the patients who go onto the trials tend to be those that can participate, but you never know until you look.”
Overall, Dr. Carey said the current results suggest that, “at least from the standpoint of the therapeutic implications of this drug – which is really a pretty remarkable drug in the overall study – it behaves very similarly in this group.”
Jennifer K. Litton, MD, vice president of clinical research at University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said: “We have known that minority patients, especially Black patients, have a higher rate of triple negative breast cancer and aggressive biologies, and have had worse breast cancer outcomes in many published series.”
She told this news organization that, “additionally, they are often underrepresented in breast cancer clinical trials.”
Dr. Litton said “the very favorable outcomes” reported in “this important subset of patients who participated in the ASCENT trial” confirm the use of SG in patients with mTNBC.
To examine the clinical outcomes of Black patients in the ASCENT study, the team conduced a prespecified analysis of participants self-reporting Black race who had been randomized to SG or single-agent chemotherapy of physician’s choice, including those with and without brain metastases.
Of the 529 patients enrolled to ASCENT, 62 (12%) were Black, of whom 28 were assigned to SG and 34 to single agent chemotherapy. The two groups were generally well balanced, although six patients in the chemotherapy arm had known brain metastases at baseline versus none of those given SG.
After a median treatment duration of 5.3 months with SG and 1.6 months for single-agent chemotherapy, there was a significant improvement in PFS with SG, at 5.4 months versus 2.2 months for chemotherapy, and a hazard ratio of 0.44 (P = .008).
There was also a nonsignificant improvement in overall survival with SG at 13.8 months versus 8.5 months for chemotherapy, and a hazard ratio of 0.64 (P = .159).
The objective response rate was 32% with SG versus 6% in patients given chemotherapy, while the median duration of response was 9.2 months in the SG arm and not evaluable for chemotherapy.
The researchers note that these efficacy findings were “consistent” with those seen in the full ASCENT study population.
In terms of safety, the most common treatment-related adverse events were neutropenia, seen in 64% of SG and 61% of chemotherapy patients, diarrhea in 64% and 13%, respectively, and fatigue, in 52% and 39%, respectively.
The most common grade ≥3 events were neutropenia, in 48% and 42% of SG and chemotherapy patients, respectively, followed by anemia, in 12% and 6%, respectively, leukopenia in 8% and 16%, respectively, and febrile neutropenia in 8% and 3%, respectively.
No treatment-related deaths occurred in either treatment arm.
Dose reduction due to treatment-emergent adverse events was recorded in 28% of patients receiving SG and 35% of those assigned to single-agent chemotherapy, and discontinuations occurred in 0% and 3%, respectively.
The study was sponsored by Gilead Sciences. Dr. Carey reports research funding from Sanofi, Novartis, Genentech/Roche, and GSK; spouse serves on the board of Falcon Therapeutics.
, shows a prespecified analysis of ASCENT.
A heterogenous disease with few treatment options and poor outcomes, mTNBC has an incidence rate twice as high in Black as in White women.
Black women with mTNBC may also experience worse outcomes than other groups, with a greater risk of mortality related to disparities in access to health care and in income, delays in treatment, a higher prevalence of comorbidities, and differences in tumor biology.
Previously presented data from the phase 3 ASCENT trial showed that SG nearly doubled overall survival versus single-agent chemotherapy in pretreated women with mTNBC, with the benefit observed across patient subgroups.
Based on these findings, the Food and Drug Administration approved SG for patients with mTNBC who have received at least two prior chemotherapies, at least one of which is to have been given in the metastatic setting.
Now, an analysis of the ASCENT data in just over 60 Black women with mTNBC showed that they can expect to see their progression-free survival (PFS) improve by 56% and their overall survival increase by a nonsignificant 36% when given SG as opposed to single-agent chemotherapy.
The research (abstract P5-16-07) was presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium on Dec. 10.
The team says that Black women with mTNBC “derived a similar clinical benefit” from SG versus chemotherapy to other women in the study, and had a “manageable” safety profile, which was “consistent with the full trial population.”
Consequently, SG “should be considered a treatment option for Black patients with mTNBC who have received ≥ 2 prior chemotherapies,” at least one of which having been given in the metastatic setting.
Lead researcher Lisa A. Carey, MD, told this news organiztion that it is “very important” to show that the drug works in Black patients, adding: “We know that certain drugs don’t perform so well and it’s also true that people of color are particularly affected by TNBC.”
She said there were “only 62” Black patients in ASCENT, “so if you look at the entire trial and make assumptions that the drug performs the same in all the subsets, then sometimes you’re wrong.”
Dr. Carey, the Richardson and Marilyn Jacobs Preyer Distinguished Professor in Breast Cancer Research, UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center, Chapel Hill, N.C., said there is “emerging interest” in racial disparities in cancer outcomes.
“Black patients have more trouble with access to care,” she said, noting that “in trial populations, [the outcomes] generally seem similar because the patients who go onto the trials tend to be those that can participate, but you never know until you look.”
Overall, Dr. Carey said the current results suggest that, “at least from the standpoint of the therapeutic implications of this drug – which is really a pretty remarkable drug in the overall study – it behaves very similarly in this group.”
Jennifer K. Litton, MD, vice president of clinical research at University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said: “We have known that minority patients, especially Black patients, have a higher rate of triple negative breast cancer and aggressive biologies, and have had worse breast cancer outcomes in many published series.”
She told this news organization that, “additionally, they are often underrepresented in breast cancer clinical trials.”
Dr. Litton said “the very favorable outcomes” reported in “this important subset of patients who participated in the ASCENT trial” confirm the use of SG in patients with mTNBC.
To examine the clinical outcomes of Black patients in the ASCENT study, the team conduced a prespecified analysis of participants self-reporting Black race who had been randomized to SG or single-agent chemotherapy of physician’s choice, including those with and without brain metastases.
Of the 529 patients enrolled to ASCENT, 62 (12%) were Black, of whom 28 were assigned to SG and 34 to single agent chemotherapy. The two groups were generally well balanced, although six patients in the chemotherapy arm had known brain metastases at baseline versus none of those given SG.
After a median treatment duration of 5.3 months with SG and 1.6 months for single-agent chemotherapy, there was a significant improvement in PFS with SG, at 5.4 months versus 2.2 months for chemotherapy, and a hazard ratio of 0.44 (P = .008).
There was also a nonsignificant improvement in overall survival with SG at 13.8 months versus 8.5 months for chemotherapy, and a hazard ratio of 0.64 (P = .159).
The objective response rate was 32% with SG versus 6% in patients given chemotherapy, while the median duration of response was 9.2 months in the SG arm and not evaluable for chemotherapy.
The researchers note that these efficacy findings were “consistent” with those seen in the full ASCENT study population.
In terms of safety, the most common treatment-related adverse events were neutropenia, seen in 64% of SG and 61% of chemotherapy patients, diarrhea in 64% and 13%, respectively, and fatigue, in 52% and 39%, respectively.
The most common grade ≥3 events were neutropenia, in 48% and 42% of SG and chemotherapy patients, respectively, followed by anemia, in 12% and 6%, respectively, leukopenia in 8% and 16%, respectively, and febrile neutropenia in 8% and 3%, respectively.
No treatment-related deaths occurred in either treatment arm.
Dose reduction due to treatment-emergent adverse events was recorded in 28% of patients receiving SG and 35% of those assigned to single-agent chemotherapy, and discontinuations occurred in 0% and 3%, respectively.
The study was sponsored by Gilead Sciences. Dr. Carey reports research funding from Sanofi, Novartis, Genentech/Roche, and GSK; spouse serves on the board of Falcon Therapeutics.
FROM SABCS 2021
PD-L1 cutoff for pembrolizumab in mTNBC confirmed
recently presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
Patients enrolled in KEYNOTE-355 – which is a phase 3, placebo-controlled trial of 847 patients – were stratified by CPS scores of at least 1 and at least 10, with the latter group in which adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy was shown to significantly improve both overall survival and progression-free survival.
As it was unclear whether taking a more fine-grained approach would reveal specific CPS scores at which pembrolizumab would be beneficial, Javier Cortes, MD, PhD, International Breast Cancer Center, Barcelona, and colleagues divided the patients into four CPS levels: less than 1, 1-9, 10-19, and at least 20.
Patients with a CPS 10-19 and at least 20 given pembrolizumab alongside chemotherapy had an overall survival benefit of 29% and 28%, respectively, while the PFS improvement was 30% and 38%. In the CPS of less than 1 and 1-9 groups, there were no discernible benefits from adding the checkpoint inhibitor.
“Given the similar outcomes in the CPS 10-19 and the CPS ≥20 subgroups, a CPS of 10 or more is a reasonable cutoff to define the population of patients with metastatic TNBC that might have benefit from the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy,” Dr. Cortes said. “In my opinion, these results provide further support for pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy as a good option, maybe a standard of care for some patients ... with local recurrent unresectable or metastatic TNBC whose tumors express PD-1 CPS ≥10.”
Invited discussant Hope S. Rugo, MD, said the study demonstrates that PD-L1 CPS of at least 10 is “clearly the optimal cutoff for differentiating benefit from pembrolizumab” and confirms the combination with chemotherapy as a “standard of care in this population”.
However, there are a number of outstanding questions in the metastatic setting, she said, including the test used to determine PD-L1 expression.
“Clearly the test that you order should be matched to the planned checkpoint inhibitor, and we look forward to additional data” on the relative overlap of the assays used in both the current study and in KEYNOTE-522.
However, IMpassion130 showed there is “incomplete overlap in terms of the two antibodies and tests that have been used to define PD-L1 positivity in breast cancer,” said Dr. Rugo, professor of medicine in hematology and oncology at the University of California, San Francisco.
“For excellent responders, can chemotherapy and eventually immunotherapy be discontinued, and when is it optimal? How long should we be continuing the combination and how long should we continue the checkpoint inhibitor alone?” she asked.
“Certainly in my own clinical practice,” Dr. Rugo explained, “in those excellent responders, it’s difficult to know when to stop the checkpoint inhibitor, but sometimes toxicity tells us the answer to that question. At some point, we need to stop therapy and understand what happens to those patients.”
She said that only 38% of patients in the current study benefited from pembrolizumab. “How can we amplify the immune response in those patients who do not have PD-L1–positive disease to further extend this benefit, and can we extend the efficacy to other subtypes? There are ongoing studies evaluating this question,” Dr. Rugo said.
Dr. Cortes said that KEYNOTE-355 showed the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy led to clinically meaningful improvements in both PFS and overall survival versus chemotherapy alone in the first-line treatment of mTNBC.
However, that benefit was seen only in patients with a PD-L1 CPS of at least 10, while there was no statistically significant improvement in either PFS or overall survival in those with a CPS of at least 1.
He explained that 847 patients with previously untreated locally recurrent or metastatic TNBC, or those who had been treated at least 6 months prior to disease recurrence, were randomized 2:1 to pembrolizumab or placebo plus chemotherapy.
For the current analysis, they substratified patients by PD-L1 CPS into less than 1, which accounted for 24.9% of patients; 1-9, seen in 36.2%-38.4%; 10-19, accounting for 13.9%-14.1%; and at least 20, seen in 22.8%-24.7% of patients.
Dr. Cortes said the overall survival rate among patients with CPS of at least 10 was 70.5% for patients treated with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus 81.6% for those assigned to placebo, at a significant hazard ratio of 0.73 (P = .0093).
Among patients with CPS of at least 1, the overall survival rate was 79.1% with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy and 83.9% in those given placebo, at a nonsignificant hazard ratio of 0.86. This translated into an HR of 0.89 in the intention-to-treat analysis.
Turning to the novel subgroups, Dr. Cortes showed that the HR for overall survival for pembrolizumab versus placebo was nonsignificant in patients with CPS of at least 1, at 0.97, and in those with CPS 1-9, at 1.09.
However, the HRs were markedly improved in patients with CPD 10-19, at 0.71, and in those with CPS of at least 20, at 0.72, showing that the “relative benefit of adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy was pretty much the same ... suggesting that CPS ≥10 could be a reasonable cutoff.”
In both of these groups, there was a sustained separation in the overall survival curves starting at around 10 months.
Turning to the PFS results, Dr Cortes said the event-free rate was 65.5% with the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy in patients with PD-L1 CPS of at least 10, while those given placebo had a rate of 78.6%, at an HR of 0.66.
In patients with PD-L1 CPS of at least 1, the HR was 0.75, or 0.82 in the intention-to-treat analysis.
“As with overall survival,” he said, there was a “trend toward improved efficacy with PD-L1 enrichment with the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy, although the PFS benefit in the pembro arm was slightly greater in the CPS ≥20 subgroup, compared to the CPS 10-19 subgroup.”
However, they highlighted that the difference was “small and the confidence intervals clearly overlapped.”
Why does PD-L1 expression play a role in response to pembrolizumab in mTNBC, but not in the early disease setting as seen in KEYNOTE-522?
“This is a question we have raised many, many times and have had many debates on,” Dr. Cortes said. “They are two completely different populations with the early breast cancer setting completely different to that in metastatic disease. Maybe the microenvironment plays a different role there, maybe we have to explore more in detail other biomarkers. I also think that different drugs were used in the neoadjuvant setting. We still have many unanswered questions.”
Dr. Rugo suggested that previous studies have given some clues to these questions with reductions in PD-L1 expression and tumor-infiltrating leukocytes observed between primary and metastatic disease.
The immune differences between primary and metastatic disease lead to immune escape, she said, adding: “This is clearly complicated by mutational complexity under the pressure of treatment.”
The study was funded by Merck Sharp and Dohme. Dr. Cortes and Dr. Rugo reported relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
recently presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
Patients enrolled in KEYNOTE-355 – which is a phase 3, placebo-controlled trial of 847 patients – were stratified by CPS scores of at least 1 and at least 10, with the latter group in which adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy was shown to significantly improve both overall survival and progression-free survival.
As it was unclear whether taking a more fine-grained approach would reveal specific CPS scores at which pembrolizumab would be beneficial, Javier Cortes, MD, PhD, International Breast Cancer Center, Barcelona, and colleagues divided the patients into four CPS levels: less than 1, 1-9, 10-19, and at least 20.
Patients with a CPS 10-19 and at least 20 given pembrolizumab alongside chemotherapy had an overall survival benefit of 29% and 28%, respectively, while the PFS improvement was 30% and 38%. In the CPS of less than 1 and 1-9 groups, there were no discernible benefits from adding the checkpoint inhibitor.
“Given the similar outcomes in the CPS 10-19 and the CPS ≥20 subgroups, a CPS of 10 or more is a reasonable cutoff to define the population of patients with metastatic TNBC that might have benefit from the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy,” Dr. Cortes said. “In my opinion, these results provide further support for pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy as a good option, maybe a standard of care for some patients ... with local recurrent unresectable or metastatic TNBC whose tumors express PD-1 CPS ≥10.”
Invited discussant Hope S. Rugo, MD, said the study demonstrates that PD-L1 CPS of at least 10 is “clearly the optimal cutoff for differentiating benefit from pembrolizumab” and confirms the combination with chemotherapy as a “standard of care in this population”.
However, there are a number of outstanding questions in the metastatic setting, she said, including the test used to determine PD-L1 expression.
“Clearly the test that you order should be matched to the planned checkpoint inhibitor, and we look forward to additional data” on the relative overlap of the assays used in both the current study and in KEYNOTE-522.
However, IMpassion130 showed there is “incomplete overlap in terms of the two antibodies and tests that have been used to define PD-L1 positivity in breast cancer,” said Dr. Rugo, professor of medicine in hematology and oncology at the University of California, San Francisco.
“For excellent responders, can chemotherapy and eventually immunotherapy be discontinued, and when is it optimal? How long should we be continuing the combination and how long should we continue the checkpoint inhibitor alone?” she asked.
“Certainly in my own clinical practice,” Dr. Rugo explained, “in those excellent responders, it’s difficult to know when to stop the checkpoint inhibitor, but sometimes toxicity tells us the answer to that question. At some point, we need to stop therapy and understand what happens to those patients.”
She said that only 38% of patients in the current study benefited from pembrolizumab. “How can we amplify the immune response in those patients who do not have PD-L1–positive disease to further extend this benefit, and can we extend the efficacy to other subtypes? There are ongoing studies evaluating this question,” Dr. Rugo said.
Dr. Cortes said that KEYNOTE-355 showed the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy led to clinically meaningful improvements in both PFS and overall survival versus chemotherapy alone in the first-line treatment of mTNBC.
However, that benefit was seen only in patients with a PD-L1 CPS of at least 10, while there was no statistically significant improvement in either PFS or overall survival in those with a CPS of at least 1.
He explained that 847 patients with previously untreated locally recurrent or metastatic TNBC, or those who had been treated at least 6 months prior to disease recurrence, were randomized 2:1 to pembrolizumab or placebo plus chemotherapy.
For the current analysis, they substratified patients by PD-L1 CPS into less than 1, which accounted for 24.9% of patients; 1-9, seen in 36.2%-38.4%; 10-19, accounting for 13.9%-14.1%; and at least 20, seen in 22.8%-24.7% of patients.
Dr. Cortes said the overall survival rate among patients with CPS of at least 10 was 70.5% for patients treated with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus 81.6% for those assigned to placebo, at a significant hazard ratio of 0.73 (P = .0093).
Among patients with CPS of at least 1, the overall survival rate was 79.1% with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy and 83.9% in those given placebo, at a nonsignificant hazard ratio of 0.86. This translated into an HR of 0.89 in the intention-to-treat analysis.
Turning to the novel subgroups, Dr. Cortes showed that the HR for overall survival for pembrolizumab versus placebo was nonsignificant in patients with CPS of at least 1, at 0.97, and in those with CPS 1-9, at 1.09.
However, the HRs were markedly improved in patients with CPD 10-19, at 0.71, and in those with CPS of at least 20, at 0.72, showing that the “relative benefit of adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy was pretty much the same ... suggesting that CPS ≥10 could be a reasonable cutoff.”
In both of these groups, there was a sustained separation in the overall survival curves starting at around 10 months.
Turning to the PFS results, Dr Cortes said the event-free rate was 65.5% with the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy in patients with PD-L1 CPS of at least 10, while those given placebo had a rate of 78.6%, at an HR of 0.66.
In patients with PD-L1 CPS of at least 1, the HR was 0.75, or 0.82 in the intention-to-treat analysis.
“As with overall survival,” he said, there was a “trend toward improved efficacy with PD-L1 enrichment with the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy, although the PFS benefit in the pembro arm was slightly greater in the CPS ≥20 subgroup, compared to the CPS 10-19 subgroup.”
However, they highlighted that the difference was “small and the confidence intervals clearly overlapped.”
Why does PD-L1 expression play a role in response to pembrolizumab in mTNBC, but not in the early disease setting as seen in KEYNOTE-522?
“This is a question we have raised many, many times and have had many debates on,” Dr. Cortes said. “They are two completely different populations with the early breast cancer setting completely different to that in metastatic disease. Maybe the microenvironment plays a different role there, maybe we have to explore more in detail other biomarkers. I also think that different drugs were used in the neoadjuvant setting. We still have many unanswered questions.”
Dr. Rugo suggested that previous studies have given some clues to these questions with reductions in PD-L1 expression and tumor-infiltrating leukocytes observed between primary and metastatic disease.
The immune differences between primary and metastatic disease lead to immune escape, she said, adding: “This is clearly complicated by mutational complexity under the pressure of treatment.”
The study was funded by Merck Sharp and Dohme. Dr. Cortes and Dr. Rugo reported relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
recently presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
Patients enrolled in KEYNOTE-355 – which is a phase 3, placebo-controlled trial of 847 patients – were stratified by CPS scores of at least 1 and at least 10, with the latter group in which adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy was shown to significantly improve both overall survival and progression-free survival.
As it was unclear whether taking a more fine-grained approach would reveal specific CPS scores at which pembrolizumab would be beneficial, Javier Cortes, MD, PhD, International Breast Cancer Center, Barcelona, and colleagues divided the patients into four CPS levels: less than 1, 1-9, 10-19, and at least 20.
Patients with a CPS 10-19 and at least 20 given pembrolizumab alongside chemotherapy had an overall survival benefit of 29% and 28%, respectively, while the PFS improvement was 30% and 38%. In the CPS of less than 1 and 1-9 groups, there were no discernible benefits from adding the checkpoint inhibitor.
“Given the similar outcomes in the CPS 10-19 and the CPS ≥20 subgroups, a CPS of 10 or more is a reasonable cutoff to define the population of patients with metastatic TNBC that might have benefit from the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy,” Dr. Cortes said. “In my opinion, these results provide further support for pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy as a good option, maybe a standard of care for some patients ... with local recurrent unresectable or metastatic TNBC whose tumors express PD-1 CPS ≥10.”
Invited discussant Hope S. Rugo, MD, said the study demonstrates that PD-L1 CPS of at least 10 is “clearly the optimal cutoff for differentiating benefit from pembrolizumab” and confirms the combination with chemotherapy as a “standard of care in this population”.
However, there are a number of outstanding questions in the metastatic setting, she said, including the test used to determine PD-L1 expression.
“Clearly the test that you order should be matched to the planned checkpoint inhibitor, and we look forward to additional data” on the relative overlap of the assays used in both the current study and in KEYNOTE-522.
However, IMpassion130 showed there is “incomplete overlap in terms of the two antibodies and tests that have been used to define PD-L1 positivity in breast cancer,” said Dr. Rugo, professor of medicine in hematology and oncology at the University of California, San Francisco.
“For excellent responders, can chemotherapy and eventually immunotherapy be discontinued, and when is it optimal? How long should we be continuing the combination and how long should we continue the checkpoint inhibitor alone?” she asked.
“Certainly in my own clinical practice,” Dr. Rugo explained, “in those excellent responders, it’s difficult to know when to stop the checkpoint inhibitor, but sometimes toxicity tells us the answer to that question. At some point, we need to stop therapy and understand what happens to those patients.”
She said that only 38% of patients in the current study benefited from pembrolizumab. “How can we amplify the immune response in those patients who do not have PD-L1–positive disease to further extend this benefit, and can we extend the efficacy to other subtypes? There are ongoing studies evaluating this question,” Dr. Rugo said.
Dr. Cortes said that KEYNOTE-355 showed the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy led to clinically meaningful improvements in both PFS and overall survival versus chemotherapy alone in the first-line treatment of mTNBC.
However, that benefit was seen only in patients with a PD-L1 CPS of at least 10, while there was no statistically significant improvement in either PFS or overall survival in those with a CPS of at least 1.
He explained that 847 patients with previously untreated locally recurrent or metastatic TNBC, or those who had been treated at least 6 months prior to disease recurrence, were randomized 2:1 to pembrolizumab or placebo plus chemotherapy.
For the current analysis, they substratified patients by PD-L1 CPS into less than 1, which accounted for 24.9% of patients; 1-9, seen in 36.2%-38.4%; 10-19, accounting for 13.9%-14.1%; and at least 20, seen in 22.8%-24.7% of patients.
Dr. Cortes said the overall survival rate among patients with CPS of at least 10 was 70.5% for patients treated with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus 81.6% for those assigned to placebo, at a significant hazard ratio of 0.73 (P = .0093).
Among patients with CPS of at least 1, the overall survival rate was 79.1% with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy and 83.9% in those given placebo, at a nonsignificant hazard ratio of 0.86. This translated into an HR of 0.89 in the intention-to-treat analysis.
Turning to the novel subgroups, Dr. Cortes showed that the HR for overall survival for pembrolizumab versus placebo was nonsignificant in patients with CPS of at least 1, at 0.97, and in those with CPS 1-9, at 1.09.
However, the HRs were markedly improved in patients with CPD 10-19, at 0.71, and in those with CPS of at least 20, at 0.72, showing that the “relative benefit of adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy was pretty much the same ... suggesting that CPS ≥10 could be a reasonable cutoff.”
In both of these groups, there was a sustained separation in the overall survival curves starting at around 10 months.
Turning to the PFS results, Dr Cortes said the event-free rate was 65.5% with the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy in patients with PD-L1 CPS of at least 10, while those given placebo had a rate of 78.6%, at an HR of 0.66.
In patients with PD-L1 CPS of at least 1, the HR was 0.75, or 0.82 in the intention-to-treat analysis.
“As with overall survival,” he said, there was a “trend toward improved efficacy with PD-L1 enrichment with the addition of pembrolizumab to chemotherapy, although the PFS benefit in the pembro arm was slightly greater in the CPS ≥20 subgroup, compared to the CPS 10-19 subgroup.”
However, they highlighted that the difference was “small and the confidence intervals clearly overlapped.”
Why does PD-L1 expression play a role in response to pembrolizumab in mTNBC, but not in the early disease setting as seen in KEYNOTE-522?
“This is a question we have raised many, many times and have had many debates on,” Dr. Cortes said. “They are two completely different populations with the early breast cancer setting completely different to that in metastatic disease. Maybe the microenvironment plays a different role there, maybe we have to explore more in detail other biomarkers. I also think that different drugs were used in the neoadjuvant setting. We still have many unanswered questions.”
Dr. Rugo suggested that previous studies have given some clues to these questions with reductions in PD-L1 expression and tumor-infiltrating leukocytes observed between primary and metastatic disease.
The immune differences between primary and metastatic disease lead to immune escape, she said, adding: “This is clearly complicated by mutational complexity under the pressure of treatment.”
The study was funded by Merck Sharp and Dohme. Dr. Cortes and Dr. Rugo reported relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
FROM SABCS 2021
Pembrolizumab improves event-free survival in early TNBC
The original trial data in more than 1,100 patients with early-stage TNBC indicated that adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy prior to surgery and giving the drug for a year afterward improves event-free survival (EFS) over placebo by 37%.
Now, the researchers conducted a series of prespecified sensitivity and subgroup analyses, finding remarkably consistent EFS outcomes whether considering the addition of adjuvant chemotherapy, positive surgical margins, or disease characteristics such as nodal status and disease stage.
The analyses showed that the benefit with pembrolizumab over placebo was “robust,” said study presenter Peter Schmid, MD, PhD, Centre for Experimental Cancer Medicine, Barts Cancer Institute, Queen Mary University of London.
“These results further support pembrolizumab plus platinum-containing neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab after surgery as a new standard of care treatment regimen for patients with high-risk, early-stage TNBC,” he said.
The research was presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium on Dec. 7.
Hope S. Rugo, MD, who was invited to comment on the findings, noted that, while the sensitivity analyses showed the benefit with pembrolizumab was seen across the board, the numbers in each group of interest were “very small, making any impact unlikely.”
She continued that there also remain a number of unanswered questions, chief among them being: “Does everybody need a checkpoint inhibitor? Perhaps studies ... could help us understand which patients might do well with chemotherapy alone.”
Dr. Rugo, who is professor of medicine in the division of hematology and oncology at the Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of California, San Francisco, , added that “we need to understand the balance of risk and toxicity” asking whether there are patients whose risk of an immunotoxicity is “so high that we should not give them a checkpoint inhibitor.”
It is not clear what constitutes the optimal chemotherapy backbone. “Does everybody need carboplatin? Does everyone need a year of pembrolizumab, even with a pathologic complete response given the intriguing data from GeparNUEVO and previously the I-SPY trial?” she asked.
“Of course, we don’t know the answers to those questions,” she said, but it is nevertheless possible to draw a roadmap for the treatment of early TNBC, although the choice of adjuvant therapy following surgery is less clear.
Dr. Rugo conducted a Twitter poll to canvas opinion on what to give to patients following surgery, depending on whether or not they have a pathological complete response.
At 73%, most of almost 200 respondents said patients with a pathological complete response should continue pembrolizumab for 1 year, while 72% said that patients without a pathological complete response should receive combination therapy of pembrolizumab and either capecitabine or olaparib, depending on mutational status.
Dr. Schmid began his presentation by noting that KEYNOTE-522 was the first prospective, randomized, phase 3 trial of pembrolizumab in early TNBC in the neoadjuvant and adjuvant setting.
Previously presented results showed that adding neoadjuvant pembrolizumab to chemotherapy was associated with a clinically meaningful increase in pathological complete response, while continuing with adjuvant chemotherapy after surgery led to a clinically meaningful improvement in EFS.
Consequently, the Food and Drug Administration approved pembrolizumab in this setting for patients with high-risk early-stage TNBC.
He reminded the audience that the trial included 1,174 patients randomized 2:1 to pembrolizumab or placebo every 3 weeks alongside eight cycles of chemotherapy, followed by pembrolizumab over placebo alone for up to nine cycles after undergoing definitive surgery.
After a median follow-up of 39.1 months, 15.7% of patients treated with pembrolizumab experienced an event versus 23.9% of those in the placebo group, at a hazard ratio of 0.63 (P = .00031). At 36 months, the EFS rate was 84.5% with pembrolizumab and 76.8% in patients treated with placebo.
Dr. Schmid said that they then performed five prespecified sensitivity analyses, which revealed that the results were “consistent with the primary EFS in all five sensitivity analyses, showing the robustnesses of the event-free survival benefit in the pembrolizumab arm.”
The first analysis, he continued, is of “particular interest as it considered the impact of postsurgery new anticancer therapy. For example, the use of adjuvant capecitabine.”
Censoring 31 patients from the pembrolizumab arm who received the drug and 13 of those given placebo, the team found that the hazard ratio for EFS for pembrolizumab versus placebo was 0.64.
Removing “positive margin at last surgery” as part of the definition of EFS also did not change the results substantially, with the HR for EFS for pembrolizumab versus placebo at 0.65.
Subgroup analysis revealed “consistent EFS results,” Dr. Schmid said, irrespective of whether stratifying the patients by nodal status, overall disease stage, menopausal status, HER2 status, or lactate dehydrogenase levels.
While patients in both treatment arms who had nodal involvement had worse outcomes than those without, those in the pembrolizumab arm “still had improved outcomes, compared with placebo, suggesting that it provides benefit regardless of nodal status.”
“Similarly, the EFS benefit with pembrolizumab was irrespective of disease stage,” Dr. Schmid said. Although the EFS improvement was greater in patients with stage II rather than III disease, at a HR of 0.60 versus 0.68, it highlights “the importance of early intervention.”
He said that the “rate of adverse events with pembrolizumab was low, especially in the adjuvant setting.”
Following his presentation, Dr. Schmid was asked whether he would consider retrying immunotherapy in patients after progression on pembrolizumab.
He replied that this is currently a “data-free zone.”
However, he said: “If a patient responded immunotherapy initially, had a disease-free interval and then has recurrence, then I would consider, if the patient is PD-L1 [programmed death–ligand 1] positive, at that time to add immunotherapy. We can’t say whether those patients will derive the same benefit” as that seen in randomized controlled trials in later stage TNBC, he added, “but there is, in my opinion, little to lose, especially if we have already established the patient tolerates immunotherapy well in that setting.”
Dr. Schmid continued that he “personally found it reassuring” that, in the current study, even patients without a complete pathological response “still showed a substantially better event-free survival compared to patients without immunotherapy, so I personally would consider immunotherapy for those patients when they relapse but we can discuss what the optimal disease-free interval is.”
The study was funded by Merck Sharp and Dohme. Both Dr. Rugo and Dr. Schmid reported relationships numerous pharmaceutical companies.
.
The original trial data in more than 1,100 patients with early-stage TNBC indicated that adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy prior to surgery and giving the drug for a year afterward improves event-free survival (EFS) over placebo by 37%.
Now, the researchers conducted a series of prespecified sensitivity and subgroup analyses, finding remarkably consistent EFS outcomes whether considering the addition of adjuvant chemotherapy, positive surgical margins, or disease characteristics such as nodal status and disease stage.
The analyses showed that the benefit with pembrolizumab over placebo was “robust,” said study presenter Peter Schmid, MD, PhD, Centre for Experimental Cancer Medicine, Barts Cancer Institute, Queen Mary University of London.
“These results further support pembrolizumab plus platinum-containing neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab after surgery as a new standard of care treatment regimen for patients with high-risk, early-stage TNBC,” he said.
The research was presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium on Dec. 7.
Hope S. Rugo, MD, who was invited to comment on the findings, noted that, while the sensitivity analyses showed the benefit with pembrolizumab was seen across the board, the numbers in each group of interest were “very small, making any impact unlikely.”
She continued that there also remain a number of unanswered questions, chief among them being: “Does everybody need a checkpoint inhibitor? Perhaps studies ... could help us understand which patients might do well with chemotherapy alone.”
Dr. Rugo, who is professor of medicine in the division of hematology and oncology at the Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of California, San Francisco, , added that “we need to understand the balance of risk and toxicity” asking whether there are patients whose risk of an immunotoxicity is “so high that we should not give them a checkpoint inhibitor.”
It is not clear what constitutes the optimal chemotherapy backbone. “Does everybody need carboplatin? Does everyone need a year of pembrolizumab, even with a pathologic complete response given the intriguing data from GeparNUEVO and previously the I-SPY trial?” she asked.
“Of course, we don’t know the answers to those questions,” she said, but it is nevertheless possible to draw a roadmap for the treatment of early TNBC, although the choice of adjuvant therapy following surgery is less clear.
Dr. Rugo conducted a Twitter poll to canvas opinion on what to give to patients following surgery, depending on whether or not they have a pathological complete response.
At 73%, most of almost 200 respondents said patients with a pathological complete response should continue pembrolizumab for 1 year, while 72% said that patients without a pathological complete response should receive combination therapy of pembrolizumab and either capecitabine or olaparib, depending on mutational status.
Dr. Schmid began his presentation by noting that KEYNOTE-522 was the first prospective, randomized, phase 3 trial of pembrolizumab in early TNBC in the neoadjuvant and adjuvant setting.
Previously presented results showed that adding neoadjuvant pembrolizumab to chemotherapy was associated with a clinically meaningful increase in pathological complete response, while continuing with adjuvant chemotherapy after surgery led to a clinically meaningful improvement in EFS.
Consequently, the Food and Drug Administration approved pembrolizumab in this setting for patients with high-risk early-stage TNBC.
He reminded the audience that the trial included 1,174 patients randomized 2:1 to pembrolizumab or placebo every 3 weeks alongside eight cycles of chemotherapy, followed by pembrolizumab over placebo alone for up to nine cycles after undergoing definitive surgery.
After a median follow-up of 39.1 months, 15.7% of patients treated with pembrolizumab experienced an event versus 23.9% of those in the placebo group, at a hazard ratio of 0.63 (P = .00031). At 36 months, the EFS rate was 84.5% with pembrolizumab and 76.8% in patients treated with placebo.
Dr. Schmid said that they then performed five prespecified sensitivity analyses, which revealed that the results were “consistent with the primary EFS in all five sensitivity analyses, showing the robustnesses of the event-free survival benefit in the pembrolizumab arm.”
The first analysis, he continued, is of “particular interest as it considered the impact of postsurgery new anticancer therapy. For example, the use of adjuvant capecitabine.”
Censoring 31 patients from the pembrolizumab arm who received the drug and 13 of those given placebo, the team found that the hazard ratio for EFS for pembrolizumab versus placebo was 0.64.
Removing “positive margin at last surgery” as part of the definition of EFS also did not change the results substantially, with the HR for EFS for pembrolizumab versus placebo at 0.65.
Subgroup analysis revealed “consistent EFS results,” Dr. Schmid said, irrespective of whether stratifying the patients by nodal status, overall disease stage, menopausal status, HER2 status, or lactate dehydrogenase levels.
While patients in both treatment arms who had nodal involvement had worse outcomes than those without, those in the pembrolizumab arm “still had improved outcomes, compared with placebo, suggesting that it provides benefit regardless of nodal status.”
“Similarly, the EFS benefit with pembrolizumab was irrespective of disease stage,” Dr. Schmid said. Although the EFS improvement was greater in patients with stage II rather than III disease, at a HR of 0.60 versus 0.68, it highlights “the importance of early intervention.”
He said that the “rate of adverse events with pembrolizumab was low, especially in the adjuvant setting.”
Following his presentation, Dr. Schmid was asked whether he would consider retrying immunotherapy in patients after progression on pembrolizumab.
He replied that this is currently a “data-free zone.”
However, he said: “If a patient responded immunotherapy initially, had a disease-free interval and then has recurrence, then I would consider, if the patient is PD-L1 [programmed death–ligand 1] positive, at that time to add immunotherapy. We can’t say whether those patients will derive the same benefit” as that seen in randomized controlled trials in later stage TNBC, he added, “but there is, in my opinion, little to lose, especially if we have already established the patient tolerates immunotherapy well in that setting.”
Dr. Schmid continued that he “personally found it reassuring” that, in the current study, even patients without a complete pathological response “still showed a substantially better event-free survival compared to patients without immunotherapy, so I personally would consider immunotherapy for those patients when they relapse but we can discuss what the optimal disease-free interval is.”
The study was funded by Merck Sharp and Dohme. Both Dr. Rugo and Dr. Schmid reported relationships numerous pharmaceutical companies.
.
The original trial data in more than 1,100 patients with early-stage TNBC indicated that adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy prior to surgery and giving the drug for a year afterward improves event-free survival (EFS) over placebo by 37%.
Now, the researchers conducted a series of prespecified sensitivity and subgroup analyses, finding remarkably consistent EFS outcomes whether considering the addition of adjuvant chemotherapy, positive surgical margins, or disease characteristics such as nodal status and disease stage.
The analyses showed that the benefit with pembrolizumab over placebo was “robust,” said study presenter Peter Schmid, MD, PhD, Centre for Experimental Cancer Medicine, Barts Cancer Institute, Queen Mary University of London.
“These results further support pembrolizumab plus platinum-containing neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab after surgery as a new standard of care treatment regimen for patients with high-risk, early-stage TNBC,” he said.
The research was presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium on Dec. 7.
Hope S. Rugo, MD, who was invited to comment on the findings, noted that, while the sensitivity analyses showed the benefit with pembrolizumab was seen across the board, the numbers in each group of interest were “very small, making any impact unlikely.”
She continued that there also remain a number of unanswered questions, chief among them being: “Does everybody need a checkpoint inhibitor? Perhaps studies ... could help us understand which patients might do well with chemotherapy alone.”
Dr. Rugo, who is professor of medicine in the division of hematology and oncology at the Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of California, San Francisco, , added that “we need to understand the balance of risk and toxicity” asking whether there are patients whose risk of an immunotoxicity is “so high that we should not give them a checkpoint inhibitor.”
It is not clear what constitutes the optimal chemotherapy backbone. “Does everybody need carboplatin? Does everyone need a year of pembrolizumab, even with a pathologic complete response given the intriguing data from GeparNUEVO and previously the I-SPY trial?” she asked.
“Of course, we don’t know the answers to those questions,” she said, but it is nevertheless possible to draw a roadmap for the treatment of early TNBC, although the choice of adjuvant therapy following surgery is less clear.
Dr. Rugo conducted a Twitter poll to canvas opinion on what to give to patients following surgery, depending on whether or not they have a pathological complete response.
At 73%, most of almost 200 respondents said patients with a pathological complete response should continue pembrolizumab for 1 year, while 72% said that patients without a pathological complete response should receive combination therapy of pembrolizumab and either capecitabine or olaparib, depending on mutational status.
Dr. Schmid began his presentation by noting that KEYNOTE-522 was the first prospective, randomized, phase 3 trial of pembrolizumab in early TNBC in the neoadjuvant and adjuvant setting.
Previously presented results showed that adding neoadjuvant pembrolizumab to chemotherapy was associated with a clinically meaningful increase in pathological complete response, while continuing with adjuvant chemotherapy after surgery led to a clinically meaningful improvement in EFS.
Consequently, the Food and Drug Administration approved pembrolizumab in this setting for patients with high-risk early-stage TNBC.
He reminded the audience that the trial included 1,174 patients randomized 2:1 to pembrolizumab or placebo every 3 weeks alongside eight cycles of chemotherapy, followed by pembrolizumab over placebo alone for up to nine cycles after undergoing definitive surgery.
After a median follow-up of 39.1 months, 15.7% of patients treated with pembrolizumab experienced an event versus 23.9% of those in the placebo group, at a hazard ratio of 0.63 (P = .00031). At 36 months, the EFS rate was 84.5% with pembrolizumab and 76.8% in patients treated with placebo.
Dr. Schmid said that they then performed five prespecified sensitivity analyses, which revealed that the results were “consistent with the primary EFS in all five sensitivity analyses, showing the robustnesses of the event-free survival benefit in the pembrolizumab arm.”
The first analysis, he continued, is of “particular interest as it considered the impact of postsurgery new anticancer therapy. For example, the use of adjuvant capecitabine.”
Censoring 31 patients from the pembrolizumab arm who received the drug and 13 of those given placebo, the team found that the hazard ratio for EFS for pembrolizumab versus placebo was 0.64.
Removing “positive margin at last surgery” as part of the definition of EFS also did not change the results substantially, with the HR for EFS for pembrolizumab versus placebo at 0.65.
Subgroup analysis revealed “consistent EFS results,” Dr. Schmid said, irrespective of whether stratifying the patients by nodal status, overall disease stage, menopausal status, HER2 status, or lactate dehydrogenase levels.
While patients in both treatment arms who had nodal involvement had worse outcomes than those without, those in the pembrolizumab arm “still had improved outcomes, compared with placebo, suggesting that it provides benefit regardless of nodal status.”
“Similarly, the EFS benefit with pembrolizumab was irrespective of disease stage,” Dr. Schmid said. Although the EFS improvement was greater in patients with stage II rather than III disease, at a HR of 0.60 versus 0.68, it highlights “the importance of early intervention.”
He said that the “rate of adverse events with pembrolizumab was low, especially in the adjuvant setting.”
Following his presentation, Dr. Schmid was asked whether he would consider retrying immunotherapy in patients after progression on pembrolizumab.
He replied that this is currently a “data-free zone.”
However, he said: “If a patient responded immunotherapy initially, had a disease-free interval and then has recurrence, then I would consider, if the patient is PD-L1 [programmed death–ligand 1] positive, at that time to add immunotherapy. We can’t say whether those patients will derive the same benefit” as that seen in randomized controlled trials in later stage TNBC, he added, “but there is, in my opinion, little to lose, especially if we have already established the patient tolerates immunotherapy well in that setting.”
Dr. Schmid continued that he “personally found it reassuring” that, in the current study, even patients without a complete pathological response “still showed a substantially better event-free survival compared to patients without immunotherapy, so I personally would consider immunotherapy for those patients when they relapse but we can discuss what the optimal disease-free interval is.”
The study was funded by Merck Sharp and Dohme. Both Dr. Rugo and Dr. Schmid reported relationships numerous pharmaceutical companies.
.
FROM SABCS 2021
NHL: As a second-line treatment in phase 3 trial, tisa-cel disappoints
according to results of a randomized, phase 3 trial.
The chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy did not improve event-free survival (EFS) in this phase 3 BELINDA study, potentially because of study design decisions or imbalances in relevant patient characteristics, according to the study investigators.
Despite the negative result, insights from this study will inform the development of future clinical trials of CAR T-cell therapy, said BELINDA investigator Michael R. Bishop, MD, of the David and Etta Jonas Center for Cellular Therapy, University of Chicago.
Findings of BELINDA, presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, stand in contrast to two other high-profile CAR T-cell therapy studies also presented at the meeting. Those other studies demonstrated significant improvements in EFS in the second-line treatment of large B-cell lymphomas.
“All of us are excited to see that the other two trials were positive, and we were hoping that ours would be as well, but there are significant differences in the trial design,” Dr. Bishop said in a press conference held at the ASH meeting.
Tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel), an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, is already approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas after at least two other lines of systemic therapy.
The aim of the pivotal phase 3, randomized, multicenter BELINDA study was to evaluate tisa-cel earlier in the course of treatment for patients with more aggressive disease, according to Dr. Bishop.
About two-thirds of non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients will be cured with first-line treatment. However, very poor outcomes are seen among patients with disease that does not respond to the initial treatment or that reoccurs shortly afterward, Dr. Bishop said.
The standard of care approach for those patients is second-line therapy, he noted, usually with combination chemoimmunotherapy, followed by autologous stem cell transplant if the disease responds to chemotherapy.
“Unfortunately, only a minority of those patients will be found to have chemotherapy-sensitive disease and be able to go on to autologous stem cell transplantation,” Dr. Bishop said. “And even in that subgroup of patients, the outcomes are relatively poor.”
Accordingly, the phase 3 BELINDA study enrolled patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas that either did not respond to first-line treatment or that reoccurred within 12 months.
The primary endpoint of the study was EFS, defined as the time from randomization to either stable or progressive disease at or after a week 12 assessment or to any-cause death at any time.
While that primary endpoint was not met for tisa-cel versus standard of care therapy, two other randomized, phase 3 studies presented at the ASH meeting did demonstrate that CAR T-cell therapy extended EFS when given as a second-line lymphoma treatment.
In the randomized, phase 3 ZUMA-7 trial, axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) significantly improved EFS versus standard of care in the treatment of patients with large B-cell lymphoma refractory to or relapsed within 12 months of adequate first-line therapy, according to investigators.
Similarly, the investigators said that treatment with lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) led to a significant improvement in EFS in TRANSFORM, a randomized, phase 3 clinical trial that enrolled patients with large B-cell lymphoma that was refractory to first-line therapy or else relapsed within 12 months of that treatment.
“It’s very possible that either or both the patient characteristics and the study design is what led to the difference in the top-line study results,” lymphoma specialist Andrew M. Evens, DO, said in an interview.
There were substantial differences between the studies in terms of what was allowed as optional bridging therapy and salvage therapy, according to Dr. Evens, associate director for clinical services and director of the lymphoma program at Rutgers Cancer Institute in New Brunswick, N.J.
“In ZUMA-7, they only allowed steroids as bridging therapy,” said Dr. Evens, who was not an investigator on any of the three second-line CAR T-cell studies.
In the BELINDA study, optional platinum-based chemotherapy bridging treatment allowed in one arm of the study could have potentially delayed tisa-cel infusion until after the week 6 assessment, study investigators reported in their ASH meeting abstract.
Differences in lymphodepleting therapy prior to CAR T-cell therapy could have also played a role. According to Dr. Bishop, the total doses of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine in BELINDA were 900 mg/m2 and 75 mg/m2, respectively, while in the other two trials, doses were 1,500 mg/m2 and 90 mg/m2, respectively.
Lymphodepleting chemotherapy is “extremely important” in the success of CAR T-cell therapeutic approaches, he noted at the press conference.
Dr. Bishop reported receiving consultancy fees from Arcellx, Autolus Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CRISPR, Kite/Gilead, and Novartis. He also reported research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Kite/Gilead.
according to results of a randomized, phase 3 trial.
The chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy did not improve event-free survival (EFS) in this phase 3 BELINDA study, potentially because of study design decisions or imbalances in relevant patient characteristics, according to the study investigators.
Despite the negative result, insights from this study will inform the development of future clinical trials of CAR T-cell therapy, said BELINDA investigator Michael R. Bishop, MD, of the David and Etta Jonas Center for Cellular Therapy, University of Chicago.
Findings of BELINDA, presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, stand in contrast to two other high-profile CAR T-cell therapy studies also presented at the meeting. Those other studies demonstrated significant improvements in EFS in the second-line treatment of large B-cell lymphomas.
“All of us are excited to see that the other two trials were positive, and we were hoping that ours would be as well, but there are significant differences in the trial design,” Dr. Bishop said in a press conference held at the ASH meeting.
Tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel), an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, is already approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas after at least two other lines of systemic therapy.
The aim of the pivotal phase 3, randomized, multicenter BELINDA study was to evaluate tisa-cel earlier in the course of treatment for patients with more aggressive disease, according to Dr. Bishop.
About two-thirds of non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients will be cured with first-line treatment. However, very poor outcomes are seen among patients with disease that does not respond to the initial treatment or that reoccurs shortly afterward, Dr. Bishop said.
The standard of care approach for those patients is second-line therapy, he noted, usually with combination chemoimmunotherapy, followed by autologous stem cell transplant if the disease responds to chemotherapy.
“Unfortunately, only a minority of those patients will be found to have chemotherapy-sensitive disease and be able to go on to autologous stem cell transplantation,” Dr. Bishop said. “And even in that subgroup of patients, the outcomes are relatively poor.”
Accordingly, the phase 3 BELINDA study enrolled patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas that either did not respond to first-line treatment or that reoccurred within 12 months.
The primary endpoint of the study was EFS, defined as the time from randomization to either stable or progressive disease at or after a week 12 assessment or to any-cause death at any time.
While that primary endpoint was not met for tisa-cel versus standard of care therapy, two other randomized, phase 3 studies presented at the ASH meeting did demonstrate that CAR T-cell therapy extended EFS when given as a second-line lymphoma treatment.
In the randomized, phase 3 ZUMA-7 trial, axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) significantly improved EFS versus standard of care in the treatment of patients with large B-cell lymphoma refractory to or relapsed within 12 months of adequate first-line therapy, according to investigators.
Similarly, the investigators said that treatment with lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) led to a significant improvement in EFS in TRANSFORM, a randomized, phase 3 clinical trial that enrolled patients with large B-cell lymphoma that was refractory to first-line therapy or else relapsed within 12 months of that treatment.
“It’s very possible that either or both the patient characteristics and the study design is what led to the difference in the top-line study results,” lymphoma specialist Andrew M. Evens, DO, said in an interview.
There were substantial differences between the studies in terms of what was allowed as optional bridging therapy and salvage therapy, according to Dr. Evens, associate director for clinical services and director of the lymphoma program at Rutgers Cancer Institute in New Brunswick, N.J.
“In ZUMA-7, they only allowed steroids as bridging therapy,” said Dr. Evens, who was not an investigator on any of the three second-line CAR T-cell studies.
In the BELINDA study, optional platinum-based chemotherapy bridging treatment allowed in one arm of the study could have potentially delayed tisa-cel infusion until after the week 6 assessment, study investigators reported in their ASH meeting abstract.
Differences in lymphodepleting therapy prior to CAR T-cell therapy could have also played a role. According to Dr. Bishop, the total doses of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine in BELINDA were 900 mg/m2 and 75 mg/m2, respectively, while in the other two trials, doses were 1,500 mg/m2 and 90 mg/m2, respectively.
Lymphodepleting chemotherapy is “extremely important” in the success of CAR T-cell therapeutic approaches, he noted at the press conference.
Dr. Bishop reported receiving consultancy fees from Arcellx, Autolus Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CRISPR, Kite/Gilead, and Novartis. He also reported research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Kite/Gilead.
according to results of a randomized, phase 3 trial.
The chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy did not improve event-free survival (EFS) in this phase 3 BELINDA study, potentially because of study design decisions or imbalances in relevant patient characteristics, according to the study investigators.
Despite the negative result, insights from this study will inform the development of future clinical trials of CAR T-cell therapy, said BELINDA investigator Michael R. Bishop, MD, of the David and Etta Jonas Center for Cellular Therapy, University of Chicago.
Findings of BELINDA, presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, stand in contrast to two other high-profile CAR T-cell therapy studies also presented at the meeting. Those other studies demonstrated significant improvements in EFS in the second-line treatment of large B-cell lymphomas.
“All of us are excited to see that the other two trials were positive, and we were hoping that ours would be as well, but there are significant differences in the trial design,” Dr. Bishop said in a press conference held at the ASH meeting.
Tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel), an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, is already approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas after at least two other lines of systemic therapy.
The aim of the pivotal phase 3, randomized, multicenter BELINDA study was to evaluate tisa-cel earlier in the course of treatment for patients with more aggressive disease, according to Dr. Bishop.
About two-thirds of non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients will be cured with first-line treatment. However, very poor outcomes are seen among patients with disease that does not respond to the initial treatment or that reoccurs shortly afterward, Dr. Bishop said.
The standard of care approach for those patients is second-line therapy, he noted, usually with combination chemoimmunotherapy, followed by autologous stem cell transplant if the disease responds to chemotherapy.
“Unfortunately, only a minority of those patients will be found to have chemotherapy-sensitive disease and be able to go on to autologous stem cell transplantation,” Dr. Bishop said. “And even in that subgroup of patients, the outcomes are relatively poor.”
Accordingly, the phase 3 BELINDA study enrolled patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas that either did not respond to first-line treatment or that reoccurred within 12 months.
The primary endpoint of the study was EFS, defined as the time from randomization to either stable or progressive disease at or after a week 12 assessment or to any-cause death at any time.
While that primary endpoint was not met for tisa-cel versus standard of care therapy, two other randomized, phase 3 studies presented at the ASH meeting did demonstrate that CAR T-cell therapy extended EFS when given as a second-line lymphoma treatment.
In the randomized, phase 3 ZUMA-7 trial, axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) significantly improved EFS versus standard of care in the treatment of patients with large B-cell lymphoma refractory to or relapsed within 12 months of adequate first-line therapy, according to investigators.
Similarly, the investigators said that treatment with lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) led to a significant improvement in EFS in TRANSFORM, a randomized, phase 3 clinical trial that enrolled patients with large B-cell lymphoma that was refractory to first-line therapy or else relapsed within 12 months of that treatment.
“It’s very possible that either or both the patient characteristics and the study design is what led to the difference in the top-line study results,” lymphoma specialist Andrew M. Evens, DO, said in an interview.
There were substantial differences between the studies in terms of what was allowed as optional bridging therapy and salvage therapy, according to Dr. Evens, associate director for clinical services and director of the lymphoma program at Rutgers Cancer Institute in New Brunswick, N.J.
“In ZUMA-7, they only allowed steroids as bridging therapy,” said Dr. Evens, who was not an investigator on any of the three second-line CAR T-cell studies.
In the BELINDA study, optional platinum-based chemotherapy bridging treatment allowed in one arm of the study could have potentially delayed tisa-cel infusion until after the week 6 assessment, study investigators reported in their ASH meeting abstract.
Differences in lymphodepleting therapy prior to CAR T-cell therapy could have also played a role. According to Dr. Bishop, the total doses of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine in BELINDA were 900 mg/m2 and 75 mg/m2, respectively, while in the other two trials, doses were 1,500 mg/m2 and 90 mg/m2, respectively.
Lymphodepleting chemotherapy is “extremely important” in the success of CAR T-cell therapeutic approaches, he noted at the press conference.
Dr. Bishop reported receiving consultancy fees from Arcellx, Autolus Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CRISPR, Kite/Gilead, and Novartis. He also reported research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Kite/Gilead.
FROM ASH 2021